Betnovate
Betnovate dosages: 20 gm
Betnovate packs: 5 creams, 7 creams, 10 creams

Betnovate 20 gm generic mastercard
Nucleophilic attack by the sulfhydryl facet chain of Cys175 on the peptide bond with the previous glycine residue initiates cleavage skin care ingredients 20 gm betnovate safe. Subsequently, a second nucleophilic attack by the hydroxyl group of ldl cholesterol simultaneously forms the cholesteroyl ester of Gly174 and regenerates the free sulfhydryl facet chain of Cys175 retinol 05 acne order 20 gm betnovate overnight delivery. Cleavage is initiated by nucleophilic assault of the sulfhydryl aspect chain of Cys175 on the peptide bond with the preceding glycine residue. A second subsequent nucleophilic attack by the hydroxyl group of cholesterol concurrently forms the cholesteroyl ester of Gly174 and regenerates the free sulfhydryl facet chain of Cys175. The close homology inside and between species between Hedgehog proteins, significantly of their N-terminal signaling domains, means that the processing pathways and buildings found for any Hedgehog protein will doubtless be similar for all relations. The position of lipid modifications in Hedgehog bioactivity continues to be incompletely understood. Although the phenotypes resulting from deficiency of the processing enzymes were beforehand thought to be attributable to lack of product, the possibility must also be considered that an extra of the bioactive precursor may be a contributing factor. In the future, the development of receptor-specific antagonists that recognize alternative peptides derived from hormone precursors may provide new therapies for gastrointestinal diseases. Biogenesis and transport of secretory granules to launch website in neuroendocrine cells. From the Structure and Function of the Ribosome to New Antibiotics (Nobel Lecture). The ribosome as a platform for co-translational processing, folding and targeting of newly synthesized proteins. Signal sequences specify the concentrating on route to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Crystal structure of the complete core of archaeal sign recognition particle and implications for interdomain communication. Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome. Structure of monomeric yeast and mammalian Sec61 complexes interacting with the translating ribosome. Crystallographic evaluation of bacterial signal peptidase in ternary complex with arylomycin A2 and a beta-sultam inhibitor. The crystal structure of yeast protein disulfide isomerase suggests cooperativity between its active websites. Structure of Ero1p, supply of disulfide bonds for oxidative protein folding in the cell. Disruption of Paneth and goblet cell homeostasis and elevated endoplasmic reticulum stress in Af02-02-9780123820266/- mice. Mutational analysis of mouse Wnt-1 identifies two temperature-sensitive alleles and attributes of Wnt-1 protein important for transformation of a mammary cell line. Glycosylation and palmitoylation of Wnt-3a are coupled to supply an energetic type of Wnt-3a. Post-translational palmitoylation and glycosylation of Wnt-5a are essential for its signalling. A superfamily of membrane-bound O-acyltransferases with implications for wnt signaling. The evolutionarily conserved porcupine gene family is involved within the processing of the Wnt family. Skinny hedgehog, an acyltransferase required for palmitoylation and activity of the hedgehog signal. Hhat is a palmitoylacyltransferase with specificity for N-palmitoylation of Sonic Hedgehog. Cholesterol modification of sonic hedgehog is required for long-range signaling activity and effective modulation of signaling by Ptc1. Ghrelin-like peptide with fatty acid modification and O-glycosylation within the pink stingray, Dasyatis akajei. Tyrosine sulfation: an more and more recognised post-translational modification of secreted proteins. Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase: purification and molecular cloning of an enzyme that catalyzes tyrosine O-sulfation, a standard posttranslational modification of eukaryotic proteins. Catalytic Mechanism of Golgi-Resident Human Tyrosylprotein Sulfotransferase-2: A Mass Spectrometry Approach. Reduced body weight and increased postimplantation fetal dying in tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-1-deficient mice. Targeted disruption of tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2, an enzyme that catalyzes post-translational protein tyrosine O-sulfation, causes male infertility. A mutation in Tpst2 encoding tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase causes dwarfism related to hypothyroidism. Impaired insulin secretion from the pancreatic islets of hypothyroidal growth-retarded mice. Sequence Analysis of the Human Tyrosylprotein Sulfotransferase-2 Gene in Subjects with Chronic Pancreatitis. Role of tyrosine sulfation and serine phosphorylation in the processing of procholecystokinin to amidated cholecystokinin and its secretion in transfected AtT-20 cells. Modulation of the cleavage of the gastrin precursor by prohormone phosphorylation. Discrimination between temperature- and brefeldin A-sensitive steps in the sulfation, phosphorylation, and cleavage of progastrin and its derivatives. Neuroendocrine protein 7B2 can be inactivated by phosphorylation inside the secretory pathway. Chromogranin A: a model new proposal for trafficking, processing and induction of granule biogenesis. Chromogranin A, an "on/ off" switch controlling dense-core secretory granule biogenesis. Secretory granule biogenesis and neuropeptide sorting to the regulated secretory pathway in neuroendocrine cells. Hypertension from focused ablation of chromogranin A may be rescued by the human ortholog. Targeted ablation of the chromogranin a (Chga) gene: regular neuroendocrine dense-core secretory granules and increased expression of other granins. The significance of chromogranin A within the improvement and function of endocrine pancreas. Chromogranin A promotes peptide hormone sorting to cell granules in constitutively and regulated secreting cells: role of conserved N- and C-terminal peptides. Determinants for chromogranin A sorting into the regulated secretory pathway are also enough to generate granule-like buildings in non-endocrine cells. Carboxypeptidase E cytoplasmic taildriven vesicle transport is essential for activity-dependent secretion of peptide hormones. Molecular mechanism of attachment strategy of densecore vesicles to the plasma membrane in neuroendocrine cells.
