Diflucan
Diflucan dosages: 400 mg, 200 mg, 150 mg, 100 mg, 50 mg
Diflucan packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Cheap diflucan 200 mg online
Worsening venous congestion caused by the pooling of blood behind the failing ventricle and excessive ventricular dilation can rapidly result in fungal wart diflucan 100 mg buy discount on-line clinical deterioration fungus gnats on skin buy diflucan 200 mg. Left ventricular failure leads to pulmonary vascular congestion and progressive transudation of fluid, first into the pulmonary interstitium and then into alveoli (pulmonary edema). Right ventricular failure leads to systemic venous hypertension, which results in peripheral edema, hepatic congestion and dysfunction, and ascites. Dilation of the annulus of both the mitral or tricuspid valves from ventricular dilation leads to valvular regurgitation, additional impairing ventricular output. Increased Sympathetic Tone Sympathetic activation increases launch of norepinephrine from nerve endings within the heart and secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal glands into the circulation. Although enhanced sympathetic outflow can initially keep cardiac output by growing coronary heart price and contractility, worsening ventricular perform elicits rising degrees of vasoconstriction in an effort to keep arterial blood stress. The related improve in afterload, nevertheless, reduces cardiac output and exacerbates the ventricular failure. Chronic sympathetic activation in patients with coronary heart failure ultimately decreases the response of adrenergic receptors to catecholamines (receptor uncoupling), the number of receptors (downregulation), and cardiac catecholamine stores. Nonethe11 much less, the failing coronary heart becomes increasingly depending on circulating catecholamines. Abrupt withdrawal in sympathetic outflow or decreases in circulating catecholamine levels, similar to can occur following induction of anesthesia, could result in acute cardiac decompensation. A lowered density of M2 receptors additionally decreases parasympathetic influences on the center. Sympathetic activation tends to redistribute systemic blood move output away from the pores and skin, gut, kidneys, and skeletal muscle to the heart and mind. Although these mechanisms can initially compensate for delicate to reasonable cardiac dysfunction, with growing severity of dysfunction, they may really worsen the cardiac impairment. Many of the drug treatments of persistent heart failure serve to counteract these mechanisms. Symptoms may also enhance in some patients with careful, low-dose -adrenergic blockade. The downside in a pressure-overloaded ventricle is an increase in systolic wall stress. In this case, sarcomeres mainly replicate in parallel, resulting in concentric hypertrophy: the hypertrophy is such that the ratio of myocardial wall thickness to ventricular radius will increase. Ventricular hypertrophy, significantly that brought on by pressure overload, usually results in progressive diastolic dysfunction. The most typical reasons for isolated left ventricular hypertrophy are hypertension and aortic stenosis. He gives a history of getting passed out a minimum of as quickly as throughout considered one of these complications. Preexcitation normally refers to early depolarization of the ventricles by an irregular conduction pathway from the atria. The most common type of preexcitation is because of the presence of an adjunct pathway (bundle of Kent) that connects one of many atria with one of many ventricles. This irregular connection between the atria and ventricles allows electrical impulses to bypass the Ventricular Hypertrophy Ventricular hypertrophy can occur with or without dilation, relying on the sort of stress imposed on the ventricle. When the center is subjected to both stress or quantity overload, the initial response is to enhance sarcomere size and optimally overlap actin and myosin. With time, ventricular muscle mass begins to improve in response to the irregular stress. In the volume-overloaded ventricle, the issue is an increase in diastolic wall stress. The increase in ventricular muscle mass is adequate only to compensate for the rise in diameter: the ratio of the ventricular radius to wall thickness is unchanged. The capacity to conduct impulses along the bypass tract could be quite variable and may be only intermittent or fee dependent. Bypass tracts can conduct in both instructions, retrograde only (ventricle to atrium), or, hardly ever, anterograde solely (atrium to ventricle). The unfold of the anomalous impulse to the remainder of the ventricle is delayed as a outcome of it should be conducted by odd ventricular muscle, not by the a lot faster Purkinje system. The P�R interval is usually normal or only barely shortened with a left lateral bypass tract (the commonest location). Although most sufferers are in any other case regular, preexcitation may be related to different cardiac anomalies, including Ebstein anomaly, mitral valve prolapse, and cardiomyopathies. Depending on its conductive properties, the bypass tract in some sufferers may predispose them to tachyarrhythmias and even sudden demise. Ventricular fibrillation could be precipitated by a critically timed untimely atrial beat that travels down the bypass tract and catches the ventricle at a vulnerable interval. Alternatively, very speedy conduction of impulses into the ventricles by the bypass tract during atrial fibrillation can rapidly result in myocardial ischemia, hypoperfusion, and hypoxia and culminate in ventricular fibrillation. A historical past of syncope could also be ominous because it might indicate the power to conduct impulses very quickly by way of the bypass tract, resulting in systemic hypoperfusion and perhaps predisposing the affected person to sudden demise. Tachyarrhythmias develop as a result of both irregular impulse formation or irregular impulse propagation (reentry). Abnormal impulses outcome from enhanced automaticity, irregular automaticity, or triggered activity. Triggered exercise is the outcome of either early after-depolarizations (phase 2 or 3) or delayed after-depolarizations (after part 3). It consists of small-amplitude depolarizations that can comply with action potentials under some circumstances in atrial, ventricular, and His�Purkinje tissue. If these after-depolarizations attain threshold potential, they can outcome in an extrasystole or repetitive sustained tachyarrhythmias. Factors that can promote the formation of abnormal impulses embody increased catecholamine levels, electrolyte disorders (hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, and hypercalcemia), ischemia, hypoxia, mechanical stretch, and drug toxicity (particularly digoxin). Atrial fibrillation can happen when a cardiac impulse is performed rapidly retrograde up into the atria and arrives to discover totally different components of the atria out of section in restoration from the impulse. Few data can be found comparing the usage of totally different anesthetic agents or techniques in patients with preexcitation. Volatile anesthetics improve antegrade refractoriness in each normal and accessory pathways. Propofol, opioids, and benzodiazepines seem to have little direct electrophysiological effects, but can alter autonomic tone, generally lowering sympathetic outflow. Factors that tend to trigger sympathetic stimulation and increased cardiac automaticity are undesirable. Light anesthesia, hypercapnia, acidosis, and even transient hypoxia will activate the sympathetic system and are to be avoided.
