Albendazole
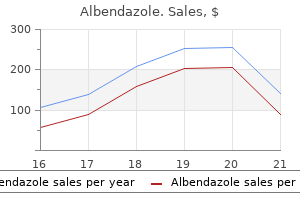
Albendazole dosages: 400 mg
Albendazole packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Generic 400 mg albendazole overnight delivery
Neoadjuvant remedy appears to trigger substantial alterations within the morphology of the tumor cells antiviral honey 400 mg albendazole mastercard. Also hiv infection from hospital albendazole 400 mg cheap without a prescription, residual foci of beforehand handled ductal adenocarcinoma may be patchy and difficult to detect. Recently, scoring systems have been devised in an attempt to consider the efficacy of chemotherapy; nevertheless, the relevance of those proposals requires further study. The difficulty in distinguishing ductal adenocarcinoma from continual pancreatitis (see Chapters fifty seven and 58) on the scientific level also applies to the microscopic analysis, and is regarded to be some of the tough distinctions in diagnostic pathology (Adsay et al, 2004a). Chronic pancreatitis may be associated with epithelial atypia, both architectural and cytologic; conversely, ductal adenocarcinoma is infamous for its deceptively bland look. Features favoring a malignant diagnosis include irregular location of glands (adjacent to muscular arteries, throughout the duodenal muscularis, adjoining to adipocytes within the peripancreatic tissue, or round nerves), architectural abnormalities within the form of the glands (cribriforming, angulation, or incomplete gland formation), and nuclear abnormalities (variation within the shape and size of nuclei among the many cells within a person gland). A fourfold variation in nuclear quantity between adjoining cells, in any other case often identified as the 4-to-1 rule, is useful to recognize carcinoma. Diagnostic issue additionally extends to the differential prognosis of ductal adenocarcinoma in metastatic websites, as a outcome of ductal adenocarcinoma usually retains its well-differentiated appearance and mimics benign or low-grade neoplasms of these sites. Common pitfalls include misinterpretation of metastatic ductal adenocarcinoma within the ovary as a major borderline ovarian mucinous cystadenoma (Young, 2007); within the lung, as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma; and within the liver, as bile duct adenoma. In the final instance, the converse-misinterpretation of bile duct adenoma as metastatic ductal adenocarcinoma-is also a major diagnostic drawback. Intratumoral heterogeneity is an important drawback within the grading of ductal adenocarcinoma, and because of this, an easier, more sensible, and more clinically related grading scheme that accounts for this heterogeneity by scoring the patterns of infiltration has been proposed (Adsay et al, 2005). The pathologic evaluation of a pancreatectomy specimen is important each for staging and in figuring out the margin of resection. Recent research have highlighted that, with extra cautious grossing protocols in pathology laboratories, in the vast majority of resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, there often are insidious carcinoma items that involve the surfaces and the margins, not visibly grossly or clinically (Adsay et al, 2012, 2014; Esposito et al, 2008; Maksymov et al, 2013; Schlitter & Esposito, 2010; Verbeke & Menon, 2009). For this reason, a size-based staging protocol has been proposed (Allen et al, 2016). Metastasis to lymph nodes is taken into account one of the essential predictors of consequence in resected ductal adenocarcinomas. Generally, at least 12 lymph nodes ought to be recognized in a pancreatoduodenectomy specimen (Adsay et al, 2009). Most of these lymph nodes are embedded within the surfaces of the pancreas or in the groove between the pancreas and duodenum. When cautious harvesting of the lymph nodes is performed (Adsay et al, 2009, 2014), metastases are detected in the lymph nodes in virtually 80% of resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (Basturk et al, 2015a). Proper identification of margins and their enough sampling are important elements in the pathologic evaluation of a pancreatoduodenectomy specimen (Adsay et al, 2012, 2014; Esposito et al, 2008; Ferrone et al, 2008; Schlitter & Esposito, 2010); nevertheless, what constitutes a margin remains controversial (Adsay et al, 2014). For instance, the anterior surfaces are regarded as a margin by some however not by others. Similarly, whether or not to think about the posterior free surfaces of the pancreas (partly similar to vena cava surface) as a margin has additionally been extremely controversial, with vastly different views by totally different authors. Readers are referred to a latest evaluation article for detailed analysis of this subject (Adsay et al, 2014). As expected, ductal adenocarcinoma exhibits immunohistochemical proof of ductal differentiation. Substantial developments have occurred in understanding the molecular carcinogenesis of ductal adenocarcinoma (see Chapter 9B). Mutation of p16 or methylation of the promoter is also common (>80%) and represents the pathogenetic hyperlink with the familial atypical multiple mole�melanoma syndrome (Hruban et al, 2001a). The latter appears to have a modest diploma of specificity for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Fanconi anemia gene alterations also have been identified (van der Heijden et al, 2003). Abnormalities in mismatch restore proteins and microsatellite instability are unusual, although pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas can happen as one of the much less common manifestations of Lynch syndrome. Replacement of the traditional cuboidal, nonmucinous ductal epithelium with columnar cells that contain plentiful apical mucin, but without architectural complexity. As the intraductal neoplasm progresses, it acquires more papillary structure and cytologic atypia. Other Invasive Carcinomas Related to Ductal Adenocarcinoma Certain kinds of carcinomas are carefully associated to , and sometimes seen in affiliation with, ductal adenocarcinoma (Klimstra & Adsay, 2009). Undifferentiated carcinoma can be thought to be the least differentiated form of ductal adenocarcinoma, by which characteristic tubule formation is now not evident or solely focal. Undifferentiated carcinomas embody sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma, anaplastic giant cell carcinoma, and carcinosarcoma. Rarely, the sarcomatoid parts of those tumors could present aberrant differentiation, together with bone and cartilage formation. Studies have shown that the osteoclastic giant cells are nonneoplastic histiocytic cells (Westra et al. The true neoplastic cells in this tumor type are the sarcomatoid mononuclear cells. Undifferentiated carcinomas with osteoclast-like giant cells usually seem well demarcated and type a large solitary mass and exhibit nodular, pushing-border infiltration. If examined fastidiously, many such tumors seem to have substantial intraductal progress. These are clearly malignant neoplasms, most exhibiting an aggressive scientific course; nonetheless, some examples with minimal ductal adenocarcinoma parts have a protracted medical course. In a current study, many of those patients experienced unexpectedly long survival, with an overall 5-year survival of 42% (Muraki et al, 2016). Squamous cell carcinoma and adenosquamous carcinoma of this region are highly aggressive tumors (Kardon et al, 2001), with a prognosis which could be worse than that of typical ductal adenocarcinoma. Medullary carcinomas appear to be considerably more widespread within the ampulla and duodenum than within the pancreas, and subsequently, earlier than a case can be classified as pancreatic, these potentialities must be excluded. Syncytial nodules of enormous, poorly differentiated epithelioid cells with a pushing pattern of invasion characterize medullary carcinomas. Goggins and colleagues (1998) found that these tumors have a extra protracted scientific course, but further knowledge are essential to define the prognosis of these rare tumors. Intraductal Neoplasms Intraductal neoplasms represent an more and more encountered and necessary category of pancreatic tumors of ductal origin, characterized by intraductal polypoid, papillary nodules which are often associated with cystic dilation of the ducts (Adsay et al, 2010, 2016; Basturk et al, 2009). Such lesions are actually also termed tumoral intraepithelial neoplasia (Adsay et al, 2015; Tanaka et al, 2006). It is estimated that about 15% of invasive adenocarcinomas in the pancreas arise from these tumor sorts. The neoplasms included beneath this umbrella of "intraductal tumors" are intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasms. Radiographic findings of ductal dilation with irregularities additionally are sometimes diagnostic. As the biology of these tumors was higher understood, and higher administration protocols had been devised, it grew to become clear that a two-tiered system is more significant and relevant. Tumors composed nearly completely of the colloid pattern-in which the mucin/epithelium ratio could be very high, and most carcinoma cells are floating inside the mucin (detached from the stroma)-have a special biology with an unusually protracted scientific course (Hruban et al, 2007; Seidel et al, 2002). Anecdotal evidence suggests that open biopsy of colloid carcinomas could contribute to dissemination, presumably due to the adherent nature of the mucin.
