Female Viagra
Female Viagra dosages: 100 mg, 50 mg
Female Viagra packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
100 mg female viagra cheap with amex
Delaying confirmation allows the fact of pregnancy to be denied and will affect development to the acceptance stage menopause 34 100 mg female viagra buy amex. Because the expectant mom is much less interested R eferences 109 menstruation in africa order female viagra 100 mg online, 168, 172, 195, 196, 205, 226. The fetus exhibits individuality in controlling the motion; the mom can neither start nor stop these actions. With the belief of the presence of one other particular person, mother and father begin acceptance of the fetus as a separate particular person. Love for the fetus as a separate particular person happens because the mother and father make investments a character in the fetus and start to establish a relationship. Fantasies about how the infant looks, its intercourse, and the wish for an ideal, wholesome toddler are frequent. The meaning of the name and who chooses it illustrate the power holder and determination maker throughout the family. Often mother and father with a strong sex desire have chosen no names for a baby of the "mistaken" gender. However, unconsciously, the parents could have a robust gender desire as evidenced by a predominance of goals about one gender. If dreams are equally divided between male and female children, there could indeed be no gender choice on the unconscious stage. This concern is experienced as desires about useless, deformed, or damaged fetuses and infants or dreams with a central theme of destruction. Parental expectations of the newborn are established earlier than start within the personification and relationship with the unseen, unheard fetus. R esearch exhibits that an in depth, high-quality prenatal attachment to the fetus is related to fewer melancholy signs in the last trimester and postpartally. In addition to better physiologic outcomes, improved psychologic outcomes include (1) improve in maternal-infant attachment behaviors, (2) better confidence and skill to cope with labor, (3) better maternal satisfaction and private management during labor, (4) enhanced maternal self-esteem, (5) optimistic attitudes toward mothering and household relationships, and (6) easier mothering. Many years ago, well being care professionals noticed no profit to the presence of the father and even wished to exclude him due to imagined "horribles" similar to increased an infection fee, malpractice fits, and disruption of routines. Parental behaviors at start similar to the following indicate involvement and investment in the infant95: � How does the mom or father look By speaking in a positive tone with words of affection and endearment, the parents relate to each other and to the brand new toddler. Spontaneously, mother and father have interaction in eye-to-eye contact and touch and explore the infant. Affectionate behaviors corresponding to kissing, fondling, cuddling, and claiming characterize optimistic parental reactions. A positive, self-affirming delivery experience for the mom enhances her emotions of empowerment and shallowness and thus her self-concept as a girl and mother. Even women who expertise a normal labor and delivery process should recount the expertise to others. Maternal notion of the events is apparent in tone and content material of the recounting. Missing pieces1 is the term used to describe the elements of labor and start which are forgotten or unavailable to recall. As mother and father see and examine the new child, they begin claiming their infant-"He has my eyes" or "She has your nostril. The new child infant is an energetic participant; he or she cues the mom with eye-to-eye contact. Even minutes-old newborns see and show a desire for the human face (within 7 to 12 inches from their face). Unless medically indicated (necessary for physical survival), newborns ought to stay with their dad and mom after delivery. Maternal depression additionally has been recognized as a threat issue for poor motherinfant interplay. With the healthy term infant, this progression happens within minutes of the first contact. After gaining confidence and preliminary information, the mother or father will maintain the toddler shut in a cuddling position. Fear of harming the small, fragile preterm infant typically prevents parents from feeling comfortable in touching her or him. Not solely the use of nurturing maternal contact but additionally the vulnerability of the untimely toddler affect how contact is perceived by the infant. O ne research showed that nurturing maternal contact was associated with more secure attachment in robust preterms and with much less safe attachment in the most weak infants (see Chapter 13). Holding and cuddling the toddler are considerably completely different from touching and exploring. Explanations for this preference include hand dominance, significance of maternal heartbeat, left breast sensitivity, and advantages in monitoring the infant. A qualitative research of first-time fathers signifies that those that wanted to be extremely involved within the care of their child reported not feeling supported by the well being care provider/ hospital insurance policies to engage in paternal and parental behaviors that favor involvement with their infant. In the caregiving relationship, both care supplier and infant give to and receive from each other. Parental expectations of new child responses embody quieting, sucking, clinging and cuddling, trying, smiling, and vocalizing. Personal wants for comfort, upkeep of homeostasis, and relief from painful experiences are infant expectations of the relationship with the care supplier. R elief from discomfort enables the toddler to respond positively to the care provider. The infant experiences the world through the caregiver and rapidly learns that the environment is both nurturing and loving or hostile and nonresponsive. Consistent, predictable nurturing and caregiving allow the toddler to develop a way of belief in the caregiver, the world, and the self (see Chapter 13). Care by mother and father is the best neonatal care scenario, as a result of the infant learns and reacts to one set of cues or caregiving behaviors. Cared for by one or two individuals, the infant can regulate his or her physiologic behavioral processes. Multiple caregivers confuse the toddler, enhance distress with feeding, trigger irritability, and upset visual attention. Care by dad and mom provides for mutual cuing and acquaintance and a natural setting for statement of parent-infant interplay. This could lead to melancholy, impaired recall, dysfunctional parenting patterns, and poorer developmental outcomes for their youngster. T behaviors and attitudes o the hospital sta (physicians, nurses, he and allied health pro essionals) 2. T sensitivity used within the course of o separation and trans er o he the in ant to the intensive care unit or, in som cases, the re erral e hospital 3. T lexibility o hospital policy regarding parental and sibling he involvem and visitation in the nursery ent 4.
