Aspirin
Aspirin dosages: 100 pills
Aspirin packs: 1 packs, 2 packs, 3 packs, 4 packs, 5 packs, 6 packs, 7 packs, 8 packs, 9 packs, 10 packs

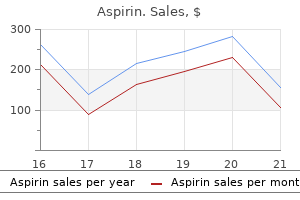
Buy cheap aspirin 100 pills online
Glucokinase found in the liver has a excessive Km for glucose and is very lively after a meal chest pain treatment home cheap 100 pills aspirin. Reversible peripartum liver failure: A new perspective on the analysis unifour pain treatment center denver nc aspirin 100 pills purchase online, therapy, and reason for acute fatty liver of pregnancy, based on 28 consecutive instances. Long-chain L-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency: A molecular and biochemical evaluate. On examination, he appears moderately unwell and is afebrile with regular very important indicators. Most doubtless diagnosis: Rhabdomyolysis (skeletal muscle cell lysis) after strenuous exercise. Treatment: Aggressive intravenous hydration to assist clear the surplus myoglobin from the serum, and correction of electrolyte abnormalities and therapy of kidney failure if current. Short exertion allows for replenishment of those essential substrates; nevertheless, long, grueling demands on muscle, such as running a marathon, can lead to relative deprivation of oxygen (because of either overexertion or dehydration and inadequate blood move to the muscles). Marathon working has been shown to effect increases in the blood and urinary concentrations of numerous biochemical parameters that result from exertional muscle harm (rhabdomyolysis) and hemolysis. In the case of marathon runners, that is usually caused by an increase within the serum lactate concentration. Other causes of rhabdomyolysis embrace cocaine intoxication, hyperthermia, convulsions, or toxins. Definitions Anion gap: A calculation of the routinely measured cations minus the routinely measured anions. Since in all fluids the sum of the positive charges (cations) should be balanced with the negative charges (anions), the anion hole is an artifact of measurement. Hematin: Heme during which the coordinated iron is in the ferric (Fe3+) oxidation state. Myoglobin: A giant heme-containing protein that is in a position to bind oxygen and release it in tissues in which the oxygen rigidity is low. The muscle obtains glucose from the blood or the breakdown of saved glycogen in the muscle. Fatty acids are acquired as free fatty acids from the blood or from the breakdown of triglycerides which are stored in the muscle. For this course of to proceed, a plentiful provide of oxygen have to be provided to the tissues. However, as exertion continues and the muscle starts to rely extra on the -oxidation of fatty acids to provide its energy wants, its oxygen demand will increase, inserting a heavier demand on the center to present oxygenated blood. This will increase the flux of glucose via the glycolytic pathway within the muscle, causing pyruvate levels to increase. Lactate in the blood is taken up by the liver and used as a carbon source within the synthesis of new glucose by the gluconeogenic pathway. Oxaloacetate is then lowered to malate by malate dehydrogenase and malate then exits the mitochondrion. In the cytosol, malate is reoxidized again to oxaloacetate by cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is transformed to fructose 6-phosphate by hydrolysis of phosphate by the enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The last reaction is hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate to glucose by glucose-6-phosphatase. Hepatic glucose produced via gluconeogenesis is then delivered to the blood to be used by the brain and muscle. This process by which extrahepatic lactate is taken again to the liver, converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis, and returned to extrahepatic tissues is called the Cori cycle. The reactions that make up the thermodynamically irreversible steps in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. This constant shock causes injury to the muscle cells, leading to a release of cellular contents to the extracellular matrix and the bloodstream. The concentrations of myoglobin, which is in high concentration in slow twitch (red) muscle fibers, and K+, which is concentrated in all cells, subsequently rise within the blood. This toxic effect is exacerbated when the urine is concentrated as a end result of dehydration. Compared to the start of the race (first mile), which of the next greatest describes the utilization of glycogen and fatty acids as fuels and quantity of oxygen consumed after running for 26 miles The liver, to preserve blood glucose levels, is synthesizing glucose through the gluconeogenic pathway. His blood alcohol was elevated at 245 mg/dL (intoxication level = one hundred fifty to 300 mg/dL), and his blood glucose was 38 mg/dL (low normal). The activity of regulatory enzymes similar to fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, hexokinase, phosphofructokinase 1, and pyruvate kinase are incessantly controlled by binding allosteric effectors. The metabolic stress results in the rise in secretion of epinephrine and other hormones that mobilize fatty acids from saved triglycerides in adipose cells. Muscle damage can result in myoglobinemia and myoglobinuria (red urine) and may crystallize within the renal tubules leading to renal insufficiency. Effect of marathon working on hematologic and biochemical laboratory parameters, together with cardiac markers. The urinalysis revealed giant glucose, and a serum random blood sugar degree was 320 mg/dL. Other organ methods concerned: Cardiovascular, eye, peripheral nerves, gastrointestinal, kidney. Biochemical basis: Insulin resistance because of a postinsulin receptor defect. Type I diabetes is characterised by insulin deficiency and often has its onset during childhood or teenage years. Risk components include obesity, household history, sedentary life type, and, in women, hyperandrogenic states or anovulation. Diabetes mellitus is now acknowledged as one of the most widespread and vital diseases facing Americans. It is estimated that 1 of 4 children born at present will turn out to be diabetic of their lifetime due to obesity and inactivity. Also, it has been noted that diabetes has a extreme impact on blood vessels, particularly in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (blockage of arteries by lipids and plaque), which may lead to myocardial infarction or stroke. Diabetes mellitus is treated as equal to a previous cardiovascular event in its threat for future atherosclerotic illness. Diabetes can be associated with immunosuppression, renal insufficiency, blindness, neuropathy, and different metabolic issues. It serves as an allosteric effector that prompts 6-phosphofructokinase-1 and inhibits fructose bisphosphatase-1, thus stimulating the movement of glucose through the glycolytic pathway and inhibiting gluconeogenesis. Glucagon: A polypeptide hormone synthesized and secreted by the -cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Glucagon is launched in response to low blood glucose levels and stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver. Insulin: A polypeptide hormone synthesized and secreted by the -cells of the islets of Langerhans within the pancreas.
