Aricept
Aricept dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Aricept packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Effective 10 mg aricept
Dynamic left ventricular outflow obstruction is attribute of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy medicine man aricept 10 mg cheap with amex. Valvular insufficiency of mitral and tricuspid valves can occur with dilated cardiomyopathy inoar hair treatment purchase aricept 10 mg otc, which also reduces contractility and ejection fraction with elevated end-systolic quantity. Infections of the heart are accompanied by irritation, though a late finding in Chagas disease is ventricular fibrosis with ventricular wall thinning. Hemochromatosis can give rise to cardiomyopathy, nevertheless it occurs much later in life. Mycobacterial infections of the center are unusual, but pericardial involvement is the most likely sample. Septicemia with bacterial infections might involve the guts, but the patient most likely would be very ill with multiple organ failure. Viridans streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus are higher known as causes of endocarditis with neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrates. Toxoplasma gondii may cause myocarditis with combined inflammatory cell infiltrates in immunocompromised sufferers. Trypanosoma cruzi is the causative agent of Chagas disease, seen most often in youngsters. There is uneven septal hypertrophy that reduces the ejection fraction of the left ventricle, particularly during exercise. Histologically, haphazardly organized hypertrophic myocardial 56 C Fibrinous pericarditis results in the tough, corrugated brownish surfaces of epicardium and mirrored pericardial sac as proven, which is usually described as a "bread and butter" appearance (after dropping the buttered bread on the carpet). Friction between epicardial and pericardial surfaces yields the rub, which can disappear with fluid assortment (serofibrinous pericarditis). Acute rheumatic fever may produce fibrinous pericarditis, however rheumatic fever is unusual at this age. Calcific aortic stenosis results in left-sided congestive coronary heart failure, with pulmonary edema as a key finding. Rheumatic coronary heart disease mainly impacts the cardiac valves, however acute rheumatic fever can produce fibrinous pericarditis. Tuberculosis is unlikely in this case as a outcome of no pulmonary lesions were seen on the radiograph. An acute myocardial infarction may be accompanied by a fibrinous exudate over the area of infarction, not the diffuse pericarditis seen on this patient. Fibrinous pericarditis is unlikely the results of an infection, but a fibrinopurulent look might suggest bacterial infection. An effusion of this size is sufficient to produce some cardiac tamponade that diminishes cardiac output; the paradoxical drop in strain (more than 10 mm Hg) is recognized as pulsus paradoxus and can be caused by pericarditis and by tamponade. Group A streptococci are liable for rheumatic fever; in the acute kind, rheumatic fever can result in fibrinous pericarditis, and within the chronic kind, it can result in serous effusions from congestive coronary heart failure. On the left side of the guts, it may possibly produce a ball-valve impact that intermittently occludes the mitral valve, resulting in syncopal episodes and possible strokes from embolization to cerebral arteries. Calcification of a bicuspid valve can result in stenosis and heart failure, but this situation is progressive. Coronary artery thrombosis results in an acute ischemic occasion, usually with chest ache. By the time left atrial enlargement with mural thrombosis and threat of embolization occurs from mitral stenosis, this patient would have been symptomatic for years. After excluding trauma, a complication of ischemic heart disease ought to be suspected. Ischemic coronary heart illness happens in sufferers of his age, and risk elements similar to weight problems, smoking, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia can play a task in its growth. Metastases from melanoma and other carcinomas can produce hemorrhagic pericarditis without tamponade. Takayasu arteritis can involve coronary arteries with aneurysms and rupture, however is most often a rare pediatric situation. Months to years later, coronary arteriopathy characteristic of cardiac transplantations may produce ischemic modifications. The most common neoplasm involving the guts is metastatic most cancers, as a outcome of primary cardiac neoplasms are uncommon. The skin lesion on this patient is likely to be a malignant melanoma, which tends to metastasize extensively, together with to the guts. Unlike atherosclerosis, the smaller coronary artery branches are preferentially affected, however the end result is identical: ischemic injury. Transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressive remedy have immune dysregulation that increases the danger for each carcinomas and lymphoid malignancies, however these are unlikely to involve the heart. A bronchoalveolar lavage is carried out, and cysts of Pneumocystis jiroveci are present. These nodules are most probably to be caused by infection with which of the following organisms A Aspergillus fumigatus B Bartonella henselae C Mycobacterium avium complex 3 A 41-year-old man has had fevers with chills and rigors for the previous 2 weeks. Chronic myelogenous leukemia Hairy cell leukemia Hodgkin lymphoma, lymphocyte depletion sort Leukemoid response Myelodysplastic syndrome four A 23-year-old girl has seen that she develops a pores and skin rash if she spends prolonged intervals outdoor. Basophilia Eosinophilia Monocytosis Neutrophilia Thrombocytosis 5 A 23-year-old man present process chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia has developed a fever and abdominal ache inside the previous week. Acute myelogenous leukemia Chronic myelogenous leukemia Infectious mononucleosis Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis 9 A 23-year-old, previously healthy man has skilled malaise and a low-grade fever and sore throat for two weeks. A Acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma B Hodgkin lymphoma, lymphocyte wealthy type C Mycobacterium tuberculosis granuloma 10 A 6-year-old boy has complained of worsening ache in the best aspect of his groin for the past week. Physical examination shows painful, swollen lymph nodes in the proper inguinal region. An inguinal lymph node biopsy is carried out, and on microscopy the node has large, variably sized, germinal facilities containing quite a few mitotic figures. On physical examination, she has a agency, fastened, irregular 3-cm mass within the higher outer quadrant of the right breast and a agency, nontender lymph node in the proper axilla. A lumpectomy and axillary node dissection are performed, and microscopic examination shows an infiltrating ductal carcinoma in the breast. His peripheral blood smear exhibits a monotonous population of small, round, maturelooking lymphocytes. Cytogenetic and molecular evaluation of the abnormal cells in his blood are most likely to reveal which of the next alterations There are 4 linear and practically healed abrasions over a 3 � 2 cm space of the distal ventral side of the right forearm and a single, zero. Histologic examination of one of the lymph nodes reveals stellate, necrotizing granulomas. Infection with which of the following is most likely to have produced these findings Bartonella henselae Cytomegalovirus Epstein-Barr virus Staphylococcus aureus Yersinia pestis 13 A study of individuals with lymphoid malignancies reveals that there are threat factors for improvement of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Which of the following is the most likely inherited situation predisposing to lymphoid malignancies Cystic fibrosis Hereditary spherocytosis Sickle cell disease Von Willebrand disease Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome 14 A 14-year-old boy complains of discomfort in his chest that has worsened over the past 5 days. A biopsy specimen of the mass is obtained and microscopically shows effacement by lymphoid cells with lobulated nuclei having delicate, finely stippled, nuclear chromatin. The oncologist tells the dad and mom that chemotherapy could be curative in vast majority of such cases. A Burkitt lymphoma B Follicular lymphoma 16 A 69-year-old man notices the presence of lumps in the right aspect of his neck which have been enlarging for the past yr.
