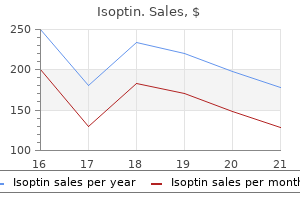
Isoptin
Isoptin dosages: 240 mg, 120 mg, 40 mg
Isoptin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Isoptin 240 mg buy with visa
This uninfused computed tomography scan demonstrates a thin rim of calcification within the wall of easy cysts (C) arteria lumbalis 240 mg isoptin cheap amex. Some renal plenty comprise both skinny heart attack grill menu prices 120 mg isoptin mastercard, peripheral calcifications and focal, central calcifications. Cross-sectional imaging helps to distinguish between benign and malignant calcified renal masses in most patients. These lesions generally grow slowly and result in bubbly lesions that focally broaden the bone. They can mimic different types of bone lesions, together with metastases, 70 GenitourinaryRadiology:TheRequisites primary bone neoplasms, and myeloma. Multiple osteomas, or bone islands, are another interesting kind of skeletal abnormality sometimes seen in affiliation with renal masses. However, if a mass is detected by urography, then some imaging options could additionally be useful to information further evaluation. Large plenty lead to calyceal splaying, stretching, and draping, whereas infiltrating renal lesions often produce little, if any, parenchymal mass impact. However, inside the infiltrated parenchyma, operate is absent or tremendously diminished, and subsequently opacification within the involved area is diminished through the nephrogram section. Because many of these plenty come up or invade the calyces, calyceal filling defects, also recognized as an oncocalyx, could also be evident on the intravenous urogram. As talked about earlier, excretory urography lacks adequate specificity for precisely characterizing any renal masses as benign or malignant. Therefore each renal mass detected with or advised by excretory urography should be imaged with another technique. With this method, 80% of detected renal masses are characterized as simple cysts, thus ending their diagnostic evaluation. This cone-down view of the kidneys demonstrates a large strong mass extending from the upper pole of the best kidney. This mass compresses and displaces calyces, and its margins (arrowheads) lengthen beyond the expected margins of the kidney. This mass is strong and enhances much like the density of the conventional renal parenchyma. A transitional cell carcinoma is present within the higher pole of this proper kidney inflicting stricturing of the upper-pole infundibulum and calyceal amputation. Extensive infiltrating lesions often lead to secondary abnormalities, including hydronephrosis and vascular encasement with diminished move to the realm of involvement. Expansile renal masses 5 mm or bigger are virtually always detectable with these two modalities. When the kidneys are imaged through the portal venous phase of liver enhancement, renal enhancement is often within the corticomedullary part and may be insufficient for detection. In this phase, hypervascular cortical plenty and hypovascular medullary tumors could also be inconspicuous and undetectable. This usually occurs approximately eighty to a hundred and twenty seconds after the initiation of intravenous distinction materials injection. Renal arteriography together with embolization could additionally be helpful in the therapy of some renal plenty. Devascularization of a tumor could additionally be performed before excision or ablation to reduce intraoperative blood loss or to enhance ablation efficacy, or to diminish symptoms from an inoperable renal malignancy. In rare cases, angiography could also be helpful in distinguishing among numerous renal lots. In specific, angiography may be an various choice to open biopsy in the prognosis of infiltrating renal neoplasms. Urothelial neoplasms, inflammatory lesions, and infarcts are almost all the time hypovascular or avascular. The fact that this tumor is usually very vascular distinguishes it from other infiltrating lesions. The classes are solitary expansile masses, multiple expansile lots, and geographic infiltrating lesions. Ball-Shaped Masses Box 3-3 lists lesions that type expansile lots on the kidney. With cross-sectional imaging, these are seen in additional than half of sufferers older than 50 years of age. Simple cysts may be seen on plain films of the abdomen as large, round, water-density plenty extending from the kidney. Renal parenchyma draped around the edges of the cyst is usually referred to as the beak or claw signal. Any variance from these standards suggests Angiography Renal angiography, once a basic element within the analysis of renal masses, is of little value within the analysis of most renal masses. Angiography has traditionally been reserved for mapping vascular supply to the kidney harboring a renal mass when a partial nephrectomy is contemplated. The cyst is water density, has an imperceptible peripheral wall, no enhancing inner elements, and a definite interface with the kidney. Renal parenchyma is draped across the edges of the cyst (arrows), the so-called "beak" or "claw" sign, indicating an intrarenal mass. It is anechoic, spherical, and has enhancement of through-sound transmission (arrows). Although they might often trigger signs due to mass impact, easy cysts are almost all the time an incidental finding of no clinical significance. The Bosniak classification system is helpful for categorizing these lesions in accordance with their etiology and serves as a guide for treatment. This uninfused computed tomog- raphy demonstrates a homogeneously high-density lesion (arrow) in the left kidney. These cysts usually contain hemorrhage or extremely concentrated proteinaceous material. Biopsy of cystic plenty will only yield a diagnostic sample in roughly 50% of cases, and therefore surgery may be wanted for definitive diagnosis of these masses. This papillary renal cell carcinoma demonstrates solid tissue with subtle peripheral enhancement (arrowheads). With development, these lesions tend to outstrip their blood provide, and central areas turn into ischemic and necrotic. This contrast-infused computed tomography demonstrates a predominantly cystic left renal mass (M). These tumors are likely to be slow-growing plenty with fronds of tissue protruding centrally from the margins. Because renal cysts are fairly widespread, cysts and tumors might happen in the same kidney and but be causally unrelated. This pattern of abnormalities is probably going related and occurs as a result of the neoplasm obstructs renal tubules and causes dilatation and cyst formation.