400 mg albendazole generic
In the intraductal progress kind hiv infection rates in australia albendazole 400 mg cheap with visa, tumor typically spreads intraluminally alongside the ducts antivirus software for mac 400 mg albendazole free shipping. Bloodborne unfold happens later, notably to the lungs (Jiang et al, 2009; Patel, 2001; Suzuki et al, 2002). These patterns are related to completely different scientific evolutions, with intraductal growth and the periductal infiltration showing the best and worst prognosis, respectively (65% survival at 5 years compared with lower than 5% at 5 years) (Jiang et al, 2009; Rizvi et al, 2014; Suzuki et al, 2002). In case of large tumors, adjoining satellite tumoral nodules are commonly observed. The pure periductal-infiltrating type and the intraductal growth sample are seldom observed (Guglielmi et al, 2009). Cytoplasm is usually pale, barely eosinophilic, and typically extra ample and clear. Mucus secretion may be highlighted by alcian blue staining, though the amount is normally small. Less differentiated tumors could show cribriform formations and/or a cordlike sample, and poorly differentiated cancers are characterised by marked mobile pleomorphism. Usually, the center of the tumor is densely sclerotic and hypocellular, and there could additionally be focal calcifications, whereas the periphery of the tumors is more mobile. Grossmacroscopy of a small and solitary, well-limited, unencapsulated white tumor developedonacirrhoticliver. In contrast, efficiency of biopsy is rather more restricted in cases of extrahepatic strictures. It is a rare condition characterized by the multicentric proliferation of columnar epithelium throughout the large bile ducts, though it could diffuse anyplace within the giant intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts (Gouma et al, 1984; Mercadier et al, 1984; Padfield et al, 1988). Biliary papillomatosis is a illness of center age or older adults, and men are affected about twice as typically as girls. Grossly, the neoplasm proliferates inside the bile duct lumen, which is filled with delicate pink-to-tan papillary excrescences. Specific differentiation of the epithelial lining could additionally be noticed, including the pancreatobiliary, intestinal, oncocytic, and gastric varieties. This invasive tumor may be a standard tubular type adenocarcinoma, or in 10% to 15% of circumstances, a mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma (Lee et al, 2004; Wan et al, 2013; Zen et al, 2006). Oncocytic variants of biliary papillomatosis have additionally been reported, sharing comparable scientific options with their nononcocytic counterparts. The oncocytic pattern is as a end result of of the presence of plentiful cytoplasmic mitochondria (Rouzbahman et al, 2007). Precancerous lesions may also develop on a flat bile duct epithelium (Kloppel et al, 2013). The abnormal cells have an increased nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, partial loss of nuclear polarity, and nuclear hyperchromasia. Macroscopiccutsection exhibiting a well-demarcated, agency, and white tumor in a macronodular cirrhosis. This has been further supported by the genetic findings that two unbiased neoplastic clones exist at shut proximity, and hence no histologic transitions exist (Fujii et al, 2000). The different two subtypes recognized are the standard (nests of mature hepatocyte-like tumor cells surrounded by small cells exhibiting immunophenotypical markers of progenitor cells) and intermediate (small homogeneous tumor cells comprising many of the tumor which may be intermediate between hepatocytes and cholangiocytes and displaying immunophenotypical markers of both) types. Importantly, these different subtypes might overlap to some extent, and furthermore, be observed together in a similar tumor. Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm these lesions had been previously reported individually as biliary cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma (see Chapter 90B). It is an unusual cystic neoplasm that accounts for less than 5% of all intrahepatic biliary cysts (Ishak et al, 1977; Soares et al, 2014; van Roekel et al, 1982). The histogenesis of biliary cystadenoma stays uncertain, though an origin from embryonic foregut rests has been advanced (Akwari et al, 1990). Almost all of those tumors occur in middle-aged girls, with a peak incidence within the fifth decade (Devaney et al, 1994). The tumor is solitary and spherical and contains white-to-yellow-to-brown mucinous or gelatinous material. Individual locules differ in size, and the internal floor is often smooth with occasional trabeculations or papillations (Ishak et al, 1977). If solid areas are current, then concern must be raised for an invasive element (Buetow et al, 1995; Devaney et al, 1994). Histologically, the cysts are lined by a simple columnar-tocuboidal epithelium with mucin-filled cytoplasm. On event, the epithelium may be pseudostratified or focally ulcerated, and goblet cells or squamous cells are typically seen. Nuclear atypias and mitoses are rare, but their presence ought to elevate the potential for complicating cystadenocarcinoma. Also acknowledged is a serous variant of biliary cystadenoma, which is distinguished by a single layer of glycogen-rich cuboidal cells just like those seen in microcystic adenomas of the pancreas. Underneath is an ovarian kind stroma, which is absent in cases arising in males (Devaney et al, 1994). Typically, this stroma is densely cellular and composed of carefully packed spindle cells harking back to ovarian stroma. This stroma stains with antibodies to estrogen and progesterone receptor, and development can happen throughout hormone replacement therapy and being pregnant (Daniels et al, 2006). Because dysplasia could additionally be patchy, and invasive tumors might arise in as many as 25% of cystadenomas (Ishak et al, 1977), the gross specimens of cystic tumors need to be rigorously examined for suspicious areas, and extensive sampling of the cyst should be performed. This rare malignancy typically develops as a complication of a biliary cystadenoma, which may or might not demonstrate the distinctive mesenchymal stroma (Ishak et al, 1977; Wheeler et al, 1985; Woods, 1981). Most patients are between 45 and 70 years of age, and men and women are equally affected. Cysts are typically multilocular, ranging in measurement from 5 cm to higher than 20 cm in diameter without connection with the bile duct. Although the gross appearance could be difficult to distinguish from biliary cystadenomas, the suspicion of malignancy should be raised if areas of stable, thickening, large papillary plenty are present (Ishak et al, 1977). Histologically, cystadenocarcinomas are often welldifferentiated adenocarcinomas, usually with an intracystic papillary part, and are composed of malignant epithelial cells with various degrees of nuclear stratification, pleomorphism, and hyperchromasia. Within the background, the benign epithelium of the preexisting cystadenoma can typically be identified. Transitions can sometimes be discerned with varying levels of epithelial dysplasia (Woods, 1981). The tumor infiltrates the underlying cyst wall, and vascular invasion and extension into adjoining hepatic parenchyma or adjoining organs are attribute of malignancy. The tumors are inclined to develop slowly, but they finally invade adjoining structures and metastasize to distant sites. In uncommon instances, the carcinoma demonstrates adenosquamous, oncocytic, or spindle-cell (pseudosarcomatous) differentiation (Moore et al, 1984; Unger et al, 1987; Wolf et al, 1992). Ciliated hepatic foregut cyst is a rare lesion, generally solitary and unilocular (Terada et al, 1990). An occasional case of squamous carcinoma arising in ciliated hepatic foregut cyst has been reported (Vick et al, 1999). Because these options are much like these seen in bronchial and esophageal cysts, a similar origin from the embryonic foregut is suggested (Wheeler et al, 1984).