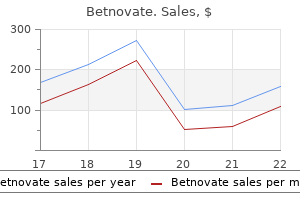
Discount betnovate 20 gm
Membrane-anchored heparin-binding epidermal growth factorlike growth factor acts as a tumor survival factor in a hepatoma cell line skin care untuk kulit berminyak betnovate 20 gm online buy cheap. The membrane-bound form of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like development factor promotes survival of cultured renal epithelial cells acne holes in face cheap 20 gm betnovate. Expression of heparin-binding epidermal growth consider human hepatocellular carcinoma. Epidermal progress factor and betacellulin mediate signal transduction by way of co-expressed ErbB2 and ErbB3 receptors. The oncogenic ErbB-2/ErbB-3 heterodimer is a surrogate receptor of the epidermal progress issue and betacellulin. ErbB2 expression will increase the spectrum and efficiency of ligandmediated signal transduction through ErbB4. Identification of betacellulin as a significant peptide progress think about milk: purification, characterization and molecular cloning of bovine betacellulin. Autocrine reworking progress factor alpha is dispensible for v-rasHa-induced epidermal neoplasia: potential involvement of alternate epidermal progress factor receptor ligands. ErbB signaling regulates lineage determination of growing pancreatic islet cells in embryonic organ tradition. Betacellulin protects from pancreatitis bu acitvation stress-activated protein kinase. Specific transgene esxpression in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under the management of the porcine insulin promoter. Betacellulin stimulates the expansion of the mouse intestinal epithelium and increases adenoma multiplicity in Apc /Min mice. A novel epidermal development factor with mitogenic activity for rat main hepatocytes. Epiregulin, a novel member of the epidermal growth issue family, is an autocrine development factor in regular human keratinocytes. Epiregulin stimulates proliferation of rabbit gastric cells in main tradition via autophosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mechanism of development promoting exercise of epiregulin in main cultures of rat hepatocytes. Involvement of deregulated epiregulin expression in tumorigenesis in vivo by way of activated Ki-Ras signaling pathway in human colon most cancers cells. Epiregulin is up-regulated in pancreatic cancer and stimulates pancreatic most cancers cell progress. Epiregulin is a potent pan-ErbB ligand that preferentially activates heterodimeric receptor complexes. Activation of ErbB4 by the bifunctional epidermal progress factor household hormone epiregulin is regulated by ErbB2. Epiregulin binds to epidermal progress factor receptor and ErbB-4 and induces tyro- 460. Cloning and biological activity of epigen, a novel member of the epidermal development factor superfamily. Epigen: the final ligand of ErbB receptors reveals intricate relationships between affinity and mitogenicity. Role of the juxtamembrane domains of the reworking growth factor-alpha precursor and the beta-amyloid precursor protein in regulated ectodomain shedding. Diverse cell surface protein ectodomains are shed by a system delicate to metalloprotease inhibitors. The shedding of membrane-anchored heparin-binding epidermal-like growth factor is regulated by the Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade and by cell adhesion and spreading. Metalloprotease-mediated ligand release regulated autocrine signaling through the epidermal development factor receptor. Take your partners, please�signal diversification by the erbB household of receptor tyrosine kinases. Crystal structure of the complicated of human epidermal progress factor and receptor extracellular domains. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the operate of regular epidermal development issue receptors by heterodimerization. All ErbB receptors aside from the epidermal development issue receptor are endocytosis impaired. Polyubiquitination of the epidermal progress factor receptor happens on the plasma membrane upon ligand-induced activation. Epidermal development factor: organic activity requires persistent occupation of high-affinity cell surface receptors. Epidermal development factor receptors: critical mediators of multiple receptor pathways. Increasing complexity of Ras sign transduction, involvement of Rho household proteins. Renewing the conspiracy theory debate: does Raf perform alone to mediate Ras oncogenesis. A Raf-independent epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine loop is necessary for Ras transformation of rat intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogenic Ha-Ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activity requires signaling Chapter eight Growth Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract 259 through the epidermal progress factor receptor. Phospholipase C-gamma1 is a guanine nucleotide change issue for dynamin-1 and enhances dynamin-1-dependent epidermal progress issue receptor endocytosis. Increase of the catalytic exercise of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Epidermal development factor receptor-stimulated intestinal epithelial cell migration requires phospholipase C exercise. Signailing through the epidermal progress factor receptor in the course of the improvement of malignancy. Diverse expression of ErbB receptor proteins throughout rat liver growth and regeneration. Hepatic sequestration and biliary secretion of epidermal progress factor: proof for a high-capacity uptake system. The effect of concentration on hepatic transport of exogenous epidermal growth issue. Epidermal growth issue influences cell proliferation, glycoproteins, and lipase exercise in human fetal abdomen. Epidermal progress factor receptors in most cancers tissues of esophagus, lung, pancreas, colorectum, breast and abdomen. Differential response to keratinocyte progress issue receptor and epidermal growth issue receptor ligands of proliferating and differentiating intestinal epithelial cells. Developmental regulation of epidermal progress factor receptor kinase in rat intestine. Receptor-mediated vectorial transcytosis of epidermal progress factor by Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.
Diseases
- Silver Russell syndrome
- Hypertensive retinopathy
- Arthrogryposis like hand anomaly sensorineural
- Staphylococcal infection
- Dementia, alcohol
- Pitt Rogers Danks syndrome
- Oculodentoosseous dysplasia recessive
- Acrocephalosyndactyly Jackson Weiss type
Betnovate 20 gm discount with amex
A layer of mesoderm, the urorectal septum, separates the regi�n between the allantois and hindgut skin care 5-8 years trusted betnovate 20 gm. This septum is derived from a wedge of mesoderm between the allantois and hindgut skin care korea yang bagus betnovate 20 gm online buy cheap. As the embryo grows and caudal folding contin �es, the tip of the urorectal septum comes to lie ci�se to the cloacal membrane. At the top of the seventh week, the cloacal mem brane ruptures, creating the anal opening for the hindgut and a ventral opening for the urogenital sinus. The upper part (two-thirds) of the anal canal is derived from endoderm of the hindgut; the lower half (one-third) is derived from ectoderm around the proctodeum. Ectoderm in the regi�n of the proctodeum on the surface of a half of the cloaca proliferates and invaginates to create the anal pit. Subsequently, degeneration of the cloacal membrane (now called the anal membrane) establishes continuity between the higher and decrease components of the anal canal. However, the cranial a part of the anal canal originates from endoderm and is due to this fact equipped by the superior rectal artery, a continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery, the artery of the hindgut. The junction between the endodermal and ectodermal regions of the anal canal is delineated by the pectinate line, just below the anal columns. At this line, the epithelium modifications from columnar to stratified squamous epithelium. Then, differentiation of the intestine and its derivatives relies upon upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endo derm (epithelium) and its surrounding meso derm (an epithelial-mesenchymal interaction). Chapter 15 � Digestive System craniocaudal group of the gut and its derivatives. The pharyn geal gut gives rise to the phaiynx and related glands (see Chapter 17). The foregut provides rise to the esophagus, the trachea and lung buds, the abdomen, and the duodenum proximal to the entrance of the bile duct. In addition, the liver, pancreas, and biliary apparatus develop as outgrowths of the endodermal epithelium of the higher a half of the duodenum. Because the higher a half of the foregut is split by a septum (the tracheoesophageal septum) into the esophagus posteriorly and the trachea and lung buds anteriorly, deviation of the septum could result in irregular openings between the trachea and esophagus. The epithelial liver cords and biliary system growing out into the septum transversum. Hematopoietic cells (present within the liver in greater numbers earlier than birth than afterward), the KupfFer cells, and connective tissue cells orig�nate within the mesoderm. The pancreas develops from a ventral bud and a dorsal bud that later fuse to kind the definitive pancreas. Sometimes, the two elements encompass the duodenum (annular pancreas), causing constriction of the intestine. At its apex, the primary loop stays briefly in open connection with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct. During the sixth week, the loop grows so quickly that it protrudes into the umbilical wire (physiological herniation). While these processes are occurring, the midgut loop rotates 270� counterclockwise. Remnants of the vitelline duct, failure of the midgut to return to the abdominal cavity, malrotation, stenosis, and duplication of components of the gut are common abnormalities. The hindgut offers rise to the regi�n from the distal third of the transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal; the distal a half of the anal canal originates from ectoderm. The hindgut enters the posterior regi�n of the cloaca (fiiture anorectal canal), and the allantois enters the anterior regi�n (future urogenital sinus). Abnormalities in the measurement of the posterior regi�n of the cloaca shift the doorway of the anus anteriorly, inflicting rectovaginal and rectourethral f�stulas and atresias. The anal canal itself is derived from endoderm (cranial part) and ectoderm (caudal part). Thus, the cranial part is supplied by the superior rectal artery from the inferior mesenteric artery, the artery of the hindgut, whereas the caudal part is supplied by the inferior rectal artery, a department of the internal pudendal artery. Prenatal ultrasound showed polyhydramnios at 36 weeks, and at delivery, the infant had extreme fluids in its mouth and issue respiration. Prenatal ultrasound at 20 weeks revealed a midline mass that appeared to contain intestines and was membrane-bound. Both develop from a typical mesodermal ridge (intermed�ate mesoderm) along the pos terior wall of the belly cavity, and initially, the excretory ducts of each techniques enter a common cavity, the cloaca. Pronephros At the start of the fourth week, the pro nephros is represented by 7 to 10 stable cell groups within the cervical regi�n. These groups form vestigial excretory units, nephrotomes, that regress earlier than extra caudal ones are shaped. By the tip of the fourth week, all indications of the pronephric system have disappeared. Mesonephros the mesonephros and mesonephric ducts are derived from intermed�ate mesoderm from upper thoracic to upper lumbar (L3) segments. Early within the fourth week of improvement, throughout regression of the pronephric system, the first excretory tubules of the meso nephros appear. Chapter16 � Urogenital System Segmented intermediate mesoderm (pronephric system) Vestigial pronephric system Vitelline duct Unsegmented intermediate mesoderm (mesonephric system) Mesonepliric excretory items Mesonephric duct �5U. Laterally, the tubule enters the longitu dinal accumulating duct known as the mesonephric or Wolffian duct. In the middle of the second month, the meso nephros forms a big ovoid organ on each side of the midline. Because the creating gonad is on its medial aspect, the ridge shaped by both organs is identified as the urogenital ri(^e. While caudal tubules are still differentiating, cranial tubules and glomeruli show degenerative adjustments, and by the tip of the second month, the bulk have disappeared. In the male, a few of the caudal tubules and the mesonephric duct persist and partic�pate in formation of the genital system, but they disappear within the female. M etanephros: the D efinitive Kidney the third urinary organ, the metanephros or permanent kidney, appears within the fifth week. Collecting System Collecting ducts of the everlasting kidney de velop from the ureteric bud, an outgrowth of the mesonephric duct ci�se to its entrance to the cloaca. The bud penetrales the meta nephric tissue, which is molded over its distal end as a cap. Subsequently, the bud dilates, forming the primitive renal pelvis, and splits into cranial and caudal portions, the longer term major calyces. These buds con tinu� to subdivide until 12 or more generations of tubules have fashioned. The tubules of the second order enlarge and absorb those of the third and fourth generations, forming the minor calyces of the renal pelvis.