100 mg female viagra discount with mastercard
Paul J menopause signs buy cheap female viagra 100 mg on-line, Chai J menstrual seizures 50 mg female viagra sale, Jeffery P, et al: Surgery for frequent atrial trunk, Cardiol Young 22:691, 2012. R adzik D, Davignon A, van Doesburg N, et al: Predictive elements for spontaneous closure of atrial septal defects diagnosed in the first three months of life, J Am Coll Cardiol 22:851, 1993. Wren C, R einhardt Z, Khawaja K:Twenty-year tendencies in prognosis of life-threatening neonatal cardiovascular malformations, Arch Dis Child Fetal N eonatal Ed ninety three:F33, 2008. By contributing to amniotic fluid, the fetal kidney as a substitute has an important position within the normal improvement of the fetus. After delivery, because the infant adapts to the exterior milieu, the kidney gradually assumes its position as regulator of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. Assessment of renal perform is a good greater challenge within the premature toddler. Abnormalities o the genitourinary system represent as much as 30% o all anomalies recognized prenatally. Although renal disease can clearly have an result on the health of the newborn, it may additionally contribute to lifelong renal pathology. Congenital renal dysplasia, renal obstructive problems, and cystic illnesses account or a substantial proportion o sufferers with endstage renal ailure. Furthermore, a growing body of information supports a hyperlink between prenatal and neonatal occasions and later hypertension and renal insufficiency in adolescents and grownup. Degeneration of the pronephros begins quickly after its formation, and regression has completely occurred by week 5. The pronephros has no excretory perform but performs an necessary function in the formation of the mesonephros. The primitive ureter of the pronephros varieties the wolffian, or mesonephric, duct through fusion of the pronephric tubular buds. The mesonephros develops from the nephrogenic wire and forms forty pairs of thinwalled tubules and glomeruli with excretory perform. Portions of the mesonephric duct system are retained in the male fetus and kind the ducts of the epididymis, the ductus deferens, and the ejaculatory duct. The remainder of the mesonephric duct system within the male infant has degenerated by the fourth month of gestation as the metanephric kidney develops. In the feminine, near-complete degeneration has occurred by the third month of gestation. The metanephric kidney is the product of a sequence of inductive interactions between the metanephric mesenchyme and epithelial ureteric bud. Initially, the ureteric bud grows from the mesonephric duct into the mesenchymal portion of the urogenital ridge; concomitantly, the metanephric mesenchyme modifications, becoming histologically distinct from the encircling tissue. These cells are the beginnings of pretubular aggregates that endure mesenchymal-to-epithelial transformation to become the segmented nephron. The condensed mesenchyme can be thought to produce numerous stem cells, which stay undifferentiated and proliferative. These cells serve to preserve a provide of precursor cells till the completion of nephron development. Thus, the epithelial portion of the grownup kidney is derived from both the metanephric mesenchyme, by way of the stem cells finally liable for particular person nephron formation, and the ureteric bud, whose migration and division determine the sample of formation of the urinary amassing system through its pretubular aggregates. The ureteric bud migrates to the most caudal finish o the nephrogenic cord and nally to the lumbar area by week 8 o gestation. Abnormalities in ascent or rotation can result in pelvic kidneys, horseshoe kidneys, or crossed fused ectopia. Because of the complex interaction of metanephric mesenchyme and ureteric bud, anomalies of the kidney often accompany anomalies of the accumulating system. N ephrogenesis is the process of nephron formation via progress and differentiation of multiple cell varieties and leads to formation of the general renal architecture. The course of begins within the renal cortex closest to the medulla (juxtamedullary nephrons) and proceeds in a dichotomous branching centrifugal sample with the outermost (superficial cortical) nephrons forming last. There are multiple phases of development and structural reorganization after the interactions between the metanephric mesenchyme and the ureteric bud. The formation of the collecting system is managed by the branching sample of the ureteric bud, and this happens at the identical time as the formation of functional nephron units. The surrounding main vessels and neural ganglia grow into the metanephros to full the remaining cell varieties, and vessel structure is much like the newborn kidney by 15 weeks of gestation. This requires a big volume of urine with a relatively excessive focus of sodium. This compares to less than 1% in a rising infant born after a full-term being pregnant. The next major accountability of the new child kidney occurs during the first week of life. Most of the postnatal discount occurs within the first week of life and is the first cause that body weight could lower by as much as 10% in breastfed time period infants and even more in premature infants. Finally, in subsequent weeks, the kidney should retain the electrolytes wanted for growth and the production of dilute urine to accommodate the large water load presented by breast milk. A substantial portion of carbohydrates, electrolytes, and nitrogenous wastes from protein absorbed from breast milk are never offered to the kidney for excretion however are as an alternative included into the growing physique. O nly when the otherwise wholesome neonatal kidney has to deal with surprising derangements of water, electrolyte, or acid�base standing secondary to premature start or illness does its relative lack of capacity to concentrate urine, excrete sodium and potassium hundreds, preserve sodium (in preterm infants), and regulate acid�base standing turn into problematic. In older kids and adults, normal kidneys can right for substantial errors in scientific judgment in water and electrolyte administration or creation and/ or correction of acid�base abnormalities. Importantly, in ants with intrauterine development restriction and those born with extremely low birth weight may by no means obtain a standard quantity o nephrons. Thus, compromised renal perform and elevated blood pressures have been reported in long-term follow-up of small preterm or intrauterine growth-restricted infants. Thus, renal arterial blood flow is roughly 5% of fetal cardiac output, compared with 25% in later life. These actors end in elevated threat o intravascular volume depletion when f uid consumption is proscribed. High protein diets or urea supplementation can improve urinary urea excretion in new child infants, thus enhancing urinary concentrating ability. In H olliday M, B T, V A arratt M ernier R, editors: L P ediatric nephrology, ed 2, B ore, 1987, W s &W altim illiam ilkins. Nevertheless, 50% o ull-term in ants void by 12 hours, 92% by 24 hours, and 99% by 48 hours o li. Causes for prolonged failure to void embrace true or perceived decreased efficient circulating quantity, main renal dysfunction, and obstruction to urine move. After transient oliguria/ anuria, urine circulate rate increases because the new child excretes the physiologically expanded fetal extracellular fluid volume as described earlier.