400 mg albendazole order
Sia D hiv infection rates among prostitutes generic 400 mg albendazole visa, et al: Integrative molecular analysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals 2 classes that have different outcomes hiv infection immediate symptoms generic 400 mg albendazole mastercard, Gastroenterology 144:829�840, 2013a. Sia D, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: pathogenesis and rationale for molecular therapeutics, Oncogene 32:4861�4870, 2013b. Spolverato G, et al: Tumor measurement predicts vascular invasion and histologic grade among sufferers present process resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, J Gastrointest Surg 18:1284�1291, 2014. Sripa B, Pairojkul C: Cholangiocarcinoma: lessons from Thailand, Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:349�356, 2008. Sriputtha S, et al: Survival price of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma sufferers after surgical remedy in Thailand, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:1107�1110, 2013. Sudo Y, et al: Oncocytic biliary cystadenocarcinoma is a form of intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the liver, Mod Pathol 14:1304� 1309, 2001. Szendroi M, et al: Asbestos bodies in a bile duct cancer after occupational publicity, Environ Res 30:270�280, 1983. Thomas M: Systemic and focused remedy for biliary tract tumors and first liver tumours, Surg Oncol Clin N Am 23:369�381, 2014. Torbenson M, et al: Bile duct dysplasia within the setting of persistent hepatitis C and alcohol cirrhosis, Am J Surg Pathol 31:1410�1413, 2007. Uchiyama K, et al: Impact of nodal involvement on surgical outcomes in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre evaluation by the Study Group for Hepatic Surgery of the Japanese Society of HepatoBiliaryPancreatic Surgery, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 18:443� 452, 2011. Valle J, et al: Cisplatin plus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer, N Engl J Med 362:1273�1281, 2010. Vallin M, et al: Unrecognised intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an evaluation of 993 adult cirrhotic liver explants, Clin Transplant 27:403� 409, 2013. Vogl T, et al: Hepatic arterial chemotherapy with gemcitabine in patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinomas and liver metastases of pancreatic cancer: a scientific research on maximum tolerable dose and treatment efficacy, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:745�755, 2006. Wang Y, et al: Prognostic nomogram for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after partial hepatectomy, J Clin Oncol 31:1188�1195, 2013. Watanapa P: Cholangiocarcinoma in sufferers with opisthorchiasis, Br J Surg 83:1062�1064, 1996. Wise C, et al: Mechanisms of biliary carcinogenesis and progress, World J Gastroenterol 14:2986�2989, 2008. Wolf H, et al: Oncocytic differentiation in intrahepatic biliary cystadenocarcinoma, Mod Pathol 5:665�668, 1992. Wong O, et al: An industry-wide epidemiologic examine of vinyl chloride workers, Am J Ind Med 20:317�334, 1991. Yamamoto M, et al: Extended resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in Japan, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 6:117�121, 1999. Yamamoto M, et al: Does gross look point out prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma Yamanaka K, et al: A single-center analysis of the survival advantages of adjuvant gemcitabine chemotherapy for biliary tract most cancers, Int J Clin Oncol 19:485�489, 2014. Yamasaki S: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: macroscopic kind and stage classification, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 10:288�291, 2003. Yen S, et al: Extrahepatic bile duct cancer and smoking, beverage consumption, past medical history and oral contraceptive use, Cancer fifty nine:2112�2116, 1987. Yi S, et al: Efficacy of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with 5-fluroruracil or gemcitabine in locally superior biliary tract cancer, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73:191�198, 2014. Yonemoto N, et al: A multi-centre retrospective evaluation of survival advantages of chemotherapy for unresectable biliary tract cancer, Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:843�851, 2007. Patients usually are seen for medical consideration after the development of jaundice secondary to biliary obstruction, and optimal patient management requires thorough workup and multidisciplinary evaluation for the right choice of patients who could also be eligible for resection. In this article we evaluation the etiology, workup, and staging of main tumors of the extrahepatic biliary tree, particularly biliary adenocarcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma, and discuss surgical and nonsurgical choices for remedy of sufferers with this challenging disease process. In complete, cholangiocarcinomas account for 3% of gastrointestinal malignancies (De Jong et al, 2012), with an annual population incidence within the West of 0. This incidence varies with geography, and in some parts of Asia the incidence could be as excessive as 113 per a hundred,000 for males and 50 per 100,000 for females (Tyson & El-Serag, 2011). In the United States, approximately 5000 new instances of cholangiocarcinoma happen yearly (De Jong et al, 2012). Anatomically, cholangiocarcinoma is categorized as both intrahepatic or extrahepatic primarily based on their location. In the United States, approximately 3000 new cases of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma happen yearly (Siegel et al, 2015), with the majority arising from the biliary confluence (hilar cholangiocarcinoma). Hilar cholangiocarcinoma was initially described by Klatskin in 1965, and these malignancies account for about 50% of all cholangiocarcinomas (De Oliveira et al, 2007). The majority of these malignancies develop sporadically, however sure risk factors for his or her improvement exist. Another risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma is biliary cystic disease, also referred to as choledochal cysts, which are congenital dilations of the biliary tree (see Chapter 46). The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with choledochal cysts is 818 estimated to range from 6% to 30% (Suarez-Munoz et al, 2013), and cholangiocarcinoma develops in these choledochal cyst patients earlier, with a mean age of 32 at analysis of malignancy in one series (Valero et al, 2012). Resection of the extrahepatic biliary tree before growth of cancer and reconstruction by Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy can result in total survival of as much as 96% (Ono et al, 2010). Even after resection of choledochal cysts, however, these patients are in danger for the late improvement of cholangiocarcinoma and require long-term surveillance (Soares et al, 2014). Parasitic infections of the bile ducts are additionally threat elements for cholangiocarcinoma (see Chapter 45). Increased risk is seen in infections from liver flukes (Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini), which lay eggs in the biliary tree, leading to continual irritation and presumed malignant transformation of the biliary epithelium (Watanapa, 1996; Watanapa & Watanapa, 2002). Infections from biliary ascariasis or hepatic schistosomiasis are also risk elements for the development of cholangiocarcinoma (Cai et al, 2011). Chronic hepatolithiasis is a danger factor for cholangiocarcinoma, which again is presumed to arise within the setting of persistent irritation of the bile ducts and biliary stasis (see Chapters 39 and 44). Hepatolithiasis, which can provide rise to recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, is uncommon within the West but is seen far more frequently in East Asia, with an incidence of 20% to 30% in sufferers undergoing surgical procedure for gallstone illness (Lee et al, 2013). Thorium dioxide emits alpha particles, is retained within the reticuloendothelial system, and has a really lengthy half-life (400 years) (Zhu et al, 2004). The use of this agent was banned in the Nineteen Sixties; however, cholangiocarcinomas could develop in patients in whom it was used even a long time after the exposure. Exposure to other chemical compounds, similar to nitrosamines, are also danger elements (Khan et al, 2008). Increased threat for cholangiocarcinoma can also be seen in genetic issues such as Lynch syndrome and biliary papillomatosis (see Chapter 48). Biliary papillomatosis is a rare disease during which a number of papules develop inside the biliary tree. Biliary papillomatosis is thus a premalignant condition, with an approximately 80% price of malignant transformation seen in one series (Lee et al, 2004), and patients should endure resection to forestall the event of cholangiocarcinoma. A, Contrast-enhanced computed tomographic scan exhibiting hilar bile duct tumor involving the best and left hepatic ducts. Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is more common than intrahepatic, and the commonest location for extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is within the biliary hilum on the confluence of the proper and left hepatic ducts.
