Micronase
Micronase dosages: 5 mg, 2.5 mg
Micronase packs: 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 360 pills

Generic micronase 2.5 mg with amex
The mesentery is present into the seventh month diabetes definition type 1 micronase 2.5 mg purchase visa, through the time that the bladder remains in the stomach cavity blood glucose 92 purchase micronase 2.5 mg on line. The bladder gradually descends into the pelvis in late fetal life and early infancy, though at start, because of the underdevelopment of the true pelvis, it nonetheless is actually an abdominal organ. In the first 2 postnatal years, its descent into the pelvis is speedy, then it slows to turn out to be full at the age of 20 years. The umbilical vesical fascia, evolving from the temporary mesentery, is shaped from the intermediate stratum of the retroperitoneal tissue. It extends cephalad to the umbilicus to enclose the urachus and the umbilical arteries and caudally to cowl the bladder, seminal vesicles, and the prostate. Lateral condensations kind the lateral true ligaments of the bladder and the puboprostatic ligaments. Sinoutricular Cord, Verumontanum, and Formation of the Prostatic Utricle As the tips of the fused and canalized m�llerian (paramesonephric) ducts meet the urogenital sinus, they stimulate the sinus epithelium to type a protuberance into the sinus, the m�llerian tubercle or verumontanum. A second protuberance develops in the course of the duct on the outside of the urogenital sinus. This projection is joined to the fused m�llerian ducts to kind the sinoutricular wire. In the male, the distal portion becomes canalized to form the prostatic utricle or vagina masculina. A dashed line across every frontal view signifies the original degree the place the wolffian duct made contact with the vesicourethral canal, defining the junction of the canal with the urogenital sinus. The frequent excretory ducts and the lengthy run ostium of the fused m�llerian ducts enter the vesicourethral canal on the verumontanum (m�llerian tubercle). The ureteral buds department from the wolffian duct proximal to the widespread excretory duct, which is steady with the cloacal horn that was derived from the tissue of the canal. With the incorporation of the cloacal horn and the frequent excretory duct into the vesicourethral canal, the wolffian duct and the ureter enter side by facet. The terminal portion of the m�llerian duct, now the prostatic utricle, opens between them. The growth of mesodermal wolffian tissue (crosshatched area) between the orifices of the ureter and the ejaculatory duct, combined with growth of the bladder wall, results in the ascent and lateral displacement of the ureteral opening. In contrast, the opening of the wolffian duct is mounted in position at the verumontanum, not only from its close embryologic association with the m�llerian duct but additionally as a result of the complete decrease portion of the urogenital sinus is fixed in strong mesodermal condensations so that enlargement can occur solely in a cephalic course. The terminations of the wolffian ducts do, in fact, move a small distance cephalad, leaving a symmetric pair of longitudinally disposed remnants as collicular the mesodermal widespread excretory duct is outlined as that portion of the wolffian duct distal to the ureteral bud. The tissue of the endodermal vesicourethral canal expands posteriorly towards the common excretory duct to type, in combination with the terminal piece of the common excretory duct, a funnel-shaped extrusion, the cloacal horn. As the cloacal horn becomes reincorporated into the canal, it carries the terminal piece of the common excretory duct into the vesicourethral canal with the ureter hooked up and varieties part of the superficial trigone. The formation of the superficial trigone begins with the fusion of the mesoderm medial to the 2 ducts. Although the orifice of the wolffian duct stays in place, the mesoderm that was initially part of the common excretory duct turns into energetic and enlarges. This mesodermal growth displaces the ureteral orifices cranially and laterally, shifting them from near the midline at the junction of the vesicourethral canal with the urogenital sinus into a lateral place in the bladder. The entire superficial trigone, a construction that extends from the verumontanum to the ureteral orifices, is shaped by this mesodermal (wolffian) growth. The dashed line reveals the level at which the wolffian duct originally made contact with the vesicourethral canal. The length of the collicular folds is a sign of the gap that the ducts and verumontanum have moved cephalad. In the mature stage, the tissue from the wolffian duct varieties the superficial trigone. Distally, within the preprostatic urethra, the verumontanum is found holding the ejaculatory ducts and prostatic utricle. Thus developmentally the muscular tissues of the superficial trigone are steady with these of the ureter, all being of wolffian origin. Ductal Incorporation in Male and Female Male the ductal mesoderm (cross-hatched area) that was incorporated into the vesicourethral canal moves cranially and laterally and carries the ureteral orifices with it. As described previously, this tissue turns into distributed as the superficial trigone within the space between the ejaculatory ducts distally and the ureteral orifices proximally. The fused m�llerian ducts enter the canal on the verumontanum, which lies on the junction of the vesicourethral canal and the urogenital sinus. The ureters penetrate the bladder wall by a straight course; later improvement supplies an indirect tunnel. Instead of resulting in a prostatic utricle, canalization of the sinoutricular wire in the feminine forms the terminal portion of the vagina. The whole female urethra develops from the urogenital sinus as the homologue of the posterior urethra of the male. The equivalent of the verumontanum containing the m�llerian prostatic utricle could be viewed as lying at the introitus. Remnants of the wolffian ducts turn out to be the epo�phoron and paro�phoron, and are also represented in the adult because the Gartner ducts that extend the size of the vagina. An insufficient response of the renal blastema to the stimulus arising from the branching ureteral bud can also end in a reduction of renal tissue. They may be associated with obstruction however can happen in inheritable syndromes within the absence of obstruction. Or the bud may develop in a comparatively irregular place in order that it makes an attempt induction of a poor area of the renal blastema. Evidence for this is that dysplasia is commonly found associated with a displaced secondary ureteral bud that empties laterally or distally into the urethra. Anomalies on the Ureteric Hiatus Paraureteral diverticula (saccules) arise on the higher extremity of the trigone simply above the ureteric orifice as a transhiatal herniation of the bladder mucosa. Deficient development of the hiatus and of the muscle of the superficial trigone is the possible cause in infants. Many are in all probability secondary to a weak internal longitudinal layer of the bladder musculature on the ureterovesical angle and to poor support from the outer longitudinal layer. With obstruction or neurogenic bladder, increased detrusor stress might trigger transhiatal herniation of the vesical mucosa to kind the so-called saccule of mucosa compelled by way of an overstretched hiatus. Hiatal diverticula disturb the submucosal course of the terminal ureter and, due to this fact, are related to reflux. They may be duplications consequent on the formation of a second bud on the wolffian duct or they might be ureteral ectopia from late arrival or vesicoureteral reflux from early arrival of the ureter at the vesicourethral canal. Even if the ureteral bud varieties at the correct place and time, it may be unduly large and end in formation of a dilated upper tract similar to is seen within the nonrefluxing nonobstructed megaureter. One rationalization is delayed rupture of the occluding epithelial membrane usually lying on the junction of the ureter and the urogenital sinus in the sixth week of gestation, when nephrogenic perform is in abeyance; persistence of the membrane leads to obstruction at that website. Another rationalization is delay in the absorption of the immature ureter into the vesicourethral canal.
