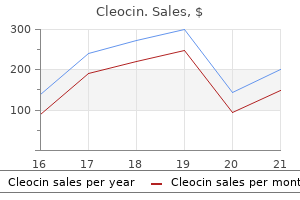
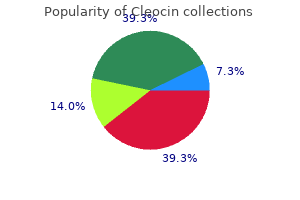
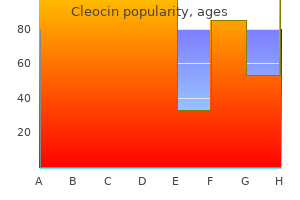
Cleocin
Cleocin dosages: 150 mg
Cleocin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills

150 mg cleocin order amex
They reside in connective tissue near small blood vessels and reply to skin care zinc oxide 150 mg cleocin amex overseas antigens by releasing the contents of their granules skin care untuk kulit berminyak cleocin 150 mg buy with mastercard, many of that are angiogenic. Resident macrophages, tissue-fixed mesenchymal cells and epithelial cells also release mediators that contribute to and perpetuate the early response. The cellularity of wound websites increases by way of proliferation and recruitment to sites of damage. Cell types attribute of skin wounds are: Leukocytes arrive on the wound website early by adherence to activated endothelium, exit from the circulation and quickly migrate into tissue by forming small focal adhesions with matrix molecules similar to fibrin, fibronectin and collagen. A family of small peptide chemoattractants (chemokines) mediates both restricted and broad recruitment of explicit leukocyte subtypes (see Chapter 2). Polymorphonuclear leukocytes from the bone marrow invade the wound web site within hours. They degrade and destroy nonviable tissue and infectious organisms by releasing their granular contents and generating reactive oxygen species, before undergoing apoptosis and digestion by macrophages. During their extra prolonged residence time in wounds, macrophages phagocytose particles and orchestrate the growing granulation tissue and healing by releasing cytokines and chemoattractants. Dendritic cells are resident antigen-presenting cells that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, pericytes and smooth muscle cells characterize a spectrum of mesenchymal cells which are recruited domestically and are also populated from mesenchymal progenitors in bone marrow. They migrate and propagate via alerts from progress elements and matrix degradation merchandise, populating a pores and skin wound by day 3 or four. These cells mediate synthesis of connective tissue (fibroplasia), tissue reworking, vascular integrity, wound contraction and wound energy. Endothelial cells sprout from existing postcapillary venules and are additionally seeded by circulating bone marrow progenitors. Nascent capillaries kind in response to growth factors and are seen in wound granulation tissue, together with fibroblasts, past day 3. Development of capillaries is critical for gasoline exchange, supply of vitamins and inflow of inflammatory cells. Reepithelialization is delayed if the migrating epithelial cells must reconstitute a damaged basement membrane. In open wounds, keratinocytes migrate between provisional matrix (see below) and preexisting or newly shaped stromal collagen, which is coated with plasma glycoproteins, fibrinogen and fibronectin. Stem cells from bone marrow, or within the skin, stem cells or progenitor cells within the hair follicle and inside the basal epidermal layer, provide renewable sources of epidermal and dermal cells able to differentiation, proliferation and migration. Stem cells for epidermal regeneration reside within the bulge region of the hair follicle and the interfollicular dermis. Dermal progenitors are additionally associated with the lower hair shaft and the follicular bulb. Marrow-derived, multipotential progenitors of fibroblasts and endothelium are recruited to sites of harm. These cells help in forming new blood vessels and new epithelium and regenerate skin constructions, similar to hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Mechanisms of Cell Migration Cell migration makes use of the most important mechanisms of wound healing, receptor-mediated responses to chemical signals (cytokines) and insoluble substrates of the extracellular matrix. Ameboid locomotion powers the quickly migrating leukocytes through wave-like membrane extensions called lamellipodia. Slower-moving cells, corresponding to fibroblasts, prolong narrower, finger-like membrane protrusions referred to as filopodia. Growth factors or chemokines bind to specific receptors on cell surfaces to set off cell polarization and 1. After cytokine activation of capillary endothelium, leukocytes and bone marrow�derived circulating stem cells connect to , and migrate between, capillary endothelial cells; penetrate the basement membrane; and enter the interstitial matrix in response to chemotactic alerts. Under the influence of locally launched angiogenic components, capillary endothelial cells lose their reference to the basement membrane and extend through the provisional matrix to kind new capillaries. During reepithelialization, groups of basal keratinocytes at the wound edge launch from underlying basement membrane, tackle a migratory behavior and penetrate between the fibrin eschar (if present) and the granulation tissue that generates wound dermis. Migrating cells change to a unique display of integrin matrix receptors that recognize provisional matrix and stromal collagen (type I) and to totally different metalloproteinases that favor migration and matrix transforming. Actin-related proteins modulate actin assembly, and quite a few actinbinding proteins act like molecular tinkertoys, rapidly setting up, stabilizing and destabilizing actin networks. The vanguard of the cell membrane impinges upon adjacent extracellular matrix and adheres to it via allosterically activated, transmembrane adhesion receptors known as integrins (see Chapter 2). These molecules present vital redundancy; lots of the 24 identified vertebrate integrin heterodimer combinations acknowledge the identical matrix components. Focal contacts develop via adherence of the integrin extracellular domain to the provisional or stromal connective tissue matrix. In vitro, focal adhesions form beneath the cell physique, whereas smaller focal contacts form at the leading edges of migrating cells. The focal contact anchors actin stress fibers, in opposition to which myosins pull to lengthen or contract the cell physique. As cells move forward, older adhesions on the rear are weakened or destabilized, allowing the trailing edge to retract. Cytoplasmic domains of integrins set off a protein cascade that anchors actin stress fibers. Integrins transmit intracellular alerts that additionally regulate cellular survival, proliferation and differentiation. These molecules allosterically alter the binding avidity of the extracellular portion of integrins by signaling via activation of their cytoplasmic tails (inside-out signaling). Integrin binding can be essential for lots of progress issue receptor signaling processes. Growth factors and integrins share a quantity of frequent signaling pathways, however integrins are unique of their capacity to arrange and anchor cytoskeleton. Cytoskeletal connections are regulated by the interaction between cell�cell and cell�matrix connections and determine the form and differentiation of epithelial, endothelial and other cells. Not surprisingly, these identical cytoskeletal connections are foci of change during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions that occur during reepithelialization of the wound floor. Basement Membrane Basement membrane, additionally called basal lamina, is a skinny, well-defined layer of specialized extracellular matrix that separates cells that synthesize it from adjoining interstitial connective tissue. It is a supportive and biological boundary important in improvement, therapeutic and regeneration, offering key indicators for cell differentiation and polarity and contributing to tissue organization. Basement membrane can additionally be a key structural and functional function of the neuromuscular synapse. Unique basement membranes type underneath completely different epithelial layers and round epithelial ducts and tubules of pores and skin and organs and round adipocytes, cowl clean and skeletal muscle cells and peripheral nerve Schwann cells and surround capillary endothelium and related pericytes.