Aricept 5 mg with visa
Psoas Compartment Block the psoas compartment block is beneficial for unilateral hip or anterior leg surgical procedure in combination with sciatic nerve block and is often performed with steerage of a nerve stimulator to get hold of a quadriceps twitch response medications known to cause pill-induced esophagitis aricept 5 mg discount fast delivery. This response is commonly obtained when a 100-mm insulated block needle is inserted 1 to 2 cm deep to the L4 (sometimes L3) transverse course of treatment lyme disease 5 mg aricept purchase with amex. Due to the priority of hematoma, retroperitoneal bleeding, or epidural unfold, careful consideration and monitoring along with an skilled practitioner are necessary for safe and effective completion of this advanced block. Femoral Nerve Block the femoral nerve may be blocked at the level of the inguinal crease with or without ultrasound steerage. When performing the femoral nerve block with ultrasound, the femoral artery is visualized at the inguinal crease. The femoral nerve seems as a hyperechoic triangular construction lateral to the artery. Nerve stimulation can be used together with ultrasound to verify a patellar or quadriceps response. Saphenous Nerve Block A saphenous nerve block can be carried out for anesthesia of the medial calf and ankle. The saphenous nerve block may be carried out on the midthigh level utilizing ultrasound guidance. The femoral artery becomes the descending genicular artery because it follows its course along the thigh. Initially, the saphenous nerve is lateral to the artery and transitions to medial in the mid- to distal thigh. Using ultrasound, the nerve could be visualized as a hyperechoic construction anterior and medial to the femoral artery, deep to the sartorius muscle. Detailed descriptions of those blocks may be present in a comprehensive regional textual content. Sciatic Nerve Block the sciatic nerve block supplies complete anesthesia to the ankle and foot when combined with a saphenous nerve block. Surgeries corresponding to mid- and hind foot fusions, open reductions and inner fixations of ankle fractures, Achilles tendon repairs, and total ankle arthroplasties can all be carried out with sciatic�saphenous nerve anesthesia with minimal intraoperative sedation required. Classically the gluteal approach (Labat) has been used, but with the popularity of ultrasound and the convenience of visualization of the sciatic nerve on the degree of the gluteal crease, extra distal approaches have come into favor. The landmarks for the gluteal method include an indirect line from the posterior superior iliac spine to the greater trochanter of the femur with the affected person in a semiprone place with the hip and knee flexed and the operative aspect up. A second line from the higher trochanter of the femur to the sacral hiatus is drawn. A third line, perpendicular to the first line, will cross the second line on the approximate needle entry point. An ultrasound-guided subgluteal method could be performed with the patient either lateral or prone. Many high-frequency probes penetrate as a lot as 6 cm, and thus the vast majority of sciatic nerves may be visible with a highfrequency probe, reducing the necessity to change probes between varied blocks. A nerve stimulator can be utilized to confirm proper identification of the sciatic nerve. A plantar flexion motor response within the foot signifies that the medial (tibial) element of the nerve is being stimulated. A dorsiflexion (common peroneal) or an eversion (superficial peroneal) response signifies the lateral components of the nerve are being stimulated. An inversion response is taken into account optimal and signifies that both elements (tibial and peroneal) are being stimulated. Regardless of stimulation, native anesthetic spread should be visualized surrounding each parts of the sciatic nerve. The popliteal block is a distal sciatic block carried out proximal to the popliteal fossa. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:994, with permission. Blocking approximately 10 to 15 cm proximal to the popliteal crease normally ensures that the 2 parts have joined. A easy approach to find the sciatic nerve for a distal (popliteal) strategy is to begin by visualizing the popliteal artery on the popliteal fossa. The tibial nerve shall be located superficial and barely lateral to the artery and appears hyperechoic. The tibial nerve can then be traced proximally, and the peroneal nerve can be seen joining the tibial element. Ankle Block Surgery on the distal foot, together with bunion surgeries, may be performed with ankle block anesthesia. Many clinicians thought of the ankle block to be a "area" block prior to now, but the use of ultrasound has made ankle block anesthesia more exact. The posterior tibial nerve could be blocked using a high-frequency ultrasound probe. The posterior tibial nerve will be located barely posterior and deep to the posterior tibial artery. The needle can be positioned out of plane starting both superior or inferior to the probe. A nerve stimulator can be utilized to affirm identification of the nerve with toe flexion. The deep peroneal nerve block could be carried out at the degree of a line between the higher borders of the medial and lateral malleoluses. Locate the anterior tibial artery and the hyperechoic deep peroneal nerve shall be lateral. The superficial peroneal nerve and saphenous nerves are blocked with a subcutaneous native anesthetic ring circumferentially around the ankle on the upper border of the medial and lateral malleoluses. Did You Know Many clinicians previously thought of the ankle block to be a "area" block, but the use of ultrasound has made ankle block anesthesia more precise. Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia and analgesia: A qualitative systematic evaluation. Ultrasound-guided low-dose interscalene brachial plexus block reduces the incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis. One hundred p.c incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis related to interscalene brachial plexus anesthesia as diagnosed by ultrasonography. Eight ball, corner pocket: the optimum needle position for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block. Supraclavicular nerve block: anatomic evaluation of a method to prevent pneumothorax. Restricted infraclavicular distribution of the native anesthetic answer after infraclavicular brachial plexus block.
