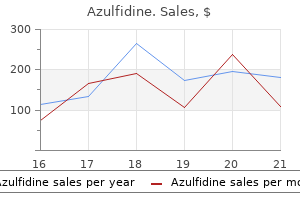
Azulfidine
Azulfidine dosages: 500 mg
Azulfidine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Purchase 500 mg azulfidine with amex
Growth pain treatment pancreatitis 500 mg azulfidine discount free shipping, physical evaluation pain management shingles head azulfidine 500 mg line, medical histories, survival and recurrence risk, Am J Med Genet 49:one hundred seventy five, 1994. De Souza E, et al: Recurrence risks for trisomies 13, 18 and 21, Am J Med Genet 149A:2716, 2009. Bruns D, et al: Birth history, physical traits, and medical survivors with full trisomy thirteen, Am J Med Genet 155A:2634, 2011. There appears to be a scarcity of correlation between the phenotype and the proportion of trisomic cells. Tendency toward prominent brow, deep-set eyes, strabismus, hypertelorism with broad nasal root and outstanding nares, full lips, everted decrease lip, micrognathia, higharched palate, cleft palate, and distinguished cupped ears with thick helices. Camptodactyly of second via fifth fingers and toes, restricted elbow supination, deep creases in palms and soles, single transverse palmar crease, major joint contracture, irregular nails. Long, slender trunk; abnormal scapula, irregular sternum, brief or webbed neck; slim pelvis; hip dysplasia; broadly spaced nipples; ureteral-renal anomalies; cardiac defects. Becker K, et al: Constitutional trisomy eight and Behcet syndrome, Am J Med Genet 149A:982, 2009. Amiable, tall particular person at four years and at sixteen years who has trisomy 8/normal mosaicism, with a standard karyotype from cultured leukocytes but trisomy eight in skin fibroblast cells. There is a few limitation of full extension of the fingers, that are partially webbed, and restricted extension of the best elbow. There is hypoplasia of the supraspinatus, trapezius, and higher pectoral musculature. In the identical 12 months, Feingold and colleagues reported the primary instance of a child with full trisomy 9 utilizing blood lymphocytes. In those that survive, failure to thrive and extreme motor and intellectual incapacity are the rule. However, several kids walk unassisted, show social action abilities, develop minimal speech and are capable of take care of some or all of their daily care wants. The incidence and severity of malformations and mental disability correlate with the share of trisomic cells within the totally different tissues. Sloping brow with narrow bifrontal diameter; upslanting, quick palpebral fissures, deeply set eyes; distinguished nasal bridge with brief root, small fleshy tip, and slit-like nostrils; prominent lip overlaying receding lower lip; micrognathia, low-set, posteriorly rotated, and misshapen ears. Joint anomalies, including abnormal position and/or perform of hips, knees, feet, elbows, and digits; kyphoscoliosis; slim chest; hypoplasia of sacrum, iliac wings, and pubic arch; hypoplastic phalanges of toes. Nonpitting edema of legs, a quantity of pilomatricomas (benign neoplasms of hair matrix cells), simian References Feingold M, et al: A case of trisomy 9, J Med Genet 10:184, 1973. Bowen P, et al: Trisomy 9 mosaicism in a new child infant with a quantity of malformations, J Pediatr 85:ninety five, 1974. Akatsuka A, et al: Trisomy 9 mosaicism with punctate mineralization in developing cartilages, Eur J Pediatr 131:271, 1979. Levy I, et al: Gastrointestinal abnormalities in the syndrome of mosaic trisomy 9, J Med Genet 26:280, 1989. Bruns D: Presenting physical characteristics, medical conditions, and developmental status of long-term survivors with trisomy 9 mosaicism, Am J Med Genet 155:1033, 2011. Note the sloping forehead, a broad and outstanding nasal bridge, prominent upper lip covering receding lower lip, and micrognathia. Note development retardation as properly as multiple contractures with prolonged elbows, flexed hips and knees. A and B, Facial features embrace short palpebral fissures, deeply set eyes; prominent nasal bridge with brief root, small fleshy tip, and slit-like nostrils; distinguished lip covering receding lower lip; micrognathia, low-set, posteriorly rotated, and misshapen ears. Most are lost as miscarriages, accounting for approximately 20% of all chromosomally abnormal spontaneous abortuses. Partial hydatidiform moles are usually related to a triploid fetus and very hardly ever endure malignant changes. Classic moles present more pronounced trophoblastic hyperplasia within the absence of a fetus. All circumstances of full triploidy either have been stillborn or have died within the early neonatal interval, with 5 months being the longest recorded survival. Individuals with diploid/triploid mixoploidy often survive and manifest a point of psychomotor retardation. Because of body asymmetry, sufferers with mixoploidy may require a heel lift for the shorter leg to forestall compensatory scoliosis, and some of these individuals may resemble those having Russell-Silver syndrome. Diagnosis of mixoploidy normally requires pores and skin fibroblast cultures, for the reason that triploid cell line might have disappeared from amongst peripheral blood leukocytes. In a quantity of cases, a triploid being pregnant has been followed or preceded by a molar pregnancy. Disproportionate prenatal development deficiency that affects the skeleton more than the cephalic area; in mixoploid individuals, skeletal development may be asymmetric. Dysplastic calvaria with massive posterior fontanel; ocular hypertelorism with eye defects, ranging from colobomata to microphthalmia; low nasal bridge; low-set, malformed ears; micrognathia. Brain anomalies, including hydrocephalus and holoprosencephaly; adrenal hypoplasia; renal anomalies, including cystic dysplasia and hydronephrosis. Ferrier P, et al: Congenital asymmetry associated with diploid-triploid mosaicism and enormous satellites, Lancet 1:80, 1964. Niebular E: Triploidy in man: Cytogenetical and clinical features, Humangenetik 21:103, 1974. A and B, Stillborn toddler with triploidy showing relatively large-appearing upper head in relation to very small face and 3-4 syndactyly of the fingers. This phenotype is according to two paternal chromosomal copies and one maternal chromosomal copy. It is the most common type of triploidy and usually results in a growth-retarded fetus with a big hydatidiform placenta. Although typically a terminal deletion with breakpoints at chromosome band 3p25, newer molecular research have shown the location of the 3p breakpoint to be variable. Many survivors are blind and deaf and work together only minimally with their environment. In one case an interstitial deletion at 3p25p26, thought to be the smallest 3p deletion associated with the characteristic phenotype, was reported. Microcephaly with flat occiput, synophrys, epicanthal folds, ptosis, brief palpebral fissures, prominent nasal bridge, small nostril with anteverted nares, long philtrum, malformed ears, micrognathia, downturned corners of mouth. References Verjaal M, De Nef J: A patient with a partial deletion of the brief arm of chromosome 3, Am J Dis Child 132:forty three, 1978. Schwyzer U, et al: Terminal deletion of the quick arm of chromosome three, del(3pter-p25): A recognizable syndrome, Helv Paediatr Acta 42:309, 1987. Nienhaus H, et al: Infant with del(3)(p25-pter): Karyotypephenotype correlation and evaluate of previously reported circumstances, Am J Med Genet forty four:573, 1992. Hirschhorn and colleagues carried out chromosome banding research in 1973 that related duplication of the 3q21qter region with a distinct phenotype that Francke and Opitz subsequently emphasized could be clinically distinguished from Brachmann�de Lange syndrome. For survivors, intellectual incapacity, progress retardation, and pulmonary infections are the rule.
Bantu Tulip (African Wild Potato). Azulfidine.
- Lung cancer, bladder infections, cancer, lung disease, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), tuberculosis (TB), arthritis, a skin condition called psoriasis, wound healing, and improving the immune system.
- What is African Wild Potato?
- Dosing considerations for African Wild Potato.
- What other names is African Wild Potato known by?
- How does African Wild Potato work?
- Trouble urinating because of an enlarged prostate, or "benign prostatic hyperplasia" (BPH).