Order micronase 2.5 mg online
Biobrane can be used to cowl partial or full thickness wounds to help prevents fluid loss and to prevent bacterial invasion diabetes mellitus in dogs treatment micronase 2.5 mg order. Trancyte is a product that combines Biobrane with a protein matrix derived from neonatal fibroblasts diabetes tagalog definition purchase micronase 5 mg with mastercard. Integra consists of a bilaminar membrane of bovine Type I collagen crosslinked with chondroiton-6-sulfate and a silicone elastomer epidermal equal. At that point the silicone layer may be removed and fifty six 592 Trauma Management an extremely thin. Nonthermal Burns Chemical Burns � Chemical burns constitute a small percentage of admissions to a burn middle. These injuries can occur at house by mishandling widespread cleaning agents or at work by industrial exposure. These reactions form ions that induce further chemical reactions, which continue to penetrate into tissues. Alkaline burns are extra widespread than acidic burns as a result of these agents make up frequent family cleansing brokers including bleach, sodium hydroxide (Drano) and lime. Electrical Burns � Electrical accidents make up less than 5% of burn heart admissions. These accidents could be initially deceiving as a result of the obvious skin involvement is small in comparability with the amount of destruction that may have occurred. These accidents are normally small thermal accidents without the sequelae seen in high voltage injuries. High voltage injuries (>1000 volts) have skin involvement at contact sites and bigger destruction of deeper tissues. Most sequelae of excessive voltage injuries happen inside the first 24 hours after the time of injury. It must also be noted that these patients should be carefully examined for fractures as excessive voltage injuries have a major incidence of falls. Patient Outcomes � Patient outcomes have improved drastically over the past 20 years. Increases in survival are due nearly exclusively to enhancements in resuscitation, the remedy of inhalation injury and enhancements in important care practices. A study in 1989 confirmed that essentially the most vital variables influencing return to work after harm are degree of fifty six Acute Burn Injury 593 burn, burns to the palms, type of work and age of the patient. These folks will have to have not solely a robust social circle but should also be keen to take part in interdisciplinary groups such as counseling, occupational and physical therapy. Fraser and Michael Muller Introduction � Inhalation injury could additionally be defined as an airway or pulmonary parenchymal injury as a result of the components of smoke: warmth, particulate matter, irritants, and asphyxiants. In the presence of burns, inhalation damage is a larger contributor to general mortality and morbidity than either proportion physique surface area burn or age, with the vast majority of victims dying on the scene, because of hypoxia and asphyxiation. Whilst the mortality associated with cutaneous burns has fallen dramatically, this enchancment has not been mirrored in inhalation damage. The problem in diagnosis and quantification of the injury, and the delay in symptom presentation account for some of these issues. There is critical morbidity and mortality both instantly and throughout recovery. At Risk � Unable to escape hearth as a end result of - Extremes of age - Immobility due to different trauma - Reduction of degree of consciousness: alcohol, medicine, effects of smoke. Assessment of Smoke Inhalation Patient � History Was the hearth in an enclosed area. Fraser, University of Queensland, Royal Brisbane Hospital, Herston, Australia Michael Muller, University of Queensland, Royal Brisbane Hospital, Herston, Australia Inhalation Injury 595 � Inspection - Stridor: signifies extreme laryngeal edema and the possibility of imminent airway obstruction - Voice hoarseness-an excellent warning sign - Tachypnea - Use of accent muscles - Persistent cough - Soot in oropharynx - Singed nasal hair � Examination Confusion/disorientation-indicating hypoxia and/or presence of asphyxiants Wheeze Soot-stained sputum Central facial burn � Burn involving central face: 60% incidence of inhalation harm. Breakdown in hemoglobin leads to minor concentrations, and a metropolis lifestyle is related to vital concentrations. Pathophysiology Inhalation injury induced by smoke may be separated into: � Thermal Injury - Air of 300�C at the oropharynx is cooled to 50�C on arrival at the trachea. This ends in depilation of the cilia and forged formation from sloughing of the necrotic tracheal and bronchial mucosa. Small airway plugging and air-trapping with subsequent bronchopneumonia and atelectasis then occurs. The immune response initiates phagocytosis-inducing free radical formation and the discharge of proteases from neutrophils. This additional fuels the systemic inflammatory response, leading to increased capillary permeability. Other merchandise embrace aldehydes, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen chloride, ammonia and phosgene; all of which can result in pulmonary edema. Soluble vapors, corresponding to acrolein, sulfur dioxide, ammonia and hydrogen chloride trigger harm to the higher airway. Chlorine and isocyanates, with intermediate solubility, trigger higher and decrease respiratory tract harm. Phosgene and oxides of nitrogen have low water solubility and trigger diffuse parenchymal harm. Hence, these may act as chemical asphyxiants, notably in an enclosed setting. Management-Early � Humidified Oxygen-Many smoke inhalation victims will require this alone, however, as signs could be slow to develop, they should proceed to be monitored carefully. Supplemental oxygen is the mainstay of remedy of carbon monoxide poisoning and humidification helps to loosen secretions and therefore aid expectoration. Intubation is indicated by the necessity to help ventilation and to defend the airway of the unconscious patient. It is the precise case of thermal injury to the higher airway that requires particular attention. This protects the decrease airway from important thermal injury, with the exception of steam inhalation. The absorption of warmth is the principle contributor to upper airway and laryngeal swelling, which can precipitate acute airway obstruction. If there are indicators suggestive of great higher airway damage (voice modifications, stridor, and air hunger), a definitive airway ought to be secured instantly. The aware patient is ready to defend his/her personal airway successfully, and elimination of those priceless protecting reflexes by sedation or excessive analgesia should be avoided if in any respect potential. Direct vision of the laryngeal inlet in the spontaneously respiration patient is the safest option. Either direct laryngoscopy, or fiberoptic bronchoscopy with native anesthesia or inhalational induction could also be used. The airway is maintained, as the patient self ventilates, and the danger of losing the airway is diminished. In burns, suxamethonium causes refractory hyperkalemia after 24-48 h in burns however can be utilized within the acute setting.