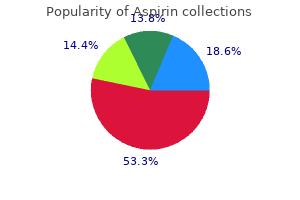
100 pills aspirin generic visa
The main olfactory pathway goes from olfactory sensory neurons to mitral and tufted cells in glomeruli within the olfactory bulb a better life pain treatment center flagstaff az 100 pills aspirin discount otc, then to the olfactory cortex groin pain treatment video cheap 100 pills aspirin fast delivery, and then to both the orbitofrontal cortex via the thalamus or the amygdala and hypothalamus. Defensive responses such as sneezing and lacrimation are triggered by noxious chemical compounds that are detected by chemoreceptors within the olfactory epithelium that ship axons to the brainstem within the trigeminal nerve. Sensory transduction of the 5 fundamental tastes-salt, bitter, sweet, bitter, and umami-involves many different mechanisms, sometimes for the same substance. In each case, the final step is a rise in intracellular [Ca2+], which triggers Ca2+-dependent exocytosis of transmitter from modified epithelial cells which have turn out to be specialized for chemoreception. Cortical management of motor neurons: By the lateral and ventral corticospinal tracts. Response throughout reverse myotatic reflex: Relaxation of muscle that had been strongly contracting. The muscular tissues that are innervated below the lesion initially turn into flaccid and lose reflex responses throughout spinal shock. Depending on the location of the lesion, numerous different bodily signs may be present, including urinary and/or fecal incontinence, decreased heart rate and pressure, and respiratory failure. Lesions of motor pathways above the spinal wire end in muscle rigidity and hyperreflexia with no period of flaccid paralysis. Decerebrate and decorticate posturing could develop with transections above the spinal wire. Definitions Motor unit: A single motor neuron plus all of the muscle fibers that it connects synaptically to . Motor neuron pool: the entire set of all motor neurons innervating a single muscle. Muscle tone: the force with which a muscle resists being lengthened, equivalent to stiffness. Motor neurons that innervate muscles in the head and neck have their cell bodies in motor nuclei in the brainstem and send their axons out the cranial nerves. All the muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron represent a motor unit. Motor units range in size from two or three fibers within the fingers, where nice control is essential, to greater than a thousand fibers in antigravity muscle tissue of the leg. Each action potential in an alpha motor neuron evokes a single twitch in every fiber in the motor unit. Large sustained contractions require the temporal summation of trains of high-frequency twitches. Small motor items are recruited more readily than are giant motor models as a end result of the scale of the motor neuron soma is proportional to the dimensions of the motor unit, and smaller somata are extra delicate to their synaptic inputs than are bigger somata (size principle). Motor neurons that innervate fast-twitch fibers fireplace at larger frequencies than do motor neurons that innervate slow-twitch fibers. Muscle size and tension are monitored by proprioceptive sensory (afferent) neurons, whose cell bodies are in dorsal root ganglia and which have peripheral terminals in specialised sensory constructions within the muscle. Muscle size properties are sensed by terminals that coil around thin intrafusal fibers in muscle spindles. These muscle fibers, which regulate sensory sensitivity, lie in parallel with the thicker extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers that do the efficient contractile work. Group Ia afferents within the spindle detect both the absolute muscle size and the rate of change in size of the intrafusal fiber. Muscle pressure properties are detected within the Golgi tendon organs, which lie in sequence with the muscle fibers and their tendons. Group Ib afferents terminate in these organs and monitor the drive exerted by extrafusal muscle contraction or passive stretch. By exciting interneurons that inhibit the identical or homonymous (synergistic) alpha motor neurons, the Ib afferents trigger the reverse (or inverse) myotatic reflex, which protects the muscle from excessive contraction. In contrast, the stretch (also generally known as the deep tendon or myotatic) reflex is initiated when Ia afferents detect stretch of the intrafusal fibers. These afferents make monosynaptic excitatory synaptic connections to alpha motor neurons, innervating the same or homonymous muscle. The Ia afferent pathway drives a homeostatic system in which imposed stretch routinely elicits a compensatory contraction-an arrangement that contributes to stability, posture, and muscle tone. These gamma motor neurons excite the intrafusal muscular tissues and forestall them from changing into flaccid when the parallel extrafusal muscle tissue contract. The activity of the gamma motor neurons, and hence the sensitivity of the stretch reflex, could be adjusted by a quantity of descending pathways from the mind. Numerous motor patterns and reflexes are mediated by spinal circuits with out the necessity for input from higher centers. In addition to the stretch and reverse myotatic reflexes, an important reflex is the withdrawal (flexor) reflex of a limb triggered by the activation of somatic nociceptor terminals within the limb. These sensory neurons activate excitatory interneurons which in flip activate flexor motor neurons that innervate the ipsilateral limb. In addition, the nociceptors activate inhibitory interneurons that produce reciprocal inhibition of the extensor motor neurons which innervate the same limb. Interneurons additionally activate a second reflex, the crossed-extensor reflex, which extends the contralateral leg to provide stability and assist during leg flexion. During defensive arm flexion, the crossed-extensor reflex causes a protecting extension of the contralateral arm. Another reflex is the scratch reflex, which involves repetitive contraction and relaxation of muscular tissues in the arm and hand which might be generated by interneuronal circuits inside the spinal cord. Groups of interneurons throughout the spinal cord additionally generate the advanced patterns of motor output answerable for locomotion. The circuits underlying these reflexes and motor patterns are used as building blocks for more complex behaviors which are managed hierarchically by greater mind structures. One is the lateral corticospinal tract (pyramidal tract), which carries instructions for aware, voluntary movements from upper motor neurons in the major motor cortex to lower motor neurons within the spinal twine that control distal muscles. Similarly, lower motor neurons that control proximal muscles obtain commands via the ventral corticospinal tract. Upper motor neurons that management muscles in the face and head ship their axons into one other pyramidal tract, the corticobulbar tract, to synapse with decrease motor neurons in brainstem motor nuclei. A second main pathway to the spinal wire is the ventromedial pathway, which consists of 4 tracts from brainstem regions which are concerned in posture and locomotion: the vestibulospinal, tectospinal, pontine reticulospinal, and medullary reticulospinal tracts. Direct and indirect enter to spinal motor neurons also comes from the cerebellum and basal ganglia. Although upper motor neurons excite lower motor neurons, in addition to interneurons, much of the descending enter to spinal motor neurons is inhibitory. Damage to descending pathways at any level above a particular spinal phase (lumped together as upper motor neuron lesions) removes these excitatory and inhibitory influences and thus produces profound results on reflexes mediated by that segment. These effects include some weak point (because of decreased excitation of alpha motor neurons and a few interneurons), increased Mechanisms of spasticity are unclear however appear to contain disinhibition of spinal neurons, including interneurons and gamma motor neurons. Transection of the spinal twine causes a interval of spinal shock for a couple of weeks during which all spinal reflexes beneath the transection are decreased severely or abolished (flaccid paralysis). This probably outcomes from sudden interruption of descending facilitatory influences.