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96661
Azulfidine 500 mg purchase on line
Potentially hazardous interactions with different medicine Antivirals: keep away from concomitant use with lamivudine st. john-clark pain treatment center in clearwater florida azulfidine 500 mg cheap free shipping. Peak serum concentrations of enalaprilat happen about four hours after an oral dose of enalapril pill pain treatment for tennis elbow generic 500 mg azulfidine amex, and the efficient halflife is eleven hours. The principal elements in urine are enalaprilat, accounting for about 40% of the dose, and intact enalapril (about 20%). In in vitro human microsomal and hepatocyte studies, hydrolysis of the amide group of the C-terminus amino acid, phenylalanine, ends in a deamidated metabolite. Hepatic metabolism by desulphation and depolymerisation also contributes to elimination. In extracorporeal circulation during haemodialysis, 1 mg/kg enoxaparin is introduced into the arterial line of the circuit firstly of the session. The dose of protamine to neutralise the effect of enoxaparin ought to equal the dose of enoxaparin: 50 anti-heparin items of protamine ought to neutralise the antifactor-Xa activity generated by 1 mg of enoxaparin. They also advise monitoring sufferers if given prolonged treatment with prophylactic doses. Dopaminergics: possibly enhances results of apomorphine; probably reduces concentration of rasagiline; max dose of selegiline is 10 mg together. It is eradicated primarily in the faeces with about 10�20% being excreted within the urine, mainly as glucuronide conjugates. Manufacturer suggests that an extended dosing interval may be required in dialysis sufferers. Entecavir is predominantly eliminated by the kidney: renal clearance is independent of dose and ranges between 360 mL/min and 471 mL/min suggesting that entecavir undergoes both glomerular filtration and web tubular secretion. High dose: 60�135 mg/m2 every 3�4 weeks, or forty five mg/m2 on days 1, 2, and three, every three weeks. Dose and frequency depend on condition and whether or not monotherapy or combination therapy Or according to native protocol. Epirubicin and its main metabolites are eradicated in faeces through biliary excretion (40% of the administered dose being recovered in the bile in seventy two hours) and to a lesser extent in urine (10% of a dose in forty eight hours). Patients with impaired hepatic operate have prolonged and elevated plasma concentrations of epirubicin � dose discount is required. Less than 5% of an eplerenone dose is recovered as unchanged drug within the urine and faeces. Following a single oral dose of radiolabelled drug, approximately 32% of the dose was excreted within the faeces and approximately 67% was excreted within the urine. Antibacterials: focus elevated by clarithromycin and telithromycin � keep away from concomitant use; concentration increased by erythromycin � reduce eplerenone dose; focus decreased by rifampicin � avoid concomitant use; avoid concomitant use with lymecycline; elevated danger of hyperkalaemia with trimethoprim. Anti-epileptics: focus reduced by carbamazepine, phenytoin and phenobarbital � keep away from concomitant use. Antifungals: focus elevated by itraconazole and ketoconazole � avoid concomitant use; concentration elevated by fluconazole � scale back eplerenone dose. Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect, increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect with post-synaptic alpha-blockers. Antivirals: concentration elevated by ritonavir � keep away from concomitant use; concentration elevated by saquinavir � reduce eplerenone dose. Pharmacokinetics of eplerenone after single and a number of dosing in topics with and with out renal impairment. Contraindicated by manufacturer due to threat of hyperkalaemia in severe renal impairment. Current proof from studies in animals means that hepatic metabolism contributes solely minimally to elimination of the intact hormone, but desialylated epoetin. Cancer: Initially 450 u/kg weekly in 3�7 divided doses and regulate in accordance with response. Elimination of desialylated drug by the kidneys, bone Pre-treatment checks and applicable correction/treatment wanted for iron, folate and B12 deficiencies, an infection, inflammation or aluminium toxicity to produce optimum response to remedy. This is a really rare condition; as a outcome of failed manufacturing of red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow, leading to profound anaemia. Resulting antibodies render the affected person unresponsive to the therapeutic results of all epoetins and darbepoetin. Dialysis anticoagulation: 4 ng/kg/minute beginning 10�15 minutes earlier than and continuing during dialysis through the arterial line, adjusted based on response (range: 0. A second metabolite, 6,15-diketo-13,14-dihydroprostaglandin F1, is fashioned by enzymatic degradation. Following the administration of radiolabelled epoprostenol to humans, at least sixteen metabolites were discovered, 10 of which have been structurally identified. Some patients might exhibit allergic reaction to buffer solution used to reconstitute epoprostenol. The concentrated solution should be filtered using the filter provided in the pack. In the urine, approximately 20% of the radioactivity excreted was an acyl glucuronide of eprosartan with the remaining 80% being unchanged eprosartan. Following intravenous [14C] eprosartan, about 61% of radioactivity is recovered in the faeces and about 37% in the urine. Following an oral dose of [14C] eprosartan, about 90% of radioactivity is recovered within the faeces and about 7% in the urine. Reduce infusion to 1 mcg/kg/minute and use with caution due to restricted expertise. A examine in patients with totally different degrees of impaired renal operate confirmed that the publicity of eribulin in sufferers with creatinine clearance 40 to 59 mL/min, n=6) was just like patients with normal renal perform while the publicity in sufferers with creatinine clearance <40 mL/ min was increased by 75%, n=4. They are present in plasma at levels that are <10% of erlotinib and display comparable pharmacokinetics as erlotinib. Erlotinib is excreted predominantly as metabolites through the faeces (>90%) with renal elimination accounting for only a small amount (approximately 9%) of an oral dose. Antacids: focus possibly reduced by antacids, give no much less than four hours before or 2 hours after erlotinib. Ulcer-healing medication: avoid with cimetidine, esomeprazole, famotidine, lansoprazole, nizatidine, pantoprazole and rabeprazole; focus reduced by ranitidine, give no less than 2 hours before or 10 hours after ranitidine; focus lowered by omeprazole � avoid. Dilute solutions are stable for 6 hours at room temperature or 24 hours in a fridge. The major metabolite of ertapenem is the ring-opened spinoff shaped by dehydropeptidase-I-mediated hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring. Of the 80% recovered in urine, roughly 38% is excreted as unchanged ertapenem and approximately 37% as the ring-opened metabolite. Anecdotally ertapenem has been used at a dose of 1 g three times a week in haemodialysis patients. Give at least 6 hours before haemodialysis session if unable to give post dialysis. It is excreted in excessive concentrations within the bile and undergoes intestinal reabsorption. About 2�5% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and as much as 12�15% of an intravenous dose could additionally be excreted unchanged by the urinary route.
Azulfidine 500 mg cheap with visa
B: Bone marrow biopsy demonstrates increased blasts pain medication for dogs spayed azulfidine 500 mg cheap with amex, a few of which display megakaryocytic differentiation treatment for dog leg pain 500 mg azulfidine cheap free shipping. C: Reticulin stains of a biopsy at low magnification show a diffuse improve within the variety of fibers all through the bone marrow house. D: Higher magnification of the bone marrow biopsy stained for reticulin shows thickened fibers that encircle particular person bone marrow cells. B: Bone marrow aspirate smear demonstrates cohesive clumps of cells consisting exclusively of irregular basophil precursors. C: Marrow biopsy reveals a hypercellular bone marrow replaced by monotonous-appearing small cells with plentiful "agranular" cytoplasm (representing basophils degranulated throughout tissue processing). A: A minute population of neoplastic myeloid blasts (in black; arrow) is seen in the background of normal regenerating myeloid blasts (in green). B: One month later, the neoplastic population is more outstanding at 1% of analyzed cells (arrow). A: Low magnification of a myeloid sarcoma arising in the chest wall of a patient affected by acute monocytic leukemia. B: the malignant behavior of this lesion is shown by the invasive progress sample consisting of finger-like projections of tumor surrounding fat globules. The blasts have the typical open chromatin pattern seen in immature cells, in distinction to the closed pattern of small mature lymphocytes (arrows). A: Nests of enormous leukemic cells infiltrate the dermis in this pores and skin biopsy from a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. B: High-power view of the appendix wall reveals infiltration by giant leukemic cells with some residual small mature lymphocytes proven on the higher left aspect. In D, negative-staining residual lymphocytes are present in the higher left aspect of the slide. A: Resected lymph node reveals almost whole effacement by a diffuse proliferation of huge pale-staining cells. D and E: Low- and medium-magnification views, respectively, of a surgically resected lymph node present replacement of nodal tissue by pale-staining leukemic cells. A and B: Low- and high-power images of a fine-needle biopsy of a lymph node reveal 420 effacement of structure by sheets of large, uniformly spaced, monotonous, leukemic cells. A: Medium-power view exhibits a cohesive nest of carcinoma cells with scalloped borders and nuclear molding present in the aspirate. C: Necrotic metastatic tumor composed of "ghost" cells seems in the biopsy specimen. A: An aspirate smear demonstrates an esthesioneuroblastoma in the bone marrow with blast-like cells possessing nice cytoplasmic projections. D and E: Low- and high-power views, respectively, of biopsy show bone marrow alternative by small, spherical, blue cells separated by fibrovascular bundles. A: Hypocellular aspirate smear from a case of undifferentiated rhabdomyosarcoma presenting in the bone marrow discloses blast-like cells. B: Pretreatment biopsy demonstrates marrow substitute by an undifferentiated small round blue cell tumor. C: Immunostaining of the pretreatment biopsy for the skeletal muscle marker sarcomeric actin exhibits strong staining in many of the tumor cells. D and E: Posttreatment biopsy reveals differentiation into sarcomeric actin constructive tube-like constructions. A: A contact prep reveals marrow replacement by undifferentiated, blast-like primitive cells. B and C: Biopsy shows infiltration of marrow by loose nests of malignant cells separated by fibrovascular bundles. In the left column of this composite determine are three examples from different blood smears illustrating the three morphologic variants of blasts: L1, L2, and L3 as seen in acute lymphoid leukemias. The L1 blast is common and may be confused, especially