Generic micronase 2.5 mg amex
Repeat hemodynamics diabetes type 1 effects micronase 2.5 mg buy low cost, reassessing pressure gradient and cardiac output diabetes 99 buy discount micronase 2.5 mg, and recalculate the valve space. If no valvuloplasty is deliberate, document a pullback to guarantee well-matched aortic strain tracings (regardless of catheter used). Position the pigtail just above the sinotubular junction, so as to keep away from contact with the valve. Steps for Left Ventriculography � Advance a pigtail catheter over a wire in usual trend into the left ventricle, making certain the wire (and, subsequently, catheter) is free in the ventricular cavity and never entangled with the mitral valvular apparatus. Complications Cerebrovascular accident, vascular Post-procedure Care Routine post-catheterization care References 1. Additionally, decreased time to ambulation is important as more hospitals adopt same-day discharge methods. When utilizing these devices, one must weigh the potential problems related to these units towards their potential advantages. Contraindications � Common femoral artery luminal diameter lower than 5 mm in diameter � Significant peripheral vascular disease � Significant luminal encroachment � More than delicate fluoroscopically visible calcification Deployment Steps � Place a guidewire (0. Use of a gauze could help to grip the slippery hydrophilic distal portion of the system. Rail the device over the guidewire till the guidewire exit port is just above the pores and skin line. Note that a slow trickle of blood may be seen if the gadget is incompletely inserted into the vessel. Continue to push the gadget ahead � typically a "give" might be felt because the system is absolutely inserted. Two things might be evident: (a) There might be firm resistance to further pull again and (b) blood move from the marker lumen will stop. Loop the suture around the trimming mechanism situated on the physique of the device to minimize it. Pull the ends of the rail (long, blue) and lock (shorter, white tip) sutures from the gadget and secure them with clamps (or wet gauze) and reinsert the guidewire again in via the port. Make sure that the two sutures as secured with adequate slack to the sterile subject utilizing a clamp. A second Preclose may be deployed however flip the device clockwise 90� for deployment as compared to the beforehand deployed Preclose. Then insert the sheath via the guidewire to perform the necessary intervention. At end of the process reinsert a long guidewire via the sheath and remove the sheath and perform the following steps to shut the arteriotomy website. The suture may be eliminated by a quick, agency tug on the lock limb of the suture � this will break the knot and allow removal of the complete size of suture. Once the knot is sufficiently pushed right down to obtain hemostasis, lock the knot by pulling the lock suture with the right hand while maintaining pressure on the rail limb with the left hand. Contraindications � Common femoral artery luminal diameter less than 5 mm in diameter � Significant peripheral vascular illness � Significant luminal encroachment � More than average fluoroscopically visible calcification Deployment Steps � Create a 5�7 mm pores and skin incision on the sheath website to accommodate the insertion of the clip delivery tube into the tissue tract. This step will deploy the locator wings contained in the blood vessel and provoke splitting of the exchange sheath. Gently push the device down on top of the artery with the right hand to seat the clip delivery tube on top of the entry site. Place the left hand on the puncture web site in the palm-down place with the clip supply tube extending up between the index and center finger. Contraindications � Common femoral artery luminal diameter less than 5 mm in diameter � Significant peripheral vascular disease � Significant luminal encroachment � More than mild fluoroscopically seen calcification Deployment Steps � Insert the Angio-Seal guidewire into the procedure sheath. If done accurately, the reference indicators (arrows) on the two pieces should match up, and there should delicate click as the 2 parts lock together. The reference indicators (arrows) on the arteriotomy locator and insertion sheath assembly ought to be facing up. Once satisfactory backflow of blood is confirmed, pull the assembly again until blood circulate stops. Then push the assembly ahead once more (typically around 1 cm) until brisk blood circulate is achieved again. At this point there ought to be some backflow of blood from around the tip of the gadget. At this level the reference indicators on the Angio-Seal device and the insertion sheath ought to match up and will face up. The deal with of the Angio-Seal gadget could have to be rocked left and right to be certain that the system is locked in the again position. As soon because the supply suture and a green tamper on the suture becomes seen, advance the tamper while maintaining tension on the suture till resistance against vessel wall is felt and in most cases a black compaction marker is revealed. Then push down on the skin using a blunt-tip sterile scissor and reduce the suture below the pores and skin level. Contraindications � Significant peripheral vascular illness � Severe calcification proximal to or on the arterial puncture website Deployment Steps � Insert MynxGrip into the procedural sheath as a lot as the white shaft marker. This maneuver confirms that the balloon is in appropriate position and is abutting the anterior floor of the vessel at the arteriotomy site. To ensure complete balloon deflation, wait till air bubbles and fluid have stopped shifting via the inflation tubing. For correct positioning the green marker on the translucent band should be placed proximal to the percutaneous access web site. Completely remove the sheath then take away air 1 cc at a time until bleeding happens at which period 1�2 cc of air is reinjected into the balloon. Withdraw 1 cc of air at a time utilizing the provided syringe and observe for any bleeding. Deployment Steps � Place the band on the mattress prior to transitioning patient over on prime of it. Prolonged use of this device has been related to arterial leg ischemia as properly as formation of deep venous thrombus. Vascular entry and closure in coronary angiography and percutaneous intervention. Preprocedural Evaluation Components History � Current signs, presentation, and angina classification. Review of prior angiograms to determine location of prior bypass graft origins and kind of catheters/devices used is necessary. Kini � Ability to take dual antiplatelet therapy and any surgeries/procedures planned within the next 12 months to determine on the sort of stent that can be inserted. They entirely perceive the procedure and have signed the informed consent" (see Table 14. As dual antiplatelet remedy is required in all patients receiving stents for at least 1 month up to 1 yr or longer, aspirin desensitization in aspirin-allergic patients ought to be performed.