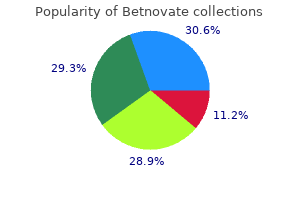
Discount 20 gm betnovate overnight delivery
The thoracic cavity is split into the pericardial cavity and two pleural cavities for the lungs by the pleuropericardial membranas acne genetics betnovate 20 gm generic mastercard. An autopsy reve�is a big dia phragmatic defect on the left aspect, with the stomach and the intestines occupying the left facet of the thorax skin care jakarta selatan betnovate 20 gm purchase on-line. It is characterised by m aturation of tissues and organs and speedy progress of the physique. These m easurements, expressed in centim eters, are correlated with the age of the fetus in weeks or m onths (Table 8. Growth in length is particularly hanging in the course of the third, fourth, and fifth m onths, whereas a rise in weight is m ost hanging over the last 2 m onths of gestation. For the needs of the following dialogue, age is calculated from the time of fertilization and is expressed in weeks or calendar m onths. One of probably the most putting adjustments happening throughout fetal life is the relative slowdown in development of the pinnacle in contrast with the remainder of the body. The eyes, initially directed laterally, transfer to the ven tral facet of the face, and the ears come to lie ci�se to their definitive position along side the head. The limbs reach their relative size in comparison with the relaxation of the physique, though the lower limbs are still somewhat shorter and less well developed than the upper extremities. Prim ary ossif�cation facilities are present in the lengthy bones and cranium by the twelfth week. Also by the 12th week, exterior genitalia develop to such a level that the sex of the fetus may be determined by external examination (ultrasound). During the sixth week, intestinal loops cause a big swelling (herniation) in the umbilical cord, however by the 12th week, the loops have withdrawn into the abdominal cavity. At the tip of the third month, reflex activity could be evoked in aborted fetuses, indicating muscular exercise. The weight of the fetus will increase lit�e during this period and by the tip of the fifth month continues to be < 500 g. The fetus is roofed with fine hair, known as lanugo hair; eyebrows and head hair are also seen. One facet of the chorion has many villi (chorion frondosum], whereas the other facet is almost clean [chorion laeve]. During the sixth m onth, the pores and skin of the fetus is reddish and has a wrinkled appearance due to the lack of underlying connective tissue. Time of Birth the date of start is most precisely indicated as 266 days, or 38 weeks, after fertilization. The oocyte is normally fertilized inside 12 hours of ovulation; nevertheless, sperm deposited in the reproductive tract up to 6 days prior to ovulation can survive to fertilize oocytes. Thus, most pregnancies occur when sexual activity occurs inside a 6-day period that ends on the day of ovulation. A pregnant girl normally will see her obstetrician when she has missed two successive menstrual bleeds. In girls with common 28-day m en strual intervals, the strategy is pretty correct, however when cycles are irregular, substantial miscalculations may be made. An further complication happens when the girl has some bleeding about 14 days after fertilization as a outcome of erosive activity by the implanting blastocyst (see Chapter four, "Day thirteen," p. By combining knowledge on the onset of the last menstrual interval with fetal length, weight, and different morphological traits typical for a given m onth of improvement, a reasonable estimate of the age of the fetus could be formulated. An correct willpower of fetal dimension and age is necessary for managing being pregnant, especially if the m different has a small pelvis or if the baby has a delivery defect. Some developmental occasions occurring through the first 7 months are indicated in Table 8. During the final 2 months, the fetus obtains well-rounded contours as the outcome of deposition of subcutaneous fats. By the tip of intrauterine Ufe, the pores and skin is roofed by a whitish, fatty substance (vernix caseosa) composed of secretory merchandise from sebaceous glands. At the end of the ninth m onth, the skull has the most important circumference of all parts of the physique, an essential reality with regard to its passage via the start canal. As the fetus begins the ninth week of development, its calls for for nutri tional and different components enhance, causing main adjustments within the placenta. Foremost among these is an increase in floor area between maternal and fetal components to facil�tate exchange. The disposition of fetal membranes can also be altered as manufacturing of amniotic fluid will increase. Changes within the Trophoblast the fetal element of the placenta is derived from the trophoblast and extraembryonic mesoderm (the chorionic p�ate); the maternal compo nent is derived from the uterine endometrium. By the beginning of the second month, the tro phoblast is characterized by a great quantity of secondary and tertiary villi, which give it a radial look. Stem (anchoring) villi lengthen from the mesoderm of the chorionic p�ate to the cytotrophoblast shell. The capillary system creating within the core of the villous stems quickly comes in contact with capillaries of the cho rionic p�ate and connecting stalk, thus giving rise to the extraembryonic vascular system. To accomplish this process, cytotropho blast ceUs endure an epithelial-to-endothelial transition. Invasi�n of the spiral arteries by cytotrophoblast cells transforms these vessels from small-diameter, high-resistance vessels to larger diameter, low-resistance vessels that may provide elevated portions of maternal blood to intervillous areas. During the following months, numerous small extensions grow out from present stem villi and lengthen as free villi into the surrounding lacunar or intervillous spaces. The syncytium and endothe lial wall of the blood vessels are then the only layers that separate the maternal and fetal circulations. Frequently, the syncytium turns into very skinny, and large pieces containing a number of nuclei may break o �f and drop into the intervillous blood lakes. These pieces, generally identified as syncytial knots, enter the maternal circulation and normally degenerate with out causing any signs. Cytotrophoblast Shell Spiral artery Intervillous area Blood vessel Cytotrophoblast^ Barrierformed by 1. The extraembryonic mesoderm penetrales the stem villi within the course of the decidual p�ate. In many small villi, the wall of the capillaries Is in direct contact with the syncytium. As pregnancy advances, villi on the embryonic pole continu� to develop and increase, giving rise to the chorion �rondosum (bushy chorion). Villi on the abembryonic pole degenerate, and by the third month, this facet of the chorion, now known as the chorion laeve, is smooth. The difFerence between the embryonic and abembryonic poles of the chorion is also reflected within the construction of the decidua, the ftinctional layer of the endometrium, which is shed during parturition. The decidua over the cho rion frondosum, the decidua basalis, consists of a compact layer of enormous cells, decidual cells, with plentiful amounts of lipids and glycogen. With growth of the chorionic vesicle, this layer turns into stretched and degenerates.