Generic 150 mg cleocin mastercard
The sum of all regional flows equals the venous return acne los angeles 150 mg cleocin trusted, which in turn determines the cardiac output skin care logos cheap 150 mg cleocin mastercard. The Aorta and Arteries Are Conducting Vessels the major capabilities of the aorta and arteries are to transport blood to the organs and convert pulsatile circulate into sustained common flow. The latter operate derives from the elastic properties of the aorta and the resistance produced by the arteriolar sphincters. Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute and represents the total blood move in pulmonary and systemic circuits. Cardiac output is the product of heart price and stroke quantity and, because the cardiac index, is commonly adjusted for physique surface space (in sq. meters) as an indicator of ventricular operate. The Microcirculation Includes Arterioles, Capillaries and Venules the blood vessels of the microcirculation are lower than a hundred M in diameter. Entry into the capillary system is guarded by precapillary sphincters, except for thoroughfare channels, which bypass capillaries and are always open. Since not all capillaries are all the time open, blood circulate to a construction may be elevated by recruiting additional capillaries. The sum of blood circulate by way of the capillary mattress, the thoroughfare channels and the arteriovenous anastomoses determines the regional blood flow. Factors that mediate and link metabolic vasodilation to cellular metabolism embrace adenosine, other nucleotides, nitric oxide, sure prostaglandins, carbon dioxide and pH. The microcirculation is an important contributor to all types of hyperemia and edema, and is a target in septic shock (see below). Vasoregulation in conducting arteries, resistance arteries and veins relies on delicate interactions between blood, endothelium, easy muscle cells and surrounding stroma. Capillary size, measured from terminal arteriole to amassing venule, ranges from 0. However, the path size by which blood cells traverse capillaries may very well be longer due to their extensive anastomoses. This truth is probably going an essential issue with respect to microvascular trade of drugs corresponding to oxygen as a result of it increases the time out there for such change to take place. The giant mixture surface area of capillaries determines that velocity is low, which further enhances microvascular trade. The density of capillaries in a tissue additionally influences microvascular change by affecting the diffusion distance. For example, within the Endothelium Provides a Continuous Partition between Blood and Tissues Endothelial cells play essential roles in anticoagulation, facilitation of migration of substances from blood to tissue and again, regulation of vessel tone (particularly that of resistance arteries) and regulation of vasopermeability (see Chapters 2 and 16). Veins and Venules Return Blood to the Heart Blood from the capillaries enters venules and ultimately veins on its route back to the heart. Veins not solely function a conduit for blood but additionally act as a blood reservoir; 64% of the entire blood volume resides within the venous system. The Interstitium Represents 15% of Total Body Volume Artery Arterioles Capillaries Blood strain (mm Hg) Total space (cm2) Venules Vein the interstitial fluid between cells offers a way for the supply of nutrients and the elimination of waste. Lymphatics Reabsorb Interstitial Fluid Interstitial fluid is reabsorbed into the circulation at the venous end of the capillary, and a small portion is drained via lymphatics. Lymphatic capillaries conduct lymph from the periphery to the central venous system by way of the thoracic duct. Normal oscillatory constrictions and relaxations of lymphatic vessels contribute to the regular return of lymph fluid to the central circulation. Note that the upper resistance because of diameter reduction in the arterioles results in a drop in perfusion pressure, the capillary network constitutes the overwhelming majority of vascular floor space and the venous system is a low-pressure, high-capacitance construction with a series of valves to prevent retrograde circulate. It is normally a physiologic response to elevated useful demand, as within the heart and skeletal muscle during train. In addition, skeletal muscle may increase its blood circulate (and thus oxygen delivery) 20-fold during train. The increased blood provide occurs by arteriolar dilation and recruitment of unperfused capillaries. Vasoactive materials released by inflammatory cells (see Chapter 2) cause dilation of blood vessels; in the skin this contributes to classic "tumor, rubor and calor" of irritation. In pneumonia, for instance, alveolar capillaries are engorged with erythrocytes as a hyperemic response to irritation. Because irritation also can harm endothelial cells and improve capillary permeability, inflammatory hyperemia is usually accompanied by edema and local extravasation of erythrocytes. The launch of the obstruction is adopted by energetic hyperemia, probably because of ischemic tissue injury and release of inflammatory brokers corresponding to histamine. Hemosiderin-laden macrophages within the lung of a affected person with congestive coronary heart failure. As a end result, strain in alveolar capillaries will increase, and these vessels turn out to be engorged with blood. Increased pressure within the alveolar capillaries has 4 major consequences: Passive Hyperemia (Congestion) Passive hyperemia, or congestion, is engorgement of an organ with venous blood. Regarding the former, resultant venous engorgement of the lungs results in accumulation of a transudate within the alveoli, which known as pulmonary edema. With acute failure of the best ventricle, the liver can turn into severely congested. Generalized will increase in venous stress, sometimes from continual heart failure, lead to slower blood circulate and a consequent improve in blood volume in lots of organs, together with liver, spleen and kidneys. In the past, coronary heart failure from rheumatic mitral stenosis was a typical reason for generalized venous congestion, but with the decline in the prevalence of rheumatic fever and the advent of surgical valve alternative, such instances are uncommon. Congestive heart failure secondary to coronary artery illness and hypertension and right-sided failure as a end result of pulmonary illness are now more frequent. Passive congestion can also be confined to a limb or an organ because of more-localized obstruction to venous drainage. Examples embrace deep venous thrombosis of the leg veins, with resulting edema of the lower extremity, and thrombosis of hepatic veins (Budd-Chiari syndrome), with secondary continual passive congestion of the liver. The released iron, in the type of hemosiderin, remains in these macrophages, that are then known as "heart failure cells". Fluid is forced from the blood into the alveolar airspaces, resulting in pulmonary edema. The presence of fibrosis and iron is viewed grossly as a agency, brown lung (brown induration). Pulmonary hypertension occurs when the pressure is transmitted to the pulmonary arterial system. This might result in right-sided heart failure and consequent generalized systemic venous congestion. A gross photograph of liver reveals nutmeg appearance, reflecting congestive failure of the proper ventricle.