Generic female viagra 50 mg visa
Gizzi C diagnosis women's health issues female viagra 50 mg buy without prescription, Papoff P women's health clinic lawrenceburg tn female viagra 100 mg discount free shipping, Campelli M, et al: Surfactant and non- invasive ventilation for preterm infants, Acta Biomed 83(suppl 1):24, 2012. Gordon P, R utledge J, Sawin R, et al: Early postnatal dexamethasone will increase the chance of focal small bowel perforation in extraordinarily low delivery weight infants, J Perinatol 19:573, 1999. Greenspan J, Wolfson M, Shaffer T: Liquid air flow, Semin Perinatol 24:396, 2000. Gregory G: R espiratory care of new child infants, Pediatr Clin North Am 19:311, 1972. Greisen G, Frederiksen P, Hertel J, et al: Catecholamine response to chest physiotherapy and endotracheal suctioning in preterm infants, Acta Paediatr Scand seventy four:525, 1985. Guven S, Bozdag S, Saner H, et al: Early neonatal outcomes of volume guaranteed air flow in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome, J Matern Fetal N eonatal Med 26:396, 2013. Herrera C, Gerhardt T, Claure N, et al: Effects of volumeguaranteed synchronized intermittent obligatory ventilation in preterm infants recovering from respiratory failure, Pediatrics one hundred ten:529, 2002. Higgins R D, Bancalari E, Willinger M, et al: Executive abstract of the workshop on oxygen in neonatal therapies: controversies and opportunities for research, Pediatrics 119:790, 2007. Hoskote A, Castle R, Hoo A, et al: Airway function in infants treated with inhaled nitric oxide for persistent pulmonary hypertension, Pediatr Pulmonol 43:224, 2008. Ingimarsson J, Bjorklund L, Curstedt T, et al: Incomplete safety by prophylactic surfactant towards the added results of large lung inflations at start in immature lambs, Intensive Care Med 30:1446, 2004. Kahramaner Z, Erdemir A, Turkoglu E, et al: Unsynchronized nasal intermittent constructive pressure versus nasal continuous positive airway stress in pretrm infants after extubation, J Matern Fetal N eonatal Med 27:926, 2014. Kahveci H, Yilmaz O, Avsar U, et al: Oral sildenafil and inhaled iloprost in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the new child, Pediatr Pulmonol, January 14, 2014. Kaiser J, Gauss C, Williams D: Tracheal suctioning is related to extended disturbances of cerebral hemodynamics in very low birth weight infants, J Perinatol 28:34, 2008. Kalyn A, Blatz S, Feuerstake S, et al: Closed suctioning of intubated neonates maintains higher physiologic stability: a randomized managed trial, J Perinatol 23:218, 2003. Karen T, Vatlatch S, Poets A, et al: the influence of oral sucrose on apnea and bradycardia in preterm infants: a randomized crossover trial, Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed ninety eight:F93, 2012. In Kattwinkel J, editor: Neonatal resuscitation provider textbook, ed 6, Elk Grove, Ill, 2011, American Academy of Pediatrics and American Heart Association. Khalof N, Brodsky N, Hurley J, et al: A prospective randomized, managed trial evaluating synchronized nasal intermittent positive stress air flow vs. Kinsella J, Cutter G, Walsh W, et al: Early inhaled nitric oxide remedy in premature newborns with respiratory failure, N Engl J Med 355:354, 2006. Klebermass-Schrehof K, Wald M, Schwindt J, et al: Less invasive surfactant administration in extraordinarily preterm infants: impact on mortality and morbidity, N eonatology 103:252, 2013. Klinger G, Beyene J, Shah P, et al: Do hyperoxaemia and hypocapnia add to the danger of brain damage after intrapartum asphyxia Knight D: Neonatal shaken baby syndrome: lessons to be realized, Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 87:F161, 2002. Knight D, Bevan C, Harding J, et al: Chest physiotherapy and porencephalic lesions in very preterm infants, J Paediatr Child Health 37:554, 2001. Kohelet D, Boaz M, Serour F, et al: Esophageal pH examine and symptomatology of gastroesophageal reflux in newborn infants, Am J Perinatol 21:85, 2004. Kumar P, and American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Fetus and Newborn: Use of inhaled nitric oxide in preterm infants, Pediatrics 133:164, 2014. Lal M, Manktelow B, Draper E, et al: Chronic lung disease of prematurity and intrauterine development retardation: a inhabitants based study, Pediatrics 111:483, 2003. Lim D, Kulik T, Kim D, et al: Aminophylline for the prevention of apnea during prostaglandin E1 infusion, Pediatrics e27:112, 2003. Lista G, Castoldi F, Bianchi S, et al: Volume guarantee versus high-frequency ventilation: lung inflammation in preterm infants, Arch Dis Child Fetal N eonatal Ed ninety three:F252, 2008. Liu J, Liu F, Liu Y, et al: Lung ultrasound for the prognosis of extreme neonatal pneumonia, Chest, May 15, 2014. Livera L, Spencer S, Thorniley M, et al: Effects of hypoxaemia and bradycardia on neonatal cerebral haemodynamics, Arch Dis Child 66:376, 1991. Locke R, Wolfson M, Shaffer T, et al: Inadvertent administration of optimistic end-distending strain during nasal cannula circulate, Pediatrics 91:135, 1993. Manzoni P, De Luca D, Stronati M, et al: Prevention of nosocomial infections in neonatal intensive care items, Am J Perinatol 30:81, 2013. Mariani