Duricef
Duricef dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg
Duricef packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 30 pills, 360 pills

Duricef 500 mg purchase with mastercard
Flexion and extension of the cervical spine could exacerbate this relationship between the vertebrae treatment vertigo purchase 500mg duricef visa. The combination of radiographic findings and neurologic indicators makes the analysis simpler to make medications diabetes purchase duricef 250 mg amex. It is troublesome to decide what to do with a person with radiographic findings alone. Prediction of future neurologic threat primarily based on constructive radiographic findings in an asymptomatic affected person is essential, but difficult to carry out. Neurologic Problems No particular symptoms may be attributed directly to congenital fusions within the cervical spine. Patients could have nonspecific complaints corresponding to headaches, syncope, weak point, and numbness. Radiculopathies are usually the end result of nerve root irritation or impingement from osteophytes on the hypermobile segments adjoining to the fused vertebrae. A extensively held perception is that the magnitude of symptoms is expounded to the placement and extent of the congenital fusion; nevertheless, many investigators have found little foundation for this belief. Neurologic problems have been reported in patients with isolated fusions of only two vertebrae. If the decision is made to proceed with surgery, there should be good communication with the anesthesia staff. The anesthesiologist ought to be comfy performing a Stagnara wake-up test in the occasion a suspected change in spinal wire operate has occurred. Neurologic monitoring is required for any congenital deformity patient undergoing surgical intervention. For severe cases of cervical kyphosis or in rigid deformities, consideration of circumferential decompression and fusion should be considered. Local harvested graft can be utilized along with supplemental freeze dried corticocancellous allograft. Regardless of the underlying condition, the anatomic deformity in the cervical spine should be recognized and addressed with standard ideas utilized. Because nearly all of the associated findings are reproducible and consistent, a scientific method should be undertaken. Aside from physical examination, associated tests have to be ordered when indicated. To date, no classification scheme can precisely establish those people in danger for neurologic harm or those that could benefit from early elective surgical intervention. As with all advanced sufferers, attention to element and proper schooling provide the best probability at successful nonoperative or operative intervention. This danger must be weighed against the drawback of shedding additional motion segments with a stabilization process. Larsen Syndrome Larsen syndrome sometimes presents with a quantity of joint dislocations, distinct facial anomalies, clubfoot, coronary heart defects and cleft palate. Anterior fusions alone are typically not really helpful in young kids because of the risk of spinal wire harm from arrest of anterior growth and continued kyphosis from posterior growth. However, in severe or inflexible kyphosis or myelopathic symptoms, anterior decompression and circumferential fusion is indicated with consideration of a postoperative halo vest. Am J Dis Child 1972;123:233�235 Daniilidis J, Maganaris T, Dimitriadis A, Iliades T, Manolidis L. Curves 60 degrees sometimes resolve spontaneously before age 6, however careful observation and shut follow-up is required. In cases with kyphosis > 60 levels or in cases by which the apex vertebra are rounded, triangular, or displaced, then progression is likely. Characteristic anomalies of the cervical backbone embody large posterior components, tall slender vertebrae, enlarged pedicles, and fusion of the aspects from C2 to C7. Preventive measures include fall prevention, avoidance of intramuscular injection, and influenza prophylaxis. Conclusion It is crucial to perform a complete review of techniques and a thorough bodily examination in all patients with a congenital 18. The long-term follow-up of patients with Klippel-Feil syndrome and congenital scoliosis. Iniencephalic deformity of the cervical backbone with Klippel-Feil anomalies and congenital elevation of the scapula; report of three cases. Congenital scoliosis and urinary tract abnormalities: are intravenous pyelograms essential The Klippel-Feil syndrome: early roentgenographic look and development of the deformity. Isolated congenital cervical block vertebrae below the axis with neurological signs. Congenital os odontoideum with Klippel-Feil anomaly and fatal atlanto-axial instability. Acta Orthop Belg 1989;fifty five:107�118 Baba H, Maezawa Y, Furusawa N, Chen Q, Imura S, Tomita K. Fehlings and Newton Cho the cervical spine offers stability and mobility to the neck, and over time it might possibly succumb to various degenerative modifications collectively referred to as cervical spondylosis. Cervical spondylosis includes all the degenerative changes associated with growing older that affect the vertebral bodies, intervertebral disks, facet joints, and spinal ligaments. This chapter critiques the anatomy and biomechanics of the cervical spine, as nicely as the scientific presentation, evaluation, and treatment choices for cervical spondylosis and stenosis. Anatomy the cervical spine is composed of seven vertebrae, but there are eight cervical nerve roots. In terms of bony anatomy, ventrally, the cervical vertebra consists of a vertebral physique linked to a posterior neural arch that collectively enclose the vertebral foramen, which includes the spinal cord. The house between the pedicles of adjacent vertebrae type the intervertebral foramen by way of which cervical nerve roots move. The lamina and pedicle on each side of the vertebrae join to an inferior and superior articular process (lateral mass), every of which articulates with the vertebrae beneath and above the vertebra, respectively. The posterior bar of bone that projects from the pedicle behind the foramen ends within the posterior tubercle. Similarly, the anterior bar of bone that tasks from the physique in front of the foramen ends within the anterior tubercle. Clinically, this suggests that starting on the posterior midpoint of the lateral mass may be thought-about secure in posterior cervical instrumentation to keep away from harm to the cervical nerve roots and vertebral artery. C1 (atlas) and C2 (axis) have a number of distinct options that distinguish them from the relaxation of the cervical spine. A transverse course of extends from each lateral mass, and every transverse course of has a foramen that contains the vertebral artery. C2 is characterised by the odontoid process (dens), which initiatives upward from the body between two lateral lots. A transverse course of extends from every lateral mass with a foramen directed upward and outward to direct the vertebral artery laterally to the foramen transversarium of C1, which is positioned lateral to that of C2 and the remainder of the cervical spine. C2 has thick laminae that be part of to kind a large spinous process that types an inverted U at its tip.
