Alesse
Alesse dosages: 0.18 mg
Alesse packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Discount 0.18 mg alesse mastercard
The safety factor caused by washdown of proteins from the interstitial spaces is about 7 mm Hg birth control pills examples alesse 0.18 mg effective. This signifies that the capillary strain in a peripheral tissue might theoretically rise by 17 mm Hg birth control killed my libido order alesse 0.18 mg visa, or approximately double the traditional value, earlier than marked edema would occur. Virtually all these potential areas have surfaces that nearly touch each other, with only a thin layer of fluid in between, and the surfaces slide over one another. The surface membrane of a possible space usu- Increased Lymph Flow as a Safety Factor Against Edema A major operate of the lymphatic system is to return the fluid and proteins filtered from the capillaries into the interstitium to the circulation. Without this steady return of the filtered proteins and fluid to the blood, the plasma quantity can be rapidly depleted, and interstitial edema would happen. The lymphatics act as a security issue towards edema as a end result of lymph flow can enhance 10- to 50-fold when fluid begins to accumulate within the tissues. This elevated lymph flow allows the lymphatics to carry away large amounts of fluid and proteins in response to increased capillary filtration, stopping the interstitial pressure from rising into the constructive strain vary. The safety factor brought on by increased lymph flow has been calculated to be about 7 mm Hg. Consequently, fluid in the capillaries adjacent to the potential house diffuses not solely into the interstitial fluid but in addition into the potential area. Proteins gather in the potential areas because of leakage out of the capillaries, just like the collection of protein within the interstitial areas all through the body. The protein have to be removed through lymphatics or other channels and returned to the circulation. In some instances, such because the pleural cavity and peritoneal cavity, massive lymph vessels come up instantly from the cavity itself. Cifarelli V, Eichmann A: the intestinal lymphatic system: functions and metabolic implications. Jussila L, Alitalo K: Vascular development components and lymphangiogenesis, Physiol Rev eighty two:673, 2002. When edema happens within the subcutaneous tissues adjoining to the potential area, edema fluid normally collects within the potential space as properly; this fluid is recognized as effusion. Thus, lymph blockage or any of the a number of abnormalities that can trigger extreme capillary filtration can cause effusion in the identical way that interstitial edema is caused. The abdominal cavity is particularly susceptible to acquire effusion fluid, and in this case, the effusion is called ascites. The other potential spaces, such as the pleural cavity, pericardial cavity, and joint areas, can become seriously swollen when generalized edema is current. Also, harm or local infection in any one of many cavities usually blocks the lymph drainage, causing isolated swelling in the cavity. The dynamics of fluid trade in the pleural cavity are discussed in detail in Chapter 39. These dynamics are mainly consultant of all the opposite potential spaces as properly. The normal fluid pressure in most or all the potential spaces within the nonedematous state is adverse in the identical means that this pressure is adverse (subatmospheric) in loose subcutaneous tissue. For water and just about all electrolytes within the physique, the balance between intake (due to ingestion or metabolic production) and output (due to excretion or metabolic consumption) is maintained largely by the kidneys. This regulatory perform of the kidneys maintains the steady internal environment needed for the cells to perform their numerous actions. The kidneys perform their most important capabilities by filtering the plasma and eradicating substances from the filtrate at variable charges, depending on the wants of the physique. Ultimately, the kidneys clear unwanted substances from the filtrate (and subsequently from the blood) by excreting them in the urine while returning substances that are needed again to the blood. The kidneys additionally remove most toxins and different international substances which may be produced by the body or ingested, corresponding to pesticides, drugs, and meals additives. If consumption exceeds excretion, the amount of that substance in the body will improve. If consumption is lower than excretion, the quantity of that substance within the physique will lower. Although temporary (or cyclic) imbalances of water and electrolytes may happen in varied physiological and pathophysiological situations associated with altered consumption or renal excretion, the maintenance of life is decided by restoration of water and electrolyte balance. The capability of the kidneys to alter sodium excretion in response to modifications in sodium consumption is super. This phenomenon is also true for water and for most 321 Regulation of Water and Electrolyte Balances. For kidneys are the primary means for eliminating most of the waste products of metabolism that are now not wanted by the body. The kidneys produce 1,25- ihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcid triol),theactiveformofvitaminD,byhydroxylatingthis vitamin at the "number one" place. Calcitriol is essential for regular calcium deposition in bone and calcium reabsorption by the gastrointestinal tract. As discussed in Chapter eighty, calcitriol plays an important position in calcium and phosphate regulation. Effect of accelerating sodium intake 10-fold (from 30 to 300 mEq/day) on urinary sodium excretion and extracellular fluid volume. The shaded areas symbolize the online sodium retention or internet sodium loss, determined by the distinction between sodium consumption and sodium excretion. In the following few chapters, we discuss the particular mechanisms that let the kidneys to carry out these superb feats of homeostasis. As discussed in amino acids and different precursors throughout prolonged fasting, a course of referred to as gluconeogenesis. With chronic kidney disease or acute failure of the kidneys, these homeostatic features are disrupted, and severe abnormalities of physique fluid volumes and composition rapidly happen. With complete renal failure, enough potassium, acids, fluid, and different substances accumulate within the body to trigger death within a few days except clinical interventions similar to hemodialysis are initiated to restore, at least partially, the physique fluid and electrolyte balances. Each kidney of the adult human weighs about a hundred and fifty grams and is in regards to the measurement of a clenched fist. The kidney is surrounded by a troublesome fibrous capsule that protects its delicate internal structures. If the kidney is bisected from prime to backside, the two major areas that may be visualized are the outer cortex and the inner medulla areas. The medulla is divided into eight to 10 cone-shaped plenty of tissue called renal pyramids. The base of each pyramid originates at the border between the cortex and medulla and terminates in the papilla, which projects into the house of the renal pelvis, a funnel-shaped continuation of the upper finish of the ureter. The outer border of the pelvis is split into open-ended pouches called major calyces that stretch downward and divide into minor calyces, which acquire urine from the tubules of each papilla. Chapter 19, the kidneys play a dominant position in longterm regulation of arterial strain by excreting variable amounts of sodium and water. The kidneys also contribute to short-term arterial pressure regulation by secreting hormones and vasoactive components or substances. The kidneys con- tribute to acid�base regulation, along with the lungs and body fluid buffers, by excreting acids and by regulating the body fluid buffer shops. The kidneys are the one technique of eliminating sure kinds of acids from the physique, corresponding to sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid, that are generated by the metabolism of proteins.