150 mg cleocin buy fast delivery
Suspicion of extraluminal obstruction warrants surgical session for omentopexy or lysis of adhesions if possible skin care adha cleocin 150 mg buy discount online. Other catheter-related complications normally arise acutely postinsertion and embody intraperitoneal hemorrhage and intestinal perforation acne keloidalis nuchae pictures cleocin 150 mg cheap with mastercard. The remedy generally contains immediate catheter removal, surgical restore, and systemic antibiotics. Critically unwell sufferers have multiple threat elements for the development of peritonitis, and each effort to stop its development ought to be employed to optimize outcomes. These include routine administration of topical antibiotics to the exit web site, draining of the fluid and prophylactic use of antibiotics earlier than invasive procedures, addition of antifungal prophylaxis throughout antibiotic remedy, and resting the peritoneum throughout intercurrent intraabdominal events similar to colitis. Secondary peritonitis ought to be suspected within the event of focal abdominal ache or tenderness, isolation of anaerobes or multiple organisms from peritoneal fluid, or failure to reply to appropriate antibiotic remedy. These usually can be managed by discount in fill volumes and switching to hemodialysis if possible. Catheter malfunction manifests as failure of outflow and presumably influx and normally is as a end result of of constipation, catheter malposition, pericatheter leak, catheter kinking, or intraluminal obstruction with fibrin. Initial administration consists of administration of laxatives, verification of catheter place, and administration of intraluminal thrombolytics when applicable. The use of nephrotoxins similar to aminoglycosides and radiocontrast materials should be avoided wherever potential. Intraabdominal surgery requires momentary peritoneal rest till the peritoneum has been deemed to have had enough time to get well. Chapter 185 / Treatment of Peritonitis and Other Clinical Complications of Peritoneal Dialysis within the Critically Ill Patient 1125. Staphylococcus aureus prophylaxis and tendencies in gram-negative infections in peritoneal dialysis patients. The association between exit website infection and subsequent peritonitis amongst peritoneal dialysis sufferers. Ultrasonography within the administration of exit website infections in peritoneal dialysis sufferers. Examine solute and quantity management using peritoneal dialysis in critically sick acute kidney injury patients. Compare peritoneal dialysis with other forms of renal replacement therapy in critically unwell acute kidney injury sufferers in regard to outcomes. Examine the variations in price for peritoneal dialysis in critically ill acute kidney damage patients. Compare the dangers and advantages that peritoneal dialysis might have over different forms of renal alternative remedy in critically unwell patients with acute kidney harm. Despite the inherent variations amongst these modalities, the superiority of one over the opposite has not been demonstrated clearly. Furthermore, vascular access could also be restricted, significantly among critically sick infants and young children, or may be tough to acquire, such as in sufferers with coagulation issues or vital vascular disease. The need for anticoagulation, intermittent or continuous, can be a concern as a end result of it might increase bleeding risk and is associated with higher utilization of assets for monitoring adequacy of anticoagulation. There was important heterogeneity between the results of the randomized trials (I2 = 73%, p =. In both research, fast correction in metabolic derangement whereas sustaining an ultrafiltration price of roughly 2L/day occurred. Obviously, this system requires both two catheters or a catheter with twin lumens. Urea clearances of 30 to 50 mL/min often are achieved with this technique, with the potential for even higher clearances. Furthermore, although venous access and peritoneal access can lead to infection, central venous entry is also associated with the development of venous thrombosis, particularly in the femoral and subclavian veins, placing sufferers at risk for embolic events. In addition, the placement of central venous access can result in central venous stenosis, which can have important long-term sequelae, notably for kids. Peritoneal entry, however, is most likely not uniformly achievable, significantly in patients who lately have undergone bowel surgery. Factors corresponding to intestinal edema, liver dysfunction, and renal dysfunction considerably affect the absorption and metabolism of such drugs. However, fluctuations in drug ranges nonetheless most likely occur, which may result in periodic subtherapeutic levels. This feature might result in more fixed steady-state ranges of drugs and possibly larger efficacy. These investigators discovered that elevated midcycle intraabdominal pressure correlated with reduced pulmonary compliance and increased airway resistance. The elevated stomach pressure could also be prevented partially by using extra frequent cycling of lower dialysate volumes. Other pulmonary problems are the development of pleural effusions from migration of peritoneal fluid into the thorax, which could be managed with lower dialysate volumes and supine dialysis. The use of heparin anticoagulation can lead to bleeding and could additionally be contraindicated in patients with a bleeding diathesis or current surgical procedure. Furthermore, patients handled with heparin typically develop heparin antibodies, precluding its use. The use of citrate can ameliorate a few of these issues with heparin however adds further to complexity and value. The latter requires additional central access, elevating the risk of infection, particularly fungemia. Furthermore, the dangers of anticoagulation and the necessity for central access might preclude their use. However, many of those research do have limitations; subsequently further research in this area is required. Karl Nolph to the previous version of this chapter, in addition to his contributions to peritoneal dialysis and the field of nephrology normally. Infectious complications of this modality are a priority, and nice care must be taken to adhere to sterile method. International survey on the administration of acute kidney injury in critically ill sufferers: yr 2007. Chapter 186 / Comparison of Peritoneal Dialysis With Other Treatments for Acute Kidney Injury 1128. High-volume peritoneal dialysis in acute kidney harm: indications and limitations. Peritoneal-extracorporeal recirculation dialysis a method for improving efficiency of peritoneal dialysis. Hemofiltration and peritoneal dialysis in infection-associated acute renal failure in Vietnam.
