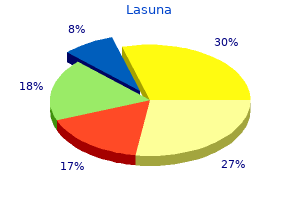
Lasuna
Lasuna dosages: 60 caps
Lasuna packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles

Buy lasuna 60 caps without a prescription
In cadaveric donation cholesterol and stress trusted 60 caps lasuna, the pancreas is harvested with the hooked up duodenum and vasculature cholesterol levels canada 60 caps lasuna amex. The air-filled donor duodenum (arrow) is anastomosed to the small bowel in the best lower quadrant. There is a simultaneous kidney transplant with hydronephrosis within the left lower quadrant. It may be anastomosed to the recipient external iliac vein, inferior vena cava, or superior mesenteric vein. The hooked up donor duodenum, which collects the (A) exocrine secretions of the pancreas, could also be anastomosed to the recipient small bowel or bladder. For those allografts that have a duodenum-to-bladder anastomosis, the top of the pancreas is oriented caudally toward the bladder. The Y-graft is shown (arrow); also seen are the distal elements of the donor superior mesenteric artery (white arrowhead) and splenic artery (black arrowhead). Normal early postoperative Doppler evaluation of the allograft arteries shows a low-resistance waveform. The transplanted pancreas has the same morphology and echotexture as a native pancreas in situ. In the instant postoperative period, trace peripancreatic fluid may be current and should resorb over time. The Y-graft and the donor pancreatic arteries have a low-resistance Doppler waveform. Hyperacute rejection occurs instantly after transplantation from cytotoxic antibodies that were already present within the recipient. Hyperacute rejection results in vascular thrombosis, which may be mistaken for main thrombosis. The gray-scale ultrasound findings of acute rejection embody graft enlargement and parenchymal heterogeneity. The use of resistive indices to help within the analysis of rejection in pancreatic allografts is controversial. When there (A) is clinical concern for acute rejection, an important function of ultrasound is not to diagnose rejection however to assess vessel patency and information biopsy. On imaging, the pancreas becomes atrophic and fibrotic because of the chronic inflammation of small vessels and acinar atrophy attribute of persistent rejection. Consequently the parenchyma of the allograft is echogenic and thinned on ultrasound. Vascular Complications Vascular thrombosis is the second most typical reason for graft failure, often occurring throughout the first 6 weeks. Venous thrombosis is extra frequent than arterial thrombosis and is reported to happen in 0. Other vascular issues embody anastomotic stenosis and, rarely, pseudoaneurysm and arteriovenous fistula. Anastomotic stenoses can be detected on Doppler ultrasound by the finding of turbulence on the stenosis and a focal elevation of velocity. Other Complications Pancreatitis in the allograft is reported to happen in up to 10% patients. Fluid collections related to the allograft may also be because of postoperative hemorrhage (hematoma and seroma), lymphoceles, urinomas, and bowel leaks. Anastomotic leaks may happen at every of these areas in addition to leakage from the duodenal stumps. Other bowel issues include cytomegalovirus colitis or enterocolitis because of immunosuppression and pseudomembranous colitis because of antibiotic use in the operative interval. Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder is a rare complication of pancreatic transplants. The presence of lymphadenopathy or of liver or bowel plenty ought to raise suspicion. Differential Diagnosis Ultrasound findings in rejection are sometimes nonspecific: They embrace graft enlargement, parenchymal heterogeneity, and mild elevation of the resistive index. Spectrum of imaging findings after pancreas transplantation with enteric exocrine drainage: part 2, posttransplantation issues. Role of color Doppler sonography in post-transplant surveillance of vascular complications involving pancreatic allografts. Sonographic evaluation of acute pancreatic transplant rejection: morphology-Doppler analysis versus guided percutaneous biopsy. It has a selection of capabilities that embrace phagocytosis, fetal hematopoiesis, adult lymphopoiesis, immune response, and erythrocyte storage. Normal Splenic Anatomy the spleen is supported by the peritoneal ligaments (splenorenal, phrenicocolic, and gastrosplenic ligaments) of the left higher quadrant. This area is often 2 cm lengthy and is located alongside the posterior aspect of the spleen, where it lies in proximity to the anterior higher left kidney. Recognizing the situation of the naked space may be useful in attempting to differentiate intraperitoneal fluid from pleural fluid. Along its medial aspect the splenorenal ligament encases the tail of the pancreas and splenic artery and vein. These structures insert into the splenic hilus by the attachments of the ligament. The gastrosplenic ligament extends from the greater curvature of the abdomen, attaching the spleen to the stomach. The gastrosplenic ligament is in continuity with the gastrocolic ligament and incorporates the short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels. The phrenicocolic ligament extends from the splenic flexure of the colon to the left hemidiaphragm and provides a supportive attachment between the spleen and left hemidiaphragm. The regular grownup spleen weighs approximately a hundred and fifty g (varying from eighty to 300 g) and measures roughly 11 by 7 by four cm. Spleen dimension and weight decrease in aged adults, typically after the seventh decade of life. Most practices use a longitudinal measurement of 12 cm as the higher limit of normal for spleen size. Branching networks of trabeculae extend from the internal capsular floor into the spleen, dividing it into communicating compartments. The red pulp consists of slender, nonanastomosing arterial vessels; thin-walled venous vessels referred to as splenic sinuses; plates of cells referred to as splenic cords that lie between sinusoids; and purple pulp veins that drain the sinusoids. The group of the lymphoid cells throughout the white pulp is similar to that found within the cortex of a lymph node. T cells are normally found within the periarteriolar sheath and B cells are found in major and secondary follicles. The complete spleen is usually not usually visualized on an belly radiograph due to gasoline in the adjoining splenic flexure of the colon or within the abdomen.