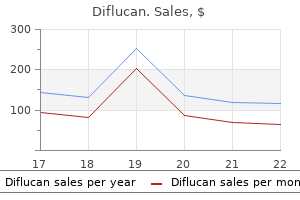
Purchase diflucan 400 mg visa
In a human peripheral nerve the onset of native anesthetic inhibition usually observe this sequence: autonomic earlier than sensory before motor fungus plural diflucan 200 mg order online. But at regular state fungus gnat nepenthes discount diflucan 400 mg amex, if sensory anesthesia is present, normally all modalities are inhibited. The nature of the intermediate chain is the premise of the classification of native anesthetics as either esters or amides (Table 16�2). Local anesthetics are weak bases that at physiological pH normally carry a optimistic charge on the tertiary amine group. Physicochemical properties of native anesthetics depend on the substitutions in the fragrant ring, the type of linkage within the intermediate chain, and the alkyl teams hooked up to the amine nitrogen. Potency is elevated by including massive alkyl teams to a parent molecule (compare tetracaine with procaine, or bupivacaine with mepivacaine). The minimum focus of local anesthetic that will block nerve impulse conduction is affected by several elements, including fiber measurement, kind, and myelination; pH (an acidic environment antagonizes clinical nerve block); frequency of nerve stimulation; and electrolyte concentrations (hypokalemia and hypercalcemia antagonize blockade). Less potent, less lipid-soluble agents (eg, lidocaine or mepivacaine) usually have a sooner onset than stronger, extra lipid-soluble brokers (eg, ropivacaine or bupivacaine). Local anesthetics with a pKa closest to physiological pH could have (at physiological pH) a higher fraction of nonionized base that more readily permeates the nerve cell membrane, generally facilitating a more rapid onset of motion. It is the lipid-soluble free-base kind that extra readily diffuses across the neural sheath (epineurium) and through the nerve membrane. The importance of pKa in understanding differences amongst local anesthetics is usually overstated. It has been asserted that the onset of action of native anesthetics immediately correlates with pKa. Other factors, corresponding to ease of diffusion through connective tissue, can affect the onset of motion in vivo. The significance of the ionized and nonionized types has many scientific implications for these agents that exist in each types. Local anesthetic solutions are ready commercially as watersoluble hydrochloride salts (pH 6�7). Because epinephrine is unstable in alkaline environments, commercially formulated native anesthetic options containing epinephrine are typically extra acidic (pH 4�5) than the comparable "plain" solutions missing epinephrine. As a direct consequence, these commercially formulated, epinephrine-containing preparations may have a decrease fraction of free base and a slower onset than solutions to which the epinephrine is added by the clinician immediately previous to use. Similarly, the extracellular base-to-cation ratio is decreased and onset is delayed when native anesthetics are injected into acidic (eg, infected) tissues. Some researchers have found that alkalinization of native anesthetic solutions (particularly commercially prepared, epinephrine-containing ones) by the addition of sodium bicarbonate (eg, 1 mL eight. Interestingly, alkalinization additionally decreases pain throughout subcutaneous infiltration. Highly lipid-soluble local anesthetics have an extended period of motion, presumably as a end result of they extra slowly diffuse from a lipid-rich environment to the aqueous bloodstream. Sustained-release techniques using liposomes or microspheres can considerably extend native anesthetic duration of action. Unfortunately, solely bupivacaine and ropivacaine show some clinically helpful selectivity (mostly throughout onset and offset of block) for sensory nerves; nonetheless, the concentrations required for surgical anesthesia nearly at all times result in some motor blockade. Systemic absorption of injected local anesthetics is dependent upon blood move, which is set by the next factors. Presence of additives-Addition of epinephrine- or much less commonly phenylephrine-causes vasoconstriction at the website of administration. The consequent decreased absorption reduces the peak native anesthetic focus in blood, facilitates neuronal uptake, enhances the quality of analgesia, prolongs the length of analgesia, and limits poisonous side effects. Vasoconstrictors have more pronounced results on length of shorter-acting than on longeracting brokers. For example, addition of epinephrine to lidocaine normally extends the period of anesthesia by a minimal of 50%, however epinephrine has restricted impact on the duration of bupivacaine peripheral nerve blocks. Epinephrine and clonidine can even increase analgesia via activation of 2-adrenergic receptors. Coadministration of dexamethasone or different steroids with local anesthetics can delay blocks by as a lot as 50%. Mixtures of native anesthetics (eg, ropivacaine and mepivacaine) produce nerve blocks with onset and length which are intermediate between the 2 father or mother compounds. Local anesthetic agent-More lipid-soluble local anesthetics that are extremely tissue sure are additionally more slowly absorbed than less lipid-soluble brokers. Most mucous membranes (eg, tracheal or oropharyngeal mucosa) provide a minimal barrier to native anesthetic penetration, resulting in a rapid onset of motion. Intact pores and skin, on the opposite hand, requires topical application of a excessive concentration of lipidsoluble native anesthetic base to guarantee permeation and analgesia. Dermal analgesia enough for inserting an intravenous catheter requires about 1 h under an occlusive dressing. Distribution Distribution is decided by organ uptake, which is set by the following factors. In explicit, the lung extracts significant amounts of native anesthetic in the course of the "first move"; consequently, patients with right-to-left cardiac shunts are more prone to poisonous side effects of lidocaine injected as an antiarrhythmic agent. Tissue/blood partition coefficient-Increasing lipid solubility is related to greater plasma protein binding and also larger tissue uptake of local anesthetics from an aqueous compartment. Tissue mass-Muscle offers the greatest reservoir for distribution of native anesthetic agents within the bloodstream due to its giant mass. Biotransformation and Excretion the biotransformation and excretion of local anesthetics is outlined by their chemical construction. For all compounds little or no nonmetabolized native anesthetic is excreted by the kidneys. Ester hydrolysis is fast, and the water-soluble metabolites are excreted in the urine. Patients with genetically deficient pseudocholinesterase would theoretically be at increased risk for poisonous unwanted aspect effects from ester native anesthetics, as metabolism is slower, however clinical evidence for this is missing, most likely as a end result of various metabolic pathways can be found within the liver. In distinction to other ester anesthetics, cocaine is primarily metabolized (ester hydrolysis) within the liver. Amides-Amide native anesthetics are metabolized (N-dealkylation and hydroxylation) by microsomal P-450 enzymes within the liver. The fee of amide metabolism is dependent upon the specific agent (prilocaine > lidocaine > mepivacaine > ropivacaine > bupivacaine) but total is constantly slower than ester hydrolysis of ester native anesthetics. Decreases in hepatic function (eg, with cirrhosis) or in liver blood flow (eg, congestive heart failure, -blockers, or H2-receptor blockers) will scale back the speed of amide 8 1. Esters-Ester local anesthetics are predom- metabolism and potentially predispose patients to having higher blood concentrations and a greater risk of systemic toxicity.
50 mg diflucan generic
Although markedly smaller fungus gnats winter order 100 mg diflucan visa, it may be thought of a midline "continuation" of the aorta fungal sinus generic diflucan 100 mg without prescription, during which case its lateral branches, the small lumbar arteries and lateral sacral branches, would even be included as a half of the paired parietal branches. The veins that correspond to the unpaired visceral branches of the aorta are instead tributaries of the hepatic portal vein. The branches comparable to the paired visceral branches of the abdominal aorta embrace the right suprarenal vein, the right and left renal veins, and the proper gonadal (testicular or ovarian) vein. The common iliac lymph nodes obtain lymph from the external and inside iliac lymph nodes. Lymph from the common iliac lymph nodes passes to the right and left lumbar lymph nodes. Lymph from the alimentary tract, liver, spleen, and pancreas passes alongside the celiac and superior and inferior mesenteric arteries to the pre-aortic lymph nodes (celiac and superior and inferior mesenteric nodes) scattered around the origins of these arteries from the aorta. Lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes of the posterior abdominal wall and lymphatic trunks of the 1273 abdomen. All lymphatic drainage from the decrease half of the body converges within the abdomen to enter the start of the thoracic duct. These nodes obtain lymph immediately from the posterior stomach wall, kidneys, ureters, testes or ovaries, uterus, and uterine tubes. They additionally receive lymph from the descending colon, pelvis, and lower limbs via the inferior mesenteric and common iliac lymph nodes. Efferent lymphatic vessels from the massive lumbar lymph nodes type the best and left lumbar lymphatic trunks. The inferior finish of the thoracic duct lies anterior to the bodies of the L1 and L2 vertebrae between the proper crus of the diaphragm and the aorta. Consequently, primarily all of the lymphatic drainage from the lower half of the physique (deep lymphatic drainage inferior to the extent of the diaphragm and all superficial drainage inferior to the extent of the umbilicus) converges within the stomach to enter the start of the thoracic duct. The thoracic duct ascends via the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm into the posterior mediastinum, where it collects extra parietal and visceral drainage, notably from the left higher quadrant of the physique. The duct ultimately ends by entering the venous system on the junction of the left subclavian and inner jugular veins (the left venous angle). Hiccups outcome from irritation of afferent or efferent nerve endings, or of medullary centers in the brainstem that management the muscle tissue of respiration, particularly the diaphragm. Hiccups have many causes, similar to indigestion, diaphragm irritation, alcoholism, cerebral lesions, and thoracic and stomach lesions, all which disturb the phrenic nerves. Paralysis of a hemidiaphragm can be recognized radiographically by its everlasting elevation and paradoxical motion. Referred Pain from Diaphragm Pain from the diaphragm radiates to two different areas because of the difference in the sensory nerve supply of the diaphragm (Table 5. Pain ensuing from irritation of the diaphragmatic pleura or the diaphragmatic peritoneum is referred to the shoulder area, the realm of pores and skin provided by the C3�C5 segments of the spinal twine (see the Clinical Box "Visceral Referred Pain" earlier on this chapter). Irritation of peripheral regions of the diaphragm, innervated by the inferior intercostal nerves, is more localized, being referred to the skin over the costal margins of the anterolateral belly wall. The frequent cause of this harm is severe trauma to the thorax or abdomen during a motor vehicle accident. Most diaphragmatic ruptures are on the left side (95%) as a end result of the substantial mass of the liver, intimately associated with the diaphragm on the right side, offers a physical barrier. This a half of the diaphragm is generally formed solely by fusion of the superior and inferior fascias of the diaphragm. When a traumatic diaphragmatic hernia