Discount 5 mg micronase overnight delivery
These beads are typically removed at time of repeat debridement to enable for wound closure diabetes mellitus y sus complicaciones pdf buy 2.5 mg micronase with mastercard. Antibiotics are given for 48 hours and restarted for an additional 24-48 hours for repeat debridements till the wound is closed diabetes mellitus type 2 impaired skin integrity micronase 2.5 mg generic without prescription. With fashionable reconstruction techniques corresponding to bone transport, vascular bone transfer and bone grafting, excessive circumstances of bone loss may be effectively managed. Free tissue switch has confirmed to be extremely useful in managing intensive delicate tissue loss. Despite these advances, however, many cases of "profitable" limb salvages are actually examples of expertise over purpose. The true measure of success in these circumstances should embody a measure of the functionality of the reconstructed tibia in addition to the particular person hooked up to the tibia. In addition to objective medical criteria, ideally psychological and social components must also be factored into the choice. It is properly accepted, nonetheless, that if amputation is an possibility, it should be carried out on the day of harm as opposed to delaying the decision till a later time. Patients are rather more accepting of an amputation when carried out primarily than of 1 performed after an preliminary debridement. In the first scenario, the patient accepts the amputation because of the injury, whereas within the second situation, the patient views the delayed amputation as a failure of remedy. The severity of the soft tissue injury can be a factor, notably if a comorbidity exists that would preclude timely reliable soft tissue reconstruction. Prolonged hypotension will are probably to lengthen the zone of harm of the local tissues and thus is a factor for amputation. It is well accepted forty two Long Bone Fractures and the General Surgeon 441 that harm to the posterior tibial nerve, resulting in loss of plantar sensation, is an efficient predictor of amputation. Amputation is very probably with an ipsilateral foot or ankle damage and concomitant high-grade open tibial injury. Compartment Syndrome � Extremities which are subjected to high-energy blunt trauma can suffer compartment syndrome. The extremities are composed of fascial areas, the compartments, which include muscles, nerves, arteries and veins. These facial areas are of fastened volume due to the inexpansiveness of fascial. If the volume of a fixed area is elevated, the laws of physics dictate that the pressure of that space will enhance. Compartment syndrome happens when the strain in a fascial space increases to the point of inflicting ischemic harm to the structures that traverse that compartment. Injury can precipitate a compartment syndrome by way of hemorrhage, increased capillary permeability secondary to irritation, and postischemic swelling secondary to prolonged extrinsic compression. The five Ps are Pressure, meaning a feeling of tightness on exterior compression, Pallor, duskiness of the soft tissues, Pain, an elevated notion of ache, Pulselessness, and Paresthesia. The most reliable check in an awake and alert affected person is pain, and more particularly, pain out of proportion for the harm. In addition, passively stretching the involved compartment will end in considerably increased ache. Clearly, a patient with a tibial fracture could have pain, but this pain is normally controllable with immobilization and analgesic medicine. A patient with a compartment syndrome will continue to have uncontrollable pain despite these measures. These embrace utilizing an 18-gauge needle attached to a manometer, wick catheters, slit catheters and stic catheters. The stic catheter has the benefit of portability however is only reliable when used for momentary measurements. These pressure suggestions have all been primarily based on different measurement methods. Originally described because the distinction between imply arterial pressure, 42 442 Trauma Management � forty two � � � a latest research demonstrated a excessive diploma of reliability of using the distinction between diastolic stress and measured compartment pressure. In this examine, a delta P measurement of diastolic strain minus the measured compartment stress of less than 30mm Hg. Fasciotomy in an isolated harm is limb saving, but in a multiply injured patient, it have to be thought-about life saving. In a multiply injured patient, missed compartment syndromes can lead to myoglobinuria, renal failure, and sepsis, thus probably contributing to multiple system organ failure. The forearm has three compartments, a superficial and a deep flexor compartment, and an extensor compartment. When decompressing the forearm, consideration should also be given to the carpal tunnel as properly to avoid compression of the median nerve. The tibia has 4 compartments, which embody the anterior, lateral, superficial and deep posterior. Decompression may be accomplished utilizing the classic twoincision approach where a medial and lateral incision is made and the respective fascia recognized and incised. Similarly, using a protracted single lateral incision, the intermuscular septum between the anterior and lateral compartments is recognized, and the respective compartments are launched adjoining to the septum, followed by identifying and incising the fascia of the superficial posterior compartment. The deep posterior is identified by retracting the peroneal compartment anteriorly and the superficial compartment posteriorly and following the interosseous membrane. It is necessary to keep in mind the situation of the peroneal nerve as it may be injured. It is also important to keep incisions wide and to launch the fascia to the extent of the musculotendinous junction to find a way to ensure an entire decompression. The presence of a fracture is an absolute indication for instant fracture stabilization after decompression. All open tibia fractures should have 4 compartment fasciotomies carried out as a part of their irrigation and debridement. In addition to the forearm and tibia, compartment syndromes can happen although much less frequently, in the hand, foot, thigh, buttocks, and arm. Fractures with Associated Vascular Injury � Long bone fractures with an related vascular harm that jeopardizes the viability of the limb are of extremely high priority. Long Bone Fractures and the General Surgeon 443 � A frequent area of contention occurs relating to the sequencing of those instances, whether the fracture stabilization ought to occur first versus the vascular restore. On the other hand, fracture stabilization could also be a prolonged process and thus will extend ischemia time if it have been to occur previous to vascular repair. Clearly, it is unnecessary to carry out a vascular repair only to hold the fracture unstabilized, because the repair could be doomed with any subsequent motion, or to ask that the fracture be maintained in an malaligned manner. And conversely, it is senseless to carry out lengthy fracture stabilization and permit the extremity to turn out to be ischemic.