in infants, with the traditional small mature lymphocytes that are proven in lots of the blood smears for comparison. C: the latter is confirmed with reticulin stains displaying elevated numbers of thickened fibers. Marrow fibrosis often precludes circulate cytometric evaluation of leukemic cells from dry aspirate smears. In these cases, efforts ought to be made either to disaggregate biopsy specimens for move cytometry or, alternatively, to purchase biopsies for immunohistochemistry. Neoplastic blasts are current within the background of normal maturing B cells (hematogones; green dots) and polytypic mature B cells (red dots). Acute leukemia incidence and patient survival among youngsters and adults within the United States, 2001�2007. Many patients are asymptomatic and present with cytopenia(s) on routine blood rely analysis. Some sufferers could present with symptoms and/or complications from a beforehand unrecognized cytopenia, corresponding to infection, bleeding, straightforward bruising, and general fatigue. Erythrocytes might present macrocytosis, anisocytosis, basophilic stippling, and Pappenheimer bodies. Erythroid precursors in the bone marrow might present nuclear and/or cytoplasmic abnormalities. The former consist of budding, internuclear bridging, the presence of multiple nucleus per cell, karyorrhexis (fragmentation), irregular chromatin (either fantastic or dense), and megaloblastic adjustments, by which the nucleus is enlarged and less mature than would be anticipated based on the degree of cytoplasmic hemoglobinization. Eosinophils and basophils might have diminished granules and/or decreased nuclear lobulation. In the bone marrow, dysplastic megakaryocytes are small (micromegakaryocytes), and possess abnormal nuclei that are a number of and widely separated or have decreased or absent lobulation. The combined data from the above parameters are used to calculate 5 risk groups (Table 7. This lessens treatment-related morbidity and mortality in sufferers with a comparatively good prognosis, and permits for the aggressive therapy of disease in those with a poor prognosis. It remains a therapy of choice for children and sufferers beneath 40 years of age and can be used in some older sufferers with higher danger illness. Mutation frequency will increase with age and individuals with clonal mutations are at a higher threat of improvement of a hematologic malignancy. The bone marrow is usually hypercellular, with dysplasia most distinguished in the megakaryocytes, that are elevated and have hypolobulated nuclei; erythroid dysplasia is also typically current, however dysgranulopoiesis is uncommon. Blasts are lower than 5% of cells in the bone marrow and fewer than 1% of cells in the blood. Patients sometimes have a good prognosis and often have an excellent response to lenalidomide. Incidence and medical issues of myelodysplastic syndromes among United States Medicare beneficiaries. Refractory cytopenias with unilineage dysplasia: a retrospective analysis of refractory neutropenia and refractory thrombocytopenia. Morphology and classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes and their pathologic variants. The preleukemic syndrome: clinical and laboratory options, pure course, and administration. Diagnostic significance of dysplastic options of peripheral blood polymorphs in myelodysplastic syndromes.
500 mg azulfidine generic visa
Affected people have vertical talus; ulnar deviation; extreme camptodactyly; and a distinctive facies blue sky pain treatment center/health services azulfidine 500 mg buy cheap on line, including a triangular shape neck pain treatment kerala azulfidine 500 mg with visa, prominent nasolabial folds, downslanting palpebral fissures, small mouth, and a distinguished chin. Distal arthrogryposis in affiliation with short stature, cleft palate, submucous cleft palate or bifid uvula, ptosis, epicanthal folds, delicate facial asymmetry, and brief neck (see Hall et al, 1982). Distal arthrogryposis in association with brief stature; unusual stance with brief heel cords and pes cavus; quick neck; ptosis; immobility of face with or with out keratoconus and decreased ocular vary of motion; smooth, shiny, tapering fingers with mild camptodactyly; restrictive chest illness (see Hall et al, 1982). Distal arthrogryposis in affiliation with sensorineural hearing loss (see Stewart and Bergstrom, 1971). Plantar flexion contractures related to delicate contractures of hips, elbows, wrists, and fingers (see Stevenson et al, 2006). Position deformities (88%): bilateral calcaneovalgus (33%), bilateral equinovarus (25%), mixtures (30%). Hip involvement (38%): congenital dislocations, decreased abduction, mild flexion, contracture deformities. The arms finally unclench and should have residual camptodactyly and ulnar deviation. The parent of an affected youngster may probably categorical the gene via gentle hand contractures only. Bamshad M, et al: A revised and prolonged classification of the distal arthrogryposis, Am J Med Genet sixty five:277, 1996. A�C, Note the joint contractures involving arms and feet in a baby at delivery and at 7 months of age. Through an extensive evaluate of published cases, Hall in 2009 delineated 20 distinct familial varieties. The predominant features of all types are secondary to decreased intrauterine movement. Rigid expressionless face; outstanding eyes; hypertelorism; telecanthus; epicanthal folds; poorly folded, small, and posteriorly angulated ears; depressed nasal tip; small mouth; high-arched palate; micrognathia. Apparent quick neck; polyhydramnios, shortgut syndrome with malabsorption, small or irregular placenta, relatively brief umbilical twine. Although nearly all of those live-born die of the issues of pulmonary hypoplasia inside the first month of life, it is very important acknowledge that the ultimate prognosis for youngsters with this dysfunction depends on the cause of the decreased fetal motion. The central nervous system and most skeletal muscles are normal with the exception of disuse atrophy. Chen H, et al: the Pena-Shokeir syndrome: Report of five circumstances and additional delineation of the syndrome, Am J Med Genet sixteen:213, 1983. Lav E, et al: Fetal akinesia deformation sequence (PenaShokeir phenotype) associated with acquired intrauterine mind injury, Neurology forty seven:1467, 1991. The course of the dysfunction in all cases is progressive, with downhill deterioration. It is characterised by virtually no growth and rising cachexia regardless of apparently enough caloric consumption, ending in dying, which is normally from pulmonary infections that complicate emaciation. Reduced white matter of mind with gray mottling, subependymal focal gliosis of the third ventricle, focal microgyria, hypoplasia of temporal and hippocampal gyri, hypoplasia of optic tracts and chiasm, agenesis of corpus callosum, intracranial calcification in areas of lenticular nuclei and hemispheric white matter. Severe mental incapacity, occasional infantile spasms, axial hypotonia and peripheral hypertonia, hyporeflexia or areflexia, sensorineural listening to loss. Microcephaly, prominent root of the nose, massive ear pinnae, upper lip overlapping decrease lip, micrognathia (mild). Blepharophimosis with deep-set eyes, microphthalmia, cataracts, nystagmus, microcornea with optic atrophy. Camptodactyly, delicate flexion contractures of the elbows and knees, rocker-bottom ft with vertical talus, posteriorly positioned second metatarsal, longitudinal groove within the soles along the second metatarsal. Unusual skin pigmentation on sun-exposed areas, photosensitivity, hirsutism, kyphoscoliosis, extensively set nipples, shallow acetabular angles, coxa valga, longitudinal groove on soles, osteoporosis, renal defects, genital hypoplasia. It was separated from other circumstances associated with pterygia by Hall and colleagues in 1982. De Die-Smulders and colleagues distinguished an "early" and a late form of the deadly multiple pterygium syndrome. The early group is genetically heterogeneous with both autosomal and X-linked recessive circumstances represented. Within the late group, all familial instances have pedigrees consistent with autosomal recessive inheritance. Epicanthal folds; ocular hypertelorism; flat nostril; cleft palate; small mouth; micrognathia; downslanting palpebral fissures; low-set, malformed ears. Flexion contractures involving elbows, shoulders, hips, knees, ankles, hands, and ft. Present in the following areas: chin to sternum, cervical, axillary, antecubital, crural, popliteal, and ankles. Small chest; cryptorchidism; hypoplastic dermal ridges and creases; neck edema and free skin; radiologic proof of undermodeling of long bones and hypoplasia of vertebrae, sacrum, ileum, ischium, ribs, clavicles, and scapulae; skinny, gracile long bones. Polyhydramnios is present in roughly one third of circumstances and hydrops in multiple half. Decreased fetal exercise and an elevated incidence of breech presentation have been documented. A�C, Stillborn toddler with ocular hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, multiple joint contractures, and pterygia bridging nearly all joints. An extra family with three affected siblings from a first-cousin mating was reported by Laxova and colleagues in 1972. The ordinary reason for death is respiratory failure or sepsis secondary to pores and skin breakdown. Microcephaly (84%); lissencephaly (40%); absence of corpus callosum (53%); hypoplasia of cerebellum (53%) and hypoplasia of pons; absence of olfactory bulbs. Sloping forehead (100%); ocular hypertelorism (94%); protruding eyes with absent lids (40%); flattened nostril; spherical, gaping mouth and thick everted lips; micrognathia (97%); large ears; quick neck. Yellow subcutaneous tissue coated by skinny, transparent, scaling skin and edema (85%); ichthyosis (50%). Short limbs, syndactyly of fingers and toes (60%), extreme puffiness of arms and toes, overlapping of digits, calcaneovalgus, vertical talus, flexion contractures of main joints with pterygia (79%), poorly mineralized bones. Cataracts (25%), microphthalmia, persistence of some embryonic structures of eye, absent eyelashes and head hair, muscular atrophy with hypertrophy of fatty tissue, hypoplastic or atelectatic lungs, hypoplastic genitalia (50%), polyhydramnios, brief umbilical twine, small placenta. Shapiro I, et al: Neu-Laxova syndrome: Prenatal ultrasonographic prognosis, scientific and pathological research, and new manifestations, Am J Med Genet forty three:602, 1992. A�C, Newborn with microcephaly, sloping brow, protruding eyes with absent lids, flat nostril, gaping mouth and thick lips, scaling skin with edema, excessive puffiness of palms and toes, syndactyly, and joint contractures. Most of the features are constraint-related, the results of restricted in utero motion secondary to the faulty pores and skin. The majority of affected people are stillborn on account of pulmonary hypoplasia. Intubation is extremely tough due to the temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Mutations in both of those genes result in defective functioning of lamin A, ensuing in the characterization of restrictive dermopathy as a laminopathy. Enlarged fontanels, hypertelorism, entropion, small pinched nose, small mouth with ankylosis of the temporomandibular joints, mouth mounted in the "O" place, micrognathia, dysplastic ears.