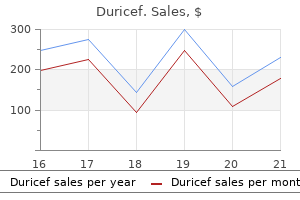
Discount duricef 250 mg without prescription
Surgical administration of lumbo sacral nerve root hemangioblastomas in von HippelLindau syndrome medications like abilify duricef 250 mg order without a prescription. Surgical administration of spinal twine hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel Lindau disease symptoms irritable bowel syndrome duricef 250 mg order mastercard. Secondary holocord syringomyelia with spinal hemangioblastoma: a report of two instances. McCormick nearly all of intradural spinal tumors come up exterior of the spinal wire. With few exceptions these neoplasms are benign, properly circumscribed, and amenable to complete surgical resection. As in the intracranial house, nerve sheath tumors and meningiomas account for most tumors that come up outdoors the substance of the central nervous system. Although spinal extramedullary tumors share many features with their intracranial counterparts, there are numerous distinctive elements of those tumors that merit separate consideration. This chapter describes the incidence, epidemiology, pathology, scientific presentation, differential analysis, analysis, and administration issues of patients with extramedullary tumors of the spinal cord. Differential Diagnosis From a scientific perspective, the differential diagnosis of intradural extramedullary tumors includes many circumstances. Patients with cervical tumors who develop progressive myelopathy might overlap with patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, or persistent disk herniation with spinal twine compression. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or other progressive or recurring medical myelopathies, corresponding to multiple sclerosis, vitamin B12 deficiency, and Lyme illness, might have clinical profiles similar to these tumors. Thoracic tumors current either with radicular ache or myelopathy and include persistent thoracic disk herniation or stenosis as a part of the differential analysis. Type I dural arteriovenous fistulas may current with a slowly progressive myelopathy and should be thought of within the differential prognosis. Tumors of the cauda equina most often overlap with far more frequent benign extradural spinal conditions, such as spinal stenosis, disk herniation, and degenerative spine situations. Nerve sheath tumors, meningiomas, and filum terminale ependymomas account for many extramedullary neoplasms. Most of these tumors occur in adults and, as such, current later in life than do intramedullary spinal tumors. The exception to that is filum terminale ependymomas, that are just like intramedullary ependymomas when it comes to occurrence. Clinical Features the scientific features of intramedullary tumors typically mirror their benign, slow-growing nature. Early signs are often fairly delicate, typically intermittent, and of considerable duration. In many circumstances tumors attain a large size previous to analysis, which reflects spinal cord and cauda equina lodging to these slow-growing tumors. Early occurrence of radicular ache in the distribution of the basis of origin of a nerve sheath tumor is a standard but not common complaint of sufferers with these tumors. Cervical tumors typically present with proximal arm weakness and impairment of nice motor control with gait disturbance. Spasticity or an ataxic gait is common with thoracic wire compression, whereas ache and bowel/bladder dysfunction are widespread with cauda equina compression. Urinary retention, with or without overflow incontinence, is the most common type of bladder dysfunction. Nerve Sheath Tumors Nerve sheath tumors are categorized as schwannomas or neurofibromas. Although proof from tissue culture, electron microscopy, and immunohistochemistry supports a common Schwann cell origin for neurofibromas and schwannomas, the morphological heterogeneity of neurofibromas suggests participation of additional cell sorts such as perineural cells and fibroblasts. Neurofibromas and schwannomas benefit separate consideration because of their distinct demographic, histological, and organic characteristics. The histological look of neurofibromas consists of an abundance of fibrous tissue and the conspicuous presence of nerve fibers within the tumor stroma. Their histological appearance consists of elongated bipolar cells with fusiform, darkly staining nuclei arranged in compact interlacing fascicles with an inclination toward palisade formation (Antoni A). Neurofibromas characterize the next proportion of ventral root tumors and infrequently exhibit dumbbell development. Brachial or lumbar plexus neurofibromas may prolong centrally into the intradural space alongside a quantity of nerve roots. These tumors must be distinguished from the rare mobile schwannoma that shows aggressive histological options but is related to a good prognosis. Depending on the precise point of origin and the scale of the tumor, nerve sheath tumors can be totally intradural, extradural, or have both intradural and extradural elements that evince a characteristic dumbbell shape. Because they usually come up from the dorsal root, they typically lie dorsolateral to the spinal cord. Lesions with a major extradural component often erode bone over time and may displace essential native anatomic buildings, although these will all the time lie outside the tumor margin if the tumor is benign. They are sometimes usually associated with the dura mater with the tumor mass compressing the spinal cord. Less than 10% of the time, spinal meningiomas exhibit vital extradural extension, though they might be completely extradural. Histologically, the vast majority of spinal meningiomas are benign and fall into the identical subtypes as seen intracranially. Younger patients are more likely to harbor the surgically recalcitrant angioblastic subtype, however true malignant meningiomas are exceedingly rare within the backbone. Filum Terminale Tumors the vast majority of filum terminale tumors are myxopapillary ependymomas. Paragangliomas are less common, whereas astrocytomas, hemangioblastomas, and cavernous malformations are uncommon. About 40% of spinal canal ependymomas come up inside the filum terminale,15 most in its proximal intradural portion. Filum ependymomas and cauda equina nerve sheath tumors occur with about equal frequency. Myxopapillary ependymomas are by far the most common histological type encountered within the filum terminale. Their histological look consists of a papillary association of cuboidal or columnar tumor cells surrounding a vascularized core of hyalinized and poorly cellular connective tissue. Meningiomas Meningiomas are the second most typical intradural extramedullary spinal tumor after schwannomas. The female preponderance seen in intracranial meningiomas is even more pronounced in the spine, with surgical series reporting female/male ratios of 4:110 to as excessive as 9:1. This formulation likely influences the discovering that virtually all of spinal meningiomas are intradural, ex- Paragangliomas Paragangliomas are uncommon tumors that originate from the neural crest and will arise from the filum terminale or cauda equina. Identification of dense core neurosecretory granules on electron microscopy establishes the diagnosis. Complete resection is normally possible besides for large tumors that are tightly adherent to the cauda equina. Diagnostic Imaging Magnetic resonance imaging is the procedure of selection for the prognosis and analysis of intradural tumors.