Discount alesse 0.18 mg mastercard
Nevertheless birth control pills menstrual cramps 0.18 mg alesse order overnight delivery, the cardiac lesions play an important function in leading to birth control and weight loss 0.18 mg alesse purchase fast delivery the final irreversible stage of shock. Deteriorative lesions also occur in the kidneys, especially in the epithelium of the kidney tubules, resulting in kidney failure and sometimes uremic demise several days later. Deterioration of the lungs additionally typically results in respiratory distress and death several days later, referred to as the shock lung syndrome. Metabolic derangements that oc- tors just discussed that may lead to additional progression of shock are forms of positive feedback-that is, each enhance within the degree of shock causes an additional enhance within the shock. In mild degrees of shock, the unfavorable suggestions mechanisms of the circulation, including sympathetic reflexes, reverse stress-relaxation mechanism of the blood reservoirs, and absorption of fluid into the blood from the interstitial areas, can easily overcome the constructive suggestions influences and, subsequently, cause restoration. Ironically, even in this irreversible stage, remedy can, on uncommon events, return the arterial strain and even the cardiac output to regular or close to regular for brief intervals, but the circulatory system nonetheless continues to deteriorate, and death ensues in one other jiffy to few hours. However, the cardiac output soon begins to fall once more, and subsequent transfusions have less and less effect. Progressive stage Transfusion cur in shocked tissue can result in acidosis all through the physique. This outcomes from poor delivery of oxygen to the tissues, which greatly diminishes oxidative metabolism of the foodstuffs. When this happens, the cells acquire most of their energy by the anaerobic process of glycolysis, which leads to extra lactic acid within the blood. In addition, poor blood flow via tissues prevents regular removal of carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide reacts regionally within the cells with water to type excessive concentrations of intracellular carbonic acid, which, in flip, reacts with various tissue chemical compounds to kind further intracellular acidic substances. Thus, one other deteriorative impact of shock is generalized and local tissue acidosis, resulting in additional progression of the shock. Therefore, in severe shock, a stage is eventually reached at which the particular person will die, despite the fact that vigorous therapy might nonetheless return the cardiac output to normal for short durations. The high-energy phos- phate reserves within the tissues of the physique, especially within the liver and heart, are tremendously diminished in severe shock. Essentially all the creatine phosphate has been degraded, and nearly all of the adenosine triphosphate has downgraded to adenosine diphosphate, adenosine monophosphate and, ultimately, adenosine. Loss of fluid from all fluid compartments of the body is known as dehydration; this situation also can scale back the blood volume and trigger hypovolemic shock similar to that resulting from hemorrhage. Some of the causes of this type of shock are the following: (1) extreme sweating; (2) fluid loss in severe diarrhea or vomiting; (3) extra lack of fluid by the kidneys; (4) inadequate intake of fluid and electrolytes; or (5) destruction of the adrenal cortices, with lack of aldosterone secretion and consequent failure of the kidneys to reabsorb sodium, chloride, and water, which occurs within the absence of the adrenocortical hormone aldosterone. Often, the shock outcomes simply from hemorrhage brought on by the trauma, however it could also occur even without hemorrhage as a result of extensive contusion of the physique can damage the capillaries sufficiently to permit extreme loss of plasma into the tissues. This phenomenon ends in greatly lowered plasma quantity, with resultant hypovolemic shock. Various makes an attempt have been made to implicate toxic factors released by the traumatized tissues as one of the causes of shock after trauma. Traumatic shock, therefore, appears to outcome mainly from hypovolemia, although there may additionally be a moderate diploma of concomitant neurogenic shock caused by lack of vasomotor tone, as discussed subsequent. Distention of the gut in intestinal obstruction partly blocks venous blood move in the intestinal partitions, which will increase intestinal capillary stress, causing fluid to leak from the capillaries into the intestinal walls and intestinal lumen. Severe burns or other denuding conditions of the skin trigger lack of plasma via the denuded pores and skin areas so that the plasma volume becomes markedly lowered. Instead, the vascular capability increases so much that even the traditional quantity of blood is incapable of filling the circulatory system adequately. One of the main causes of this situation is sudden lack of vasomotor tone all through the body, ensuing particularly in massive dilation of the veins. The function of vascular capacity in helping regulate circulatory operate was discussed in Chapter 15, where it was noted that an increase in vascular capability or a decrease in blood volume reduces the imply systemic filling strain, which reduces venous return to the guts. Diminished venous return caused by vascular dilation known as venous pooling of blood. Some neurogenic components that can cause loss of vasomotor tone include the next: 1. Deep general anesthesia often depresses the vasomotor heart sufficient to cause vasomotor paralysis, with ensuing neurogenic shock. Spinal anesthesia, particularly when this extends all the means in which up the spinal cord, blocks the sympathetic nervous outflow from the nervous system and can be a potent cause of neurogenic shock. Also, even though mind ischemia for a couple of minutes almost always causes excessive vasomotor stimulation and elevated blood strain, extended ischemia (lasting >5�10 minutes) could cause the alternative effect-total inactivation of the vasomotor neurons within the mind stem, with a consequent decrease in arterial pressure and development of severe neurogenic shock. Septic shock is extremely essential to the clinician because, apart from cardiogenic shock, septic shock is currently the most frequent reason for shock-related dying in the hospital. Peritonitis caused by unfold of infection from the uterus and fallopian tubes, typically ensuing from an instrumental abortion performed beneath unsterile situations 2. Peritonitis ensuing from rupture of the gastrointestinal system, generally caused by intestinal illness or by wounds 3. Generalized bodily infection resulting from unfold of a skin an infection similar to streptococcal or staphylococcal infection 4. Generalized gangrenous infection ensuing specifically from gasoline gangrene bacilli, spreading first by way of peripheral tissues and finally through the blood to the inner organs, particularly the liver 5. Infection spreading into the blood from the kidney or urinary tract, typically attributable to colon bacilli. It results primarily from an antigen-antibody reaction that rapidly occurs after an antigen to which the individual is sensitive enters the circulation. One of the principal effects is to trigger the basophils within the blood and mast cells in the pericapillary tissues to release histamine or a histamine-like substance. The histamine causes the following: (1) a rise in vascular capability due to venous dilation, thus inflicting a marked decrease in venous return; (2) dilation of the arterioles, resulting in significantly reduced arterial strain; and (3) significantly elevated capillary permeability, with fast loss of fluid and protein into the tissue areas. The internet impact is a good reduction in venous return and, sometimes, such critical shock that the person could die within minutes. Intravenous injection of large quantities of histamine causes histamine shock, which has traits nearly identical to those of anaphylactic shock. There are many varieties of septic shock due to the many forms of bacterial infections that may trigger it, and because infection in numerous parts of the physique produces totally different results. Most circumstances of septic shock, however, are caused by Gram-positive bacteria, followed by endotoxin-producing Gram-negative micro organism. Often marked vasodilation all through the physique, especially within the contaminated tissues three. High cardiac output in perhaps half of sufferers, brought on by arteriolar dilation within the contaminated tissues and by high metabolic rate and vasodilation elsewhere within the physique, resulting from bacterial toxin stimulation of cellular metabolism and from a high body temperature four. Sludging of the blood, brought on by purple cell agglutination in response to degenerating tissues 5. As the infection becomes more extreme, the circulatory system normally turns into concerned because of direct extension of the an infection or secondarily because of toxins from the bacteria, with resultant lack of plasma into the contaminated tissues by way of deteriorating blood capillary partitions. There lastly comes some extent at which deterioration of the circulation turns into progressive in the identical means that progression happens in all different kinds of shock.
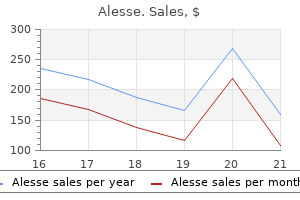
0.18 mg alesse discount
Greater Effect of Sympathetic Nervous Reflexes in Maintaining Arterial Pressure Than in Maintaining Cardiac Output birth control pills kidney disease alesse 0.18 mg purchase on-line. The reason for this difference is that the sympathetic reflexes are geared extra for sustaining arterial strain than for sustaining cardiac output birth control 5 years buy alesse 0.18 mg amex. They increase the arterial strain mainly by increasing the entire peripheral resistance, which has no beneficial effect on cardiac output. However, the sympathetic constriction of the veins is necessary to keep venous return and cardiac output from falling too much, in addition to their role in maintaining arterial strain. This second plateau outcomes from activation of the central nervous system ischemic response, which causes extreme stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system when the brain begins to expertise lack of oxygen or excess buildup of carbon dioxide, as mentioned in Chapter 18. This effect of the central nervous system ischemic response could be referred to as the "last-ditch stand" of the sympathetic reflexes of their try and hold the arterial stress from falling too low. A special worth of the maintenance of nor- mal arterial strain, even in the presence of lowering cardiac output, is safety of blood flow via the coronary and cerebral circulations. In addition, in each vascular beds, local blood move autoregulation is excellent, which prevents reasonable decreases in arterial strain from significantly lowering their blood flows. Therefore, shock of this lesser degree is identified as nonprogressive shock or compensated shock, meaning that the sympathetic reflexes and other elements compensate enough to stop further deterioration of the circulation. The factors that trigger an individual to recuperate from reasonable levels of shock are the negative feedback control mechanisms of the circulation that attempt to return cardiac output and arterial pressure again to regular ranges. Baroreceptor reflexes, which elicit highly effective sympathetic stimulation of the circulation 2. Increased secretion by the posterior pituitary gland of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), which constricts the peripheral arterioles and veins and tremendously will increase water retention by the kidneys 6. Increased secretion by the adrenal medullae of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which constricts the peripheral arterioles and veins and increases the center fee 7. The animals on this experiment were anesthetized and bled rapidly until their arterial pressures fell to different levels. Crossing this critical threshold by even a quantity of milliliters of blood loss makes the eventual distinction between life and dying. Thus, hemorrhage beyond a sure critical level causes shock to become progressive. Cardiac melancholy Decreased venous return the angiotensin and vasopressin mechanisms, in addition to the reverse stress-relaxation that causes contraction of the blood vessels and venous reservoirs, all require 10 to 60 minutes to respond utterly, but they assist tremendously in rising