20 gm betnovate purchase visa
Expression of reworking development factor alpha in human tissues: immunohistochemical examine and northern blot evaluation acne rash betnovate 20 gm buy free shipping. Transforming growth factor alpha: expression, regulation, and organic activities acne causes 20 gm betnovate order overnight delivery. Differential regulation of remodeling development factor alpha autoinduction in a nontransformed and transformed epithelial cell. Epidermal development factor and insulin-like progress factor I upregulate the expression of the epidermal development factor system in rat liver. Transforming progress factor alpha could additionally be a physiological regulator of liver regeneration by the use of an autocrine mechanism. The coupling between transforming progress factor-alpha and the epidermal development issue receptor during rat liver regeneration. Type beta reworking progress factor reversibly inhibits the early proliferative response to partial hepatectomy within the rat. Transforming growth issue alpha levels in liver and blood correlate better than hepatocyte progress issue with hepatocyte proliferation throughout liver regeneration. Liver regeneration and hepatocarcinogenesis in remodeling growth factor-alpha-targeted mice. Evolution of neoplastic growth in the liver of transgenic mice co-expressing c-myc and remodeling growth factor-alpha. Transforming development factoralpha and epidermal progress issue receptor in chronic liver illness and hepatocellular carcinoma. Differential binding and organic activities of epidermal progress issue and transforming progress issue alpha in a human pancreatic cancer cell line. Trophic motion of epidermal growth issue on the pancreas and gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. Insulin, remodeling progress elements, and substrates modulate progress of guinea pig pancreatic duct cells in vitro. Production of remodeling development factor alpha in human pancreatic cancer cells: proof for a superagonist autocrine cycle. Serum levels of remodeling progress factor alpha in gastrointestinal cancer patients. Malignant transformation of duct-like cells originating from acini in remodeling development factor transgenic mice. Transforming development factor alpha dramatically enhances oncogene-induced carcinogenesis in transgenic mouse pancreas and liver. A murine tumor progression model for pancreatic cancer recapitulating the genetic alterations of the human disease. Expansion of Pdx1-expressing pancreatic epithelium and islet neogenesis in transgenic mice overexpressing remodeling progress issue alpha. Analysis of expression profiles of islet-associated transcription and development factors throughout beta-cell neogenesis from duct cells in partially duct-ligated mice. Transgenic expression of epidermal progress issue and keratinocyte growth factor in beta-cells results in substantial morphological adjustments. Transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal progress issue expression in human fetal gastrointestinal tract. Immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor alpha in the growing rat colon. Developmental expression of reworking progress factor-alpha and epidermal development factor receptor proteins within the human pancreas and digestive tract. Paracrine motion of reworking development factor-alpha in rectal crypt epithelium of people. Increased expression of transforming development factor-alpha and epidermal progress issue receptors in rat continual reflux esophagitis. Transforming progress factor alpha and epidermal growth factor ranges in regular human gastrointestinal mucosa. Transforming progress issue alpha expression in regular gastric mucosa, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia and gastric carcinoma�an immunohistochemical study. Immunolocalization of transforming development factor-alpha in regular and diseased human gastric mucosa. Differential distribution of reworking growth factor-alpha immunohistochemistry inside whole gastric mucosa in rats. Specificity of the localization of transforming progress factor-alpha immunoreactivity in colon mucosa. Basolateral sorting of remodeling progress factor-alpha precursor in polarized epithelial cells: characterization of cytoplasmic domain determinants. Myristoylated Naked2 escorts remodeling progress factor alpha to the basolateral plasma membrane of polarized epithelial cells. Trophic impact of multiple development elements in amniotic fluid or human milk on cultured human fetal small intestinal cells. Mitogenic response of canine fundic epithelial cells in short-term culture to transforming development factor alpha and insulinlike growth factor I. Anti-sense reworking growth factor a oligonucleotides inhibit autocrine stimulated proliferation of a colon carcinoma cell line. Establishment of conditionally immortalized epithelial cell traces from both colon and small gut of grownup H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mice. Metalloproteinases and reworking progress factor-alpha mediate substance P-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and proliferation in human colonocytes. Effects of epidermal growth issue and dimethylhydrazine on crypt size, cell proliferation, and crypt fission within the rat colon. Effects of intraluminal epidermal progress factor on mucosal proliferation in the small intestine of adult rats. Increased intestinal epithelial proliferation in metallothioneinetransforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Overexpression of epidermal development issue induced hypospermatogenesis in transgenic mice. Intravenous epidermal progress factor/urogastrone increases small-intestinal cell proliferation in congenital microvillous atrophy. Enhancement of intestinal growth in neonatal rats by epidermal development consider milk. Epidermal growth factor reduces the development of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Transepithelial transport of epidermal progress factor by absorptive cells of suckling rat ileum. Urogastrone-epidermal growth issue is trophic to the intestinal epithelium of parenterally fed rats. Cell proliferation in the small gut and colon of intravenously fed rats: effects of urogastroneepidermal development factor.