5 mg aricept cheap with mastercard
The result of immunofluorescence staining with anti-IgG and anti-C3 antibodies is unfavorable symptoms rheumatoid arthritis 10 mg aricept sale. Which of the next additional microscopic findings is more than likely to be seen on this biopsy Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Glomerular basement membrane thickening Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis Infiltrations by neutrophils Mesangial proliferation Necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis 11 A 48-year-old man has had elevated swelling in the extremities for 2 months medicine for depression buy aricept 10 mg visa. A renal biopsy was accomplished, and microscopic examination confirmed diffuse thickening of the basement membrane. Immunofluorescence staining with antibody to the C3 element of complement was optimistic in a granular pattern in the glomerular capillary loops. Which of the following immunologic mechanisms was most probably liable for the glomerular changes noticed within the biopsy specimen A Antibodies that react with basement membrane collagen B Antibodies towards streptococci that cross-react with the basement membrane C Cytotoxic T cells directed against renal antigens D Deposition of immune complexes on the basement membrane E Release of cytokines by inflammatory cells 12 A 7-year-old boy has turn into less active over the previous 10 days. Urinalysis exhibits no blood, glucose, or ketones, and microscopic examination exhibits no casts or crystals. He has two more episodes of proteinuria over the following 4 years, each of which respond to corticosteroid therapy. A Cytokine-mediated visceral epithelial cell injury B Cytotoxic T cell�mediated tubular epithelial cell injury C IgA-mediated mesangial cell damage D Immune complex�mediated glomerular injury E Verocytotoxin-induced endothelial cell damage thirteen A 44-year-old man with increasing malaise for the past month now could be bothered by increasing swelling within the palms and legs. A renal biopsy specimen is obtained, and immunofluorescence staining with antibody to the C3 element of complement produces the sample shown within the figure. Which of the following underlying disease processes is most probably to be current in this man Which of the next findings by electron microscopy is more than likely to characterize this illness course of A renal biopsy is done; microscopic examination reveals hypercellular glomeruli and prominent ribbonlike deposits alongside the lamina densa of the glomerular basement membrane. Which of the following forms of glomerulonephritis is more than likely to be present on this patient Chronic glomerulonephritis Dense deposit illness Membranous nephropathy Postinfectious glomerulonephritis Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis 15 A 12-year-old woman has experienced rising malaise for the past 2 weeks. Laboratory findings show proteinuria on dipstick urinalysis, but no hematuria or glucosuria. A renal biopsy is carried out and microscopic examination shows that roughly 50% of the glomeruli in the specimen are affected by the lesion proven within the determine. Dense deposit illness Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Minimal change illness Nodular glomerulosclerosis Postinfectious glomerulonephritis Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis 18 A 25-year-old man has a 5-year history of celiac sprue. Four days after a mild higher respiratory infection, he begins passing darkish red-brown urine. The darkish urine persists for the subsequent three days and then turns into clear and yellow, only to turn out to be red-brown once more 1 month later. A renal biopsy specimen from the glomeruli of this patient is most probably to present which of the next alterations A Diffuse mobile proliferation and basement membrane thickening B Granular staining of the basement membrane by anti-IgG antibodies C Mesangial IgA staining by immunofluorescence D Subepithelial electron-dense deposits E Thrombosis inside the glomerular capillaries 19 One week after a gentle flulike illness, a 9-year-old boy has an episode of hematuria that subsides within 2 days. Which of the following glomerular constructions is most likely to present structural alterations on this boy Basement membranes Capillaries Mesangium Parietal epithelium Podocytes 16 A 46-year-old Hispanic man has had increasing malaise with complications and straightforward fatigability for the previous 3 months. A renal biopsy is completed; gentle microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen shows that approximately 50% of the glomeruli appear normal, but the remaining show that a portion of the capillary tuft is sclerotic. After being handled with immunosuppressive remedy consisting of prednisone and cyclophosphamide, her condition improves. Which of the following serologic studies is most probably to be optimistic in this affected person On physical examination, he has bilateral sensorineural listening to loss and corneal erosions. By electron microscopy, the glomerular basement membrane exhibits areas of attenuation, with splitting and lamination of lamina densa in different thickened areas. An stomach ultrasound scan shows bilaterally and symmetrically small kidneys with no masses. Amyloidosis Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Chronic glomerulonephritis Microscopic polyangiitis Nodular glomerulosclerosis 24 A 33-year-old girl with a historical past of intravenous drug use comes to the emergency department because she has had a high fever for the past 2 days. She has a palpable spleen tip, bilateral costovertebral angle tenderness, and diastolic cardiac murmur. Which of the following greatest describes the probably gross appearance of the kidneys in this patient A Enlarged, and replaced by 1- to 4-cm, fluid-filled cysts B Marked pelvic and calyceal dilation with thinning of the cortices C Normal size, with clean cortical surfaces D Shrunken, with uniformly finely granular cortical surfaces E Slightly swollen, with scattered petechial hemorrhages F Small and asymmetric, with irregular cortical scars and marked calyceal dilation G Wedge-shaped areas of yellow-white cortical necrosis 25 A 55-year-old girl with poorly controlled hyperglycemia for a number of years now has had burning ache on urination for the previous three days. Physical examination reveals a 2-cm ulceration on the pores and skin of the heel and lowered sensation in the decrease extremities. Urinalysis exhibits 1+ proteinuria; 2+ glucosuria; and no blood, ketones, or urobilinogen. A urine tradition accommodates more than 100,000 colony-forming units/mL of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Which of the following pathologic findings is most likely to be present in both her kidneys A Deposits of IgG and C3 in the glomerular basement membrane B Effacement of podocyte foot processes C Formation of glomerular crescents D Mesangial deposits of IgA E Necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis F Nodular hyaline mesangial deposits 22 An post-mortem research is performed involving persons with gross pathologic findings of bilaterally small kidneys (<100 g) that have a coarsely granular floor look. Microscopic examination shows sclerotic glomeruli, a fibrotic interstitium, tubular atrophy, arterial thickening, and scattered lymphocytic infiltrates. Over the previous year, she has observed soreness of her muscle tissue and joints and has had a 4-kg weight loss. She has ache on deep inspiration, and a friction rub is heard on auscultation of the chest. Aldosterone Endothelin Erythropoietin Natriuretic peptide Vasopressin 26 A 58-year-old man is found to have gentle hypertension. Blood/serum check for which of the next is most probably to be irregular in this patient Anti�glomerular basement membrane antibody Antinuclear antibody Anti�neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody Anti�streptolysin O C3 nephritic factor Hemoglobin A1c Hepatitis B surface antigen 29 A 19-year-old lady has had a fever and chills accompanied by right flank ache for the past 3 days. Laboratory findings present a serum glucose degree of seventy seven mg/dL and creatinine level of 1 mg/dL. His serum urea nitrogen stage increases to 38 mg/dL, and he undergoes hemodialysis for 3 weeks. His condition improves, however the urine output remains higher than 3 L/day for 1 week earlier than the urea nitrogen returns to normal. Acute pyelonephritis Acute tubular damage Malignant nephrosclerosis Membranous nephropathy Renal vein thrombosis 30 A 51-year-old woman has had dysuria and urinary frequency for the previous week. On bodily examination, her temperature is 38� C, and he or she has pain on palpation over the left costovertebral angle. Microscopic examination of the urine shows quite a few neutrophils, and a urine tradition is positive for Escherichia coli. Acute tubular necrosis Crescentic glomerulonephritis Hydronephrosis Necrotizing papillitis Renal calculi 28 A 63-year-old man is in stable situation after an acute myocardial infarction when he turned hypotensive for 3 hours before paramedical personnel arrived. Over the next week, the serum urea nitrogen degree increases to 48 mg/dL, the serum creatinine stage will increase to 5 mg/dL, and the urine output decreases. He undergoes hemodialysis for the following 2 weeks after which develops marked polyuria, with urine output 31 A 53-year-old girl has had fever and flank ache for the previous 2 days. Laboratory findings present serum urea nitrogen degree of sixty eight mg/dL and creatinine degree of 7. Acute tubular injury Chronic glomerulonephritis Hydronephrosis Renal cell carcinoma Renal papillary necrosis 32 A 30-year-old girl has had rising malaise with nocturia and polyuria for the past year. A renal ultrasound scan exhibits an enlarged right kidney with pelvic and calyceal enlargement and cortical thinning; the left kidney seems normal. A right-sided nephrectomy is performed, and grossly there are giant U-shaped scars at the poles with underlying blunted calyces. Microscopic examination exhibits inflammatory infiltrates extending from the medulla to the cortex, with tubular destruction and extensive interstitial fibrosis.