60 caps lasuna buy amex
Pseudocysts might have a extra complicated appearance on imaging cholesterol levels ratio canada lasuna 60 caps buy visa, with septations cholesterol medication with grapefruit 60 caps lasuna discount amex, particles and wall calcification. Nonparasitic splenic cysts: a report of 52 cases with radiologicpathologic correlation. Splenic Hemangioma Definition Hemangiomas are the most typical benign primary neoplasms of the spleen. Demographic and Clinical Features Splenic hemangiomas are mostly discovered in middle-aged adults. Most hemangiomas are small lesions discovered incidentally and the overwhelming majority of sufferers are asymptomatic. Splenic hemangiomas can also occur as part of generalized angiomatosis in Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome. Symptoms or issues are uncommon and are typically seen in sufferers with massive lesions. On medical examination, such patients could have a nontender palpable mass within the left upper quadrant, which may symbolize the hemangioma or splenomegaly because of the hemangioma. Kasabach-Merritt syndrome (anemia, thrombocytopenia, and coagulopathy) has also been reported in sufferers with giant hemangiomas. Pathology Hemangiomas could additionally be single or multiple and could also be cystic or strong on gross pathology. Smaller hemangiomas are most likely to be solid whereas larger cavernous lesions can develop thrombosis, infarction, fibrosis, and pseudocystic degeneration. Calcium deposition could additionally be current in agency fibrotic areas of the lesion or within the surrounding intratumoral cystic areas. Histologically splenic hemangiomas are nonencapsulated proliferations of vascular channels of variable measurement, ranging from capillary to cavernous, lined with a single layer of endothelium filled with red blood cells. There could additionally be a number of small punctate calcifications or peripheral curvilinear calcification. The lesion sometimes exhibits no inner blood circulate on shade or energy Doppler ultrasound. The rim-enhancing lesions might turn into more homogeneously enhancing in the late portal venous or delayed phases of distinction enhancement. Discrete mottled areas of heterogeneous enhancement rather than centripetal enhancement have been described. Coarse calcification might happen in areas of degeneration or long-standing thrombosis. Dynamic intravenous gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted photographs show a number of patterns of enhancement: (1) homogeneous arterial section enhancement with persistent enhancement within the remaining phases of distinction enhancement; (2) peripheral enhancement within the arterial part with gradual centripetal enhancement that becomes homogeneous in the delayed section; (3) peripheral enhancement with centripetal progression and central persistent low sign intensity in areas of fibrosis. Large hemangiomas could have extra heterogeneous and complex patterns of signal intensity and enhancement owing to intralesional hemorrhage, infarction, thrombosis, and/ or fibrosis. In comparison with hepatic hemangiomas, splenic hemangiomas are rather more variable in their enhancement patterns. Differential Diagnosis Hamartoma: May be difficult to precisely differentiate from hemangioma on imaging. Lymphoma: Rarely an incidental finding since patients with lymphoma are often symptomatic. Nomenclature and Classification the excellence between capillary and cavernous hemangioma is made pathologically by the relative dimension of the vascular channels inside the lesion. Demographic and Clinical Features Splenic hamartomas occur equally in women and men of any age. Most sufferers are asymptomatic and the invention of a splenic hamartoma is an incidental discovering. Rarely thrombocytopenia and anemia may occur from sequestration of hematopoietic cells inside the hamartoma. Splenic hamartomas have been reported to happen in patients with hamartomas elsewhere within the body and in affiliation with tuberous sclerosis and a Wiskott-Aldrichlike syndrome. Pathology Grossly splenic hamartoma is well-circumscribed, solid mass that compresses the adjacent splenic parenchyma. Microscopically hamartomas contain a mixture of unorganized vascular channels lined by endothelial cells and surrounded by fibrotic cords of predominant splenic purple pulp with or with out white pulp. They may comprise coarse, shadowing calcification, which is believed to be from prior ischemia or hemorrhage. The vascularity is assumed to replicate the hypervascularity of the pink pulp contained inside the hamartoma. Areas of cystic change or degeneration could cause a hamartoma to appear extra heterogeneous on all pulse-weighted sequences. The T2-weighted picture (B) exhibits predominantly excessive however blended signal intensity, and the T1-weighted intravenous gadoliniumenhanced image (C) shows nodular peripheral enhancement (arrow in C). The significance of recognizing and identifying splenic hamartomas is to differentiate them from malignant lesions of the spleen, corresponding to lymphoma and metastasis. Differential Diagnosis Hemangioma: May be tough to precisely differentiate from hamartoma on imaging. Lymphoma: Rarely an incidental finding, since sufferers with lymphoma are usually symptomatic. Metastasis: Should be thought-about in the differential analysis of splenic mass in a patient with evidence of a main malignancy. Solid Masses in the Spleen 611 Nomenclature and Classification Splenic hamartomas may also be referred to as splenoma, splenadenoma, or nodular hyperplasia of the spleen. Management/Clinical Issues the prognosis of splenic hamartoma may be advised when the standard imaging options are current. If the discovering is incidental, the diagnosis of hamartoma could be presumed within the majority of sufferers. It is usually hyperechoic relative to the normal spleen on ultrasound and hypervascular on shade Doppler. This large group of diseases occurs over a wide age range and features a spectrum of neoplasms of various biologic behaviors. Clinical signs and signs of lymphoma include the classic abdominal ache or palpable mass, palpable splenomegaly, weight reduction, fever, fatigue, and night sweats. Enlarged lymph nodes within the neck, axillae, or inguinal areas may be clinically palpable. Patients with mediastinal lymph nodes or pulmonary involvement could expertise cough, dyspnea, and/or chest ache. Those with splenic involvement could have symptoms of higher stomach or left-upper-quadrant fullness, tenderness, a palpable spleen, or a left-upper-quadrant mass on bodily examination. Pathology Lymphomas in the spleen, whether or not major or part of diffuse illness, have the same histopathologic and immunologic features as nodal lymphomas. In some cases there could also be no identifiable mass on gross inspection, with disease evident only on histologic examination. Discrete plenty might manifest as miliary nodules involving the complete parenchyma, multiple randomly distributed nodules of varying dimension, a large solitary mass, or a quantity of giant plenty.