G, Cifuentes J, Carlo W: R andomized trial of permissive hypercapnia in preterm infants, Pediatrics 104:1082, 1999. Marinelli P, O rtiz A, Alden E: Acquired eventration of the diaphragm: a complication of chest tube placement in neonatal pneumothorax, Pediatrics 67:552, 1981. Migliori C, Bottino R, Angeli A, et al: High frequency partial liquid ventilation in two infants, J Perinatol 24:118, 2004. Mikolka P, Mokra D, Kopincova J, et al: Budesonide added to modified porcine surfactant improve the lung functions in meconium aspiration syndrome, Physiol Res 62(suppl):S191, 2013. Mokra D, Calkovska A: How to overcome surfactant dysfunction in meconium aspiration syndrome Mokra D, Mokry J,Tonhajzerova I: Anti-inflammatory remedy of meconium aspiration syndrome: advantages and risks, Respir Physiol N eurobiol 187:52, 2013. Moretti C, Giannini L, Fassi C, et al: Nasal flow-synchronized intermittent constructive strain ventilation to facilitate weaning in very low-birthweight infants: unmasked randomized controlled trial, Pediatr Int 50:85, 2008. Mori R, Kusuda S, Fujimura M: Antenatal corticosteroids promote survival of extremely preterm infants born at 22-23 weeks gestation, J Pediatr 159:110, 2011. Mosca F, Colnaghi M, Agosti M, Fumagalli M: High-flow nasal cannula: transient style or new technique of non-invasive ventilator help Mosca F, Colnaghi M, Lattanzio M, et al: Closed versus open endotracheal suctioning in preterm infants: results on cerebral oxygenation and blood quantity, Biol N eonate seventy two:9, 1997. Moya F, Gadzinowski J, Bancalari E, et al: A multicenter, randomized, masked, comparison trial of lucinactant, colfosceril palmitate, and beractant for the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome among very preterm infants, Pediatrics one hundred fifteen:1018, 2005. Neonatal Inhaled Nitric Oxide Study Group: Inhaled nitric oxide in full-term and practically full-term infants with hypoxic respiratory failure, N Engl J Med 336:597, 1997. Noori S, Friedlich P, Wong P, et al: Cardiovascular effects of sildenafil in neonates and infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia and pulmonary hypertension, N eonatology ninety one:92, 2007. Noori S, McCoy M, Friedlich P, et al: Failure of ductus arteriosus closure is related to elevated mortality in preterm infants, Pediatrics 123:e138, 2009. Northway W, R osan R: R adiographic features of pulmonary oxygen toxicity in the newborn: bronchopulmonary dysplasia, Radiology 91:forty nine, 1968. Nuntnarumit P, Bada H,Yang W, et al: Cerebral blood move velocity changes after bovine pure surfactant instillation, J Perinatol 4:240, 2000. Nyp M, Sandritter T, Poppinga N, et al: Sildenafil citrate, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and disordered pulmonary fuel trade: any benefits Okasaki K, Kondo M, Kato M, et al: Serum cytokine and chemokine profiles in neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome, Pediatrics 121:e748, 2008.
Buy discount female viagra 100 mg online
Finally breast cancer socks female viagra 100 mg order without a prescription, with the clamping of the umbilical cord teva women's health birth control buy generic female viagra 50 mg line, umbilical venous move ceases and the ductus venosus begins to close, with anatomic closure taking roughly 1 to 2 weeks. Deoxygenated blood returns to the guts by the inferior and superior venae cavae and enters the right atrium, proper ventricle, pulmonary artery, and pulmonary circulation the place oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Oxygenated blood then returns to the guts through the pulmonary venous system and enters the left atrium, left ventricle, and finally the aorta and systemic arterial system. Table 24-2 exhibits the most typical genetic abnormalities related to congenital heart defects. Children with chromosomal abnormalities corresponding to trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and trisomy 21 typically have vital congenital coronary heart illness. For example, 1p36 deletion syndrome is a microdeletion with as a lot as 71% of sufferers having a structural abnormality. Traditionally, the etiology o congenital coronary heart de ects has been viewed as multi actorial, involving a complex interaction between genetic and environmental actors. For example, women with pregestational diabetes or women with excessive alcohol consumption are at increased threat for having an toddler with a heart defect. Maternal phenylketonuria, maternal systemic lupus erythematosus, or maternal infections also increase the danger of congenital coronary heart illness for offspring. We now acknowledge that use of assisted reproductive expertise also ends in increased danger for a heart defect in fetuses conceived by these strategies. Table 24-1 lists the commonest maternal and familial threat factors for cardiac malformations. Box 24-1 lists fetal threat factors associated with an * R eferences 5, 35, forty two, fifty nine, 62, 63. Un ortunately, lower than hal o kids with congenital heart illness receive a prenatal diagnosis. Better screening methods are required along with referral for detailed fetal echocardiogram for any baby at elevated threat of having coronary