Discount aspirin 100 pills visa
In this case dna pain treatment center order aspirin 100 pills overnight delivery, insulin and C-peptide levels would each be elevated treatment pain ball of foot order aspirin 100 pills visa, and a sulfonylurea screen can additionally be appropriate in this affected person. Serum alkaline phosphatase is a measure of bone formation, not resorption, as are serum osteocalcin and serum propeptide of sort I procollagen. Biochemical Markers of Bone Metabolism in Clinical Use Bone formation Serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase Serum osteocalcin Serum propeptide of type I procollagen Bone resorption Urine and serum cross-linked N-telopeptide Urine and serum cross-linked C-telopeptide Urine whole free deoxypyridinoline Urine hydroxyproline Serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase Urine hydroxylysine glycosides 11. It is commonest in postmenopausal girls, but the incidence can also be rising in men. Estrogen loss probably causes bone loss by activation of bone reworking websites and exaggeration of the imbalance between bone formation and resorption. Clinical determinations of bone density are mostly measured at the lumbar backbone and hip. An evaluation for secondary causes of osteoporosis ought to be thought-about in individuals presenting with osteoporotic fractures at a young age and these that have very low Z-scores. Initial analysis should embody serum and 24-h urine calcium levels, renal perform panel, hepatic perform panel, serum phosphorous degree, and vitamin D levels. The most common hormone sample is a decrease in whole and unbound T3 levels as peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 is impaired. Teleologically, the fall in T3, essentially the most energetic thyroid hormone, is thought to restrict catabolism in starved or ill sufferers. This patient undoubtedly has irregular thyroid perform exams on account of his injuries from the motorcar accident. Over the course of weeks to months, as the patient recovers, thyroid function will return to regular. However, measures of bone resorption might assist in the prediction of danger of fracture in older sufferers. In girls over sixty five years old, even within the presence of normal bone density, a excessive index of bone resorption ought to immediate consideration for remedy. Measures of bone resorption fall shortly after the initiation of antiresorptive therapy (bisphosphonates, estrogen, raloxifene, calcitonin) and supply an earlier measure of 12. Her elevated alkaline phosphatase provides further evidence of energetic bone turnover. Second-generation oral bisphosphonates corresponding to tiludronate, alendronate, and risedronate are wonderful choices due to their capability to decrease bone turnover. They ought to be taken within the morning, on an empty abdomen, sitting upright to minimize the chance of reflux. Duration of use is determined by the scientific response; usually 3�6 months are wanted to see the alkaline phosphatase begin to normalize. Thyroid perform ought to be monitored intently; some sufferers may require low-dose thyroid hormone substitute. The intensive group received multiple administrations of insulin every day together with schooling and psychological counseling. Improvement in glycemic control resulted in a 47% discount in retinopathy, a 54% reduction in nephropathy, and a 60% reduction in neuropathy. There was a nonsignificant development towards enchancment in macrovascular problems. Individuals receiving intensive glycemic management had a discount in microvascular events but no important change in macrovascular problems. Multiple viruses have been implicated, however none have been definitively recognized because the trigger for subacute thyroiditis. The diagnosis can be ignored in patients as the signs mimic pharyngitis, and it frequently has a equally benign course. Autoimmune hypothyroidism must be thought-about; nonetheless, the tempo of her illness, the tenderness of the thyroid on examination, and her previous viral sickness make this diagnosis less probably. Catscratch fever is a normally benign sickness that presents with lymphadenopathy, fever, and malaise. It is brought on by Bartonella henselae and is frequently transmitted from cat scratches that penetrate the epidermis. In the primary part of the illness, thyroid irritation leads to follicle destruction and launch of thyroid hormone. In the second part, the thyroid is depleted of hormone and hypothyroidism results. A restoration section sometimes follows during which decreased inflammation allows the follicles to heal and regenerate hormone. This is an rare incidence at present as the parathyroid glands are better able to be identified each earlier than and during surgery. Hypocalcemia following removing of the parathyroid glands could start any time in the course of the first 24�72 h, and monitoring of serial calcium ranges is really helpful for the primary seventy two h. The earliest symptoms of hypocalcemia are usually circumoral paresthesias and paresthesias with a "pins-and needles" sensation in the fingers and toes. The improvement of carpal spasms upon inflation of the Review and Self-Assessment blood pressure cuff is a traditional signal of hypocalcemia and is named Trousseau signal. Chvostek signal is the other basic sign of hypocalcemia and is elicited by tapping the facial nerve within the preauricular space inflicting spasm of the facial muscular tissues. Maintenance therapy with calcitriol and vitamin D is important for ongoing remedy of acquired hypoparathyroidism. Alternatively, surgeons might implant parathyroid tissue into the soft tissue of the forearm, if it is thought that the parathyroid glands shall be eliminated. Hypomagnesemia can cause hypocalcemia by suppressing parathyroid hormone release regardless of the presence of hypocalcemia. While this patient has taken a medicine that can trigger a dystonic reaction, the spasms that she is experiencing are more according to tetanic contractions of hypocalcemia than dystonic response. Finally, measurement of pressured important capacity is mostly used as a measurement of illness severity in myasthenia gravis or Guillain-Barr� syndrome. The presence of a secretory diarrhea is confirmed by a stool osmolal gap [2(stool Na + stool K) � (stool osmolality)] <35 and persistence during fasting. The differential prognosis contains gastrinoma, laxative abuse, carcinoid syndrome, and systemic mastocytosis. When hypercalcemia is extreme (>15 mg/dL), signs incessantly embrace dehydration and altered mental status. Initial remedy consists of large-volume fluid administration to reverse the dehydration that results from hypercalciuria. If the calcium stays elevated, as on this patient, additional measures ought to be undertaken to decrease the serum calcium. Calcitonin has a rapid onset of motion with a decrease in serum calcium seen inside hours. It decreases serum calcium by preventing bone resorption and release of calcium from the bone. Thus, in this affected person with ongoing severe symptomatic hypercalcemia, addition of both calcitonin and pamidronate is the most effective remedy. The addition of a thiazide diuretic is contraindicated as a outcome of thiazides trigger elevated calcium resorption within the kidney and would worsen hypercalcemia.