Order 60 caps lasuna fast delivery
These can have an result on any a half of the digestive system: the oral cavity might type incompletely cholesterol ratio range buy 60 caps lasuna with amex, causing cleft lip and/or palate; the trachea and oesophagus may not separate completely cholesterol medication linked to dementia lasuna 60 caps purchase otc, inflicting a tracheo-oesophageal fistula; the abdominal wall could not totally enclose the digestive system, causing a gastroschisis or exomphalos; the outside opening of the anus may not kind, inflicting imperforate anus. A discussion of every of these, and different much less common malformations, may be found in neonatal textbooks. Initially, a purely liquid food plan is beneficial; either breast milk or toddler formulation. As the toddler develops tongue movements and swallowing coordination, semi-solid meals are launched (weaning). Culture, socioeconomic standing, religious practices and personal preference of the dad and mom all affect weaning practices. This results in completely different families choosing whether or not to introduce gentle meals, onerous meals, whether the father or mother leads by introducing Box 12. Increased focus of fats to present vitality; in particular, long-chain polyunsaturated fat for mind improvement. The toddler has much less amylase to digest this, however breastmilk is high in mammary amylase to help this digestion. Human milk is a much less effective buffer; which means acids move into the lumen and acidify the lumen. Breastmilk contains enzymes, immunoglobulin A, development elements and a few hormones, which help regular development, growth and maturation. The age at which weaning is recommended does change as new analysis and suggestions emerge. There are ideas that late weaning might be a trigger for improvement of inappropriate immune responses to food (allergiessee Chapter 7). However, in late weaning, the primary publicity to these overseas proteins is usually through the skin within the form of proteins found in house mud. This is made worse by the cultural bathing of babies; frequent bathing leads to very dry skin and resultant breaches within the epidermis by way of which the international proteins can enter. At a later date, when this meals substance is then ingested for the first time, an immune response already exists, and the child could present a meals allergy. As the toddler becomes a toddler, their handyeouth coordination will develop to allow them to use a spoon by themselves. However, this bodily development additionally coincides with social and emotional growth (see Chapter 1). Children are growing repeatedly, and this requires a proportionately giant variety of energy per kilogram physique weight. They additionally require a high-protein diet to be able to build new cells, along with replacing worn out cells. Fats are also needed for the production of latest cells and for the manufacturing of development hormones; nutritional vitamins A, D, E and K are also only fats soluble. This could be confusing for parents where societal pressures are to stop obesity and to eat a low-fat food plan. The strategy of digestion begins with the sight or scent of food, or sounds associated with predicted meals consumption. This prepares the alimentary canal for the arrival of food by releasing those digestive juices needed for processing the anticipated intake of meals. Cranial nerve X (vagus nerve) is responsible for stimulating the digestive system (see Chapter 15). A drop in blood glucose levels causes the alpha cells of the pancreas to launch glucagon. This converts the glycogen saved within the liver back into glucose to increase blood glucose again to regular limits (4 mmol/L). This is the purpose at which the digestive juices containing all the enzymes essential to digest the predicted meals intake will start to be activated at the sight and smell of food. Any considerations over a baby being under- or chubby have to take these issues into consideration; and although bodily reasons need to be thought-about, safeguarding points when it comes to neglect should also stay a consideration. However, so as to function, every needs a blood provide and drainage, and innervation. Arterial blood supply to the gastrointestinal system is offered by the coeliac artery (foregutoesophagus to proximal duodenum); the superior mesenteric artery (midgutdistal duodenum to proximal transverse colon); the inferior mesenteric artery (provide the blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract distal transverse colon to anus); the marginal artery of the colon (joins the superior mesenteric artery and inferior mesenteric artery). The proximity of the lymphatic system to the circulatory system and the gastrointestinal tract implies that dissolved nutrients may even cross into the lymph. This is particularly essential for the motion of fats (see section on small intestine). The community of nerves relays alerts to the brain by way of the spinal wire at a subconscious level, controlling peristalsis and release of mucus and enzymes. The mouth the mouth is a cavity lined with stratified squamous epithelial cells (see Chapter 6). This allows exhausting items to come into contact with the buccal lining without causing vital trauma. The mouth contains the enamel, the tongue and three pairs of salivary glands: the parotid, the submandibular and the sublingual. The anterior portion of the roof of the mouth consists of the onerous palate, and the posterior portion consists of the taste bud from which the uvula hangs. However, the tooth do erupt in a typical pattern: decrease incisors adopted by upper incisors followed by first molars adopted by canines adopted by second molars (with decrease usually