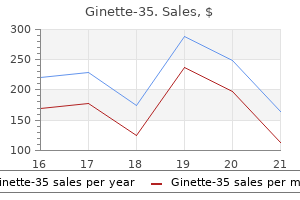
Ginette-35
Ginette-35 dosages: 2 mg
Ginette-35 packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Purchase 2 mg ginette-35 with visa
In animal experiments menstruation nation bobs burgers ginette-35 2 mg buy, it has been discovered that extreme hypertension results in women's health healthy food discount ginette-35 2 mg free shipping increased per fusion of the mind and an augmentation of the edema surrounding contusions and hemorrhages. This displays a failure of autoregulatory vascular mechanisms, with ensuing transudative edema in broken areas of the mind. Observations such as these empha size the necessity for quick correction of hypotension in severely head-injured patients. In decreasing high ranges of blood strain, diuretics, beta-adrenergic blocking brokers, or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are usually used, quite than agents that probably dilate the cerebral vasculature (nitroglycerin and nitroprusside, hydralazine, and some of the calcium channel blockers could current this risk). Hypotension must be corrected by vasopres sor agents similar to phenylephrine or norepinephrine. Agents that scale back gastric acid production-or the equal, antacids by abdomen tube to hold gastric acidity at a pH above 3. Restlessness is managed by diazepam, propofol, or an analogous drug, however provided that careful nursing fails to quiet the patient and supply sleep for a number of hours at a time. Fever is counteracted by antipyretics similar to acetamino phen and, if needed, by a cooling blanket. The use of morphine or bromocriptine to quiet episodes of vigorous extensor posturing and accompanying adrenergic activ ity already has been mentioned. If death or severe incapacity is to be prevented, operation in these circumstances must be undertaken earlier than the advanced indicators of brainstem compression-decerebrate or decorticate posturing, hypertension, bradycardia have appeared. The use of decompressive craniectomy in sufferers with progressive and intractable traumatic brain swelling has been a subject of renewed interest, after having been practically deserted a quantity of many years ago. Guerra and colleagues reported on fifty seven such sufferers, mostly younger adults, who underwent broad frontotemporal craniec tomy, unilateral in 31 and bilateral in 26. These authors have been of the opinion that these outcomes represented a big enchancment over the anticipated end result in this particular group of sufferers. Further trials of decompressive craniectomy after extreme traumatic mind injury are being undertaken. The remedy of the final medical diseases relat ing to protracted coma was outlined in Chap. According to Jennett and Bond, these mental and character adjustments are a larger handicap than focal neurologic ones so far as social adjustment is anxious. In open head wounds and penetrating brain accidents, Grafman and coworkers found that the magnitude of tissue loss and location of the lesion have been the primary components affecting the end result. The prognosis of head injury is influenced by sev eral different factors as talked about. Russell pointed out long ago that the severity of the damage as measured by the period of traumatic amnesia is a useful prognostic index. Some elements of prognosis have been mentioned earlier but the next common comments serve to body the prob lem. In the survey of the large European Brain Injury Consortium, comprising 1 zero,005 adult patients, the damage with a period of amnesia lasting less than Of sufferers 1 h, 95 percent have been again at work inside 2 months; if the amnesia lasted longer than 24 h, only eighty % had returned to work within 6 months. However, approximately 60 percent his massive series nonetheless had signs at the end of 2 months, and 40 % on the end of 18 of the patients in months. Of essentially the most severely injured (those comatose for a quantity of days), many remained completely dis abled. However, the degree of restoration was usually higher than one had expected; the motor impairment, aphasia, and dementia tended to lessen and typically cleared. Improvement may continue over a period of 31 percent; three p.c had been left in a persis tent vegetative state, and 16 p.c remained severely disabled neurologically (Murray et al). Data from the extensively analyzed Traumatic Coma Data Bank are comparable, as reported by Marshall and coworkers proved deadly in 3 or more years. Obviously; multiple-organ damage and, notably, hypotension within the hours immediately after harm, have major results, not just on survival, however in some studies, with neurocognitive and behavioral end result. The signs of focal brain disease, whether due to closed head injuries or open and penetrating ones, have a tendency all the time to ameliorate because the months move. Many of the signs of brainstem illness (cranial nerve dysfunction and ataxia) enhance also, normally within the first 6 months after injury Gennett and Bond) and often to a shocking extent. These function a warning to the neurologist to assign the diagnostic labels of vegetative and minimally conscious state solely after careful and ideally, repeated examinations and then to mood communication with the family and different physicians by an appropriate degree of uncertainty as to outcome. Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology: Summa ry of proof based guideline replace: Evaluation and management of con cussion in sports. Demetriades zero, Charalambides K, Chahwan S, et aJ: Non-skeletal cervical backbone accidents: Epidemiology and diagnostic pitfalls. Jennett B, Teasdale G: Management of Head Injuries: Contemporary Neurologt; no 20. Kampfl A, Franz G, Aichner F, et at: the persistent vegetative state after closed head damage: Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings in 42 patients. J craniectomy within the therapy of severe refractory posttraumatic cerebral edem a. Skippen P, Seear M, Poskitt K, et a l: Effect of hyperventi la tion on regional cerebral blood flow in head-injured children. It has lengthy been the follow to set apart a group of dis eases of the mind and spinal twine in which destruction of myelin, termed cylinders are spared. A comparatively selective degeneration of myelin may happen in some small ischemic foci because of vascular occlusion or in bigger confluent areas, as is the case in Binswanger disease (see Chap. The thought of a demyelinating disease is an abstraction that serves primarily to focus attention on one of many more strik ing and distinctive features of one group of pathologic processes. Another unifying feature of most of these important infl ammatory demyelinating illness is mul the generally accepted pathologic criteria of a demy elinating illness are of nerve fibers with processes is the participation of an inflammatory reaction 34). In addition, for reasons that may turn out to be relative sparing of the opposite components (2) infiltration of clear in subsequent discussion, the persistent progressive leukodystrophies of childhood and adolescence. But, as famous further on, their nature is uncertain, whereas some are clearly caused by a vasculopathy. A broad classification of the infl ammatory demyelin demyelination has ating ailments is given in Table 36-1. In distinction, numerous ailments during which demyelin ation is a distinguished function are thought of part of this category, as mentioned earlier. The broad nature of disseminated lesions was recognized to pathologists within the early nineteenth century significantly as described by Carswell, Cruveilhier and later, Frerichs, but J. M Charcot at the Salpetriere later within the century is justly credited with the primary serious study of the scientific and pathologic aspects of the disease. Graft-versus-host illness the idea of early clinicopathologic correlation and the scientific technique in neurology. It is subsequently among the most venerable of neurologic illnesses and some of the essential by advantage of its frequency, chronicity, and tendency to affect younger adults. Cruveilhier (circa 1 835), in his authentic description of the illness, attributed it to suppression of sweat, and since that point there has been countless speculation in regards to the etiology. While most of the early theories are anachronistic within the gentle of present day ideas, others are still of curiosity. The historical elements may be discovered in the corresponding chapter of the textual content by Compston and colleagues.