heart disease (see Box 24-1). Labor and supply problems ought to be rigorously examined for danger elements that would affect the cardiovascular system. The timing o the murmur through the cardiac cycle is important; diastolic murmurs are nearly never harmless. The depth (loudness), high quality (harsh, vibratory), location, and radiation o the murmur can all be used to assist make a analysis. Despite the presence of many heterogeneous forms of heart disease, a restricted number of signs and signs present within the neonate. Murmurs related to semilunar valve stenosis and atrioventricular valve insufficiency are inclined to be noted very shortly after birth. The age o the neonate when the murmur is rst noted offers an essential clue skin, nail beds, and mucous membranes) is one o the most typical presenting signs o congenital heart illness within the neonate. Cyanosis happens with congenital coronary heart illness when deoxygenated venous blood abnormally shunts "right to left" inside the coronary heart and then enters the systemic arterial system once more (without going through the lungs to decide up oxygen). True central cyanosis must be di erentiated rom acrocyanosis (blueness o the arms and eet only), which is a standard nding within the neonate. Cyanosis within the new child should be di erentiated between cardiac and noncardiac causes. Primary lung disease (see Chapter 23) is a typical reason for labile cyanosis as a outcome of persistent pulmonary hypertension. Clinical cyanosis can happen with out hypoxemia in a neonate with methemoglobinemia and polycythemia. The hyperoxia check is bene cial in di erentiating respiratory illness rom cyanotic heart disease. The hyperoxia take a look at is performed by obtaining arterial blood gas measurements (preferably from the best radial artery) when the infant is in room air after which after the infant has been in 100% oxygen for five to 10 minutes. R outine pulse oximetry is per ormed in asymptomatic newborns a ter 24 hours o li e however be ore hospital discharge (see Chapter 31). If a cardiac lesion is present that allows a xed right-to-le t shunt, rising inspired oxygen could have little e ect on the arterial blood gases. However, if the cyanosis is caused by a di usion de ect within the lungs (pulmonary disorder), the diploma o cyanosis o ten decreases with growing inspired oxygen. R espiratory misery most o ten happens with congenital heart illness when the lungs turn into too "moist. Signs and signs of respiratory distress embrace tachypnea, retractions, nasal flaring, head bobbing, and abdominal breathing. In the early stages, the neonate could also be tachypneic and tachycardic with an increased respiratory e ort, diaphoresis, hepatomegaly, and delayed capillary re ll. Because the neonatal myocardium has fewer contractile elements and is poorly innervated by the sympathetic nervous system, capacity to increase stroke volume is proscribed. There ore neonatal will increase in cardiac output are achieved primarily by rising the heart price. Hypertrophy and dilation o the center occur in response to a stress or volume overload. The gallop rhythm is an abnormal lling sound that may be current with congestive coronary heart failure. Decreased ef cardiac output results in a compensatory redistribution of blood move to vital tissues. Peripheral tissue per usion is decreased, which results in decreased peripheral pulses and poor capillary re ll. A decrease in peripheral perfusion is usually subtle, however is an alarming signal of declining cardiac output and impending cardiovascular collapse. Capillary re ll and peripheral pulses are essential to monitor within the youngster at risk or decreased cardiac output. Poor urine output could be a sign o poor central per usion and, as such, urine output ought to be monitored carefully. Congestive coronary heart ailure results in an increase in metabolic price and elevated activity o the autonomic nervous system, leading to diaphoresis. In neonates, that is most regarding during feedings or other durations of increased metabolic calls for. This results in elevated pressures in the proper atrium, central venous system, and hepatic system. Hepatomegaly outcomes rom hepatic venous congestion and is an easily evaluated signal o systemic venous overload. The decreased per usion to peripheral tissues and the elevated vitality wanted by the guts in ailure leaves little energy or activities such as eeding and crying. The basal metabolic i fee is increased in neonates with congestive heart ailure, and cardiac inefficiencies because of a congenital coronary heart lesion trigger the guts to work harder and thus require more power. Poor growth and ailure to thrive happens rom the mismatch between above-normal caloric wants and below-normal capability to eat. Most infants require larger calorie method or expressed breastmilk supplemented with high-calorie components. Supplemental eeding tubes additionally lower the amount o work required to eed, so they can be bene cial to assist augment the caloric consumption and decrease the caloric needs o an in ant. Hypotension is an alarming sign that will recommend worsening cardiac perform and poor cardiac output.