erupting earlier than every upper). During this time, infants will often experience some ache, and the irritation causes extreme salivation, often inflicting excoriated pores and skin across the mouth. Many mother and father additionally report a mild fever (the youngster feeling hot to touch however not above 37. As the permanent tooth develop underneath the deciduous enamel, the pressure stimulates the roots to be reabsorbed, ensuing within the deciduous tooth becoming free. This needs consideration in kids present process surgical procedure, as free teeth could be inadvertently dislodged and swallowed or aspirated. The first and second major molars are replaced by the first and second everlasting premolars; an additional three molars then erupt in every quadrant of the mouth. Once the meals passes the pharynx, further movement through the digestive tract is under involuntary management till defecation, which is a learnt, voluntary action. The chewing of meals within the mouth mixes it with mucus and salivary amylase, starting the digestion of starches. It, once more, has stratified epithelial cells, allowing the passage of solid food with minimal damage. The stratified epithelial cells are interspersed with mucus-secreting goblet cells, which assist to lubricate the food throughout its passage. As meals passes down the oesophagus, salivary amylase activity in digesting starches continues. Food passes by the mechanical strategy of peristalsis, which is possible as a result of the encompassing muscle structure, with alternate contraction and lengthening of round and longitudinal muscle tissue. The submucosaa layer of connective tissue below the mucosa, with blood vessels and nerves. The muscularisthis is two layers of muscle tissue at right angles to each other: one circular and one longitudinal.
60 caps lasuna order with amex
Long phase thickening of the bile duct wall cholesterol lowering foods cinnamon generic lasuna 60 caps with amex, prestentoic dilatation recommended cholesterol levels nz 60 caps lasuna with amex, and isolated extrahepatic bile duct involvement are attribute of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Intrahepatic bile duct involvement is much less frequent in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Cholangitis 501 Cholangiocarcinoma: Progressive duct dilatation over time, marked duct dilatation, a protracted confluent wall stricture, mural thickening, and mass lesion should raise suspicion of cholangiocarcinoma. Management/Clinical Issues Small duct primary sclerosing cholangitis is a variant of major sclerosing cholangitis during which typical cholestatic clinical and histologic features of main sclerosing cholangitis are noticed however with normal cholangiographic features. Liver biopsy is essential in cases suggesting small duct main sclerosing cholangitis. Patients with main sclerosing cholangitis have a threat of as a lot as 10% to 15% of creating cholangiocarcinoma. The diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with main sclerosing cholangitis is challenging, since ductal adjustments of major sclerosing cholangitis can mask the presence of cholangiocarcinoma. Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive disease that can finally result in end-stage liver illness. Although ursodeoxycholic acid, corticosteroids, or therapy with different immunosuppressive agents may be given, a major problem in the administration of main sclerosing cholangitis is the lack of an efficient established medical remedy. Key Points Cholangiography Essential for the prognosis of main sclerosing cholangitis. Multiple segmental strictures in the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts alternating with a standard or mildly dilated duct, producing a "beaded" look. Diagnosis after exclusion of the cause of secondary sclerosing cholangitis together with IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Utility of serum tumor markers, imaging, and biliary cytology for detecting cholangiocarcinoma in main sclerosing cholangitis. IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Definition IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is the biliary manifestation of IgG4-related disease, which is a multiorgan systemic disease characterised by abundant infiltration of IgG4-immunoreactive plasma cells with marked interstitial fibrosis, high serum IgG4 concentrations, and a good response to steroid therapy. Previously this disease was referred to as autoimmune pancreatitisclerosing cholangitis. Demographics and Clinical Features A majority of sufferers are males in their sixties who typically current with obstructive jaundice. Up to 88% of patients additionally present with autoimmune pancreatitis, but the reported incidence is variable. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis can also happen in patients without a historical past of autoimmune pancreatitis or IgG4-related illness. Pathology Histologic features of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis are principally similar to these noticed in different organs of IgG4-related illness. The affected bile ducts are diffusely thickened by a large lymphoplasmacytic infiltration intermingled with a storiform fibrosis. Imaging Findings Transabdominal ultrasound has restricted value for the analysis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Cholangiography typically demonstrates prestenotic dilatation with long continuous strictures often isolated to the distal bile ducts. Patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis are usually youthful (30 to forty years of age) and less symptomatic than those with IgG4-related disease. Multifocal intrahepatic duct involvement with quick segmental strictures and a