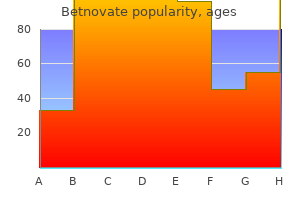
Cheap betnovate 20 gm visa
Differential methylation of tissue- and cancer-specific CpG island shores distinguishes human induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem cells and fibroblasts skin care zamrudpur 20 gm betnovate purchase visa. A potential cohort study shows distinctive epigenetic, genetic, and prognostic features of synchronous colorectal cancers skin care lounge generic betnovate 20 gm without a prescription. The human colon cancer methylome reveals comparable hypo- and hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores. Helicobacter pylori an infection promotes methylation and silencing of trefoil issue 2, leading to gastric tumor development in mice and humans. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency and low dietary folate reduce tumorigenesis in Apc min/ mice. Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel illness reveal innate, adaptive, and regulatory mechanisms of host dialogue with the microbiota. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine intestine microbiome independently of weight problems. Metagenomic approaches for defining the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel ailments. Ten years of genetics and genomics: what have we achieved and where are we heading Association of cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype with the antiplatelet effect and medical efficacy of clopidogrel remedy. Chapter four Signaling Pathways Induced by G-protein-coupled Receptors Enrique Rozengurt 4. It is estimated that over half of all pharmaceuticals currently in the marketplace act by concentrating on these receptors directly or indirectly. It is likely that these research will determine potential targets and suggest novel strategies for therapeutic interventions. In addition to biophysical techniques and mutation evaluation, numerous crystal buildings have been solved confirming the elemental seven-transmembrane area structure of those receptors, also revealing possible sites for the binding of agonistic ligands and allosteric modifiers. Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins), composed of -, -, and -subunits, transduce exterior indicators from heptahelical receptors to intracellular effectors. G proteins are categorised in accordance with their -subunits into 4 subfamilies: Gs, Gi, Gq, and G12. Depending on the particular G, a discrete number of downstream signaling effectors are engaged. Chapter four Signaling Pathways Induced by G-protein-coupled Receptors 77 activation into biological responses, together with mitogenesis. Indeed, several ligands and receptors have been identified that preferentially sign through both G-protein- or -arrestin-mediated pathways. The amplitude and frequency of the Ca2 oscillations encode necessary organic information implicated within the regulation of mitochondrial activity, differential gene expression, and cell proliferation. Specifically, cell exposure to insulin rapidly enhanced signaling produced by agonists that act through Gq-coupled heptahelical receptors. These -subunits interact with downstream targets that regulate cell morphology, migration, and proliferation. The exact role of Ser-910 phosphorylation stays unclear, with a latest report suggesting that it plays an inhibitory position in Ras-transformed cells. A current systematic characterization of somatic mutations in cancer genomes has revealed mutations and amplifications of Gs in quite lots of human cancers. Interestingly, Rap1, a member of the Ras household initially identified as an inhibitor of Raf-1/Ras interplay, appears to stimulate B-Raf exercise in cells that categorical this member of the Raf family. The Rb pocket proteins (pRb, p107, and p130) play a crucial position in G1/S development, no much less than in part, through binding and inactivation of factors. Many of the pathways concerned are additionally engaged by tyrosine kinase agonists, offering ample potentialities for cross talk. A main task for the lengthy run shall be to establish all the contributing molecules, define their useful importance, and elucidate the spatio-temporal relationships within this complicated signaling network. The writer thanks James Sinnett-Smith for important reading of the manuscript and for his invaluable help in the preparation of the figures. Signal transduction pathways in the mitogenic response to G protein-coupled neuropeptide receptor agonists. Lysophospholipids and their G protein-coupled receptors in inflammation and immunity. Protease-activated receptor signalling, endocytic sorting and dysregulation in most cancers. Growth of small cell lung most cancers cells: stimulation by multiple neuropeptides and inhibition by broad spectrum antagonists in vitro and in vivo. Identification of a receptor for peptides of the bombesin household in Swiss 3T3 cells by affinity cross-linking. Convergent signalling within the motion of integrins, neuropeptides, progress factors and oncogenes. Autocrine loops, signal transduction, and cell cycle abnormalities in the molecular biology of lung most cancers. Cell development control by G protein-coupled receptors: from signal transduction to sign integration. Roles of G-protein-coupled receptor signaling in most cancers biology and gene transcription. Leucine-rich repeat-containing g-proteincoupled receptors as markers of adult stem cells. G Protein-coupled receptor oligomerization: implications for g protein activation and cell signaling. Heterodimerization of G proteincoupled receptors: specificity and useful significance. Recommendations for the recognition and nomenclature of g proteincoupled receptor heteromultimers. Regulated dimerization of the thyrotropinreleasing hormone receptor impacts receptor trafficking however not signaling. A monomeric G protein-coupled receptor isolated in Chapter four Signaling Pathways Induced by G-protein-coupled Receptors 89 41. Rescue of defective G protein�"coupled receptor function in vivo by intermolecular cooperation. Mapping allosteric connections from the receptor to the nucleotidebinding pocket of heterotrimeric G proteins. Receptor-mediated activation of heterotrimeric g-proteins: current structural insights. Loss of affiliation between activated G[alpha]q and G[beta][gamma] disrupts receptor-dependent and receptor-independent signaling. Ric-8A potentiates Gq-mediated signal transduction by appearing downstream of G protein-coupled receptor in intact cells. Seven transmembrane receptors as shapeshifting proteins: the impression of allosteric modulation and functional selectivity on new drug discovery.
Cistus ladaniferus (Labdanum). Betnovate.
- Bronchitis, diarrhea, edema, hernia, leprosy, hardening of the spleen, expelling mucus from the chest, use as a stimulant, emptying and cleansing the bowel, stopping or preventing bleeding, and other uses.
- How does Labdanum work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Labdanum?
- Dosing considerations for Labdanum.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96307
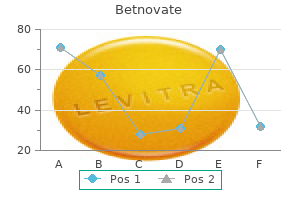
Purchase 20 gm betnovate with amex
An inverted V is thus created on the malar eminence; the left and right hyperlinks are the second and third cuts, respectively acne keloidalis treatment betnovate 20 gm quality. The fourth cut extends through the orbital floor of the frontal bone posteriorly toward the superior orbital fissure acne jawline generic betnovate 20 gm with mastercard. If more medial entry is required, the supraorbital nerve can be mobilized from its foramen with an osteotome. If the foramen is excessive above the orbital rim, the nerve can be sacrificed, but brow numbness will result. It extends posteriorly from the inferior orbital fissure across the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and thru the posterior orbit. Alternatively, it can connect the fourth and fifth cuts simply proximal to the superior orbital fissure. A rongeur can be utilized to take away the residual bony island of the larger wing of the sphenoid until the dural fold of the superior orbital fissure is identified. Importantly, the orbitozygomatic method may be tailored to go well with individual circumstances (modified orbitozygomatic approach) when a lesion requires much less rostral visualization. However, for many deep-seated lesions, full elimination of the orbital roof and zygoma is indicated. To guarantee exact reapproximation at closure, holes can be drilled for a cranial fixation plate earlier than the osteotomy is removed. Tacking sutures are placed deep towards the orbital apex and anchored around the safe fishhooks. The operating microscope is then introduced into the sphere, and a transsylvian or subtemporal approach is undertaken in atraumatic style. The working distance to lesions in the parasellar area and the interpeduncular fossa is about 3 cm shorter with an orbitozygomatic method than with a standard frontotemporal approach. A extra upward and oblique view of the sylvian fissure, third ventricle, and higher brainstem can be achieved with much less retraction on the temporal and frontal lobes. Patients ought to be forewarned of great postoperative periorbital edema and diplopia, which often resolve inside per week. On postoperative day 1, sufferers can start jaw workout routines to avoid restricted range of motion of the temporomandibular joint because of scarring of the temporomandibular ligament and joint capsule. Atrophy of the temporalis muscle may be minimized by utilizing monopolar cauterization judiciously and by reapproximating the superior aspect of the temporalis muscle to a small muscle cuff of fascia left alongside the superior temporal line. The patient may be positioned lateral, susceptible, or supine with a sandbag beneath the ipsilateral shoulder. In the supine position, the head is turned flat, parallel with the floor, and the neck is flexed such that a finger can be placed between the mandible and clavicle. Excessive rotation or flexion during positioning could cause neurovascular compromise, particularly in sufferers with extracranial carotid illness or degenerative cervical spondylosis. Alternatively, the affected person can be positioned susceptible or within the lateral decubitus place. The skin incision starts above the auricle and curves behind the ear inferiorly four to six cm behind the mastoid and 6 to 8 cm behind the exterior auditory canal. Inferiorly, it extends just under the mastoid tip into the sternocleidomastoid muscle. If the incision is