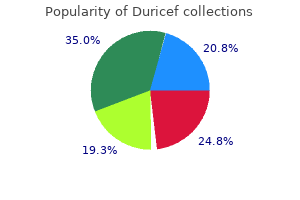
Duricef 250 mg buy line
Because of the extensive nature of this surgical procedure keratin intensive treatment buy generic duricef 500mg online, anterior and posterior fixation methods are sometimes used medicine ball chair generic duricef 500mg with mastercard, with the posterior instrumentation extending into the upper thoracic backbone. This dramatic transition is centered across a single movement section creating significant biomechanical forces. With compromise of help constructions as happens with pathological processes or iatrogenic destabilization, the presence of those deformative forces can lead to progressive kyphosis with subsequent narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of the spinal twine. In this region the anterior elements function to switch compressive loads between adjoining vertebral ranges, whereas the posterior components provide stabilization through attachments to supporting paraspinal extensors muscular tissues and ligamentous constructions. Disruption of both component of this dynamic help construction can lead to progressive instability, deformity, and pain. Following induction, the affected person is positioned prone on the operating room desk and GardnerWells tongs are utilized. Alternatively, a Mayfield headholder could also be used to rigidly fixate the cranium and stabilize the neck within the prone place. The neck is positioned in a impartial or barely lordotic position, but its position may be altered after decompression is performed to treat kyphotic deformities. Careful padding of the shoulders, elbows, and wrists within the impartial position is important to stop peripheral nerve damage. Care should be taken to repair the affected person in an anatomic and neutral position to attain the absolute best functionally regular position postoperatively. Fluoroscopy ought to be used to visualize cervical alignment before the surgical procedure and through placement of instrumentation. This could be linked to thoracic pedicle screws with a domino connection (side-to-side connector) or a tapered rod. In basic, the T1 pedicles are inclined to be bigger with a extra rounded cross section in contrast with the ovoid pedicles elsewhere in the thoracic backbone. With both technique, the preoperative imaging research must be fastidiously examined to determine the medial angulation of the pedicle. The relationships of the transverse processes to the pedicles must be famous and may typically be useful when determining the place to begin for the pedicle screws. Posterior Cervicothoracic Exposure A normal midline strategy is performed with the incision centered over the spinous processes. The length of the incision is determined by the number of segments to be included in the assemble. It is beneficial that the incision extend one spinous process above and beneath the planned space of fixation to guarantee adequate publicity and to attain proper, uninhibited working angles for accurate placement of the instrumentation. The paraspinal muscular tissues are then elevated in a subperiosteal method with the delicate tissue exposure extended to the lateral edge of the lateral lots within the cervical spine and to the lateral edges of the transverse processes within the thoracic spine. Modified wire�rod constructs had been the primary to be developed; nonetheless, these have been largely supplanted by constructs incorporating rod�screw technologies. They are the thinnest within the cervical backbone and make traditional techniques for lateral mass screw placement tougher and more likely to result in a fracture. In many instances, C7 pedicle screw placement provides a safer, more secure web site of fixation than lateral mass screws. Techniques for placement primarily based on bony landmarks that have been described advocate a pedicle entry level for the C7 pedicle 1 mm inferior to the midportion of the facet joint with 25 to 30 degrees medial angulation and perpendicular to the posterior arch. Alternatively, the pedicle could also be recognized by direct palpation with a cervical ball-tip probe if a laminotomy has already been carried out. After figuring out the superior, medial, and inferior borders of the pedicle, the place to begin is located, and a 2-mm bur or an awl is used to penetrate the posterior cortex. Minimal pressure must be used when advancing the probe or the drill, to enable it to discover its method in the confines of the pedicle. After advancing into the vertebral physique, the walls of the pedicle may be palpated with a small, versatile balltip probe. Frequently, a portion of the pedicle might want to be tapped, as a outcome of the dense cortical bone. The screw can then be positioned, with palpation of the borders of the pedicle, once more with the balltip probe, to confirm Cervical Spine Lateral Mass Screw Placement Lateral mass fixation has turn out to be the mainstay for stabilization of the subaxial cervical spine. Various techniques have been described including those of An, Magerl, Anderson, and RoyCamille. Preparation of the insertion site includes clear publicity of the boundaries of the lateral mass. After identification of the correct place to begin, we advocate making a small pilot hole with a 2-mm round bur or axe. The lateral mass screws must be directed 30 to forty levels rostrally and 20 levels laterally. A fixed cease drill bit must be used and measured to the screw length as measured on the preoperative imaging. After drilling the opening, a fantastic, blunttipped probe is used to affirm the integrity of the walls of the opening and to verify that the cortex has not been penetrated. The pedicle finder is eliminated, and a pedicle probe is used to palpate five distinct bony borders, including a ground and 4 partitions to ensure no bony breach. The applicable size of the screw is decided by measuring the size of this probe utilizing a clamp. The start line for lateral mass fixation is 1 mm medial to the center of the lateral mass. The medial boundary is the inflection of the lamina and aspect, the lateral boundary is the edge of the articular mass, and the superior and inferior boundaries are the respective facet joints. The mass screws should be directed 30 to 40 levels rostrally and 20 degrees laterally. The starting point for the C7 pedicle is 1 mm inferior to the midportion of the facet joint with 25 to 30 degrees medial angulation and perpendicular to the posterior arch. Translaminar Screw Placement In cases with unfavorable upper thoracic pedicle anatomy, translaminar screws present an effective different to pedicle screw fixation. The trajectory is roughly alongside the angle of the ipsilateral lamina, with the target being the intersection of the ipsilateral transverse course of and superior aspect. To place bilateral translaminar screws, the starting factors need to be barely completely different cephalad caudal, and the lateral trajectories should be barely divergent, to avoid collision of the screws. Furthermore, intact bony arches are needed, and as such this method is used comparatively sometimes. Thoracic Pedicle Screw Placement the identical ideas used for C7 pedicle screw placement apply for placement of higher thoracic spine pedicle screws. Wide exposure of the lamina and lateral mass (C7) and transverse processes (T1�T2) is carried out with removal of the medial aspect of the transverse strategy of T1�T2 to allow the top of the pedicle screw to be seated. The place to begin of the T1 to T2 pedicles is more lateral and more inferior than for the decrease thoracic backbone. Once a posterior cortical breach is made with a bur or an axe, a pedicle finder or a highspeed drill is placed into the bottom of the pedicle alternatively.