Cheap micronase 2.5 mg mastercard
Penetrating trauma of the back and flank is a extra doubtless reason for colonic damage diabetes symptoms numb toes micronase 2.5 mg purchase amex. Wall thickening of 3 mm has been mentioned as abnormal diabetes symptoms signs in dogs buy micronase 5 mg visa, however with incomplete distention, this is troublesome to decide. This streakiness may indicate edema from direct mesenteric harm or chemical irritation from spilled intestinal contents, or it could be attributable to a small amount of fluid or blood. Renal Trauma � Renal damage is frequent in blunt abdominal trauma and is often related to accidents of the adrenal gland. The delayed scans after 2-10 minutes will show that the arterial leak gets diluted and fewer dense after distinction is stopped, but the urinary leak turns into extra dense. A striated nephrogram, in all probability from stasis of urine in the blood-filled tubules, similar to the nephrogram of pyelonephritis, and is one other appearance of contusion. As with subcapsular hematomas in other organs, the capsule remains intact and accommodates hemorrhage. Associated hemorrhage and urine can leak into the renal parenchyma and the leaves of the renal fascia as nicely as into the anterior pararenal space. Unlike simple fractures, a shattered kidney does embody damage to the major segmental vessels that often end in major blood loss. This signal of hypovolemia occurs before scientific manifestations of hypotension or tachycardia. Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm � Pseudoaneurysms are eccentric saccular collection of distinction adjacent to the injured artery which will comprise thrombus. These have an eccentric focus of hyperdensity and surrounding low and heterogeneous density hematoma. The Foley catheter is clamped for no much less than 5 minutes earlier than the start of scanning. This may be very delicate for bladder accidents, and by comparing to the precystogram research, bladder extravasation can be distinguished from bowel or vascular extravasation. Traumatic left groin pseudoaneurysm of left femoral artery with brightly enhancing eccentric focus of contrast and surrounding blood. Bilateral pubic rami fractures (curved arrows) with associated obturator internus (o) hematomas. The potential house within the anterior abdominal wall between transversalis fascia and parietal peritoneum, extends superiorly within the belly wall and may encompass the anterior and lateral parts of the peritoneal cavity. Evaluation of the affected person with blunt stomach trauma: An proof primarily based strategy. Velmahos and Pantelis Vassiliu Definition and Mechanisms � Compartment syndrome occurs when the pressure increases within the tissue surrounded by a decent fascial envelope past a crucial stage necessary to maintain tissue perfusion. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the rise in stress is caused by tissue edema or intracompartmental bleeding. However, a number of different less frequent causes may result in increased intracompartmental pressures: snake chew, electrocution, intensive exercise, acute venous obstruction, infiltrated infusion. Pathophysiology � An initial ischemic insult by any of the above mentioned causes produces cell damage and increases the capillary permeability. Postischemic swelling occurs leading to additional compression of the intracompartmental tissue and aggravating the cellular ischemia. Upon reperfusion, the sudden provide of plentiful oxygen to the ischemic tissue leads to formation of oxygen free radicals that are answerable for ongoing cellular injury and increased fluid leak within the third house with resulting edema. Experiments have shown that after a stress of 20 mmHg, comparatively small increases in intracompartmental volume (bleeding, tissue swelling) trigger exponential will increase in strain. Nerve tissue is the most delicate to it, shows indicators of dysfunction Trauma Management, edited by Demetrios Demetriades and Juan Asensio. Pantelis Vassiliu, Division of Trauma/Critical Care, University of Southern California School of Medicine, Los Angeles, California, U. The anterior compartment lies between the tibia and the fibula and incorporates the anterior tibial artery and deep peroneal nerve, which innervates all the muscular tissues of the compartment and provides sensation to the primary net area of the foot. The lateral compartment lies over the fibula and contains the superficial peroneal nerve but no main vessel. The deep posterior compartment contains the tibioperoneal arterial trunk and the tibial nerve. The lateral compartment contains the neurovascular bundle and is the least regularly concerned of the three. The volar compartment accommodates all of the flexors of the hand, in addition to the ulnar and radial arteries, and median and ulnar nerves. The dorsal compartment accommodates the cellular wad, which may be thought of as a separate compartment. The brachial vessels and musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar nerves are in the anterior compartment, whereas the radial nerve is within the posterior. There are four hand compartments: central palmar, thenar, hypothenar, and interosseus. Similarly, the foot has 4 compartments: central, medial, lateral, and interosseous. Symptoms and Signs � the 6 Ps constitute the hallmark of compartment syndrome: pain, stress, paresthesia, paralysis, pulseless, and pallor. Pain is characteristically out of proportion even within the presence of associated extremity injuries. Paresthesia is an early symptom and needs to be evaluated alongside the distribution of the involved nerves, whereas paralysis signifies prolonged pressure on the nerve. Measurement of Pressures 38 � Intracompartmental pressures are measured immediately by the introduction of a needle into the compartment, linked to a pressure transducer. Pressures above 30 mmHg are thought of clearly abnormal, and pressures in the 20 to 30 mmHg vary are in the "grey zone". Complications of Compartment Syndrome � Local and systemic issues might come up. Because amassed poisonous substances are launched in the general circulation at the time of reperfusion, central organs, including the heart, lungs, or kidneys suffer an acute insult. The likelihood of great systemic insults is proportional to the quantity of ischemic muscle. Therefore, reperfusion of compartments which comprise giant muscles, ischemic for prolonged intervals of time, is associated with a better incidence of systemic cardiorespiratory abnormalities. Treatment � the treatment of compartment syndrome is instant stress launch by opening of the fascial envelope. A lateral incision halfway between the tibia and fibula is used to decompress the anterior and lateral compartments. A medial incision, about 2 finger-breadths medial to the tibia, is used to decompress the superficial and deep posterior compartments. All 4 compartments could be decompressed by a lateral incision, overlying the fibula, by elevating enough pores and skin flaps. In the infrequent event that the medial compartment is concerned, a further medial incision is necessary. The volar compartment can be decompressed by a medial S-shaped or straight incision, and the dorsal by a straight lateral incision.