Proven cleocin 150 mg
In a secondary circuit acne y estres buy cheap cleocin 150 mg line, the filtered albumin-rich plasma fraction is handled by two absorber columns: a neutral resin absorber and an anion exchanger for removal of negatively charged toxins acne 404 nuke book download cleocin 150 mg order with visa. The purified albumin-rich plasma fraction is reinfused into the first circuit where, in a second step, typical hemodialysis is performed to remove water-soluble molecules. There is well-established evidence of interplay between lung and kidney features, and lots of critically sick sufferers could require concomitant extracorporeal kidney and lung support. In sufferers with hyperinflammation (mainly throughout sepsis), extracorporeal blood purification therapies have the potential to modulate the host inflammatory response via the removal of inflammatory mediators and/or bacterial toxins. When faced with a patient with advanced healthcare needs, practitioners can use a growing variety of extracorporeal remedy choices. For sufferers with a quantity of organ failure, an rising panoply of choices is being developed, including extracorporeal therapies for sepsis, and for cardiac, pulmonary, and liver failure. In this advanced scenario, a multidisciplinary medical care staff composed of specialists from completely different disciplines Chapter 177 / Nomenclature: Techniques and highly educated nurses is essential to the success of the treatment. We present a framework for harmonization of terminology to scale back the errors and complications that may end result from poor understanding and inadequate delivery of the prescribed therapies. Homogenized nomenclature is also necessary when reporting machine features and medical parameters to enable examine comparisons and advance our understanding on this area, ultimately allowing for enhancements in medical follow and affected person outcomes. We belief that new publications, electronic medical records, and machine software program shall be designed and operated in compliance with the agreed terminology to enable consistent data collection and comparability. Standardized definitions regarding machines performing continuous renal alternative therapies are important to keep away from describing the same idea with different names. The harmonization of terminology in extracorporeal renal alternative therapies will assist to reduce errors and issues that may end result from poor understanding and insufficient delivery of the prescribed therapies. Dialyzer and machine applied sciences: software of current advances to clinical follow. Nomenclature for renal substitute therapy and blood purification techniques in critically unwell sufferers: sensible functions. Clinical nursing for the applying of steady renal replacement therapy within the intensive care unit. Renal replacement therapy in particular situations: heart failure and neurological injury. Renal alternative remedy in special settings: extracorporeal help devices in liver failure. Artificial extracorporeal liver support remedy in sufferers with severe liver failure. Fractionated plasma separation and adsorption system: a novel system for blood 24. The Prometheus system for extracorporeal help of mixed liver and renal failure. Bench to bedside evaluate: extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal, previous present and future. The first worldwide consensus conference on continuous renal replacement remedy. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in sufferers with septic shock because of peritonitis: a multicenter randomized control trial. All of those components may have an important impact on the final efficiency of the technique. Discuss the dialysate compartment and the affect of various dialysate flow/dwell times on efficacy of treatment. Basically, the compartment can be divided right into a bulk area and a boundary layer of fluid, near the peritoneal membrane. Furthermore, several variables should be taken under consideration, such because the time of infusion and drainage, the dwell time, the circulate of dialysate, its temperature and composition, and the possible use of tidal strategies. In this region, the correlation is very steep, and clearance displays significant changes even in the presence of minimal changes within the dialysate flow. However, minimal variations in dialysate move rate might require altering from 4 to five exchanges per day. This region is therefore dialysate flow-dependent or flow-limited, as a result of the quantity of dialysate per day is the factor that chiefly limits the clearance worth. In this region, it might be theoretically easy to increase the dialysate flow by a couple of milliliters per day to achieve much larger clearances and, consequently, important increases in Kt/V. The solely attainable approach to improve the dialysate circulate without elevating the number of exchanges is to enhance the quantity of answer per trade. To obtain the same fractional clearance in patients weighing 60 and ninety kg, the clinician must schedule four exchanges per day, with 2-L and 3-L baggage, respectively. They are the quantity of fluid used, the frequency of exchanges, the dwell time, and the sort of solution employed. However, the final efficacy of the remedy is determined by the anatomic and useful components of the dialytic system, such because the peritoneal circulation (blood compartment), the mesothelium (peritoneal membrane), and the dialysate compartment. Once these components are described clearly, different parameters of each approach become the foundations for an adequate therapy prescription and an important factor in remedy delivery. The second a half of the curve is the standard area of automated or intermittent peritoneal dialysis. The dialysate flows might range significantly owing to a variation of the dwell time from 30 min to zero and in the number of exchanges per day. Based on a 30-minute dwell time with 20 minutes for influx and outflow, 12 two-for-one exchanges can be carried out in a single day for an general length of 10 hours. When the dwell time is reduced to 0 and the dialysate move is due to this fact increased, the clearance rises to 22 to 30 mL/min with a complete clearance per day of 18 L/day. A good compromise could be the usage of a tidal volume of answer, which may enhance the dialysate volume artificially and enable higher utilization of the floor space obtainable for the exchanges. This parameter relies on the calculation made for each single subject of the maximal clearance theoretically achievable at infinite blood and dialysate flow rates. The regions of the curve just mentioned describe the connection between dialysate flow and solute transport. Other components, corresponding to dialysate temperature, intraperitoneal volume, and dialysate osmolality, are further components affecting solute transport, either by increasing the diffusion course of or by adding some convective transport due to increased ultrafiltration rates. Peritoneal Dialysis Membrane the peritoneal dialysis membrane is a living structure that can be thought-about more a useful barrier than a precisely defined anatomic structure. According to this mannequin, human peritoneum seems to behave as a membrane with a series of differently sized pores as follows: giant pores (25 nm; macromolecule transport), small pores (5 nm; micromolecule transport), and ultra-small pores (water transport). The anatomic construction of those ultrasmall pores corresponds to the "water channels" created by a selected protein "aquaporin" performing as a carrier for water molecules. This model locates the main resistance to transport on the stage of the capillary wall, concerning all different anatomic buildings as a negligible website of resistance.

