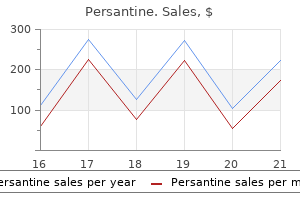
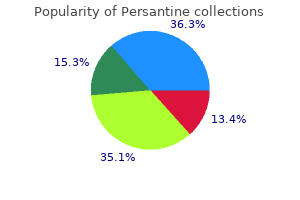
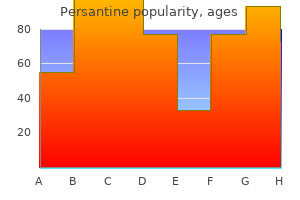
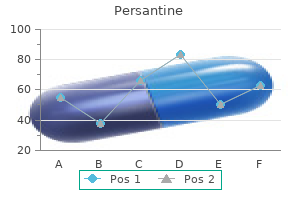
Persantine
Persantine dosages: 100 mg, 25 mg
Persantine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

Discount persantine 25mg on-line
Rubrospinal fibres in non-human primates also set up monosynaptic connections with motor neurones innervating distal limb muscles 714x treatment 25 mg persantine order otc. Rubrospinal neurones receive cortical afferent fibres primarily from the precentral gyrus treatment keloid scars 25 mg persantine order overnight delivery. Group B pathways provide the capacity for impartial, flexion-biased actions of the limbs and shoulders, and particularly of the elbows and palms. The termination of the 2 teams of brain stem pathways is essentially overlapped by that of the corticospinal pathway arising from motor areas of the frontal lobe. Functionally, this a part of the corticospinal system enhances the brain stem controls. In addition, it provides the capability for fractionation of movements, as exemplified by particular person finger actions, which are probably executed by way of direct corticospinal connections with motor neurones. They connect neurones inside the identical phase or other neurones in additional distant segments of the spinal wire and thus subserve intrasegmental and intersegmental integration and coordination. Propriospinal fibres are concentrated primarily across the margins of the gray matter. Descending pathways finish on particular subgroups of propriospinal neurones, and these in flip relay to motor neurones and other spinal neurones. The system mediates all those automated features that continue after transection of the spinal twine, together with sudomotor and vasomotor actions and bowel and bladder functions. Some propriospinal axons are very quick and span only one section; others run the entire size of the wire. The shortest axons lie immediately adjoining to the grey matter, and the longer ones are situated more peripherally. Propriospinal neurones may be categorized in accordance with the length of their axons as lengthy, intermediate or brief. Axons from the long propriospinal neurones of the cervical cord descend bilaterally, whereas those from the corresponding lumbosacral neurones ascend mainly contralaterally. Propriospinal fibres in the totally different components of the white funiculi are distributed preferentially to particular areas of the spinal grey matter. In the spinal enlargements, the propriospinal fibres in the dorsolateral funiculus project to the dorsal and lateral elements of the intermediate zone and in addition to spinal motor neurones that supply distal limb muscle tissue, especially those of the arms and toes. Other propriospinal fibres run in the medial a part of the ventral funiculus and journey mainly to the ventromedial part of the intermediate zone, which characteristically accommodates long propriospinal neurones, and to motor neurones innervating axial and girdle muscle tissue. Tract of Lissauer the tract of Lissauer, or the dorsolateral tract, lies between the apex of the dorsal horn and the floor of the spinal wire, the place it surrounds the incoming dorsal root fibres. It is present all through the spinal twine and is most developed within the upper cervical regions. These axons bifurcate into ascending and descending branches as they enter the cord. The branches travel in the tract of Lissauer for one or two segments and give off collaterals, which end on and around neurones within the dorsal horn. The tract additionally contains propriospinal fibres, some of which are short axons of small substantia gelatinosa neurones, which reenter the dorsal horn. She had experienced some tingling paraesthesia within the feet before going to mattress but had no other neurological complaints. A prognosis of acute transverse myelitis is made, and he or she is given a course of corticosteroids. At follow-up three months later, she is strolling with a walker and exhibits severe spasticity in the legs, with exaggerated reflexes and extensor plantar responses. Discussion: Acute transverse myelitis is an acute or subacutely evolving idiopathic inflammatory dysfunction of the spinal twine, normally presenting as an acute sensorimotor segmental myelopathy. The lesions usually involve a quantity of adjacent segments of the spinal twine; both gray and white matter are affected. It may happen after systemic an infection; a quantity of sclerosis, vasculitis and different autoimmune situations have additionally been implicated. High-dose corticosteroid treatment may be