the arterial pressure or rising the circulatory filling strain, thereby rising the return of blood to the center. Thus, a constructive suggestions cycle has developed, whereby the shock turns into increasingly more severe. An anesthetized animal was bled till the arterial pressure fell to 30 mm Hg, and the pressure was held at this level by additional bleeding or retransfusion of blood, as required. Note from the second curve within the figure that there was little deterioration of the guts through the first 2 hours, however by four hours, the center had deteriorated about 40%. Then, rapidly, over the last hour of the experiment (after 4 hours of low coronary blood pressure), the heart deteriorated completely. In the most recent levels of shock, however, deterioration of the center is probably the most important issue in the last deadly development of the shock. Shock has been instructed to trigger tissues to launch poisonous substances, similar to histamine, serotonin, and tissue enzymes, that cause additional deterioration of the circulatory system. Experimental research have proved the significance of a minimum of one toxin, endotoxin, in some kinds of shock. This exercise helps delay depression of cardiac output and especially helps stop decreased arterial strain. For example, through the first 4 to eight minutes, full circulatory arrest to the mind causes essentially the most intense of all sympathetic discharges, but by the end of 10 to quarter-hour, the vasomotor heart becomes so depressed that no additional evidence of sympathetic discharge may be demonstrated. Diminished blood circulate to the intestines often causes enhanced formation and absorption of this poisonous substance. The circulating toxin then causes elevated cellular metabolism, despite insufficient nutrition of the cells, which has a specific impact on the heart muscle, inflicting cardiac despair. Endotoxin can play a significant role in some forms of shock, particularly septic shock, mentioned later on this chapter. As shock turns into time, blockage happens in most of the very small blood vessels within the circulatory system, and this blockage additionally causes the shock to progress. Because tissue metabolism continues regardless of the low circulate, large quantities of acid, both carbonic acid and lactic acid, continue to empty into the native blood vessels and greatly enhance the native acidity of the blood. This acidic effect, plus different deterioration products from the ischemic tissues, causes native blood agglutination, leading to minute blood clots and leading to very small plugs within the small vessels. After many hours severe, many indicators of generalized cellular deterioration happen all through the physique. The liver is very affected mainly because of the shortage of sufficient nutrients to assist the usually excessive rate of metabolism in liver cells, but in addition partly because of the exposure of the liver cells to any vascular toxin or different irregular metabolic issue occurring in shock. Among the damaging cellular results which are recognized to happen in most physique tissues are the following: 1. Active transport of sodium and potassium via the cell membrane is greatly diminished. As a result, sodium and chloride accumulate in the cells, and potassium is misplaced from the cells. This phenomenon decreases the blood quantity even more, with a resultant further decrease in cardiac output, making the shock nonetheless extra severe. Mitochondrial activity within the liver cells, in addition to in many other tissues of the body, becomes severely depressed. Lysosomes in the cells in widespread tissue areas begin to break open, with intracellular release of hydrolases, which cause further intracellular deterioration. Cellular metabolism of vitamins, such as glucose, ultimately turns into greatly depressed within the last phases of shock. The actions of some hormones are depressed as nicely, together with nearly 100 percent despair of the actions of insulin. All these effects contribute to further deterioration of many organs of the physique, together with particularly the next: (1) the liver, with melancholy of its many metabolic and detoxing capabilities; (2) the lungs, with eventual growth of pulmonary edema and poor capacity to oxygenate the blood; and (3) the guts, thereby additional miserable its contractility. Not all cells of the Positive Feedback Deterioration of Tissues in Shock and Vicious Cycle of Progressive Shock. All the fac- body are equally broken by shock because some tissues have higher blood provides than others. For instance, the cells adjacent to the arterial ends of capillaries obtain higher vitamin than cells adjacent to the venous ends of the same capillaries. Therefore, extra nutritive deficiency occurs across the venous ends of capillaries than elsewhere. If an individual is in shock attributable to hemorrhage, the very best therapy is normally transfusion of complete blood. If the shock is attributable to plasma loss, the most effective remedy is administration of plasma. When dehydration is the cause, administration of an acceptable electrolyte solution can appropriate the shock. Plasma can often substitute adequately for entire blood as a outcome of it increases the blood quantity and restores normal hemodynamics. In these cases, varied plasma substitutes have been developed that carry out almost precisely the identical hemodynamic capabilities as plasma.
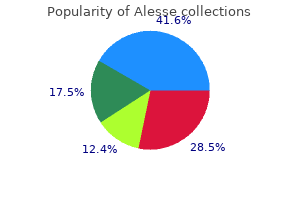
Alesse 0.18 mg cheap line
Chapter 47 Sensory Receptors birth control comparison 0.18 mg alesse with mastercard, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information Predictive Function of the Rate Receptors birth control movement alesse 0.18 mg buy discount line. For instance, the receptors of the semicircular canals within the vestibular equipment of the ear detect the speed at which the head begins to flip when an individual runs around a curve. Using this info, an individual can predict how a lot he or she will flip inside the next 2 seconds and can modify the movement of the legs forward of time to hold from shedding balance. Likewise, receptors situated in or close to the joints help detect the rates of movement of the totally different parts of the physique. For example, when a person is working, information from the joint price receptors permits the nervous system to predict the place the ft shall be throughout any precise fraction of the following second. Nerve Fibers That Transmit Different Types of Signals and Their Physiological Classification Some signals need to be transmitted to or from the central nervous system extraordinarily quickly; otherwise, the data can be useless. An example of that is the sensory signals that apprise the mind of the momentary positions of the legs at each fraction of a second throughout running. In the overall classification, the fibers are divided into sorts A and C; the type A fibers are further subdivided into, and fibers. Type A fibers are the standard massive and medium-sized myelinated fibers of spinal nerves. Type C fibers are the small unmyelinated nerve fibers that conduct impulses at low velocities. The C fibers constitute more than half of the sensory fibers in most peripheral nerves, as nicely as all the postganglionic autonomic fibers. Therefore, the following classification is frequently used by sensory physiologists. Fibers from the annulospiral endings of muscle spindles (17 microns in diameter on common; these fibers are -type A fibers within the common classification). Fibers from the Golgi tendon organs (16 micrometers in diameter on average; these fibers also are -type A fibers). Fibers from most discrete cutaneous tactile receptors and from the flower-spray endings of the muscle spindles (8 micrometers in diameter on common; these fibers are - and -type A fibers in the common classification). Unmyelinated fibers carrying ache, itch, temperature, and crude touch sensations (0. The different gradations of depth can be transmitted either by using growing numbers of parallel fibers or by sending extra action potentials alongside a single fiber. These two mechanisms are known as, respectively, spatial summation and temporal summation. To the left is the effect of a weak stimulus, with only a single nerve fiber in the midst of the bundle stimulated strongly (represented by the red-colored fiber), whereas a number of adjacent fibers are stimulated weakly (half-red fibers). The other two views of the nerve cross part show the effect of a moderate stimulus and a robust stimulus, with progressively extra fibers being stimulated. Thus, the stronger indicators spread to increasingly more fibers, a phenomenon known as spatial summation. A second means for transmit- enon of spatial summation, whereby growing signal power is transmitted through the use of progressively greater numbers of fibers. This figure shows a section of pores and skin innervated by a giant quantity of parallel pain fibers. Each of these fibers arborizes into tons of of minute free nerve endings that function pain receptors. The complete cluster of fibers from one pain fiber frequently covers an space of skin as massive as 5 centimeters in diameter. The number of endings is massive within the heart of the sector but diminishes toward the periphery. One can even see from the figure that the arborizing fibrils overlap these from other ache fibers. Therefore, a pinprick of the pores and skin normally stimulates endings from many various pain fibers concurrently. For instance, the complete cerebral cortex could be thought of to be a single massive neuronal pool. Other neuronal pools include the completely different basal ganglia and the particular nuclei within the thalamus, cerebellum, mesencephalon, pons, and medulla. Also, the entire dorsal grey matter of the spinal cord might be thought of one long pool of neurons. Yet, regardless of their differences in operate, the swimming pools also have many comparable rules of operate, described within the following sections. The neuronal space stimulated by each incoming nerve fiber is identified as its stimulatory area. Note that large numbers of the terminals from every input fiber lie on the nearest neuron in its "area," but progressively fewer terminals lie on the neurons farther away. Note that input fiber 1 has more than sufficient terminals to trigger neuron a to discharge. Input fiber 1 also contributes terminals to neurons b and c, but not sufficient to cause excitation. Nevertheless, discharge of these terminals makes each these neurons extra likely to be excited by signals arriving through other incoming nerve fibers. Therefore, the stimuli to these neurons are mentioned to be subthreshold, and the neurons are said to be facilitated. Similarly, for enter fiber 2, the stimulus to neuron d is a suprathreshold stimulus, and the stimuli to neurons b and c are subthreshold, but facilitating, stimuli. In the central portion of the field on this figure, designated by the circled space, all the neurons are stimulated by the incoming fiber. Therefore, that is said to be the discharge zone of the incoming fiber, also known as the excited zone or liminal zone. To each side, the neurons are facilitated but not excited; these areas are referred to as the facilitated zone, also referred to as the subthreshold zone or subliminal zone. This mechanism is the other of facilitation, and the whole area of the inhibitory branches is called the inhibitory zone. The degree of inhibition within the heart of this zone is nice due to giant numbers of endings in the center and becomes progressively much less toward its edges. Amplifying divergence means merely that an enter sign spreads to an increasing number of neurons because it passes by way of successive orders of neurons in its path. This type of divergence is attribute of the corticospinal pathway in its control of skeletal muscles, with a single large pyramidal cell in the motor cortex capable, beneath extremely facilitated circumstances, of thrilling as many as 10,000 muscle fibers. For example, info transmitted up the dorsal columns of the spinal cord takes two courses in the lower a half of the mind: (1) into the cerebellum; and (2) on via the lower areas of the mind to the thalamus and cerebral cortex. Likewise, within the thalamus, virtually all sensory information is relayed into still deeper structures of the thalamus and, on the same time, to discrete regions of the cerebral cortex. The significance of this type of convergence is that neurons are almost by no means excited by an action potential from a single input terminal.