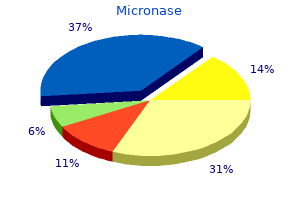
Micronase 5 mg online buy cheap
The peritoneum in the groin is separated from the transversalis fascia by adipose tissue diabetes type 1 dka micronase 5 mg cheap on line, leaving it poorly supported diabetes type 2 eggs discount micronase 5 mg without prescription. During hernia restore, the redundant portion should be excised, leaving only sufficient for a tension-free closure. Internal Inguinal Ring Above the middle of the inguinal ligament, where the transversalis fascia is dense and supplemented by the aponeurosis of the transversus, is a gap that varieties the lateral margin of the inguinal canal at the inner inguinal ring. A portion of peritoneum has been separated from the wire structures; it will be excised and closed at its base. It is that this association on both facet of the internal ring that in belly straining can act like a shutter. The buildings within the feminine groin are much less complicated than in the male because only the round ligament requires passage via the body wall. The coats of the spherical ligament are just like these of the spermatic twine: external spermatic fascia, cremasteric fascia and muscle, and inside spermatic fascia. Transversalis Fascia and Related Ligaments the transversalis fascia is exposed after elimination of the peritoneum and the properitoneal fat. In the pelvis, the transversalis fascia is steady with the endopelvic fascia, the portion that surrounds the exit websites of pelvic viscera, and the iliac fascia, all overlaying the epimysium of the underlying muscles. The transversalis fascia attaches posteriorly to that part of the iliac crest that lies between the origins of the iliacus and transversus abdominis and in addition attaches to the posterior margin of the inguinal ligament from the anterior superior iliac spine and over the iliac vessels. The posterior rectus sheath ends on the arcuate line, so the lower part of the muscle is roofed only with transversalis fascia. The exterior iliac artery and vein, earlier than they exit via the femoral sheath beneath the inguinal ligament. The thickened transversalis fascia is supplemented inferiorly by contributions from the transversus abdominis aponeurosis. The inside (deep) inguinal ring is a gap within the transversalis fascia, strengthened on the inferomedial portion by transversely arched fibers of the transversus abdominis that run laterally toward the anterior superior iliac backbone, forming the anterior crus of the deep crural arch. Bowel that had prolapsed into the hernia has been retracted back into the peritoneal cavity. Hernias that develop medial to the inferior epigastric vessels, in the area designated "direct house," are designated direct inguinal hernias. Those that develop lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, within the area designated "oblique house," are designated oblique inguinal hernias. The mesh is designed to cowl the websites the place direct, oblique, and femoral hernias may develop. It arises from the lateral a part of the inguinal ligament so that the tendon becomes the roof of the inguinal canal as it arches over it as the transversus abdominis arch to attach to the pubic crest and the pectineal line. It is in this medial and inferior area, the posterior wall of the inguinal canal, that the fibers of the transversus aponeurosis splay out, exposing the thinner transversalis fascia between them. The rectus abdominis tendon at its insertion along the pubic crest and tubercle shows a 2-cm extension of its investing fascia on the pectineal line that types the true falx inguinalis (Henle). Alternatively, the falx inguinalis is described as a dense portion of the transversus aponeurosis that inserts into the superior pubic ramus, part of the conjoined tendon. Its lateral border suits across the medial wall of the femoral sheath to lie 1 cm beneath and anterior to the pectineal line. It extends laterally from the base of the lacunar ligament alongside the pectineal line with additions from the pectineal fascia. The aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis and the iliopubic tract insert along the pectineal line subsequent to the medial half of the pectineal ligament; by way of the pectineal ligament the transversalis fascia is offered a line of insertion into the superior ramus of the pubis. Laterally, the pectineal ligament diverges extra caudally than the insertions of the muscular tissues of the anterior body wall. Iliopubic Tract the iliopubic tract (sometimes referred to as the anterior femoral sheath) seems as the thickened fibrous decrease border of the transversalis fascia that runs caudal to and parallel with the inguinal ligament. It marks the junction of the stomach a half of the transversalis fascia from that of the thigh. It is derived from the fascia of the outer stratum on the posterior side of the anterior stomach wall and from the identical stratum in the iliopsoas space (iliacus fascia). Whether it additionally contains fibers from the transversus abdominis aponeurosis has not been agreed on. The inguinal ligament is a superficial structure as a part of the external oblique layer of the groin, whereas the iliopubic tract is part of the deep, transversalis layer. The iliopubic tract is attached laterally along the iliac crest and to the anterior superior iliac spine, where the iliacus and lowest fibers of the transversus abdominis be a part of it. It then curves over the psoas main and the femoral artery and vein, making up a part of the anterior femoral sheath. In this way, the transversalis fascia is supplemented by transversely arched fibers that run laterally towards the anterior superior iliac backbone and medially behind the rectus abdominis. Its fibers pass medially to insert into the superior ramus of the pubis and into the pectineal ligament. Other, extra inferior fibers curve down to insert in the more lateral part of the pectineal ligament, thus defining the medial border of the femoral canal. They serve to strengthen the inferomedial portion of the rim of the internal inguinal ring and are an necessary component in hernia repair. Although a double layer of investing fascia, known as interparietal fascia, separates the transversus abdominis from the interior oblique over most of their extent, close to the inguinal canal and the conjoined tendon, the two muscle tissue are firmly connected to each other. Internal Oblique Removal of the transversus abdominis exposes the superficial portion of the conjoined tendon and shows the relation of the external oblique aponeurosis to the inguinal ligament. A double layer of interparietal fascia separates the internal and exterior indirect. In this space the internal indirect is especially muscular, with its fibers working transversely. The decrease portion of the internal indirect that originates laterally from the iliac fascia varieties an arch over the spermatic twine between the internal and exterior rings. A actually conjoined tendon might not type as a outcome of this arch from the interior oblique may terminate within the linea alba or rectus sheath with out curving downward in firm with the transversus to the pubic crest. The reflected inguinal ligament is an attenuated group of fibers ensuing from an expansion of the lateral crus of the inguinal ligament that passes behind the medial finish of the superficial inguinal ring. The lacunar ligament has three sides: (1) its base is attached to the pubic tubercle, (2) its inferior concave portion bounds the femoral canal medially, and (3) its deep margin connects with the pectineal fascia. It marks the sharp posterior edge of the pectineal surface (pectin), a triangular surface that lies on the superior ramus of the pubis from the pubic tubercle to the iliopubic eminence. The inguinal ligament attaches to the anterior superior iliac backbone on the finish of the iliac crest. Boundaries of the Inguinal Canal In a frontal view, the inguinal canal is seen as a potential triangular opening between the inferior margins of the exterior indirect and transversus abdominis aponeuroses, about four cm in size, starting at the lateral margin of the internal inguinal ring. The spermatic wire passes through it from its preperitoneal position to a subcutaneous one, carrying the layers of the abdominal wall with it. The roof consists of the lowermost fibers of the internal oblique and transversus abdominis as they arch over the canal to be a part of collectively because the conjoined tendon.