Buy isoptin 40 mg with visa
As it progresses further and the dentine turns into concerned blood pressure medication with a b 240 mg isoptin order with amex, there may be signs of sensitivity or gentle discomfort to cold and hot arrhythmia grand rounds 240 mg isoptin generic with mastercard. Pulpitis the development of dental caries entails the tooth pulp, resulting in irritation of the pulp, and is termed pulpitis. Percussion of the concerned tooth with a dental probe localizes the affected tooth. As the method continues, the an infection may additional spread into the alveolar bone, resulting in a dento-alveolar abscess. A sinus could develop intraorally in the alveolar mucosa or could drain extraorally via the facial pores and skin over the jaws. Dental caries and its sequelae are the most typical explanation for the loss of teeth in younger adults. There is an overgrowth of the interdental papilla, which turns into bulbous and surrounds the whole tooth. Red, oedematous gingiva, bleeding on brushing or on probing, and halitosis are the clinical indicators and signs of gingivitis. Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is an acute condition related to poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, smoking, upper respiratory infection and basic debilitation. It could be a rapidly progressive situation that begins on the suggestions of the interdental papillae, spreads along the gingival margins and destroys the periodontia, which typically results in cancrum oris. In acute leukaemia of childhood, gingivitis may be a presenting sign as a outcome of the abnormal white cell function. The region requires a defence from infection however the only response the cells can mount is to infiltrate the gums in large numbers. Dental Cysts and Gingival Tumours A cyst is a fluid-filled cavity lined with epithelium, and dental cysts are quite common within the oral cavity. They occur both as a outcome of an contaminated tooth or are related to an impacted or lacking tooth. Rarely, cysts can be developmental in origin, growing from epithelial remnants of the dental follicle. In this, a pocket varieties between the teeth and gums by which plaque and food particles accumulate. There is a progressive lack of alveolar bone, and the tooth gradually becomes cell and is ultimately misplaced. Juvenile and Rapidly Progressing Periodontitis Aggressive periodontitis can happen even earlier than puberty or in early grownup life. Malignant Tumours Malignant tumours arising from dental tissue are uncommon, however oral squamous cell carcinoma is type of widespread and arises from the oral mucosa and gingiva. They are the commonest benign odontogenic tumours of epithelial and mesenchymal origin. They can be broadly categorised into two classes: compound odontomes, which resemble a tooth construction, and complex odontomes, which encompass a haphazard conglomerate of enamel, dentine and pulp. Herpes is transmitted by mucosal contact, usually kissing or the sharing of objects such as toothbrushes and utensils. These Ameloblastomas Ameloblastomas (previously known as an adamantinomas) are benign but domestically aggressive tumours arising from the mandible, or much less commonly from the maxilla. They are slow-growing and tend to current in the second to fifth decades of life, with no gender predilection. Vesicles or ulcers develop in the again of the throat and palate, and last for about 10�14 days. Lesions typically occur within the cutaneous distribution of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. There is a prodromal part of itching and tingling adopted after hours or days by the eruption of a cluster of small blisters full of clear fluids and involving only one side of the face alongside the distribution of the branch of the trigeminal nerve. The lesions heal in about 2 weeks, but they may get secondarily contaminated or, in uncommon circumstances, result in a neuralgic kind of pain within the distribution of the concerned nerve. They are characterized by a spherical or oval ulcer involving any a part of the oral mucosa. There are three kinds of apthous ulcer: � Minor apthous ulcers, which are smaller than 10 mm, often last for 7�10 days and heal with out scarring. Oral Candidiasis Oral candidias, also referred to as thrush, is regularly caused by Candida albicans or much less generally by Candida glabrata or Candida tropicalis. Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochaete Treponema pallidum. Oral manifestations could also be seen in all of the three levels of this disease: � In the first stage, a painless sore, open, moist ulcer known as a chancre affects the lip and tongue. Although usually arising idiopathically, pemphigoid may be drug-induced, notably by penicillamine. Lichen Planus Lichen planus is a standard idiopathic lesion that impacts the pores and skin and oral mucosa. The erosive or atrophic forms of lichen planus might present as irregular erosions on the tongue or palate; this is doubtlessly malignant in lower than three per cent of cases. Pemphigus and Pemphigoid Pemphigus is the term given to a bunch of doubtless lethal issues that are all characterised by autoantibodies directed in opposition to intercellular substances or stratified squamous cell epithelium. It is a subepithelial immune illness by which the autoantibodies act in opposition to zones of the Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a possible premalignant situation that appears as a white patch involving the oral mucosa. Approximately 3 per cent of leukoplakia lesions endure malignant transformation over time. The two frequent varieties are homogenous, which has an everyday appearance and a flat or barely raised floor, and nonhomogenous, which has an irregular, raised, thick or erythematous look. Sublingual keratosis is a white patch seen on the floor of the mouth and has a better incidence of malignant transformation. It is generally associated with the utilization of tobacco and has a high potential to endure malignant transformation. The risks related to this syndrome embrace a powerful tendency to develop most cancers in multiple sites. While the hamartomatous polyps themselves have solely a small malignant potential (less than 3 per cent), patients with the syndrome have an increased risk of creating carcinomas of the pancreas, liver, lungs, breast, ovaries, uterus, testes and other organs. There is also a severe burning sensation within the oral cavity, with intolerance to spicy food. This is a premalignant condition with a 5 per cent incidence of malignant transformation to oral squamous cell carcinoma over a 15 yr period. Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes happen in three patterns � varieties 1, 2A and 2B � although the categories sometimes overlap. Leukoedema Leukoedema is a benign abnormality of the buccal mucosa characterized by a filmy, opalescent-to-whitish grey look as a end result of folding of the mucosa. White Spongy Naevus White spongy naevus is an autosomal dominant lesion that seems more generally in childhood or early adult life. Fordyce Spots Multiple, pinhead-sized, whitish to yellowish papules on the buccal mucosa or lips brought on by ectopically located sebaceous glands. Genetic components, smoking, alcohol consumption and continual irritation from the sharp cusp of a tooth are the other aetiological components.