Buy generic aricept 5 mg line
Aspirin has antiplatelet effects that take days to occur symptoms blood clot leg aricept 10 mg buy discount on line, and bleeding (not thrombosis) is the main danger medicine man pharmacy aricept 10 mg discount on-line. Tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase are fibrinolytic agents, with the former used acutely to deal with circumstances similar to coronary thrombosis, though the latter additionally could additionally be used for venous clot lysis. Warfarin therapy prolongs the prothrombin time by interfering with vitamin K�dependent clotting issue synthesis within the liver. The abnormalities are produced by small platelet-fibrin thrombi in small vessels in multiple organs. Many of the clotting elements which might be instrumental within the in vitro measurement of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation, as measured by the prothrombin time, are synthesized in the liver. Increased fibrin break up merchandise counsel a consumptive coagulopathy, corresponding to disseminated intravascular coagulation. Marrow examination in this case exhibits quite a few megakaryocytes, which excludes decreased manufacturing. Peripheral platelet destruction is usually immunologically mediated and can result from well-known autoimmune illnesses similar to systemic lupus erythematosus, or it can be idiopathic. Hemophilia B, similar to hemophilia A, results in delicate tissue bleeding, and the partial thromboplastin time is prolonged, but the platelet rely is normal. In von Willebrand disease, bleeding is as a end result of of abnormal platelet adhesion, but platelet numbers are normal. Von Willebrand illness is a standard bleeding dysfunction, with an estimated frequency of 1%. Joint hemorrhages are a characteristic of hemophilia A and B, not von Willebrand disease. X-inactivation ("unfavorable lyonization") can clarify this phenomenon and will explain why feminine carriers of hemophilia A or B generally tend to bleed. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is characterized by the presence of antiplatelet antibodies and thrombocytopenia. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia characterized by renal failure and central nervous system abnormalities. Von Willebrand disease is caused by decreased platelet adhesion and has options resembling thrombocytopenia. In this case, the partial thromboplastin time partly corrects, indicating that some inhibitor could also be current. Mucocutaneous bleeding is more typical for platelet problems and von Willebrand illness. Hemophilia A and hemophilia B are X-linked inherited conditions, so males are primarily affected. There can be uncommon new mutations (such as in Queen Victoria), which introduce the gene right into a household. Mild (1% to 5%) and average (5% to 75%) exercise is commonly asymptomatic besides in severe trauma. The platelet aggregation studies described here are attribute for this dysfunction. Disseminated intravascular coagulation ends in consumption of all coagulation elements and platelets, so the prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time are elevated with thrombocytopenia. Scurvy ensuing from vitamin C deficiency causes bleeding into delicate tissues and pores and skin from increased capillary fragility, but platelet number and function are regular. Von Willebrand disease is among the commonest bleeding issues and outcomes from qualitative or quantitative defects in von Willebrand issue. You discovered that proper phlebotomy process requires labeling the tubes just after drawing the blood, not handing the tubes to someone else for labeling and potential mix-up. Though hepatitis C infection continues to be potential, but uncommon, from transfused blood, this an infection has an incubation interval of months. Granulocyte enzymes are released, increasing capillary permeability and resulting in sudden pulmonary edema with respiratory misery. Platelet transfusion might cause alloimmunization and subsequent platelet destruction with future platelet transfusion. The causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum, is often killed at fridge temperatures. A term infant is delivered with no apparent external anomalies, however quickly after birth the infant has respiratory misery. Extralobar sequestration Foregut cyst Hyaline membrane disease Oligohydramnios sequence Tracheoesophageal fistula 2 A 30-year-old man is hospitalized after a motorized vehicle accident by which he sustains blunt trauma to his chest. On physical examination, there are contusions to the proper aspect of the chest, however no lacerations. Within 1 hour after the accident, he develops sudden problem respiratory and marked ache on the proper aspect. Interstitial fibrosis Patchy infiltrates Pleural effusion Pneumothorax Ventilation/perfusion mismatch three A 58-year-old man with ischemic coronary heart disease undergoes coronary artery bypass graft surgical procedure beneath basic anesthesia. Two days postoperatively, he experiences growing respiratory difficulty with lowering arterial oxygen saturation. On bodily examination, his coronary heart rate is regular at 78/min, respirations are 25/min, and blood stress is 135/85 mm Hg. Over the next 2 days he has subcutaneous delicate tissue swelling with nonpainful crepitance on palpation of the right chest wall. Acid Air Blood Lymph Pus the Lung 227 8 A 48-year-old man has gradually rising dyspnea and a 4-kg weight loss over the past 2 years. He has smoked two packs of cigarettes per day for 20 years, however not for the previous yr. Physical examination exhibits an increase in the anteroposterior diameter of the chest. A chest radiograph reveals bilateral hyperlucent lungs; the lucency is especially marked in the upper lobes. Which of the following is more than likely to contribute to the pathogenesis of his disease A Abnormal epithelial cell chloride ion transport B Decreased ciliary motility with irregular dynein arms C Impaired hepatic release of 1-antitrypsin D Macrophage recruitment and release of interferon- E Release of elastase from neutrophils 9 A 20-year-old, beforehand healthy man is jogging one morning when he trips and falls to the ground. Which of the following underlying illnesses is most likely to have produced this complication Asthma Bronchiectasis Centriacinar emphysema Chronic bronchitis Distal acinar emphysema Panlobular emphysema 5 A 68-year-old man has had worsening dyspnea and orthopnea for the previous 3 years with elevated production of frothy sputum. A chest radiograph exhibits bilateral interstitial infiltrates, distinct Kerley B lines, and a prominent left coronary heart border. Aldosteronoma Bilateral adrenal atrophy Chronic glomerulonephritis Ischemic heart illness Pulmonary fibrosis Small cell carcinoma 6 A 26-year-old lady with postpartum sepsis is afebrile on antibiotic remedy, however she has had worsening oxygenation over the previous 3 days. Which of the following microscopic findings is most probably to be present in her lungs Alveolar hyaline membranes Arterial plexiform lesions Interstitial fibrosis Lymphocytic infiltrates Respiratory bronchiolar destruction 10 A 49-year-old man has had increasing dyspnea for the past 4 years. Which of the next illness processes ought to most frequently be suspected as a trigger of these findings Centrilobular emphysema Chronic pulmonary embolism Diffuse alveolar damage Nonatopic bronchial asthma Sarcoidosis Silicosis 7 After a hemicolectomy to take away a colon carcinoma, a 56-year-old man develops respiratory misery.