beaded, pruned-tree, diverticulum-like look is suggestive of main sclerosing cholangitis. Solitary lesions with irregular margins, eccentric wall thickening, invisible bile duct lumen within the concerned phase, more outstanding wall thickening (more than three mm), distinction enhancement on the arterial- and portal-phase pictures, and an abrupt transition between the traditional and concerned bile duct might counsel a potential cholangiocarcinoma. It is necessary to be conscious of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and to make an correct prognosis, since this situation exhibits a good response to steroids. Other organ involvement of IgG4-related illness can occur synchronously or metachronously. Imaging options: Long segmental, symmetric, circumferential thickening of the bile duct wall, frequently with prestenotic dilatation and distinction enhancement on the delayed-phase photographs. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiogram reveals a beaded look of the intrahepatic ducts (arrows) owing to alternating areas of biliary stricturing and mild dilatation. Intrahepatic bile duct involvement is much less frequent than in typical main sclerosing cholangitis. Such bile duct wall thickening can mimic the appearance of main sclerosing cholangitis or cholangiocarcinoma. The wall of the gallbladder can be thickened and displays IgG4-related cholecystitis (arrowheads). Clinical variations between primary sclerosing cholangitis and sclerosing cholangitis with autoimmune pancreatitis. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: autoimmune pancreatitis and extrapancreatic manifestations. Demographics and Clinical Features Neuroendocrine neoplasms may develop in nearly any organ, however primary biliary neuroendocrine neoplasm comprises less than 1% of all neuroendocrine neoplasms. The frequent bile duct is the most typical anatomic web site, adopted by the hilar bile duct, the cystic duct, and the widespread hepatic duct. Management/Clinical Issues Patients with biliary neuroendocrine neoplasms show extraordinarily variable clinical outcomes according to the histopathologic subtype. Since surgical procedure provides the only potential treatment, aggressive surgical remedy is mostly advocated in sufferers with resectable biliary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct Definition Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct is characterized by dilated bile ducts distended by a papillary or villous biliary neoplasm masking delicate fibrovascular stalks. Demographics and Clinical Features Clinical signs embody recurrent higher abdominal ache, fever, chills, and jaundice, that are related to obstruction of the bile duct by tumor or to the presence of extreme mucin. Intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct have been reported extra regularly in East Asian international locations and may have an association with intrahepatic stones or liver fluke infestation. Pathology Intraductal papillary neoplasms develop slowly and have a tendency to spread along the mucosal floor. Synchronous and metachronous intraductal papillary neoplasms can develop within the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. According to degree of mobile and nuclear atypia, intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct are classified as low, intermediate, or high grade. Intraductal papillary neoplasms could be related to invasive carcinoma and may be categorized as an intraductal growth kind of cholangiocarcinoma. Intraductal papillary neoplasms with cystic luminal dilatation can have an analogous appearance to biliary cystadenomas but can be distinguished histologically with the criteria of luminal communication with the bile duct and absence of ovarian stroma at histopathology. Carcinoid of the extra-hepatic bile duct: a case report with long-term follow-up and evaluation of literature. High-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the gallbladder and bile duct: report of 4 cases with pathological correlation. Non-functioning well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor of the extrahepatic bile duct: an uncommon suspect Further Reading Imaging Findings Imaging options of intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct range by tumor measurement, the amount of mucin produced by tumors, the places of tumors (large duct versus peribiliary gland), and the degree of bile duct obstruction.
Order lasuna 60 caps fast delivery
The puborectal muscle is necessary for reflex contraction in case of sudden enhance in abdominal stress; it decrease the anorectal angle cholesterol free foods chart lasuna 60 caps otc, strikes the anus and anorectal junction anteriorly normal cholesterol levels new zealand generic lasuna 60 caps on line, and contributes to the closing of the urogenital hiatus. The most prevalent explanation for fecal incontinence is an exterior sphincter abnormality, for which obstetric trauma is crucial instigating issue. Different layers of the anal sphincter complex may be distinguished due to tissue-dependent reflection. Some layers are poorly reflective (hyporeflective, darker), whereas different layers are extremely reflective (hyperreflective, brighter). The poorly reflective ring of the inner anal sphincter is the clearest landmark. At T2-weighted photographs a quantity of buildings produce low-intensity (hypointense-striated muscles) alerts, while other buildings produce high-intensity (hyperintense-smooth muscles, fat) indicators. The images present scar tissue of the exterior sphincter in addition to anterior to the external sphincter on the left anteriorly (compare with right side). Coronal indirect T2-weighted turbo spin-echo picture from a 60-year-old girl with