Buy isoptin 40 mg
Lesions of the dentition comprise an essential a half of the lesions of the mouth and a information of these conditions is essential blood pressure korotkoff sounds 40 mg isoptin generic overnight delivery. An examination reveals a quantity of lesions on the lips and buccal mucosae; some are tiny and vesicular heart attack trey songz cheap 40 mg isoptin amex, while some have damaged down to type shallow ulcers. The lesions are in the form of small vesicles that break down to form shallow ulcers. Herpes zoster lesions are normally unilateral, and lie alongside the distribution of a particular branch of the trigeminal nerve; they might be fairly painful. Oral malignancy presents with non-healing ulcers or frank growths that bleed to the contact, are sometimes indurated and may be accompanied by enlarged neck nodes. Leukoplakia appears as a whitish plaque-like lesions within the absence of any obvious trigger, and carries a small however definite malignant potential. Submucous fibrosis, or progressive stiffening of the oral mucosa, with trismus may rework into malignancies. This assertion is untrue as ameloblastomas are normally benign tumours which might be domestically aggressive. All of the following are premalignant lesions of the oral cavity except which one For every of the following descriptions, choose the most likely analysis from the record of lesions and tumours of the oral cavity under: 1 Dental cyst 2 Leukoplakia three Oral squamous cell cancer 4 Pemphigus 5 Ranula 6 Submucous fibrosis 7 Erythroplakia 8 Epulis a A 5-year-old lady presents with a swelling in her oral cavity. On examination, a fluctuant swelling could be seen on the ventral facet of the tongue, extending to the floor of the mouth. The surface of the oral swelling shows distended veins, and clear fluid may be aspirated from the swelling. A ranula is a cystic swelling that arises from the sublingual salivary gland, and its usual position is within the anterior ground of mouth. The finding of a tough neck node within the submandibular region (which is the usual draining area of oral cavity) further substantiates the diagnosis. Atresia of the posterior nares, which can be bony or membranous, may result from persistence of the primitive bucconasal membrane. Unilateral atresia may go unnoticed, however bilateral atresia presents quickly after delivery with intermittent asphyxia or asphyxia during feeding. The child may show cyanosis at relaxation however an improvement on crying (paradoxical cyanosis). An absence of condensation after putting a chilly spatula beneath the nostrils and an inability to cross a soft plastic tube by way of the nose are seen in atresia. Rhinitis Acute and Chronic Rhinitis Acute rhinitis presents with rhinorrhoea, nasal obstruction and constitutional disturbances. Chronic rhinitis might present as relapsing assaults of acute rhinitis (lasting greater than 12 weeks) or secondary to sinusitis. On posterior rhinoscopy, a mulberry-like enlargement of the posterior end of the inferior turbinate is seen. Secondary atrophic rhinitis can observe granulomatous infection, intensive nasal surgical procedure and trauma. Vasomotor Rhinitis Vasomotor rhinitis presents with sneezing, watery rhinorrhoea and nasal obstruction of unknown aetiology. Hereditary components, psychological components, atmospheric situations and dusty environments might trigger paroxysmal symptoms. Syphilis Congenital syphilis causes a purulent rhinitis, vestibule excoriation and other stigmata in infants as much as about three months of age. In the acquired form, it might trigger a chancre as a hard, painless, ulcerated papule with non-tender rubbery nodes at about 3�6 weeks of age. A secondary type could trigger persistent rhinorrhoea, with crusting and fissuring of the vestibule at about 6�9 weeks. The gumma occurs within the tertiary stage after 1�5 years and impacts the periosteum of the septum, leading to perforation of the bony septum and ensuing within the characteristic saddle deformity. Mucocoeles Frontoethmoidal mucocoeles are common due to the complexity of the drainage. They current as headache, orbital displacement and visible disturbances within the late phases. It presents with nodules on the septum, nasal obstruction, crusting, anosmia and a purulent discharge. Leishmaniasis Nasopharyngeal leishmaniasis causes ulceration of the mucosa and should recur years after the unique infection, destroying the facial tissues. A non-invasive fungal ball regularly presents as a unilateral postnasal discharge and allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. More virulent types of tuberculosis affecting the nose may give rise to a tuberculoma (a mucosal, ulcerative type), which erodes the cartilaginous septum and inferior turbinate. Isolated sinus involvement can present with delicate tissue infiltration and bony destruction. It may cause atrophic rhinitis, septal perforation or dorsal saddling in the late levels. Angiofibroma this can be a regionally invasive vascular tumour that arises in the sphenopalatine foramen. Adolescent boys present with repeated epistaxis, nasal obstruction, anosmia, broadening of the nose and facial swelling. On examination, a fleshy pinkish nasal and nasopharyngeal mass bulging over the soft palate could also be seen, with rhinolalia clausa (abnormal speech attributable to a nasal and nasopharyngeal block) and poorly developed secondary sexual characteristics. Malignancy of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses these tumours current mainly in the advanced levels, the maxilla being the commonest web site. Occupational exposure to wooden mud, chemical inhalation, smoking and genetic factors are predisposing factors. The tumour may lengthen: � to the nasolacrimal duct (causing epiphora); � medially to the nasal cavity (leading to a blocked nostril, anosmia and bleeding); � inferiorly to the hard palate (giving rise to free enamel, the need for a change of dentures and lesions over the palate); � posteriorly to the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (causing trismus and trigeminal nerve deficits); � laterally to the cheek (producing fullness); � superiorly to the orbit (resulting in proptosis and diplopia). Ethmoidal tumours lead to anosmia, widening of the space between the eyes, proptosis, nasal blockage and diplopia. Sphenoidal sinus tumours may lengthen into the cavernous sinus and lead to nerve deficits, most commonly lateral rectus palsy (from harm to the abducent nerve). It outcomes from hyperplasia and fibrosis of the sebaceous glands within the skin, and occurs in relation to pimples rosacea. In subluxation of the septum, caudal deviation of the septum is seen on lifting the nose. There is marked despair, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid rotating backwards and the septum collapsing inwards. Severe forms of fracture may cause cerebrospinal fluid leaks with dural tears and pneumocephalus as a result of a fracture of the anterior cranium base and posterior wall of the frontal sinus. Erosion could occur from acid fumes in chromium platers, cocaine abuse and persistent inflammatory circumstances, or after a haematoma. The perforation might manifest as crusting, epistaxis, nasal blockage, whistling noises on nasal respiratory (with smaller defects) and rhinolalia (with larger defects). Epistaxis is caused by trauma, surgical procedure, inflammatory and neoplastic conditions, a low atmospheric strain with dry weather at high altitude, systemic problems with a deranged the Phar ynx 383 coagulation profile, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and anticoagulant overdose. There may be an identifiable cause of nasal obstruction such as a polyp or septal deviation.