Diseases
- Oliver McFarlane syndrome
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Ruvalcaba Myhre syndrome
- Metageria
- Renoanogenital syndrome
- IFAP syndrome
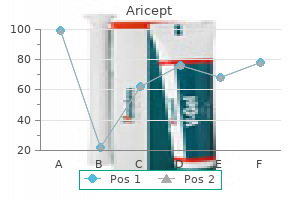
Cheap aricept 5 mg line
Unfortunately 4 medications list generic 5 mg aricept fast delivery, no single index of diastolic function utterly characterizes this portion of the cardiac cycle or precisely predicts those at greatest danger of growing heart failure in response to altering load situations treatment low blood pressure discount 5 mg aricept overnight delivery. Thus, each invasive and noninvasive assessments of ventricular rest, filling, and compliance could also be needed. Although these indices have prognostic worth, noninvasive methods have largely supplanted them. Did You Know In the aged, agerelated autonomic nervous system dysfunction interferes with the baroreceptor reflex arc, such that hypotension-induced compensatory increases in blood stress and coronary heart rate are less pronounced than in younger adults. Each pulse is definitely separated into systole and diastole by the dicrotic notch, with the peak strain corresponding the systolic pressure and the lowest strain being the diastolic strain. The pulse stress waveform adjustments as one moves distally within the systemic arterial tree because of arterial branching and adjustments in vessel elasticity. Because the large arteries have elastic elements and properties, the arterial system is distensible and in a place to keep positive strain throughout the cardiac cycle. Thus, only a portion of the vitality of cardiac contraction leads to ahead capillary flow, with the rest saved as potential energy within the elastic recoil of the arteries, a property often recognized as the Windkessel effect, which serves to make peripheral circulate much less pulsatile. Vascular Resistance For the systemic circulation, the blood strain, cross-sectional area, and quantity capacitance range broadly across its arterial, microcirculatory, and venous components. The arterioles serve as the principal points of resistance to blood move within the systemic circulation, producing roughly 95% reduction in mean intravascular stress. Whereas excessive doses will lead to predominate activation of -adrenergic receptors and result in enhanced vasoconstriction. Local metabolic activity plays an important position in regional control of vascular resistance because arterioles lie throughout the organ itself and are exposed to the native environment. Video 3-10 Circulatory System Blood Flow and Pressures three Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology 61 1. This course of is accomplished by modifications in vascular resistance (upper panel) that are unbiased of neural and hormonal influence. Autoregulation refers to the intrinsic tendency of a specific organ or tissue bed to maintain fixed blood circulate regardless of changes in arterial strain, impartial of hormonal or neural mechanisms. Autoregulation is often energetic inside a specific range of arterial pressures, within which fixed flow is achieved by adjustments in vascular resistance. Outside this range, blood move varies proportionately to arterial stress, with clinical consequences of ischemia (low pressure) or hyperemia (high pressure). The human organs with the most clinically relevant autoregulation options are those whose perfusion is physiologically critical-the mind, kidney, and heart (7). Baroreceptor Function In addition to the instant regulation of blood move by autoregulation on the tissue stage, extra widespread and short-term adjustments in systemic arterial pressure are additionally regulated by the baroreceptor reflex (Table 3-1. This inverse relation between arterial blood strain and heart price was first described by Etienne Marey in 1859 and serves to preserve cardiac output and arterial stress under various circumstances such as postural changes, train, and hypovolemia. The afferent limb of the reflex is initiated by pressuresensitive stretch receptors within the carotid sinus and the aortic arch that relay sensory information to the medullary vasomotor heart by way of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. Elevated blood stress leads to efferent vagal nerve traffic to the guts that slows coronary heart rate and reduces contractility (to reduce blood pressure). In contrast, low blood stress leads to efferent sympathetic tone by way of the spinal cord and sympathetic chain that will increase both coronary heart price and contractility, and also results in peripheral vasoconstriction. One clinical utility of the baroreceptor reflex is the efficiency of exterior carotid massage in sufferers with supraventricular tachycardia. The baroreceptor reflex also underlies the everyday observation of compensatory tachycardia in sufferers with hypovolemic hypotension. Conversely, irregular baroreceptor reflex responses can happen in patients with neurologic impairments at any point alongside the reflex arc. For example, age-related autonomic dysfunction within the elderly is often manifest by postural syncope as a result of reductions in cerebral perfusion stress and flow. Vascular Compliance, Capacitance, and Control As blood exits the capillary mattress, it passes first through venules after which a steadily lowering variety of veins of accelerating size. The vascular system cross-sectional space within the small and large veins is similar to that within the small and large arteries. Compared with their corresponding arterial structures, however, venous constructions are typically barely bigger in diameter, have thinner walls containing much less three Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology sixty three vascular easy muscle, and possess far larger capacitance (lower vascular resistance). This 10 to 20 occasions larger compliance means that veins can accommodate massive modifications in blood quantity with solely a small change in strain. These embrace skeletal muscle contraction in the limbs (muscle pump), intrathoracic strain changes related to respiratory activity (thoraco-abdominal pump), exterior vena cava compression, and forces of gravity related to postural modifications (8,9). Skeletal muscle contractions in the legs and arms, together with pressure-passive one-way venous valves in peripheral veins, augment venous return, significantly throughout train. Muscle contraction compresses veins inside giant muscle groups and forces venous blood centrally, whereas skeletal muscle rest decompresses veins and draws in blood from the distal limb and adjacent veins. Repeated compression�decompression cycles rapidly propel venous blood centrally and improve venous return. Patients with incompetent venous valves are unable to augment their venous return with train or postural modifications and should experience syncope underneath these circumstances. Spontaneous respiration changes the transmural stress in veins passing by way of the intrathoracic cavity and modifies venous return. During inspiration, diaphragmatic descent and thoracic cage enlargement create adverse intrathoracic strain, whereas on the similar time elevating intra-abdominal stress. Conversely, spontaneous expiration will increase intrathoracic strain and impairs venous return. The total impact of spontaneous ventilation is to enhance venous return in contrast with apneic conditions because imply intrathoracic pressures are barely negative over the whole respiratory cycle. In distinction, positive stress air flow increases mean intrathoracic pressures, impairs venous return, and might negatively impression cardiac output. Blood Volume and Distribution Total physique water constitutes 60% of physique weight (42 L in a 70-kg person), with 40% (28 L) in the intracellular space and 20% (14 L) within the extracellular area. Plasma quantity accounts for one-fifth (3 L) of the extracellular quantity, and erythrocyte volume (2 L) is part of the intracellular volume; therefore, blood quantity is 5 L in a 70-kg particular person. Blood quantity is nonuniformly distributed all through the circulatory tree, with approximately 65% in the systemic venous system, 15% in the systemic arterial system, 10% within the pulmonary circulation, and the rest within the coronary heart and systemic microcirculation. This process occurs in the rich network of capillaries that are only 5 to 10 m in diameter, yet so overwhelming in quantity that the sixty four Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals total floor space of the network is 20 instances larger than that of all the small and larger arteries. Water and solutes diffuse in each directions across the capillary wall, with water and water-soluble molecules. Thus, the capillary wall acts as a semipermeable membrane across which water, gases, and small substrates move primarily by diffusion according to focus gradients (10). In the microvasculature, osmotic pressure is essentially determined by protein focus (particularly albumin) and is termed oncotic stress. According to the Starling speculation, fluid filtration throughout the porous capillary wall is determined by the stability between the hydrostatic and oncotic stress gradients throughout the wall, in addition to by the scale and variety of intercellular clefts. The hydrostatic strain gradient favors water movement out of the capillary and is slightly higher than the oncotic strain gradient that favors water movement into the capillary. The relation between these components is governed by the Starling equation: F = Kf * ([Pc - Pt] - [pc - pi]), where F is the fluid movement across the capillary wall, Kf is the filtration fixed of the capillary membrane (reflecting its permeability), Pc is the capillary hydrostatic strain (higher on the arteriolar aspect of the capillary than on the venular aspect of the capillary), Pt is the tissue hydrostatic stress (typically near zero), is the reflection coefficient (a correction issue for protein permeability of the capillary wall), laptop is the plasma oncotic strain, and pi is the interstitial oncotic strain.