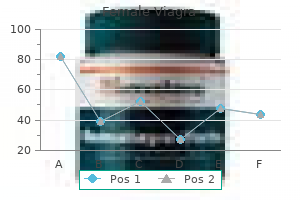
100 mg female viagra buy with amex
Calculate the whole magnification of the nucleus of a cell being noticed via a compound mild microscope with a 10* ocular lens and an oil immersion lens pregnancy day by day female viagra 50 mg discount mastercard. The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ; that of an electron microscope women's health clinic ulladulla female viagra 50 mg trusted, (b). The maximum decision of a compound microscope is (c) ; that of an electron microscope, (d). One benefit of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e). Assume you stain Clostridium by making use of a basic stain, carbolfuchsin, with heat, decolorizing with acid-alcohol, and counterstaining with an acidic stain, nigrosin. In 1996, scientists described a brand new tapeworm parasite that had killed no much less than one person. Endospores may be seen as refractile buildings in unstained cells and as colorless areas in Gram-stained cells. Why is it necessary to do an endospore stain to confirm the presence of endospores In 1882, German bacteriologist Paul Erhlich described a way for staining Mycobacterium and noted, "It may be that all disinfecting brokers which are acidic shall be without impact on this [tubercle] bacillus, and one must be limited to alkaline agents. Laboratory diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection is based on microscopic examination of Gram-stained pus. In a Gram stain, a step might be omitted and still allow differentiation between gram-positive and gram-negative cells. Prokaryotes lack membrane-enclosed organelles, specialised constructions that keep it up numerous activities. Other cellular microbes-fungi (yeasts and molds), protozoa, and algae-are eukaryotes. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells can have a sticky glycocalyx surrounding them. In nature, most micro organism are discovered sticking to stable surfaces, together with other cells, somewhat than free-floating. The Serratia bacteria in the photograph are connected to plastic; the sticky glycocalyx dried into filaments during microscopic examination. An instance of the issue posed by biofilms in hospital water provides is described within the Clinical Case. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes each contain nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. They use the identical kinds of chemical reactions to metabolize meals, build proteins, and store power. It is primarily the structure of cell partitions and membranes, and the absence of organelles (specialized cellular structures which have specific functions), that distinguish prokaryotes from eukaryotes. The chief distinguishing traits of prokaryotes (from the Greek phrases which means prenucleus) are as follows: 1. Advances in microscopy reveal a couple of membrane-enclosed organelles (for example, some inclusions). However, prokaryotes lack other membraneenclosed organelles similar to nuclei, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Eukaryotes (from the Greek phrases which means true nucleus) have the next distinguishing characteristics: 1. They have a quantity of membrane-enclosed organelles, together with mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complicated, lysosomes, and generally chloroplasts. Cell division normally entails mitosis, in which chromosomes replicate and an similar set is distributed into every of two nuclei. Division of the cytoplasm and other organelles follows so that the two cells produced are similar to one another. Although bacteria and archaea look comparable, their chemical composition is different. It is estimated that 99% of the micro organism in nature exist in biofilms (see pages 54 and 156�157). They could also be spherical coccus (plural: cocci, meaning berries), rod-shaped bacillus (plural: bacilli, meaning little rods or strolling sticks), and spiral. In the top Q micrograph, a couple of joined pairs of bacilli could function examples of diplobacilli. We will talk about structures exterior to the cell wall, the cell wall itself, and constructions internal to the cell wall. Among the possible constructions exterior to the prokaryotic cell wall are the glycocalyx, flagella, axial filaments, fimbriae, and pili. Glycocalyx (meaning sugar coat) is the overall term used for substances that encompass cells. If the substance is organized and is firmly connected to the cell wall, the glycocalyx is described as a capsule. Not all bacteria have all the constructions proven; solely buildings labeled in pink are present in all bacteria. Some constructions play particular roles, for instance: in bacterial virulence (capsule), in bacterial identification (cell wall or flagella), and in targets of antimicrobial brokers (cell wall). Plasmids encode data corresponding to genes for resistance to antibiotics or the manufacturing of toxins. In certain species, capsules are essential in contributing to bacterial virulence (the degree to which a pathogen causes disease). Capsules often shield pathogenic micro organism from phagocytosis by the cells of the host. The polysaccharide capsule of Klebsiella also prevents phagocytosis and permits the bacterium to adhere to and colonize the respiratory tract. Through attachment, bacteria can grow on various surfaces similar to rocks in fast-moving streams, plant roots, human tooth, medical implants, water pipes, and even other micro organism. Streptococcus mutans (M-tanz), an important reason for dental caries, attaches itself to the surface of enamel by a glycocalyx. A glycocalyx can also shield a cell towards dehydration, and its viscosity could inhibit the motion of vitamins out of the cell. Flagella Some prokaryotic cells have flagella (singular: flagellum), that are long filamentous appendages that propel micro organism. The long outermost area, the filament, is fixed in diameter and incorporates the globular (roughly spherical) protein flagellin organized in a number of chains that intertwine and type a helix round a hole core. The filament is hooked up to a slightly wider hook, consisting of a unique protein. The third portion of a flagellum is the basal physique, which anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane. The basal body is composed of a small central rod inserted into a sequence of rings.