Isoptin 40 mg buy discount online
Nerve branches to the seminal vesicles pulse pressure 14 isoptin 40 mg buy visa, prostate blood pressure medication viagra order 40 mg isoptin with mastercard, urethra, and corpora cavernosa travel collectively within the neurovascular bundle, which is roughly 5 to 6 cm in length and is positioned posteriorly and laterally to the posterior or rectal floor of the prostate. After crossing over the distal ureter, it bends anteromedially to cross between the posterior surface of the bladder and the higher pole of the seminal vesicle (S). It descends to the bottom of the prostate, becoming a member of the duct of the seminal vesicle to type the ejaculatory duct (open arrow). Transverse ultrasound image by way of the mid scrotum exhibits a small proper hydrocele that enables for visualization of a testicular appendage (arrow) arising from the best testicle, a functionless remnant of the paramesonephric duct. R C the glandular anatomy of the prostate in the transverse (A) and sagittal (B) planes. The major diagnoses to be considered are testicular torsion, epididymitis, orchitis, and testicular neoplasms. Benign diseases, frequently inflammatory, predominate within the epididymis and scrotum. Other widespread non-neoplastic scrotal masses, similar to hydrocele or hernia, additionally contain the extratesticular space. By distinction, a malignant neoplasm is the most likely analysis every time a focal or diffuse intratesticular mass is detected. Sonography is ideal for the preliminary examination of the patient with an atraumatic scrotal course of as a outcome of high-resolution photographs of the scrotum (obtained with 7. Ultrasonography is accurate for distinguishing a testicular mass from one that originates in the extratesticular area in 95% of patients. Torsion of the Spermatic Cord Torsion refers to an irregular twist of the spermatic cord that causes testicular ischemia. In the neonatal period and in infants, the testicle and spermatic wire are connected loosely to the scrotum, and the entire wire above the level of the scrotum may undergo torsion (extravaginal torsion). Another anatomic situation that predisposes infants and adolescents to torsion is the anomalous suspension of the testicle inside the tunica vaginalis. In this condition fixation of the testicle to the posterior scrotal wall is incomplete. In addition, the mesenteric attachment of the spermatic cord to the testis is abnormally brief, permitting the testis to fall ahead and rotate within the tunica vaginalis (intravaginal torsion). This so-called bell clapper deformity entails both testicles in 70% of sufferers, and simultaneous bilateral torsion might occur in 5% of sufferers. Therefore surgical remedy of unilateral testicular torsion calls for contralateral orchiopexy. Torsion also could occur when the mesorchium, which normally attaches the testis to the epididymis, is abnormally long. This structural anomaly permits the testicle to torque on its own axis, resulting in a less widespread kind of intravaginal torsion. Other buildings throughout the scrotum could endure torsion and present with an analogous clinical image. The commonest of those is torsion of the appendix testis, a remnant of the m�llerian duct system. Once torsion has occurred, testicular salvage depends on expeditious prognosis and prompt surgical detorsion. Spontaneous detorsion and retorsion significantly complicate the clinical and imaging diagnoses. Twists of less than 360 degrees may be current for relatively longer durations before testicular viability and function are irreversibly misplaced. Surgery may be indicated if torsion is diagnosed past the period of testicular viability (late or missed torsion). Orchiopexy of the other testicle may be needed, and a number of other sources suggest that the devitalized testicle must be eliminated as a result of the liberation of proteins from the necrotic testicle can result in the formation of autoantibodies that, theoretically, might compromise the formation or maturation of sperm from the contralateral testicle, impairing future fertility. The most popular methodology of screening for torsion of the spermatic twine is high-resolution ultrasonography with color Doppler imaging (Box 8-3). Comparison studies in kids and adults suggest that the sensitivity is in the 85% to 100% vary, and sonography is often readily accessible and may be carried out quickly. The sonographic appearance of testicular torsion depends on the period of the torsion. Because the epididymis is also supplied by the testicular artery, it might be enlarged and hypoechoic and a reactive hydrocele may be seen. Interrogation of the spermatic wire may reveal twisting of the vessels, finest seen with colour Doppler imaging. Epididymitis and Other Extratesticular Masses A summary of extratesticular lesions is offered in Table 8-1. The sufferers might have acute or subacute pain and they could complain of fever and dysuria. Epididymitis is believed to be attributable to the descending spread of an infection from the urethra or prostate via the vas deferens. The cardinal sonographic sign of epididymitis is epididymal enlargement (Box 8-4). Thickening of the scrotal pores and skin or presence of a reactive hydrocele, or each could also be seen. A advanced fluid collection across the testicle may indicate complication by pyocele, and inhomogeneous echogenicity or a focal hypoechoic area in the testicle could point out the presence of orchitis (which complicates epididymitis in approximately 20% of patients), or testicular ischemia. The regular epididymis demonstrates minimal detectable circulate, even at the lowest attainable move settings. In as many as 20% of sufferers, epididymitis may present as hyperemia on colour Doppler imaging, with an otherwise regular gray-scale look. Hypervascularity could additionally be focal, sparing the epididymal head or tail, in as many as 25% of sufferers. The commonest tumor of the epididymis is the adenomatoid tumor, a benign hamartoma often discovered within the epididymal tail. A, Transverse gray-scale images via the right and left testicles reveal an enlarged left testicle with patchy areas of decreased echogenicity within the testicular substance, as in contrast with the right. B, Color Doppler photographs at the same stage reveal no detectable blood circulate inside the left testicle. At surgery, the left testicle was not salvageable and orchiopexy was carried out on the best testicle. A, Longitudinal gray-scale ultrasound image through the upper left testicle and spermatic wire, obtained for evaluation of left inguinal swelling, reveals a stable, hyperechoic mass (M) throughout the spermatic cord, extending into the upper scrotum. B, Enhanced axial computed tomography picture by way of the upper thighs and scrotum confirms the fatty nature of the mass (arrow), according to a spermatic wire lipoma, the most typical extratesticular scrotal neoplasm. A, Longitudinal gray-scale image through the lateral side of the proper testicle (T) reveals diffuse enlargement of the epididymis.