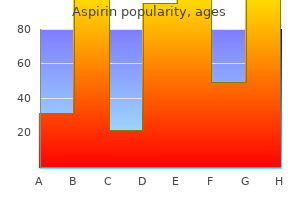
Purchase aspirin 100 pills online
The role of the Pap smear is paramount in early detection of cervical dysplasia to afford timely remedy and avoid development to invasive cervical cancer pain treatment center houston tx buy aspirin 100 pills lowest price. Even after the development of cervical cancer pain treatment herpes zoster aspirin 100 pills generic mastercard, a Pap smear has an important role in detection because analysis early within the illness course of might provide a better prognosis. Treatment of early cervical most cancers presents a ninety five p.c treatment rate, whereas extra superior stages usually result in dying in additional than a third of cases. This underscores the importance of diligent efforts by the physician in counseling sufferers to receive an annual Pap smear. Microscopic sections of the cervix reveal atypical dysplastic squamous epithelial cells in the decrease onethird of the epithelium. Which of the following is one of the best pathologic analysis for this cervical biopsy specimen Histologic examination of this lesion is most probably to reveal which of the following abnormalities Koilocytes are squamous epithelial cells that have nuclei with dense, hyperchromatic, condensed chromatin encompass by a transparent house. These adjustments are present in biopsy specimens from the cervix, but they can be seen in Pap smears from the cervix the place these abnormal dysplastic cells have a attribute elevated nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. The most common histologic sort of invasive malignancy of the cervix is squamous cell carcinoma. Microscopy may reveal extensive variations (pleomorphism) of irregularly formed squamous epithelial cells which can have intracytoplasmic keratin. Cervical squamous cell carcinoma arises from earlier squamous dysplasia of the cervix that has progressed from gentle dysplasia to moderate dysplasia to extreme dysplasia and finally to contain the total thickness of the cervical epithelium (carcinoma in situ). The latter then becomes invasive squamous cell carcinoma when atypical cells invade through the basement membrane. Cervical squamous cell carcinoma is then classified as being either microinvasive or invasive. The vast majority of circumstances of cervical dysplasia and most cancers are associated with human papillomavirus, notably subtypes sixteen and 18. The best methodology for analyzing a visual cervical lesion is biopsy, not a Pap smear. The Pap smear has decreased the incidence of cervical most cancers in the United States dramatically. On examination, she has a normal-sized, nontender uterus, and a 9-cm proper adnexal mass is palpated. Although benign cystic teratomas are often asymptomatic, bigger dermoids (as on this case) can present with pelvic pain, strain, fullness, or dyspareunia. Oral contraceptives additionally tremendously decrease the likelihood of the mass being a physiologic ovarian mass (follicular cyst, hemorrhagic corpus luteum cyst, and so on. Although some disagreement exists over the timing and indications for surgery in complicated masses underneath 6 cm or simple cysts of any size, a 9-cm complicated ovarian mass almost all the time needs to be explored surgically. Upon affirmation of benign intraoperative findings, efforts should be directed at salvaging all regular tissue from the affected ovary and removing solely that tissue which has undergone neoplastic degeneration. Endometrioma: A large (6- to 8-cm) loculated collection of endometrial tissue that may develop in the pelvis in females with endometriosis. As this tissue degenerates, it turns brownish in color and is named a "chocolate cyst. Ovarian torsion: A condition in which the ovary twists on its attachment to the infundibulopelvic ligament, thus interrupting ovarian blood provide. This normally is seen in conjunction with pathologic enlargement of the ovary and could be dynamic (intermittent) in nature or complete; the latter ends in infarction and necrosis of the affected ovary. Table 10-1 lists the differential diagnoses of a pelvic mass, and Table 10-2 lists the categories of ovarian neoplasms. Because of the pluripotent nature of germ cells, teratomas can differentiate into tissues derived from all three embryologic cell strains (endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm). Functional thyroid tissue is present in approximately 12 p.c of benign cystic teratomas, and barely this tissue will proliferate into the predominant mobile factor in the teratoma. This distinctive teratoma hence is referred to as struma ovarii and will secrete sufficient practical thyroid hormone to trigger acute thyrotoxicosis in approximately 5 percent of circumstances. Benign cystic teratomas are normally asymptomatic and are found most commonly during routine gynecologic screening or by the way throughout unassociated surgical or radiographic procedures. Larger teratomas give rise to acute adnexal torsion in roughly eleven percent of cases. Other vital complications include secondary infection and acute hemorrhage with the potential for septic and/or hypovolemic shock. Rupture or perforation is seen in less than 5 p.c of cases and happens more frequently in association with pregnancy. When acute rupture occurs, spillage of the contents of the teratoma into the belly cavity usually precipitates a surgical emergency, whereas more continual leakage of contents can produce a extreme chemical peritonitis that also requires surgical intervention. Other germ cell tumors include dysgerminomas, endodermal sinus tumors, and choriocarcinomas. Endodermal sinus tumors usually secrete -fetoprotein, whereas choriocarcinomas secrete human chorionic gonadotropin. Malignant serous cystadenocarcinomas are the most common, often presenting with ascites. Mucinous tumors may turn out to be very massive, generally exceeding 30 lb in weight; their rupture can result in chronic bouts of bowel obstruction (pseudomyxoma peritonei). Stromal tumors of the ovary are often functional, secreting estrogen (granulosa-theca cell tumors) or androgens (Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors). These neoplasms can present as precocious puberty, postmenopausal bleeding, or hirsutism. The mass is resected surgically and after examining histologic sections the diagnosis of benign teratoma (dermoid cyst) is made. A tumor mass composed of a uniform proliferation of blood vessels and fibroblasts B. A tumor mass composed of a quantity of cysts lined by ciliated columnar epithelial cells E. Cystic teratoma Dysgerminoma Endodermal sinus tumor Granulosa cell tumor Mucinous tumor [10. Evaluation finds an ulcerative mass positioned along the lesser curvature of the abdomen along with bilateral ovarian lots. Mucinous tumors of the ovary, the histology of which reveals the presence of nonciliated mucinous columnar epithelial cells much like the endocervix, can rupture and trigger widespread abdominal dissemination of the mucinous material. This situation, which is called pseudomyxoma peritonei, may trigger compression of belly organs, such because the bowel or kidneys. The benign cystic teratoma or dermoid cyst is the most typical type of ovarian tumor in females younger than age 30 years. Dermoid cysts, which often have solid and cystic components when discovered within the ovary, are composed of parts from a quantity of embryonic layers, similar to mature pores and skin, bone, cartilage, and enamel. Thus, the adnexal mass is more probably to be an estrogen-secreting granulosa-theca cell tumor. The androgen-secreting tumors are often SertoliLeydig cell tumors and should cause virilism. Histology sometimes shows "signet ring" cells, during which intracytoplasmic mucin fills the cell and pushes the nucleus to the periphery of the cell, leading to the histologic appearance of a signet ring.
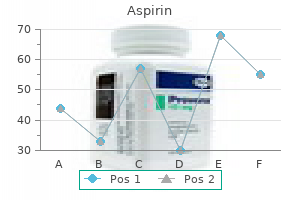
Aspirin 100 pills generic amex
Chylomicrons are shaped in the epithelial cells of the intestine and are responsible for the transport of dietary lipids pain management for old dogs buy discount aspirin 100 pills on-line. Dietary triglycerides are hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase within the lumen of the small gut pain treatment center richmond ky 100 pills aspirin otc. The free fatty acids and monoglycerides are absorbed by the microvilli of the intestinal epithelial cells. In the epithelial cell, the fatty acids and monoglycerides are reformed into triglycerides, which are packaged with phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B-48 into chylomicrons. The newly synthesized chylomicrons are secreted into the lymph and enter the bloodstream by way of the thoracic duct. The fatty acids are taken up by the adipose or muscle cells; glycerol is recycled back to the liver. The remnants are taken into the hepatocytes by endocytosis and degraded in the lysosome to fatty acids, amino acids, ldl cholesterol, glycerol, and phosphate. Chylomicrons appear in the blood stream shortly after consumption of a meal containing fat. However, the clearance rate for chylomicrons is quick and blood is usually freed from chylomicrons following an overnight fast. Hypertriglyceridemia can be the results of a genetic dysfunction in one of the proteins involved in lipoprotein metabolism, or it could come up secondarily to a quantity of other disorders, together with diabetes mellitus, obesity, and alcohol abuse, and as a facet impact of some medications corresponding to -blockers, oral estrogens, and some diuretics. Decreased lipoprotein lipase exercise is the outcomes of the failure of the pancreatic -cells to produce and secrete insulin. Insulin stimulates the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase; within the absence of insulin, lipoprotein lipase activity within the capillary beds is low. One of the primary patients you encounter is an 8-monthold lady brought to the clinic because of excessive exhaustion and fatigue. On further questioning of the mom, she stories