Diseases
- Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy
- Berardinelli Seip congenital lipodystrophy
- Hypoparathyroidism familial isolated
- Chromosome 18 long arm deletion syndrome
- Lockwood Feingold syndrome
- Chromosome 14q, partial deletions
- Cutis verticis gyrata thyroid aplasia mental retardation
- Maumenee syndrome
Order ginette-35 2 mg on-line
The return of muscle power happens primarily in the first 3 to 4 months and might be the outcomes of morphologic restitution of partially broken nerve cells pregnancy over 35 ginette-35 2 mg cheap otc. Branching of axons of intact motor cells with collateral reinnervation of muscle fibers of denervated motor models can also play a component menstruation starter kit ginette-35 2 mg cheap amex. Fifty-two such instances were recorded by the Centers for Disease Control over a 4-year interval. Most of them had been brought on by one of many echoviruses and a smaller quantity to Coxsackie enteroviruses, particularly strains 70 and 71. The former sickness leaves little residual paralysis, however the Coxsackie viruses, which have been studied in sev eral outbreaks within the United States, Bulgaria, and Hungary, have had more variable results. Enterovirus 70 causes acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis in limited epidemics and is adopted by a poliomyelitis in 1 of every 10,000 cases. European outbreaks of enterovirus 71, known within the United States as a cause of hand-foot-and-mouth disease and of aseptic meningitis, have resulted in poliovirus-type paraly sis, together with a number of deadly bulbar circumstances (Chumakov et al). The tendency of West Nile virus to cause a poliomyelitis has already been talked about. The suggestion that the late onset of progressive weak spot after poliomyelitis ("postpolio syndrome") would possibly characterize a gradual infection has by no means been verified. Claims have additionally been made numerous occasions over the years for a viral cau sation of a number of sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and different degenerative ailments, but the proof in all cases has been questionable. The established human sluggish infections of the nervous system brought on by conventional viruses embrace subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (measles virus), progressive koencephalopathy ac virus). They are caused by conven tional viruses and are to not be confused with a gaggle of subacute and persistent neurologic illnesses that rubella panencephalitis, and progressive multifocal leu Our personal experience with this form of poliomyelitis has consisted of a quantity of patients who had been referred through the years for paralyzing illnesses initially thought to be Guillain-Barre syndrome (Corson and Ropper). The evolving electromyographic changes indicated that the paralysis was brought on by a loss of anterior hom cells quite than by a motor neuropathy or a purely motor radiculopathy, however this distinction was not at all times sure. Su bacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis this disease was first described by Dawson in 1934 underneath the name "inclusion body encephalitis" and extensively studied by Van Bogaert, who renamed it subacute scleros ing panencephalitis. Never a common disease, the situation occurred till just lately at a price of about 1 case per 1 million youngsters per year and now, with the introduction and widespread use of measles vaccine, it has virtually disappeared. Children and adolescents had been affected for the most part, the disease not often appearing past the age of 10 years. Initially there was a decline in proficiency at college, mood outbursts and different adjustments in character, diffi culty with language, and loss of interest in usual activities. These quickly give way to a severe and progressive intellec tual deterioration in association with focal or generalized seizures, widespread myoclonus, ataxia, and generally visible disturbances caused by progressive chorioretinitis. As the illness advances, rigidity, hyperactive reflexes, Babinski signs, progressive unresponsiveness, and signs of autonomic dysfunction seem. A sequence of 39 such adult circumstances from India with imply age of 21 years was reported by Prashanth and coworkers, the oldest patient a 43-year old. The main options have been similar in most ways to childhood cases, except that several had visible distur bances and two had extrapyramidal features, raising the potential of prion illness. Myoclonus was current early in the illness in 26 and developed later in all instances; the movements were described as "gradual," a characteris tic alluded to in different sequence. In two instances that occurred in pregnant ladies, blurred imaginative and prescient and weak point of limbs was followed by akinetic mutism, without a hint of myoclonus or cerebellar ataxia. Nevertheless, the professional gressive ataxic-myoclonic chronic dementia in a ci:tild is so typical that bedside analysis was normally attainable. These proteins have been shown to symbolize mea sles-virus-specific antibody (Mehta et al). Histologically, the lesions contain the cerebral cortex and white matter of each hemispheres and the mind stem. Destruction of nerve cells, neuronophagia, and perivenous cuffing by lymphocytes and mononuclear cells indicate the viral nature of the an infection. Eosinophilic inclusions, the histopathologic hallmark of the illness, are found within the cytoplasm and nuclei of neurons and glia cells. Virions, thought to be measles nucleocapsids, have been observed within the inclu sion-bearing cells examined electron microscopically. How a ubiquitous and transient viral an infection in a seemingly normal young baby allows the event, many years later, of a rare encephalitis is a matter of hypothesis. In this sort, measles or publicity to measles precedes the encephalitis by 1 to 6 months. Seizures (often epilepsia par tialis continua), focal neurologic indicators, stupor, and coma are the primary options of the neurologic illness and result in demise within a quantity of days to a couple of weeks. Aicardi and colleagues have isolated measles virus from the mind of such a affected person. In a sense, this subacute measles encephalitis is an opportunistic infection of the mind in an immunodeficient affected person. There are, nonetheless, descriptions of youngsters with the congenital rubella syndrome in whom a progressive neurologic deterioration occurred after a stable period of as tuberculosis or sarcoidosis. A number of instances occur in sufferers receiving immunosuppressive medicine for renal transplantation, multiple sclerosis (see Chap. Any one or some combination of hemiparesis progressing to quadriparesis, visible field defects, cortical blindness, aphasia, ataxia, dysarthria, dementia, confusional states, and coma are manifestations. Seizures are infrequent, occurring in solely about In most instances, demise happens in apparently associated to acquired somewhat than to congenital rubella. Since then, this late-appearing progressive syn drome seems to have disappeared, no particular new circumstances having been reported prior to now 30 years nevertheless it nonethe much less stays of organic curiosity. On a background of the features of congenital rubella, a decade later there occurred a deterioration in habits and college efficiency, typically associated with seizures, and, soon thereafter, a progressive impairment of mental function (dementia). Clumsiness of gait was an early symptom, adopted by a frank ataxia of gait and then of the limbs. It is character ized by widespread demyelinating lesions, mainly of the cerebral hemispheres however sometimes of the brainstem and cerebellum, and, not often, of the spinal twine. The lesions differ significantly in measurement and severity-from microscopic foci of demyelination to large multifocal zones of destruc tion of both myelin and axons involving giant components of a cerebral or cerebellar hemisphere. Many of the reactive astro cytes in the lesions are gigantic and contain deformed and bizarre-shaped nuclei and mitotic figures, adjustments which are seen in any other case only in malignant glial tumors. Also, on the periphery of the lesions, the nuclei of oligo dendrocytes are significantly enlarged and contain irregular inclusions. It is thought to be dormant within the kidney or bone marrow till an immuno suppressed state permits its energetic replication. This syndrome has with out identification of the agent) of the nervous system in people. The unique symptoms have been ophthalmoplegia and pronounced somnolence, from which the disease took its name. Some sufferers had been overly active, and a third group manifested a disorder of movement in the type of bradykinesia, catalepsy, mutism, chorea, or myoclonus. However, essentially the most extraordinary feature was the appear ance of a parkinsonian syndrome, after an interval of weeks or months (occasionally years), in a high propor tion of survivors.