happens, the abdomen, small gut and mesentery, transverse colon, and spleen could herniate by way of this space into the thorax. Hiatal (hiatus) hernia, a protrusion of part of the stomach into the thorax by way of the esophageal hiatus, was discussed earlier on this chapter. The constructions that move through the esophageal hiatus (vagal trunks, left inferior phrenic vessels, esophageal branches of the left gastric vessels) may be injured in surgical procedures on the esophageal hiatus. Herniation almost always happens on the left owing to the presence of the liver on the best. Posterolateral defect of the diaphragm is the only relatively frequent congenital anomaly of the diaphragm, occurring roughly as soon as in 2,200 newborn infants (Moore, Persaud, and Torchia, 2016). Because of the resultant pulmonary hypoplasia, the mortality price in these infants is high (approximately 76%). An an infection may unfold by way of the blood to the vertebrae (hematogenous spread), notably throughout childhood. Pus from the psoas abscess passes inferiorly alongside the psoas muscle within this fascial tube over the pelvic brim and deep to the inguinal ligament. Pus can also reach the psoas fascia by passing from the posterior mediastinum when the thoracic vertebrae are diseased. The inferior a part of the iliac fascia is often tense and raises a fold that passes to the interior aspect of the iliac crest. The superior a part of this fascia is unfastened and will kind a pocket, the iliacosubfascial fossa, posterior to the abovementioned fold. Part of the large intestine, such as the cecum and/or appendix on the best aspect and the sigmoid colon on the left side, may turn out to be trapped in this fossa, inflicting considerable ache. Posterior Abdominal Pain the iliopsoas muscle has in depth, clinically necessary relations to the kidneys, ureters, cecum, appendix, sigmoid colon, pancreas, lumbar lymph nodes, and nerves of the posterior abdominal wall. When any of these buildings is diseased, motion of the iliopsoas usually causes pain. Because the psoas lies alongside the vertebral column and the iliacus crosses the sacro-iliac joint, illness of the intervertebral and sacro-iliac joints may cause 1279 spasm of the iliopsoas, a protective reflex. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas in advanced stages invades the muscle tissue and nerves of the posterior belly wall, producing excruciating ache due to the close relationship of the pancreas to the posterior belly wall. Partial Lumbar Sympathectomy the therapy of some patients with arterial illness within the decrease limbs might embrace a partial lumbar sympathectomy, the surgical removing of two or extra lumbar sympathetic ganglia by division of their rami communicantes. The surgeon splits the muscles of the anterior belly wall and moves the peritoneum medially and anteriorly to expose the medial edge of the psoas major, along which the sympathetic trunk lies. Consequently, the surgeon carefully retracts them to expose the sympathetic trunks that often lie in the groove between the psoas major laterally and the lumbar vertebral bodies medially. Pulsations of a large aneurysm can be detected to the left of the midline; the pulsatile mass could be moved easily from side to side. Acute rupture of an stomach aortic aneurysm is associated with extreme pain in the abdomen or back. If unrecognized, such an aneurysm has a mortality rate of practically 90% due to heavy blood loss (Swartz, 2014). Surgeons can repair an aneurysm by opening it, inserting a prosthetic graft, and sewing the wall of the aneurysmal aorta over the graft to defend it. Many vascular issues formerly handled with open restore, together with aneurysm restore, are actually being handled by means of endovascular catheterization procedures.
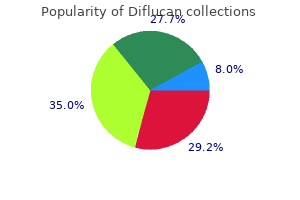
Diflucan 200 mg otc
This potential area descends to the level of the tenth rib in the midaxillary line fungus juice discount diflucan 150 mg amex. Its existence have to be stored in thoughts when doing a splenic needle biopsy fungus humungous order diflucan 400 mg with visa, or when injecting radiopaque materials into the spleen for visualization of the hepatic portal vein (splenoportography). In this case, both the biliary and pancreatic duct methods are blocked and neither bile nor pancreatic juice can enter the duodenum. However, bile might back up and enter the pancreatic duct, often resulting in pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). A similar reflux of bile sometimes results from spasms of the hepatopancreatic sphincter. Normally, the sphincter of the pancreatic duct prevents reflux of bile into the pancreatic duct; nevertheless, if the hepatopancreatic ampulla is obstructed, the weak pancreatic duct sphincter could also be unable to stand up to the excessive stress of the bile in the hepatopancreatic ampulla. If an adjunct pancreatic duct connects with the main pancreatic duct and opens into the duodenum, it may compensate for an obstructed main pancreatic duct or spasm of the hepatopancreatic sphincter. First, a fiberoptic endoscope is passed via the mouth, esophagus, and abdomen. Then the duodenum is entered and a cannula is inserted into the most important duodenal papilla and superior beneath fluoroscopic management into the duct of choice (bile duct or pancreatic duct) for injection of radiographic contrast medium. Utilizing the fluoroscopic visualization offered by the distinction medium, devices operated through the endoscope are then utilized for the intervention. The accessory pancreatic tissue may contain pancreatic islet cells that produce glucagon and insulin. Pancreatic damage may result from sudden, extreme, forceful compression of the stomach, such because the force of impalement on a steering wheel in an vehicle accident. Because the pancreas lies transversely, the vertebral column acts as an anvil, and the traumatic force could rupture the friable pancreas. Rupture of the pancreas incessantly tears its duct system, allowing pancreatic juice to enter the parenchyma of the gland and to invade adjacent tissues. Subtotal Pancreatectomy Pancreatectomy, partial or complete surgical elimination of the pancreas, is most commonly carried out when pancreatic tumors are detected (see "Pancreatic Cancer" below). However, subtotal or partial pancreatectomy is utilized to remove ruptured portions of the pancreas and for the remedy of continual pancreatitis after nonsurgical choices have failed. Subtotal pancreatectomy reduces pancreatic secretion by reducing the size of the pancreas. While surgical removal of the physique and tail is easier, the anatomical relationships and blood provide of the head of the pancreas, bile duct, and duodenum make it unimaginable to take away the entire head of the pancreas without removing the duodenum and terminal bile duct (Skandalakis et al. Usually, a rim of the pancreas is retained alongside the medial border of the duodenum to protect the duodenal blood provide. Because of the posterior relationships of the pancreas, most cancers of the pinnacle usually compresses and obstructs the bile duct and/or the hepatopancreatic ampulla. Obstruction of the biliary tract, usually the frequent bile duct or ampulla, ends in the retention of bile pigments, enlargement of the gallbladder, and obstructive jaundice. The Whipple procedure for cancer of the pancreas and biliary tract (pancreatoduodenectomy) is probably the most generally performed for tumors of the pancreas. It is a fancy operation to remove part of the top of the pancreas, a part of the duodenum, and the gallbladder. Tumors that develop in the physique and tail of the pancreas are eliminated by a subtotal procedure referred to as distal pancreatectomy. The individual is requested to take a deep breath because the examiner presses posterosuperiorly with the proper hand and pulls anteriorly with the left hand (Bickley, 2016). Subphrenic Abscesses Peritonitis may result in the formation of localized abscesses (collections of purulent exudate, or pus) in varied parts of the peritoneal cavity. A frequent website for pus to acquire is in the best or left subphrenic recess or house. Subphrenic abscesses are more common on the best facet due to the frequency of ruptured appendices and perforated duodenal ulcers. A subphrenic abscess is usually drained by an incision inferior to , or via, the bed of the 12th rib (Ellis, 2013), making it unnecessary to create a gap within the pleura or peritoneum. An anterior subphrenic abscess is usually drained through a subcostal incision located inferior and parallel to the proper costal margin. More recently, especially for the rationale that creation of the cauterizing scalpel and laser surgical procedure, it has become potential to perform hepatic segmentectomies. This procedure makes it attainable to take away (resect) solely these segments that are affected by a tumor. These injuries are often managed by eradicating the international materials and packing or embolization (deliberate blocking of blood vessels to management bleeding) when needed. Every effort is made to avoid resection of the liver for trauma; resection is a last resort. In such cases, the surgeon must decide whether to carry out a segmentectomy or lobectomy. Hepatomegaly the liver is a delicate extremely vascular organ that receives a large amount of blood instantly earlier than it enters the heart. Any rise in central venous stress is directly transmitted to the liver, which enlarges as it becomes engorged with blood. Marked temporary engorgement stretches the fibrous capsule of the liver, producing pain around the lower ribs, notably in the proper hypochondrium. In addition to diseases that produce hepatic engorgement such as congestive heart failure, bacterial and viral diseases corresponding to hepatitis trigger hepatomegaly (liver enlargement). When the liver is massively enlarged, its inferior edge may be readily palpated beneath the proper costal margin and may even reach the pelvic brim in the proper lower quadrant of the stomach. The liver is a typical web site of metastatic carcinoma (secondary cancers spreading from organs drained by the portal system of veins. Cancer cells may pass to the liver from the thorax, particularly from the proper breast, due to the communications between thoracic lymph nodes and the lymphatic vessels draining the naked space of the liver. Although many industrial solvents, similar to carbon tetrachloride, produce cirrhosis, the condition develops most regularly in persons suffering from continual alcoholism. The liver has nice practical reserve; therefore, the metabolic proof of liver failure is late to seem. Fibrous tissue surrounds the intrahepatic blood vessels and biliary ducts, making the liver agency and impeding the circulation of blood via it (portal hypertension). Less commonly, a portosystemic or portocaval shunt could also be percutaneously or surgically created, anastomosing the portal and systemic venous systems (see the Clinical Box "Portosystemic Shunts," p. Liver Biopsy Hepatic tissue may be obtained for diagnostic functions by liver biopsy. Because the liver is located in the proper hypochondriac region the place it receives safety from the overlying thoracic cage, the needle is commonly directed by way of the best tenth intercostal space in the midaxillary line. Before the doctor takes the biopsy, the person is requested to maintain his or her breath in full expiration to scale back the costodiaphragmatic recess and to reduce the potential for damaging the lung and contaminating the pleural cavity. In approximately 4% of people, nonetheless, the gallbladder is suspended from the liver by a short mesentery, growing its mobility. Mobile gallbladders are topic to vascular 1197 torsion and infarction (sudden insufficiency of arterial or venous blood supply). Variations in Cystic and Hepatic Ducts Occasionally, the cystic duct runs alongside the widespread hepatic duct and adheres intently to it.