Cleocin 150 mg order online
C1qrs and C3 additionally directly bind microbial constructions and thus serve as elements of innate immunity acne x ray best 150 mg cleocin. Activated innate system pathways facilitate the acute inflammatory response acne tips purchase cleocin 150 mg mastercard, which plays an essential position in host protection. Acute irritation is characterised by a stereotyped set of vascular modifications together with vasodilatation, slowing of blood move, leakage of fluid into the extravascular space, focus of leukocytes and an ordered set of leukocyte-endothelial activation, binding and recruitment/ extravasation events (see Chapter 2). The innate immune system additionally participates in host defense through the antiviral response. Finally, the activated innate immune system additionally facilitates the adaptive immune response via induction of the "second signal". As progenitor cells differentiate into lymphocytes, pink blood cells, neutrophils and so forth, they lose proliferative capability. Prevailing fashions of hematopoiesis/lymphopoiesis recommend that primitive stem cells give rise to committed progenitors (the hierarchical model) or that stem cells can develop both into progenitor cells or back to stem cells (the cell cycle or continuum model). At 6 weeks, the first web site of hematopoiesis shifts to fetal liver and then to bone marrow. The latter process begins at 2 months and by 6 months has fully shifted to bone marrow. While sequential adjustments within the primary website of hematopoiesis are properly outlined, there are intervals of overlap. The relative proportions of lymphocytes within the peripheral blood and central and peripheral lymphoid tissues differ. In distinction to blood, solely 30%�40% of splenic and bone marrow lymphocytes are T cells. Lymphocytes destined to become T lymphocytes migrate to the thymus where they turn out to be both / or / T cells. Lymphoid progenitor cells destined to turn into T cells exit the bone marrow and migrate to the thymus. The early thymus is colonized by progenitors that give rise to T cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. Much of the optimistic selection of thymocytes happens within the cortex; unfavorable choice tends to occur by way of exposure of developing thymocytes to corticomedullary dendritic cells. Lineage-specific differentiation and thymic number of T lymphocytes are basic to understanding the immune response and autoimmunity, respectively. B-1 and marginal zone B cells develop from immature B lymphocytes by way of a special program than do B cells that coexpress IgM and IgD. B cells differentiate within the bone marrow into mature B cells and in some circumstances further into antibody-secreting plasma cells. Similar to T-lymphocyte development, the microenvironments of fetal liver and bone marrow are crucial to B-cell growth. In each sites, solely B lymphocytes that survive pass by way of the multiple steps necessary to produce floor immunoglobulin. Conversely, when surface immunoglobulin binds too avidly to self-antigens, developing B cells are negatively selected and eradicated. Analogous to T cells, B lymphocytes express a floor antigen-binding receptor, membrane immunoglobulin (mIg), with the same antigen-binding specificity because the soluble immunoglobulin that may in the end be secreted by the corresponding terminally differentiated plasma cells. Mononuclear Phagocytes, Antigen-Presenting Cells and Dendritic Cells Mononuclear phagocytes, chiefly monocytes, make up 10% of white blood cells. Circulating monocytes give rise to resident tissue macrophages together with, amongst others, Kupffer cells (liver), alveolar macrophages (lung) and microglial cells (brain). First, dendritic cells that have phagocytized proteins, microbes and so forth elsewhere. Soluble lymph-borne substances corresponding to intact viruses or high� molecular-weight particles/molecules additionally enter lymph nodes via afferent lymphatics. Within the subcapsular sinus, viruses, particles and high�molecular-weight molecules are engulfed by macrophages/dendritic cells that process and present antigen to cortical B cells that make antibody. Activated macrophages produce quite so much of cytokines and soluble mediators of host protection. In the case of lymph nodes, immune complexes arrive by way of afferent lymphatics, and in spleen, via blood. Antigen presentation by follicular dendritic cells results in generation of memory B lymphocytes. They are current in B-lymphocyte�rich lymphoid follicles, thymic medulla and plenty of peripheral websites, including intestinal lamina propria, lung, genitourinary tract and pores and skin. Upon publicity, Langerhans cells engulf antigen, migrate to regional lymph nodes by way of afferent lymphatics and differentiate into extra mature dendritic cells. Individual nodes are encapsulated, vascularized and internally structured in a fashion that facilitates antigen processing and presentation by follicular dendritic cells to B cells in the B-lymphocyte� wealthy cortical follicles and by dendritic cells to T cells in the T-lymphocyte�rich parafollicular cortex. The anatomic organization of the B-cell�rich and T-cell�rich areas of a lymph node is dictated by the region-specific construction of reticular fibers, the composition of stromal cells and complementary units of domestically produced chemokines and lymphocytespecific chemokine receptors. Potential antigens (viruses, higher�molecular-weight particles/molecules and lower�molecular-weight molecules) enter lymph nodes by way of afferent lymphatic vessels. Thymic lymphocytes (thymocytes) originate from the bone marrow as progenitors committed to T-lymphocyte improvement. Maturation occurs because the cells percolate first by way of the cortex and then the medulla before egress. Follicular arteriole Antibodies and T-Cell Receptors Mediate Adaptive Immunity Antibodies Antibody perform was acknowledged over a century ago when serum from animals previously uncovered to attenuated diphtheria toxin specifically protected naive animals from diphtheroid micro organism. Secreted by plasma cells and B lymphocytes, soluble Ig molecules bind a broad variety of complementary antigens with high degrees of specificity and affinity. They recognize quite a lot of organic (and nonbiological) molecules together with proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and others. Membrane-bound Igs serve as receptors that may mediate B-lymphocyte activation upon antigen binding. Both secreted and membrane Igs encompass paired mild chains and heavy chains that collectively kind antigen-binding websites. Splenic white pulp features a sheath of T lymphocytes wrapped round and along the central arteriole, collections of B lymphocytes around and alongside the marginal sinuses (marginal zone B cells) and follicular B-cell aggregates. Here, molecules are taken up, processed by the dendritic cells and offered to T lymphocytes. The construction and function of lymph nodes allows the "sorting" of incoming agents/molecules in a fashion that optimizes antigen presentation to both B or T cells, which, in turn, constitute key pivot factors to the event of adaptive immune responses. Spleen the spleen initiates adaptive immune responses to bloodborne antigens and removes aged and broken pink blood cells, circulating immune complexes and opsonized microbes. As evidenced by the elevated susceptibility of asplenic patients to infection by encapsulated bacteria, the spleen is especially essential to the development of antibody-mediated immunity. Induction of adaptive immunity in the spleen happens within the lymphocyte-rich white pulp, while particle clearance occurs inside the pink pulp.