Discount azulfidine 500 mg visa
Melnick M wrist pain treatment exercises 500 mg azulfidine otc, et al: Familial branchio-oto-renal dysplasia: A new addition to the branchial arch syndromes dna pain treatment center cheap azulfidine 500 mg with amex, Clin Genet 9:25, 1976. Heimler A, Lieber E: Branchio-oto-renal syndrome: Reduced penetrance and variable expressivity in 4 generations of a giant kindred, Am J Med Genet 25:15, 1986. The designation branchio-oculofacial syndrome was launched by Fujimoto and colleagues. Premature graying of scalp hair normally begins round 18 years but has been seen as early as 10 years. Sinus/fistulous tract (45%), atrophic skin lesion/aplasia cutis congenita/scarring (57%), hemangiomatous lesion (36%). Lacrimal duct obstruction (78%), colobomata (47%), microphthalmia/anophthalmia (44%), upslanting palpebral fissures (48%), telecanthus (58%), myopia (46%). Low-set, posteriorly rotated, over-folded or malformed ears (85%); hypoplastic superior helix (43%); conductive hearing loss (71%); supra-auricular sinuses (15%). Abnormal higher lip (90%), which includes pseudocleft (appearance of repaired cleft lip), incomplete or full cleft lip; dental abnormalities (56%); micrognathia (50%). Fujimoto A, et al: New autosomal dominant branchiooculo-facial syndrome, Am J Med Genet 27:943, 1987. McCool M, Weaver D: Branchio-oculo-facial syndrome: Broadening the spectrum, Am J Med Genet 49:414, 1994. Note the pseudocleft of the lip and the low-set, posteriorly rotated ears with hypoplastic superior helix. Severe sensorineural hearing loss happens in the majority of instances, and patients can profit from hearing aids. Macrocephaly within the new child period, massive anterior fontanel, ocular hypertelorism, outstanding eyes, flat nasal bridge, downslanting palpebral fissures, brief nose, posteriorly rotated ears. Partial or complete agenesis of corpus callosum, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, omphalocele/umbilical hernia, proteinuria. Donnai D, Barrow M: Diaphragmatic hernia, exomphalos, absent corpus callosum, hypertelorism, myopia, and sensorineural deafness. Postmortem photograph: observe open metopic suture, frontal bossing, downslanting palpebral fissures, ocular hypertelorism, broad nose and vermillion border of higher lip, and on the lateral view, posteriorly angulated ear and flattened facial profile. Death in the postneonatal period may result from swallowing problems, gastroesophageal reflux, or aspiration and postoperative airway problems which are the result of cranial nerve dysfunction. Although postnatal growth deficiency has been present in some instances, most sufferers have been appropriate size for gestational age, with linear development shifting right down to or beneath the third percentile through the first 6 months of life, which in some instances has been due to growth hormone deficiency. Hypoplasia of the semicircular canals leads to steadiness disturbances and delays in the attainment of motor milestones. Venous malformations of the temporal bone can lead to critical problems throughout otologic surgical procedure if not identified. This class of proteins is assumed to be essential in early embryologic growth by affecting chromatin construction and gene expression. Colobomas, including isolated iris coloboma without visible impairment, clinical anophthalmos, and retinal coloboma. Structural defects, together with small ears, cupshaped or lop ears, triangular-shaped concha, and hypoplastic semicircular canal. Hearing loss, together with either sensorineural or combined sensorineural, and conductive deafness, starting from mild to profound. Tetralogy of Fallot, patent ductus arteriosus, double-outlet right ventricle with an atrioventricular canal, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, right-sided aortic arch. Micropenis and cryptorchidism in males; lack of spontaneous onset of puberty in females. A and B, Newborn infants with choanal atresia, aberrant auricles, and micrognathia. The white forelock could additionally be present at birth only to become pigmented early in life; the hair could turn out to be prematurely gray or white. Deafness, the most serious feature, is sensorineural, congenital, and often nonprogressive. It can be unilateral or bilateral and varies from slight to profound, although normally the latter. The defect appears to be in the organ of Corti, with atrophic adjustments within the spiral ganglion and nerve. Lateral displacement of inner canthi with short palpebral fissures and lateral lacrimal dystopia; broad and high nasal bridge with hypoplastic alae nasi; medial flare of bushy eyebrows, which can meet in midline; hypochromic iridis; partial albinism manifested by hypopigmented ocular fundus and white eyelashes, eyebrows, and forelock. Deafness, aplasia of the posterior semicircular canal, premature graying, broad mandible. Patent metopic suture, strabismus, rounded tip of nose, full lips with accentuated "cupid bow" to higher lip, easy philtrum, cleft lip and palate, anisocoria, cardiac anomaly (ventricular septal defect), imperforate anus, Sprengel anomaly, supernumerary vertebrae and ribs, neural tube closure defect, scoliosis, multicystic dysplastic kidney, absence of vagina and adnexa uteri. Features of sort I with the addition of upper limb defects, including hypoplasia of muscular tissues, flexion contractures, carpal bone fusion, and syndactyly. Pingault V, et al: Review and update of mutations inflicting Waardenburg syndrome, Hum Mutat 31:391, 2010. A and B, Note the lateral displacement of the medial canthi, the broad nasal bridge with hypoplastic ala nasi, medial eyebrow flare, and hypochromic iridis. A, Note the lateral displacement of the internal canthi (telecanthus) with brief palpebral fissures, anisochromia of irides, bushy eyebrows with medial flare, broad and high nasal bridge, a rounded tip of the nostril, and a smooth philtrum. B and C, A white hair forelock and skin adjustments over her leg are reflective of patchy hypopigmentation. In the Forties, Franceschetti and Klein made in depth stories on this situation and referred to as it mandibulofacial dysostosis. The growth of the facial bones during infancy and childhood results in some cosmetic enchancment that may be enhanced by cosmetic surgery. Franceschetti A, Klein D: the Mandibulofacial Dysostosis: A New Hereditary Syndrome, Copenhagen, 1949, E. Peterson-Falzone S, Pruzansky S: Cleft palate and congenital palatopharyngeal incompetency in mandibulofacial dysostosis, Cleft Palate J thirteen:354, 1976. The Treacher Collins Syndrome Collaborative Group: Positional cloning of a gene involved in the pathogenesis of Treacher Collins syndrome, Nat Genet 12:130, 1996. As the great majority of those sufferers are of regular intelligence, the early recognition of deafness and its correction with hearing aids or surgery are of great significance for improvement. Writzl K, et al: Genital anomalies in a patient with Treacher Collins syndrome, Am J Med Genet 146:2169, 2008. Note the hair extending onto the lateral cheek, downslanting palpebral fissures, malar hypoplasia, malformed ears, and micrognathia. E and F, Note proof of a cleft of the zygomatic bone and the coloboma of each upper and decrease lids.