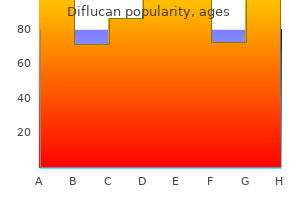
Buy diflucan 100 mg free shipping
The superficial popliteal lymph nodes are usually small and lie within the subcutaneous tissue antifungal mouth 100 mg diflucan cheap overnight delivery. The deep popliteal lymph nodes encompass the vessels and obtain lymph from the joint capsule of the knee and the lymphatic vessels that accompany the deep veins of the leg fungus gnats ladybugs order diflucan 200 mg line. The lymphatic vessels from the popliteal lymph nodes comply with the femoral vessels to the deep inguinal lymph nodes. The anterior (dorsiflexor or extensor) compartment contains four muscular tissues (the fibularis tertius lies inferior to the level of this section). The posterior (plantarflexor or flexor) compartment, containing seven muscle tissue, is subdivided by an intracompartmental transverse intermuscular septum right into a superficial group of three (two of that are generally tendinous/aponeurotic at this level) and a deep group of 4. The popliteus (part of the deep group) lies superior to the level of this section. The anterior compartment of the leg, or dorsiflexor (extensor) compartment, is positioned anterior to the interosseous membrane, between the lateral floor of the shaft of the tibia and the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula. The anterior compartment is bounded anteriorly by the deep fascia of the leg and pores and skin. The deep fascia overlying the anterior compartment is dense superiorly, providing part of the proximal attachment of the muscle immediately deep to it. With unyielding constructions on three sides (the two bones and the interosseous membrane) and a dense fascia on the remaining aspect, the relatively small anterior compartment is especially confined and therefore most vulnerable to compartment syndromes (see the medical box "Containment and Spread of Compartmental Infections in the Leg"). These dissections show the continuation of the anterior and lateral leg muscle tissue into the foot. The thinner parts of the deep fascia of the leg have been eliminated, leaving the thicker portions that make up the extensor and fibular retinacula, which retain the tendons as they cross the ankle. At the ankle, the vessels and the deep fibular nerve lie midway between the malleoli and between the tendons of the lengthy dorsiflexors of the toes. Synovial sheaths surround the tendons as they pass beneath the retinacula of the ankle. The superior extensor retinaculum is a powerful, broad band of deep fascia, passing from the fibula to the tibia, proximal to the malleoli. The inferior extensor retinaculum, a Y-shaped band of deep fascia, attaches laterally to the anterosuperior floor of the calcaneus. It varieties a robust loop across the tendons of the fibularis tertius and the extensor digitorum longus muscular tissues. These muscle tissue pass and insert anterior to the transversely oriented axis of the ankle (talocrural) joint and, therefore, are dorsiflexors of the ankle joint, elevating the forefoot and depressing the heel. The lengthy extensors additionally pass alongside and connect to the dorsal side of the digits and are thus extensors (elevators) of the toes. The latter is important to a clean gait and is essential to deceleration (braking) relative to operating and strolling downhill. During standing, the dorsiflexors reflexively pull the leg (and thus the center of gravity) anteriorly on the mounted foot when the physique begins to lean (the center of gravity begins to shift too far) posteriorly. In so doing, its tendon is positioned farthest from the axis of the ankle joint, giving it the most mechanical advantage and making it the strongest dorsiflexor. This dissection shows the muscle tissue of the anterolateral leg and dorsum of the foot. The common fibular nerve, coursing subcutaneously throughout the lateral aspect of the head and neck of the fibula, is essentially the most commonly injured peripheral nerve. In this deeper dissection of the anterior compartment, the muscular tissues and inferior extensor retinaculum are retracted to show the arteries and nerves. The central band inserts into the base of the center phalanx, and the lateral slips converge to insert into the base of the distal phalanx. It could play a special proprioceptive role in sensing sudden inversion after which contracting reflexively to defend the anterior tibiofibular ligament, probably the most generally sprained ligament of the physique. It is likely considered one of the two terminal branches of the frequent fibular nerve, arising between the fibularis longus muscle and the neck of the fibula. The deep fibular nerve then exits the compartment, continuing across the ankle joint to supply intrinsic muscle tissue (extensors digitorum and hallucis brevis), and a small area of the pores and skin of the foot. The smaller terminal branch of the popliteal artery, the anterior tibial artery, begins at the inferior border of the popliteus muscle. At the ankle joint, midway between the malleoli, the anterior tibial artery changes names, becoming the dorsalis pedis artery (dorsal artery of the foot). The popliteal artery begins on the site of the adductor hiatus (where it may be compressed) after which lies successively on the distal finish of the femur, joint capsule of the knee joint, and popliteus muscle (not visible) earlier than dividing into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries on the inferior angle of the popliteus fossa. Sniderman, Associate Professor of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. These muscle tissue have their fleshy bellies in the lateral compartment however are tendinous as they exit the compartment throughout the frequent synovial sheath deep to the superior fibular retinaculum. Developmentally, the fibularis muscle tissue are postaxial muscular tissues, receiving innervation from the posterior divisions of the spinal nerves, which contribute to the sciatic nerve. However, as a result of the fibularis longus and brevis move posterior to the transverse axis of the ankle (talocrural) joint, they contribute to plantarflexion on the ankle-unlike the 1716 postaxial muscles of the anterior compartment (including the fibularis tertius), that are dorsiflexors. As evertors, the fibularis muscular tissues act on the subtalar and transverse tarsal joints. In practice, the primary function of the evertors of the foot is not to elevate the lateral margin of the foot (the frequent description of eversion) but to depress or repair the medial margin of the foot in support of the toe off part of strolling and, particularly, operating and to resist inadvertent or extreme inversion of the plantarflexed foot (the place during which the ankle is most susceptible to injury). When standing (and particularly when balancing on one foot), the fibularis muscles contract to resist medial sway (to recenter a line of gravity, which has shifted medially) by pulling laterally on the leg whereas miserable the medial margin of the foot. To take a look at the fibularis longus and brevis, the foot is everted strongly in opposition to resistance; if appearing usually, the muscle tendons can be seen and palpated inferior to the lateral malleolus. Its broad tendon grooves the posterior facet of the lateral malleolus and can be palpated inferior to it. Occasionally, nonetheless, the fibularis tertius passes anteriorly to connect on to the proximal phalanx of the fifth digit. Instead, perforating branches and accompanying veins provide blood to and drain blood from the compartment. Proximally, perforating branches of the anterior tibial artery penetrate the anterior intermuscular septum. Inferiorly, perforating branches of the fibular artery penetrate the posterior intermuscular septum, along with their accompanying veins (L. The posterior compartment and the muscles inside it are divided into superficial and deep subcompartments/muscle groups by the transverse intermuscular septum. The tibial nerve and posterior tibial and fibular vessels provide each elements of the posterior compartment but run in the deep subcompartment deep (anterior) to the transverse intermuscular septum. The smaller deep subcompartment, like the anterior compartment, is bounded by the two leg bones and the interosseous membrane that binds them collectively, plus the transverse intermuscular septum. Because the nerve and blood vessels 1719 supplying the complete posterior compartment and the only of the foot move through the deep subcompartment, when swelling happens, it leads to a compartment syndrome that has critical penalties, corresponding to muscular necrosis (tissue death) and paralysis. Inferiorly, the deep subcompartment tapers as the muscle tissue it incorporates become tendinous. The retinaculum is subdivided deeply, forming separate compartments for each tendon of the deep muscle group, in addition to for the tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery as they bend across the medial malleolus. Muscles of the posterior compartment produce plantarflexion on the ankle, inversion at the subtalar and transverse tarsal joints, and flexion of the toes.