Purchase cleocin 150 mg on line
Acute kidney damage is an impartial threat factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality skin care japanese product 150 mg cleocin order free shipping, longer length of stay and extended mechanical air flow in critically unwell children: a two-center retrospective cohort research skin care heaven coupon cleocin 150 mg purchase without prescription. Protein/energy debt in critically ill children in the pediatric intensive care unit: acute kidney injury as a serious risk issue. Resting vitality expenditure and nitrogen stability in critically unwell pediatric sufferers on mechanical ventilation. Energy expenditure in one hundred ventilated, critically sick kids: enhancing the accuracy of predictive equations. Continuous renal substitute remedy amino acid, hint metal and folate clearance in critically unwell children. Nitrogen and amino acid balance during whole parenteral vitamin and continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in critically ill anuric youngsters. Duration of extracorporeal therapy in acute maple syrup urine illness: a kinetic model. Energy metabolism, nitrogen steadiness, and substrate utilization in critically unwell youngsters. Specific nutritional issues in acute kidney harm, handled with non-dialysis and dialytic modalities. Compare mortality rates observed in varied critically ill pediatric populations during which acute kidney harm develops. Analyze outcomes for youngsters who acquire acute kidney harm in phrases of need for renal replacement therapy. Identify medical variables related to increased mortality in critically ill kids with acute kidney harm who obtain renal substitute remedy. Review long-term sequelae in youngsters who survive an episode of acute kidney damage. Williams noted survival decreased from 87% to 12% as the number of affected organs increased from 2 to 4. The 10% to 20% fluid accumulation threshold had been observed as nicely in the single-center research famous above. Interestingly, though this 40% survival was decrease than for youngsters smaller than 10 kg, there was no difference in survival between sufferers smaller than 5 kg versus 5 to 10 kg. In our heart, sufferers with an underlying analysis of hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome, transposition of the great arteries, or anomalous pulmonary venous return obtain peritoneal dialysis instantly postoperatively so as to stop fluid accumulation. Acute kidney injury develops early within the intensive care unit course of critically unwell children. The degree of fluid overload is an independent risk issue for demise in children with acute kidney damage, especially those who require renal alternative therapy. Signs of persistent renal damage remain in many children after an episode of acute kidney harm. Mortality for critically unwell children with acute kidney injury is larger among infants younger than 1 yr of age. Childhood acute renal failure: 22-year expertise in a college hospital in southern Thailand. Association Between Progression and Improvement of Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Critically Ill Children. Effect of fluid overload and dose of alternative fluid on survival in hemofiltration. Timing of continuous renal substitute therapy and mortality in critically unwell children*. Weight-based willpower of fluid overload status and mortality in pediatric intensive care unit patients requiring continuous renal alternative therapy. Fluid overload and fluid removal in pediatric patients on extracorporeal membrane 24. Fluid Overload Is Associated With Late Poor Outcomes in Neonates Following Cardiac Surgery. Fluid overload is related to impaired oxygenation and morbidity in critically sick children*. Comparison of steady versus intermittent furosemide administration in postoperative pediatric cardiac sufferers. Risks of acute renal failure after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery in kids: a retrospective 10-year case-control research. Acute renal failure complicating pediatric cardiac surgery: a comparison of survivors and nonsurvivors following acute peritoneal dialysis. Do peritoneal catheters remove pro-inflammatory cytokines after cardiopulmonary bypass in neonates High-dose fenoldopam reduces postoperative neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocaline and 1230. Acute kidney harm related to excessive nephrotoxic medicine publicity results in continual kidney disease after 6 months. Risk factors for and outcomes of acute kidney harm in neonates undergoing advanced cardiac surgery. Improved outcomes with peritoneal dialysis catheter placement after cardiopulmonary bypass in infants. Infants with oliguria, volume overload, multi-organ dysfunction, and metabolic issues could be treated efficiently with methods which have been established in larger youngsters and adults. Identify specific risks and complications of renal replacement therapy in infants. Highlight advantages and downsides of various renal replacement modalities for the critically sick infant. Chapter 206 / Renal Replacement Therapy for the Critically Ill Infant lifesaving when circumstances warrant. Careful preparation, communication, and coordination between various hospital specialists, including nephrologists, neonatologists, surgeons, nurses, nutritionists, and pharmacists, can maximize the likelihood of success for these critically sick infants. Indications are just like these for older kids or adults with the extra need to begin therapy within the setting of suboptimal development or incapability to provide adequate diet to the infant because of fluid limitations. Acute intoxication, both with endogenous toxins as seen with inborn errors of metabolism or exogenous toxins ensuing from iatrogenic events, represents one other scientific scenario that may require therapy by dialysis. Hemodialysis can remove toxins rapidly and is usually the popular remedy for severe intoxication in older youngsters and adults. For infants, hemodialysis is similarly more efficient than peritoneal dialysis in this setting and ought to be considered for the treatment of intoxication. Fluid restriction as part of conservative management for a affected person with gentle renal dysfunction probably might result in decreased diet. Children with vascular abnormalities, certain kinds of cardiac disease, or hemodynamic points could also be suboptimal candidates for extracorporeal perfusion. The approach is comparatively simple, and protocols for therapy within the newborn are well established. These catheters are available various sizes; smaller catheters can be found to be used within the newborn and small infant. Either a surgically placed catheter or percutaneously inserted momentary catheters may be used. Peritoneal dialysate is obtainable in standardized concentrations that are obtainable commercially.