Albendazole 400 mg buy lowest price
The high concentration of albumin is believed to facilitate elimination of nonpolar molecules known to bind to albumin primary hiv infection symptoms rash generic albendazole 400 mg with amex. Detoxification of these nonpolar waste molecules occurs when the albumin passes over adsorbent columns hiv infection and aids symptoms discount albendazole 400 mg fast delivery, including an anion trade resin column and an activated charcoal column (Steiner et al, 2004). The secondary circuit also features a typical low-flux dialysis for cleansing of water-soluble molecules. The etiologies of cirrhosis had been hepatitis C in 1 affected person and alcohol abuse in the remaining; the precipitating occasions had been unknown in 10 instances. A limitation of this research was its quick interval from randomization to liver transplantation (approximately 16 hours). Moreover, this examine displays the excessive efficacy of liver transplantation, with 1 year survival rates approaching and often exceeding 90%. Primary finish points have been survival possibilities at days 28 and ninety, regardless of liver transplantation. Therefore many investigators consider that liver help at this degree of complexity requires the usage of a biologic part that contains a mammalian liver tissue preparation. Accordingly, investigators have used numerous biologic configurations to help a failing liver consisting of whole livers, hepatocyte transplantation, primary hepatocytes and hepatocyte-based cell traces. Ex Vivo Liver Perfusion In 1965, Eiseman and colleagues (1965) reported the utilization of xenogeneic (porcine) liver hemoperfusion to treat eight comatose patients. None of these sufferers survived, however transient clinical improvement, such as awakening from the comatose state, was reported. Later, in 1967, Burnell and colleagues (1967) reported using human-human cross-circulation in the treatment of three patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Evident after the remedies have been signs of hyperacute rejection, corresponding to gastrointestinal bleeding, hemolysis, and thrombocytopenia, and fewer specific signs, corresponding to fever and nausea, that may subside after each session. Hemoperfusion of human organs not suitable for transplantation have been additionally reported, together with two of three sufferers bridged to transplantation in 1993 (Fox et al, 1993). Prometheus features by fractionating the plasma component of blood, during which the fractionated plasma is detoxified because it passes through two adsorption columns. Hepatocyte Transplantation Transplantation of hepatocytes is promising for sufferers with inherited liver issues, such as tyrosinemia (Grompe et al, 1994) and hyperbilirubinemia Crigler-Najjar syndrome (Fox et al, 1998), which eventually lead to liver failure. The possibility of treating liver insufficiencies with hepatocyte transplantation has been investigated through the years. The infusion of purified glucocerebridase in patients with enzyme problems, such as Gaucher disease, has been attempted (Brady et al, 1974). Allogeneic hepatocyte transplantation to animals with enzyme deficiencies is a promising choice. Studies in the mid1970s showed conjugation of bilirubin in Gunn rats with deficiency in the enzyme uridine diphosphate glucoronyltransferase after alloinfusion of functional hepatocytes in the portal vein alone (Matas et al, 1976), and each the portal vein and intramuscularly (Groth et al, 1977). A semipermeable membrane consisting of a hollow-fiber module on this instance separates the 2 compartments. The molecular weight cut-off of the semipermeable membrane might range from 65 kDa to 0. Depending on the hydration standing and kidney operate of the patient, water could be removed from the albumin resolution as ultrafiltrate from a high-flux dialysis module. Experimental models of liver failure and genetic defects of liver metabolism point out that transplanted hepatocytes can assume the total range of capabilities of intact whole livers (Arkadopoulos et al. Intraportal infusions of hepatocytes in humans succeeded the intraportal infusion of purified enzymes. These issues have partially been corrected by hepatocyte transplantation, and these attempts have shown a proof of precept for cell transplantation remedy (Hughes et al, 2012; Strom et al, 2006). These methods differ in perfusion price, cell supply, cell mass, and period of treatment (continuous vs. The indications have been liver failure caused by viral and toxic etiologies and decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis and sepsis. The system contained pig hepatocytes in liquid suspension together with activated charcoal granules. The 20-mL system was perfused by way of an external Scribner atrioventricular shunt. However, it was not till the mid-1970s that Wolf and colleagues (1975) placed hepatoma cells in the extra-fiber house of the hollow-fiber cartridge and confirmed that an extracorporeal device was capable of performing liver-specific capabilities, similar to conjugating bilirubin. The authors concluded that the HepatAssist System, and its use of xenogeneic pig hepatocytes, was secure with regard to zoonosis; all sufferers examined negative for porcine endogenous retrovirus after remedy. The HepatAssist System used a hollow-fiber� primarily based configuration with membrane pore measurement of roughly 0. Two teams of sufferers have been studied: these judged to nonetheless have a potentially recoverable lesion (group 1, 17 patients) and sufferers who already fulfilled standards for transplantation (group 2, 7 patients). All patients in the Millis study have been efficiently bridged to transplantation, and the 30-day mortality price was 20% (1 affected person died). The etiologies included primary biliary cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, major nonfunction, and liver trauma. Two of seven died, including the affected person with liver trauma and subsequent liver transplantation. The trial utilized isolated main porcine hepatocytes (as a lot as 230 g) contained in a radial flow bioreactor. The trial demonstrated security; all eight sufferers had been efficiently bridged to transplantation, and all were alive at the 3 year follow-up. The survival rate was no less than 33% (2/6), and none of the patients was listed for transplantation. The authors applied a hollow-fiber configuration by which plasma circulated contained in the hole fibers with the first porcine hepatocytes positioned on the outside of the hole fibers. The reported mortality rate was 25%, but the size of the follow-up period was not talked about. Hepatic Cirrhosis, Portal Hypertension, and Hepatic Failure Chapter eighty Support of the failing liver 1187 hollow-fiber bioreactor loaded with 10 billion major porcine hepatocytes. Extracorporeal Liver Support and Study End Points Should survival be the most important end point to assess liver help The ideal clinical finish level is transplant-free survival, thus assessing the impact of a therapy on avoiding liver transplantation and its short-term and long-term morbidities. There are, nonetheless, different important finish points, such as improvement in symptoms. However, use of the nonbiologic remedy in choose teams of sufferers, corresponding to drug overdose or extreme hepatic encephalopathy, could additionally be justifiable. These two reviews have been uncontrolled evaluations of nonbiologic liver help methods. Future research should tackle when to initiate liver assist therapy and the period of remedy. The trials carried out thus far have proven safety and proof of concept; however, efficacy information to convincingly demonstrate assist of a affected person with a failing liver are nonetheless lacking. Various novel configurations have been undertaken to enhance hepatocyte viability and useful activity in the quest to enhance gadget efficacy.
Cheap albendazole 400 mg line
This is very relevant relating to differentiation and grade of particular person tumors hiv infection after 1 year symptoms generic albendazole 400 mg line, which have a major influence on prognostication and selection of remedy (Klimstra et al hiv infection rate in nigeria discount 400 mg albendazole fast delivery, 2010). Although not anatomically helpful in operative planning, somatostatin receptor scintigraphy and octreoscanning are helpful in evaluating the overall illness extent and the positioning of the primary when not acknowledged by different research; these are additionally useful in modifying therapy strategies (Slooter et al, 2001). Approximately 20% of sufferers with carcinoid syndrome may have clinically evident carcinoid coronary heart disease, and a fair bigger proportion may have occult coronary heart disease detectable by echocardiography (Bernheim et al, 2007). The recognition of carcinoid coronary heart illness demands a radical cardiac evaluation (Fox et al, 2004). The main implication of carcinoid coronary heart illness is the presence of proper coronary heart failure and the consequently elevated systemic venous pressures that can trigger a pulsatile liver (implying hepatic vein pressures >25 mm Hg), which precludes hepatic resection. The presence of clinically important carcinoid coronary heart disease dictates medical remedy, and sometimes even valve replacement, previous to resection of the first small intestinal carcinoid and the hepatic metastases (Moller et al, 2003). Survival after surgical repair of carcinoid heart disease is improved in contrast with medical remedy, even without surgical treatment of hepatic metastases (Connolly et al, 1995). Some patients could also be candidates for hepatic resection after repair of carcinoid heart disease, relying upon goal decreases in systemic venous hypertension and the diploma of functional cardiac enchancment (Connolly et al, 2002; Lillegard et al, 2011). Conversely, hepatic resection has been associated with decreased cardiac progression of the carcinoid coronary heart illness and improved prognosis (Bernheim et al, 2008). Any patient with the carcinoid syndrome requires preoperative and intraoperative somatostatin analogue remedy to prevent a carcinoid disaster (Oberg et al, 2004), a scientific syndrome of life-threatening intraoperative hypotension or hypertension and extreme flushing with or without concurrent bronchospasm or arrhythmias. To date, the frequency and components predictive of this perianesthetic complication stay unknown. Prevention is crucial, and acceptable remedy ought to be prescribed in all patients present process intervention for metastatic carcinoid tumors (Kinney et al, 2001). Short-acting analogues are most popular, even when the affected person has acquired the long-acting analogue within 30 days. Management ought to encompass subcutaneous short-acting somatostatin analogue on call to operation and intravenous infusion of the analogue all through the operation and in restoration. Additional intraoperative increases in infusion charges are appropriate for unexplained intraoperative hemodynamic instability. Resection of hepatic metastases is generally indicated provided that full resection of the primary and regional illness is possible. Resection of hepatic metastases should be carried out concurrently, if all gross metastases may be excised. If nearly all of the hepatic disease can be resected (or ablated), cytoreductive resection should be thought of as a end result of each survival and symptom-free high quality of life could also be improved (Chambers et