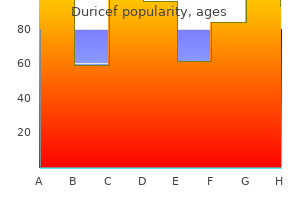
500mg duricef discount visa
Natural History and Surgical Outcome the decision to function is evident in sufferers with symptomatic lumbosacral lipomas medications qt prolongation duricef 500mg without prescription. Large series have proven that lack of neurologic perform is unlikely to be regained completely within the majority of circumstances medications nursing 250mg duricef with visa. Some authors have advocated a conservative strategy after weighing the actual danger of perioperative insult versus the potential threat of decline. Studies have proven that 33 to 40% of asymptomatic infants are more doubtless to deteriorate over the course of 10 years. Due to the progressive nature of this disease and the irreversible nature of the deficits, prophylactic surgery was beforehand performed on nearly all of asymptomatic sufferers. However, in a big collection Pierre-Kahn et al2 reported that greater than half of asymptomatic sufferers who underwent prophylactic surgery went on to have neurologic decline within 120 months of surgical procedure. In 2010, Pang et al26 reported the long-term neurologic standing of a gaggle of 86 asymptomatic sufferers who had undergone complete resection and a group of 116 sufferers who had undergone partial resection. The results for the group of sufferers with a partial resection were in preserving with the Pierre-Kahn research and with later pure historical past studies, with a progression-free survival of 43% at 12 years. However, the cohort of asymptomatic patients with total resections produces a powerful progressionfree survival of ninety eight. The outcomes of this research would counsel that prophylactic surgery is prepared to change the natural historical past of the illness only if a complete resection is completed. Preoperative Evaluation All patients with a confirmed or suspected lumbosacral lipoma should endure a full physical and neurologic evaluation. This contains special evaluation of the lumbar area, and neurologic exam of the extremities, perineum, and sphincter. This is essential in establishing a baseline, and it also may help in speaking the danger and expected outcomes of the surgery to the patient and household. Imaging for patients with lumbosacral lipomas is designed to assist in both prognosis and surgical planning. Spinal ultrasound is a useful tool to screen for lumbosacral lipomas within the neonate. Routine X-rays reveal the presence and the level of a bony defect or different malformation similar to diastematomyelia, in addition to the presence or absence of scoliosis. Lack of ossification in newborn sufferers makes the interpretation of X-rays tough and subsequently of questionable worth. This is crucial to understand the connection between the lipoma and the spinal twine. Although the sagittal view confirms the level of the lesion in relationship to the spinal twine and vertebra, the axial sequence demonstrates any rotation and the relationship of the lipoma to b a. Surgical Technique Goals the goals of surgical intervention are to untether and decompress the spinal wire, avoid damage to useful neural tissue, and prevent the re-tethering of the twine. These objectives can be completed by separating adhesions, removing as a lot of the lipoma as potential, with the goal of complete lipoma resection. Positioning After induction of general anesthesia, appropriate intravenous access is positioned. A single intraoperative dose of both cefazolin or clindamycin is given 1 hour before incision and redosed each 6 hours. After the initial induction of anesthesia, neuromuscular paralytics are prevented to allow improved suggestions from the nerve root in the course of the operation. After the patient is positioned inclined, bolsters are placed beneath the iliac crest and chest to minimize intraabdominal strain. Once the affected person is in place, a midline incision is remodeled the lipoma that gives access to the whole size of the pathology. This incision may be curved at the caudal side to gain access to low-lying uneven lipomas. A curved incision has the extra benefit of avoiding the intergluteal cleft and avoiding the chance of fecal contamination. Once the pores and skin is open, the subcutaneous fats is identified and removed from the skin flaps, with care taken to not devascularize the skin. Often, a fatty stalk connects the subcutaneous potion to the intraspinal lipoma through a defect within the lumbosacral fascia. When the fascial defect is recognized, the fat lateral and dorsal could be eliminated with scissors and bipolar cautery. If the neural placode lies dorsal to the spinal canal, ultrasonic aspiration ought to be used to prevent potential injury to the underlying neural buildings. Once the subcutaneous portion is debulked and the neck of the lipoma is free of the encircling fascial defect, the fascia is opened in the midline to expose the adjoining lamina and spinous course of. A subperiosteal dissection can then be carried out to take away musculature from the lamina and medial aspect. The lower extent of the bony publicity should prolong 1 cm past the neural placode quite than the lipoma. Caudal fat could lengthen down into the thecal sac, which becomes irrelevant as quickly as the conus has been detached. The dura rostral to the lipoma is then opened within the midline and retracted to expose the spinal twine. The dural edge is then adopted caudally to establish the dural attachment to the neck of the lipoma. Working within the subdural space, sharp dissection is then used to reduce the dural attachments from the lipoma. The dural cuts may be joined caudal to the lipoma, thereby completing the dorsal launch. The dura lateral to the lipoma can then be retracted to expose the full extent of the intradural involvement. Then, the intersection of the lipoma, pia, and spinal twine, additionally referred to because the fusion line, could be recognized. Using low settings on the ultrasonic aspirator, the central mass of fat is debulked. The debulking is sustained till the neural placode can be identified, leaving only a skinny layer of remaining fats. Another method is to use sharp dissection to separate the lipoma from the placode. The dissection begins rostrally the place the anatomic relationships among the many fats, spinal twine, and nerves are clear. Microscissors are then used to establish a white airplane between the lipoma and placode. The incision is sustained caudally, with attention paid to remaining medial to the fusion line. The rostral dura is opened within the midline and retracted to expose the spinal wire. The dissection begins rostrally where the anatomic relationship among the many fats, spinal cord, and nerves is evident. Microscissors or a scalpel is then used to determine and separate the aircraft between the lipoma and placode.