that she was beforehand breastfeeding however had to cease to return to work. To feed all of her different children, she has had to dilute her method with water to make the formulation last more for the entire family. After your physical examination is carried out, you diagnose the infant with extreme malnutrition and aid the mom with assets to increase food intake for his or her household. In marasmus, a toddler normally between the ages of 1 to three years has inadequate caloric intake leading to lack of subcutaneous fat, loose wrinkled pores and skin, and either flat or distended abdomen ensuing from atropic belly wall muscles. Be conversant in the metabolic change in fasting states as compared to hunger. Definitions Marasmus: Malnutrition resulting from insufficient intake of protein and calories. Kwashiorkor: Malnutrition resulting from insufficient consumption of protein although the intake of total energy is adequate. Ketone bodies: the quick chain fatty acid metabolites acetoacetate and -hydroxybutyrate and acetone. Triglyceride: A glycerol molecule with every hydroxyl group esterified with a fatty acid moiety. Monoglyceride: A glycerol molecule with one hydroxyl group esterified with a fatty acid moiety. The case description reveals that the child lives in a third-world nation, and the bodily findings reveal that the kid suffers from protein-calorie-deficient starvation, or marasmus. Fasting and hunger characterize adjustments from the baseline metabolic interactions between tissues that exist in the fed state. Each of three states-fed, fasting, and starvation-must be considered from the standpoint of the whole physique primarily as a result of the constituent tissues have different requirements for their dietary sources. For example, pink blood cells have an absolute requirement for glucose because the exclusive meals source from which vitality is derived. Brain tissue usually has an exclusive preference for glucose, the exception being in advanced starvation when the brain can use ketone bodies for energy production. Glucose, fatty acids from triglycerides, and amino acids are provided by the food plan and used differentially by the tissues. In the liver, glucose is used for storage as glycogen or converted to fatty acids for formation into triglycerides for storage in adipose tissue. Amino acid carbon skeletons are used for metabolic intermediates for vitality manufacturing or fatty acid synthesis. Resting muscle takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen and makes use of amino acids for protein synthesis. Resting muscle prefers fatty acids and ketone bodies over glucose to fulfill its vitality calls for. Glucose metabolism offers vitality and glycerol 3-phosphate for triglyceride formation and storage utilizing fatty acids transported to adipose cells as triglycerides in lipoprotein particles. The liver shifts from consumption of glucose for glycogen storage to mobilization of its glycogen shops to release glucose to the bloodstream to supply the glucose requirements of the brain and purple blood cell. Increased blood glucose triggers release of insulin and a decrease within the launch of glucagon and lipolytic hormones. The power required for gluconeogenesis is derived by increasing -oxidation of fatty acids mobilized from adipose storage websites. Blood glucose ranges start to decrease, triggering homeostatic mechanisms to forestall it from reducing dramatically. This happens solely in liver mitochondria due to its crucial position in gluconeogenesis. The b-oxidation of fatty acids that happens within the mitochondrial matrix provides the vitality for gluconeogenesis within the liver. Mobilization of fatty acids during times in which the liver is synthesizing glucose through the gluconeogenic pathway. The fatty acids are transported throughout the mitochondrial inside membrane as carnitine derivatives utilizing the carnitine shuttle. The activation of fatty acids and transport into the mitochondrion through the carnitine shuttle. The newly produced fatty acylCoA repeats the cycle of steps in -oxidation releasing another acetyl-CoA and onward till the final cleavage step that hydrolyzes acetoacetyl-CoA to two molecules of acetyl-CoA. Thus hunger represents an intensification of the metabolic adjustments of the fasting state with some significant differences seen only in prolonged starvation. The brain adapts to use ketone bodies as a supply of power, thus reducing its utilization of glucose. Muscle exercise decreases as results of the mobilization of muscle protein, which itself slows as the period of hunger will increase. In brain and the central nervous system an adaptive change occurs permitting this tissue to use ketone bodies as an power source relieving both the whole body demand for glucose and the utilization of muscle protein as a carbon source for gluconeogenesis within the liver. Thus the main differences between starvation and the postfeeding quick are the adaptive capability of the brain and central nervous system to use ketone our bodies to satisfy a few of their energy demand and within the ranges of circulating ketone bodies which may be high enough to spill over into the urine in important portions.
Myroxylon balsamum var. balsamum (Tolu Balsam). Aspirin.
- What is Tolu Balsam?
- Bedsores, bronchitis, cancer, cough, cracked nipples, lips, reducing lung swelling (inflammation), and minor skin cuts.
- Dosing considerations for Tolu Balsam.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Tolu Balsam work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96373
100 pills aspirin proven
The destruction of bone manifests as osteolytic lesions pain management after shingles 100 pills aspirin purchase overnight delivery, bone pain shingles and treatment for pain generic aspirin 100 pills with amex, pathologic fractures, and hypercalcemia. It is believed that cytokines which are osteoclast-activating components produced by the neoplastic plasma cells activate osteoclasts, resulting in bone destruction and elevated serum calcium. Hypercalcemia could cause fatigue, depression, mental confusion, nausea, and cardiac arrhythmias. In giant portions, they may trigger renal failure, tissue amyloid deposition, and hyperviscosity syndrome. The commonest serum monoclonal Ig (M protein) is IgG (50 percent), adopted by IgA (20 percent) and light chains (15 percent). These antibodies secreted by the neoplastic plasma cells are faulty, resulting in an impaired humoral immunity, making the patients susceptible to infections by encapsulated bacteria similar to pneumococci. The accompanying neutropenia and impaired humoral immunity result in increased and recurrent infections. The bone marrow has an elevated variety of plasma cells, often greater than 30 % of all cells, with giant foci, nodules, or sheets of plasma cells. In the peripheral blood, mature and immature forms of plasma cells are seen with rouleaux formation, pink blood cells that are stuck together like stacked coins. Diagnosis is made in symptomatic patients with progressive disease that fulfills one major and one minor criterion or three minor standards, which should embody 1 and a pair of. Laboratory examination finds elevated serum calcium and protein however normal serum levels of albumin. Which of the following modifications is most likely to be seen in a bone marrow biopsy from this particular person Diffuse infiltration of myeloblasts Few cells with elevated reticulin Multiple sheets of plasma cells Paratrabecular lymphoid aggregates Scattered atypical and immature megakaryocytes [28. A bone marrow biopsy finds greater than 80 percent plasma cells infiltrating the marrow, however no elevated monoclonal protein (M spike) is found in the peripheral blood. Bence Jones proteinuria Heavy chain illness IgA a number of myeloma Plasma cell leukemia Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [28. A bone marrow aspiration and a biopsy reveal roughly 5 p.c plasma cells throughout the marrow. Multiple myeloma is the commonest major malignancy arising in the bone of adults. It is a malignant neoplasm that outcomes from the monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow, normally greater than 30 p.c of all cells current. This proliferation of plasma cells causes destruction of the bone and produces a number of osteolytic lesions, bone pain, and elevated calcium levels in the serum. These adjustments end result in the traditional clinical triad seen with multiple myeloma: hypercalcemia, multiple lytic bone lesions, and elevated plasma cells within the bone marrow. These neoplastic plasma cells secrete giant quantities of immunoglobulin, the components of which can be detected with serum and urine protein electrophoresis as M proteins (monoclonal immunoglobulins). Bence Jones proteins are essential because if the neoplastic plasma cells secrete solely Bence Jones proteins, they are going to be filtered into the urine from the blood, and no M spike will be seen with serum protein electrophoresis. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance is a dysfunction characterised by the presence of monoclonal protein (M spike) in peripheral blood in a person with no apparent irregular mobile proliferation. In approximately 25 percent of sufferers, there are coexisting extracardiac anomalies. Congenital coronary heart defects could be detected in stillbirths as a lot as 10 times extra incessantly than in stay births. Girls more incessantly current with atrial septal defects and patent ductus arteriosus. In contrast, most left-sided obstructions, similar to complete transposition of nice arteries, aortic coarctation, aortic stenosis, and atresia, are present in boys. The resultant shunting of blood from left to proper can lead to elevated blood flow to the lungs and pulmonary vascular changes, pulmonary hypertension, and coronary heart failure. Schematic illustration of a traditional coronary heart and a heart with ventricular septal defect. Shunt: Path of blood move that results from irregular communication from chamber to chamber, chamber to vessel, or vessel to vessel. Paradoxical embolism: Result of right-left shunt during which thromboemboli bypass the lung and may access the overall circulation immediately. Shunts could also be from left to proper or from proper to left, relying on the affected heart chamber or vessels. Types of right-to-left shunts embody tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of great arteries, persistent truncus arteriosus, tricuspid atresia, and total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Of these, the most common sort of abnormality is tetralogy of Fallot, which normally outcomes from displacement anterosuperior and left of the infundibular septum during embryologic growth. Classic tetralogy has severe pulmonary stenosis with right-to-left shunt, and sufferers are cyanotic. Paradoxic emboli might occur in patients with right-to-left shunts (see Table 29-1). Obstructive forms of congenital heart illness embrace coarctation of the aorta, aortic stenosis, and pulmonary stenosis. Embryologically, that is thought to occur due to decreased blood move into the ascending aorta, increased move to the pulmonary artery or ductus arteriosus, or extension of contractile tissue into the aorta. Approximately one-third of those sufferers have coarctation as an isolated anomaly. Syndromes that might be associated with coarctation embody DiGeorge and Turner syndromes. Coarctation leads to hypertension within the ascending aorta with left ventricular hypertrophy. Hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome happens in sufferers with aortic valve atresia and an intact ventricular septum. This in all probability results from a decrease in left-sided blood flow throughout embryogenesis. The mortality from this condition is extremely high, typically occurring within the first 6 weeks of life. The goal of the operations is to enable the proper ventricle to pump oxygenated blood. Causative Factors and Treatment There are multiple causative components in the growth of congenital heart disease, including genetic elements and congenital infections corresponding to rubella. Drugs, together with alcohol, amphetamines, anticonvulsants, chemotherapeutics, lithium, thalidomide, and retinoic acid, have been related to fetal coronary heart disease. In addition, females with system illness such as diabetes and lupus are at greater threat of having babies with coronary heart abnormalities. In sufferers with uncorrectable situations, coronary heart transplantation may be an possibility. The family just lately immigrated from Mexico, and she or he has not been evaluated by a physician. Which of the following is the most probably congenital heart disease on this affected person Cyanosis requires mixing of deoxygenated blood into the systemic circulation, which can be seen in tetralogy of Fallot. Ventricular septal defect is the most common congenital heart illness and often presents in neonates at roughly four weeks of age with congestive coronary heart failure.
Syndromes
- Peeling of the skin
- Is it worse after exercise?
- Aluminum
- Ear
- Caffeine
- Breathing difficulty (from breathing in the chemical)
- Swelling of any area of the body
100 pills aspirin buy
Neurosyphilis is detected in solely four to 9 % of patients with tertiary syphilis chronic pain treatment uk aspirin 100 pills purchase mastercard. However natural pain treatment for dogs aspirin 100 pills purchase, over the course of months and even a long time after infection, the signs can range from meningitis (usually throughout the first year) to overt neurologic signs (may not occur for more than a decade) such as basic paresis, tabes dorsalis, Charcot joints, and Argyll Robertson pupil. Cardiovascular syphilis or aortitis is current in as a lot as eighty five percent of patients with tertiary syphilis, though only roughly 10 percent are symptomatic. Aortitis demonstrates widening of the aorta with occasional linear calcifications and narrowing of the aortic annulus, leading to aortic regurgitation. General paresis reflects widespread parenchymal illness that ends in neurologic deficiencies. Tabes dorsalis is the end result of demyelination of the posterior column, dorsal roots, and dorsal ganglia, inflicting neurosensory loss which will result in Charcot joints. Argyll Robertson pupil, which is seen in each tabes dorsalis and basic paresis, is a small, irregular pupil that reacts to lodging however not to mild. Congenital syphilis is more readily transferred early in the maternal infection (75 to ninety percent) than in late infection (35 percent). Fetal lesions first appear across the fifth month of gestation, coinciding with fetal immunocompetence. The resulting an infection regularly ends in stillbirth and late abortion, although liveborn infants may be subclinical and later develop symptomatic disease. Congenital syphilis is associated with saber shins, saddle nose deformity and deafness. Laboratory exams embody darkfield microscopy and phase distinction microscopy, which can be used to visualize the spirochete organism in a tissue pattern from a syphilitic lesion. Serologic testing for syphilis infection focuses on two types of detectable antibodies: nontreponemal and treponemal. Many infectious and noninfectious processes can produce a false constructive in both kinds of assays, similar to systemic lupus erythematosus, being pregnant, and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Argyll Robertson pupils Bitemporal hemianopia Hutchinson incisor Perifollicular hemorrhages Retrobulbar palsy [41. Microscopic examination of a smear made from one these vesicles reveals scattered multinucleated big cells with ground-glass nuclei. Infection with which of the following organisms is the most likely the reason for these adjustments Neurosyphilis impacts the central nervous system in a minority of people with untreated late tertiary syphilis. Signs and signs of neurosyphilis are diverse and embody meningitis, common paresis, tabes dorsalis, and the Argyll Robertson pupil. Tabes dorsalis results from degeneration of the dorsal columns and dorsal roots of the spinal wire along with loss of dorsal root ganglion neurons. This ends in impaired joint place sensation (proprioception), ataxia, and lack of ache sensation. Herpes simplex virus is the most typical infectious vulvar disease in the United States. The primary or first episode is normally systemic, and sufferers complain of fever, muscle aches, and joint ache. The virus then can lay dormant within the dorsal root ganglion and reactivate, resulting in native symptoms. Gummata are gray-white rubbery lesions which would possibly be characteristic of symptomatic tertiary syphilis. These lesions have central coagulative necrotic areas which may be surrounded by palisading macrophages and a mononuclear infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells. Congenital syphilis might result in miscarriage, development restriction, or hydrops fetalis in being pregnant. Its results on the infant are divided into early, including nasal snuffles, skin lesions, hepatomegaly, and bony malformations, and late, together with interstitial keratitis (blindness), notched central incisor teeth, and deafness. Tertiary syphilis mostly includes neurosyphilis and sometimes manifests as gummata in varied elements of the body, including the center. He complains of progressive fatigue during the last three months and has not visited a physician for over a yr. Involvement of the hemopoietic system is widespread, inflicting lymphadenopathy, anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia. These results can be because of the virus itself, consequences of antiviral therapy, or opportunistic infections. Histologic research and tradition of the lymph nodes or bone marrow are sometimes diagnostic. Bone marrow aspirates could reveal malignancy or a fungal an infection such as histoplasmosis. Disseminated disease after reactivation can result in fever, weight loss, hepatosplenomegaly, and lymphadenopathy. Bone marrow involvement is widespread, with pancytopenia famous in approximately one-third of patients. Western blot check: A laboratory blood test to detect the antibodies to specific antigens. Pancytopenia: A marked reduction within the number of purple blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Guillain-Barr� syndrome: A polyneuritis that happens with a viral an infection that causes symmetric pain and weakness within the extremities and even paralysis. Parenteral transmission contains intravenous drug abuse, sharing of needles, and needlesticks. It is tough to quantify per-contact threat as a end result of people at risk can have interaction in a wide selection of sexual practices. The weight reduction can be multifactorial, and naturally nausea and vomiting contribute to weight loss secondary to a decreased caloric consumption. There can be an increased metabolic price that exacerbates the decrease in caloric intake. It can be difficult to diagnose as a outcome of the symptoms are nonspecific, similar to fever, cough, and shortness of breath. The cornerstone of prognosis consists of the chest radiograph, which reveals diffuse or perihilar infiltrates. Up to 10 p.c can have a standard chest radiograph, and the rest of this group has atypical infiltrates. Definitive analysis is obtained in 50 to eighty % by a Wright-Giemsa stain of induced sputum. Sputum induction is carried out by having sufferers inhale an aerosolized resolution of three percent saline produced by an ultrasonic nebulizer. Other pulmonary infections include bacterial, mycobacterial, and viral pneumonias. Noninfectious pulmonary ailments embrace Kaposi sarcoma, nonHodgkin lymphoma, and interstitial pneumonitis. These individuals can present clinically with headache, focal neurologic deficits, seizures, or altered psychological status. The prognosis is based on a constructive latex agglutination test or a constructive tradition of cerebral spinal fluid.