al, 2008; Knox et al, 2004; Mayo et al, 2010; Sarmiento et al, 2003). Malignant Tumors Chapter 93 Hepatic metastasis from neuroendocrine cancers 1357 Several elements have an effect on the pure historical past of both carcinoid and noncarcinoid cancers (Durante et al, 2009). Clearly, liver metastases are essentially the most important issue adversely affecting consequence (Moertel 1987; Pape et al, 2008a). Carcinoid heart illness occurs only within the presence of metastatic carcinoid tumor to the liver independently and predicts poor survival. The survival of sufferers with clinically severe carcinoid coronary heart disease is approximately 1. Patients with carcinoid heart disease ought to be thought of for hepatic surgery, as acknowledged earlier, because cardiac illness development is decreased and prognosis is improved (Bernheim et al, 2008). Up to 75% of patients who current with midgut or hindgut tumors are more likely to have liver metastases, specifically, the nonfunctioning group, and people with a pancreatic main (likely to be excessive grade) have the highest fee of liver involvement (Steinmuller et al, 2008). In a series of 35 patients with hepatic metastases, 60% of which have been from gastrinomas, the 5-year survival was roughly 70%. In sufferers who reply to chemotherapy, further cytoreduction is a sound and direct technique of offering aid from signs. However, whether cytoreduction by resection is extra advantageous than that from different liverdirected therapies lacks evidentiary help (see Chapter 96A). Based on these premises, hepatic cytoreduction, both by hepatic resection or other liver-directed therapy, should be undertaken to address scientific endocrinopathies and improve survival when feasible. Importantly, the amount of residual tumor, not the percentage of tumor removed, is essential to the diploma and durability of the scientific response. In fact, the goal should be full cytoreduction either grossly intraoperatively or complete cytoreduction by imaging postoperatively. Reduction of more than 90% of the volume of hepatic metastases (a previously described threshold) can end result in significantly completely different residual cancer volumes based on variations of the incident metastatic volume. Both time-to-recurrence of symptoms and survival are related to residual metastatic cancer volume. In attempting to reduce the residual tumor volume, theoretically, resection (or transplantation) provides the potential for a extra "complete" cytoreduction without affecting other treatment options. The sequential combination of resection with other liver-directed therapies could additionally be indicated to truly decrease the residual tumor quantity. Focusing on minimizing any residual illness, the definition of resectable liver disease is extra restrictive. Patients with restricted unilobar or bilobar illness may be thought of for resection, with or with out adjunctive measures such as ablation, once more assuming all identifiable disease can be addressed in this manner. However, these patients with a diffuse metastatic burden are unlikely to benefit from surgical resection with gross illness remaining and are doubtless more acceptable for consideration of either transplantation or catheter-based therapies. Furthermore, the appropriate number of patients for resection and the definition of resectability stay debatable. Initially, we showed that debulking hepatic resection could possibly be performed safely, and total survival approached 75% at four years (Que et al, 1995). Subsequent findings in one hundred seventy sufferers present process hepatic resections confirmed that symptoms resolved in 98% of patients. Median time to recurrence of symptoms was 45 months, however 40% of patients were asymptomatic at 5 years. Overall survival was 61% and 35% at 5 and 10 years, respectively, and perioperative mortality fee was 1. Importantly, a threshold of 90% quantity discount was chosen empirically as a variety issue for hepatic resection in most reports. The total quantity of tumor and resected tumor has been estimated solely, and no information specifically determine 90% because the optimum threshold. Overall survival has not differed considerably in most sequence by margin standing (R0, R1 vs. R2), though a latest international multicenter evaluation did show a significantly decreased survival for R2 resections in sufferers with endocrinopathies (Mayo et al, 2010). An extra consideration is the sample of metastatic illness and the extent of resection required. Preoperative portal vein embolization with staged hepatic resection has been used successfully. Additionally, a single-stage resection combining extended hepatic resection with ablation has additionally been used (Glazer et al, 2010). However, the enthusiasm for extended resections should be tempered by the belief that the overall frequency of recurrence or development after hepatic resection is approximately 60% to 80% at 5 years, and nearly 100% by 10 years, and the elimination of enormous volumes of normal liver with prolonged resections might limit future therapeutic options. Similar to the initial resection, the extent and distribution of hepatic recurrence dictates the choice of therapy.
Echinaceawurzel (Echinacea). Albendazole.
- What other names is Echinacea known by?
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs), migraine headaches, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), eczema, hayfever, allergies, bee stings, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), influenza (flu), and other conditions.
- How does Echinacea work?
- Dosing considerations for Echinacea.
- Is Echinacea effective?
- Preventing vaginal yeast infections when used with a medicated cream called econazole (Spectazole).
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Preventing recurrent genital herpes.
- What is Echinacea?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96942
Purchase albendazole 400 mg amex
Sasatomi E hiv infection rates us order 400 mg albendazole fast delivery, et al: Precancerous conditions of gallbladder carcinoma: overview of histopathologic characteristics and molecular genetic findings hiv infection early stages purchase 400 mg albendazole with visa, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 7(6):556�567, 2000. Sato M, et al: Localized gallbladder carcinoma: sonographic findings, Abdom Imaging 26(6):619�622, 2001. Serra I, et al: Risk components for gallbladder most cancers: an international collaborative case-control examine, Cancer 78(7):1515�1517, 1996. Sharma A, et al: Best supportive care compared with chemotherapy for unresectable gall bladder most cancers: a randomized controlled research, J Clin Oncol 28(30):4581�4586, 2010a. Shimizu Y, et al: Should the extrahepatic bile duct be resected for domestically advanced gallbladder most cancers Shindoh J, et al: Tumor location is a robust predictor of tumor development and survival in T2 gallbladder cancer: a global multicenter research, Ann Surg 2014. Shinkai H, et al: Surgical indications for small polypoid lesions of the gallbladder, Am J Surg 175(2):114�117, 1998. Shirai Y, et al: Inapparent carcinoma of the gallbladder: an appraisal of a radical second operation after simple cholecystectomy, Ann Surg 215(4):326�331, 1992a. Shirai Y, et al: Radical surgery for gallbladder carcinoma: long-term results, Ann Surg 216(5):565�568, 1992b. Shirai Y, et al: Identification of the regional lymphatic system of the gallbladder by vital staining, Br J Surg 79(7):659�662, 1992c. Shoup M, Fong Y: Surgical indications and extent of resection in gallbladder most cancers, Surg Oncol Clin N Am 11(4):985�994, 2002. Stunell H, et al: Imaging of adenomyomatosis of the gall bladder, J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 52(2):109�117, 2008. Sumiyoshi K, et al: Pathology of carcinoma of the gallbladder, World J Surg 15(3):315�321, 1991. Suzuki S, et al: Appraisal of surgical treatment for pT2 gallbladder carcinomas, World J Surg 28(2):160�165, 2004. Takahashi T, et al: Aberrant promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in gallbladder carcinoma and chronic cholecystitis, Clin Cancer Res 10(18 Pt 1):6126�6133, 2004. Thorbjarnarson B, Glenn F: Carcinoma of the gallbladder, Cancer 12:1009�1015, 1959. Togawa O, et al: Management of occluded uncovered metallic stents in patients with malignant distal biliary obstructions utilizing coated metallic stents, J Clin Gastroenterol 42(5):546�549, 2008. Toyonaga T, et al: Completion radical surgery after cholecystectomy for by chance undiagnosed gallbladder carcinoma, World J Surg 27(3):266�271, 2003. Verderame F, et al: Gemcitabine and oxaliplatin combination chemotherapy in superior biliary tract cancers, Ann Oncol 17(Suppl 7):vii68�vii72, 2006. Yamaguchi K, Enjoji M: Carcinoma of the gallbladder: a clinicopathology of 103 patients and a newly proposed staging, Cancer 62(7):1425� 1432, 1988. Yamaguchi A, et al: Carcinoma in situ of the gallbladder with superficial extension into the Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses and mucous glands, Gastroenterol Jpn 27(6):765�772, 1992. Yamaguchi K, Tsuneyoshi M: Subclinical gallbladder carcinoma, Am J Surg 163(4):382�386, 1992. Zhang M, et al: Correlated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and P53, Bax in benign and malignant diseased gallbladder, Ann Anat 185(6):549�554, 2003. As with other primary adenocarcinomas of the upper gastrointestinal tract, these tumors often current with symptoms caused by superior local or metastatic illness. They are biologically aggressive, and surgical resection, where possible, is the only identified probably curative therapy. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is also referred to as peripheral cholangiocarcinoma, cholangiolar cancer, or cholangiocellular carcinoma, and these terms have previously been used interchangeably. Cholangiocellular carcinoma was first used in 1959 by Steiner and Higginson to describe a subtype of cholangiocarcinoma during which the glands are small and common with inconspicuous lumina and resemble proliferating cholangioles. Foster and Berman (1977) described solely thirteen circumstances in their summary of early hepatic surgical procedure in the United States whereas they current 112 resections for hepatocellular carcinoma and forty seven circumstances of hepatoblastoma. This low number of resections could characterize the frequency with which superior illness was recognized at presentation. This suggests that the tumors could have completely different etiologic components despite similar microscopic morphology. The highest incidence worldwide is recorded in northeast Thailand (96 per 100,000) (Khan et al, 2002). However, a selection of particular risk elements are acknowledged, many of which lead to chronic irritation of the biliary epithelia. Most of these danger factors contribute to the development of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. There are 5000 to 6000 new circumstances identified yearly within the United States (Jemal et al, 2009; Vauthey & Blumgart 1994) and over one thousand cases annually in the United Kingdom (Khan et al, 2002). This signifies that cholangiocarcinoma is sometimes seen by basic surgeons or gastroenterologists, and its rarity has annoyed attempts to design therapeutic trials. Infection with liver flukes may be current, but recurrent pyogenic cholangitis appears to be a separate situation and may develop in the absence of parasitic infection (Kim et al, 2003). Congenital Biliary