Buy discount micronase 5 mg
The blue colour on the left indicates elevated warmth associated to the presence of the varicocele juvenile onset diabetes symptoms order micronase 2.5 mg on-line. The area at proper diabetes definition by who buy micronase 5 mg fast delivery, missing blue shade, represents the relative coolness of the right scrotal contents. However, greater than one-third of cases have two or extra spermatic vein trunks on the stage of the interior ring, which can be missed during an inguinal method. Phlebography is reserved for failures to determine what explicit venous anomaly is current. That the testicular vein could be ligated with out apparent harm to the testis is a sign of the wealthy collateral circulation through the vasal and cremasteric vessels. Venous Drainage the veins come up diffusely from a dense microvascular mattress concerning the tubules. They be part of amassing venules, which move both peripherally or centrally, in contrast to the arteries, which are organized peripherally in the testis. The peripherally directed veins reach the tunica vasculosa and continue on the anterolateral facet of the testis, where they form massive channels on the surface. The centrally directed veins, providing the principal drainage of the testis, run to the rete testis, cross by way of the posterior floor of the tunica albuginea on the mediastinum, and are joined by veins from the anterior portion of the epididymis before they reach the pampiniform plexus. Lymphatic Drainage of the Testis and Epididymis Testicular Lymphatics the lymph within the network of intertubular tissue of the testis passes into channels in the interlobular septula. Some of these channels reach the mediastinum, where they type several larger trunks, however the majority pass kind of immediately through the tunica albuginea. All of these channels course along the upper posterior border of the testis to type a series of 4 to eight collector vessels that accompany the spermatic cord. At the crossing of the ureter, they separate from the blood vessels and deviate medially to terminate in the precaval nodes and the nodes in regards to the aorta at the site of origin of the testis. Usually, several vessels join one of the precaval nodes, whereas none might be a part of an adjoining node. In half the cases, the preaortic nodes obtain one or two trunks, and in 10% of circumstances, the node on the angle of the renal vein with the inferior vena cava receives one. Although the lumbar sympathetic trunk lies posterior to the outer stratum of the retroperitoneal fascia, it might be resected with the lymph nodes with ensuing anejaculation. Epididymal Lymphatics the lymph vessels run to the floor of the epididymis to be part of those within the epididymal tunic. Collectors from the top and body run with the department of the epididymal artery that supplies that area; similarly, those from the tail be a part of the appropriate branch. The collectors accompanying the epididymal artery ascend with the testicular vessels, whereas these accompanying the deferential artery run with that vessel to an exterior iliac node. In addition, small vessels connect the anterior portion of the testis with the pinnacle of the epididymis. Scrotal Lymphatics the network of lymphatics that covers all parts of the scrotum is very dense about the raphe, the positioning where the lymph vessels be part of the two units of collecting trunks. The superior trunks come up on the base of the penis, move round to the dorsum, and run with the penile trunks to the superomedial group of the superficial inguinal nodes. Seven or eight inferior trunks come up more posteriorly along the raphe, run in the genitofemoral fold to the lateral a part of the scrotum, and end in the inferior, lateral, and medial superficial inguinal nodes. Anastomoses generally occur between the lymphatics of the penile pores and skin and people of the skin of the adjacent thigh. Vessels from the perineal pores and skin join the inferior collecting trunks of the scrotum, which drain into the inferomedial group of superficial inguinal nodes. From the left testis, two-thirds of the collectors run to the lateral aortic nodes, particularly these mendacity most cephalad, and some terminate as low as the bifurcation; the opposite third finish within the preaortic nodes. Rarely, a lymph vessel could run on to the exterior iliac nodes after ascending with the vessels of the vas deferens. In the testis, terminal plexuses happen perivascularly and within the interstitial tissue. Reflex contraction of the dartos muscle in response to cold throws the well-vascularized scrotum into heat-conserving folds. In addition, a rich community of superficial nerve endings in the scrotal skin reflexively transmits indicators of heat and cooling for contraction or leisure of the cremaster muscle. Index A Abdomen somatic nerve provide, 29, 30f ureteral course in, 202, 203f Abdominal aorta, 8�9, 8f, 9f Abdominal body wall anterior, blood supply to , 78�79, 79f anterolateral, construction and function of, 71�79, 72t external indirect and attachments, 72�73, 73f extraperitoneal tissues, 77�78 inside stratum, 77 inside oblique and attachments, 73�74, 74f intercostal muscles, seventy four decrease, construction and function of, 71�79, 72t outer stratum, 77�78, 78f peritoneum, 77�78, 78f rectus abdominis, seventy six, 76f rectus sheath, 76�77, 77f linea alba, seventy seven, 77f topography, 71�72, 72f fascial layers and, 71�72 transversalis fascia, 77�78 transversus abdominis and attachments, 74�76, 75f blood supply, 75 conjoined tendon, 75 nerve supply, 75�76 serratus anterior, 75 Abdominal wall anterior blood provide to , 78�79, 79f lymphatic drainage and, seventy nine muscles, growth, 69�70 myotomes and, 69, 70f somites and, 69, 69f trunk muscles and, 69�70, 70f Abdominis rectus, seventy six, 76f transversus, 87 and attachments, 74�76, 75f inguinal area and, external strategy to , 110 Adnexae ligaments, 297�298, 297f structure and performance, 348�350 Adrenal cortex, 169, 169f, 169t Adrenal glands, 151�209 adrenal cortex origin and, 169, 169f, 169t anomalies, a hundred and seventy, 171f arteries, 208�209 blood provide, 169 arteries and, 169 veins