Aspirin 100 pills order mastercard
Other unwanted effects embrace delicate glucose intolerance because of gosy pain treatment center aspirin 100 pills buy generic on line transient insulin suppression shoulder pain treatment home cheap 100 pills aspirin overnight delivery, asymptomatic bradycardia, hypothyroxinemia, and native injection website discomfort. External radiation therapy or high-energy stereotactic methods are used as adjuvant therapy for acromegaly. Patients could require interim medical therapy for a number of years prior to attaining maximal radiation benefits. Combined remedy with octreotide and cabergoline may induce additive biochemical management compared to both drug alone. The ensuing cortisol elevation restrains the inflammatory response and enables host safety. Thus, the neuroendocrine stress response displays the net results of highly built-in hypothalamic, intrapituitary, and peripheral hormone and cytokine indicators. It is characterized by fatigue, weakness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and, sometimes, hypoglycemia. Typical features of persistent cortisol extra include thin, fragile skin; central weight problems; hypertension; plethoric moon facies; purple striae and simple bruisability; glucose intolerance or diabetes mellitus; gonadal dysfunction; osteoporosis; proximal muscle weak spot; signs of hyperandrogenism (acne, hirsutism); and psychological disturbances (depression, mania, and psychoses) (Table 2-11). Hematopoietic features of hypercortisolism include leukocytosis, lymphopenia, and eosinopenia. The protean manifestations of hypercortisolism make it difficult to decide which sufferers mandate formal laboratory evaluation. Certain features make pathologic causes of hypercortisolism extra likely-these embrace characteristic central redistribution of fat, thin skin with striae and bruising, and proximal muscle weak point. In youngsters and in younger females, early osteoporosis could also be particularly outstanding. The main reason for death is cardiovascular disease, however infections and danger of suicide are also increased. Measurement of 24-h urine free cortisol is a exact and cost-effective screening test. Alternatively, the failure to suppress plasma cortisol after an overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test can be used to establish sufferers with hypercortisolism. The remission fee for this process is ~80% for microadenomas but <50% for macroadenomas. Metyrapone (2�4 g/d) inhibits 11-hydroxylase activity and normalizes plasma cortisol in as a lot as 75% of sufferers. Side effects embody nausea and vomiting, rash, and exacerbation of pimples or hirsutism. Side effects of mitotane embody gastrointestinal signs, dizziness, gynecomastia, hyperlipidemia, pores and skin rash, and hepatic enzyme elevation. The use of steroidogenic inhibitors has decreased the necessity for bilateral adrenalectomy. Removal of each adrenal glands corrects hypercortisolism but may be related to a big morbidity price and necessitates everlasting glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid alternative. This is particularly true in women, in whom the rapidly fluctuating gonadal steroid ranges differ all through the menstrual cycle. Estrogens act on the hypothalamic and pituitary ranges to control gonadotropin secretion. Testosterone feedback in men also happens on the hypothalamic and pituitary levels and is mediated partly by its conversion to estrogens. The subunit is widespread to these glycoprotein hormones; specificity is conferred by the subunits, which are expressed by separate genes. Hypogonadism is the commonest presenting function of grownup hypopituitarism, even when different pituitary hormones are also deficient. As famous above, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is a standard presenting feature of hyperprolactinemia. A variety of inherited and purchased disorders are associated with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism nedasalamatebook@gmail. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in these problems is reversed by removal of the annoying stimulus, or caloric replenishment. Presentation and Diagnosis In premenopausal girls, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism presents as diminished ovarian perform leading to oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, infertility, decreased vaginal secretions, decreased libido, and breast atrophy. In hypogonadal grownup men, secondary testicular failure is related to decreased libido and efficiency, infertility, decreased muscle mass with weakness, lowered beard and body hair growth, soft testes, and attribute fantastic facial wrinkles. Laboratory Investigation Central hypogonadism is related to low or inappropriately normal serum gonadotropin levels within the setting of low intercourse hormone concentrations (testosterone in males, estradiol in women). Because gonadotropin secretion is pulsatile, valid assessments may require repeated measurements or using pooled serum samples. Normal responses differ based on menstrual cycle stage, age, and sex of the affected person. Testosterone could also be administered by intramuscular injections every 1�4 weeks or using patches that are changed day by day (Chap. In premenopausal ladies, cyclical alternative of estrogen and progesterone maintains secondary sexual traits and integrity of genitourinary tract mucosa and prevents premature osteoporosis (Chap. They are the commonest type of pituitary adenoma and are normally macroadenomas on the time of diagnosis as a outcome of medical features are inapparent till tumor mass effects happen. Based on immunohistochemistry, most clinically nonfunctioning adenomas could be proven to originate from gonadotrope cells. It is essential to distinguish this circumstance from true prolactinomas, as most nonfunctioning tumors reply poorly to therapy with dopamine agonists. Laboratory Investigation the aim of laboratory testing in clinically nonfunctioning tumors is to classify the kind of tumor, to determine hormonal markers of tumor exercise, and to detect potential hypopituitarism. Free -subunit levels may be elevated in 10�15% of patients with nonfunctioning tumors. Because this pattern of hormone checks can be seen in primary gonadal failure and, to some extent, with aging (Chap. For nonfunctioning and gonadotropin-secreting tumors, the diagnosis often rests on immunohistochemical analyses of resected tumor tissue, because the mass effects of these tumors often necessitate resection. However, for larger macroadenomas, transsphenoidal surgery reduces tumor dimension and relieves mass results. Preexisting hypopituitarism that results from tumor mass effects generally improves or may resolve utterly. Within 5�6 years following profitable surgical resection, ~15% of nonfunctioning tumors recur. Thyroid-replacement remedy must be initiated after establishing adequate adrenal function. Moreover, free thyroid hormone ranges are regular in these problems, most of that are familial.