Cheap ginette-35 2 mg otc
When calcified women's health magazine birth control article cheap 2 mg ginette-35 mastercard, they appear in radio graphs as curvilinear opacities that observe the outline of the ventricle menstrual cycle 8 days apart generic ginette-35 2 mg fast delivery. Rarely, nodules of abnormal tissue are observed within the basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal wire. Under the microscope the tubers are seen to be composed of interlacing rows of plump, fibrous astro cytes (much like an astrocytoma, although lacking in glial fibrillar protein). In the cerebral cortex and gan glionic buildings, derangements of structure outcome from the presence of abnormal-appearing cells: significantly enlarged "monstrous," or "balloon" neurons and glia cells-often troublesome to distinguish from one another. Also, displaced normal-sized neurons contribute to the chaotic histologic appearance. Gliomatous deposits may impede the foramina of Monro or the aqueduct or ground of the fourth ventricle, causing hydrocephalus. Neoplastic transformation of irregular glia cells, a not infrequent prevalence, often takes the type of a large-cell astrocytoma, less typically of a glioblastoma or meningioma. Recently, certain relationships have been drawn between the balloon cells of this illness and related cells in focal cortical dysplasias (see Crino and colleagues for details). It is the early stage of the illness and the fonnes frustes that give trouble, and right here the skilled der matologist may be of nice help. Epilepsy-that is, flexion spasms in infancy-and delay in psychomotor develop ment are by no means diagnostic of tuberous sclerosis, as they occur in many ailments. It is in these circumstances, and likewise in each sizable population of the epileptic or developmentally delayed, especially when the household history is unrevealing, that a seek for the dermal equivalents of the disease-the hypomelanotic ash-leaf spots, adenoma sebaceum, collage nous skin patch, phakoma of the retina, or subungual or gin gival fibromas-is so rewarding. The discovering of any considered one of these lesions supplies affirmation of the partial and atypi cal case. Adenoma sebaceum could often occur alone and is easily confused with pimples vulgaris within the adolescent. The historical past of epilepsy or demonstration of developmental delay is useful however neither is a requisite for the analysis of tuberous sclerosis (see the monograph by Gomez). Clinics that treat large numbers of these sufferers recom mend imaging of the kidneys and lungs and, in children, echocardiography. Serial examinations to detect enlarge ment of the subependyrnal tumors is advised yearly for those youthful than age 21 years and each 2 to 3 years thereafter, however the most effective course of action if a glioma emerges has not been clearly established. To an increasing degree, neurosur geons are excising single epileptogenic cortical tubers in otherwise comparatively normal kids. There are about 15 specialized facilities in the United States, and several overseas, which are expert at caring for these sufferers and establishing a regimen of radiologic surveillance. Of the severe instances, approximately 30 p.c die earlier than the fifth yr, and 50 to seventy five p.c earlier than attaining adult age. Status epilepticus accounted for many deaths up to now, but improved medicine remedy has decreased this hazard. Neoplasias take their toll; the authors have had a number of such sufferers who died of malignant gliomas arising in striatothalarnic regions. The typical medical picture, often identifiable at a look, consists of a quantity of cir cumscribed areas of elevated pores and skin pigmentation accom panied by dermal and neural tumors of assorted sorts. The condition generally identified as a quantity of idiopathic neuro mas was the subject of a monograph by R. Smith in 1849; even at the moment, he referred to examples recorded by different writers. It was von Recklinghausen, however, who, in 1882, gave the definitive account of its medical and pathologic options. The subsequent studies of the illness by Yakovlev and Guthrie; Uchtenstein; Riccardi; and Martuza and Eldridge; and extra recently by Creange and colleagues; and the excellent monographs of Crowe and colleagues and of Riccardi and Mulvihill are informative references that present a complete analysis of the scientific, pathologic, and genetic knowledge pertaining to the illness. Epidemiology Crowe and associates calculated the prevalence of the disease to be 30 to forty per one hundred,000, with the expectancy of 1 case in every 2,500 to three,300 births over 50 years in the past and these rates pertain in the all collection from the current era. Approximately half of their circumstances had affected family members, and in all cases the distribution of circumstances within a household was according to an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. The illness has been observed in all races in different elements of the world, and males and females are about equally affected. More recently, Nothing may be offered in the method in which of prevention other than genetic counseling. Antiepileptic remedy of the usual type suppresses the convulsive tendency roughly successfully and should be applied assiduously. It is often pointless to try the excision of tumors, particularly in severely affected individuals (with the exception of renal hamartomas that impair kidney function). Both are inherited in an autosomal dominant sample with a excessive degree of penetrance, however half the circumstances are a results of spontaneous mutations. The classic type of the disease with a quantity of neurofibromas, described beneath, is brought on by a mutation located near the centromere on chromosome 17 in a gene called neurofi bromin (Barker et al). The second type, in which the principle characteristic is bilateral acoustic nerve neuromas, described additional on, is brought on by a mutation within the merlin gene (also known as schwannomin). Virtually all fami lies manifest totally different mutations and there have been no clear associations between particular mutations and phenotypic characteristics except that the uncommon full deletion results in early onset multiple neurofibromas, developmental delay, and facial dysmorphism. The pathogenesis is less obscure now that the genes implicated in each illnesses have been recognized. Usually these are the sufferers with the slightest diploma of cutaneous abnor mality. Of the remaining two-thirds, most consulted a physician because of the disfigurement produced by the pores and skin tumors or as a end result of a number of the neurofibromas were producing neurologic signs. The patches of cutaneous pigmentation, appearing shortly after delivery and occurring wherever on the body, represent the obvious medical expression of the dis ease. In the majority of sufferers, spots of hyperpigmentation (cafe-au-lait lesions) and cutaneous and subcutaneous neurofibromatous tumors are the basis of medical diag nosis. Pigmentary adjustments in the skin are practically at all times current at delivery, but neurofibromas are rare at that age. Exceptionally, a neurofibroma of a cranial nerve or a spinal root (some instances with compression of the cord), disclosed during imaging of the backbone or a neurosurgical intervention, may be the initial manifestation of the disease. In a survey of pigmented spots in the skin, Crowe and associates discovered that 10 % of the traditional inhabitants had a number of spots of this type; nonetheless, anybody with greater than 6 such spots, some exceeding 1. The look of a quantity of cutaneous and subcuta neous tumors in late childhood or early adolescence is the opposite principal characteristic of the disease. They assume many shapes-flattened, sessile, peduncu lated, conical, lobulated, and so on. When pressed, the delicate tumors tend to invaginate by way of a small opening within the pores and skin, giving the sensation of a seedless raisin or a scrotum without a testicle. This phenomenon, spoken of as "buttonholing," is useful in distinguishing the lesions of this disease from different pores and skin tumors, for instance, a number of lipomas. The subcutaneous neural tumors, that are also multiple, take two varieties: (1) agency, discrete nodules attached to a nerve or (2) an overgrowth of subcutaneous tissue, typically reaching huge size.
Order ginette-35 2 mg on line
In some instances women's health center in newport news va 2 mg ginette-35 buy with visa, few changes were demonstrable in the mind menstrual questionnaire cheap ginette-35 2 mg on line, although there had been a distinguished dementia during life. Contrariwise, widespread inflam matory adjustments may be discovered without clinical abnor malities having been recorded during life. Odd sei zures, together with epilepsia partialis continua, have been noticed with this dysfunction, however they must be uncom mon. Sensory symptoms may be associated to neuronal loss in the posterior horns, traced to the commonly related lack of neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (sensory neuronopathy and sensory neuropathy) as mentioned earlier and mentioned additional on. Most patients with small cell lung most cancers and any of the forms of paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis have been discovered to harbor circulating polyclonal IgG antibodies (anti-Hu, or antineuronal antibody h;pe 1) that bind to the nuclei of neurons in lots of regions of the brain and spinal twine, dorsal root ganglion cells, and peripheral autonomic neurons. Cancers of the prostate and breast and neuroblastoma may not often produce a similar anti body. Treatment Despite a few stories of improvement with plasma exchange or intravenous gamm a globu lin, the results of remedy have been disappointing. However, these few patients who did enhance had treat ment from the onset of signs, and this is possibly a method of limiting the neuronal loss. Many sufferers have a non-descript prodrome of malaise, fatigue, headache excessive sleepiness, or low fever. The teratoma in one of their sufferers was located in the mediastinum as a substitute of the ovary and uncommon circumstances have occurred with small cell lung most cancers, including in men. We have been impressed with the autonomic overac tivity in the patients under our care with this syndrome. Episodes of hypertension, tachycardia and diaphoresis may be pronounced, as is excessive salivation, pupillary dilation, and different signs of sympathetic dysfunction, individually or concurrently. These sufferers show brainstem signs, significantly loss of hori zontal gaze, and facial and pharyngeal spasms or abdom inal myoclonus. Treatment A premium is connected to early identifi cation of this disorder and rapid removing of the ovary containing the teratoma or resection