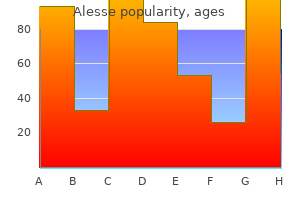
Alesse 0.18 mg buy on-line
The function of this nephron section is principally to allow simple diffusion of gear through its walls birth control pills and depression alesse 0.18 mg generic online. About 20% of the filtered water is reabsorbed in the loop of Henle birth control pills vitamin deficiency purchase 0.18 mg alesse, and almost all of this occurs in the thin descending limb. About 25% of the filtered a nice deal of sodium, chloride, and potassium are reabsorbed within the loop of Henle, largely within the thick ascending limb. The 1-sodium, 2-chloride, 1-potassium co-transporter within the luminal membrane transports these three ions from the tubular lumen into the cells, utilizing the potential vitality launched by the diffusion of sodium down an electrochemical gradient into the cells. Sodium is also transported into the tubular cell by sodium-hydrogen countertransport. The positive cost (+8 mV) of the tubular lumen relative to the interstitial fluid forces cations similar to Mg2+ and Ca2+ to diffuse from the lumen to the interstitial fluid through the paracellular pathway. There can be significant paracellular reabsorption of cations, corresponding to Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+, within the thick ascending limb as a result of the slight positive charge of the tubular lumen relative to the interstitial fluid. This optimistic cost forces cations corresponding to Mg2+ and Ca2+ to diffuse from the tubular lumen via the paracellular house and into the interstitial fluid. The thick segment of the ascending loop of Henle is just about impermeable to water. Therefore, most of the water delivered to this section remains in the tubule, regardless of reabsorption of large amounts of solute. The next a part of the distal tubule is very convoluted and has lots of the similar reabsorptive characteristics of the thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. That is, it avidly reabsorbs most of the ions, together with sodium, potassium, and chloride, however is nearly impermeable to water and urea. Approximately 5% of the filtered load of sodium chloride is reabsorbed in the early distal tubule. Chloride diffuses out of cell into the renal interstitial fluid by way of chloride channels within the basolateral membrane. The thiazide diuretics, which are widely used to treat problems such as hypertension and coronary heart failure, inhibit the sodium-chloride co-transporter. The low intracellular sodium focus in flip supplies a good gradient for movement of sodium from the tubular fluid into the cell. This co-transport protein in the luminal membrane makes use of the potential vitality launched by downhill diffusion of sodium into the cell to drive the reabsorption of potassium into the cell towards a concentration gradient. The principal cells reabsorb sodium and water from the lumen and secrete potassium ions into the lumen. The sort A intercalated cells reabsorb potassium ions and secrete hydrogen ions into the tubular lumen. This pump maintains a low sodium focus contained in the cell and, due to this fact, favors sodium diffusion into the cell through particular channels. The principal cells are the first websites of motion of the potassium-sparing diuretics, including spironolactone, eplerenone, amiloride, and triamterene. Spironolactone and eplerenone are mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists that compete with aldosterone for receptor websites in the principal cells and subsequently inhibit the stimulatory results of aldosterone on sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. This, in flip, decreases transport of potassium into the cells and in the end reduces potassium secretion into the tubular fluid. For this reason, sodium channel blockers, in addition to aldosterone antagonists, decrease urinary excretion of potassium and act as potassium-sparing diuretics. The early distal tubule has many of the similar traits as the thick ascending loop of Henle and reabsorbs sodium, chloride, calcium, and magnesium but is nearly impermeable to water and urea. The late distal tubules and cortical collecting tubules are composed of two distinct cell types, the principal cells and intercalated cells. The principal cells reabsorb sodium from the lumen and secrete potassium ions into the lumen. Type A intercalated cells reabsorb potassium and bicarbonate ions from the lumen and secrete hydrogen ions into the lumen. The reabsorption of water from this tubular segment is managed by the focus of antidiuretic hormone. Intercalated Cells Can Secrete or Reabsorb Hydrogen, Bicarbonate, and Potassium Ions. Intercalated cells play a major role in acid�base regulation and represent 30% to 40% of the cells within the accumulating tubules and amassing ducts. Hydrogen is generated on this cell by the action of carbonic anhydrase on water and carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid, which then dissociates into hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions. The hydrogen ions are then secreted into the tubular lumen and, for each hydrogen ion secreted, a bicarbonate ion becomes available for reabsorption throughout the basolateral membrane. Type A intercalated cells are especially important in eliminating hydrogen ions while reabsorbing bicarbonate in acidosis. Type B intercalated cells have features reverse to those of sort A cells and secrete bicarbonate into the tubular lumen whereas reabsorbing hydrogen ions in alkalosis. Aldosterone antagonists compete with aldosterone for binding websites within the cell and subsequently inhibit the consequences of aldosterone to stimulate sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. Sodium channel blockers immediately inhibit the entry of sodium into the sodium channels. The chloride-bicarbonate counter-transporter on the apical membrane of sort B cells known as pendrin and is completely different than the chloridebicarbonate transporter of sort A cells. Induction of chronic metabolic alkalosis increases the variety of type B intercalated cells, which contribute to increased excretion of bicarbonate, whereas acidosis will increase the variety of type A cells. The practical traits of the late distal tubule and cortical amassing tubule can be summarized as follows: 1. The tubular membranes of both segments are virtually completely impermeable to urea, just like the diluting segment of the early distal tubule. Thus, virtually all the urea that enters these segments passes on by way of and into the amassing duct to be excreted in the urine, although some reabsorption of urea happens within the medullary accumulating ducts. Both the late distal tubule and cortical collecting tubule segments reabsorb sodium ions, and the rate of reabsorption is controlled by hormones, especially aldosterone. The chloride-bicarbonate counter-transporter on the apical membrane of kind B cells known as pendrin and is completely different than the chloride-bicarbonate transporter of kind A intercalated cells. This is in distinction to the relatively small gradient (4- to 10-fold) for hydrogen ions that may be achieved by secondary active secretion within the proximal tubule. The medullary accumulating ducts actively reabsorb sodium and secrete hydrogen ions and are permeable to urea, which is reabsorbed in these tubular segments. The reabsorption of water in medullary collecting ducts is controlled by the concentration of antidiuretic hormone. Thus, the intercalated cells play a key role in acid� base regulation of the body fluids.