Cystic Disease (see Chapter 46) Untreated choledochal cysts carry an increased danger of developing malignant change. Hepatic Cirrhosis and Viral Infections (see Chapters 70 and 76) the danger of creating cholangiocarcinoma is elevated in sufferers with cirrhosis (10. It has been instructed the increasing incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in the West is expounded to the rising prevalence of continual liver illness and chronic viral an infection (Shaib & El-Serag, 2004; Shaib et al, 2005). Diabetes and weight problems are also associated with an increased danger of cholangiocarcinoma (Malhi & Gores 2006; Oh et al, 2005). Parasitic Infections (see Chapter 45) Chronic infection with the liver flukes Opisthorchis viverrini and Clinorchis sinensis is carefully related to elevated danger of creating cholangiocarcinoma in Southeast Asia (Hasweel-Elkins et al, 2008; Jang et al, 2008; Sripa & Pairojkul, 2008; Sripa et al, 2007; Watanapa, 1996; Watanapa & Watanapa, 2002). However, mechanical irritation, excreted metabolic products, and the actions of proinflammatory cytokines, significantly those who stimulate the discharge of nitric oxide from activated white blood cells, could all play a role (Sripa et al, 2007). A additional parasitic hepatic infestation is brought on by the trematode Fasciola hepatica or Fasciola gigantica. These parasites are widespread all through Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. Hepatolithiasis (see Chapters 39 and 44) Recurrent pyogenic cholangiohepatitis is characterized by recurrent episodes of ascending cholangitis, hepatolithiasis, biliary stricturing, and dilation. Patients present with recurrent episodes of cholangitis and, on investigation, have significant hepatolithiasis and related inflammatory biliary strictures (Chu et al, 1997). The imply interval between the Benign Biliary Tumors (see Chapters forty eight and 90B) the development of biliary cystadenocarcinomas from biliary cystadenomas is uncommon and, normally, happens if a cystadenocarcinoma is untreated for many years. Biliary cystadenomas with out ovarian stromal tissue appear to be at higher threat of C. Patients present with cystadenocarcinomas in the sixth or seventh decade of life, whereas cystadenomas current at an earlier age (Buetow et al, 1995). Chemical Agents Thorotrast (thorium dioxide) was used as a radiologic distinction agent between 1928 and 1950. It accumulates within the reticuloendothelial cells within the liver and spleen and will increase the risk of growing cholangiocarcinoma by 300 instances compared with the general population (Lipshutz et al, 2002; Rubel & Ishak, 1982).
Syndromes
- Diabetes in the birth mother
- Shock
- When hiking in an area known to have snakes, wear long pants and boots if possible.
- General anesthesia: You are asleep and pain-free
- Viral infections (such as Herpes simplex)
- Consumer groups
- HIV testing
- Fever
Order albendazole 400 mg with visa
Predictions in regards to the level of obstruction and diploma of isolation of the biliary tree could be made primarily based on the preprocedure imaging research hiv infection rates in african countries generic albendazole 400 mg on-line. Patients with Bismuth kind I obstruction can have the whole liver drained with one catheter or stent hiv infection rates in the us generic albendazole 400 mg, because proper and left ducts communicate freely. Barring one of the previously talked about contraindications, these sufferers have a main stent placed. Some suggest that survival is healthier when either side of the liver are drained (Chang et al, 1998). In both case, we favor to stent into the common bile duct and not into the duodenum if attainable so as to preserve function of the sphincter of Oddi. One benefit of the extra anatomic Y-shaped configuration stent placement is that if stent occlusion occurs, both stents are approachable endoscopically. In this case, and within the absence of some other contraindication, a affected person being drained for pruritus alone might have a primary stent placed, because only a small portion of the liver must be drained to alleviate pruritus. We use this as a rule of thumb, regardless of that in a sequence of 149 sufferers drained at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, we discovered solely a marginally vital difference within the variety of patients attaining a bilirubin lower than 2 mg/dL, based on the estimated volume of liver drained. In this evaluation, 6 (29%) of 21 sufferers with lower than one third of the liver drained attained a bilirubin stage under 2 mg/dL, whereas this was achieved in sixty five (51%) of 128 sufferers with multiple third of the liver drained (P =. After stent placement, if the bilirubin fails to fall to the desired stage, a second drainage process can be performed. If an internal/external drainage catheter is positioned, and subsequently the serum bilirubin normalizes without proof of cholangitis, the affected person can bear stenting of that portion of the liver drained by the catheter. When the preliminary drainage is on the right aspect, and the tumor has prolonged up the right hepatic duct in order to isolate the anterior and posterior divisions from each other and from the left hepatic duct, side-by-side self-expanding metallic stents may be positioned on the best to drain both the anterior and posterior ducts. Alternatively, when the left facet of the liver is useful, a left drainage may be performed as the following step; then one stent may be placed from the left, and another may be placed from the best. Although a big distinction in patency is reported when multiple stent is placed in a noncoaxial method (Maybody et al, 2009), the mean patency of multiple stents is almost 6 months, justifying stent placement. The ideas of biliary drainage are simple, however when high bile duct obstruction is present, the planning is advanced, and execution could be tough. The patient must have sufficient of the liver drained to be free of cholangitis and pruritus and to effect a discount in serum bilirubin to obtain chemotherapy, if indicated. Given that no distinction in stent patency is reported if the stent is inserted for proximal or distal obstruction, that a big difference in patency is seen when multiple stent is positioned, and that decrease complication charges are reported when stents are positioned primarily, major stent placement ought to be considered whenever possible (Inal et al, 2003a, 2003c; Maybody et al, 2009). With proper technique, together with peripheral bile duct puncture, critical bleeding complications are unusual. Because the hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct journey side by side inside portal triads, blood could enter the bile duct during catheter exchanges, leading to hemobilia within the quick postprocedure period (see Chapter 125). Hemobilia usually clears within 24 hours, and new or recurrent hemobilia throughout the first few days of drainage usually is said to catheter malposition. If the catheter is pulled out from its authentic position, a catheter sidehole might turn out to be positioned adjoining to a portal vein department; this problem can be corrected by simply repositioning the catheter, but the catheter is usually upsized as well. No matter the place the preliminary puncture is carried out to opacify the biliary tree, makes an attempt are at all times made to puncture a peripheral bile duct for catheter placement, preferably a fourth-order or fifth-order branch. The more peripheral the bile duct punctured, the smaller the accompanying hepatic artery department, and the lower the danger of arterial damage and postprocedure bleeding. Despite prophylactic antibiotic protection, sepsis may happen instantly after or inside several hours of drainage and should be handled appropriately (Smith et al, 2004). This is most regularly manifested by the development of rigors with normal or low body temperature, however hypotension and fever can also occur. Sepsis is managed with continued administration of appropriate antibiotics, enlargement of intravascular volume, and pressor support if necessary. Blood cultures should be drawn to identify organisms answerable for the bacteremia. This is particularly essential for these with preprocedure fever, biliary-enteric anastomosis or sphincterotomy, previous endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or an indwelling stent or catheter. Although positive bile cultures are extra frequent in sufferers with benign bile duct obstruction, cultures are constructive in additional than half of patients with malignant obstruction. Five percent of patients without fever, earlier biliary surgery, or endoscopic or percutaneous intervention have constructive bile cultures (Brody et al, 1998). Leaking is most often associated to the catheter turning into malpositioned in order that one or more sideholes are not inside the biliary tree however are in the catheter tract or even outside the patient. Leakage may also be seen with lack of adequate sideholes above the level of obstruction. Anything that impedes the move of bile from above the obstruction, either through the catheter to beneath the obstruction or right into a drainage bag, will lead to bile leaking again alongside an established tract. For a properly positioned catheter with an acceptable variety of sideholes, the issue is definitely remedied by catheter change. Patients with capped internal-external catheters may have bile leak back alongside the catheter tract when egress of bile is obstructed internally. Distal sidehole occlusion is the commonest cause, and this downside is definitely remedied by catheter exchange. Patients with duodenal obstruction or impaired small bowel motility may be relegated to obligate exterior drainage. The greatest remedy is to set up internal biliary drainage with stent placement as expeditiously as possible. Ascites may be tapped frequently or drained by a Tenckhoff catheter in an try to enable time for tract maturation. These methods typically fail ultimately, and as a final resort, a stoma system is positioned around the entry site to contain the ascites. The consequence is determined by the situation of the underlying hepatic parenchyma, the diploma of isolation of the biliary tree, and the technical abilities of the operator. A thorough understanding of useful biliary anatomy and the supply of high-quality C. Malignant Tumors Chapter 52 Interventional methods in hilar and intrahepatic biliary strictures 859 imaging are necessary to optimize consequence. Although pruritus could additionally be palliated by draining even one section of the liver, lowering the serum bilirubin to normal or near-normal is greatest achieved by draining at least 30% of the liver, assuming the underlying parenchyma is relatively normal. Contamination of undrained elements of the biliary tree may outcome from drainage catheter placement, with ongoing or recurrent cholangitis becoming an issue. For this purpose, primary stent placement must be thought-about when 30% or extra of the liver could be drained at the initial process. Malignant Tumors Chapter fifty two Interventional strategies in hilar and intrahepatic biliary strictures 859. Green C, et al: Does stent placement across the ampulla of Vater improve the risk of subsequent cholangitis Inal M, et al: Percutaneous placement of biliary metallic stents in sufferers with malignant hilar obstruction: unilobar versus bilobar drainage, J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(11):1409�1416, 2003a.