of one other inciting tumor. Improvement after tumor removal is associated with subsidence of the antibody titer over many weeks and an excellent outcome happens in a majority of cases. Decisions regarding oophorectomy are difficult in view of lowering fertility in younger women. It is affordable to start these same immune therapies whereas awaiting surgical procedure in instances that are highly symptomatic. It must be emphasized that a nondescript, mainly sensory neuropathy is a extra common accompaniment of systemic most cancers, and it may or is probably not related to the anti-Hu antibody. The sensory neuronopathy and neuropathy had been first described by Denny-Brown in 1948 and are notable as a outcome of they served to introduce the modem-day con cept of paraneoplastic neurologic illness. The initial symptoms in each processes are numbness or paresthe sia, generally painful, in a limb or in both feet. Over a period of days in some cases, however more typically over weeks, the initially focal signs turn into bilateral and may spread to all limbs and their proximal portions and then to the trunk. It is that this widespread and proximal distribu tion and the involvement of the face, scalp, and sometimes the oral and genital mucosa that mark the method as a sen sory ganglionitis and radiculitis and when subacute are highly suggestive of a paraneoplastic course of. As the illness progresses, all types of sensation are significantly lowered, leading to disabling ataxia and pseu doathetoid actions of the outstretched arms. The reflexes are misplaced, but not at all times at the outset, and energy is relatively preserved. Autonomic dysfunction-including constipation or ileus, sicca syndrome, pupillary areflexia, and orthostatic hypotension-is typically associated. Also, a nearly pure type of peripheral autonomic fail ure has been recorded as a paraneoplastic phenomenon (paraneoplastic dysautonomia). One of our patients with sensory neuronopathy had gastric atony with deadly aspi ration after vomiting and one other died of surprising cardiac arrhythmia. Very early within the illness, the electro physiologic research may be normal, but this soon offers method to a lack of all sensory potentials, generally with indications of a gentle motor neuropathy. As with paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis, most of the cases related to small cell lung cancer demonstrate the anti-Hu antibody. In reviewing this subject in 1970, Adams and Victor had been capable of discover only forty one pathologically verified instances; in a subsequent evaluation (Henson and Urich), just a few extra instances were added. At the Cleveland Metropolitan General Hospital, in a sequence of 1,700 consecutive autopsies in adults, there have been 5 situations of cerebellar degeneration related to neoplasm. In the experience of Henson and Urich, about half of all patients with nonfamilial, late-onset cerebellar degeneration proved ultimately to be harboring a neoplasm. Large series of instances have been reported from the Mayo Clinic and the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (Hammock et al and N. We see a quantity of such instances yearly, but have also encountered numerous instances of an identical syndrome with no cancer evident and no antibodies which may be in all probability a results of various causes summarized in Chap. In approximately one-third of the cases, the underly ing neoplasm has been within the lung (most often a small cell carcinoma)-a determine reflecting the high incidence of this tumor. However, the affiliation of ovarian carcinoma and lymphoma, notably Hodgkin disease, account ing for roughly 25 and 15 p.c, respectively, is significantly greater than could be expected on the basis of the frequency of these malignancies. Carcinomas of the breast, bowel, uterus, and other viscera have accounted for most of the remaining cases (Posner, 1995). The cerebellar signs have a subacute onset and regular progression over a interval of weeks to months; in more than half the instances, the cerebellar indicators are acknowledged earlier than these of the associated neoplasm. Symmetrical ataxia of gait and limbs-affecting arms and legs kind of equally-dysarthria, and nystag mus are the usual manifestations; some have vertigo. Striking in fully developed cases has been the severity of the ataxia, matched by few different illnesses. Occasionally, myoclonus and opsoclonus or a fast-frequency myoclonic tremor could additionally be related ("dancing eyes-dancing feet," as famous later). Lambert-Eaton syndrome is known to occur with cerebellar degeneration as paraneoplastic diseases. These are nicely emphasised within the collection of 47 patients collected by Anderson and col leagues and the 55 circumstances by Peterson et al, who tabulated these noncerebellar neurologic features. Pathologically, there are diffuse degenerative modifications of the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei. Purkinje cells are affected prominently and all components of the cerebellar cortex are concerned. Degenerative modifications in the spinal cord, involving the posterior columns and spinocerebellar tracts, have been discovered not often. The cer ebellar neuronal degeneration is incessantly related to perivascular and meningeal clusters of inflamma tory cells. Henson and Urich regard the inflammatory adjustments as an impartial course of, a part of a subacute paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis (see below). This view is supported by the discovering that the precise antibodies linked to cerebellar degeneration differ from these found in paraneoplastic inflamm atory lesions in different parts of the nervous system. Anti-Purkinje cell antibodies (termed "anti-Yo") may be discovered within the sera of about half of patients with parane oplastic cerebellar degeneration and in the giant majority of these associated to carcinoma of the breast or feminine geni tal tract, linking the medical syndrome and this antibody intently. Anderson and colleagues report a similar proportion however point out that several anti-Purkinje antibodies in addition to the highly attribute one could additionally be discovered by special methods. In an equal variety of instances without antibodies, half are males with lung cancer, a few of whom show the anti-Hu antibody.
Populi cortex (Aspen). Ginette-35.
- What is Aspen?
- Dosing considerations for Aspen.
- How does Aspen work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Arthritis-like problems, prostate discomforts, back trouble, nerve pain, and bladder problems.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96269
2 mg ginette-35 order
Currently pregnancy magazines order 2 mg ginette-35 otc, a spectrum of no less than 12 problems of peroxisomal operate is recognized breast cancer graphics buy ginette-35 2 mg line, all of them character ized by deficiencies in the peroxisomal enzyme of fatty acid oxidation. However, the most widely known peroxisomal issues are adreno leukodystrophy and Refsum disease, however the Zellweger cerebrohepatorenal syndrome can be thought-about a proto kind. Each variant could be recognized by its attribute profile of elevated long- and very-long-chain fatty acids, and the precise prognosis can be confirmed by enzymol ogy of cultured fibroblasts or amniocytes. For an authoritative dialogue of peroxi somal biogenesis, the reader is referred to the article by Gould and Valle. Poor feeding and failure to acquire weight, instability of temperature (mainly hypothermia), and seizures turn out to be apparent in early infancy. The hair is normal at delivery however the secondary growth is lusterless and depigmented and looks like metal wool; hairs break easily and beneath the microscope they seem twisted (pili torti). Radiologic examination exhibits metaphysial spurring, mainly of the femurs, and subperiosteal cal cifications of the bone shafts. Arteriography discloses tortuosity and elongation of the cerebral and systemic arteries and occlusion of some. The mixture of intracerebral hemorrhage and metaphysial bone spurs, which may be interpreted as "nook fractures," has led in some instances to the erroneous analysis of kid abuse. There was a diffuse lack of neurons within the relay nuclei of the thalamus, the cerebral cortex, and the cerebellum (granule and stellate cells) and of dendritic arborizations of residual neurons of the motor cortex and Purkinje cells. Furthermore, as a end result of copper fails to cross the placenta, a severe reduction of copper within the mind and liver is obvious from start. In this sense, the abnormality of copper metabolism is the other of that in Wilson disease. The state of affairs, however, could additionally be extra complicated, as samples of intestinal tissue show a buildup of copper that indi cates the issue is in mobilization of copper from the gut to the bloodstream. Other copper-dependent enzymes present impaired operate, corresponding to cytochrome oxidase. The ratio of dopamine to norepinephrine and dihydroxyphenylacetic acid to dihydroxyphenylglycol proved, of their research, to be essentially the most delicate and spe cific for early detection. This has allowed the neonatal identification of cases in families with affected kids and resulted in normal neurodevelopment in a couple of youngsters who had been treated with copper starting within the first weeks of life. However, even early handled instances displaying restricted neurodevelopment survive and present some neurologic advance, not like the past experience in which few sur vived past 5 or 6 years. Only rarely does an inherited metabolic illness fall into a couple of of those cat egories. There can also be appreciable value in beginni ng the diagnostic process by classifying the syndrome as a leukodystrophy or a poliodystrophy (disease predomi nantly affecting neurons, see further on), although this distinction is simpler to make within the older baby. Once the most important category of illness has been identified, appropriate analysis depends on particular medical and laboratory options tabulated under (Tables 37-5 and 37-6). Neurologic indicators which would possibly be roughly particular for sure metabolic illnesses are as follows: 1. Abolished tendon reflexes with particular Babinski indicators: globoid cell (Krabbe) leukodystrophy, occasion ally Leigh disease, and (beyond infancy) metachro matic leukodystrophy Peculiar eye actions, pendular nystagmus, and head rolling: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, Leigh illness; later, hyperbilirubinemia and Lesch-Nyhan hyperuricemia (see below) Marked rigidity, opisthotonos, and tonic spasms: Krabbe, Alpers disease, or childish Gaucher illness (classic triad: trismus, strabismus, opisthotonos) Intractable seizures and generalized or multifocal myoclonus: Alpers disease Intermittent hyperventilation: Leigh disease and con genital