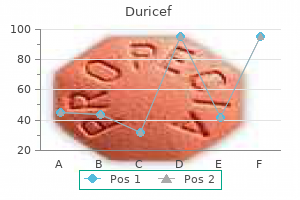
Buy 250mg duricef
To guarantee a competent higher airway symptoms women heart attack duricef 500 mg buy overnight delivery, endotracheal intubation could also be required for a quantity of days with the patient in a head-up place until the edema resolves medicine everyday therapy purchase 250 mg duricef with visa. A optimistic end-expiratory strain of 5 cm H2O on the ventilator tends to stop atelectasis. Nursing the affected person in a rotokinetic mattress can assist with pulmonary drainage in chosen sufferers. Nutritional Support Optimal vitamin is important to the restoration of any stressed patient. The pharyngeal and upper airway edema that happens following this process impedes swallowing for several days or even weeks. Maintenance of the metabolic stability is facilitated by preoperative placement of a feeding gastrostomy/jejunostomy to guarantee enteric alimentation. Effectively supplying dietary assist helps to avoid mucosal bacterial eighty two I Occipital-Cervical Junction translocation and sepsis; it also helps to promote earlier rehabilitation of these patients. All patients complain of dysphagia to some extent instantly postoperatively; it clears spontaneously within 1 to 2 weeks of surgical procedure in most patients. This risk can be minimized with broad release of the fascial planes, thus minimizing the diploma and pressure of retraction wanted for visualization. Prolonged dysphagia will in the end resolve as properly, and the feeding entry could be removed after a caloric intake assessment confirms sufficient oral consumption. Nonunion is a particular concern in sufferers with abnormal bone physiology because of superior inflammatory conditions in addition to ongoing immunolytic and steroid medical therapies. Some patients complain of persistent ache or regression toward their preoperative neurologic baseline. This emphasizes the significance of avoiding or minimizing resection of the inferior portion of the arch during publicity. Removal of the strut is required and a posterior fusion and instrumentation may be performed, usually at the same session. The use of implanted or exogenously utilized bone stimulation gadgets can be used on the discretion of the surgeon. They may be managed with irrigation and debridement followed by a course of closed irrigation, with the location of a closed wound irrigation system along side intravenous antibiotics. The closed wound irrigation method is very effective in clearing an infection while preserving the fusion mass and instrumentation. This will improve however will remain evident on medical examination even after a quantity of years. Careful dissection resulting in reduced retraction drive is the best way to decrease this harm. By tunneling the catheter several centimeters using the Tuohy needle, the life span of the drain could be dramatically extended. The drainage may be controlled by quantity or stress regulation at the discretion of the treating surgeon. One various that has enhanced the success of drainage in our patients is the utilization of closed, steady drainage. Drainage through this technique is began at eight mL per hour after which steadily titrated over the first day to 12 to 14 mL per hour. External orthoses, such as a halo brace, are often not sufficient as the only real supply of stability after this procedure. In cases where arthrodesis is performed and instrumentation is placed, the halo head ring is connected to the halo vest. Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs are taken month-to-month to verify the stability of the construct. At three months the pinnacle ring is launched from the vest, and flexion/extension radiographs are taken. If motion is current, then the vest is reattached to the pinnacle ring and the affected person undergoes 6 additional weeks of stabilization. If instability persists at that point, then the patient undergoes an elective posterior cervical or occipitocervical fusion. Conclusion the retropharyngeal method to the occipitocervical junction is predicated on careful and complete dissection of sequential layers of cervical fascia investing the submandibular triangle. This procedure presents a wider publicity with more versatility and security than the transoral path to this area. Laser facilitates dissection of the thick ligaments and muscle/tendon insertions that in any other case add to the difficulty of surgically exposing the deep structures out there with this approach. An anterior high cervical retropharyngeal approach for C1-C2 intrafacetal fusion and transarticular screw insertion. Anterior retropharyngeal fixation C1-2 for stabilization of atlantoaxial instabilities: study of feasibility, technical description and preliminary results. Factors predictive of voice and swallowing outcomes after anterior approaches to the cervical backbone. Chronic rheumatoid arthritis and long-term immunosuppressive drug therapy are circumstances that put sufferers at higher danger for complications with this process. These sufferers ought to in all probability endure posterior occipital cervical arthrodesis somewhat than an anterior fusion process due to osteoporosis, poor bone high quality, and the necessity to proceed medical therapies that impair fusion. Neurosurgical purposes of fibrin glue: augmentation of dural closure in 134 sufferers. Careful publicity of this area is important due to the exquisitely important regional buildings and the necessary structural assist provided by the posterior bony anatomy and ligaments. This approach may be employed for posterior fossa lesions, or it can be used to carry out a decompression or fusion involving the occiput and cervical backbone. In preoperative discussions with the affected person, the risks inherent to operating particularly in this space must be emphasised. In addition to the chance of harm to the spinal cord, brainstem, and nerve roots, threat of harm to the vertebral artery must be mentioned. The vertebral artery could be injured in quite a few ways throughout surgery in this area. A unilateral vertebral artery harm is unlikely to lead to an infarct in the posterior cerebral circulation except the contralateral artery is hypoplastic, however the threat of stroke have to be mentioned with the patient. Potential need for long-term antiplatelet or blood thinning agents if vertebral dissection is encountered also wants to be discussed. The threat of a delayed infarct from a thromboembolism should even be considered, and the affected person should also be warned about potential procedures with interventional radiology should there be a vertebral artery injury. Moreover, damage to the vertebral artery may preclude completion of the planned operation. The problems of driving a car, due to the issue of checking the blind spot, and the want to buy new automotive mirrors should be discussed with the patient. The issues that the patient will encounter in performing actions of day by day residing with a fused occipitocervical area must be mentioned and documented. Another issue particular to surgical procedure in this region is that the C2 nerve roots generally have to be sacrificed to facilitate placement of C1 lateral mass screws.