positioned too far anteriorly, the scalp, muscle, and bone obscure visualization of the cerebellopontine angle. Surgical judgment ought to all the time prevail inasmuch as the surgeon must be familiar with surface skull landmarks that approximate the locations of the major sinuses. The asterion is an unreliable external landmark for the transverse-sigmoid junction, however a line drawn from the root of the zygoma to the inion (the superior nuchal line) is an efficient approximation of the transverse sinus. Typically, the transverse-sigmoid junction is avoided by inserting the burr gap beneath this line, 2 cm under the asterion, two thirds of it behind and a 3rd of it in front of the occipitomastoid suture. After the burr gap is accomplished, a craniotomy may be customary behind the sigmoid sinus and under the transverse sinuses. The bone up to the transverse and sigmoid sinuses may be rongeured to reveal their edges. Alternatively, the mastoid air cells may be drilled immediately to expose the sigmoid and transverse sinuses and then the craniotomy could be performed. The bone over the sigmoid and transverse sinuses may be drilled, first with a chopping burr and then with a diamond burr, and a skinny shell of internal cortical bone left. The remaining thin shell of bone can be removed safely with a Penfield dissector or curet. Alternatively, a small linear incision, angled within the course of the jugular bulbar, can be remodeled the cerebellar hemisphere. After the cerebellum is relaxed, the dural opening is completed in a curvilinear trend with its base on the transverse-sigmoid junction. Intradurally, the junction of the tentorium and petrous bone on the superior and lateral extents of the dural opening should be visualized. FarLateralApproach the far lateral or transcondylar method has several modifications and variations. It basically entails a partial condylectomy, with or without resection of the lateral mass of C1. This strategy permits the surgeon to attain an anterolateral trajectory to the brainstem, and it eliminates the necessity to traverse contaminated mucosal structures through the transoral or transfacial route. First described by Heros26 and later modified by Spetzler and Grahm,27 this method provides access to lesions of the vertebrobasilar junction, inferolateral pons, anterolateral medulla, and upper cervical spinal wire. Its potential disadvantages include craniocervical instability, vertebral artery injury, wound infection, meningitis, or decrease cranial nerve deficits. Various positions, together with the modified park bench, sitting, lateral decubitus, supine with the pinnacle rotated, and lateral or half-lateral decubitus, have been used with this approach. At our institution, we prefer a modified park bench position by which the operating table is extended 10 to 20 cm by inserting a rigid plastic board underneath the mattress. The dependent arm is cradled in a padded sling between the desk edge and the Mayfield head holder (Codman, Inc. The clivus is introduced perpendicular to the ground by performing 4 maneuvers on the neck: (1) flexion within the anteroposterior aircraft until the chin is one fingerbreadth from the clavicle, (2) rotation 45 degrees contralateral to the side of the lesion, (3) lateral flexion 30 degrees down toward the other shoulder (also the floor), and (4) slight distraction to extend the interval between the foramen magnum and C1 so that the surgeon can look down the axis of the brainstem and work between the horizontally oriented cranial nerves. The ipsilateral shoulder must also be retracted inferiorly with material tape to permit larger freedom of movement with the microscope. The affected person ought to be taped securely to the bed to permit frequent and excessive rotation. Multiple pores and skin incisions have been described, together with the hockey-stick, lazy S, and simple paramedian linear incision. The conventional hockey-stick skin incision begins in the midline at C2 or C3, proceeds superiorly, and curves anteriorly and laterally to the mastoid tip. Monopolar cauterization is used to develop a aircraft below the superficial muscle fascia. A small muscle cuff is cut and left hooked up to the superior nuchal line for reapproximation of the fascia and muscles on the finish of the process. Muscle is then stripped off the laminae of C1 and C2 with a Penfield dissector or gauze sponge.
Betnovate 20 gm discount overnight delivery
Moreover, the proposed similarity of colon most cancers stem cells with normal intestinal stem cells may present an excellent problem in the design of therapies that may eradicate colorectal cancer whereas preserving the adult intestinal stem cells required for continued repopulation of the intestinal epithelium skin care yang aman 20 gm betnovate discount with visa. If the parallel between these two stem cells extends to Notch regulatory components, focused Notch therapies for colon cancer might also be expected to focus on normal tissue because Notch is centrally essential for a quantity of elements of epithelial cell homeostasis skin care jerawat discount betnovate 20 gm free shipping. Character modifications attributable to mutation of a whole region of a Chromosome in Drosophila. Chromosomal deficiencies and the embryonic improvement of Drosophila Melanogaster. Making a distinction: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. The Abruptex domain of Notch regulates negative interactions between Notch, its ligands and Fringe. Effects of S1 cleavage on the construction, floor export, and signaling exercise of human Notch1 and Notch2. Hartmann D, de Strooper B, Serneels L, Craessaerts K, Herreman A, Annaert W, et al. Presenilin clinical mutations can affect gamma-secretase exercise by completely different mechanisms. Dissociated phenotypes in presenilin transgenic mice define functionally distinct gamma-secretases. The Notch ligands, Jagged and Delta, are sequentially processed by alpha-secretase and presenilin/ gamma-secretase and launch signaling fragments. The Notch ligands, Delta1 and Jagged2, are substrates for presenilin-dependent "gamma-secretase" cleavage. Mouse Fbw7/Sel-10/Cdc4 is required for notch degradation during vascular development. Id sustains Hes1 expression to inhibit precocious neurogenesis by releasing unfavorable autoregulation of Hes1. Key fundamental helix-loop-helix transcription factor genes Hes1 and Ngn2 are regulated by Pax3 throughout mouse embryonic development. Regulation of Notch signaling throughout T- and B-cell growth by O-fucose glycans. Contributions of chaperone and glycosyltransferase actions of O-fucosyltransferase 1 to Notch signaling. Protein O-fucosyltransferase 1 is a vital part of Notch signaling pathways. Fringe glycosyltransferases differentially modulate Notch1 proteolysis induced by Delta1 and Jagged1. Fringe differentially modulates Jagged1 and Delta1 signalling through Notch1 and Notch2. Drosophila neuralized is a ubiquitin ligase that promotes the internalization and degradation of delta. Ligand endocytosis drives receptor dissociation and activation within the Notch pathway. Deltex acts as a positive regulator of Notch signaling by way of interactions with the Notch ankyrin repeats. Establishment of intestinal identification and epithelial-mesenchymal signaling by Cdx2. Organizing cell renewal within the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial management. Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many various websites of cell-cell interplay in the mouse embryo. Disruption of hedgehog signaling reveals a novel function in intestinal morphogenesis and intestinal-specific lipid metabolism in mice. Deconvoluting the gut: molecular evidence for a major role of the mesenchyme in the modulation of signaling cross discuss. Indian hedgehog regulates intestinal stem cell destiny via epithelialmesenchymal interactions during growth. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling is essential for terminal differentiation of the intestinal secretory cell lineage. Crypt-restricted proliferation and commitment to the Paneth cell lineage following Apc loss in the mouse gut. Inducible Cre-mediated management of gene expression within the murine gastrointestinal tract: effect of loss of beta-catenin. Essential requirement for Wnt signaling in proliferation of grownup small gut and colon revealed by adenoviral expression of Dickkopf-1. Indian Hedgehog is an antagonist of Wnt signaling in colonic epithelial cell differentiation. Notch signaling is required for the maintenance of enteric neural crest progenitors. A presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase-like protease mediates launch of Notch intracellular area. A presenilin-1/gamma-secretase cleavage releases the E-cadherin intracellular area and regulates disassembly of adherens junctions. Modulation of notch processing by gammasecretase inhibitors causes intestinal goblet cell metaplasia and induction of genes identified to specify intestine secretory lineage differentiation. Hes1-deficient mice show precocious differentiation of Paneth cells within the small gut. Intestinal deletion of Pofut1 within the mouse inactivates notch signaling and causes enterocolitis. Mind bomb 1 is important for generating useful Notch ligands to activate Notch. Delta-Notch signalling controls commitment to a secretory fate within the zebrafish intestine. A mammalian helix-loop-helix factor structurally related to the product of Drosophila proneural gene atonal is a optimistic transcriptional regulator expressed within the growing nervous system. Mouse atonal homolog 1 directs intestinal progenitors to secretory cell rather than absorptive cell fate. Math1 expression redefines the rhombic lip derivatives and divulges novel lineages throughout the brainstem and cerebellum. Autoregulation and multiple enhancers control Math1 expression in the growing nervous system. The intestine-specific homeobox gene Cdx2 induces expression of the essential helix-loop-helix transcription issue Math1. Hyperactive Wnt signaling changes the developmental potential of embryonic lung endoderm. Jagged 1 is a beta-catenin target gene required for ectopic hair follicle formation in grownup epidermis. Rodilla V, Villanueva A, Obrador-Hevia A, Robert-Moreno A, Fernandez-Majada V, Grilli A, et al. Jagged1 is the pathological hyperlink between Wnt and Notch pathways in colorectal cancer. The ets-domain transcription issue Spdef promotes maturation of goblet and paneth cells in the intestinal epithelium.