lactic acidosis (also nonprogressive familial agenesis of vermis) Strabismus, hypotonia, seizures, lipodystrophy: carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome Ocular abnormalities of specific diagnostic value in 3. Equally nonspecific are options similar to irritability and extended crying; poor feeding, difficulty in swallowing, inanition, and retarded development; failure of fixation of gaze and following transfer ments of the eyes (often misinterpreted as blindness); and tonic spasms, clonic jerks, and focal and generalized seizures. Rapid pendular nystagmus: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, rarely Krabbe leukodystrophy, Cockayne syndrome (later age) 2. Macular cherry-red spots: Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff variant, some circumstances of infantile Niemann Pick disease, and barely lipofuscinosis (see Table 37-4) 3. Enlarged liver and spleen: childish Gaucher disease and Niemarm-Pick illness; one kind of hyperarnm o nemia; Sandhoff disease; later, the mucopolysacchari doses and mucolipidoses three. Enlarging head without hydrocephalus (macroceph aly): Canavan spongy degeneration of infancy, some cases of Tay-Sachs illness, Alexander illness 4. Storage granules and vacuolated lymphocytes: Niemarm-Pick illness, generalized 1 gangliosidosis 7. A patho logic course of in the nervous system is reliably ascertained by the apparent progression of a neurologic dysfunction, such as a lack of ability to walk and to converse, which normally parallels a regression in other high-level (quasi intellectual) capabilities. Diseases characterized by seizures and myoclonus might show more difficult to interpret, for the seizures could occur at any age from a variety of distant or quick neurologic causes and, if frequent, could trigger a major impairment of psychomotor function. The results of anticonvulsant medications might add to the impairment of cortical function. An added difficulty arises when, for numerous years, the heredi tary metabolic abnormality merely slows development. Indicative of gray matter disease (polio disease-are described right here due to their clinical importance and since they exemplify different varieties of biochemical defects. Reference can also be made to certain other aminoacidurias, described within the first a half of this chapter, which, like Hartnup illness, are associated with intermittent ataxia. Only passing comments are made concerning the other aminoacidurias, that are exceedingly rare or have only an unsure effect on the nervous sys tem. A detailed account of those problems could be found within the monograph of Scriver and coworkers. Choreoathetosis and ataxia, spastic paralysis, and signs of sensorimotor tract involvement happen later. Neuronal storage diseases, similar to those described within the earlier section, as well as neuroaxonal dystrophy and the lipofuscinoses, conform to the pattern of grey matter diseases (see Table 37-5). Metachromatic leuko dystrophy, globoid-cell (Krabbe) illness, sudanophilic leukodystrophy, and spongy degeneration of infancy (Canavan disease) exemplify white matter illnesses (see Table 37-6). Thus, as predicted by Galton, the final word phenotype is a product of "nature and nurture" (Scriver and Clow). Twenty other aminoacidopathies result in a defect in the r enal transport of amino acids, some of which secondarily harm the nervous system. Hyperactivity, aggressivity, self clumsy gait, fantastic tremor of the palms, poor coordination, repetitious digital mannerisms and other 37-1 indicates the relative frequency of those diseases and Table 37-2 summarizes the practical tests for his or her identification. Athetosis, dystonia, and frank cerebellar ataxia have been described but should be uncommon. Also, seizures happen in a small minority of severely affected sufferers, taking the shape at first of flexor spasms and later of absence and grand mal attacks. A musty body odor (because of phen ylacetic acid excretion) can usually be detected. The few such cases reported and summarized by Kasim and colleagues, with a case of their own, devel oped a progressive spastic paraparesis, some with delicate dementia. The phenylalanine ranges were at values that replicate complete or partial enzyme deficiency. But screening by the Guthrie (ferric chloride) test will reliably establish the patient at risk.
Order ginette-35 2 mg with visa
These embrace visible menopause bleeding ginette-35 2 mg order without prescription, auditory women's health magazine big book of exercises discount ginette-35 2 mg mastercard, and somatosensory-evoked responses and the much less standardized and sometimes tested perceptual delay on visible stimulation; electro oculography; altered blink reflexes; and a change in flicker fusion of visible photographs. Some sufferers may have a whole clinical remission after the preliminary attack, or, there may be a collection of exacerbations, every with com plete remission; rarely, such exacerbations may be extreme sufficient to have brought on quadriplegia and pseudobulbar palsy. A further 20 % relapsed in 5 to 9 years, and one other 10 % in 10 to 30 years. Not solely the length of this interval is remarkable, but additionally the fact that the basic pathologic course of can remain potentially lively for such a long time. Perhaps not surprisingly, they found that a high diploma of disability, as measured by the Kurtzke Disability Status Scale, was reached earlier in sufferers with a higher number of assaults, a shorter first interattack interval, and a shorter time to reach a state of average disability. Kurtzke had earlier reported that the feature most predictive of long-term incapacity was the degree of disability at 5 years from the primary symptom. The common relapse rate in estab lished instances declines in every trimester, reaching a degree lower than one-third of the expected fee by the third trimester. However, there appears to be an increased risk of exacer bations, as a lot as twofold, in the first few months postpartum (Birk and Rudick). An intensive examine of 269 pregnancies by Confavreux and colleagues (1998) established a fee of relapse of 0. A small number of patients die inside several months or years of the onset, however the average period of the ill ness is in extra of 30 years. At the end of 25 years, one-third of the surviving sufferers had been nonetheless working and two-thirds have been nonetheless ambulatory (Percy et al). Other statistical analyses have given a much less optimistic prognosis; these have been reviewed by Matthews. Patients with mild and quiescent types of the illness are, of course, less likely to be included in such surveys. Although distinctive, considered one of our patients relapsed and developed large brainstem demyelination and coma after 30 years (confirmed by postmortem examination) and instances of an aggressive myelopathy that seems after years are well-known. No environmental, dietary, or activity-related adjustments are identified to alter the course of the illness. Extensive brainstem demyelin ation of subacute evolution, involving tracts and cranial nerves sequentially, may be mistaken for a pontine glioma. The lesions could also be small and single, a number of, or confluent in large regions (Akasbi). Nevertheless a number of the lesions represent small zones of infarct necrosis rather than demyelination and are traceable to small-vessel occlusion. Others may be auto immune and demyelinating and this group of processes that have an result on the cerebral white matter remains tough to understand. In a quantity of situations, inflammatory demyelin ation without vascular changes may be seen. The distinction may be notably troublesome in rare instances of the vasculitic process during which the neurologic manifestations take the form of a relapsing or steroid-responsive myelitis. The distinguishing options of Beh<;et disease are recurrent iridocyclitis and meningitis, mucous mem brane ulcers of mouth and genitalia, and signs of articular, renal, lung, and multifocal cerebral illness. The chronic types of brucellosis in the Mediterranean regions and Lyme borreliosis all through North America and Europe may trigger myelopathy or encephalopathy with multiple white matter lesions on imaging studies, however in every case the historical past and different options of the disease assist to establish the infectious sickness (see Chap. Such sufferers require cautious evaluation for the presence of spinal twine compression from neoplasm or cervical spondylosis. As a general rule, lack of abdominal reflexes, erectile dysfunction, and disturbances of blad der operate happen early in the midst of demyelinating myelopathy but late or under no circumstances in cervical spondylosis. A particular downside arises when imaging procedures reveal a regional swelling of the spinal wire suggestive of a tumor. In a patient with this discovering and a subacute, saltatory myelopathy restricted to several adjacent levels (usually thoracic), a seek for an arteriovenous mal formation or fistula may be required. In several of our patients, this discovering has led to an ill-advised try at spinal twine biopsy. A subpial pattern of enhancement with gadolinium is helpful in figuring out sarcoid. Platybasia and basilar impression of the cranium also wants to be thought of within the differential diagnosis, however patients with these conditions usually have a characteris tic shortening of the neck; photographs of the base of the cranium are diagnostic. In each of these cases, a solitary, stra tegically positioned lesion might give rise to a variety of neuro logic signs and indicators referable to the lower brainstem and cranial nerves, cerebellum, and higher cervical wire, giving the impression of dissemination of lesions. The latter are generally distin guished by their familial incidence and other associated genetic traits; by their insidious onset and gradual, regular development; and by their relative syrrunetry and stereo typed scientific pattern. Intactness of stomach reflexes and sphincter perform and the presence of pes cavus, kyphoscoliosis, and cardiac disease are different options that favor the analysis of a heredodegenerative dysfunction (see Chap. The many therapeutic trials of recent years, using primarily anti-inflammatory and irrununosuppres sive are summarized under. Therefore, as discussed earlier, therapy ought to be guided by the nature of the illness in each particular person and with consideration of the unwanted aspect effects and dangers of each of the increasing group of obtainable therapies. Corticosteroids Under the affect of corticoste roids, recovery from an acute attack, together with an attack of optic neuritis, seems to be hastened. As to the dosage of corticosteroids for an acute assault, plainly initially a high dose is simpler however this has been disputed, as noted beneath. A brief