extreme fecal incontinence exhibits average atrophy of the exterior sphincter (E) and puborectal muscle (P) (compare with the conventional inner obturator muscle). There is scar tissue of the exterior and internal sphincters anteriorly (not shown). Axial indirect T2-weighted turbo spin-echo image in a 31-year-old lady with fecal incontinence demonstrates a big anterior defect (arrows) of the exterior sphincter (E). Lesions of the interior sphincter are often traumatic- from both obstetric trauma or surgical procedure. Lesions are both recognized as a focal defects, with typically retraction and thickening of the intact sphincter part, or as scarring (hypointense inside sphincter). In obstetric trauma lesions of the inner sphincter typically coincide with external sphincter lesions. For inner sphincter defects less evidence on imaging is out there than for defects of the exterior sphincter. Defects of the puborectal muscle are uncommon in patients with fecal incontinence and almost always coincide with lesions of the exterior and/or internal sphincter. In sufferers with urogenital prolapse, these lesions may be part of paravaginal defects. Since each techniques have comparable accuracy, using endoanal ultrasound as the preliminary method for the detection of exterior sphincter defects is most popular. However, apart from defects, atrophy of the external sphincter is an important discovering in patients with fecal incontinence. It is related to decreased anal incremental strain and poor end result in sufferers treated by anterior anal repair. Atrophy can also concern the internal sphincter; an internal sphincter thickness of two mm or much less in middle-aged or older individuals must be thought-about as atrophy. They are identified as a complete hypoechogenic gap within the area of the repair or as no decrease within the extent of the external anal sphincter defect in contrast with the defect depicted at baseline. Imaging can subsequently be thought-about in patients with poor consequence to determine its cause. Here the extent of the defect/scarring ought to be reported-for instance, describing the involved area as grades of the 360-degree circumference. This is easiest when the puborectal muscle has a traditional appearance; if not, often comparison with the internal obturator muscle facilitates the identification of fatty replacement. A comparability of the muscle bulk and fatty substitute facilitates grading into delicate, average, and severe. This grading correlates nicely with anal manometry findings; (incremental) squeeze strain is more and more decreased in sufferers with increasing grades of external sphincter atrophy. Management/Clinical Issues the workup of sufferers with fecal incontinence is aimed at figuring out causes amenable to remedy. The first step contains an intensive historical past taking and bodily examination; this entails inspection of the perineum. The latter gives useful data however is inaccurate for determining external anal sphincter defects of less than 90 degrees. Several anofunctional exams can be found; mostly anal manometry and rectal sensitivity/capacity measurements are used. Anal manometry evaluates sphincter operate by measuring pressures at totally different factors along the anal canal. Pressures at rest replicate inside anal sphincter operate and at squeeze external anal sphincter perform. Manometry provides correct information about anal sphincter perform however is unable to differentiate between sphincter dysfunction due traumatic harm versus that stemming from atrophy. Rectal capability can be 298 Gastrointestinal Imaging decided by inflating a balloon with air contained in the rectum or by using a barostat system. Sensory threshold, urge sensation, and maximal tolerated volume can be decided. Hyposensitivity could be associated with neurogenic problems, while hypersensitivity could be associated to inflammatory bowel issues, irradiation, and irritable bowel syndrome. Anal and rectal sensitivity measurements consider the nerve provide of the anus and rectum by passing electrical present between bipolar electrodes. In many facilities anal manometry is part of the routine workup, usually in combination with one or more different useful tests and imaging. Imaging is used for the detection of defects or atrophy of the exterior and inner sphincters. Conservative measures embody medicine, dietary recommendations, and pelvic flooring rehabilitation. Surgery is used for those patients not responding to conservative measures, primarily those with an anterior sphincter defect. Imaging is crucial in figuring out these defects, as anorectal examination has limitations, particularly for smaller exterior sphincter defects (less than ninety degrees). Patients with an anterior exterior sphincter defect can be handled by anterior anal repair; the defect is handled by overlapping the defect. Sacral nerve stimulation, dynamic graciloplasty, and an artificial sphincter are considered as primary therapy options when conservative treatment or anterior anal sphincter repair (in sufferers with an anterior external sphincter defect) has failed. Patients with an internal sphincter defect may be handled by the injection of a bulk agent and imaging could be carried out to visualize the localization of the agent. Key Points Obstetric trauma is a significant reason for fecal incontinence; it may lead to anterior sphincter defects or generalized external sphincter atrophy. Sirlin Normal Anatomy Two completely different techniques are used to describe liver anatomy: traditional anatomy and practical anatomy. The classic anatomy system is predicated on the surface appearance of the liver and divides the liver into 4 lobes: left, proper, quadrate, and caudate.