Discount aricept 10 mg without prescription
Eventually medications 1-z buy discount aricept 5 mg on line, the dilated pelvi-calyceal system extends deep into the renal cortex so that a skinny rim of renal cortex is stretched over the dilated calyces and the external floor assumes lobulated look medications ok for pregnancy generic 5 mg aricept fast delivery. An essential level of distinction between the sectioned surface of advanced hydronephrosis and polycystic kidney illness (page 657) is the direct continuity of dilated cystic spaces. There is progressive atrophy of tubules and glomeruli alongwith interstitial fibrosis. Cortical Adenoma Cortical tubular adenomas are more widespread than different benign renal neoplasms. The cells of the adenoma are normally uniform, cuboidal with no atypicality or mitosis. However, size of the tumour quite than histologic criteria is considered extra significant parameter to predict the behaviour of the tumour-those larger than 3 cm in diameter are potentially malignant and metastasising. Microscopically, the cysts are lined by tubular epithelium whereas the stroma between the cysts contains mesenchymal tissue with some immature blastemal or abortive tubules. A third malignant renal tumour is urothelial carcinoma occurring extra commonly in the renal pelvis is described in the next section together with different tumours of the lower urinary tract. Adenocarcinoma of Kidney (Synonyms: Renal cell carcinoma, Hypernephroma, Grawitz tumour) Hypernephroma is an old misnomer under the mistaken perception that the tumour arises from adrenal rests due to the resemblance of the tumour cells with clear cells of the adrenal cortex. This most cancers includes 70 to 80% of all renal cancers and happens most commonly in 50 to 70 years of age with male preponderance (2:1). Microscopically, it exhibits mobile progress of spindle cells derived from secondary mesenchyme. Another vital attribute is the frequent presence of tumour thrombus in the renal vein which may prolong into the vena cava. The tumour cells have a wide selection of patterns: solid, trabecular and tubular, separated by delicate vasculature. The residual kidney is compressed on one aspect and shows obliterated calyces and renal pelvis. The most typical presenting abnormality is haematuria that happens in about 60% of circumstances. The sectioned surface exhibits substitute of virtually whole kidney by the tumour leaving a skinny strip of compressed renal tissue at lower finish (arrow). A defect in chromosome 11p13 leads to abnormal development of metanephric blastema with out differentiation into normal tubules and glomeruli. A larger incidence has been seen in monozygotic twins and instances with household historical past. Grossly, the tumour is normally quite massive, spheroidal, replacing most of the kidney. On cut section, the tumour exhibits characteristic variegated appearance- gentle, fishflesh-like grey-white to cream-yellow tumour with foci of necrosis and haemorrhages and grossly identifiable myxomatous or cartilaginous components. Microscopically, nephroblastoma exhibits mixture of primitive epithelial and mesenchymal elements. Most of the tumour consists of small, round to spindled, anaplastic, sarcomatoid tumour cells. In these areas are current abortive tubules and poorly-formed glomerular structures. Mesenchymal elements similar to smooth and skeletal muscle, cartilage and bone, fat cells and fibrous tissue, could additionally be seen. The prognosis of the tumour with combination therapy of nephrectomy, post-operative irradiation and chemotherapy, has improved significantly and the 5-year survival nows 80-90%. Secondary Tumours Leukaemic infiltration of the kidneys is a typical finding, particularly in chronic myeloid leukaemia. This is a situation during which the whole ureter or only the higher part is duplicated. Ureterocele is cystic dilatation of the terminal a part of the ureter which lies throughout the bladder wall. This is a rare situation owing to congenital developmental deficiency of anterior wall of the bladder and is related to splitting of the overlying anterior stomach wall. Rarely, there could also be persistence of the urachus during which urine passes from the bladder to the umbilicus. Myocarditis led to dilation of the ventricle so severe that the mitral valve grew to become incompetent. Rheumatic heart disease is now unusual, and the number of youngsters that require prophylactic antibiotic therapy to prevent just one case is >10,000. Chronic inflammatory circumstances might produce reactive systemic amyloidosis, but that is unlikely to occur given the restricted and episodic nature of the streptococcal infection that causes rheumatic coronary heart disease. Fibrosis and fusion of the mitral valve leaflets develop over weeks to months and point out persistent rheumatic valvulitis. The strains of group A streptococci that lead to acute rheumatic fever are less more doubtless to cause glomerulonephritis, so an elevated creatinine level is unlikely. The probe passes through a perforated leaflet, typical of infective endocarditis attributable to highly virulent organisms corresponding to Staphylococcus aureus. The verrucous vegetations of acute rheumatic fever are small and nondestructive, and the analysis is usually recommended by an elevated anti�streptolysin O titer. Rheumatic heart illness develops after the immune response directed in opposition to the bacterial antigens (similar to cardiac antigens, and thus a type of molecular mimicry) damages the guts as a outcome of streptococcal antigens cross-react with the heart. The mitral and aortic valves are most commonly affected, so right ventricular dilation from tricuspid 42 E Infective endocarditis is current in this man. Only a murmur may present a clue, and the upper pitch goes with a smaller defect. The remaining listed options represent less frequent sites for anomalies or areas the place infectious endocarditis could develop. The impaired functioning of the mitral valve (most doubtless regurgitation) would give rise to left atrial dilation and left ventricular failure with pulmonary edema. Septic emboli from the mitral valve vegetation might attain the systemic circulation and provides rise to abscesses. Infection of an arterial wall can weaken the wall, ensuing in aneurysm formation and the potential for rupture. Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve outcomes from a defect in connective tissue, whether or not nicely defined or unknown; the mitral valve leaflets are enlarged, hooded, and redundant. Lesions on the right facet of the valve can produce septic emboli that contain the lungs, but vegetations on the left side embolize to the systemic circulation, producing lesions in the spleen, kidneys, or mind. Pulmonary abscesses can occur from right-sided infective endocarditis, because septic emboli pour into the pulmonary arterial circulation. Calcific aortic stenosis could additionally be seen in older people with tricuspid valves, or it could be a complication of bicuspid valves. The valvular vegetations with infective endocarditis are friable and may break off and embolize. The time course of weeks suggests a subacute form of bacterial endocarditis resulting from infection with a less virulent organism, such as viridans streptococci.