Purchase isoptin 120 mg on line
The junctional zone (arrow) is thickened (>12 mm) on this sagittal T2weighted picture blood pressure 5545 purchase isoptin 240 mg overnight delivery, a discovering characteristic of adenomyosis pulse pressure factors best isoptin 120 mg. A masslike area in the uterine fundus (short arrow) is much less well defined, less hypointense, and accommodates several hyperintense cystic foci, appropriate with an adenomyoma. Sexually transmitted infections normally begin as cervicitis, which ascends to secondarily contain the endometrial cavity and fallopian tubes. An infectious salpingitis could be the full extent of illness or, via tubal spillage, peritoneal spread of an infection may result in a local peritonitis and oophoritis. Adnexal adhesions could cause fusion of the infected tube and ovary, termed a tubo-ovarian advanced. When fever, leukocytosis, and ache persist despite intravenous antibiotic administration, surgery has been the standard alternative, although tubo-ovarian abscess has been managed successfully with percutaneous catheter drainage. Potential sequelae of tubal irritation, significantly if recurrent or extreme, are infertility and ectopic pregnancy brought on by tubal strictures or dysmotility. Hydrosalpinx is dilatation of the ampullary phase of the tube that accompanies distal obstruction; pyosalpinx refers to purulent infection of a dilated tube. Debris or low-level inner echoes could also be seen inside the dilated fallopian tube. In some patients it might be tough to differentiate a dilated fallopian tube from bowel loops or distended pelvic veins. The absence of peristalsis or move in hydrosalpinx and pyosalpinx may be documented on Doppler sonography. Complex adnexal plenty on transabdominal sonograms may characterize hydrosalpinx/pyosalpinx, tubo-ovarian complicated, or tubo-ovarian abscess. A, Transverse transabdominal ultrasound image shows a tubular construction with a thickened wall in the best adnexa adjoining to the urinary bladder, according to a dilated and infected fallopian tube. B, On transvaginal ultrasound, a dilated fallopian tube with thickened endosalpingeal folds (arrows), thick wall, and inside debris is seen adjoining to the best ovary (asterisk). This motion occurs as a end result of adhesions tether the ovary and tubes to surrounding viscera. Contrast materials from the left tube is starting to pool next to the left fallopian tube (arrow). B, A late film after evacuation of distinction materials from the uterine cavity reveals two persistent focal collections of contrast material attributable to pelvic adhesions. A and B, Peritoneal thickening (arrowhead), slightly elevated density of the pelvic fat (inflammatory fats stranding) (arrow), and a small quantity of free pelvic fluid are seen in a patient with cervical movement tenderness, gentle peritonitis, and constructive cervical swab for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A complicated cystic mass is demonstrated in the proper adnexa, according to a tuboovarian abscess in this patient who offered with signs and physical examination findings of pelvic inflammatory illness. Patients with tubo-ovarian abscess usually are ill and should current with pelvic ache, marked adnexal tenderness, high fever, nausea, and emesis. Clinically and radiographically, tubo-ovarian abscess could be tough to distinguish from ovarian torsion, diverticular or other pelvic abscesses, and appendicitis. Patients normally are handled with intravenous hydration, analgesics, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. The ovary frequently is enlarged, and regular ovarian morphology is unrecognizable in most sufferers. In sufferers with severe cases, there may be irregular septations and fluid/debris ranges that distort the adnexa utterly. The inflammatory nature of these masses is suggested by the loss of distinct fat planes between the mass and pelvic viscera and by thickening of the uterosacral ligaments. In a patient with clinically recognized pelvic inflammatory disease not responsive to medical therapy, a complex fluid assortment with an air-fluid level (arrow) is identified in the left adnexa, consistent with a tubo-ovarian abscess. This outcomes from unfold of infection alongside the right paracolic gutter or by way of the lymphatic system. Large ovarian cysts and cystic neoplasms, similar to mature cystic teratomas (dermoids) and cystadenomas, predispose to torsion. Torsion of a traditional ovary is uncommon and potential etiologies embody an excessively lengthy or tortuous mesosalpinx or mesosalpingeal vessels, and tubal spasm. A A advanced cystic mass in the pelvis with adjacent inflammatory fat stranding was diagnosed as a tubo-ovarian abscess at surgery. A cystic ovarian neoplasm, endometrioma, or abscess of nongynecologic origin may have an identical imaging appearance. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography image in a affected person with proper upper quadrant ache reveals enhancement of the liver capsule (arrows) secondary to peritoneal spread of infection from pelvic inflammatory disease. Venous thrombosis and hemorrhage ensue, ultimately compromising arterial perfusion and leading to complete infarction. The ovary could also be so enlarged that it assumes a midline place, usually superior to the uterine fundus. B, On color Doppler ultrasound, an enlarged proper ovary with no inner blood circulate is seen. In addition, a torsed and edematous pedicle and engorged straight vessels may be draped around the ovary. An enlarged left ovary was recognized in a affected person with the acute onset of left-sided pelvic ache, and no inner vascular flow could probably be demonstrated with spectral Doppler imaging. The attenuation of the torsed ovary could also be heterogeneous, as a end result of variable perfusion. Decreased or absence of venous circulate in the ovary is the most common discovering at Doppler imaging. Preservation of arterial flow may be seen secondary to the dual blood provide to the ovary, or because of sufferers presenting for analysis before the development of arterial occlusion. Uterine Leiomyoma Uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are benign smoothmuscle tumors that are detected in 20% to 30% of ladies (Box 7-7). An elevated prevalence and fee of growth have been reported in African-American girls. Gynecologic signs which are attributed to fibroids include menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, pelvic pain, dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea, infertility, and symptoms associated to strain on adjoining pelvic organs. About 5% of leiomyomas are associated with irritative urinary tract symptoms, acute or continual urinary retention, or ureteral compression; nonetheless, a majority of fibroids are asymptomatic. Rarely, a pedunculated subserosal fibroid could detach from the uterus and develop as a separate mass in the broad ligament (intraligamentous or broad-ligament fibroid). The pure history of unmanaged leiomyomas is such that regression, or a minimum of stabilization, occurs after menopause; nevertheless, hyaline, myxoid, cystic, purple (hemorrhagic), or fatty degeneration of leiomyomas could happen. Rarely, leiomyosarcoma might come up from a pre-existing leiomyoma; nevertheless, most leiomyosarcomas are thought to arise de novo from the smooth-muscle cells of the myometrium. Large leiomyomas can intervene with the growth of the fetus and, when located within the decrease uterine phase, might trigger dystocia. Complications associated to uterine leiomyomas are one of the frequent indications for main surgery in girls.