Purchase lasuna 60 caps amex
The psychosocial penalties of this situation are overwhelming and embrace cholesterol ratio of 2.4 lasuna 60 caps cheap amex, among others cholesterol test without fasting cheap 60 caps lasuna free shipping, diminished self-esteem, social isolation, and nervousness over probably having sudden episodes. The embarrassment and humiliation this downside causes makes it a taboo topic for many individuals. Fecal incontinence is a crucial cause for nursing residence placement, as as a lot as 45% of nursing home residents are estimated to have some form of fecal incontinence. Women are thought to be more affected than males as a outcome of obstetric trauma is the major explanation for fecal incontinence; this female predominance decreases with growing age. The purpose for this discrepancy is unknown, nevertheless it could be relate to the age and gender of individuals who actively search medical consideration. Other causes for sphincter abnormalities embrace anorectal surgical procedure similar to hemorrhoidectomy and fistula surgical procedure. Anatomy and Pathology the anal sphincter is a multilayered cylindrical structure; from inside out it includes the submucosa/subepithelium, inside sphincter, intersphincteric area (with longitudinal layer) and the striated muscles external sphincter (the decrease outer half) and puborectal muscle (the upper outer half). Most necessary in sufferers with fecal incontinence is analysis of the external sphincter. The major role of the striated external sphincter is voluntary closure and reflex closure; further, it helps the anal resting tone. The inner anal sphincter is important for the resting tone of the anal sphincter. Damage to the sleek muscle of the inner anal sphincter usually has a less profound effect than injury to the exterior sphincter supplied that the other sphincter muscles are intact. Each segment constitutes an autonomous unit that has its personal vascular inflow, outflow, and biliary drainage-important feature for surgical planning and making certain viability of the remaining liver after surgical resections. The portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct are centrally positioned in every segment, while the hepatic veins (vascular outflow) are peripherally positioned. The segments are numbered in a clockwise direction from an anterior viewpoint, starting with the caudate lobe as phase I. They are divided each longitudinally alongside the hepatic veins and transversely by way of the proper and left portal pedicles. The liver receives twin blood move from the hepatic portal veins and the hepatic arteries. Blood exits the liver through the hepatic veins, which empty into the inferior vena cava. Approximately 25% of the blood provide to the liver derives from the hepatic artery, whereas the remaining 75% derives from the portal vein. Knowledge of this anatomy is necessary in providing anatomic info for hepatic surgical procedure and transplantation. The frequent bile duct, the portal vein, and correct hepatic artery enter the porta hepatis, or hilum, before dividing into left and right branches, which provide the practical left and right lobes. Color, spectral and power Doppler are sometimes used, as they supply info on blood flow and perfusion. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound makes use of injected microbubble-based distinction brokers to evaluate blood flow and lesion vascularity. The liver segments are divided longitudinally by the hepatic veins and transversely by the proper and left portal veins. The most common anatomy of the best and left hepatic arteries is to arise from the right hepatic artery. Common variants embody a changed proper hepatic artery that arises from the superior mesenteric artery, an accessory replaced proper hepatic artery from the superior mesenteric artery, a changed left hepatic artery arising from the left gastric artery, and the frequent hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery or aorta. Ultrasound assessment of liver stiffness as a marker of liver fibrosis is an emerging indication. Initial evaluation of vascular and biliary anastomoses in posttransplant patients. Provides imaging in real time and can be utilized as a therapeutic software to information invasive procedures. Transverse gray-scale image of liver on the junction of the hepatic veins with the inferior vena cava reveals regular echogenicity. Sagittal gray-scale picture by way of the porta hepatis (B) exhibits normal-caliber primary portal vein. Shadowing from ribs and gas-filled loops of bowel introduce blind spots that may cause focal liver lesions to be missed. While ultrasound is used incessantly as a screening take a look at for fatty liver in sufferers with persistent elevation of aminotransferases, ultrasound has limited accuracy for the diagnosis of fatty liver. Both hepatic fats accumulation and fibrosis have comparable sonographic appearances, doubtlessly inflicting diagnostic confusion. Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis can scatter the ultrasound beam, thus altering the hepatic echotexture and limiting the sensitivity of ultrasound for the detection of focal lesions. The hepatic arterial section includes the early arterial (typically at 20 to 25 seconds) and late arterial (typically at 35 to forty seconds) phases. Although hepatic neoplasms obtain their blood supply primarily from the hepatic artery, enhancement of focal lesions is inconsistent in the early arterial section and could also be weak or absent as a outcome of it takes time for the contrast agent to pass from the hepatic artery through the capillary mattress of the tumor and leak into the tumor interstitium. In the late arterial phase, leakage of contrast agent into the tumor interstitium has begun; thus this phase coincides with the peak of tumor enhancement. There is average enhancement of portal venous blood but no enhancement of hepatic veins and only mild enhancement of the liver parenchyma. The late arterial phase has been proven to be superior to the early arterial phase for lesion diagnosis in medical studies. For this cause most facilities get hold of images from the late however not the early arterial part. The portal venous part happens about 60 to ninety seconds after the start of contrast injection. It coincides with the peak of enhancement of the liver parenchyma, because the liver is fed predominantly by the portal vein. Hepatic veins are enhanced in this part, as contrast has transited by way of the sinusoids and into the draining veins. A delayed section at about 3 to 5 minutes after the start of distinction injection is usually useful for the characterization of focal liver lesions, notably hepatocellular carcinoma. During this section, the contrast agent is partially equilibrated between the vascular and interstitial compartments while being cleared from the liver parenchyma, blood vessels, and rest of the physique by renal excretion. Images with even greater delay (about 10 to 15 minutes) may be acquired in choose circumstances to additional characterize liver lesions with progressive temporal enhancement patterns, such as cholangiocellular carcinoma (cholangiocarcinoma) and slow-filling hemangiomas. As illustrated on this case, the late arterial part is characterised by enhancement of the hepatic artery (arrows) and portal veins but not the hepatic veins. The number of phases performed is dependent upon the research indication and institutional preferences. Isotropic voxel measurement is routinely achievable with modern scanners, permitting high-quality three-dimensional reformation of images. Relatively free of movement or other imaging artifact even in sufferers with restricted ability to cooperate.