5 mg aricept buy overnight delivery
The internet effect of this shift in K+ steadiness is cellular hyperpolarization medications similar buspar 10 mg aricept quality, which closes the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel and also facilitates leisure treatment 2nd degree heart block buy generic aricept 10 mg online. Vasodilation reduces venous return, contributing to declines in left and proper ventricular end-diastolic quantity, strain, and wall stress, and in addition reduces systemic and pulmonary arterial pressures, which decreases left and proper ventricular end-systolic wall stress, respectively. Simultaneously, nitrovasodilators enhance myocardial oxygen provide via direct dilation of epicardial coronary arteries in the absence and presence of flow-limiting stenoses. A progressive attenuation of hemodynamic responses to nitrovasodilators may develop in other patients as a outcome of sympathetic nervous system and renin�angiotensin�aldosterone axis activation. This phenomenon (pseudo-tolerance) accounts for the rebound hypertension that might be noticed after abrupt discontinuation of nitrovasodilator therapy. Inhibition of guanylate cyclase exercise is more than likely answerable for true tolerance to natural nitrates. A "drug holiday" is a helpful technique for reversing this impact in patients requiring extended remedy in the intensive care unit. Administration of N-acetylcysteine, a sulfhydryl donor, may also be effective 250 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals for reversing true tolerance. Notably, extended use of organic nitrates may trigger methemoglobinemia, intervene with platelet aggregation, and produce heparin resistance. It is also essential to recognize that natural nitrates must also be used with warning in sufferers receiving phosphodiesterase type V inhibitors. At decrease doses, this natural nitrate produces venodilation without inflicting a big decrease in systemic vascular resistance. Arterial strain and cardiac output fall in response to the discount in preload, regardless of a modest baroreceptor reflex�mediated enhance in heart price. Nitroglycerin also decreases pulmonary arterial pressures and vascular resistance. Overshoot hypotension and tachycardia is a particularly common setting of hypovolemia, similar to is often observed in sufferers with poorly controlled important hypertension and parturients with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Nitroglycerin improves the stability of myocardial oxygen supply to demand via its actions as a direct coronary vasodilator (which increases supply) and its systemic hemodynamic results (which reduce demand). Nitroglycerin dilates both normal and poststenotic epicardial coronary arteries, enhances blood flow by way of coronary collateral vessels, and preferentially improves subendocardial perfusion. These results are notably essential in patients with acutely decompensated coronary heart failure resulting from myocardial ischemia. Under these circumstances, administration of nitroglycerin may precipitate life-threatening hypotension by compromising coronary perfusion strain, reducing coronary blood circulate regardless of epicardial vasodilation, and worsening ischemia. These traits make sodium nitroprusside a first-line drug for the treatment of hypertensive emergencies. Unlike nitroglycerin, sodium nitroprusside is comparatively contraindicated in patients with acute myocardial ischemia because the drug causes irregular redistribution of coronary blood move away from ischemic myocardium (coronary steal) by producing higher coronary vasodilation in vessels that perfuse regular myocardium in contrast with those that provide the ischemic territory. Sodium nitroprusside is often mixed with a 1 adrenoceptor antagonist corresponding to esmolol to decrease arterial pressure, depress myocardial contractility, and scale back ascending aortic wall stress in sufferers with acute kind A aortic dissection until direct surgical management of the damage can be achieved. Clinical use of sodium nitroprusside is restricted by its toxic metabolites, which predictably accumulate when administration is extended or comparatively excessive doses are used. Metabolism of sodium nitroprusside produces cyanide, which binds with cytochrome C to inhibit cardio metabolism and trigger lactic acidosis. The latter metabolite could accumulate in sufferers with renal insufficiency and produce neurologic issues including delirium and seizures. Hydralazine Hydralazine is a direct vasodilator that reduces intracellular Ca2+ concentration in vascular clean muscle, no much less than partly, by activating adenosine triphosphate� delicate potassium channels. This motion produces direct relaxation of small arteries and arterioles in coronary, cerebral, splanchnic, and renal vascular beds, declines in systemic vascular resistance, and decreases in arterial pressure. The main reduction in afterload stimulates baroreceptor reflex�mediated tachycardia and will increase cardiac output. The magnitude of tachycardia noticed with administration of hydralazine is often larger than anticipated based solely on baroreceptor reflexes alone and will instead mirror a direct impact of the drug on other centrally mediated cardiovascular regulatory mechanisms. The pronounced tachycardia related to administration of hydralazine might produce acute myocardial ischemia in patients with critical coronary stenoses primarily based on increases in myocardial oxygen demand and reductions in coronary perfusion pressure. Hydralazineinduced tachycardia responds appropriately to 1 adrenoceptor antagonists, but warning should be exercised as a outcome of further declines in arterial stress can also occur. Calcium Channel Antagonists Calcium channels are uneven biochemical pores consisting of at least 4 subunits (1, 2/, and with or without) that traverse many biologic membranes. Under quiescent conditions, Ca2+ channels are closed, but they could open through a voltage-dependent (requiring cell depolarization) or receptoroperated (activation) mechanism to allow Ca2+ entry into the cell or an organelle. Myocardial and vascular easy muscle cell membranes contain two distinct kinds of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels which may be denoted based on the relative length of pore opening: T (transient) and L (long). There are 4 main classes of chemically distinct Ca2+ channel antagonists: (a) 1,4-dihydropyridines. Did You Know All Ca2+ channel blockers produce larger relaxation of arterial than venous vascular clean muscle. All Ca2+ channel antagonists trigger higher leisure of arterial in contrast with venous vascular smooth muscle. Calcium channel antagonists enhance myocardial oxygen provide by way of coronary arterial vasodilation and inhibition of coronary artery vasospasm. However, you will want to notice that some dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel antagonists might inadvertently increase myocardial oxygen demand as a end result of baroreceptor reflex�induced tachycardia, and as a result, could not constantly produce anti-ischemic results in sufferers with coronary artery illness. For the sake of brevity, the dialogue right here is proscribed to two intravenous dihydropyridines which are generally used for the remedy of perioperative hypertension. Nicardipine produces cardiovascular results which are just like nifedipine however has an extended half-life than the latter drug. Like different dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel antagonists, nicardipine preferentially dilates arteriolar vessels, which decreases arterial pressure. As a outcome, stroke quantity and cardiac output are comparatively preserved or could increase. Nicardipine-induced decreases in arterial stress trigger will increase in heart price by way of activation of baroreceptor reflexes, but the tachycardia noticed throughout administration of nicardipine is much less pronounced than usually happens with sodium nitroprusside at comparable levels of arterial strain. Because of its relative lengthy half-life, nicardipine is primarily used for remedy of sustained perioperative hypertension and not for acute, usually transient, hypertensive episodes which are generally observed throughout surgical procedure. Clevidipine Clevidipine is a comparatively new, ultrashort-acting dihydropyridine L-type voltagegated Ca2+ channel antagonist with a plasma half-life of roughly 2 minutes after intravenous administration. Like nicardipine and nifedipine, clevidipine exerts pronounced effects at the less negative resting membrane potentials typically noticed in vascular clean muscle cells, however demonstrates decrease potency in cardiac myocytes by which resting membrane potentials are substantially extra unfavorable. As a results of these variations in mobile electrophysiology, clevidipine is very selective for arterial vascular easy muscle and is nearly devoid of unfavorable chronotropic or inotropic effects. Because tissue and plasma esterases are responsible for clevidipine metabolism, little to no accumulation of the drug occurs even within the setting of hepatic or kidney dysfunction. Bench-to-bedside evaluation: Inotropic drug remedy after adult cardiac surgery-a systemic literature evaluate. Nitrates and other nitric oxide donors in cardiology: Current positioning and perspectives. Inotropes and vasopressors: Review of physiology and scientific use in heart problems. The a1 adrenoreceptor-mediated vasoconstriction happens through what signaling mechanism How will the continual administration of therapeutic doses of propranolol affect the hemodynamic response to intravenous epinephrine Compared with epinephrine at low doses, norepinephrine produces a higher enhance in blood stress because it causes: A.