40 mg isoptin visa
Progressive immunodeficiency develops and uncommon (opportunist) infections and neoplastic processes happen blood pressure testing 40 mg isoptin cheap with amex. Without remedy heart attack pain in left arm isoptin 240 mg generic, the length of medical latency varies broadly among people and will final for 2�8 years. Dysfunction of the humoral (antibody) response has many manifestations including: � a global increase in antibodies (hypergammaglobulinaemia); � a failure of the operate and formation of antibodies. Patients might repeatedly present to the healthcare providers over a protracted time frame with apparently unlinked bodily complaints. Multiple specimens for microbiology, virology, cytology and histopathology are of paramount significance. There could additionally be extreme mucosal involvement of the entire gastrointestinal tract in addition to of the conjunctiva. Access to remedy and the availability of newer medications stay restricted in some nations. Classically seen on the lower limbs, residual pigmentation develops as therapeutic occurs. Extensive inflammatory reactions, usually to present pathogens (viable or non-viable), are the most common trigger. As this affected person population ages, the need for surgical interventions, such as coronary revascularization, is likely to rise. The following descriptions include the physical manifestations that a surgical apply is most likely to encounter. By definition, the syndrome requires that the lymph nodes be current at two or more extrainguinal sites for a minimum of 3�6 months with no other prognosis or explanation for his or her presence. The most regularly involved node teams are the posterior and anterior cervical, occipital, axillary and submandibular. The key ideas are as follows: � a single pathology can present in several techniques. For instance, the symptoms of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and odynophagia (painful swallowing) could occur with fungal, viral or neoplastic lesions, and all these have to be excluded. However, open biopsy is indicated in a affected person with systemic symptoms if the cytology of an aspirate is unfavorable. It happens at a prevalence just like or greater than that seen within the general inhabitants, but its onset is often sudden. Involvement of the palms, soles and skin folds, together with the groin, is especially widespread in superior immunodeficiency. Herpes virus infections occur with increasing frequency as the immune system deteriorates. Prison tattoos and tattoos undertaken where needle-sharing or reuse is possible enhance the risk of blood-borne acquisition of the virus. These lesions are painful and, as shown here, commonly secondarily contaminated with micro organism. The typical blisters are often absent, leaving a broadly sloughed ulcerated appearance. They happen as solitary or multiple plaques or nodules, and range from a number of millimetres to several centimeters in diameter. The raised lesions are surrounded by much less obvious subcutaneous lesions that trigger lymphoedema by lymphatic obstruction. The characteristic small, pearly, firm, umbilicated papules are discovered on epithelial surfaces. Ominous lesions corresponding to lymphomas may present in diverse types, such as ulcers, lots and plaques. Biopsies for diagnostic purposes are regularly indicated to exclude a sinister lesion. Biopsy may be required to exclude lymphoma or infections such as fungal or mycobacterial lesions or syphilitic gummata. In adults with no immunodeficiency, such massive in depth lesions on this distribution would be extremely unusual. Trauma from consuming with subsequent secondary an infection might lead to extreme ache and weight loss. The typical erythematous base from which the white plaques have sloughed off is often painful. Unilateral tonsillar swelling raises concerns of a neoplastic cause and biopsy is usually indicated. Difficulties with swallowing and speech may occur, and important weight reduction is a severe complication. The typical presentation is multiple, small painful ulcers with surrounding erythema. This analysis was made following a biopsy, undertaken after a failure of antiherpetic treatment. Aneurysms are reported especially in sub-Saharan Africa and can be atypically located and multiple. Often a quantity of coexisting organisms are isolated, together with bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Specimens ought to be despatched for virological, bacterial, mycobacterial, fungal and histopathological research. Raised lesions could trigger obstruction with wheezing, cough and recurrent bacterial infections. It is frequent for several pathogens to coexist, and failure to respond to first-line remedy necessitates additional investigations for different pathogens and pathologies. Both show an in depth mid- and decrease zone perihilar interstitial course of typical of P. Oesophagoscopy is the process of alternative as a definitive diagnosis (or diagnoses) may be obtained by biopsies and brushings. As 10 per cent of patients have a number of pathologies, specimens have to be despatched for mycobacterial, viral, fungal and histological testing. Ulceration due to Epstein�Barr virus is comparatively uncommon and predominantly happens within the mid-oesophageal region. Nausea and epigastric ache commonly accompany the dysphagia but might occur independently. Abdominal Pain Pain generally presents as: (1) epigastric ache with or without oesophageal symptoms, (2) right higher quadrant ache with or with out jaundice, (3) left or proper iliac fossa ache, or (4) diffuse stomach ache. As inflammation and ulceration of the colon progresses, acute ischaemic colitis could occur. This can lead to extreme ache, huge haemorrhage, poisonous megacolon and perforation. Diarrhoea Chronic diarrhoea (lasting for greater than 1 month) is extremely common and impacts a minimal of forty per cent of patients with advanced immunodeficiency.