Lasuna 60 caps cheap visa
This look could mimic a strong mass arising from the stomach (exophytic) cholesterol levels beef order lasuna 60 caps free shipping, adrenal gland cholesterol cheese chart buy lasuna 60 caps fast delivery, or pancreas. Miscellaneous Disorders of the Stomach 101 Treichel J, Gerstenberg E, Palme G, et al. Gastric Bezoar Definition A gastric bezoar is a conglomerate intragastric mass consisting of amassed ingested materials, which may consist of food or different matter. Demographic and Clinical Features Gastric bezoars are rare, with an incidence of less than 1% in the common inhabitants. Bezoars are sometimes related to prior gastric surgical procedure, diabetes, gastroparesis, or a psychiatric history. Gastroparesis may be an underlying think about as many as 60% of sufferers with out prior gastric surgery. Gastric bezoars have additionally been reported in sufferers with neuropathy or myotonic dystrophy. Most bezoars are symptomatic, with signs as a result of the mechanical results of the overseas physique within the abdomen. Large bezoars or bezoars in the setting of prior gastric surgical procedure could cause gastric outlet obstruction. Classically this occurs when a person has eaten unripe persimmons, which comprise substances that coagulate on contact with gastric acid, producing a sticky materials that traps other ingested matter. Currently as a lot as 75% of patients with phytobezoars have undergone prior gastric surgery. Trichobezoars are composed of hair and occur predominantly in mentally ill feminine sufferers who chew and ingest their own hair. A small percentage of bezoars contain each hair and vegetable matter and are referred to as trichophytobezoars. In current years a pharmacobezoar composed of ingested drugs has been acknowledged, occurring extra commonly with sustained-release drugs. A bezoar might type in a gastric remnant or pouch in the setting of distal gastrectomy or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass respectively. Anastomotic strictures, poor mechanical breakdown, and delayed emptying of ingested material predispose to bezoar development. Loss of regular pyloric perform, low gastric acidity, and decreased peristalsis also probably contribute. Gastric bezoars also occur within the setting of gastroparesis, neuropathy, and myotonic dystrophy. Abdominal radiographs might suggest a bezoar; barium research can confirm the prognosis. Barium studies present a conglomerate spherical to ovoid mottled mass-like filling defect surrounded by barium (B) Pathology A bezoar is an intragastric mass or concretion consisting of accrued ingested materials. Bezoars normally kind in the abdomen but can move into the small bowel and cause obstruction. At fluoroscopy with positional changes, most bezoars are cellular within the gastric lumen besides when a bezoar occupies most of the gastric lumen. Rarely, a really smooth bezoar may seem as a large filling defect surrounded against this in the stomach. Air bubbles are noted within the interstices and the bezoar could also be surrounded by fluid or oral distinction. Large bezoars are inclined to fill the lumen with air bubbles diffusely distributed all through the mass. It may be difficult to differentiate a bezoar from a great amount of retained food within the stomach. In obstruction of the small bowel due to a migrated bezoar, dilated small bowel may be seen proximal to the mass with collapsed distal loops. Management/Clinical Issues Bezoars can resolve spontaneously or with dietary restriction. Symptomatic bezoars may be treated endoscopically (with dissolution or suction) or surgically. Bezoar-induced obstruction not often improves with conservative remedy; surgery is usually required. A second operation may be necessary due to recurrent bowel obstruction from residual bezoars. Gastric bezoars: reassessment of clinical and radiographic findings in 19 sufferers. Demographic and Clinical Features Morbid obesity has elevated dramatically in the United States and western international locations in current times and has become a significant health downside. Surgical Procedure A small gastric pouch is created to bypass most of the abdomen, duodenum, and proximal jejunum (excluded or biliopancreatic limb) from the path of meals. This most often creates a short jejunal stump and an antegrade-flowing jejunal limb (alimentary limb). The small gastric pouch and slender stoma trigger early and extended satiety (restrictive). Postsurgical Complications Despite the success of this procedure, serious problems may happen and are often identified with imaging studies. The most serious early complication recognized radiologically is postoperative leak. Other early problems could include acute obstruction (often as a result of postoperative edema and or hematoma), acute distention of the excluded abdomen, ileus, and staple line leak. Complications that occur within the late postoperative period (greater than 1 month postoperatively) might embrace staple line disruption/dehiscence, obstruction, internal hernia, belly wall hernia, intussusception, stomal stenosis, and marginal ulcers. A small gastric pouch is created (arrowhead) and a Roux jejunal limb is anastomosed to the gastric pouch via a small stoma. There is a jejunojejunal anastomosis (arrow) of the alimentary and biliopancreatic limbs, typically within the left midabdomen, with a downstream frequent channel. Radiologists should be succesful of acknowledge the postsurgical anatomy and diagnose potential issues. In the early postoperative period or with potential perforation, a small amount of water-soluble distinction is administered. Overhead radiographs are obtained until distinction passes the small bowel anastomosis, as obstruction and rarely leak may occur at this site. Imaging of the remainder of the small bowel could additionally be deferred till the late postoperative period. Communication with the excluded stomach because of gastrogastric fistula, staple line disruption, or dehiscence might develop within the early or late postoperative course. Stomach Following Bariatric Surger y 105 location could be confirmed by rotating the patient to the proper to opacify the distal abdomen and duodenum. Retrograde opacification of the excluded abdomen is a delayed finding that may appear on overhead radiographs as a group at the left of the stoma.