Azulfidine 500 mg buy discount on-line
Diuretics: focus of eplerenone decreased � keep away from concomitant use; increased threat of osteomalacia with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors pain treatment with acupuncture generic 500 mg azulfidine with amex. Oestrogens and progestogens: metabolism accelerated jaw pain treatment home buy cheap azulfidine 500 mg line, lowered contraceptive impact. Charcoal haemoperfusion and haemodialysis simpler than peritoneal dialysis for poisoning. Only about 10�13% of an intravenous dose is excreted unchanged within the urine, and the fate of the rest of the drug is unknown. Anti-arrhythmics: elevated concentration with amiodarone; focus of disopyramide and mexiletine and probably dronedarone lowered � avoid with dronedarone. Antibacterials: level increased by clarithromycin, chloramphenicol, isoniazid, metronidazole, sulfonamides and trimethoprim (+ antifolate effect); concentration elevated or decreased by ciprofloxacin; concentration of doxycycline and telithromycin reduced � avoid with telithromycin; concentration reduced by rifamycins. Anti-epileptics: focus of both medication reduced with carbamazepine, concentration may be increased by carbamazepine, eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, oxcarbazepine, stiripentol and topiramate; concentration of ethosuximide, energetic oxcarbazepine metabolite, retigabine, rufinamide (concentration of phenytoin presumably increased), topiramate and valproate probably decreased; focus of eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, perampanel, tiagabine and zonisamide lowered; focus of phenobarbital often increased; phenobarbital and valproate may alter focus; focus lowered by vigabatrin. Antimalarials: keep away from with piperaquine with artenimol; mefloquine and pyrimethamine antagonise anticonvulsant effect; increased antifolate effect with pyrimethamine. Antivirals: presumably decreased concentration of abacavir, darunavir, indinavir, lopinavir, ritonavir and saquinavir; concentration of boceprevir and rilpivirine decreased � keep away from; focus presumably increased by indinavir and ritonavir; concentration increased or decreased with zidovudine; avoid with etravirine and telaprevir Calcium-channel blockers: ranges increased by diltiazem; focus of diltiazem, felodipine, isradipine, nimodipine and verapamil lowered; keep away from with isradipine and nimodipine. Cytotoxics: metabolism possibly inhibited by fluorouracil; elevated antifolate effect with methotrexate; concentration of busulfan, eribulin, etoposide and imatinib reduced � avoid with imatinib; focus presumably reduced by cisplatin; presumably lowered concentration of axitinib, enhance axitinib dose; possibly decreased focus of crizotinib � avoid; avoid with cabazitaxel, gefitinib, lapatinib and vemurafenib; concentration of irinotecan and its lively metabolite reduced. Muscle relaxants: long-term use of phenytoin reduces effects of nondepolarising muscle relaxants, but acute use could enhance effects. Total phenytoin levels have to be adjusted for hypoalbuminaemia and uraemia (levels of 5�12 mcg/mL could also be enough). Increase dose progressively (25�50 mg/day at weekly intervals); demonstrates saturation kinetics. Phenytoin absorption is markedly reduced by concurrent nasogastric enteral vitamin administration. Addiphos: peripherally � give every vial (20 mL) diluted to 250�500 mL with glucose 5% over 6�12 hours; centrally � 20 mL vial made up to 60 mL with glucose 5% over 6�8 hours via syringe driver. Fleet phosphate enema can be added to dialysate for hypophosphataemia in haemodialysis patients. Management of hypophosphatemia in nocturnal hemodialysis with phosphate containing enema: A technical study. Excessive doses of phosphate may trigger hypocalcaemia and metastatic calcification. Patients with obstructive jaundice requiring oral vitamin K should be prescribed the water-soluble preparation menadiol sodium diphosphate � dosage vary is comparable. Antibacterials: avoid concomitant use with macrolides and moxifloxacin (increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias). Antimalarials: keep away from concomitant use with artemether/lumefantrine and piperaquine with artenimol; elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with mefloquine and quinine � keep away from concomitant use. Antipsychotics: elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with droperidol, phenothiazines or sulpiride � keep away from concomitant use. Antivirals: concentration elevated by atazanavir, boceprevir, efavirenz, fosamprenavir, indinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and telaprevir, increased threat of ventricular arrhythmias � keep away from concomitant use. Cytotoxics: use crizotinib with warning; avoid with lapatinib; increased threat of ventricular arrhythmias with vandetanib � keep away from; increased threat of ventricular arrhythmias with arsenic trioxide. Following oral administration of radiolabelled pioglitazone to man, recovered label was mainly in faeces (55%) and a lesser quantity in urine (45%). There has been a case report of rhabdomyolysis 6 months after beginning therapy in a patient. Roundworms: 4 g sachet stirred into a glass of milk or water and drunk instantly; repeat at monthly intervals for as much as three months if re-infection danger. Acts within the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract which is unbiased of any systemic absorption. Piracetam is excreted virtually utterly in urine and the fraction of the dose excreted in urine is impartial of the dose given. Antivirals: increased danger of haematological toxicity with zidovudine; focus elevated by ritonavir. Methotrexate: penicillins can cut back the excretion of methotrexate (increased risk of toxicity). About 45% of a dose may be excreted in the urine as mecillinam, primarily throughout the first 6 hours. Mecillinam is partly excreted with bile, giving rise to biliary concentrations about three times the serum ranges. Accumulation may occur in patients with severe renal impairment, so use the lower dose if using for extended periods of time. Unlikely to work in folks with little residual kidney function as works by renal excretion into the bladder, the place its website of motion is. Over half of a dose is excreted in the urine, chiefly as metabolites; a major proportion is excreted within the faeces. The primary metabolite of pizotifen (N-glucuronide conjugate) has an extended elimination half-life of about 23 hours. The primary elimination route of posaconazole is by way of the faeces (77%) the place 66% of a dose is excreted unchanged. About 14% of a dose is excreted in the urine with solely trace quantities excreted unchanged. Antibacterials: rifamycins could cut back posaconazole focus; keep away from concomitant administration unless profit outweighs risk; rifabutin concentration increased. Antidiabetics: posaconazole can decrease glucose concentrations, monitor glucose ranges in diabetic sufferers. Anti-epileptics: phenytoin, carbamazepine and phenobarbital might scale back posaconazole focus � keep away from concomitant administration except benefit outweighs threat. Antipsychotics: elevated danger of ventricular arrhythmias with pimozide � keep away from concomitant use; presumably increase quetiapine levels � scale back dose of quetiapine. Antivirals: focus of atazanavir elevated; concentration reduced by efavirenz and presumably fosamprenavir; presumably increases saquinavir ranges; increased threat of ventricular arrhythmias with telaprevir. Posaconazole can increase ciclosporin concentration � dose discount may be required. Cytotoxics: probably improve everolimus concentration � keep away from; avoid with lapatinib; reduce dose of ruxolitinib; possibly inhibits metabolism of vinblastine & vincristine, elevated danger of neurotoxicity. Ergot alkaloids: may increase ergot alkaloid concentration resulting in ergotism � keep away from concomitant administration. Sirolimus: could enhance focus of sirolimus � regulate sirolimus dose as required based on levels. Ulcer-healing drugs: cimetidine could reduce posaconazole concentration by 39% � avoid concomitant administration unless benefit outweighs danger; avoid with histamine H2-antagonists and proton pump inhibitors. Some units give extra concentrated solution centrally: 100�200 mmol/100 mL sodium chloride zero.
Syndromes
- To be effective, this treatment must be started within 3 to 4 1/2 hours of when the symptoms first started.
- Diverticulosis (abnormal pouches in the colon)
- Seizures
- Brushing too hard
- Breast enlargement and breast tenderness
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- Oatmeal baths may be soothing and may help to loosen scales. You can use over-the-counter oatmeal bath products. Or, you can mix 1 cup of oatmeal into a tub of warm water.