Isoptin 40 mg trusted
The facial features include a generalized expansion of the cranium on the fontanelles blood pressure pregnancy cheap isoptin 120 mg with amex, outstanding brow protrusion blood pressure for heart attack isoptin 240 mg generic with mastercard, pronounced decrease jaw protrusion and macroglossia. In infancy and childhood, there could also be widely spaced eyes with puffy eyelids, a broad depressed nasal bridge, thick lips and macroglossia. They often start at puberty and will continue to improve in quantity and dimension throughout adulthood. Sinusitis of the frontal and ethmoidal sinuses normally occurs secondary to maxillary sinusitis. Frontal sinusitis may cause ache or fullness within the forehead or above the eyes, whereas ethmoid sinusitis may cause ache or pressure ache between or behind the eyes, as well as headaches. Rarely, an infective pathology in the sphenoid sinus may cause lateral rectus palsy due to an associated osteitis affecting the abducens nerve. Chronic sinusitis is an inflammation of the nasal airway and sinuses that lasts for greater than 12 weeks. It could also be a sequela of acute sinusitis or secondary to other circumstances that predispose to chronic inflammation of the sinuses corresponding to allergic rhinitis, cystic fibrosis, ciliary dyskinesia or an immunocompromised state. Anatomical variations that hinder the conventional drainage of a sinus may lead to persistent sinusitis. Diagnosis is scientific and is confirmed by the next symptoms: � � � � Mucopurulent drainage; Nasal obstruction; Pain, stress or fullness within the face; A decreased sense of smell. The problems of sinusitis are diversified and should happen because of osteitis or a spread of infection along the veins or lymphatics. The proximity of the sinuses to the orbit may give rise to orbital issues, which have been described as passing by way of 5 levels: preseptal cellulitis, orbital cellulitis, subperiosteal abscess, orbital abscess and cavernous sinus thrombosis. The signs and signs worsen progressively by way of lid oedema, chemosis (conjunctival oedema), a restriction of movement of the extraocular muscular tissues and, finally, ophthalmoplegia. It is often precipitated by a preceding higher respiratory tract an infection, usually of viral origin. Among infections of bacterial origin, the commonest causative agents are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis. Sinusitis mostly affects the maxillary sinus and is characterised by ache in the cheek or upper teeth which could be referred to other areas of the face. The pain usually worsens Chronic infections are often seen in the paranasal sinuses, face and jaws, and are extra common within the tropics. Tuberculosis of the sinuses often occurs secondary to infection at a primary location elsewhere. Tuberculosis may involve the pores and skin of the face and is identified as lupus vulgaris. This is characterized by painful cutaneous lesions with a nodular appearance which are most often seen on the face around the nose, eyelids, lips, cheeks and ears. Actinomycosis is a chronic an infection mostly affecting the face and the jaws (lumpy jaw). Deep Infections Deep infections of the face and neck are in almost all instances secondary to dental infection or tonsillitis. It is characterised by a pus assortment between the buccinator muscle and the subcutaneous tissue. There is brawny oedema on the cheek, tenseness of the pores and skin, ache and infrequently trismus. Patients have an elevated floor of the mouth, fever, trismus, odynophagia and, in severe circumstances, respiratory misery and even stridor. They may be related to defects of fusion of the embryonic components forming the facial skeleton and maxilla, or they could happen secondary to an unerupted tooth or dental circumstances. Dermoid cysts are developmental cysts that usually come up on the strains of embryological fusion. The most typical location is in the midline of the root of the nose, and the cysts might even lengthen intranasally. Benign Tumours A massive number of benign jaw tumours could additionally be encountered in the bones of the jaws. These may be broadly classified into odontogenic (arising in relation to the dental structures) and non-odontogenic tumours. It is often painless and remains asymptomatic till it enlarges, producing a gradual jaw expansion that causes facial asymmetry. Malignant Tumours Squamous carcinomas are the most common malignant tumours of the upper aero-digestive tract. They could occur in any a half of the higher airway lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Although the most typical sites are the oral cavity and oropharynx, they could additionally seem within the jaws and face. Here they might occur in the paranasal sinuses and nasal passages, or in the higher or decrease jaw. Unilateral nasal obstruction, unilateral epistaxis and nasal discharge are suspicious of malignancy. Invasion of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve might lead to facial pain or facial paraesthesias. Malignant melanomas arise as polypoidal plenty on the septum or lateral partitions of the nose. Basal cell carcinomas (rodent ulcers) are often seen on the face above a line becoming a member of the angle of the mouth to the ear lobe. The lesion often begins as a raised papule, which may ulcerate with pearly white beaded edges because it progresses. This classification is based on the course of the fracture line that defines the level above which the midfacial skeleton is undamaged: � Line I runs transversely, simply above the ground of the nose and thru the lower third of the nasal septum. It passes via the infraorbital foramen and runs beneath the zygomaticomaxillary suture to lengthen backwards through the lateral pterygoid plates. The fracture line runs through the nasal bone and continues posteriorly via the ethmoid bone, crosses the lesser wing of the sphenoid and then runs laterally upwards to the frontozygomatic suture. Infraorbital nerve harm gives rise to anaesthesia within the space between the inferior orbital margin and the higher lip, the facet of the nostril being spared. Inferior alveolar nerve damage leads to anaesthesia of the mental area, while supraorbital nerve damage leads to anaesthesia above the attention. Examination for instability of the maxilla may be possible within the unconscious or anaesthetized affected person. Zygomatic Fractures Fractures of the zygoma may be part of Le Fort fractures or happen as isolated accidents. The damage might involve the temporomandibular joint, the infraorbital canal and the frontozygomatic suture with resultant painful mastication, numbness of the cheek and diplopia. Temporomandibular joint dislocation may be distinguished from a condylar fracture in that it produces a prominence anterior to the articular eminence and a hollow within the glenoid fossa.