Alesse 0.18 mg buy generic
These crystals elongate the cell and give it the looks of a sickle somewhat than a biconcave disc birth control pills refill buy alesse 0.18 mg mastercard. The precipitated hemoglobin additionally damages the cell membrane birth control pills 5 hours late order alesse 0.18 mg, so the cells turn into highly fragile, resulting in serious anemia. These antibodies make the Rh-positive cells fragile, leading to rapid rupture and inflicting the kid to be born with a critical case of anemia. This change decreases the resistance to blood circulate in the peripheral blood vessels, thus far greater than regular quantities of blood circulate by way of the tissues and return to the heart, thereby greatly rising cardiac output. Moreover, hypoxia resulting from diminished transport of oxygen by the blood causes the peripheral tissue blood vessels to dilate, allowing an additional improve within the return of blood to the center and growing the cardiac output to a still greater level-sometimes three to four instances normal. Thus, one of many major effects of anemia is significantly increased cardiac output, as nicely as increased pumping workload on the heart. Even although 446 Chapter 33 Red Blood Cells, Anemia, and Polycythemia the increased cardiac output in persons with anemia partially offsets the lowered oxygen-carrying impact of the anemia as a end result of, despite the very fact that every unit amount of blood carries solely small portions of oxygen, the rate of blood flow could also be increased enough that almost regular portions of oxygen are actually delivered to the tissues. Consequently, throughout train, which greatly increases tissue demand for oxygen, excessive tissue hypoxia outcomes and acute cardiac failure may ensue. A frequent sort of secondary polycythemia, referred to as physiological polycythemia, happens in those that live at altitudes of 14,000 to 17,000 feet, the place the atmospheric oxygen could be very low. The blood depend is generally 6 to 7 million/mm3, which allows these folks to perform reasonably excessive ranges of steady work, even in a rarefied atmosphere. In addition to physi- that regulate return of blood to the center, as discussed in Chapter 20, increasing blood viscosity decreases the speed of venous return to the center. Conversely, the blood quantity is greatly increased in polycythemia, which tends to increase venous return. The arterial strain can be normal in most people with polycythemia, although in about one-third of them, the arterial strain is elevated. This implies that the blood pressure�regulating mechanisms can normally offset the tendency for elevated blood viscosity to improve peripheral resistance and, thereby, enhance arterial stress. Beyond certain limits, however, these rules fail, and hypertension develops. The color of the skin depends to a great extent on the amount of blood in the pores and skin subpapillary venous plexus. Furthermore, as a outcome of blood passes sluggishly via the skin capillaries earlier than coming into the venous plexus, a bigger than regular amount of hemoglobin is deoxygenated. The blue colour of all this deoxygenated hemoglobin masks the purple colour of the oxygenated hemoglobin. Therefore, an individual with polycythemia vera ordinarily has a ruddy complexion, with a bluish (cyanotic) tint to the skin. Green R: Vitamin B12 deficiency from the angle of a training hematologist. Renassia C, Peyssonnaux C: New insights into the links between hypoxia and iron homeostasis. Polycythemia vera is attributable to a genetic aberration in the hemocytoblastic cells that produce the blood cells. In polycythemia vera, not only does the hematocrit improve, however the complete blood quantity additionally will increase, typically to nearly twice normal. Also, many blood capillaries turn out to be plugged by the viscous blood; the viscosity of the blood in polycythemia vera typically increases from the conventional of three occasions the viscosity of water to 10 instances that of water. Many of these infectious brokers are able to causing serious abnormal physiological operate or even death in the occasion that they invade deeper tissues. We are also exposed intermittently to different highly infectious bacteria and viruses in addition to these which may be normally present, and these brokers can cause acute deadly ailments similar to pneumonia, streptococcal infection, and typhoid fever. Our bodies have a particular system for combating the completely different infectious and poisonous brokers. These cells work collectively in two methods to prevent disease: (1) by really destroying invading bacteria or viruses by phagocytosis; and (2) by forming antibodies and sensitized lymphocytes that will destroy or inactivate the invader. This article discusses the primary of those methods, and Chapter 35 discusses the second. The granulocytes and monocytes protect the body against invading organisms by ingesting them (by phagocytosis) or by releasing antimicrobial or inflammatory substances that have a quantity of effects that help in destroying the offending organism. The lymphocytes and plasma cells function mainly in reference to the immune system, as mentioned in Chapter 35. Finally, the operate of platelets is particularly to activate the blood-clotting mechanism, discussed in Chapter 37. They are fashioned partially in the bone marrow (granulocytes and monocytes and some lymphocytes) and partially within the lymph tissue (lymphocytes and plasma cells). As we see later, the granulocytes and monocytes have a special ability to "hunt down and destroy" a overseas invader. The completely different cells of the myelocyte sequence are shown: 1, myeloblast; 2, promyelocyte; 3, megakaryocyte; 4, neutrophil myelocyte; 5, young neutrophil metamyelocyte; 6, band neutrophil metamyelocyte; 7, neutrophil; eight, eosinophil myelocyte; 9, eosinophil metamyelocyte; 10, eosinophil; eleven, basophil myelocyte; 12, basophil; 13�16, phases of monocyte formation. Then, when the necessity arises, varied factors trigger them to be launched (these factors are mentioned later). These megakaryocytes fragment in the bone marrow and the small fragments, generally recognized as platelets (or thrombocytes), then move into the blood. In occasions of great tissue an infection, this whole life span is usually shortened to only a few hours as a end result of the granulocytes proceed much more rapidly to the contaminated area, carry out their functions, and within the process, are themselves destroyed. The monocytes also have a short transit time, 10 to 20 hours in the blood, earlier than wandering through the capillary membranes into the tissues. These tissue macrophages are the basis of the tissue macrophage system (discussed in higher detail later), which provides persevering with protection towards an infection. After a couple of hours, they cross out of the blood again into the tissues by diapedesis/extravasation. In different phrases, about 30,000 platelets are shaped every day for each microliter of blood. They embody the 1 following: (1) some of the bacterial or viral toxins; (2) degenerative products of the inflamed tissues; (3) a number of reaction products of the complement advanced (discussed in Chapter 35)activatedininflamedtissues;and(4)several reaction products attributable to plasma clotting in the inflamed space, as nicely as different substances. Movement of neutrophils by diapedesis or extravasation by way of capillary pores and by chemotaxis towards an space of tissue injury. First, most pure buildings within the tissues have easy surfaces, which resist phagocytosis. Second, most pure substances of the physique have protective protein coats that repel the phagocytes. Third, the immune system of the body (described in Chapter 35) develops antibodies against infectious brokers such as bacteria. The antibodies then adhere to the bacterial membranes and thereby make the bacteria especially vulnerable to phagocytosis.