Buy 20 gm betnovate with visa
Thus, the willpower of caspase 3 activity produced results identical to histological methods and offered an extra technique for examining cell demise in vivo acne queloide 20 gm betnovate order with mastercard. It is apparent from the beforehand discussed experiments that knockout studies are extremely helpful in determining whether or not or not a specific protein is concerned in apoptosis acne zeno betnovate 20 gm discount fast delivery. Using morphological techniques and caspase 3 activation, the variety of apoptotic cells was approximately twofold larger in the mice in which IkB kinase had been ablated in comparison with controls following remedy with eight Gy -radiation. Whole-cell extracts of isolated intestinal epithelial cells from the conditional IkB kinase knockout mice contained higher levels of p53 than the controls. One of them entails ChK1, a serine/threonine checkpoint kinase, which is energetic at S-phase and G2/M checkpoints. Even though cells died, the gut was capable of compensate by re-populating itself with cells containing practical Chk1. A major role in these cells of the Fas/FasL system is controlling the immune response by regulating the variety of lymphocytes. Fas can additionally be expressed in non-lymphoid tissues at websites of immune privilege (ovaries, uterus, testes) and at websites commonly infiltrated by lymphocytes (small and large gut, liver, and lung). Cell loss is especially essential in tissues that proliferate as rapidly as the intestinal epithelium. Several groups have explored the importance of apoptosis within the response to small bowel resection by analyzing the consequences of varied gene products concerned in apoptosis on the adaptive response. Seven days following resection there have been significant increases in all of those parameters in each teams and no significant variations in the will increase. The apoptotic index was decided by counting apoptotic cells within the crypts, and the outcomes indicated that apoptosis was not altered within the p53-null mice following small bowel resection. In each groups, apoptosis increased approximately 25%, which matched the 23% improve in proliferation. Although this correlation helps a task for apoptosis in sustaining the new equilibrium in cell progress, its significance has not been established. The major conclusion from this research was that the increase in apoptosis following small bowel resection occurs through a p53-independent mechanism. They concluded that intestinal hyperplasia following resection was considerably elevated within the mice overexpressing Bcl-2. In the mice overexpressing Bcl-2, these increases have been considerably larger than within the wild-type resected group. Studies involving the genetic manipulation of the Bax gene, nevertheless, have shed considerable light on the position of apoptosis in the adaptive response to small bowel resection. They observed the similar old increases in ileal moist weight, crypt depth, and proliferative rates in both groups. Resection significantly increased the rate of apoptosis in the management group; nevertheless, the apoptotic index within the Bax-null mice was unchanged. These knowledge supported the conclusion that elevated apoptosis following small bowel resection is Bax dependent, and that enterocyte proliferation and apoptosis are regulated through totally different mechanisms throughout intestinal adaptation. They also discovered important elevated levels of caspase eight and Fas protein following resection of Bax/ mice. In the adapting Bax/ gut, increased apoptosis was confined to the crypts and was accompanied by increased cell proliferation. Bax/ mice exhibited an adaptive response comparable in magnitude to the Bax/ animals; nonetheless, it occurred with out a rise in cell proliferation and with an precise lower in apoptosis. The authors concluded from these knowledge that adaptation-induced, Bax-dependent apoptosis could be the limiting issue determining the magnitude of the adaptive response. Thus, these information and conclusions are in disagreement with these described by Tang et al. Crossing the animals prevented the increased apoptosis observed within the waved-2 mice. To summarize the research, apoptosis following large small bowel resection seems to be unbiased of p53 and depending on Bax. Following transient occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery, apoptosis occurred within the undifferentiated epithelial cells of the proliferative compartment in addition to in the differentiated cells of the villus. The response in the villous cells was sevenfold over baseline, compared to twofold in the crypt cells. The biggest improve in apoptosis occurred at the villous tip, perhaps reflecting the chance that hypoxia was greatest in this area. Comparisons of p53/ and p53/ mice additionally indicated that apoptosis following ischemia reperfusion is p53 impartial. These investigators used a fatty acid binding protein promoter to supply transgenic mice that overexpressed Bcl-2 fivefold in both crypt and villous cells. Forced expression of Bcl-2 reduced apoptosis by roughly 50% in both crypts and villi in comparison with normal littermates. They additionally discovered that compelled expression of Bcl-2 brought on an identical reduction of p53-dependent apoptosis of crypt epithelial cells in response to -irradiation. Thus, the flexibility of Bcl-2 to inhibit apoptosis happens independently of whether p53 is concerned within the response. In this study, 60 minute ischemia followed by 60 minutes of reperfusion have been used to generate damage. In some cases, the 60 minute occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery was preceded by a strategy of preconditioning, which consisted of 20 minutes of occlusion followed by 5 minutes of reperfusion. These experiments had been conducted in rats and the major stimulus caused an approximate sevenfold improve in apoptosis, which was decreased 30% by preconditioning. Peroxidation of lipids lowered the mitochondrial membrane potential, which led to the discharge of cytochrome c, caspase 9 activation, and eventually, the activation of caspase 6 in the small bowel mucosa. Each step on this scheme was inhibited significantly by ischemia preconditioning, which resulted in the discount of apoptosis. Numerous research have recognized a quantity of totally different courses of compounds with radioprotective results on the small bowel mucosa. The authors discovered increased stem cell survival and instructed that it acts by stimulating cell proliferation. The toxicity derived from the loss of mucosal cells consists of diarrhea, dehydration, and bacterial an infection, which can lead to sepsis and shock. This sequel frequently limits the dose of therapeutic agent and, hence, the effectiveness of the therapy. There are threshold ranges of radiation above which the bone marrow and intestinal mucosa are unable to repopulate. In mice, exposure to 7�15 Gy of complete physique radiation kills most proliferating cells of the bone marrow, but enough stem cells survive to repopulate the tissue. After 8�14 Gy of radiation, many proliferating intestinal epithelial cells are killed, but a enough number of stem cells survive to repopulate the mucosa. To investigate whether endothelial apoptosis was causally liable for the broken intestinal epithelium, these investigators examined the responses of mice during which the acid sphingomyelinase (asmase/) gene had been knocked out. These animals fail to synthesize the pro-apoptotic lipid, ceramide, in endothelia following irradiation. Apoptosis of the intestinal epithelia, damage to the intestine, and dying had been prevented following irradiation within the asmase/ mice.