Syndromes
- Headache
- Chronic diseases including infection and cancer
- Changes in taste or smell
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Petrolatum
- Rash
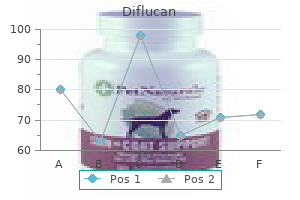
Diflucan 200 mg buy with amex
The x descent is absent antifungal yoga mat cheap diflucan 400 mg visa, and a distinguished cv wave is often present on the central venous stress waveform fungus workshop trusted diflucan 200 mg. Thermodilution cardiac output measurements are falsely elevated due to the tricuspid regurgitation. Choice of Agents the choice of anesthetic brokers should be primarily based on the underlying dysfunction. Coagulopathy secondary to hepatic dysfunction ought to be excluded previous to any regional approach. Pathophysiology Chronic left ventricular failure often results in sustained will increase in pulmonary vascular pressures. The persistent enhance in afterload causes progressive dilation of the thin-walled right ventricle, and extreme dilation of the tricuspid annulus ultimately leads to regurgitation. An increase in end-diastolic volume permits the right ventricle to compensate for the regurgitant quantity and preserve an efficient ahead circulate. Because the right atrium and the vena cava are compliant and can normally accommodate the quantity overload, imply right atrial and central venous pressures are generally only barely elevated. Acute or marked elevations in pulmonary artery pressures enhance the regurgitant quantity and are reflected by an increase in central venous pressure. Moreover, sudden marked will increase in right ventricular afterload sharply reduce the effective proper ventricular output, cut back left ventricular preload, and may precipitate systemic hypotension. Chronic venous hypertension leads to passive congestion of the liver and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Severe right ventricular failure with underloading of the left heart can also produce right-to-left shunting by way of a patent foramen ovale, which can lead to marked hypoxemia. As the right heart dilates, it acquires a more spherical shape, the best ventricle extends to the apex of the heart, and the interventricular septum is flattened. The threat of antibiotic administration is often thought-about larger than the potential for growing perioperative endocarditis. Because the underlying disorder is mostly extra essential than the tricuspid regurgitation itself, remedy is aimed on the underlying illness process. Endocarditis is believed to happen in areas of cardiac endothelial injury, the place in cases of bacteremia, bacteria can be deposited and multiply. Areas of elevated myocardial blood flow velocity result in broken endothelium, offering a template for bacterial adherence and progress. Aspirin can also be indicated on this inhabitants, in addition to in sufferers with bioprosthetic valves, to stop thrombus formation. Heparin could be discontinued 4 to 6 hours prior to surgery and then restarted as quickly as surgical bleeding permits, till the affected person could be restarted on warfarin therapy. Fresh frozen plasma or prothrombin complex concentrates could also be given, if wanted, in an emergency situation to interrupt warfarin therapy. Patients with congenital heart disease might therefore be encountered during noncardiac surgery and obstetric deliveries. Knowledge of the anatomy of the unique heart structure defect and of any corrective repairs is crucial previous to anesthetizing the affected person with congenital heart illness. The advanced nature and ranging pathophysiology of congenital coronary heart defects make classification difficult. Most patients present with cyanosis, congestive coronary heart failure, or an asymptomatic abnormality. Cyanosis is often the result of an abnormal intracardiac communication that enables unoxygenated blood to attain the systemic arterial circulation (right-to-left shunting). Congestive heart failure is most outstanding with defects that both obstruct left ventricular outflow or markedly increase pulmonary blood flow. The latter is usually due to an irregular intracardiac communication that returns oxygenated blood to the best heart (left-to-right shunting). Whereas right-to-left shunts generally lower Congenital Heart Disease Preoperative Considerations Congenital heart disease encompasses a seemingly countless record of abnormalities that could be detected in infancy, early childhood, or, less commonly, maturity. The natural historical past of some defects is such that patients typically survive to adulthood (Table 21�15). Moreover, the variety of surviving adults with corrected or palliated coronary heart illness. Survival prior to surgical correction with some anomalies (eg, transposition, whole anomalous venous return, pulmonary atresia) is dependent upon the simultaneous presence of another shunting lesion (eg, patent ductus arteriosus, patent foramen ovale, ventricular septal defect). Chronic hypoxemia in sufferers with cyanotic heart disease usually results in erythrocytosis. This improve in purple cell mass, which is due to increased erythropoietin secretion from the kidneys, serves to restore tissue oxygen focus to regular. Unfortunately, blood viscosity also can rise to the purpose at which it might intervene with oxygen delivery. When tissue oxygenation is restored to normal, the hematocrit is steady (usually <65%), and symptoms of the hyperviscosity syndrome are absent, the patient is alleged to have compensated erythrocytosis. Phlebotomy is usually not really helpful if signs of hyperviscosity are absent and the hematocrit is lower than 65%. Platelet counts tend to be low-normal, and tons of sufferers have defects in the coagulation cascade. Hyperuricemia typically happens due to elevated urate reabsorption secondary to renal hypoperfusion, and may end up in progressively impaired kidney operate. Preoperative echocardiography is invaluable in defining the anatomy of the defect(s) and to confirm or exclude the existence of other lesions or problems, their physiological significance, and the consequences of any therapeutic interventions. Arrhythmias Hypoxemia Pulmonary hypertension Existing shunts Paradoxical embolism Bacterial endocarditis whose circumstances are inoperable and may be awaiting cardiac transplantation. Although the administration of the primary group of sufferers could be the similar as that of regular patients (except for consideration of prophylactic antibiotic therapy), the care of others requires familiarity with the advanced pathophysiology of those defects (Tables 21�17 and 21�18). For the aim of anesthetic administration, congenital heart defects may be divided into obstructive lesions, predominantly left-to-right shunts, or predominantly right-to-left shunts. Obstructive Lesions Pulmonic Stenosis Pulmonary valve stenosis obstructs right ventricular outflow and causes concentric right ventricular hypertrophy. Valve leaflets are often partially fused and display systolic doming on echocardiography. The proper ventricle undergoes hypertrophy, and poststenotic dilation of the pulmonary artery is commonly present. Symptomatic patients readily develop fatigue, dyspnea, and peripheral cyanosis with exertion because of the restricted pulmonary blood move and increased oxygen extraction by tissues. With extreme stenosis, the pulmonic valve gradient exceeds 60 to eighty mm Hg, relying on the age of the patient. Right-to-left shunting may also happen in the presence of a patent foramen ovale or atrial septal defect. Cardiac output may be very depending on an elevated coronary heart rate, but excessive will increase in the latter can compromise ventricular filling. Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty is generally thought-about the preliminary treatment of choice in most sufferers with symptomatic pulmonic stenosis.