Purchase 500 mg azulfidine
A biopsy from the base of the tongue shows necrosis and extensive infiltration of tissue with atypical large lymphoid cells composed of immunoblasts with giant pain treatment center lexington azulfidine 500 mg discount with visa, single pain treatment center syracuse ny azulfidine 500 mg discount visa, central nucleoli (white arrows) and centroblasts with a number of smaller nucleoli situated close to the nuclear membrane (black arrows). These blood smears show circulating, massive nucleolated lymphoid cells, some with clefted nuclear contours. For comparison, mature small lymphocytes are present near the lower left corners of each figures. C: the bone marrow biopsy is totally changed by sheets of poorly preserved, malignant cells that show in depth crush artifact. These "double-hit" lymphomas, in addition to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, when confined to blood and marrow at the time of analysis, are simply misdiagnosed as precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. This cervical lymph node specimen confirmed whole effacement by a proliferation of enormous atypical lymphoid cells with outstanding nucleoli and in affiliation with tangible physique macrophages. An post-mortem lung from a affected person with lymphomatoid granulomatosis reveals extensive involvement with a quantity of necrotizing lesions. B: Lung biopsy displaying giant lymphoid cells restricted to blood vessels and displaying a vasculitic pattern of involvement, with fibrinoid necrosis and angioinvasion. A and B: A supraclavicular lymph node biopsy reveals dense fibrous tissue and in depth coagulative tumor necrosis intimately associated with sheets of large, malignant lymphoid cells. C: the malignant cells have giant, eosinophilic staining nucleoli (black arrow) and mitotic figures (white arrow). A: the biopsy of an stomach mass exhibits, at low energy, the traditional "starry sky" appearance of quickly proliferating malignant cells intermixed with bigger histiocytes actively engulfing tumor debris. B: Higher power reveals intermediatesized cells which are uniform in measurement and form, with a number of small basophilic nucleoli. This bone marrow biopsy demonstrates total alternative by rapidly growing tumor cells, a few of which exhibit apoptosis admixed with "starry-sky" histiocytes engulfing tumor particles. This blood smear reveals L3-type lymphoblasts with multiple nucleoli and basophilic staining, vacuolated cytoplasm. The ideograms of chromosomes 8, 14, and the respective by-product chromosomes are to the left in color; the corresponding G-banded chromosome pairs are to the proper. The tumor incorporates sheets of atypical plasmacytoid cells with a excessive mitotic fee. Gross lymph node specimens have been reduce to present characteristic homogenous sample ("fish flesh" appearance) of a lymph node diffusely concerned by persistent lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (A), as in contrast with the nodular, heterogeneous look of a lymph node involved with metastatic cancer (B). Frequent smudged or "basket" cells, which are nuclear remnants of damaged cells, can be seen. B: Mantle cell lymphoma has small lymphocytes, condensed chromatin, and scant cytoplasm. C: Hairy cell leukemia has lymphopenia, ample cytoplasm with a central nucleus, and cytoplasmic projections. D: Splenic marginal zone lymphoma has lymphocytosis and irregular, eccentric nuclei. An internal mammary node is diffusely effaced by a proliferation of small, mature lymphocytes with high N:C ratios and condensed chromatin. Pale staining proliferation facilities are composed of prolymphocytes and immunoblasts-larger cells with vesicular nuclei and nucleoli. The lymph node is diffusely changed by small mature lymphocytes with high N:C ratios and condensed chromatin. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma; diffuse marrow involvement. A blood smear demonstrates mature lymphocytosis (A), and numerous magnified views of a marrow biopsy are shown (B�D). Diffuse infiltration includes full effacement of bone marrow architecture by sheets of lymphoma cells. D: Deletion of the p53 gene (red) at 17p13 as compared with a centromere 17 management (green). In this gross specimen, the spleen is homogeneously enlarged by diffuse infiltration of the red pulp. For comparability, a traditional small lymphocyte is current within the higher left nook of the determine. Multiple small (1- to 3-mm) discrete nodules of expanded white are diffusely distributed all through the splenic parenchyma. The spleen is diffusely infiltrated by macroscopically seen nodular expansions of white pulp. Perivascular nodules made up of monotonous-appearing, well-spaced, medium-sized lymphoid cells are shown. The typical cells in this disease are mature-appearing, medium-sized lymphocytes with ample cytoplasm that varieties villous projections. A: Marrow biopsy shows a largely sinusoidal pattern of marrow involvement by lymphoma. B and C: Highpower views show small-sized lymphoma nuclei (compared with the bigger endothelial nucleus; arrow in B), which possess a condensed chromatin pattern and common nuclear contours. Clinical photograph of eye exhibiting fleshy "salmon-color patch" of the superficial ocular floor. This gastric biopsy demonstrates intensive involvement by well-spaced, medium-sized lymphoid cells that invade and destroy glands to form lymphoepithelial lesions (arrow). Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Uniformly, well-spaced, medium-sized lymphoid cells invade and destroy glands to type lymphoepithelial lesions (bottom proper image). A lymph node and subjacent parotid gland demonstrate a vaguely nodular proliferation (A and B) of well-spaced monocytoid lymphocytes invading germinal facilities (C) and glandular structures to form lymphoepithelial lesions (D). Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma; lymph node involvement by extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Right flank mass in a patient affected by recurrent Waldenstr�m macroglobulinemia. This lymph node is totally effaced by diffuse sheets of monotonous-appearing plasma cells, some exhibiting intranuclear inclusions of monoclonal immunoglobulin in the type of Dutcher our bodies (arrows). A�C: Bone marrow biopsy sections show diffuse replacement of the marrow by a small lymphocytic/plasma cell population that reveals restricted IgM expression by immunohistochemistry. D: Mixed population of lymphocytic/plasmacytoid cells is seen in a marrow aspirate smear. Transmission electron micrographs of cells from a case of hairy cell leukemia show numerous cytoplasmic villous projections at low magnification (A), and at greater power (B), the characteristic ribosomal�lamella complexes composed of concentrically arranged sheets of membranes alternating with rows of ribosomes are seen. Large atypical lymphoid cells, "flower cells" with convoluted nuclei, are seen circulating in blood (A) and in involved lymph nodes (B� E). Ethmoid sinus tissue fragments from a 38-year-old woman show intensive necrosis and an angiocentric, pleomorphic population of large atypical lymphoid cells combined with some histiocytes, small lymphocytes, and rare plasma cells. B: Blood smear showing medium-sized lymphoid cells with pale rims of cytoplasm and slightly irregular nuclear contours. C: the lymphoma cells usually specific the / T-cell receptor, as shown within the flow cytometric scattergram (arrow).
Order azulfidine 500 mg overnight delivery
Elimination half-lives of about 14 to 24 and 23 to 46 hours have been reported for dosulepin and its metabolites knee joint pain treatment 500 mg azulfidine with mastercard, respectively myofascial pain treatment guidelines 500 mg azulfidine cheap amex. Clonidine: Tricyclics antagonise hypotensive effect; increased danger of hypertension on clonidine withdrawal. Calcium-channel blockers: enhanced hypotensive impact, increased threat of first dose hypotensive impact. Doxepin is excreted within the urine, mainly within the type of its metabolites, either free or in conjugated kind. Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Alcohol: increased sedative impact. About 40�50% of a dose is excreted in bile within 7 days, of which about half is excreted as unchanged drug and the rest as metabolites. To avoid undue dilution in urine, the patient must be instructed not to drink any fluid within the 12 hours prior to instillation. Above this level, the danger of irreversible congestive cardiac failure increases greatly. Patients with impaired hepatic perform have prolonged and elevated plasma concentrations of each the drug and its metabolites. Liposomal preparations out there: up to ninety mg in 250 mL glucose 5%; if greater than 90 mg dilute in 500 mL glucose 5%. About 40% of the administered dose is eliminated in three days in lively kind within the urine. However, the vast majority of a dose of doxycycline is excreted within the faeces after chelation in the intestines. Urinary concentrations are roughly 10 occasions higher than plasma concentrations at the same time. In the presence of impaired renal function, urinary elimination decreases, faecal elimination will increase and the half-life stays unchanged. About 6% of an oral dose is excreted in the urine (entirely metabolites) and 84% within the faeces (metabolites and unchanged drug). Potentially hazardous interactions with different drugs Anti-arrhythmics: increased danger of myocardial despair with other antiarrhythmics; elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with amiodarone or disopyramide � keep away from concomitant use. Antibacterials: increased threat of ventricular arrhythmias with clarithromycin, telithromycin & erythromycin; concentration reduced by rifampicin � avoid concomitant use. Anticoagulants: increased anticoagulant effect with coumarins & phenindione; increased dabigatran focus � avoid concomitant use; avoid concomitant use with rivaroxaban. Anti-epileptics: focus possibly decreased by phenytoin, carbamazepine and phenobarbital � avoid concomitant use. Antifungals: concentration elevated by ketoconazole � avoid concomitant use; keep away from concomitant use with itraconazole, posaconazole & voriconazole. Antivirals: avoid concomitant use with ritonavir; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with saquinavir � keep away from concomitant use. Beta-blockers: increased danger of myocardial melancholy; concentration of metoprolol & propranolol probably elevated; increased danger of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol � keep away from concomitant use. Calcium-channel blockers: focus elevated by nifedipine; increased risk of bradycardia & myocardial despair with diltiazem & verapamil. An enhance in plasma creatinine (mean improve 10 mol/l) has been observed in healthy subjects and in sufferers. In most patients this enhance happens early after remedy initiation and reaches a plateau after 7 days. It is really helpful to measure plasma creatinine values prior to and seven days after initiation of dronedarone. If a rise in creatininemia is observed, serum creatinine should be remeasured after an additional 7 days. If no further increase in creatinine is observed, this value ought to be used as the new reference baseline considering that this might be expected with dronedarone. If serum creatinine continues to rise then consideration must be given to additional investigation and discontinuing remedy. About 75% of a dose is excreted within the urine, with 1% being excreted unchanged; 11% appears in the faeces. Potentially hazardous interactions with different drugs Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive impact; results of thiopental enhanced. Analgesics: elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with methadone; increased danger of convulsions with tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative results with opioids. Antibacterials: elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with moxifloxacin and macrolides � avoid concomitant use. Antidepressants: increased danger of ventricular arrhythmias with fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, sertraline or tricyclics � avoid. Antimalarials: avoid concomitant use with artemether/lumefantrine and piperaquine with artenimol; elevated risk of ventricular arrhythmias with chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine or quinine � avoid. Beta-blockers: enhanced hypotensive impact; elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol � avoid. Hormone antagonists: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with tamoxifen � keep away from. Both cytochromes P450�2D6 and 1A2 catalyse the formation of the two major metabolites, glucuronide conjugate of 4-hydroxy duloxetine and sulphate conjugate of 5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine. Based upon in vitro research, the circulating metabolites of duloxetine are thought-about pharmacologically inactive. The renally excreted metabolites 4-hydroxy duloxetine glucuronide and 5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine sulphate had been 7�9 occasions greater than in people with regular renal perform. Contraindicated in uncontrolled hypertension because of potential risk of hypertensive crisis. Eculizumab incorporates solely naturally occurring amino acids and has no recognized lively metabolites. Human antibodies are predominately catabolised by lysosomal enzymes to small peptides and amino acids. A 1 hour session of plasma exchange causes a 50% decline in focus of eculizumab. Approximately 14�34% of a radiolabelled dose of efavirenz was recovered within the urine and fewer than 1% of the dose was excreted in urine as unchanged efavirenz. Potentially hazardous interactions with other medication Antibacterials: concentration of rifabutin lowered. Antifungals: itraconazole, posaconazole and voriconazole focus reduced; voriconazole increases efavirenz focus � scale back dose of efavirenz by 50% and increase dose of voriconazole to 400 mg twice daily; possibly reduces caspofungin focus � might probably have to increase caspofungin dose. Antipsychotics: probably elevated threat of ventricular arrhythmias with pimozide � keep away from concomitant use; presumably reduces aripiprazole concentration � improve aripiprazole dose. Anxiolytics and hypnotics: threat of extended sedation with midazolam � keep away from concomitant use. Monitor levels of cholesterol as will increase of 10�20% in total ldl cholesterol have been reported.