Diseases
- Pseudoachondroplasia
- Synesthesia
- Overhydrated hereditary stomatocytosis
- Procrastination
- Transverse myelitis
- Lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Choreoacanthocytosis amyotrophic
- Meningeal angiomatosis cleft hypoplastic left heart
Alesse 0.18 mg generic free shipping
Conversely birth control pills quarterly buy 0.18 mg alesse overnight delivery, if a person remains in darkness for a really long time birth control success rate alesse 0.18 mg order line, the retinal and opsins in the rods and cones are transformed back into the light-sensitive pigments. Furthermore, vitamin A is converted back into retinal to improve lightsensitive pigments, the final limit being determined by the quantity of opsins in the rods and cones to mix with the retinal. Note that the sensitivity of the retina could be very low on first getting into the darkness, but within 1 minute, the sensitivity has already elevated 10-fold-that is, the retina can reply to light Photochemistry of Color Vision by the Cones We beforehand identified that the photochemicals within the cones have almost precisely the same chemical composition as that of rhodopsin within the rods. The only distinction is that the protein portions, or the opsins-called photopsins in the cones-are barely totally different from the scotopsin of the rods. The retinal portion of all of the visible pigments is strictly the identical in the cones and rods. The color-sensitive pigments of the cones, therefore, are mixtures of retinal and photopsins. Only certainly one of three forms of color pigments is current in each of the totally different cones, thus making the cones selectively sensitive to totally different colors-blue, green, or red. Receptor and Neural Function of the Retina 100,000 Value of Light and Dark Adaptation in Vision. At the top of 20 minutes, the sensitivity has increased about 6000-fold and, at the end of forty minutes, it has increased about 25,000-fold. The early portion of the curve is brought on by adaptation of the cones as a end result of all of the chemical occasions of vision, together with adaptation, happen about four times as rapidly in cones as in rods. Therefore, regardless of speedy adaptation, the cones stop adapting after only a few minutes, whereas the slowly adapting rods continue to adapt for a lot of minutes and even hours, with their sensitivity growing tremendously. Additional sensitivity of the rods is brought on by neuronal signal convergence of a hundred or more rods onto a single ganglion cell within the retina; these rods summate to increase their sensitivity, as discussed later in the chapter. This change can cause adaptation of roughly 30fold within a fraction of a second due to adjustments within the amount of light allowed by way of the pupillary opening. The other mechanism is neural adaptation, involving the neurons in the successive levels of the visual chain in the retina and within the brain. That is, when gentle intensity first will increase, the indicators transmitted by the bipolar cells, horizontal cells, amacrine cells, and ganglion cells are all intense. However, most of these alerts lower rapidly at totally different phases of transmission within the neural circuit. Although the diploma of adaptation is only a fewfold somewhat than the various thousandfold that happens throughout adaptation of the photochemical system, neural adaptation happens in a fraction of a second, in distinction to the various minutes to hours required for full adaptation by the photochemicals. In tween the limits of maximal dark adaptation and maximal mild adaptation, the eye can change its sensitivity to mild as much as 500,000 to 1 million instances, with the sensitivity mechanically adjusting to changes in illumination. An instance of maladjustment of retinal adaptation happens when a person leaves a movie theater and enters the bright daylight. Then, even the dark spots within the photographs appear exceedingly brilliant, and as a consequence, the complete visual picture is bleached, with little contrast amongst its totally different components. This poor vision stays until the retina has adapted sufficiently in order that the darker areas of the picture not stimulate the receptors excessively. As an instance of the extremes of light and darkish adaptation, the intensity of daylight is about 10 billion instances that of starlight, but the eye can operate each in shiny sunlight after mild adaptation and in starlight after darkish adaptation. This section is a dialogue of the mechanisms whereby the retina detects the completely different gradations of color in the visual spectrum. On the idea of shade imaginative and prescient tests, the spectral sensitivities of the three kinds of cones in people have proved to be primarily the identical as the light absorption curves for the three forms of pigment found within the cones. Demonstration of the diploma of stimulation of the different color-sensitive cones by monochromatic lights of four colors- blue, green, yellow, and orange. Thus, the ratios of stimulation of the three kinds of cones on this case are ninety nine:forty two:zero. Conversely, a monochromatic blue light with a wavelength of 450 nanometers stimulates the pink cones to a stimulus value of zero, the green cones to a price of 0, and the blue cones to a price of 97. Likewise, ratios of 83:eighty three:0 are interpreted as yellow, and ratios of 31:67:36 are interpreted as green. About equal stimulation of Red-green shade blindness is a genetic disorder that happens nearly completely in males. Yet, color blindness virtually never happens in females because a minimal of one of many two X chromosomes almost always has a normal gene for every type of cone. Because the male has just one X chromosome, a missing gene can result in colour blindness. Because the X chromosome within the male is all the time inherited from the mom, by no means from the father, shade blindness is handed from mother to son, and the mother is said to be a shade blindness provider. In the top chart, an individual with regular colour vision reads "seventy four," whereas a red-green color-blind person reads "21. The photoreceptors-the rods and cones-which transmit indicators to the outer plexiform layer, where they synapse with bipolar cells and horizontal cells 2. The horizontal cells, which transmit signals horizontally within the outer plexiform layer from the rods and cones to bipolar cells 3. The bipolar cells, which transmit alerts vertically from the rods, cones, and horizontal cells to the inner plexiform layer, the place they synapse with ganglion cells and amacrine cells four. The amacrine cells, which transmit indicators in two instructions, either directly from bipolar cells to ganglion cells or horizontally throughout the internal plexiform layer from axons of the bipolar cells to dendrites of the ganglion cells or to different amacrine cells 5. This kind of cell transmits alerts within the retrograde path from the inner plexiform layer to the outer plexiform layer. These alerts are inhibitory and are believed to management lateral spread of visual signals by the horizontal cells in the outer plexiform layer. Furthermore, the perception of white may be achieved by stimulating the retina with a proper mixture of only three chosen colours that stimulate the respective kinds of cones about equally. When a single group of color-receptive cones is missing from the eye, the person is unable to distinguish some colors from others. A person with loss of purple cones known as a protanope; the general visual spectrum is noticeably shortened on the lengthy wavelength end due to an absence of the purple cones. A colorblind one that lacks green cones known as a deuteranope; this person has a superbly normal visible spectral width as a outcome of pink cones are available to detect the lengthy wavelength purple shade. However, a deuteranope can solely distinguish 2 or three totally different hues, whereas anyone with regular vision sees 7 unique hues. Neural group of the retina, with the peripheral space to the left and the foveal area to the best. In this chart (upper panel), a person with regular vision reads "seventy four," however a red-green color-blind individual reads "21. This illustration reveals three neurons in the direct pathway: (1) cones; (2) bipolar cells; and (3) ganglion cells. In addition, horizontal cells transmit inhibitory signals laterally within the outer plexiform layer, and amacrine cells transmit indicators laterally within the inner plexiform layer. Three bipolar cells are proven; the middle of these connects solely to rods, representing the type of visual system present in lots of lower animals.

Purchase 0.18 mg alesse otc
Despite the intense inhibition of the peripheral muscles birth control pills in the 80s safe alesse 0.18 mg, irregular muscle actions do occur along with birth control pills year invented purchase alesse 0.18 mg line the rapid actions of the eyes. Sleep researchers additionally divide sleep into two entirely several types of sleep that have different qualities, as described in the following section. Slow-Wave Sleep We can understand the characteristics of deep slow-wave sleep by remembering the final time we have been stored awake for more than 24 hours and the deep sleep that occurred during the first hour after going to sleep. This sleep is exceedingly restful and is associated with decreases in peripheral vascular tone and plenty of different vegetative features of the physique. For example, 10% to 30% decreases occur in blood stress, respiratory fee, and basal metabolic fee. Although slow-wave sleep is frequently called "dreamless sleep," dreams and sometimes even nightmares do occur throughout slow-wave sleep. An earlier principle of sleep was that the excitatory areas of the upper brain stem, the reticular activating system, simply turned fatigued in the course of the waking day and have become inactive as a result. An necessary experiment changed this pondering to the current view that sleep is brought on by an active inhibitory process, as a result of it was discovered that transecting the mind stem at the stage of the midpons creates a brain cortex that by no means goes to sleep. In other phrases, a center located under the midpontile stage of the mind stem appears to be required to trigger sleep by inhibiting other elements of the brain. Neuronal Centers, Neurohumoral Substances, and Mechanisms That Can Cause Sleep-Possible Role for Serotonin Stimulation of a quantity of particular areas of the brain can produce sleep with characteristics close to these of pure sleep. The raphe nuclei within the lower half of the pons and within the medulla is essentially the most conspicuous stimulation area for causing nearly pure sleep. Nerve fibers from these nuclei unfold domestically in the mind stem reticular formation and also upward into the thalamus, hypothalamus, most areas of the limbic system, and even the neocortex of the cerebrum. Therefore, it has been assumed that serotonin is a transmitter substance related to the manufacturing of sleep. Stimulation of some areas in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius can also trigger sleep. This nucleus is the termination in the medulla and pons for visceral sensory indicators coming into by means of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. Sleep may be promoted by stimulation of several areas within the diencephalon, including (1) the rostral a part of the hypothalamus, primarily in the suprachiasmal space, and (2) an occasional area in the diffuse nuclei of the thalamus. This phenomenon can additionally be true of bilateral lesions in the medial rostral suprachiasmal space in the anterior hypothalamus. In both cases, the excitatory reticular nuclei of the mesencephalon and Chapter 60 States of Brain Activity-Sleep, Brain Waves, Epilepsy, Psychoses, and Dementia upper pons seem to become released from inhibition, thus inflicting intense wakefulness. Indeed, typically lesions of the anterior hypothalamus could cause such intense wakefulness that the animal actually dies of exhaustion. Experiments have proven that the cerebrospinal fluid and the blood or urine of animals which were kept awake for several days include a substance or substances that will cause sleep when injected into the brain ventricular system of another animal. One probably substance has been recognized as muramyl peptide, a low-molecularweight substance that accumulates in the cerebrospinal fluid and urine in animals stored awake for a quantity of days. When solely micrograms of this sleep-producing substance are injected into the third ventricle, nearly natural sleep happens within a few minutes, and the animal may keep asleep for a number of hours. Another substance that has comparable effects in causing sleep is delta sleep�inducing peptide, a nonapeptide discovered in the cerebrospinal fluid after electrical stimulation of the thalamus to induce sleep. Several different potential sleep components, largely peptides, have been isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid or neuronal tissues of the brain stem of animals saved awake for days. It is possible that prolonged wakefulness causes progressive accumulation of a sleep issue or components in the mind stem or cerebrospinal fluid that lead(s) to sleep. Then, after the brain remains activated for lots of hours, even the neurons within the activating system presumably turn out to be fatigued. Consequently, the constructive feedback cycle between the mesencephalic reticular nuclei and the cerebral cortex fades and the sleep-promoting effects of the sleep