100 pills aspirin trusted
On the opposite hand pain treatment for arthritis on the hip cheap aspirin 100 pills without prescription, the extent of aldosterone appears to be subnormal in relationship to the hyperkalemia kidney pain treatment aspirin 100 pills discount on-line. Hypoaldosteronism may additionally be associated with high renin levels and low or elevated levels of aldosterone (see below). Severely ill patients may also have hyperreninemic hypoaldosteronism; such sufferers have a excessive mortality rate (80%). Before the prognosis of isolated hypoaldosteronism is taken into account for a affected person with hyperkalemia, "pseudohyperkalemia". Then, the response of renin and aldosterone ranges to stimulation (upright posture, sodium restriction) must be measured. Low renin and aldosterone ranges set up the analysis of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism. This inherited situation is brought on by a mutation within the epithelial sodium channel. However, patients with hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism could require higher doses of mineralocorticoid to correct hyperkalemia. This need poses a potential risk in sufferers with hypertension, delicate renal insufficiency, or congestive heart failure. An alternative approach is to scale back salt intake and to administer furosemide, which can ameliorate acidosis and hyperkalemia. In severe congenital virilizing hyperplasia, the adrenal output of cortisol may be so compromised as to trigger adrenal deficiency despite adrenal hyperplasia. Partial enzyme deficiencies can be expressed after adolescence, predominantly in women with hirsutism and oligomenorrhea but minimal virilization. Late-onset adrenal hyperplasia may account for 5�25% of circumstances of hirsutism and oligomenorrhea in girls, depending on the inhabitants. At start, there could also be enlargement of the clitoris, partial or full fusion of the labia, and generally a urogenital sinus in the feminine. If the labial fusion is almost complete, the female toddler has external genitalia resembling a penis with hypospadias. The excessive androgen levels result in accelerated progress, in order that bone age exceeds chronologic age. Because epiphyseal closure occurs early, progress stops, however truncal growth continues, the attribute appearance being a short baby with a welldeveloped trunk. In addition to cortisol deficiency, aldosterone secretion is decreased in approximately one-third of the patients. Hypertension and hypokalemia happen because of the impaired conversion of 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone, resulting in the accumulation of 11deoxycorticosterone, a potent mineralocorticoid. This uncommon disorder causes decreased manufacturing of cortisol and shunting of precursors into the mineralocorticoid pathway with hypokalemic alkalosis, hypertension, and suppressed plasma renin activity. Female sufferers have primary amenorrhea and lack of growth of secondary sexual traits. Because of poor androgen production, male patients have either ambiguous exterior genitalia or a feminine phenotype (underandrogenization). Exogenous glucocorticoids can correct the hypertensive syndrome, and therapy with acceptable gonadal steroids leads to sexual maturation. The diagnosis is additional instructed by the discovering of hypertrophy of the clitoris, fused labia, or a urogenital sinus within the feminine or of isosexual precocity within the male. Demonstration of elevated levels of 17-hydroxyprogesterone in amniotic fluid at 14�16 weeks of gestation allows prenatal detection of affected female infants. Prenatal genetic testing can be attainable in households in whom the precise genetic defect is known. These infants and kids usually crave salt and have laboratory findings indicating deficits in each cortisol and aldosterone secretion. The diagnosis is confirmed by demonstrating increased ranges of 11-deoxycortisol in the blood or elevated quantities of tetrahydro-11-deoxycortisol within the urine. Adrenal androgen output is well suppressed by the standard low-dose (2 mg) dexamethasone check. Because of its low cost and intermediate half-life, prednisone is the drug of alternative except in infants, in whom hydrocortisone is usually used. Skeletal progress and maturation must also be monitored carefully, as overtreatment with glucocorticoid substitute therapy retards linear growth. Adrenal insufficiency is manifest throughout the first 2 years of life as hyperpigmentation, convulsions, and/or frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. This gene encodes an orphan nuclear receptor that plays an necessary role within the improvement of the adrenal cortex and also the hypothalamic-pituitarygonadal axis. Thus, patients present with indicators and symptoms secondary to deficiencies of all three major adrenal steroids-cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenal androgens-as nicely as gonadotropin deficiency. Finally, a uncommon cause of hypercortisolism without cushingoid stigmata is primary cortisol resistance because of mutations in the glucocorticoid receptor. Miscellaneous Conditions Adrenoleukodystrophy causes severe demyelination and early demise in kids, and adrenomyeloneuropathy is associated with a mixed motor and sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia in adults; both disorders are associated with elevated circulating ranges of very lengthy chain fatty acids and trigger adrenal insufficiency. The definitive prognosis is made by demonstrating an elevation of precursors of cortisol biosynthesis within the blood or urine or by direct demonstration of the genetic defect. Screening for this defect is best performed by assessing the presence or absence of the chimeric gene. Because the irregular gene could also be current within the absence of hypokalemia, its frequency as a cause of hypertension is unknown. Individuals with suppressed plasma renin levels and juvenile-onset hypertension or a history of early-onset hypertension in first-degree relations must be screened for this dysfunction. High Plasma Renin Activity Bartter syndrome is characterised by extreme hyperaldosteronism (hypokalemic alkalosis) with moderate to a hundred thirty marked will increase in renin activity and hypercalciuria, however normal blood pressure and no edema; this disorder usually begins in childhood. Bartter syndrome is brought on by a mutation within the renal Na-K-2Cl co-transporter gene. The pathogenesis entails a defect within the renal conservation of sodium or chloride. The renal loss of sodium is assumed to stimulate renin secretion and aldosterone manufacturing. Hyperaldosteronism produces potassium depletion, and hypokalemia further elevates prostaglandin manufacturing and plasma renin activity. In some cases, the hypokalemia may be potentiated by a defect in renal conservation of potassium. Gitelman syndrome is an autosomal recessive trait characterised by renal salt wasting and, as a result, as in Bartter syndrome, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. As a consequence, affected individuals have low blood stress, low serum potassium, low serum magnesium, and high serum bicarbonate. Gitelman syndrome outcomes from loss-of-function mutations of the renal thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl co-transporter. The defect is within the genes encoding the or subunits of the epithelial sodium channel. Both renin and aldosterone ranges are low, owing to the constitutively activated sodium channel and the ensuing excess sodium reabsorption in the renal tubule. Patients can be recognized both by documenting an elevated ratio of cortisol to cortisone within the urine or by genetic evaluation.