Purchase isoptin 240 mg with mastercard
Cancer of the cervix or uterus entails the posterior wall of the bladder within the midline prehypertension food 120 mg isoptin generic with amex, whereas invasion from a malignancy of the sigmoid colon or rectum tends to involve the left lateral bladder wall blood pressure potassium isoptin 40 mg discount with amex. Metastatic disease to the bladder from a distant major most cancers is uncommon; however, it could occur with cancers of the stomach, breast, or lung. Exposure to industrial carcinogens, cigarette smoking, and abuse of analgesics are associated with an increased danger of urothelial cancer of the urinary tract. Pelvic irradiation for gynecologic malignancies also may be related to a higher risk of bladder cancer. An association exists between schistosomiasis of the urinary tract and squamous cell cancer of the bladder; roughly 50% of the malignant tumors related to schistosomiasis are of this cell kind. Chronic irritation and infection of the bladder related to neurogenic bladder, longterm catheter drainage, bladder calculi, or recurrent cystitis also lead to an elevated incidence of squamous metaplasia and most cancers. Urothelial atypia or dysplasia is taken into account to be a premalignant condition, and some kinds of metaplastic and proliferative cystitis (cystitis glandularis) are thought-about precursors of cancer. Tumor stage, as ascertained before management, is crucial prognostic think about patients with bladder cancer. The depth of invasion by way of the bladder wall is an excellent predictor of recurrence, metastatic disease, and survival. However, recurrences often may be controlled with transurethral bladder resection, and muscle-invasive tumors (stage T2 or higher) develop in only 10% to 15% of patients. When the tumor has infiltrated the bladder muscularis at preliminary presentation, lymphatic and distant spread often follows. The 5-year survival rates mirror the significance of depth of invasion: for non-muscle-invasive tumors, 30% to 80% of patients survive 5 years, whereas for deep muscleinvasive tumors, the 5-year survival price is 10% to 20%. Distant metastases to the lungs and mediastinum, liver, and bone are as common as native recurrence in remedy failures amongst patients with muscle-invasive tumors. Like prognosis, management of urinary bladder carcinoma is determined by depth of neoplastic invasion of the bladder wall and by extent of native and distant metastases. Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancers (stage Tis, Ta, or T1) are managed with native fulguration. Muscleinvasive tumors (T2) and tumors invading perivesical fats (T3) are managed with complete cystectomy, and if local or distant metastases are in depth, palliative radiation or chemotherapy is offered. Plain belly radiography is of little worth within the detection of bladder cancer however it may reveal focal calcification associated with a papillary bladder tumor in zero. Its ability to demonstrate small bladder tumors is limited, but it might be useful to detect synchronous upper tract urothelial neoplasms. In one study, solely 60% of recognized bladder tumors were detected with commonplace urography. Given the restrictions of the obtainable imaging modalities for the detection of bladder tumors, cystoscopy stays the gold commonplace for evaluation of the urinary bladder. Cystoscopy has been proven to have 95% sensitivity and 93% specificity for the detection of bladder cancer. Cystoscopy additionally has the advantage of permitting concurrent biopsy and resection of bladder tumors. At surgery, a noninvasive (superficial) papillary urothelial carcinoma was removed. The bladder trigone and posterolateral bladder walls are essentially the most frequent sites of origin of urothelial cancers; solely 2% of bladder carcinomas originate in bladder diverticula. Patients with synchronous or metachronous upper tract disease have a better prevalence of multifocal and recurrent bladder most cancers. Sonography is occasionally used to consider lesions of the bladder wall and lumen. Meticulous technique and adequate bladder distention are important for optimal transabdominal sonography. The location and size of the tumor have the greatest influence on detection with sonography. Tumors higher than 3 cm in diameter or these with related calcification extra usually are overstaged. Although microscopic invasion of the perivesical fats (stage T3a) is inconceivable to detect on imaging, in lots of establishments microscopic perivesical fat invasion with no different pelvic viscera involvement is managed with radical cystectomy and lymph node dissection, as if it had been stage T2b disease. On imaging, elevated attenuation of the perivesical fats (perivesical fats stranding) adjoining to a tumor could also be reactive or inflammatory in etiology somewhat than representing extravesical extension of tumor. Size thresholds above which tumor involvement is recommended are a most length of 13 mm and a maximum short-axis diameter of 10 mm. Percutaneous fine-needle biopsy of enlarged or borderline nodes could also be necessary for extra correct nodal staging. On T2-weighted pictures, the muscularis propria is seen as a hypointense band of tissue within the bladder wall. Although it may be troublesome to assess the depth of muscle invasion precisely (superficial vs. One research reported the staging accuracy for differentiating noninvasive from muscle-invasive disease, and organ-confined from non-organ-confined disease to be 85% and 82%, respectively. A, the anteroposterior movie from a urogram exhibits a big, lobulated filling defect in the bladder (arrow). There was no opacification of both the best kidney or ureter during this examination. B, Transverse sonogram of the proper kidney demonstrates echogenic lots in the markedly dilated renal pelvis (solid arrow) and in a quantity of dilated calyces (open arrows). C, Antegrade pyelography shows multiple irregular filling defects in the dilated renal accumulating system. B, On a coronal reformatted picture, a filling defect (arrow) is current in the proximal proper ureter. High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma was identified at transurethral resection. In an adult with painless hematuria, an ill-defined filling defect and delicate dilatation of the best ureter were noted on intravenous urography (not shown). Although correct evaluation of the depth of muscle invasion (invasion of the inside half vs. A, A pedunculated mass originates from the focally thickened inferolateral wall of the bladder. There is increased attenuation of the perivesical fats (arrow) adjacent to this mass. At whole cystectomy, tumor invasion of the perivesical fats was seen (stage T3 disease). B, There is a broad-based, sessile mass originating from the inferolateral wall of the bladder. Increased density is seen within the perivesical fat (open arrow) lateral and posterior to the bladder mass.