interval of corticosteroid administration gener ally produces few adverse effects however some patients com plain of insomnia and some will develop depressive or manic signs. Patients who, because of clinical relapse on withdrawal of the medication, require oral remedy for greater than a number of weeks are subject to the consequences of hypercortisolism, together with the facial and truncal cosmetic changes of Cushing syndrome, hypertension, hyperglyce mia and erratic diabetic control, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis of the pinnacle of the femur, and cataracts; much less typically, there may be gastrointestinal hemorrhage and activation of tuberculosis or pneumocystis. It should be acknowl edged that the corticosteroid regimens and dosages in frequent use are derived from anecdotal expertise (the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial being an exception) and that certain sufferers appear, a minimum of for a time period, to respond higher to one or another methodology of treatment. One restricted trial has shown some profit, in sufferers with relapsing-remitting illness, of month-to-month infusions of intravenous immunoglobulin (0. In this examine, it was found that using intravenous meth ylprednisolone adopted by oral prednisone did, certainly, pace the restoration from visible loss, although at 6 months there was little difference between patients handled in this method and people handled with placebo. They reported that remedy with oral prednisone alone slightly elevated the danger of latest episodes of optic neuritis. In a subsequent randomized trial performed by Sellebjerg and colleagues, it was discovered that methylprednisolone 500 mg orally for five days had a helpful impact on visual function at 1 and 3 weeks. However, at 8 weeks, no impact could presumably be shown (compared with the placebo-treated group), nor was there an effect on the subsequent relapse price. One concern with the longer term administration of interferon is the event of antibodies to the drug. After a period of years, 30 percent of patients show antibodies with every day administration, 18 p.c with alternate-day use, and fewer than 5 p.c with weekly use. More current adjustments within the preparation of interferon have led to reported charges of only 2 % with antibodies after 1 yr of use. There is a few proof that the presence of these antidrug anti bodies diminishes the effectiveness of interferon. In severe circumstances, prednisone 10 mg taken an hour earlier than, a couple of hours after, and once more 6 to 8 hours after injection may be effective. There can also be a tendency to depres sion in prone patients treated with interferon, and in our experience, this info, when brazenly discussed with the patient, has generally influenced the choice concerning choice of remedy.
Ginette-35 2 mg buy cheap line
The small brainstem hemorrhages secondary to temporal lobe herniation and brainstem compression (Duret hemor rhages) menstrual bleeding generic 2 mg ginette-35 with mastercard, hypertensive encephalopathy womens health 1200 calorie meal plan 2 mg ginette-35 with amex, and mind purpura could be included in a stroke. The vessel that ruptures, giving rise to the hemorrhage, is normally a small penetrating artery that originates from a larger trunk. Multiple, almost simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages elevate the potential of amyloid angiopathy or a bleeding diathesis (see further on) but might happen when one typical hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage causes hyper pressure, which in flip leads to one or more additional hemorrhages. The extravasation of blood into the substance of the brain forms a roughly round or oval mass that disrupts the tissue and might grow in volume if the bleeding contin ues. If the hemorrhage is giant, midline constructions are displaced to the other aspect of the skull and the reticular acti vating and respiratory facilities are compromised, leading to coma and demise in the manner described in Chap. It has been long identified that both the size and the situation of the clot decide the diploma of secondary brainstem compression and this was confirmed by Andrew and associates. It is predominantly a result of persistent hyperten sion and degenerative modifications in cerebral arteries. Hydrocephalus might happen as a result of bleeding into the ventricular system or from compression of the third ventricle. Before the clot types, red cells settle in the dependent part of the hematoma and form a menis cus with the plasma above; that is particularly susceptible to happen in cases of anticoagulant-induced hemorrhage. Hematomas, when examined in post-mortem material, comprise solely lots of pink blood cells and proteins; hardly ever one sees a couple of remnants of destroyed brain tissue. The hematoma is usually surrounded by petechial hemorrhages from torn arterioles and venules. Within a couple of days, hemoglobin merchandise, primarily hemo siderin and hematoidin, start to seem. This begins inside a few days and imparts a brownish hue to the periphery of the clot. Phagocytosis of pink cells begins inside 24 h, and hemosiderin is first noticed across the margins of the clot in 5 to 6 days. The clot changes shade gradually over a number of weeks from darkish purple to pale pink, and the border of golden-brown hemosiderin widens. In 2 to three months, larger clots are filled with a chrome-colored thick fluid, which is slowly absorbed, leaving a smooth-walled cavity or a yellow-brown scar. The iron pigment (hematin) becomes dispersed and studs adjoining astrocytes and neurons and may persist nicely past the border of the hemorrhage for years. After 2 to three weeks, the encircling edema begins to recede and the density of the hematoma decreases, first at the periphery. There may be a hoop of enhancement from the hemo siderin-filled macrophages and the reacting cells that kind a capsule for the hemorrhage. At one level a quantity of weeks after the bleed, the appearance could transiently simulate a tumor or abscess. As deoxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin kind, the hematoma signal turns into brilliant, on Tl-weighted pictures and darkish on T2. When methemoglobin disappears and solely hemosiderin stays, the complete remaining mass is hypodense on T2-weighted photographs, as are the surrounding deposits of iron. Massive refers to hemorrhages several centimeters in diam eter, often bigger than 50 mL; small applies to those 1 to 2 em in diameter and fewer than 20 mL in quantity. The volume and placement relate to end result and the nature of the initial neurologic deficit. Takebayashi and coworkers, in an electron microscopic research; found breaks in the elastic lamina at multiple sites, virtually at all times at bifurcations of the small vessels. Possibly these represented factors of secondary rupture from tearing of small vessels by the increasing hema toma. Amyloid impregnation of vessel walls represents a unique mechanism for vessel rupture, as discussed further on. With smaller hemorrhages, the clinical image conforms more intently to the identical old temporal profile of a stroke, i. Vomiting on the onset of intracerebral hemorrhage occurs far more regularly than with infarction and likewise suggests bleeding as the purpose for an acute hemiparesis. The thalamic hemorrhage (B) has extended into the posterior hom of the proper lateral ventricle and the cerebel lar hemorrhage (D) has extended into the fourth ventricle. Seizures, usually focal, happen within the first few days in only 10 p.c of cases of supratentorial hemorrhage, rarely on the time of the ictus and extra commonly as a delayed event, months or years after the hemorrhage. Therefore, headache, acute hyperten sion, and vomiting with hemiplegia in the case of bleeding into the cerebral hemisphere are the cardinal features and serve most dependably to distinguish hemorrhage from ischemic stroke. In the localization of an intracerebral hemorrhage, ocular indicators could additionally be particularly useful. The incidence of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage is higher in African Americans than in whites and it happens with larger frequency in people of Japanese descent. There has lengthy been a notion that acute hyperten sion can precipitate the hemorrhage. This is predicated on the recognized prevalence of cerebral hemorrhage at moments of extreme fright or anger or intense excitement, pre sumably because the blood pressure rises abruptly past its chronically elevated stage. However, in fully 90 % of situations, the hemorrhage occurs when the patient is calm and unstressed, based on Caplan (1993). The level of blood stress rises early in the middle of the hemorrhage however the preceding persistent hypertension is normally of the "essential" sort. Nonetheless, causes of hypertension should always be considered-renal disease, renal artery sto sis, eclampsia, pheochromocytoma, hyperaldosterorusm, adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticosteroid excess and, in fact, sympathetically active medication as talked about. In the series reported by Brott and colleagues, 25 p.c have been found to have enlarged in the first hour and one other 12 p.c in the first day. Blod m cee bral tissue is absorbed slowly over months durmg which time signs and indicators recede. Chronic hypertension is related to bleeding into the putamen, thalamus, pons, and cerebellum. Neurologic symptoms and signs range barely with the exact web site and measurement of the extravasation, however hemiplegia from interruption of the capsule is a constant feature of medium-sized and. With large hem orrhages, sufferers lapse virtually immediately right into a tupor with hemiplegia and their situation visibly detenorates because the hours pass. Within a few minutes or less the face sags on one aspect, speech becomes slurred or aphasic, the arm and leg weaken an are flaccid, an d. These events, occurring progressively over a penod of several minutes or more, are strongly suggestive of intracerebral bleeding. More advanced stages are charac terized by signs of upper brainstem comprssion (coa); bilateral Babinski signs; irregular or interrmttent resprra tion; dilated, fastened pupils, first on the facet of the clot; and decerebrate rigidity. Neuroirnaging has disclosed the frequent occr rence of many smaller putaminal hemorrhages, which in former years would have been misdiagnosed as embolic or thrombotic strokes. With hemorrhages con fined to the anterior section of the putamen, the hemi plegia and hyperreflexia are inclined to be less extreme and o clear more quickly according to Caplan (1993). With small posterior lesions, weak point can be delicate and is attended by sensory loss, hemianopia, impaired visual pursuit to the other facet, Wernicke-type aphasia (left-sided lesions), and anosognosia (right-sided).