Diflucan 400 mg effective
The academic content is (as of 2018) obtainable without charge antifungal hair loss diflucan 400 mg free shipping, and the certification and continuing schooling process is out there for a reasonable payment definition de fungus diflucan 200 mg trusted. The course covers all types of electrical surgical models in the working room and makes suggestion for his or her right use and safety precautions. Long respiration tubes with excessive compliance increase the difference between the amount of gas delivered to a circuit by a reservoir bag or ventilator and the volume actually delivered to the patient. With an absorber, the circle system prevents rebreathing of carbon dioxide at recent fuel flows which are thought of low (fresh gasoline move 1 L) or even contemporary gas flows equal to the uptake of anesthetic gases and oxygen by the affected person and the circuit itself (closedsystem anesthesia). Because of the unidirectional valves, equipment lifeless area in a circle system is proscribed to the realm distal to the point of inspiratory and expiratory gas mixing at the Y-piece. Breathing systems provide the ultimate conduit for the delivery of anesthetic gases to the patient. Many totally different circuit designs have been developed, each with various degrees of efficiency, convenience, and complexity. This article critiques the most important respiration systems: insufflation, draw-over, Mapleson circuits, the circle system, and resuscitation systems. Most classifications of breathing systems artificially consolidate functional traits (eg, the extent of rebreathing) with bodily traits (eg, the presence of unidirectional valves). Carbon dioxide accumulation under head and neck draping is a hazard of ophthalmic surgical procedure performed with native anesthesia. Insufflation may additionally be used to preserve arterial oxygenation during temporary intervals of apnea (eg, throughout bronchoscopy). Instead of blowing gases across the face, oxygen is directed into the lungs through a tool placed in the trachea. As the patient inhales, air passes through the gauze, vaporizing the liquid agent, and carrying excessive concentrations of anesthetic to the affected person. The vaporization lowers mask temperature, leading to moisture condensation and a drop in anesthetic vapor strain (vapor stress is proportional to temperature). This approach may be used in locations or situations by which compressed medical gases are unavailable (eg, battlefields). The fraction of inspired oxygen (Fio2) can be supplemented using an open-ended reservoir tube of about four hundred mL, attached to a T-piece on the upstream side of the vaporizer. Across the medical range of tidal volume and respiratory fee, an oxygen move rate of 1 L/min gives an Fio2 of 30% to 40%, or with 4 L/min, an Fio2 of 60% to 80%. There are a quantity of commercial draw-over techniques obtainable that share widespread properties (Table 3�1). The relative location of these elements determines circuit efficiency and is the premise of the Mapleson classification (Table 3�2). Portable Low resistance to gasoline flow Usable with any agent1 Controllable vapor output 1 Components of Mapleson Circuits A. The compliance of the respiration tubes largely determines the compliance of the circuit. For example, if a breathing circuit with a compliance of 8 mL gas/cm H2O is pressurized during supply of a tidal volume to 20 cm H2O, a hundred and sixty mL of the tidal quantity shall be lost to the circuit. The a hundred and sixty mL characterize a mix of gas compression and breathingtube enlargement. This is an important consideration in any circuit delivering positive-pressure air flow by way of respiratory tubes (eg, circle systems). Fresh Gas Inlet Gases (anesthetics combined with oxygen or air) from the anesthesia machine constantly enter the circuit through the contemporary fuel inlet. Adjustable Pressure-Limiting Valve (Pressure-Relief Valve, Pop-Off Valve) As anesthetic gases enter the respiration circuit, pressure will rise if the gas influx is greater than the mixed uptake of the patient and the circuit. Exiting gases enter the operating room atmosphere or, ideally, a waste-gas scavenging system. Assisted and managed ventilation require constructive pressure throughout inspiration to increase the lungs. Performance Characteristics of Mapleson Circuits Mapleson circuits are lightweight, inexpensive, and simple. Because a contemporary gas move equal to minute air flow is sufficient to prevent rebreathing, the Mapleson A design is the most environment friendly Mapleson circuit for spontaneous air flow. Although some alveolar and fresh gas exits through the valve during inspiration, no gas is vented throughout expiration, since the exhaled fuel stagnates in the course of the expiratory section of positive-pressure ventilation. As a outcome, very excessive fresh gas flows (greater than thrice minute ventilation) are required to stop rebreathing with a Mapleson A circuit throughout managed ventilation. Thus, simply shifting parts utterly alters the contemporary gas requirements of the Mapleson circuits. A drawback of this coaxial circuit is the chance of kinking or disconnection of the contemporary gas inlet tubing. Periodic inspection of the inner tubing is mandatory to determine this complication; if unrecognized, both of those mishaps may result in vital rebreathing of exhaled fuel. Carbon Dioxide Absorber and the Absorbent Rebreathing alveolar gas conserves warmth and humidity. In an attempt to avoid these issues, the circle system adds extra components to the breathing system. Reaction end merchandise embrace warmth (the warmth of neutralization), water, and calcium carbonate. It consists primarily of calcium hydroxide (80%), together with sodium hydroxide, water, and a small quantity of potassium hydroxide. Another absorbent, barium hydroxide lime, is no longer used because of the attainable elevated hazard of fireplace in the respiratory system. A pH indicator dye (eg, ethyl violet) modifications colour from white to purple as a consequence of accelerating hydrogen ion focus and absorbent exhaustion. Although exhausted granules might revert to their original colour if rested, no significant restoration of absorptive capability happens. Granule dimension is a compromise between the upper absorptive surface area of small granules and the decrease resistance to gasoline move of bigger granules. Increasing the hardness of soda lime by adding silica minimizes the danger of inhalation of sodium hydroxide mud and also decreases resistance of gas flow. Additional water is added to absorbent during packaging to provide optimal situations for carbonic acid formation. Volatile anesthetics can be damaged right down to carbon monoxide by dry absorbent (eg, sodium or potassium hydroxide) sufficiently to cause clinically measureable carboxyhemoglobin concentrations. The formation of carbon monoxide is best with desflurane; with sevoflurane, it happens at a higher temperature. It possesses higher inertness than soda lime, resulting in much less degradation of volatile anesthetics (eg, sevoflurane into compound A or desflurane into carbon monoxide). Higher concentrations of sevoflurane, extended publicity, and low-flow anesthetic approach seem to increase the formation of compound A. Compound A has been proven to produce nephrotoxicity in animals however has by no means been associated with unwell effects in people. The granules of absorbent are contained inside one or two canisters that match snugly between a head and base plate.