Cleocin 150 mg purchase with mastercard
Lymphocyte (and neutrophil) homing into websites of irritation is mediated by totally different sets of leukocyte and endothelial cell adhesion molecules (see Chapter 2) acne mask 150 mg cleocin generic mastercard. Class I molecules are heterodimers consisting of a 44-kd polymorphic transmembrane glycoprotein and a 12-kd nonpolymorphic molecule skin care vancouver buy cleocin 150 mg free shipping, 2-microglobulin. The latter lacks a membrane element and is noncovalently associated with the larger heavy chain. Structural polymorphism occurs primarily within the extracellular domains of the -chain. Antigens are acknowledged by cytotoxic T cells during graft rejection and T-lymphocyte�mediated killing of virus-infected host cells within the context of histocompatibility. These are structurally comparable molecules expressed totally on cells involved in antigen presentation. Activated macrophages ingest microorganisms and kill through a collection of chemical reactions that contain enzymes and both reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates. Conversely, these antigens are main immunogens and thus targets in transplant rejection. Humoral Immunity Antibodies produced by B lymphocytes and plasma cells are integral to the effector branch of humoral immunity. As noted, the various immunoglobulin isotypes decide effector operate (Table 4-3). Pentavalent IgM and properly spaced IgG molecules (IgG subclasses 1, 2 and 3) effectively bind (fix) C1qrs, resulting in activation of the classical complement cascade and generation of its attendant proinflammatory mediators. Regulatory functions include augmentation or suppression of immune responses, usually by way of secretion of particular helper or suppressor cytokines. Effector functions include secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and killing of cells that categorical overseas or altered membrane antigens. Th1 lymphocytes have been related to cell-mediated phenomena and Th2 cells with allergic responses. Suppressor cells inhibit the activation section of immune responses; cytotoxic cells kill target cells that specific international antigens. In flip, an activated T helper cell acknowledges an antigen-specific B cell through its receptor. In certain conditions, the protective results of an immune response result in dangerous penalties, which may range from momentary discomfort to substantial damage. For example, in the process of ingesting and destroying bacteria, phagocytic cells (neutrophils and macrophages) usually trigger harm to surrounding tissue. An immune response that leads to tissue damage is broadly referred to as a hypersensitivity response. Many illnesses are categorized as immune issues or immunologically mediated conditions, by which an immune response to a overseas or self-antigen causes injury. Immune- or hypersensitivity-mediated illnesses are widespread and embrace hives (urticaria), asthma, hay fever, hepatitis, glomerulonephritis and arthritis. Hypersensitivity reactions are classified based on immune mechanism (Table 4-4). B-Lymphocyte Interactions Mature B cells exist primarily in a resting state, awaiting activation by international antigens. Activation requires cross-linking of mIg receptors via antigens introduced by accessory cells and/or interactions with membrane molecules of helper T cells by way of a mechanism known as cognate T-cell�B-cell assist. If an insufficient extra signal is supplied, proliferating B cells return to a resting state and enter the reminiscence cell pool. B-lymphocyte proliferation may be seen as germinal centers, inside which B cells endure further somatic gene rearrangements to generate cells that produce the various immunoglobulin isotypes and subclasses (Table 4-3). In the presence of antigen, T cells produce helper cytokines that stimulate isotype switching or induce proliferation of beforehand committed isotype populations. The final stage of B-cell differentiation into antibodysynthesizing plasma cells requires exposure to extra merchandise of T lymphocytes. However, some polyvalent agents instantly induce B-cell proliferation and differentiation into plasma cells, bypassing the requirements for B cell growth and differentiation components. Such agents are referred to as Type I, or immediate-type hypersensitivity, reactions: IgE antibody is shaped and binds high-affinity receptors on mast cells and/or basophils through its Fc area. Subsequent antigen binding and cross-linking of IgE set off fast (immediate) release of products from these cells, leading to the characteristic manifestations of urticaria, bronchial asthma and anaphylaxis. Less commonly, the antigen is an intrinsic structural element of the extracellular matrix. Such antigen�antibody coupling prompts complement, which in flip lyses the cell (cytotoxicity) or damages the extracellular matrix. Resulting immune complexes deposit in tissue where complement activation results in recruitment of leukocytes, which mediate tissue injury. Older children and adults initially produce IgM following antigenic challenge but quickly shift towards IgG synthesis. IgE-Mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions (Type I) Immediate-type hypersensitivity entails localized or generalized reactions that happen instantly (within minutes) after publicity to an antigen or "allergen" to which the person has been previously sensitized. Clinical manifestations rely upon the site of antigen exposure and extent of sensitization. For instance, when a response involves the skin, the characteristic native reaction is a "wheal and flare," or urticaria. When the conjunctiva and upper respiratory tract are involved, sneezing and conjunctivitis outcome and we speak of hay fever (allergic rhinitis). There is a high degree of genetically determined variability in susceptibility to type I hypersensitivity reactions, and prone people are said to be "atopic. High avidity (Kd = 10-15 M) of IgE binding accounts for the time period cytophilic antibody. Once uncovered to a selected allergen that elicits IgE, a person is sensitized; subsequent exposures to that allergen or a cross-reacting epitope induce instant hypersensitivity reactions. Once IgE is elicited, repeat publicity to antigen typically induces additional IgE antibody, rather than antibodies of other courses. Upon reexposure, recognition of the soluble antigen or allergen by IgE coupled to its surface Fc receptor prompts the mast cell or basophil. To activate the cell, antigen must cross-link at least two adjoining IgE antibody molecules. For instance, some people develop urticaria after publicity to an ice dice (physical urticaria) or pressure (dermographism). The complement-derived anaphylatoxic peptides, C3a and C5a, can instantly stimulate mast cells by a special receptor-mediated process. These cell-activating occasions trigger release of saved granule constituents and speedy synthesis and launch of other mediators. It induces constriction of vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle, causes microvascular dilation and will increase venule permeability. Histamine also will increase gastric acid secretion through H2 histamine receptors and provokes the cutaneous wheal-and-flare reaction. In the lungs, it causes the early manifestations of instant hypersensitivity, together with bronchospasm, vascular congestion and edema. Other preformed merchandise released from mast cell granules include heparin, a series of neutral proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin carboxypeptidase and acid hydrolases) and each neutrophil and eosinophil chemotactic factors.