and, 169 collateral circulation, 198 development, 169 fetal chromaffin our bodies and, distribution of, 169, 170f perform, 172�178 lymphatics, 209 medulla origin and, 169, 169f, 169t nerves, 209 posterior body wall, 178�179 relationships, 208�209, 209f construction, 172�178, 207�208, 207f, 208f surgical planes, 177�178, 177f vascular supply, 208�209, 209f veins, 209 Adrenal vein, 13 Adventitia, 6 Alar plates, 25 Allantoenteric diverticulum, 211, 213f Allantoic duct, hindgut incorporation of, 211, 212f Allantois, four formation, 211, 211f urachus formation and, 225�226 Anastomotic loops, 22 Anorectal anomalies, 231�235 imperforate anus, 231, 232f low infralevator rectal anomalies, 231�233 rectourethral fistula, 231, 232f Anterior division, 193�194 Anterior lamina, 172�174 Anterolateral body wall, 67�80 stomach physique wall, construction and function of, 71�79, 72t belly muscle improvement and, 69�70 stomach wall muscle growth, 69�70 anomalies, 70�71 prune belly syndrome and, 70�71, 70f, 71f Anus agenesis embryogenesis of, 233, 234f with perineal fistula, 233, 233f atresia, 232 canal development, 47�48 imperforate, 231, 232f membrane, persistent, 232 stenosis, 232 Aortic arches, 3 Aortic hiatus, 8 Appendix blood supply, 61�62, 62f vermiform, 60�61, 60f, 61f Arcuate ligament, median, 24 Arterial blood supply. It is an evolving discipline that applies analytical and quantitative strategies to consider the validity of available medical information, with the overall goal of identifying scientifically sound information or "best proof. Environment that Created the Need for Evidence-Based Medicine Traditional medical practice has been based on the basic assumption that physicians educated by way of rigorous medical faculty programs, postgraduate training packages, persevering with schooling actions, journals, personal experiences, and interplay with colleagues are properly outfitted to constantly render right diagnoses and do the right issues for their sufferers. Individual physicians are anticipated to combine complicated info by way of "scientific judgment" or the "artwork of medicine" [6]. The use of more formal analytical methods and mathematical models to determine options to these questions has been largely restricted to research projects. Research in the Seventies and Nineteen Eighties documented a number of main flaws in these elementary assumptions and stimulated an increasing give consideration to "technology evaluation" [9]. Wick Assessment of the Institute of Medicine emphasized as lately as the early Nineteen Eighties the need to develop well-designed research to consider applied sciences [10, 11]. Medical information proliferate at an ever-increasing fee and often embody a variety of features which are far too advanced, uncertain, or even contradictory for evaluation utilizing easy "If�Then" logic. These problems have led to a deeper appreciation for the necessity to incorporate computerbased analytical methods which are extra broadly used in different disciplines corresponding to epidemiology, engineering, and enterprise [6, 17�21]. They include numerous analytical tools of Decision Analysis theory such as choice trees, utility concept, and Bayes theorem that can be used to estimate the validity of diagnostic exams, carry out cost-effectiveness evaluation, analyze with metaanalysis the effectiveness of assorted interventions, render more consistent and efficient decisions that have an result on the welfare of individual sufferers, and evaluate the effectiveness of the various paradigms utilized in medical care [6, 18�21]. Project in 1981 to promote using literature evaluations and tips for numerous topics [24]. The emphasis was on particular person physicians amassing computerized literature searches 1 Introduction to Evidence-Based Pathology and Laboratory Medicine 5 looking on the sensitivity and specificity of tests, deciding on a check, assigning a pretest chance, calculating a posttest chance, and creating a administration plan. Basic Process for the Identification of Best Evidence and Its Integration into Guidelines, Rules, or Other Protocols 1. Formulation of particular questions regarding the diagnosis, prognosis, causation, and/or therapy of a patient with a specific medical drawback Evidence-based questions ideally attempt to handle these issues which might be most relevant to the materials being studied [1, 3�5]. These questions have to address an in depth question whose answer will present useful and sensible information for affected person care. For example, if a pathologist is interested in evaluating the results of the immunostains of a particular neoplasm, the summary of proof from the literature would wish to embrace particular questions such as: Which tissues were studied Did the study have sufficient energy to detect important variations in immunoreactivity Sackett and associates have instructed the usage of 5 steps for the identification of "finest proof" and its integration with private medical experience and values into guidelines, guidelines, or different protocols that can be utilized for the care of particular person patients (Table 1. Are the patients in the examine being referred to similar to these of the doctor utilizing the evidence Will the evidence in hand have a major influence in managing the illness in query Wick of questions instructed by Sackett and colleagues to be considered in the assessment of research that report "prognostic" info. Search for specific data within the scientific literature Hundreds of electronic bibliographic databases are at present out there on-line. Such a bewildering array of data sources has stimulated the development of better search engines like google and yahoo that apply more advanced methods than easy Boolean searches based on the analysis of beforehand indexed information [36�39]. For instance, the builders of the extensively used net search engine Google have recently sponsored the event of Google Scholar to automatically analyze and extract citations from quite lots of "scholarly". This figure shows the web web page of Essential Evidence Plus, sponsored by a writer, WileyBlackwell 1 Introduction to Evidence-Based Pathology and Laboratory Medicine 7.