centers take over, resulting in fast transition from wakefulness again to sleep. This overall theory might explain the rapid transitions from sleep to wakefulness and from wakefulness to sleep. Therefore, it has been postulated that the big acetylcholine-secreting neurons in the upper mind stem reticular formation might, via their extensive efferent fibers, activate many portions of the mind. Orexin (also called hypocretin) is produced by neurons within the hypothalamus that present excitatory enter to many other areas of the brain where there are orexin receptors. Loss of orexin signaling as a end result of faulty orexin receptors or destruction of orexin-producing neurons causes narcolepsy, a sleep problem characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep that may happen, even when a person is speaking or working. Patients with narcolepsy can also expertise a sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy) that can be partial or even extreme enough to trigger paralysis during the attack. These observations point to an necessary position for orexin neurons in sustaining wakefulness, but their contribution to the traditional day by day cycle between sleep and wakefulness is unclear. Even delicate sleep restriction over a couple of days may degrade cognitive and physical performance, total productivity, and the health of an individual. The important role of sleep in homeostasis is perhaps most vividly demonstrated by the reality that rats disadvantaged of sleep for two to three weeks may actually die. Despite the obvious significance of sleep, our understanding of why sleep is an essential part of life remains to be restricted. Sleep causes two major kinds of physiological effects: first, effects on the nervous system, and second, results on different functional methods of the physique. Mammals, and even invertebrate animals, sleep more within the setting of infectious as well as non-infectious diseases. This spontaneous activity in flip excites both the cerebral cortex and the peripheral nervous system, each of which ship numerous optimistic feedback indicators again to the same reticular activating nuclei to activate them nonetheless further. Motor and Integrative Neurophysiology Lack of sleep actually impacts the features of the central nervous system. Prolonged wakefulness is often associated with progressive malfunction of the thought processes and sometimes even causes abnormal behavioral actions. We are all conversant in the increased sluggishness of thought that happens towards the end of a protracted wakeful interval, however as properly as, an individual can turn into irritable and even psychotic after pressured wakefulness. Therefore, we can assume that sleep in a quantity of methods restores both regular levels of brain exercise and normal "stability" among the many different functions of the central nervous system. Sleep has been postulated to serve many functions, together with the next: (1) neural maturation; (2) facilitation of learning or memory; (3) focused erasure of synapses to "forget" unimportant info which may clutter the synaptic network; (4) cognition; (5) clearance of metabolic waste products generated by neural activity in the awake mind; and (6) conservation of metabolic energy. There is a few evidence for each of these features, however evidence supporting each of those ideas has been challenged. We would possibly postulate that the principal worth of sleep is to restore natural balances among the neuronal centers, which is important for total health. The particular physiological capabilities of sleep, however, remain a thriller and are the subject of a lot research. Both the intensity and the patterns of this electrical activity are decided by the level of excitation of various elements of the brain resulting from sleep, wakefulness, or brain issues corresponding to epilepsy or even psychoses. The intensities of brain waves recorded from the surface of the scalp range from zero to 200 microvolts, and their frequencies vary from as soon as each few seconds to 50 or extra per second. The character of the waves relies on the degree of activity in respective components of the cerebral cortex, and the waves change markedly between the states of wakefulness and sleep and coma. At other times, distinct patterns do seem, some of that are characteristic of specific abnormalities of the mind corresponding to epilepsy, which is discussed later. These waves occur most intensely in the occipital area but can additionally be recorded from the parietal and frontal areas of the scalp.

Alesse 0.18 mg cheap
However birth control pill 7 hours late 0.18 mg alesse with amex, the long-lived plasma cells reside in tissues such as the bone marrow and gut-associated lymphoid tissue and can proceed producing antibodies for many years birth control comparison chart alesse 0.18 mg order on-line, offering lifelong immunity against infectious diseases corresponding to measles and smallpox. High titers of smallpox-specific antibodies, for instance, have been detected in the blood of topics vaccinated in childhood, 70 years previously. Also, older survivors of the 1918 H1N1 influenza virus pandemic were proven to possess highly practical, virus-neutralizing antibodies to this virulent virus 90 years after they have been contaminated. Thus, plasma cells that produce virus-neutralizing antibodies can be sustained for so much of a long time after publicity, even into the tenth decade of life in people. Nature of Antibodies Antibodies are gamma globulins referred to as immunoglobulins (Igs) that have molecular weights between 160,000 and 970,000 and constitute about 20% of all of the plasma proteins. All the immunoglobulins are composed of combinations of sunshine and heavy polypeptide chains. Structure of the standard IgG antibody, showing it to be composed of two heavy polypeptide chains and two mild polypeptide chains. Time course of the antibody response in the circulating blood to a main injection of antigen and to a secondary injection several weeks later. Yet, in all immunoglobulins, each heavy chain is paralleled by a light-weight chain at considered one of its ends, thus forming a heavy-light pair; there are all the time no less than two and as many as 10 such pairs in every immunoglobulin molecule. The constant portion determines different properties of the antibody, establishing such factors as antibody diffusivity within the tissues, adherence to specific buildings within the tissues, attachment to the complement complicated, ease with which the antibodies move through membranes, and other organic properties of the antibody. A combination of noncovalent and covalent bonds (disulfide) holds the sunshine and heavy chains together. The amino acid organization has a unique steric form for every antigen specificity, so when an antigen comes into contact with it, multiple prosthetic groups of the antigen match as a mirror picture with these of the antibody, thus allowing for rapid and tight bonding between the antibody and antigen. When the antibody is very particular, there are so many bonding sites that the antibody-antigen coupling is exceedingly sturdy, held collectively by (1) hydrophobic bonding; (2) hydrogen bonding; (3) ionic sights; and (4) van der Waals forces. It also obeys the thermodynamic mass action regulation: ka = Concentration of sure antibody antigen Concentration of antibody � Concentration of antigen is especially concerned in allergic reactions. The IgM class is also interesting because a large share of the antibodies formed in the course of the main response are of this sort. Mechanisms of Action of Antibodies Antibodies act mainly in two ways to shield the body in opposition to invading agents: (1) by direct attack on the invader; and (2) by activation of the complement system that then has a number of technique of its personal for destroying the invader. Ka known as the affinity constant and is a measure of how tightly the antibody binds with the antigen. A small proportion of the antibodies, which consist of combinations of up to 10 mild and 10 heavy chains, has as many as 10 binding sites. There are 5 gen- eral courses of antibodies, respectively named IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, and IgE. Because of the bivalent nature of the antibodies and the multiple antigen sites on most invading brokers, the antibodies can inactivate the invading agent in certainly one of a quantity of methods, as follows: 1. Agglutination, by which multiple massive particles with antigens on their surfaces. Neutralization, during which the antibodies cover the poisonous websites of the antigenic agent four. Most of the protection occurs via the amplifying effects of the complement system, described subsequent. Complement is a collective time period that describes a system of about 20 proteins, many of that are enzyme precursors. All these are present normally among the plasma proteins within the blood, as properly as among the many proteins that leak out of the capillaries into the tissue spaces. The enzyme precursors are normally inactive however can be activated by the so-called classical pathway. That is, when an antibody binds with an antigen, a specific reactive website on the fixed portion of the antibody becomes uncovered, or activated, and this in turn binds instantly with the C1 molecule of the complement system. The C1 enzymes which are shaped then activate successively rising quantities of enzymes in the later levels of the system so that from a small beginning, an extremely massive, amplified response occurs. One of the merchandise of the complement cascade, C3b, strongly activates phagocytosis by neutrophils and macrophages, 4. It typically enhances the number of micro organism that might be destroyed by many hundredfold. One of crucial of all the merchandise of the complement cascade is the membrane attack advanced (also known as the cytolytic complex), which is a mixture of multiple complement components designated as C5b6789. This membrane attack complex inserts itself into the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, creating pores which are permeable to ions and causing osmotic rupture of the cell membranes of micro organism or different invading organisms. The complement products additionally change the surfaces of the invading organisms, inflicting them to adhere to each other, thus selling agglutination. The complement enzymes and different complement products can assault the constructions of some viruses and thereby render them nonvirulent. Fragment C5a initiates chemotaxis of neutrophils and macrophages, thus inflicting large numbers of these phagocytes to migrate into the tissue space adjacent to the antigenic agent. Fragments C3a, C4a, and C5a activate mast cells and basophils, causing them to launch histamine, heparin, and several different substances into the native fluids. These substances, in flip, cause elevated local blood circulate, increased leakage of fluid and plasma protein into the tissue, and different local tissue reactions that help inactivate or immobilize the antigenic agent. These same elements play a significant function in irritation (discussed in Chapter 34) and allergy, mentioned later. In addition to inflammatory results caused by activation of the mast cells and basophils, a number of different complement merchandise contribute to native inflammation. These merchandise cause (1) the already elevated blood move to increase still further; (2) the capillary leakage of proteins to be increased; and (3) the interstitial fluid proteins to coagulate within the tissue areas, thus preventing movement of the invading organism through the tissues. Cell-to-cell adhesion proteins enable the T cell to bind to the antigen-presenting cell long enough to turn into activated. The principal difference is that as a substitute of releasing antibodies, entire activated T cells are formed and released into the lymph. These T cells then cross into the circulation, are distributed all through the body, move through the capillary partitions into the tissue spaces, back into the lymph and blood once more, and flow into many times all through the physique, generally lasting for months or even years. Also, T-lymphocyte reminiscence cells are fashioned in the identical way that B reminiscence cells are fashioned within the antibody system. That is, when a clone of T lymphocytes is activated by an antigen, most of the newly formed lymphocytes are preserved within the lymphoid tissue to turn out to be additional T lymphocytes of that particular clone; in fact, these memory cells even spread throughout the lymphoid tissue of the complete body. Therefore, on subsequent publicity to the same antigen anywhere within the physique, release of activated T cells happens far more rapidly and much more powerfully than during first publicity. Antigen-Presenting Cells, Major Histocompatibility Complex Proteins, and Antigen Receptors on T Lymphocytes. The interplay of cell adhesion proteins is crucial in permitting the T cells to bind to antigen-presenting cells lengthy enough to turn out to be activated. The antigens on the surface of antigen-presenting cells bind with receptor molecules on the surfaces of T cells in the identical means that they bind with plasma protein antibodies. These receptor molecules are composed of a variable unit just like the variable portion of the humoral antibody, but its stem part is firmly sure to the cell membrane of the T lymphocyte. In fact, acquired immune responses often require help from T cells to begin the process, and T cells play a significant position in helping get rid of invading pathogens.