Generic 400 mg diflucan with visa
Coronary vasospasm can additionally be a explanation for transient transmural ischemia in some sufferers; most vasospastic episodes occur at preexisting stenotic lesions in epicardial vessels and may be precipitated by a selection of components fungus gnats compost buy diflucan 400 mg otc, including emotional upset and hyperventilation (Prinzmetal angina) fungus gnats plants get rid diflucan 100 mg purchase with amex. Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease the general method in treating sufferers with ischemic coronary heart disease is five-fold: A. Optimal blockade ends in a resting heart fee between 50 and 60 beats/min and prevents appreciable will increase with train (<20 beats/min improve during exercise). Available brokers differ in receptor selectivity, intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity, and membrane-stabilizing properties (Table 21�8). Agents with intrinsic sympathomimetic properties are better tolerated by sufferers with delicate to average ventricular dysfunction. Certain -blockers (bisoprolol, carvedilol, and extendedduration metoprolol) enhance survival in sufferers with continual coronary heart failure. Blockade of 2-adrenergic receptors also can mask hypoglycemic symptoms in patients with diabetes, delay metabolic recovery from hypoglycemia, and impair the handling of enormous potassium masses. Cardioselective (1-receptor-specific) agents, though usually better tolerated than nonselective brokers in sufferers with reactive airways, must still be used cautiously in such sufferers. Patients on long-standing -blocker remedy ought to have these agents continued perioperatively. Agent Acebutolol Atenolol Betaxolol Esmolol Metoprolol Bisoprolol Oxprenolol Alprenolol Pindolol Penbutolol Carteolol Labetalol Propranolol Timolol Sotalol1 Nadolol Carvedilol 1 1-Receptor Selectivity + ++ ++ ++ ++ + Half-Life 2�4 h 5�9 h 14�22 h 9 min 3�4 h 9�12 h 1�2 h 2�3 h 3�4 h 5h 6h 4�8 h 3�6 h 3�5 h 5�13 h 10�24 h 6�8 h Sympathomimetic + -Receptor Blockade Membrane Stabilizing + � + + ++ + + + + + � + � ++ + � Also possesses distinctive antiarrhythmic properties. The effects and makes use of of probably the most generally used calcium channel blockers are proven in Table 21�9. Calcium channel blockers scale back myocardial oxygen demand by lowering cardiac afterload and augment myocardial oxygen supply by way of coronary vasodilation. Its tendency to lower afterload usually offsets any adverse inotropic impact. Nicardipine and clevidipine generally have the same effects as nifedipine but are shorter appearing, and clevidipine is particularly useful as a vasodilator infusion. Nimodipine is primarily utilized in stopping cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. All calcium channel blockers potentiate depolarizing and nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking brokers and the circulatory results of volatile agents. Nifedipine and comparable brokers can potentiate systemic vasodilation by unstable and intravenous brokers. Nitrates Nitrates lower venous and arteriolar tone, improve vascular capacitance, and scale back ventricular wall tension. Prominent venodilation makes nitrates excellent brokers when congestive heart failure is also current. Even minor degrees of dilation at stenotic sites may be enough to increase blood move, as a outcome of move is immediately associated to the fourth power of the radius. Nitrate-induced coronary vasodilation preferentially will increase subendocardial blood move in ischemic areas. This favorable redistribution of coronary blood move to ischemic areas could additionally be dependent on the presence of collaterals in the coronary circulation. Nitrates can be utilized for both the remedy of acute ischemia and prophylaxis towards frequent anginal episodes. Careful evaluate of anticoagulant/antiplatelet medicines is a mandatory factor of preanesthetic evaluation, particularly if neuraxial anesthesia is being considered (see Chapter 45). Combination Therapy Moderate to extreme angina incessantly requires combination therapy with two or extra courses of agents. Most studies affirm that perioperative end result is expounded to illness severity, ventricular operate, and the sort of surgery to be undertaken. In some research, upkeep of chronic -receptor blockers in the perioperative interval has been proven to reduce perioperative mortality and the incidence of postoperative cardiovascular problems; nonetheless, different research have shown an increase in stroke and demise following preoperative introduction of -blockers to at-risk patients. Consequently, initiating therapy with -blockers in at-risk sufferers who will undergo surgical procedure is not really helpful. History crucial signs to elicit embrace chest ache, dyspnea, poor train tolerance, syncope, or near syncope. Activity ought to be described in phrases of everyday tasks, similar to walking or climbing stairs. Arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities are extra frequent in patients with previous infarction and in those with poor ventricular function. The chest radiograph can be utilized to exclude cardiomegaly or pulmonary vascular congestion secondary to ventricular dysfunction. Holter Monitoring Continuous ambulatory electrocardiographic (Holter) monitoring is beneficial in evaluating arrhythmias, antiarrhythmic drug remedy, and severity and frequency of ischemic episodes. Frequent ischemic episodes on preoperative Holter monitoring correlate properly with intraoperative and postoperative ischemia. Holter monitoring showing no ischemic episodes has a wonderful negative predictive worth for postoperative cardiac issues. Electrocardiographic proof of ischemia often turns into obvious solely throughout angina. Prior infarction may be manifested by Q waves or lack of R waves in the leads closest to the infarct. A myocardial ischemic response at low levels of train is associated with a significantly increased risk of perioperative issues and long-term cardiac events. Other vital findings embody modifications in blood strain and the occurrence of arrhythmias. These scans can locate and quantitate areas of ischemia or scarring and differentiate between the two. Perfusion defects that fill in on the redistribution phase symbolize ischemia, not earlier infarction. Magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, and computed tomography scans are more and more getting used to outline coronary artery anatomy and decide myocardial viability. Significant stenosis of the left major coronary artery is of great concern as a end result of disruption of flow on this vessel could have adverse results on almost the entire left ventricle. Ventriculography, measurement of the ejection fraction, and measurement of intracardiac pressures, additionally present essential information. Indicators of serious ventricular dysfunction include an ejection fraction lower than 50%, a left ventricular end-diastolic strain larger than 18 mm Hg, a cardiac index less than 2. Satisfactory premedication minimizes sympathetic activation, which adversely impacts the myocardial oxygen supply� demand steadiness. Overmedication is equally detrimental and should be prevented because it may lead to hypoxemia, respiratory acidosis, and hypotension. Most clinicians now restrict premedication to small doses of intravenous midazolam (or the equivalent) given immediately earlier than invasive procedures or earlier than transporting the affected person to the working theater. Preoperative drugs should usually be four continued till the time of surgery.
Buy 50 mg diflucan overnight delivery
Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block A superior laryngeal nerve block is commonly administered with endotracheal intubation in the aware patient antifungal diet plan buy 200 mg diflucan otc. This method is used for perioral endoscopy fungus quizlet discount 400 mg diflucan amex, transesophageal echocardiography, and laryngeal and esophageal instrumentation. The needle is inserted midway between the thyroid cartilage and the hyoid, 1�5 cm anterior to the larger horn of the hyoid. The needle passes through the thyrohyoid membrane and the anesthetic agent bathes the interior laryngeal nerve, the larger terminal department of the superior laryngeal nerve. Anesthesia of the laryngeal mucosa happens superior to the vocal folds and consists of the superior surface of these folds. Cancer of Larynx the incidence of most cancers of the larynx is excessive in people who smoke cigarettes or chew tobacco. Most individuals present with persistent hoarseness, often related to otalgia (earache) and dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing). Enlarged pretracheal or paratracheal lymph nodes may indicate the presence of laryngeal cancer. Vocal rehabilitation may be completed by an electrolarynx, a tracheo-esophageal prosthesis, or esophageal speech (regurgitation of ingested air). Age Changes in Larynx the larynx grows steadily till approximately 3 years of age, after which little 2354 growth occurs until roughly 12 years of age. Owing to the presence of testosterone at puberty in males, the partitions of the larynx strengthen, and the laryngeal cavity enlarges. In boys, all the laryngeal cartilages enlarge and the laryngeal prominence becomes conspicuous in most males. The anteroposterior diameter of the rima glottidis virtually doubles its prepubescent measurement in males, the vocal folds lengthening and thickening proportionately and abruptly. This progress accounts for the voice changes that occur in males: the pitch usually becomes an octave lower. The thyroid, cricoid, and most of the arytenoid cartilages often ossify as age advances, commencing at roughly 25 years of age in the thyroid cartilage. Foreign Bodies in Laryngopharynx When meals passes by way of the laryngopharynx throughout swallowing, some of it enters the piriform fossae. If the thing is sharp, it may pierce the mucous membrane and injure the internal laryngeal nerve. The superior laryngeal nerve and its internal laryngeal department are additionally susceptible to injury throughout removal of the item if the instrument used to take away the international body accidentally pierces the mucous membrane. Injury to these nerves might end in anesthesia of the laryngeal mucous membrane as far inferiorly as the vocal folds. Young children swallow quite so much of objects, most of which reach the stomach and move through the alimentary tract without issue. In some cases, the overseas physique stops on the inferior end of the laryngopharynx, its narrowest part. Foreign our bodies within the pharynx are often eliminated under direct imaginative and prescient via a pharyngoscope. Infection from the enlarged pharyngeal tonsils might spread to the tubal tonsils, inflicting swelling and closure of the pharyngotympanic tubes. Impairment of hearing could end result from nasal obstruction and blockage of the pharyngotympanic tubes. Infection spreading from the nasopharynx to the middle ear causes otitis media (middle ear infection), which may produce temporary or permanent listening to loss. Sometimes the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils are removed throughout the identical operation (tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy; T&A). This uncommon cervical canal outcomes from persistence of remnants of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch and 2nd pharyngeal groove (Moore et al. It first passes by way of the subcutaneous tissue, platysma, and fascia of the neck to enter the carotid sheath. It then passes between the inner and the external carotid arteries on its method to its opening in the tonsillar sinus. Branchial Sinuses and Cysts When the embryonic cervical sinus fails to disappear, it may retain its reference to the lateral floor of the neck by a branchial sinus, a narrow canal. Although branchial cysts may be present in infants and kids, they might not enlarge and turn into seen till early adulthood. Therefore, care should be taken to avoid injury to these nerves throughout elimination of the cyst. Most esophageal accidents are iatrogenic (physician triggered; 50�75%), occurring in conjunction with endoscopy, esophageal dilation, procedures involving strictures brought on by radiation or tumor, and airway accidents. The latter occur because the airway lies anterior to the esophagus and supplies some protection to it. Esophageal accidents are often 2360 occult (hidden), which makes the damage difficult to detect, especially if it is isolated. Painful swallowing in some patients suggests extension of the tumor to peri-esophageal tissues. Enlargement of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes additionally suggests esophageal cancer. Compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerves by an esophageal tumor produces hoarseness. Zone I: consists of the root of the neck and extends from the clavicles and the manubrium to the level of the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage. Structures in danger are the cervical pleurae, apices of lungs, thyroid and parathyroid glands, trachea, esophagus, widespread carotid arteries, jugular veins, and the cervical region of the vertebral column. Structures at risk are the superior poles of the thyroid gland, thyroid and cricoid cartilages, larynx, laryngopharynx, carotid arteries, jugular veins, esophagus, and cervical region of the vertebral column. Structures in danger are the salivary glands, oral and nasal cavities, oropharynx, and nasopharynx. Radical Neck Dissections Radical neck dissections are carried out when most cancers invades the cervical lymphatics. During the process, the deep cervical lymph nodes and tissues around them are eliminated as utterly as potential. The purpose of the dissection is to remove all tissue that bears lymph nodes in a single piece. The deep cervical lymph nodes, significantly those positioned alongside the cervicodorsal trunk, could also be involved in the spread of most cancers from the thorax and abdomen. Respiratory layer of cervical viscera: the larynx is the superior finish of the decrease respiratory tract, modified to regulate entry into or shut off the lower respiratory tract. Alimentary layer of cervical viscera: Although generally thought-about a half of the alimentary tract, the pharynx is shared with the respiratory system.