Duricef 250 mg purchase on-line
Once utterly uncovered medicine nausea duricef 500 mg online, pedicle screws are inserted from the upper instrumented vertebra to the lower instrumented vertebraexcept at the degree of deliberate osteotomies symptoms leukemia 250mg duricef cheap otc. The osteotomy requires removing of the interspinous liga- ments, the ligamentum flavum, and the superior and inferior articular processes bilaterally. The interspinous ligaments are eliminated all the means down to the level of the ligamentum flavum, and the median raphe is identified. The spinous course of on the degree of osteotomy is resected using a Horsley bone cutter or rongeur. Although this might be performed in a quantity of methods, we prefer making a trough across the lamina and pars on both sides and then removing the bilateral inferior aspects and part of the lamina as a single piece using a Capener gouge. In explicit, on the lateral finish, the construction between the upper and decrease pedicles should be removed completely to stop nerve root impingement during osteotomy closure. Also, each the superior and inferior lamina should be undercut to provide adequate room for neural components when the osteotomy is closed. Appropriately contoured rods are then positioned, and the ultimate construct is tightened while applying compression throughout ultimate tightening of the set screws. Also, each the superior and inferior lamina ought to be undercut to present adequate room for the neural parts when the osteotomy is closed. Once posterior publicity of the backbone is completed through careful meticulous subperiosteal dissection, consideration is directed toward placement of instrumentation and subsequent performance of osteotomy. Before the osteotomy is begun, pedicle screws should be positioned cephalad and caudad to the supposed osteotomy website, as they are going to be used to help safe and stabilize the spine after the osteotomy. The osteotomy requires that all of the posterior components (spinous course of and lamina) on the degree of the osteotomy be eliminated. Generally all the posterior elements from 1 cm below the pedicle screws of the vertebra above the osteotomy website to 1 cm above the pedicle screws of the vertebra under the osteotomy web site should be resected. A extensive central decompression is completed, followed by exposure of the exiting roots bilaterally. The transverse processes are excised at their bases which can be performed with an osteotome or a Kerrison rongeur. Then, careful dissection of the lateral wall of the vertebral physique is carried out in a posterior to anterior direction with a small Cobb retractor, taking nice care to avoid harm to the segmental vessels. A malleable retractor is positioned lateral to the vertebral physique within the subperiosteal plane to preserve the exposure. The pedicles are identified bilaterally and are resected with Leksell rongeurs, carefully avoiding the exiting nerve roots. Through the working window of the pedicle, the posterior vertebral body is decancellated. After this, curettes are used to osteotomize the vertebral body medially, laterally, cranially, and caudally. The cortical shell of the vertebral body is left intact to defend neural components and epidural vessels. Temporary fixation should be achieved with a short lived rod earlier than a considerable portion of the body is eliminated, to prevent neurologic harm due to sudden translation of the spine. After decancellation has been completed within the posterior aspect of the vertebra extending from lateral wall to lateral wall, the posterior vertebral physique wall is then "green-sticked" with a reverse-angle curette, pushing the bone anteriorly into the physique. The lateral wall is resected in a wedge form utilizing a Leksell rongeur working towards the anterior aspect of the spine. This will produce a symmetric closure of the osteotomy web site, correcting the sagittal deformity. The anterior cortex have to be maintained to stop subluxation of the backbone throughout closure. Separate rods secured to the fixation points proximal and distal to the osteotomy may be connected via dominoes. In this way, "construct-to-construct" compression could additionally be performed and this may scale back the chance of fixation failure. It is really helpful to extensively open the canal centrally on the osteotomy site to be in a position to inspect the dura for buckling and to probe the neural foramina with a Woodson elevator to make certain the absence of any neural compression. We choose to use iliac screws to protect in opposition to S1 pedicle screw pullout or failure in lengthy constructs extending above L2. This could be performed to handle sagittal imbalance with a coexistent coronal deformity. More bone along the lateral wall of the vertebral physique is resected on the aspect of the convexity in contrast with the quantity of bone resected alongside the concavity. This not only permits the restoration of sagittal alignment but also helps to restore coronal alignment. Curves with a pointy angle could be greatest corrected by a resection of a single vertebral physique, whereas curves which are broad and sweep- ing could require a resection of multiple vertebral bodies at the apex to minimize stretching of the neural components. Once accomplished, the spinal column can be shortened and the mixed sagittal and coronal deformity corrected by way of a combination of translation and compression. A metallic cage, structural autograft, or allograft may be used to reconstruct the vertebral column after correction of the deformity to bridge the defect left by resection of the vertebral body. Because this process circumferentially disconnects the spinal column, acquiring a fusion at this stage is paramount. Following positioning of the affected person as described above appropriate posterior publicity of the backbone is obtained. Complete publicity ought to be carried out to each transverse processes to facilitate the removing of the vertebral bodies. Complete removing of the posterior elements (spinous processes, lamina, and side joints) ought to be carried out to the level of the segments that have to be removed, which is usually the apex of the deformity. In the thoracic spine, one could elect to sacrifice one or each exiting nerve roots to present elevated exposure for the removal of the vertebral physique. The the rest of the cancellous portion of the vertebra is totally removed to the top plates of the adjoining disks above and under. Once the rib is eliminated, a temporary rod is positioned opposite the working facet to stabilize the backbone and shield the neural parts. This could be done later however ought to be carried out earlier than eradicating a considerable part of the vertebral physique. We prefer putting a brief rod after finishing the osteotomy on the primary side and before working from the contralateral aspect. A careful subperiosteal dissection of the gentle tissue is carried out alongside the lateral wall of the vertebral physique utilizing a small Cobb elevator, as talked about earlier. It could be managed by electric cauterization or hemostatic brokers corresponding to Surgicel, Gelfoam, and cottonoid. The pedicles are identified bilaterally and are resected with a Leksell rongeur following by piecemeal resection of the vertebral body and the disks above and under with out interfering with the posterior vertebral wall, which is stored intact till the top to defend the thecal sac.