Cheap 500 mg azulfidine mastercard
The Potter/oligohydramnios sequence Babies are typically born with the mixture of squashed facial options sciatica pain treatment options azulfidine 500 mg generic without prescription, severe talipes pain treatment without drugs azulfidine 500 mg online buy cheap, dislocated hips, progress deficiency and lethal pulmonary hypoplasia. Oligohydramnios develops due to defective urinary output by the child, or continual leakage. The major causes of lowered urinary output are bilateral renalagenesis (1/3000 births), polycystic kidneydiseaseType1 and obstruction of the urethra. Renal agenesis lessons as a malformation, which through oligohydramnios causes secondary deformations, the mix constituting a syndrome and the sequence of events, a sequence. Multipleabnormalities 1 Sequences are cascades of results, for example Pierre�Robin sequence, in which a major defect in mandibular improvement produces secondary glossoptosis (drooping tongue) and cleft palate. Features Similar to Turner syndrome (Chapter 37), however affecting both sexes: brief stature, neck webbing, increased carrying angle on the elbow, also learning difficulties, hypertelorism, down-slanting palpebral fissures, low-set ears and congenital heart illness. An anterior defect results in either anen cephaly or encephalocele (absence or protrusion of the brain). A posterior defect can lead to lumbosacral myelocele or meningomyel ocele (protruding spinal twine uncovered, or lined by meninges), spina bifida and leg deformity (see Chapter 51). Holoprosencephaly Holoprosencephaly is failure of cleavage of the embryonic forebrain, resulting in severe psychological impairment and abnormal facies, in Congenital abnormalities, pre-embryonic, embryonic and of intrinsic causation Embryology and congenital abnormalities one hundred fifteen severe circumstances cyclopia. It can be associated with Triploidy thirteen (see Chapter 36) and Smith� Lemli�Opitz syndromes (see Chapter 60), maternal diabetes mellitus (see Chapter 46) and a variety of other deletions and mutations in varied genes. It can arise from intracranial haemorrhage, an infection or genetic defect, or be idiopathic. Duodenalatresia At week 7 the midgut is strong; duodenal atresia occurs when the lumen fails to open. Lissencephaly(smoothbrain) this is attributable to faulty neuronal migration at 3�5 months. It can be related to epilepsy and mental retardation and is a function of Miller�Dieker syndrome and other issues (see Chapter 40). As an isolated condition it has an empiric recurrence danger of 10% (see Chapter 13). Macrocephalyandmicrocephaly these phrases apply to head circumferences greater than the 97th and fewer than the third centile (see Chapter 49). Congenital coronary heart defects Heart growth happens at 3�8 weeks and developmental defects occur in 7/1000 live births. Congenital coronary heart defects can result in insufficient oxygenation of blood and/or poor perfusion of tissues (see also Chapters 48 and 51). Partial chromosomal duplication or deficiency may cause postnatal neurodevelopmentaldelay, pre- or postnatal growthdelay, dysmorphism or dying. The aetiology of two-thirds of congenital defects is unknown or multifactorial, but a genetic component is suspected in about a third. Other pathogenic influences embody irregular maternal physiology and infection, publicity to medicines and non-prescription medicine, environmental chemical substances and external bodily influences. Extrinsic brokers, particularly chemical compounds, that trigger delivery defects are called teratogens. Toxoplasmosis Maternal infection with the Protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, confers a 20% risk to the fetus through the first trimester, rising to 75% within the second and third trimesters. Rubella(Germanmeasles) Rubella virus causes cardiovascular malformations in 15�20% of all babies infected in the first trimester. It is multifactorial, positively associated with breech birth and neuromuscular disorder and commonest in populations by which babies are swaddled. Maternal illness Diabetesmellitus(see Chapter52) High maternal blood glucose levels in early pregnancy as a end result of Type 1 diabetes mellitus is related to a two- to three-fold improve in congenital abnormalities, including heart disease, neural tube defects, sacral agenesis, femoral hypoplasia, holoprosencephaly and sirenomelia. Congenitalmyotonicdystrophy this will occur in association with hypotonia, respiratory insufficiency, mental retardation and can be deadly (see additionally Chapter 28). Phenylketonuria(see Chapter8) Uncorrected high maternal blood ranges of phenylalanine can cause severe psychological retardation, microcephaly and congenital heart disease. Pyloricstenosis Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pyloric sphincter muscles result in projectile vomiting, constipation and dehydration in early infancy (see Chapter 50). Epilepsy There is a two to 4 instances elevated incidence (to 5�10%) of birth defects in babies uncovered prenatally to antiepileptic medication, and the number increases if more than one drug is used. The really helpful maternal treatment is single drug therapy if possible, avoiding sodium valproate. Other predisposing circumstances are systemiclupuserythematosus and Gravesdisease (see Chapter 65). Arthrogryposis is a heterogeneous group of malformations characterised by stiffness and contracture of the knee, elbow and/or wrist joints and infrequently dislocation of the hips. They are classified as: myopathic; neuropathic; affecting connective tissue; limiting fetal motion. Children born to mothers who consumed excess alcohol during being pregnant can have midface hypoplasia, quick palpebral fissures, a long clean philtrum and delicate developmental delay. Environmentalchemicals Lead, methylmercury and hypoxia are probably the most widely recognized hazards. Physical agents � Prolongedhyperthermia in early pregnancy may cause microcephaly, microphthalmia and neuronal migration defects. Overview the center comes into existence very early in development and, in fact, performs a vitally necessary survival role all through improvement and later life. This signifies that its personal improvement at any explicit time is intrinsically associated to efficiency of its function at the moment. The fluid dynamic forces that exist inside the coronary heart as a result of the blood circulate it constantly maintains are exploited in the further moulding of its type. A major reconstruction happens within the coronary heart and adjacent vessels at start, because the supply of oxygenated blood switches from the placenta to the lungs. Before full closure a new aperture, the ostium secundum, forms dorsally by programmed cell demise within the septum primum. Finally a second interatrial septum forms, the septum secundum, extending down from the roof on the proper facet of the ostium secundum, leaving an oval window known as the foramen ovale. Initial growth During the 2nd week of growth the guts consists of a pair of thin-walled, muscular tubes beneath the ground of the pharynx. Two massive veins deliver blood to the guts and a single giant artery, the truncus arteriosus directs it ahead into the overall circulation. This is initially bifurcated, however the right sinus horn and veins enlarge and turn out to be incorporated into the proper atrium, whereas the left gets obliterated. Septum formation in the atrioventricular canal Up to the top of the 4th week inflowing blood from the sinus venosus passes by way of the big atrioventricular canal instantly into the widespread ventricle. Following this fusion, every endocardial cushion turns into surrounded by proliferating mesenchymal tissue, which then hollows out, leaving robust sheets of connective tissue covered by endothelium, anchored to the ventricular wall by muscular cords. Formation of cardiac septa the most important septa are shaped at 27�37 days by two totally different kinds of course of. At some sites endocardial cushions develop and thicken, narrowing down the channels between them. Septa are also fashioned by enlargement of the lumen of the chamber on both sides, normally at the facet of proliferation of neighbouring tissues. Septum formation within the atrium the frequent atrium turns into divided into left and proper chambers by improvement of vertical septa.