0.18 mg alesse purchase amex
At the start of flight birth control for women hd discount 0.18 mg alesse amex, easy linear acceleration happens birth control pills packaged wrong alesse 0.18 mg generic online, at the end of flight, deceleration occurs, and every time the car turns, centrifugal acceleration happens. The pulmonary arterial pressure turns into elevated even more than the traditional elevation that occurs throughout acclimatization. The purple blood cell mass becomes so nice that the blood viscosity will increase severalfold. This increased viscosity tends to decrease tissue blood move so that O2 delivery also begins to lower. This vasoconstriction results from the hypoxic vascular constrictor effect that usually operates to divert blood flow from low-O2 to high-O2 alveoli, as explained in Chapter 39. However, as a outcome of all the alveoli are now within the low-O2 state, all of the arterioles become constricted, the pulmonary arterial strain rises excessively, and the best side of the center fails. The alveolar arteriolar spasm diverts a lot of the blood circulate through nonalveolar pulmonary vessels, thus causing an extra of pulmonary shunt blood circulate the place the blood is poorly oxygenated, which further compounds the problem. It can also be obvious that the pressure of acceleration is immediately proportional to the sharpness of the turn (the much less the radius). If the force with which the particular person presses against the seat becomes 5 instances the traditional weight throughout pull-out from a dive, the drive performing on the seat is+5G. If the airplane goes through an out of doors loop in order that the person is held down by the seat belt, unfavorable G is applied to the body. If the pressure with which the individual is held down by the seat belt is the same as the weight of the physique, the negativeforceis-1G. Effects of Centrifugal Acceleratory Force on the Body (Positive G) Effects on the Circulatory System. The most essential impact of centrifugal acceleration is on the circulatory system as a end result of blood is cell and may be translocated by centrifugal forces. When an aviator is subjected to positive G, blood is centrifuged towards the lowermost a half of the physique. In addition, as stress in the vessels of the lower body will increase, these vessels passively dilate in order that a significant portion of the blood from the upper body is translocated into the lower vessels. Changes in systolic (top of curve) and diastolic (bottom of curve) arterial pressures after abrupt and persevering with publicity of a sitting person to an acceleratory force from prime to bottom of 3. This secondary restoration is brought on mainly by activation of the baroreceptor reflexes. Extremely high acceleratory forces for even a fraction of a second can fracture the vertebrae. Anaviatorcanusually undergo outside loops up to unfavorable acceleratory forces of-4to-5Gwithoutcausingpermanentharm,although inflicting intense momentary hyperemia of the top. Occasionally, psychotic disturbances lasting for 15 to 20 minutes occur on account of mind edema. However, the vessels contained in the skull show much less tendency for rupture than can be expected for the following reason. The cerebrospinal fluid is centrifuged towards the top at the similar time that blood is centrifuged toward the cranial vessels, and the greatly elevated pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid acts as a cushioning buffer on the outside of the mind to stop intracerebral vascular rupture. As a end result, the eyes usually turn into temporarily blinded with what is recognized as redout. However, the presence of air within the lungs still allows for displacement of the heart, lung tissues, and diaphragm into significantly irregular positions regardless of submersion in water. Effects of Linear Acceleratory Forces on the Body Acceleratory Forces in Space Travel. However, blast-off acceleration and touchdown deceleration can be super; both are forms of linear acceleration, with one being constructive and the other adverse. Therefore, the rationale for the reclining seats used by astronauts may be understood. Problems additionally happen during deceleration when the spacecraft re-enters the atmosphere. A individual traveling at Mach 1 (the pace of sound and of quick airplanes) could be safely decelerated in a distance of about zero. First,iftheaviator tightens his or her abdominal muscle tissue to an extreme degree and leans forward to compress the abdomen, a few of the pooling of blood in the giant vessels of the abdomen could be prevented, delaying the onset of blackout. Also, particular 558 Chapter 44 Aviation, High Altitude, and Space Physiology to the sq. of the speed, which alone will increase the required distance for decelerations between Mach 1 versus Mach one hundred by about 10,000-fold. Therefore, deceleration have to be completed much more slowly from a high velocity than from a lower velocity. Weightlessness (Microgravity) in Space A particular person in an orbiting satellite tv for pc or a nonpropelled spacecraft experiences weightlessness, or a state of nearzero G force, generally called microgravity. However, the gravity acts on the spacecraft and the individual at the similar time so that each are pulled with precisely the identical acceleratory forces and in the identical path. As the rate of fall will increase, the air resistance tending to sluggish the fall also will increase. Finally, the deceleratory pressure of the air resistance precisely balances the acceleratory pressure of gravity, so after falling for about 12 seconds, the person will be falling at a terminal velocity of 109 to 119 miles/ hour (175 feet/sec). If the parachutist has already reached terminal velocity before opening the parachute, an "opening shock load" of as a lot as 1200 pounds could happen on the parachute shrouds. The usual-sized parachute slows the autumn of the parachutist to about one ninth the terminal velocity. In other words, the pace of touchdown is about 20 feet/sec, and the pressure of impression against the earth is 1/81, the impact drive without a parachute. Even so, the drive of influence continues to be nice enough to cause appreciable injury to the physique unless the parachutist is properly educated in landing. Actually, the drive of influence with the earth is about the same as that which might be experienced by jumping with no parachute from a height of about 6 toes. Unless forewarned, the parachutist might be tricked by her or his senses into hanging the earth with prolonged legs, and this position, on touchdown, will result in tremendous deceleratory forces along the skeletal axis of the body, leading to fracture of his pelvis, vertebrae, or leg. Consequently, the educated parachutist strikes the earth with knees bent but muscle tissue taut to cushion the shock of touchdown. In some earlier space missions, a capsule atmosphere containing pure O2 at about 260 mm Hg strain was used however, in trendy area travel, gases about equal to these in regular air are used, with four instances as much nitrogen as O2 and a total pressure of 760 mm Hg. The presence of nitrogen in the mixture tremendously diminishes the probability of fireside and explosion. It also protects in opposition to development of local patches of lung atelectasis that usually happen when breathing pure O2 as a result of O2 is absorbed rapidly when small bronchi are briefly blocked by mucous plugs. For this cause, recycling techniques have been proposed to use the identical O2 time and again. Some recycling processes depend upon purely bodily procedures, similar to electrolysis of water to launch O2.