400 mg albendazole purchase with mastercard
Although modifications in vascular resistance to circulate of blood between the splanchnic bed and the best atrium seem to be the preliminary occasions within the improvement of portal hypertension hiv infection symptoms in infants albendazole 400 mg discount, numerous other hemodynamic modifications contribute to and amplify the elevated portal blood strain hiv infection rate in puerto rico discount 400 mg albendazole. There is a hyperdynamic circulatory state with elevated cardiac and decreased splanchnic arteriolar tone, each of which improve portal influx. Changes in intravascular quantity also play an necessary position, as do alterations in adrenergic tone in the splanchnic system. These observations have led to guidelines for using nonselective -blockers as pharmacologic remedies choices for portal hypertension in adults (Garcia-Tsao et al, 2007). However, as a end result of the most important medical impact is that of bleeding from esophageal varices, direct treatment of variceal hemorrhage or shunt surgery in chosen instances (see Chapters 82 to 87) remains the first strategy, except within the presence of liver decompensation, during which case the therapy of choice is liver transplantation (see Chapters 112, 116, and 118). In extrahepatic portal hypertension, or in the presence of compensated liver disease, signs may be absent. The liver is usually small and impalpable; with an intrahepatic cause; nevertheless, it can be enlarged, exhausting, or nodular with a small proper lobe and/ or splenomegaly. Cutaneous options such as spider angiomata, outstanding periumbilical veins (caput medusae), and palmar erythema might present a clue to the presence of liver disease. However, the looks of latest spider angiomata or more than five or six may be indicative. They are incessantly observed within the vascular drainage of the superior vena cava and feature a central arteriole from which radiate quite a few nice vessels, ranging from 2 to 5 mm in diameter. Other cutaneous features embrace straightforward bruising; nice telangiectasia on the face and higher back; white spots, most frequently on buttocks and arms, which when examined with a lens show the beginnings of spider angiomata; and clubbing of the fingers. On intranasal examination, prominent telangiectasia of the realm of Little is frequent and is related to recurrent epistaxis. Children with cholestatic liver illness may have predominant indicators or signs of persisting jaundice or pruritus. The liver is often enlarged, and xanthelasma, malnutrition, and deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins, significantly vitamins D and K, may be prominent features. Signs of hepatic encephalopathy are subtle and uncommon in kids with portal hypertension. Malnutrition with lowered lean tissue and fats stores as properly as poor linear progress is a wellrecognized and important feature resulting from malabsorption and impaired protein synthesis (Chin et al, 1992). Spontaneous bruising brought on by impaired hepatic manufacturing of clotting components and thrombocytopenia on account of hypersplenism are each indicators of advanced illness. Cirrhosis with decompensation can also be related to changes within the systemic and pulmonary circulations and with arteriolar vasodilation, elevated blood volume, a hyperdynamic circulatory state, and cyanosis on account of intrapulmonary shunting. Ultrasonography allows visualization and measurement of the scale, patency, and circulate of the portal vein; the prevalence of a cavernoma; and details about liver size and homogeneity (see Chapter 15). Renal cysts on ultrasound or a suggestive household history may present a clue to the analysis of congenital hepatic fibrosis. Echocardiography is helpful to exclude major cardiac causes of hepatic venous outflow obstruction. Liver biopsy both aids within the analysis of cirrhosis or excludes liver disease, as in the case of extrahepatic obstruction. Differentiation between cirrhosis and presinusoidal and extrahepatic causes of portal hypertension, corresponding to congenital hepatic fibrosis and extrahepatic portal hypertension, can generally trigger diagnostic difficulties. In each of those latter circumstances, no indicators of persistent liver illness are obvious, and aminotransferases and synthetic liver function are normal. Hepatic Cirrhosis, Portal Hypertension, and Hepatic Failure Chapter seventy eight Portal hypertension in kids 1171 hepatocytes are normal histologically, however prominent, abnormal bile ducts appear in broad bands of fibrous tissue, although nodules are absent. Mild derangement of coagulation parameters may be evident secondary to an underlying coagulation dysfunction, similar to a protein C or S deficiency. Obstruction of hepatic venous outflow causes centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis, with fibrosis that extends from central veins to portal tracts. A full range of laboratory and imaging investigations should be performed before a liver biopsy. Such investigations may be diagnostic for the underlying trigger and will enable appropriate dealing with of the liver biopsy specimen in regard to particular histologic and biochemical analysis, notably for metabolic issues. Suspected obstruction to hepatic venous outflow requires venography and/or cardiac catheterization, that are the diagnostic procedures of alternative in such circumstances. Pressure gradient measurements could also be helpful throughout venous blocks and to determine the magnitude of the portal strain. Encephalopathy rarely requires specific therapy, however ascites can be a main drawback and infrequently does require particular treatment (see Chapter 81). The administration of those and other complications of portal hypertension in children is primarily medical and is beyond the scope of this chapter (see Chapters eighty one to 87). In most instances, direct therapy of varices is indicated before considering surgery as a end result of the varied choices for creation of a surgical shunt are oblique remedies for varices by reduction of portal strain. The four primary factors that influence any choice for the application of shunt surgery in children are the chance of variceal bleeding, the potential evolution of spontaneous shunts over time, the presence or absence of liver disease, and the portal vascular anatomy. Variceal hemorrhage presents clinically as a necessity for emergency remedy or as a need for prophylaxis of preliminary or subsequent rebleeding. Most of the data in regards to the management of variceal hemorrhage have come from giant managed trials in adults, and the pediatric literature is usually descriptive from case sequence or cohorts, with some exceptions. As soon because the blood transfusion is available and the affected person has a safe intravenous infusion line and is hemodynamically secure, referral to a tertiary middle with expertise in the management of variceal hemorrhage in youngsters is recommended. Initial melena or other indicators of a sentinel hemorrhage could precede sudden hematemesis and shock, which require speedy blood transfusion to prevent demise. Significant bleeding with hypotension impairs hepatic perfusion, often causes deterioration of liver perform, and precipitates ascites and encephalopathy. Initial fluid management within the form of crystalloids, followed by pink blood cell transfusion, is necessary, and any coagulopathy ought to be corrected with vitamin K and recent frozen plasma. Pharmacologic remedy with a short-acting splanchnic vasoconstrictor must be initiated. Octreotide is the drug of choice in this circumstance (maximum dose, 1 �g/kg/hr intravenously or 2 to 4 �g/kg/8 hr subcutaneously for twenty-four hr, or till bleeding has ceased) due to fewer side effects (Moitinho et al, 2001). Studies in adults have indicated that an adjunctive vasodilator, corresponding to nitroglycerine within the form of a 10 mg patch, could scale back these hemodynamic issues. Nasogastric intubation is an important a half of administration, permitting the documentation of ongoing bleeding and the removal of blood that might precipitate encephalopathy. There is a excessive incidence of rebleeding once the tube is removed and subsequently should solely be use as a briefly measure to a extra definitive remedy. A Emergency Surgical Approaches and Emergency Portosystemic Shunts B Emergency creation of portosystemic shunts or other surgical therapy is normally a final resort for persistent, acute, exsanguinating variceal hemorrhage (see Chapters 84 to 87). Patients with shunts who come to the emergency department usually have gastric variceal bleeding.