Generic 500 mg azulfidine with visa
It is a reversible inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase pain diagnosis and treatment center tulsa ok cheap azulfidine 500 mg amex, which blocks purine synthesis in T- and B-cell lymphocytes pain treatment wellness center azulfidine 500 mg order online. Six of the 29 liveborn infants had major malformations, including 2 with external auditory canal atresia, 1 with tracheoesophageal fistula, one with hydronephrosis, 1 with an atrial septal defect, and 1 with an occipital meningocele. Cleft lip with or with out cleft palate; thick, everted lower lip; microtia with aural atresia; micrognathia; ocular hypertelorism; arched eyebrows. P�rez-Ayt�s A, et al: In utero exposure to mycophenolate mofetil: A attribute phenotype Jackson P, et al: Intrauterine exposure to mycophenolate mofetil and multiple congenital anomalies in a new child: Possible teratogenic impact, Am J Med Genet A 149A:1231, 2009. Hoeltzenbein M, et al: Teratogenicity of mycophenolate confirmed in a prospective study of the European Network of Teratology Information Services, Am J Med Genet A 158A:588, 2012. A, Newborn with hypertelorism, ptosis of the left eyelid, higher bilateral cleft lip, micrognathia, microtia and absence of the exterior auditory canal. The incidence of problems within the offspring of girls infected with varicella before the 20th week of being pregnant is between 1% and 2%. The occurrence of the fetal varicella syndrome following maternal infection from 20 to 28 weeks has solely rarely been reported. Hypoplasia with or with out rudimentary digits, with or with out paralysis, and atrophy of limb; clubfoot. Although it has previously been advised that nearly all of the survivors have had mental disability with seizures, potential research indicate that a wide spectrum of severity exists for this disorder. Autonomic dysfunction including neurogenic bladder, hydroureter, and esophageal dilatation and reflux resulting in pneumonia, and anal/vesicle sphincter dysfunction. Higa K, et al: Varicella-zoster virus infections throughout pregnancy: Hypothesis in regards to the mechanisms of congenital malformations, Obstet Gynecol sixty nine:214, 1987. Mouly F, et al: Prenatal analysis of fetal varicella-zoster virus an infection with polymerase chain reaction of amniotic fluid in 107 cases, Am J Obstet Gynecol 177:894, 1997. A�C, Note the hydrocephalus, brief limbs with severe neurologic compromise, and cicatricial skin changes in limbs. Although research in the human are limited, issues of development, growth, and dysfunction of the brain much like these seen within the animal research have been documented. The nature of the defects relates to the timing and extent of the hyperthermia somewhat than to its cause. Most of the related instances have been tentatively associated to febrile illness, with the patient having a temperature of 38. The length of the high fever has been 1 day or extra, often several days, which is unusual in the first third of gestation. The illness has various, with influenza, pyelonephritis, and streptococcal pharyngitis being the most common. Two cases have been thought of secondary to severe hyperthermia induced by prolonged sauna bathing (30�45 minutes), and one case was thought to be associated to very extended hot tub bathing. Retrospective human studies of more than one hundred seventy cases of neural tube defect, together with anencephaly, meningomyelocele, and occipital encephalocele, have disclosed an overall historical past of maternal hyperthermia through the week of neural tube closure (21�28 days) in approximately 10% of the circumstances, whereas no such historical past was determined within the controls. These findings are suitable with the speculation that hyperthermia is one cause for neural tube defects in the human. A 14% incidence of "febrile" illness during early pregnancy in the mothers of 113 embryos with neural tube defects who had been aborted therapeutically was documented. The embryos have been obtained via the Congenital Anomaly Research Center of Kyoto University. The history of maternal fever was documented earlier than or instantly after the fetal loss, earlier than the neural tube defect was documented. In addition, a quantity of craniofacial anomalies, including microcephaly, small midface, microphthalmia, micrognathia, and infrequently cleft lip with or with out palate, cleft palate alone, conotruncal heart defects, and ear anomalies, as well as mental disabilities, autism, and hypotonia have been reported. Of importance, the fever-associated autism risk was decreased amongst moms who took antipyretics. A single potential study involving one hundred fifteen pregnant women who reported a fever of 38. The combined prevalence of all main structural malformations was increased however not considerably so in these girls in group 1. In addition, the precise craniofacial anomalies previously documented in retrospective research have been discovered extra incessantly in the offspring of pregnant women in group 1. Reports of Moebius sequence, oromandibular-limb hypogenesis syndrome, and amyoplasia congenita disruption sequence in association with maternal hyperthermia in the second trimester of being pregnant level to a vascular etiology for some hyperthermiarelated defects and counsel that not all antagonistic outcomes are restricted to first-trimester exposure. In addition to potential dysmorphogenesis in early gestation, maternal hyperthermia has been related to a rise in spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, and prematurity. Miller P, et al: Maternal hyperthermia as a possible reason for anencephaly, Lancet 1:519, 1978. Shiota K: Neural tube defects and maternal hyperthermia in early being pregnant: Epidemiology in a human embryo inhabitants, Am J Med Genet 12:281, 1982. Upper left, Encephalocele; maternal historical past of high fever between days 23 and 25 of gestation. Upper proper, An 18-month-old severely retarded boy with hypotonic diplegia, micropenis, unilateral microphthalmia, cleft palate, and micrognathia. Lower left, A 12-year-old severely retarded girl with hypotonic diplegia, midface hypoplasia, micrognathia, incomplete ear morphogenesis, and a cardiac defect. Lower right, A 14-month-old toddler with average hypotonic diplegia and developmental deficiency, who has a hypoplastic midface with gentle ocular hypertelorism, low nasal bridge, and prominent auricles. Also, several of the sufferers described by Senior would possibly symbolize examples of this syndrome. Moderate-to-severe intellectual incapacity, severe speech impairment, moderate-tosevere hypotonia, seizures, autistic options. Mild microcephaly, coarse facies, a wide mouth with full lips, flat nasal bridge, broad nasal tip, anteverted nares, long philtrum, abnormal ears, bushy eyebrows, lengthy eyelashes, periorbital fullness, ptosis, excessive palate. Hypoplastic to absent fifth finger and toenails, with lesser hypoplasia in different digits; absence of terminal phalanges (particularly of the fifth digit); lax joints with radial dislocation at elbow; coxa valga; small patellae. Visual issues, listening to loss, abnormal/ delayed dentition, congenital coronary heart defects Coffin-Siris Syndrome 753 problems and recurrent higher and decrease respiratory tract infections are frequent throughout adolescence. This marked scientific variability and its correlation with particular genotypes needs to be additional investigated. All mutations identified to date follow an autosomal dominant inheritance sample, though autosomal recessive inheritance stays suspected, primarily based on several sibling pairs born to unaffected dad and mom. This situation has marked phenotypic similarities to the Coffin-Siris syndrome, and the 2 conditions have been proven allelic. Senior B: Impaired development and onychodysplasia: Short youngsters with tiny toenails, Am J Dis Child 122:7, 1971. Bodurtha J, et al: Distinctive gastrointestinal anomaly related to Coffin-Siris syndrome, J Pediatr 109: 1015, 1986. Swillen A, et al: the Coffin-Siris syndrome: Data on mental improvement, language, habits and social abilities in 12 children, Clin Genet 48:177, 1995. Coulibaly B, et al: Coffin-Siris syndrome with a number of congenital malformations and intrauterine death: Towards a greater delineation of the severe finish of the spectrum, Eur J Med Genet 53:318, 2010. A�D, Note the coarse face, wide mouth with full lips, long eyelashes, and hypoplastic fifth fingernails. Note the marked similarities to Coffin-Siris syndrome together with the sparse hair, coarse face, extensive mouth with full lips and long eyelashes.