Discount aricept 10 mg with visa
Celecoxib reaches peak plasma concentrations in 2 to 4 hours after oral administration and is extensively protein certain symptoms thyroid problems aricept 10 mg order visa. Patients with hepatic and renal illness could have higher and extra prolonged plasma concentrations symptoms by dpo 10 mg aricept cheap mastercard. Excretion in breast milk is minimal, and the American Academy of Pediatrics considers ibuprofen to be compatible with breastfeeding. Ketorolac is metabolized by glucuronidation, and more than 90% is excreted in the urine inside 2 days. Celecoxib undergoes biotransformation to carbolic acid and glucuronide metabolites, which are excreted in urine and feces. Therefore, ketamine may be particularly useful in patients taking opioids chronically. After intraoperative ketamine administration, patients report decrease postoperative pain depth for as much as 48 hours and have lower morphine necessities for 24 hours. Its use could additionally be contraindicated in sufferers in whom tachycardia and hypertension could lead to morbidity, similar to those with ischemic coronary heart illness, heart failure, and stroke. Induction doses of ketamine are 1 to 4 mg/kg intravenously or 2 to 4 mg/kg intramuscularly. In addition to intravenous and intramuscular administration, ketamine has been given by the subcutaneous, oral, rectal, and intranasal routes. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics the onset of action after intravenous administration is rapid (within seconds) and the half-life is 2 to three hours. Bioavailability is much decrease for intranasal and oral administration, although intranasal administration is associated with a rapid onset of motion. Metabolism and Excretion Ketamine undergoes in depth hepatic metabolism by the cytochrome 3A4 to the energetic metabolite norketamine. Substantial first-pass metabolism results in higher norketamine production after oral administration. Drug Interactions and Adverse Effects No significant drug interactions are reported with ketamine. Adverse events after ketamine administration are dose related and more probably at anesthetic doses (>1 mg/kg) than at analgesic doses. The most common opposed occasions associated with ketamine are psychomimetic, including hallucinations, emergence phenomena, vivid dreams, and blunted have an result on. Ketamine is twice as likely as placebo to cause hallucinations, although this effect could also be attenuated by premedication with a benzodiazepine. Patients are additionally twice as more likely to report pleasant goals after ketamine administration compared with placebo. Ketamine can have important cardiovascular results, together with tachycardia, hypertension, and increased systemic and pulmonary vascular 172 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals resistance. Alpha2 Adrenergic Agonists: Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine Indications and Dose the two adrenergic receptor agonists clonidine and dexmedetomidine are indicated for sedation and analgesia (11). Because of the reduction in sympathetic exercise and agitation, dexmedetomidine causes a state paying homage to non� rapid eye movement physiologic sleep with out impaired cognitive operate. This mixture makes them interesting to be used in the intensive care setting to facilitate early extubation. There can be evidence of postoperative morphinesparing impact and decreased emergence delirium in children. Clonidine is available as a tablet, as an injectable solution, and as a transdermal patch. When used within the perioperative interval for anxiolysis, sedation, and analgesia, typical oral doses are between zero. Intravenous dosing is between 1 and 5 g/kg over 30 to 60 minutes, generally followed by an infusion of zero. A bolus dose is usually administered over a number of minutes to promote the achievement of steady state. However, significant hemodynamic derangements can happen with the oft-recommended bolus dose of 1 g/kg over 10 minutes, so caution is warranted. Mechanism of Action Dexmedetomidine and clonidine are agonists of the two receptors, which are found throughout the mind and are essential within the regulation of dopamine and norepinephrine as nicely as concerned in multiple physiologic processes. The posterior horn of the spinal cord is probably the most important web site of analgesic exercise, although pain transmission within the sensory nerves can also be affected. Dexmedetomidine is more specific to the 2A receptors than clonidine; 2A receptors mediate sedation, analgesia, and hypotension within the locus ceruleus. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Clonidine has near one hundred pc oral bioavailability, with peak plasma concentrations occurring at 1 to 3 hours; half of the preliminary dose is recovered unchanged in the urine. Clonidine is taken into account a long-acting drug, whereas dexmedetomidine is considerably shorter performing. Clonidine and dexmedetomidine endure hepatic and renal metabolism and elimination. Drug Interactions and Adverse Effects Bradycardia, hypotension, and hypertension could happen with each dexmedetomidine and clonidine. Endogenous Opioids Endogenous opioids and opioid receptors are situated all through the peripheral and central nervous systems. Endogenous opioids embrace the enkephalins, dynorphins, and -endorphins, that are produced from large protein precursors by proteolytic cleavage. Opioid Receptors the opioid receptors are G-protein coupled receptors, with seven transmembrane portions, intracellular and extracellular loops, and significant homology among the opioid receptor subtypes. Binding of opioid agonists leads to G-protein activation and primarily inhibitory effects that decrease neuronal excitability (decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate manufacturing and calcium ion influx, elevated potassium ion efflux), though it ought to be noted that opioid binding will increase manufacturing of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. The and agonists are concerned in constructive reinforcement, whereas agonists produce aversion, hallucinations, and malaise. The and antagonists thus overcome the euphoric effects of opiate medicine, while antagonists produce constructive results. Mechanism of Opioid Analgesia In the spinal wire, opioids inhibit the release of substance P from primary sensory neurons within the dorsal horn, attenuating the transmission of painful stimuli from peripheral nerves to the cerebral cortex. In the brainstem, opioids act at descending inhibitory pathways to attenuate painful stimuli. There can be exercise of opioid agonists in the forebrain and the reward constructions of the mind. Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia, Tolerance, and Dependence Opioid tolerance is a well-described phenomenon in which continual opioid use leads to a requirement for rising doses of opioids to reach an analogous analgesic effect. Acute opioid tolerance, or rising opioid necessities after solely transient publicity to opioids, has also been advised, however its existence is controversial. Analgesic tolerance will increase more than tolerance to the respiratory depressant effects, thus narrowing the therapeutic window of those brokers (12). Opioid-induced hyperalgesia is less properly understood, and, in contrast to opioid tolerance, refers to an increased response to usually painful stimuli. Although each opioid tolerance and opioid-induced hyperalgesia may manifest as increasing opioid requirements to attain the specified analgesic impact, distinguishing between the two is essential because opioids worsen the problem of opioid-induced hyperalgesia.