Cheap 400 mg albendazole with visa
He gave descriptions of amebae antiviral drugs for flu purchase albendazole 400 mg overnight delivery, including structure ebv antiviral albendazole 400 mg buy discount, dimension, motility, intracytoplasmic parts, and drawings. L�sch named the amebae after his affected person; Amoeba coli was proved in a while sequencing of the genome (Tovar et al, 1999); and a calreticulin-like protein and Golgi apparatus were detected in the amebae (Gonzalez et al, 2002). Stephanos Kartulis, a Greek doctor, found amebae in intestinal ulcers in sufferers from Egypt in 1885 and noted that he never found amebae from nondysenteric cases (Kartulis, 1886). The first effective remedy got here from Brazil in the form of ipecac; emetine was isolated from ipecac in the nineteenth century. Leonard Rogers (1912), professor of pathology at Medical College Hospital in Calcutta, India, reported successful therapy of both intestinal and hepatic amebiasis by injectable salts of emetine. The Thirties witnessed the introduction of two essential hydroxyquinolines launched by Anderson and Koch in 1931 and by a number of others. Although largely changed by imidazoles in the Eighties, hydroxyquinolines remain helpful right now. In 1966, Powell and his colleagues demonstrated the effectiveness of metronidazole as an amebicidal agent in each intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis. Epidemiology Approximately one tenth of the world inhabitants is believed to be infected with E. Amebiasis is the third most common parasitic reason for demise worldwide (Li & Stanley, 1996). However, current prevalence and morbidity data obtained by way of molecular methods enable building of more dependable map of endemic regions of amebiasis around the globe, similar to on the Asian subcontinent (India, Bangladesh), Africa, Asian Pacific (Thailand, Japan), and South and Central America (Mexico, Colombia) (Ximenez et al, 2009). In developed international locations, it continues to be encountered sporadically in immigrants or travelers from endemic zones, low socioeconomic teams, residents of establishments, and male homosexuals (Ravdin & Stauffer, 2005). In the United States and Europe, gay males are principally colonized with E. In addition, a latest report suggests that parasite genotype performs a role in determining consequence of an infection by E. On the opposite hand, the natural historical past of the illness seems to be the identical as in nonimmunosuppressed sufferers (Kershenobish & Corona, 2008). Cysts represent the infective kind through fecal-oral transmission by way of meals, water, or direct person-to-person contact. Cysts survive the acid of the abdomen and travel by way of the small gut, and throughout the terminal ileum or colon, trophozoites emerge to complete the life cycle (Guerrant, 1986). Cysts can survive for 45 minutes in feces lodged beneath fingernails and for 1 month in soil at 10� C. They stay infective in contemporary water, seawater, and sewage but are destroyed by drying, iodine, and heat. Pathogenesis the illness course is determined by three virulence components: lectin (a floor protein), amebapores (small peptides), and cysteine proteases. Trophozoite adhesion to the colonic wall is mediated by lectin, which outcomes in persistent infection, and caspase three activation, which is a vital step in cell necrosis and abscess formation (Huston et al, 2003). Amebapores are inserted by the trophozoite into the host cell, the place they puncture the lipid bilayer and form a portal of entry into the host. Cysteine proteases contribute to degradation of the extracellular matrix proteins and disruption of cell monolayers (Que & Reed, 1997). It is anticipated that antiamebic antibodies protective towards invasive infection would block lectin binding and neutralize amebapore and cysteine proteases. In addition, experimental proof suggests that liver cell necrosis is elevated when neutrophils are present together with E. Forces exerted on a parasite that adheres to the endothelium are thus much decrease within the sinusoids and should partly clarify why the parasite crosses the endothelium within these structures. Lack of tight junctions in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells can facilitate crossing by the parasite, creating a larger breach when reaching the hepatic parenchyma (Blazquez et al, 2007). Microarrays have been used to compare virulent and avirulent trophozoites (those unable to type liver abscesses) from the identical pressure (Santi-Rocca et al, 2008). Breastfed neonates have a low incidence because of the presence of immunoglobin A (IgA) and low iron content in breast B. Infection and Infestation Chapter seventy three Amebiasis and different parasitic infections 1085 subsequent irritation are options of liver an infection by E. Although some regions of the genome encode highly conserved proteins, other areas exhibit excessive degrees of polymorphism (Haghighi et al, 2002). The purification of trophozoites from completely different organs of the same patients revealed that their tropism was linked to totally different genotypes (Ali et al, 2007). A Host Defense and Potential for Vaccine Development It has not been definitively established which mechanism is answerable for invasion or recurrence (Ravdin & Guerrant, 1982). The second line of adaptive immune response constituted by activated lymphocytes and macrophages is the important effector mechanism towards E. Oral vaccines that use amebic antigens have been developed and tested in animals (Lotter et al, 2004; Mann et al, 1997; Snow & Stanley, 2006). Trophozoites that efficiently penetrate the colonic mucosal barrier cause invasive illness, enter the portal system, and travel to the liver. The cecum is the commonest web site of amebic colitis, and the proper lobe of the liver is extra generally affected because of drainage of the right portal department from the best side of the colon. The fluid itself is free from any amebae, which can be found at the increasing edge of the abscess cavity with little irritation. Amebae are recognized to lyse neutrophils, and the release of neutrophilic mediators may promote hepatocyte dying and extension of the abscess. Lack of fibrotic response by the encompassing tissue with centrifugal extension ends in extension of the abscess to the Glisson capsule, which is immune to the amebae. Left lobe abscesses are less frequent, but because of the smaller quantity of the left liver, abscesses on this location are more prone to rupture the capsule (Thomas & Ravindra, 2000). Vascular and biliary structures could traverse the abscess cavity; due to the intrahepatic overlaying of the Glisson capsule, such structures are immune to the process of liquefactive necrosis. However, these buildings could be mistaken for septa within the abscess cavity, and fracturing of these strands can lead to hemorrhage or biliary leak, or it may possibly create a communication between the vascular and biliary channels and end in hemobilia and jaundice (Singh et al, 2008). The abscess wall is often sick defined with a minimal host response of fibrous tissue, however long-standing abscesses might develop a fibrous wall and should even calcify (Rogers et al, 1980). In treated cases, full resolution is the rule, however it may take 6 months to 2 years or longer (Thomas & Ravindra, 2000) than the usual time for pyogenic abscesses to resolve (Sudhamshu & Sharma, 2009). Treatment with steroids, malignancy, males having sex with males, superior age, and malnutrition might be thought of danger components for extreme illness (Guerrant, 1986; Li & Stanley, 1996). Asymptomatic carriers, or cyst passers, may excrete cysts for a short interval, but the majority of these patients clear the an infection inside 12 months. The time between penetration of colonic mucosa and harm to hepatic parenchyma is unknown. Active diarrhea normally occurs in lower than 30% of sufferers at any time earlier than presentation despite intestinal an infection by E. In most circumstances, normal stool microscopy results are adverse, but in analysis studies, cultures of stool have been optimistic for E. Concomitant hepatic abscess is present in only one third of patients with amebic colitis.