Betnovate 20 gm discount overnight delivery
Importantly, because tumors are thought to come up from a single mutated cell and arguably that cell is a stem cell, methods are badly needed to establish stem cell niches and permit lineage tracing from stem cell progeny in human tissues acne scar removal cream betnovate 20 gm cheap with mastercard. The crypt base stem cells type the rapidly biking stem lgr5 constructive stem cell inhabitants acne 9 year old betnovate 20 gm cheap without prescription. There is evidence that there could additionally be slowly cycling stem cells at cell place 4 which may be label-retaining and, in some components of the mouse intestine, seem to specific Bmi1. The niche cells are the pericryptal myofibroblasts and mesenchymal origin, which sheath the bottom of the crypt and, on the area of interest hypothesis, provide inductive alerts maintaining the area of interest. The stem cells give rise to the transitamplifying cells, which expand the stem cell output and are responsible for many of the cell manufacturing. When stem cell progeny go away the area of interest, they enter a different setting that permits differentiation. In the neonatal mouse, nevertheless, earlier than the institution of this Paneth cell inhabitants density gradient, Paneth cell formation is restricted to positions 5 and above, supporting the existence of a stem cell zone as the underlying mechanism of restricted Paneth cell formation in the grownup. Such labeled phagosomes have been subsequently noticed in all four differentiated cell forms of the crypt (although only a single endocrine cell was found with an unlabeled phagosome). However, it has been suggested that the data showed more cell deaths occurring at cell positions 4�6 than on the crypt base, which was confirmed following external radiation of the crypt. However, a few of these cells migrate downward and have been seen in the Paneth cell zone, and all differentiated cells present in positions 1�4 migrated down from their origin in position 5 or above. Most of the intercalated cells categorical this gene and most appear to be biking with a cell cycle time of about 24 hours. The recognized kinetics of Paneth cell alternative requires a Paneth cell precursor at cell place 4 to maneuver downward to exchange Paneth cells. Later, labeled Paneth cells turn out to be more numerous in decrease positions and ultimately seem in position 1. Bjerknes and Cheng19 proposed that Paneth cells originate in position 5 or above after which migrate downward, again in preserving with the stem cell zone speculation. Stem cells in positions 1�4 receive no sign to differentiate and only those stem cells that migrate up out of the stem cell zone into position 5 shall be so induced. Lgr5 constructive Paneth cells appear at the top of the Paneth cell zone and transfer downward, and thus, in some ways, the current data from Clevers Lab help the earlier stem cell zone hypothesis of Bjerknes and Cheng. It has just lately been proven that the deletion of Apc in lgr5 optimistic cells leads to their transformation within days. Transformed stem cells stay situated at the crypt base and lead to the event of microadenomas, which become macroscopic adenomas inside 3�5 weeks and a stem cell/progenitor cell hierarchy is maintained in early neoplastic lesions. However, Apc deletion in transitamplifying cells leads to very limited adenoma growth. Lineage tracing in grownup mice reveals that these cells can generate the whole intestinal epithelium. Activation of Wnt signaling in Prom1/C-L mice by a Cre-dependent mutant allele of -catenin resulted in substitute of the mucosa of the entire small gut with neoplastic cells with high-grade Chapter 12 Stem Cells within the Gastrointestinal Tract 363 intraepithelial neoplasia and adenoma formation. The common place of the first non-Paneth cell is cell place 4 or 5 from the base. Because of crypt geometry and the uneven distribution of Paneth cells in the base of the crypt, these could presumably be positioned anyplace between cell place 3 and as high as cell position 8 or 9. However, the scenario is further difficult by the fact that greater than four cells per crypt possess the ability to regenerate a crypt, perhaps amounting to as many as 30�40 per crypt,37,38 implying that a stem cell hierarchy or age construction exists, and that along with the actual stem cells answerable for lineage era in regular circumstances, many different cells can regenerate the tissue if it is experimentally damaged by high doses of radiation. These information replicate recent research in Drosophila, the place, in niches that include multiple stem cells, similar to these maintaining the germ cells, lost stem cells are changed by division of neighboring stem cells or by reversion of transit cells, even from far away. In these experiments, cells are uncovered to the label during development or regeneration following cytotoxic insult, in order that stem cells are in division. Thus sister chromatid exchange would seem to happen in stem cells55 and there are alternative hypotheses that explain this phenomenon. Importantly, as with the lgr5/prominin1 cells referred to earlier, the induction of a stable type of -catenin in these cells was enough to rapidly generate adenomas. Thus, these data assist the existence, no less than in the proximal small bowel, of self-renewing stem cells with multilineage capability. Mushashi-1 can also be strongly expressed in creating crypts (2-day-old mice), which might be predicted to be enriched with stem cells. Moreover, even with the extra promising markers, a potential drawback is that neither the operate nor the expression mechanism is as but understood, which makes definitive conclusions troublesome in some circumstances. Apart from the apparent contradiction between these two fashions, there have been early attempts to integrate each ideas. There has been a move by several groups to propose a common speculation that states renewal systems have advanced two forms of stem cell - quick and slow biking. There is a "reserve" pool of quiescent stem cells, corresponding to the 4 label retaining stem cells, possibly together with the label retaining cells, with the active cycling crypt base lgr5 positive stem cells that divide about each 24 hours. Certainly, as Fuchs66 pointed out, stem cells face nice challenges; for example, during being pregnant, the mammary epithelium undergoes a large transforming as hair follicles endure destruction, dormancy, and regeneration. In the gut, along with the constant need for cell renewal, irritation or other harm can place enormous demands on the epithelium and, consequently, on the stem cell niches, emphasizing the necessity to regulate swiftly to maintain homeostasis. Implicitly, stem cells will need to change the speed at which they renew themselves or cycle. Certainly, about two-thirds of the long-term hemopoietic stem cells are in the G0 section at anyone time,sixty six whereas in the hair follicle, early in improvement, a population of infrequently biking cells with many molecular characteristics of stem cells appears throughout the bulge that later drives the hair cycle. In comparability, cells in the mid region of the crypt had cycle times closer to 12 hours. However, labeled progeny had been generated inside a day, which may only happen if the Bmi1 cells are actively dividing. These cells have been distributed in a sample alongside the crypt�villus axis considered similar to long-term, label-retaining cells. They appear proof against tissue harm, and lineage-tracing studies confirmed that these mTert cells produced all differentiated intestinal cell sorts, endured long run, and made a contribution to the regenerative response following damage. The inter-relationships between the cells bearing a number of lineage-labeling markers shall be fascinating. Whatever the case, the migration dynamics, with lgr5 daughters migrating upward differentiating Paneth cells migrating downward, and a possible long-lived stem cell seated additional up in the crypt, are more doubtless to be very complicated indeed. These cells have an age-structure and cells with an extended mitotic history showed an increased likelihood of differentiation. The niche can also be thought to manage stem cell number, division, and polarity within the dermis,81 the nervous system,eighty two and the hemopoietic system. Lineage tracing confirmed that lgr5 positive stem cell hierarchy is maintained in such organoids. This suggests the cell-autonomous ability of single stem cells to perform within the absence of a niche composed of non-epithelial cells. Some of the factors forming this environment are recognized, however not all of the components that management these important processes are clear. For instance, within the Drosophila intestinal epithelium, Notch signaling is the principal regulator.