Cheap duricef 500mg with visa
The patient would present with mechanical back pain medicine park oklahoma order 500mg duricef otc, and research such as magnetic resonance imaging would show spondylolisthesis or fluid within the facet joint or side diastasis medicine quetiapine 250 mg duricef overnight delivery, with the possible want for a fusion for stability. Cheng and Peter Morone Indications Unilateral laminectomy, also referred to as a hemilaminectomy, is carried out in a fashion just like that described for bilateral lumbar laminectomy. Restricting the publicity to a single aspect facilitates limiting the scale of the initial pores and skin incision, muscle dissection, and bone removal. The primary reason for performing a hemilaminectomy is to create an exposure that permits completion of a foraminotomy, a microdiscectomy, or each. The affected person is positioned in the standard prone position, supported on a regular spinal frame or chest rolls. The stomach should grasp free to keep away from increased pressure within the epidural veins, which may result in increased bleeding in the course of the procedure. This position avoids strain on the stomach however could make visualizing the midline anatomy more difficult. Once the patient is properly positioned, prepped, and draped, lateral fluoroscopy is used to locate the appropriate lumbar level to reduce the size of the incision required. The interlaminar area is now clearly defined along with the inferior fringe of the rostral lamina and the inferior fringe of the caudal lamina. The ligamentum superior flavum is detached from the inferior surface of the lamina above using a fantastic curette. In these instances, a portion of the inferior lamina might must be removed with a high-speed drill to gain access to the ligamentum flavum. The most inferior edge of the hemilamina is definitely removed with a Leksell rongeur. The ligamentum flavum is indifferent more cephalad as needed, and the hemilaminectomy is completed with 45-degree angled Kerrison punches. The rostral extent of bone removing required to expose the disk varies from one particular person to one other and from one spinal level to another. Advantages � � � Small pores and skin incision Unilateral muscle dissection Minimal bone removal Disadvantages � � � Decreased exposure, limiting the operative corridor Unable to visualize the entire lamina anatomy Increased danger of side harm secondary to decreased visualization 579 580 V Lumbar and Lumbosacral Spine. For example, the L5-S1 disk area lies roughly at the degree of the interlaminar house. Indeed, some people have a particularly giant L5-S1 interlaminar house, making bone removing either unnecessary or minimal. However, as one progresses cephalad, the disk space becomes more cephalad in relation to the interlaminar space, and, therefore, publicity requires proportionately more bone elimination. Some bone from the medial side of the aspect or the pars interarticularis could need to be removed to obtain sufficient lateral exposure. This is particularly necessary with a big disk herniation to mobilize and retract the nerve root with out undue strain. Although the side may be undercut to improve lateral exposure, the side capsule should be preserved. Once the bone removing is complete, a small quantity of bone wax utilized with a Penfield instrument will simply management bleeding from the bone. To expose the nerve root and underlying disk, the ligamentum flavum must be eliminated. This task could be achieved in a quantity of methods; we perform it within the following manner. Using loupe magnification and a headlight (the operating microscope can be used), the ligamentum flavum is grasped with a finetoothed forceps and incised longitudinally using a No. At this point, the fibers of the ligamentum flavum may be somewhat easily split longitudinally to enlarge the opening. A small cottonoid is inserted into the epidural space to protect the dura, and a generous window of ligament is excised. During lateral bony removing, disruption of the aspect capsule can lead to significant, sometimes disabling, postoperative back ache. Zuckerman Indications A lumbar diskectomy stays one of the most widespread procedures performed by neurosurgeons for nerve root compression and radiculopathy. Larger incisions and exposures for elimination of a disk herniation have largely been supplanted by smaller, less invasive procedures. However, open lumbar microdiskectomy still stays the gold commonplace, with its excellent outcomes in opposition to which other methods should be in contrast, as the newer strategies accomplish the same aim with completely different strategies for access to the pathology. Given the various nomenclature used for lumbar diskectomies, clarification of the terminology is required. That is, the primary method and visualization defines the service, and a lumbar microdiskectomy is typically considered open until in any other case specified. As nicely, indications for a microdiskectomy alone without surgical stabilization depend upon the anticipated pure history after surgical procedure. Disks can both bulge (where the annulus is intact), herniate (where the annulus tears and the disk protrudes), or turn out to be sequestered (the herniation is completely separate from the disk). In phrases of classification, a quantity of gross pathological and radiographic grading scales exist. The T2 sequence can be used to determine the thecal sac and nerve root effacement, and the T1 sequence assesses the quantity of epidural fats within the foramen; a disk compressing the foramen could have little to no fat in the foramen. On physical examination, a positive straight leg check is delicate, whereas a contralateral straight leg test is extra specific for a disk herniation. The sort of disk herniation is essential to successful operative treatment, and there are several types. Before continuing with any bone removing, the level is once more confirmed with fluoroscopy. The ligamentum flavum is detached from the surface of the inferior lamina, as it attaches on the edge not like the superior lamina, utilizing a fantastic curette. A hemilaminotomy is carried out with Kerrison rongeurs taking the ligamentum flavum as it turns into the medial aspect joint capsule. If a drill is preferred for the hemilaminotomy, this can be done before the ligamentum flavum is violated to assist shield the dura beneath. The extent of the bone elimination for the hemilaminotomy is determined by the situation of the disk fragment or the level of the disk herniation. Depending on the cranial/caudal location, more of the superior lamina or inferior lamina is taken off to entry the herniated components. The rostral extent of the hemilaminectomy required varies from one spinal stage to one other. However, as one progresses cephalad, the disk house becomes extra cephalad in relation to the interlaminar house and, subsequently, publicity requires proportionally more bone removing. Some bone from the medial facet of the side or the pars interarticularis might need to be eliminated to obtain sufficient lateral exposure of the underlying disk. This is very important with large disk herniations to mobilize and retract the nerve root without undue stress. However, it is necessary to watch the quantity of pars remaining to keep away from an iatrogenic or delayed pars fracture and subsequent spondylolysis. This can be accomplished with the operating microscope or using surgical loupes and a headlight.