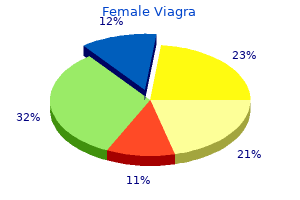
Purchase 100 mg female viagra mastercard
Near or term in ants who normally start with normal Apgar scores and then decline within minutes to a ew hours a ter supply pregnancy kicks female viagra 50 mg order fast delivery. Evidence for respiratory distress breast cancer youth socks female viagra 50 mg sale, together with tachypnea, mild retractions, grunting, and flaring, may be seen. In basic, help o preterm in ants with a historical past o cesarean part (especially elective part within the late-preterm in ant-see Chapter 5), low Apgar scores, pulmonary artery hypertension, poor left ventricular perform, decrease umbilical artery pH (less than 7. Accumulation of interstitial fluid interferes with the forces that maintain the bronchioli open, inflicting collapse and air trapping. Term or late-preterm male infants with a his- the neonate with pulmonary insu ciency requires only the provision o su cient supplemental oxygen to maintain an arterial oxygen rigidity o greater than 70 to 80 mm Hg and upkeep o usual supportive neonatal care. However, the presence of perinatal infectious brokers is more widespread in pneumonia and the course of pneumonia is for an extended time period and with more assist. A vital diploma of hypoxemia or acidemia tends to constrict the pulmonary vasculature and aggravate the issue. These infiltrates are thought to characterize interstitial fluid along the bronchovascular areas. Air trapping causes the looks of gentle to average hyperaeration or inflation on the chest radiograph. Visible fluid in the pulmonary fissures and cardiomegaly also could additionally be seen on chest radiograph. Usually little greater than basic help is necessary while the traditional absorption of lung fluid through the lymphatics takes place. As the lung f uid clears, each the x-ray abnormalities and medical presentation resolve inside 72 hours. A hypoxic event before delivery stimulates intestinal peristalsis and leisure of the anal sphincter. Colonic peristalsis ensues, ensuing within the expelling o meconium into the amniotic f uid and, in extreme instances, gasping in utero that results in meconium aspiration. R espirations a ter start draw meconium rst into main airways and subsequently into the smaller airways, causing obstruction, atelectasis, air trapping, and pneumothorax. Meconium also can trigger chemical pneumonitis and inactivation o sur actant, further impairing gas trade and potentiating barotrauma. This situation happens extra o ten in time period or postterm in ants when a hypoxic episode is skilled in utero. There is pro ound cyanosis and pallor, irregular gasping respirations, and an elevated anteroposterior diameter o the chest (a barrel chest) in consequence o fuel trapping and alveolar overdistention. Cardiomegaly could additionally be current; this results from intrauterine asphyxia or cardiac hypoxia. Hypoxemia is the main drawback in meconium aspiration, and treatment ought to be directed at improving oxygenation. Mildly affected infants will regularly require only warmed, humidified oxygen by hood. Increasing severity o meconium aspiration would require elevated levels o intervention. As with any sick toddler, shut attention must be given to physiologic help and homeostasis. The organisms most often inflicting neonatal pneumonia are primarily group B streptococci and gram-negative organisms. Less generally acquired viral infections embody herpes, cytomegalovirus, varicella-zoster, and syphilis. This is commonly followed by an influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and purple blood cells. Macrophages enter the alveoli and take away intraalveolar debris, restoring normal lung functioning. Viruses and Mycoplasma organisms also may be acquired transplacentally, in the course of the delivery, or postnatally. Viral and mycoplasmal pneumonias generally involve the bronchi and peribronchial interstitium extra usually than the alveoli. Viral and mycoplasmal organisms cause lack of epithelial ciliary appendages and sloughing into the airways. This leads to stasis of mucus and secretions and bronchial obstruction with atelectasis. A secondary inflammatory response is characterised by mononuclear infiltration into the submucosa and perivascular areas inflicting narrowing of the airway lumen. Another response to this inflammatory course of is easy muscle constriction, which leads to elevated airway obstruction and bronchospasm. In severe instances of viral and mycoplasmal an infection, the inflammatory process involves the alveoli. Fungal infections, the most common being Candida infection, could also be acquired in utero, through the delivery process, or in the postnatal interval. Congenitally acquired pneumonia could be diffuse resulting from the inflammatory process at birth. Candida usually invades the pharynx and larynx and may produce a thick layer of hyphae that lines the higher and decrease respiratory tract. Despite no vital difference within the variety of constructive tracheal cultures after 2 days, a ter 5 days, cultures have been positive in 87% o the supine versus 30% o the side-lying group. Serial x-ray lms are more useful than one isolated x-ray examination in making the analysis and ollowing the course o the disease. Infiltration patterns on chest x-ray movies embody lobar consolidation; patchy alveolar infiltrates; hilar and peribronchial infiltrates; reticulogranular, nodular, or miliary infiltrates; and hazy or opaque lungs (see Table 23-13). Lung ultrasound has been proven to be a reliable diagnostic software in neonatal pneumonia. A workup or sepsis is usually part of the diagnostic evaluation for these neonates (see Chapter 22). Treatment o monia varies, depending on the infecting organism and the incidence of acquisition. Acute respiratory distress is incessantly seen in intrauterine and intrapartally acquired secondary infections. Neonates with pneumonia usually have a history of low Apgar scores, temperature instability, and poor tone and activity. Late-acquired pneumonia may have a gradual or abrupt onset, relying on the organism. Infants with chlamydial pneumonia frequently current with a characteristic staccato cough. The signs and symptoms o pneumonia o ten are nonspeci c and di cult to di erentiate rom other neonatal respiratory problems without the help of chest x-ray analysis. If the causative agent is bacterial, antibiotic therapy should be instituted a ter a sepsis workup; i viral, an antiviral agent is taken into account; i ungal, an anti ungal agent is used (see Chapter 22). Neonatal pneumonia could also be accompanied by surfactant inactivation; use of rescue surfactant for respiratory failure accompanying neonatal pneumonia may be thought of (see Box 23-12).