100 mg diflucan buy visa
Carotid Sinus Hypersensitivity In people with carotid sinus hypersensitivity (exceptional responsiveness of the carotid sinuses in numerous kinds of vascular disease) fungus gnats vodka diflucan 200 mg discount without prescription, external strain on the carotid artery could cause slowing of the heart price antifungal oral rinse discount 50 mg diflucan with visa, a fall in blood strain, and cardiac ischemia leading to fainting (syncope). In all types of syncope, symptoms outcome from a sudden and critical lower in cerebral perfusion (Shih, 2016). Alternate websites, such because the radial artery on the wrist, should be used to verify pulse fee in folks with carotid sinus hypersensitivity. The internal jugular pulse increases considerably in conditions such as mitral valve disease (see Chapter 4, Thorax), which will increase stress in the pulmonary circulation and right side of the guts. The lateral vertebral muscle tissue, consisting of the rectus capitis lateralis, splenius capitis, levator scapulae, and center and posterior scalene muscle tissue, lie posterior to this neurovascular airplane and (except for the highly positioned rectus capitis lateralis) form the floor of the lateral cervical area. The inferior boundary of the root of the neck is the superior thoracic aperture, fashioned laterally by the first pair of ribs and their costal cartilages, anteriorly by the manubrium of the sternum, and posteriorly by the physique of T1 vertebra. The visceral structures in the root of the neck are described in "Viscera of Neck. The brachial plexus and the third a part of the subclavian artery emerge between the anterior and the middle scalene muscles. The brachiocephalic veins, the primary elements of the subclavian arteries, and the internal thoracic arteries arising from the subclavian arteries are closely associated to the cervical pleura (cupula). The thoracic duct terminates in the root of the neck because it enters the left venous angle. In this dissection of the prevertebral region and root of the neck, the prevertebral layer of the deep cervical fascia and the arteries and nerves have been faraway from the best side; the longus capitis muscle has been excised on the proper aspect. The cervical plexus of nerves, arising from the anterior rami of C1�C4; the brachial plexus of nerves, arising from the anterior rami of C5�C8 and T1; and branches of the subclavian artery are seen on the left aspect. It arises within the midline from the beginning of the arch of the aorta, posterior to the manubrium. The left subclavian artery arises from the arch of the aorta, about 1 cm distal to the left widespread carotid artery. The subclavian arteries arch superolaterally, reaching an apex as they move posterior to the anterior scalene muscle tissue. As the subclavian arteries cross the outer margin of the first ribs, their name changes; they turn out to be the axillary arteries. The cervical pleurae, 2283 apices of the lung, and sympathetic trunks lie posterior to the primary a half of the arteries. The branches of the subclavian arteries are as follows: From 1st part: Vertebral artery, inner thoracic artery, and thyrocervical trunk. At the apex of this space, the artery passes deeply to course by way of the foramina transversaria of vertebrae C1�C6. Occasionally, the vertebral artery may enter a foramen extra superior than vertebra C6. In roughly 5% of individuals, the left vertebral artery arises from the arch of the aorta. The suboccipital a half of the vertebral artery courses in a groove on the posterior arch of the atlas before it enters the cranial cavity through the foramen magnum. The cranial part of the vertebral artery supplies branches to the medulla and spinal wire, components of the cerebellum, and the dura of the posterior cranial fossa. At the inferior border of the pons of the brainstem, the vertebral arteries join to type the basilar artery, which participates within the formation of the cerebral arterial circle (see Chapter eight, Head). The internal thoracic artery arises from the antero-inferior side of the subclavian artery and passes inferomedially into the thorax. The thyrocervical trunk arises from the anterosuperior side of the first part of the subclavian artery, near the medial border of the anterior scalene muscle. It has 4 branches, the most important and most necessary of which is the inferior thyroid artery, the primary visceral artery of the neck, supplying the larynx, trachea, esophagus, and thyroid and parathyroid glands, in addition to adjoining muscles. The different branches of the thyrocervical trunk are the ascending cervical and suprascapular arteries and the cervicodorsal trunk (transverse cervical artery). The branches of the cervicodorsal artery were 2284 discussed previously, with the lateral cervical area. The terminal branches of the thyrocervical trunk are the inferior thyroid and ascending cervical arteries. The latter is a small artery that sends muscular branches to the lateral muscle tissue of the higher neck and spinal branches into the intervertebral foramina. The trunk passes posterosuperiorly and divides into the superior intercostal and deep cervical arteries, which provide the first two intercostal areas and the posterior deep cervical muscular tissues, respectively. The cervical sympathetic trunk and ganglia, the carotid arteries, and the sympathetic 2286 periarterial plexuses surrounding them are shown. The proper lobe of the thyroid gland is retracted to reveal the best recurrent laryngeal nerve and center cervical (sympathetic) ganglion. The nerves of the two sides have basically the same distribution; nonetheless, they loop round completely different structures and at totally different ranges on the two sides. The right recurrent laryngeal nerve loops inferior to the proper subclavian artery at approximately the T1�T2 vertebral level. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve loops inferior to the arch of the aorta at approximately the T4�T5 vertebral degree. The sternothyroid muscular tissues have been cut to expose the lobes of the normal thyroid gland. The parathyroid glands are often embedded within the fibrous capsule on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The viscera (thyroid gland, trachea, and esophagus) are retracted to the right, and the contents of the left carotid sheath are retracted to the left. The left parathyroid glands on the posterior side of the left lobe of the thyroid gland are exposed. The recurrent laryngeal nerve ascends beside the trachea, within the angle between the trachea and the esophagus. The thoracic duct passes laterally, posterior to the contents of the carotid sheath as the thyrocervical trunk passes medially. They pass underneath the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia, between the subclavian arteries and veins, and proceed to the thorax to provide the diaphragm. The phrenic nerves are important as a result of, in addition to their sensory distribution, they supply the solely real motor provide to their own half of the diaphragm (see Chapter four, Thorax, for details). The sympathetic trunks receive no white rami communicantes in the neck (recall that white rami are only associated with spinal nerves T1�L2 or 3). The cervical portion of the trunks consists of three cervical sympathetic ganglia: superior, middle, and inferior. These ganglia receive presynaptic fibers conveyed to the trunk by the superior thoracic spinal nerves and their associated white rami communicantes, which then ascend through the sympathetic trunk to the ganglia. After synapsing with the postsynaptic neuron in the cervical sympathetic ganglia, postsynaptic neurons send fibers to the next buildings: 1.