2 mg ginette-35 purchase mastercard
Pain within the suboccipital or posterior cervical area menopause matters 2 mg ginette-35 with mastercard, mostly on the aspect of the tumor womens healthcare associates ginette-35 2 mg trusted, is normally the first and by far probably the most outstanding criticism. The latter distribution is extra frequent with tumors arising in the spinal canal and extending intracranially than the reverse. For uncertain reasons, the ache might radiate down the back, even to the lower spine. Both spine and root pain could be recognized, the latter due to involvement of either the C2 or C3 root or each. One sample is weak spot of a shoulder and arm pro gressing to the ipsilateral leg and then to the opposite leg and arm ("around-the-clock" paralysis) as discussed in Chap. Another configuration is triplegia that could be a char acteristic however not invariable sequence of events, caused by the encroachment of tumor upon the decussating cor ticospinal tracts at the foramen magnum. Occasionally, both upper limbs are concerned alone; surprisingly, there could additionally be atrophic weakness of the hand or forearm or even intercostal muscle tissue with diminished tendon reflexes properly under the level of the tumor, an observa tion made originally by Oppenheim. Sensation of intense cold within the neck and shoulders has been one other sudden criticism, and likewise "bands" of hyperesthesia across the neck and back of the top. Segmental bibrachial sensory loss has been demonstrated in a few of the circumstances and a Lhermitte sign (really a symptom) of electric-like sensations down the backbone and limbs upon flexing the neck has been reported regularly. The cranial nerve indicators most incessantly conjoined and indicative of intracranial extension of a foramen magnum tumor are dysphagia, dysphonia, dys arthria, and drooping shoulder (because of vagal, hypo glossal, and spinal accent involvement); included much less usually are nystagmus and episodic diplopia, sensory loss over the face and unilateral or bilateral facial weakness, and a Horner syndrome. Tumors that invade the anterior part of the bottom of the cranium from the frontal sinu s, nasal cavity, or the ethmoid bone, osteomas. Tumors: meningiomas, osteomas, dermoid cysts, gia nt-cell tumors, tumors of the orbit, nasopha ryngeal tumors; more not often, optic nerve gliomas; eosinophilic granulomas, angiomas, native or neighboring infections, trauma. Optic nerve glioma, infraclinoid aneurysm of the inner carotid artery, trauma, orbital tumors, Paget ctisease. Tumors of the sellar and parasel lar space, infraclinoid aneurysms of the internal carotid artery, nasopharyngeal tumors, fistulas of the sinus cavemosus and the carotid artery (traumatic), tumors of the center cranial fossa. Superior orbital fissure Rochon-Duvigneau; syndrome of the pterygopala tine fossa (Behr) and the bottom of the orbit (DeJean) commencing with a lesion of the maxillary and pterygoid rami and evolving into the superior orbital fissure. Jacod-Rollet (often combined with the syndrome of the superior orbital fissure); infraclinoid syndrome of Dandy. Foix-Jefferson; syndrome of the sphenopetrosal fissure (Bonnet and Bonnet) corresponding in part to the cavernous sinus syndrome of Raeder. Lesions of the third, fourth, sixth, and first ctivisions of the fifth nerves with ophthal moplegia, ache, and sensory disturbances within the area of V1; often exophthalmos, some vegetativ e ctisturbances. Apex of the orbit Visual disturbances, central scotoma, papilledema, optic nerve atrophy; occasional exophthalmos, chemosis. Cavernous sinus Ophthalmoplegia caused by lesions of the third, fourth, sixth, and sometimes fifth nerves; exophthalmos; vegetative ctisturbances. Jefferson distinguished three syndromes: (1) the anterior-superior, comparable to the superior orbital fissure syndrome; (2) the center, causing ophthalmoplegia and lesions of V1 and V2; (3) the cau dal, as properly as affecting the whole trigeminal nerve. Lesions of the fifth and sixth nerves with neuralgia, sensory, and motor disturbances, ctiplopia. Apex of the petrous temporal bone Gradenigo-Lannois In flammatory processes (oti tis), tumors similar to cholesteatomas, chondromas, meningiomas, neurinomas of the gasserian ganglion and trigeminal root, major and secondary sarcomas at the base of the cranium. Tumors of the sphenoid and petrosal bones and middle cranial fossa, nasopharyngeal tumors, metastases. Tumors of the glomus jugulare; neurinomas of eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh nerves; chondromas, cholesteatomas, meningiomas, nasopharyngeal and ear tumors; infections, angiomas, not often trauma. Tumors of the base of the cranium, ear, parotid; leukemic infiltrates; aneurysms, angiomas, and inflammations. Nasopharyngeal tumors, primary tumors on the base of the cranium, leukemic infiltrates of basal meninges, trauma, metastases. Lesions of ninth, tenth, and eleventh nerves with disturbance of deglutition; curtain phenomenon; sensory disturbances of the tongue, taste bud, pharynx, and larynx; hoarseness; weak point of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. Loss of twelfth nerve function (loss of regular tongue mobility) along with the signs of the jugular foramen. Lesions of the lower group of nerves (Collet-Sicard) and Bernard-Horner syndrome with ptosis and lniosis. Loss of function of all twelve cranial nerves of one aspect; in lots of circumstances, isolated cranial nerves spared; hardly ever indicators of raised intracranial stress or pyralnidal tract symptoms. Vemet Anterior occipital condyles Collet-Sicard (Vernet-Sargnon) Retroparotid area (retropharyngeal syndrome) Hal f of the base of the skull V tllaret Garcin (Guillain Alajouanine-Garcin); additionally described by Hartmann in 1904. With dermoid cysts of the upper cervical region, as within the case reported by Adams and Wegner, full and extended remissions from quadriparesis may occur. Tumors of the foramen magnum, as mentioned, should be differentiated from spinal or brainstem-cer ebellar a quantity of sclerosis, Chiari malformation with syr inx, and bony compression. Persistent occipital neuralgia with a foramen magnum syndrome is particularly sugges tive of a tumor at that web site. The early occipitonuchal ache must be differentiated from mundane essential osteoarthri tis. Treatment is surgical excision (Hakuba et al) adopted by targeted radiation if the resection is incomplete and the tumor is understood to be radiosensitive. They assume special importance as a outcome of in plenty of instances the neurologic syndrome becomes apparent earlier than the underlying tumor is found. The great variety of medical presentations of paraneoplastic encephalitis disease could be appreciated from early sequence reported by Graus and colleagues of 200 patients: sensory neuropathy, fifty four %; cerebellar ataxia, 10 percent; limbic encephalitis, 9 percent; and others, together with multiple websites, in eleven percent. Some of the paraneoplas tic issues that contain nerve and muscle-namely, polyneuropathy, polymyositis, and the myasthenic myopathic syndrome of Lambert-Eaton-are described in later chapters on these subjects. Here we current the paraneoplastic processes that involve the spinal cord, cerebellum, brainstem, and cerebral hemispheres. Comprehensive accounts of the paraneoplastic dis orders could also be found in the writings of Posner (1995), Darnell and Posner, and Dalmau and Rosenfeld. Oinical syndromes just like every of those could happen with non-small cell lung most cancers and lymphoma, most frequently within the absence of detectable antibodies. This was emphasized in the survey by Pittock and colleagues at the Mayo Clinic, who found that one-third of sera from sufferers with paraneoplas tic neurologic disorders had multiple antibody. They have suggested that this reflects the numerous immunogenic onconeural proteins that are expressed by tumors. Consequently, the relationships between specific antibodies and a clinical syndromes listed in Table 31-6 ought to be taken as approximate, or nonexclu sive. Nonetheless, certain syndromes seem to occur dis proportionately typically with specific antibodies. Small cell most cancers of the lung, adenocarcinoma of the breast and ovary, and Hodgkin disease are the tumors most often related to these problems, however the paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes happen in only a very small propor tion of patients with these tumors. The mechanisms by which carcinomas produce their remote results are incompletely understood.