Cheap cleocin 150 mg mastercard
Raising the osmotic strain within the cavity usually raises the speed of fluid removing from the body skin care 2014 cleocin 150 mg overnight delivery. Peritoneal dialysis can be used within the intensive care unit as a mode of renal replacement therapy skin care shiseido buy 150 mg cleocin visa, with the advantages of improved hemodynamic stability and no requirement for anticoagulation. The practical transport barrier in peritoneal dialysis is made up of size-selective capillary endothelia which are distributed inside the cellinterstitial matrix of subperitoneal tissue. Improving contact area between the peritoneum and intraperitoneal therapeutic solutions. Blockade of 1-integrins in pores and skin causes edema through lowering of interstitial fluid stress. Integrins: Transmembrane links between the extracellular matrix and the cell inside. Interstitial exclusion of albumin in rat tissues measured by a steady infusion methodology. Sampling of peritoneal interstitial fluid and measurements of colloid osmotic pressures after peritoneal dialysis in rats. Distributed model of peritoneal transport: implications of the endothelial glycocalyx. Reduced osmotic water permeability of the peritoneal barrier in aquaporin-1 knockout mice. Effect of elevated dialysate quantity on peritoneal surface space among peritoneal dialysis sufferers. The peritoneal membrane in peritoneal dialysis patients: estimation of its functional floor space by making use of stereologic methods to computerized tomography scans. Relationship between physique measurement, fill volume, and mass switch space coefficient in peritoneal dialysis. Chirurgische bermekungen uber die peritonealhole, mit besonderer berucksichtung der ovariotomie. Tissue sources and blood move limitations of osmotic water transport across the peritoneum. The results of lymphatic obstruction and of posture on absorption of protein from the peritoneal cavity. A pilot section I trial of steady hyperthermic peritoneal perfusion with high-dose carboplatin as major remedy of patients with small-volume residual ovarian cancer. Identification of distinct luminal domains for macromolecules, erythrocytes, and leukocytes within mammalian capillaries. Computer simulations of osmotic ultrafiltration and small-solute transport in peritoneal dialysis: a spatially distributed approach. Evaluation of intraperitoneal pressure and the impact of different osmotic brokers on intraperitoneal pressure in kids. Effects of nitroprusside on peritoneal mass transfer coefficients and microvascular physiology. Effects of intraperitoneal nitroprusside on peritoneal clearances in man and variations of dose, frequency of administration, and dwell occasions. Describe steady and intermittent strategies of peritoneal dialysis with their advantages and downsides. Analyze the expertise with high-dose peritoneal dialysis and continuous-flow peritoneal dialysis. Intermittent dialysis has a definite starting and end of therapy and often is carried out inside a interval measured in hours. In comparability, hemodialysis for 4 hours per day ends in an equal urea clearance of 33 mL/min when expressed per 24 hours, and a creatinine clearance of 24 mL/min. The dialysate sodium focus decreases in the course of the first 1 to 2 hours of a dialysis dwell with hypertonic dialysis solutions, particularly these with an osmolarity above four hundred mOsmol/L. Macrophages obtained after an overnight dwell have primarily regular immunoeffector features. However, such a schedule permits equilibrium amongst urea era, urea elimination, and plasma urea in noncatabolic sufferers. Short exchanges are more effective than long exchanges for the elimination of low-molecular-weight solutes similar to urea. However, when attainable, an 8- to 12-hour icodextrin change carried out every 24 to forty eight hours must be thought of to enhance sodium removing and preserve local peritoneal host defense. A long dwell time with the usage of icodextrin improves sodium removal and could additionally be advantageous for local host defenses. A steady ambulatory peritoneal dialysis-like schedule is effective in noncatabolic sufferers. The roles of high-volume peritoneal dialysis and continuous-flow peritoneal dialysis are nonetheless not established. The contribution of free water transport and small pore transport to the whole fluid elimination in peritoneal dialysis. Owing to the continuous dialysate circulate of a hundred of 300 mL/min, this modality mimics hemodialysis. The Chapter 181 / Choice of Peritoneal Dialysis Technique: Intermittent or Continuous 1104. Short dwell instances reduce the native defence mechanism of continual peritoneal dialysis patients. Protein and vitality consumption, nitrogen steadiness and nitrogen losses in patients handled with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Approach to the metabolic complications of peritoneal dialysis in acute kidney harm. Increasing effectivity of peritoneal dialysis: expertise with peritoneal-extracorporeal recirculation dialysis. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis: evaluation of fluid and solute elimination in a better move mannequin of fresh dialysate single move. Continuous move peritoneal dialysis: firest experience in kids with acute renal failure. The size of the dialysis classes additionally depends on the objectives of fluid and solute elimination. Other components of the dialysis prescription include determination of the suitable change volume and the dwell time. On the other hand, an trade volume for a small person with acute respiratory misery syndrome may be only zero. Dialysis solutions must be warmed to physique temperature before infusion to avoid discomfort and to improve solute transport. The temperature of the dialysate could be especially advantageous within the administration of hyperthermia and hypothermia. For handbook exchanges, gravity is the first determinant of this period, although the exchange volume, elevation of the dialysate bag, and presence of inflow resistance also play roles. The outflow interval is outlined as the time wanted to drain the peritoneal cavity of the effluent dialysate, which averages 20 to half-hour.