Female viagra 50 mg purchase online
Fat content material varies with gestational age and degree o illness; elevated at content material will increase the quantity o distribution women's health tone zone workout order female viagra 50 mg free shipping, resulting in menstruation meme 50 mg female viagra discount otc a big volume o distribution or lipophilic drugs such as propofol and fentanyl. Several anionic compounds bind to albumin and might displace bilirubin, growing ree bilirubin, thus growing its potential or toxicity. Most drug elimination pathways can turn into saturated if the dose is high sufficient and dose intervals are too frequent. So for a perfect drug maintained at steady-state concentration: (Dose/ dose interval) � F = Cl (clearance) � Css Biotransformation Biotransformation, or drug metabolism, happens mostly in the liver. O xidation, conjugation, glucuronidation, and hepatic blood f ow change with gestational and chronologic age, diseased states, and use o certain medicines. Drugs similar to acetaminophen, phenobarbital, and phenytoin, which require oxidation for elimination, stay obtainable longer and may be reworked to different active metabolites (the neonatal liver metabolizes theophylline to caffeine), or the drug might stay at significant free concentrations for a protracted interval. The risk of extended peak concentrations of obtainable drug or active metabolites for lots of prescription drugs mandates careful monitoring of drug ranges and medical circumstances to titrate dose intervals. Stated one other way: Cl = F � Dose/(dose interval � Css) Or, to tailor the dose for a desired steady-state focus: Dose price = (Cl � Css) / F the suitable dose price could be calculated if the clinician can specify the specified steady-state plasma concentration and is conscious of the clearance and bioavailability of a drug (from peak and trough ranges in a selected patient). If the desired Css = 8 mg/ L, assuming F = 1, particularly if the dose is to be given intravenously: Dose rate = (Cl � Css)/ F = (0. Examples of medications eliminated through the kidney are aminoglycosides, digoxin, diuretics, and penicillins. Doses and dose intervals of medication which have renal excretion must change with age and disease state. Tubular secretion also matures with growing gestational age and is decided by tubular function. In adults, aminoglycosides could additionally be allotted based on creatinine clearance, however in neonates less than 1 week old, serum creatinine could replicate maternal ranges, as well as renal impairment. Again, measuring ranges in cases of suspected renal impairment, whether from suspicious historical past or laboratory values, is essential to determining an appropriate dosage technique. Loading doses help expedite reaching desired therapeutic concentrations, particularly or drugs with lengthy hal -lives, by which a desired e ect is needed immediately. Drugs which are fats soluble or saved intracellularly are tougher to assess, and therapeutic ranges have to be included within the loading dose assessment. Hal -li e is related to each quantity o distribution (V) and clearance (Cl), in order that: If the amount of distribution for caffeine in preterm infants is 0. The enzymes and other compounds involved in every of those processes are topic to genetic variation that results in variation in perform. Pharmacogenetics is the research o the position o inheritance in the individual variation in drug response. Pharmacogenomics is the study o the inf uence o multiple genes, and their interaction with the one another and the setting, on drug e ects. One in 3500 individuals are homozygous for the gene encoding an atypical type of the enzyme butyrylcholinesterase, which is quite gradual to hydrolyze the succinylcholine, a condition resulting in prolonged muscle paralysis. Concurrently, an enzyme liable for N-acetylation, another form of drug metabolism, was discovered to have a standard genetic variant, such that some sufferers are quick metabolizers of medication similar to hydralazine whereas others are slow metabolizers. About 5% to 10% of the grownup Caucasian population has genetic variants of the enzyme, leading to decreased activity, and better and extra extended energetic drug ranges. It is unknown whether or not tight management of aminoglycoside ranges would reduce back threat of hearing loss. No suggestions may be made till extra in depth, population-based research are carried out. Such research must embrace accounting for drug levels and period and genotypes in assessment of danger of hearing loss. The study of pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics is new, particularly to neonatology, by which so little is presently identified about pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of commonly used medicines. In the long run, these research will lead to improved understanding of individual variation in drug response, which ought to permit development of methods to individualize care and assist keep away from issues resulting from heretofore-unaccounted-for genetic variations. The problem will be to understand how the multiple genes and environmental elements interact in fragile infants to alter risk of disease and adverse drug responses. They must also know when these are anticipated to happen and may monitor or these e ects. Dose�plasma concentration results should be recorded when therapeutic drug monitoring is finished. To optimally use drug serum levels, the anticipated blood concentration is calculated from the dosage history, and patient variables that may have an result on pharmacokinetics with the timing of blood samples are thought of. A comparability of anticipated values with measured values allows rational adjustment of future dosage. Clinical finish points have to be followed and recorded and dosage regimens adjusted accordingly. After the loading dose of 20 mg/ kg, the infant has acquired 5 mg each 24 hours for 5 days. Clinical and laboratory analysis of tachycardia contains consideration of caffeine toxicity. To estimate the concentration of caffeine, use the next method: Necessary knowledge: Total body weight: 1 kg Vd = 0. A pharmacist ought to be included within the caregiving staff to clari y dose and disposition parameters or particular person sufferers with their various situations. If a suboptimal clinical response is famous along side a subtherapeutic plasma concentration, revised estimates of clearance must be adjusted with one or two obtainable plasma concentrations. If a single stage is drawn after absorption and distribution is complete or close to regular state, then the upkeep dose method could be rearranged to calculate the revised clearance. The common-sense approach suggests that if a patient has half the anticipated concentration of a drug, then perhaps the clearance is twice the initial estimate. If the patient has twice the anticipated focus, the clearance doubtless is half the preliminary estimate. If two concentrations are available after absorption and distribution, half-life is determined by plotting the concentrations on semilog paper. The revised clearance is calculated by rearranging the half-life formulation: Clearance = 0. If this toddler has diminished clearance relative to "common," toxicity might outcome from the usual dose. Toxicity could not have been famous till day 5 because of the estimated time to steady state (Tss) of one hundred fifteen hours. This is larger than the therapeutic range for caffeine in neonates and is most probably the result of decreased clearance. To preserve a focus of 20 mg/ L: Dose = (Interval � Clrevised � Css)/ F = (24 hr � zero. Because tachycardia has resolved, an oral routine primarily based on the final two levels is begun to maintain a caffeine focus of 20 mg/ L.