Buy discount ginette-35 2 mg line
The P1 portion of the posterior cerebral artery pregnancy test calculator discount ginette-35 2 mg fast delivery, giving rise to the interpeduncular branches (that portion between the bifurcation of the basilar artery and the ostium of the posterior communicating artery) women's health clinic campbelltown ginette-35 2 mg buy discount line, can additionally be referred to as the mesencephalic artery or the basilar communicating artery. As identified by Percheron (whose name is usually applied to the biggest of these vessels), the arterial config uration of the paramedian mesencephalic arteries varies significantly: in some instances, two small vessels come up sym metrically, one from all sides; in others, a single artery arises from one posterior cerebral stem (proximal P1), which then bifurcates. In the latter case, one posterior cerebral stem provides the medial thalamic territories on both sides, and an occlusion of this artery or one widespread paramedian trunk produces a bilateral butterfly-shaped lesion in the medial elements of the diencephalon. The thalamoperforate branches (also known as paramedian thalamic arteries) come up barely more distally from the stem, nearer the junction of the posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries (P2 section of the artery) and supply the inferior, medial, and anterior elements of the thalamus. The thalamogeniculate branches arise nonetheless more distally, opposite the lateral geniculate body, and provide the geniculate physique and the central and posterior parts of the thalamus. Medial branches rising from the posterior cerebral artery because it encircles the midbrain, supply the lateral a part of the cerebral peduncle, lateral tegmentum and corpora quadrigemina, and pineal gland. Posterior choroidal branches run to the posterosuperior thalamus, choroid plexus, posterior elements of the hip pocampus, and psalterium (decussation of deep white matter fornices). Occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery produces a larger number of medical effects than occlusion of any other artery because each the higher brainstem, which is replete with essential buildings, and the inferomedial parts of the temporal and occipital lobes lie within its provide. The website of the occlusion and the arrangement of the circle of Willis will, in giant measure, decide the location and extent of the ensuing infarct. Even distal to the posterior communicating artery, an occlusion may trigger comparatively little injury if the collateral flow Posterior Cerebra l Artery Stroke Syndro m es In roughly 70 p.c of people, each poste rior cerebral arteries are fashioned by the bifurcation of the basilar artery and skinny posterior communicating arteries be part of this method to the interior carotid arteries. In 20 to 25 %, one posterior cerebral artery arises from the basilar in the usual way, but the different arises from the interior carotid, a persistent fetal pattern of circulation; fewer than 5 % have the bizarre configuration by which each come up from the corresponding carotid arter ies. Most strokes on this territory are embolic in origin however some people are predisposed to atherosclerosis in the proximal posterior cerebral artery. There can additionally be the risk of ischemia in this territory from occlu sion of extra proximal vessels, significantly the basilar artery, or infraction in the distal territory of the vessel because of international failure of cerebral perfusion, as in severe hypotension. Inferior facet of the left hemisphere exhibiting the branches and distri bution of the posterior cerebral artery and the principal anatomic structures supplied. Listed beneath are the clinical manifestations produced by infarction in these territo ries and the corresponding regions of damage. Tremor in repose has been omitted due to the uncertainty of i ts occurrence within the posterior cerebral artery syndrome. Peduncular hallucinosis might occur in thalamic-subthalamic ischemic lesions, but the exact location of the lesion is unknown. The terminus of the basilar artery and branches originating from the Pl via P3 segments. In the sequence of posterior cerebral artery strokes studied by Milandre and coworkers, the causes have been, generally, much like these of strokes in other vascular territories except that there was a better incidence of atherosclerotic occlusion (35 patients) in contrast to automobile dioembolic varieties (15 patients). Our experience has differed in that the proportion of presumed embolic occlusions has been far greater than that of other causes. Hemiballismus is often a results of occlusion of a small branch to the sub thalamic nucleus (of Luys) or its connections with the pal lidum. Occlusion of the paramedian thalamic branches to the mediodorsal nucleus is a recognized reason for an amnesic (Korsakoff) syndrome; this simulates however is less common than infarction of the hippocampi from occlu sion of the medial temporal department of the posterior cere bral artery as noted beneath. Distribution of the (1) anterior cerebral artery, (2) pos terior cerebral artery, (3) anterior and posterior choroidal arteries, (4) posterior communicating artery, and (5) internal carotid artery. The hemianopia may be incomplete and contain the higher quadrants of the visual fields more than the lower ones (see Chap. Other features seen in a number of instances are visual hallucinations in the blind parts of the visible fields (Cogan) or metamorphopsia and palinopsia (Brust and Behrens). Occipital infarcts of the dominant hemisphere could trigger alexia with out agraphia, anomia (amnesic aphasia), a wide selection of visual agnosias, and rarely some extent of impaired reminiscence. The anomias, when they occur, are most extreme for colours, however the naming of other visually presented materials such as photos, math ematical symbols, and manipulable objects may also be impaired. The affected person could treat objects as familiar-that is, describe their capabilities and use them correctly-but be unable to name them. Color anomia (a form of "cen tral achromatopsia") and amnesic aphasia are more usually current in this syndrome than is alexia. The defect in retentive reminiscence is of various severity and should or could not enhance with the passage of time. Occlusion of the small vessels supplying these territories from in situ atherothrombosis or embolic occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery is probably the most com mon cause. There is both a deep and cutaneous sensory loss, usually severe in degree, of the opposite side of the physique, together with the trunk and face, sometimes accom panied by a transitory hemiparesis. The char acteristic characteristic is all the time sensory loss that includes the whole hemibody up to the midline. After an interval, sensation begins to return, and the patient may develop pain, paresthesia, and hyperpathia within the affected parts. There may be distortion of style, athetotic posturing of the hand, and alteration of temper. Mania and depres sion have sometimes been noticed with infarction of the diencephalon and adjoining constructions, however the information are often incomplete. A complete proximal arterial occlusion results in a syndrome that mixes cortical and anterior-proximal syndromes partly or totally. As mentioned, the vascular lesion could additionally be both an embolus or an atherosclerotic thrombus. Central midbrain and subthalamic syndromes are a results of occlusion of the interpeduncular branches of the posterior cerebral artery. More frequently, the lesions are incomplete, and a sector of the vision, normally on one side, remains intact. When the visible remnant is small, imaginative and prescient might seemingly fluctu ate from moment to moment because the patient makes an attempt to seize the image within the island of intact vision, in which case hysteria may be incorrectly inferred. In bilateral lesions confined to the occipital poles, there could also be a lack of central vision only (homonymous central scotomas). With more anteriorly positioned lesions of the occipital pole, there could additionally be homonymous paracentral scotomas, or the occipital poles could additionally be spared, leaving the affected person with solely central vision. Horizontal or altitudinal subject defects are usually a results of similar restricted lesions affecting the higher or decrease banks of the calcarine sulci. With bilateral lesions that contain the inferomedial portions of the temporal lobes, together with the hippocampi and their related structures, the impairment of mem ory could additionally be severe, causing the Korsakoff amnesic state. In a quantity of of our sufferers, a solely left-sided infarction of the inferomedial temporal lobe impaired retentive reminiscence. Bilateral mesiotemporal-occipital lesions additionally cause an absence of recognition of faces (prosopagnosia). The relative sizes of the vertebral arteries differ considerably, and in roughly 10 percent of instances, one vessel is so small that the opposite is basically the one artery of supply to the brainstem.