Duricef 250mg generic visa
Treatment practices for Chiari malformation type I with syringomyelia: outcomes of a survey of the American Society of Pediatric Neurosurgeons medications for osteoporosis generic duricef 250 mg free shipping. Tailored operative method for Chiari sort I malformation using intraoperative color Doppler ultrasonography medicine grand rounds order duricef 250 mg on-line. Intraoperative ultrasonography used to determine the extent of surgery necessary during posterior fossa decompression in youngsters with Chiari malformation kind I. Surgical treatment of Chiari malformation with and with out syringomyelia: experience with 177 adult patients. Complex Chiari malformations in kids: an evaluation of preoperative threat factors for occipitocervical fusion. Institutional experience with 500 cases of surgically treated pediatric Chiari malformation kind I. Syrinx location and dimension based on etiology: identification of Chiari-associated syrinx. Teles, Kristin Huntoon, and Ehud Mendel Thoracic disk herniation is an uncommon pathology that presents vital challenges for the backbone surgeon in both its prognosis as nicely as its therapy. In recent years, enhancements in imaging techniques have resulted in the increased detection of thoracic disk disorders. The medical presentation of thoracic disk herniations may be extremely diversified, from no symptoms to axial or radicular ache, myelopathy, as nicely as symptoms mimicking these of other situations such as lumbar disk herniation and cardiac, belly, or intrathoracic issues. As a general rule, asymptomatic patients or these with solely axial ache may be efficiently managed conservatively. Thoracic diskectomy is indicated just for sufferers with refractory radicular ache or, more typically, myelopathy. The discrepancy between the small share of patients treated and the big variety of described surgical strategies for this situation highlights the challenges faced by the backbone surgeon when attempting to decide the most effective surgical approach to deal with these patients. Historically, posterior approaches have been related to excessive charges of neurologic morbidity (due to spinal twine retraction) and mortality. However, in current a long time, superior surgical strategies and new approaches have led to a major decrease within the related surgical morbidity and mortality. The surgical decision-making process relating to the best surgical approach relies primarily on the placement and characteristics of the herniated disk. Central calcified disks are better treated through an anterior or a far-lateral approach, whereas soft lateral disks can be efficiently managed via posterolateral approaches. A deep understanding of the anatomy of the thoracic cavity, spinal canal, and related neurologic structures, in addition to a correct comprehension of the risks and benefits of the most common approaches are essential for the safe application of the available surgical strategies for efficiency of thoracic diskectomies. This chapter offers a common overview of the epidemiology, pathophysiology, scientific presentation, radiological evaluation, and medical outcomes of latest printed series reporting the results of the treatment of thoracic disk herniations via different surgical approaches. Most thoracic disk herniations are positioned in the lower thoracic spine,thirteen with 75% of them occurring between T8 and T12. Giant thoracic disk herniations (defined as those who occupy greater than 40% of the spinal canal) may be present in as a lot as 15% of patients. In common, degenerative disk illness in the thoracic spine may be understood as a failure or breakdown in the underlying processes required to guarantee a correct erect posture. Although some variations within the place of buildings situated outside of the backbone (such as the pinnacle positioning and knee extension) might have a significant influence upon the general body balance, the overwhelming majority of stress attenuation and load-bearing capacity involved in the upkeep of the erect position depends on the spine. Specifically, the thoracic region is the one segment of the backbone that shows related surrounding buildings (such as the thoracic cavities, the ribs, and the sternum) which will significantly help in weight bearing. The position of dehydration of the intervertebral disks in the pathophysiology of thoracic disk disease also wants to not be overlooked. Progressive adjustments in the biochemical composition of the intervertebral disk are answerable for a change in its water content, which has been demonstrated to be practically 90% in early childhood and to decrease to lower than 70% by the eighth decade. All these underlying biochemical, anatomic, and bio- Epidemiology the prevalence of thoracic disk herniations in asymptomatic patients ranges from 5 to 37% in magnetic resonance studies1�4 and from 7 to 15% in post-mortem studies. As previously discussed, because the water content decreases, the power of the nucleus pulposus to dissipate downward forces decreases, and the intradiskal stress rises exponentially with growing axial loading. Transmission of this biomechanical stress to the annulus fibrosus could result in a disk bulge. The annulus fibrosus displays an eccentric construction, with its posterior portion being thinner. Such inherent differences might account for the scientific observation that thoracic disk herniations are much rarer than their cervical or lumbar counterparts. Disk Disease of the Thoracic and Thoracolumbar Spine paresis of stomach muscular tissues. Patients with thoracic disk also generally current some type of sensory impairment, starting from dysesthesias/paresthesias (61%) to full sensory loss. Bladder dysfunction has been reported in 24% of instances, with urgency being the commonest complaint. Spasticity and hyperreflexia occur in 58% of sufferers, and a optimistic Babinski sign can observed in 55%. Motor weakness in the lower extremity is present in 61% of sufferers: 72% of them presenting paraparesis, and the remaining 28% presenting monoparesis. These rarer symptoms embrace nausea, emesis, chest tightness, and continual constipation. Calcifications are found in 22 to 65% of thoracic herniations15 and are related to up to a 40% intraoperative incidence of dural tears. According to the authors, this signal is current in up to 45% of the herniated thoracic disks. Another cause to contemplate surgical procedure in these sufferers is the potential threat of everlasting harm to the spinal wire. It has been reported that radicular ache responds better to surgical procedure than nonradiating axial thoracic pain. In the operating room, fluoroscopy should be used to verify the right level, earlier than pores and skin incision and after the exposition of the bony landmarks. Intraoperatively, identification of the precise surgical degree could additionally be difficult within the thoracic backbone, and it should be thought-about an important step during surgery for thoracic disk herniations. As already talked about, in the course of the procedure, high-quality fluoroscopy could also be of serious assist, even in the presence of recent image-guidance techniques, such as navigation. Basically, surgery may be performed through a posterior, posterolateral, lateral or anterior approach. The most essential goal when selecting a surgical strategy is to minimize manipulation of an already compromised thoracic spinal cord. Posterolateral approaches (including the transfacetary, and the transpedicular routes, as well as the costotransversectomy technique) normally are appropriate for paracentral or lateral gentle thoracic herniations. Anterior approaches (involving either an open thoracotomy or thoracoscopy) are more suitable to tackle massive, midline, or calcified disk herniations. Recent stories have described a questionable posterior transdural diskectomy,96,ninety seven which, though feasible, raises several issues associated Treatment the natural history of asymptomatic thoracic disk herniations is comparatively benign. In a imply period of 26 months (range, 14 to 36 months), no patient developed symptoms. Of the 21 small thoracic disk herniations (defined as lower than 10% of spinal canal compromise), 18 showed no important change in size, whereas three showed a major improve in measurement. Of the 20 medium-sized thoracic disk herniations (10 to 20% of canal compromise), 16 showed either a small or no change in measurement, one showed a big increase in size, and three showed a significant lower in dimension.