of some benefit, but many patients experience permanent incapacity. In estimating the vertebral ranges of cord segments within the adult, a useful approximation is that in the cervical area, the tip of a vertebral spinous process corresponds to the succeeding twine section. The eleventh thoracic backbone overlies the third lumbar phase, and the twelfth is opposite the primary sacral section. When making this estimate by palpation of the vertebral spines, the relationship of the person spines to their vertebral bodies ought to be remembered. Complete division above the fourth cervical segment causes respiratory failure due to the loss of activity within the phrenic and intercostal nerves. Lesions between C5 and T1 paralyse all 4 limbs (quadriplegia), however the results in the higher limbs differ with the positioning of injury: on the fifth cervical section, paralysis is complete; at the sixth, every arm is positioned in abduction and lateral rotation, with the elbow flexed and the forearm supinated, due to unopposed exercise within the deltoid, supraspinatus, rhomboid and brachial flexors (all supplied by the fifth cervical spinal nerves). However, sensation is retained in areas innervated by segments above the lesion; thus, cutaneous sensation is retained within the neck and chest right down to the second intercostal house, as a end result of this space is innervated by the supraclavicular nerves (C3 and C4). At thoracic levels, division of the wire paralyses the trunk under the segmental stage of the lesion and each lower limbs (paraplegia). The first sacral neural phase is approximately level with the thoracolumbar vertebral junction; injury right here, which is common, paralyses the urinary bladder, the rectum and the muscle tissue provided by the sacral segments, and cutaneous sensibility is misplaced within the perineum, buttocks, backs of the thighs and legs and soles of the ft. The roots of lumbar nerves descending to be part of the cauda equina may be broken at this level, inflicting full paralysis of both decrease limbs. Lesions under the primary lumbar vertebra may divide or injury the cauda equina, however severe nerve injury is rare and is usually confined to the spinal roots on the degree of the trauma. Neurological symptoms may happen because of interference with the spinal blood provide, notably within the decrease thoracic and upper lumbar segments. A 30-year-old man is involved in a avenue brawl and is stabbed in the neck, with the knife penetrating at roughly the C4 degree. Examination in the emergency room demonstrates a flaccid paralysis of the right arm and leg, with loss of reflexes; lack of vibratory and position sense beneath and ipsilateral to the level of the harm; and contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation, also below the level of the lesion. Discussion: this affected person presents with typical Brown� S�quard syndrome as a manifestation of hemisection of the spinal wire at roughly the C4�5 stage. The clinical syndrome displays the level of the lesion, affecting the corticospinal tracts and posterior columns and being responsible for the ipsilateral paralysis and lack of proprioception and vibratory senses below the lesion. Involvement of the spinothalamic tract is responsible for the contralateral loss of ache and temperature sensations. Brown�S�quard syndrome is regularly of traumatic origin but could also be encountered with demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis, tumour, or different focal myelopathic problems. Neurofibromas could happen on the roots and nerves in the root canals, and as they enlarge, they turn into dumbbell formed, with each intra- and extraspinal components in continuity. The scientific image may thus embody paradoxical options as this uneven space-occupying lesion grows.
Generic 100 mg persantine otc
This consists of the olfactory trigone and tubercle medicine 750 dollars order persantine 25 mg amex, anterior perforated substance and uncus (hook) and entorhinal space of the anterior part of the future parahippocampal gyrus treatment variance 100 mg persantine discount overnight delivery. The forward growth of the temporal pole and the overall expansion of the neocortex cause the lateral olfactory gyrus to bend laterally, with the summit of the convexity mendacity on the anteroinferior corner of the creating insula. During the fourth and fifth months, a lot of the piriform area becomes submerged by the adjoining neocortex, and within the grownup, solely part of it remains visible on the inferior side of the cerebrum. At first it forms a steady, virtually round strip on the medial and inferior elements of the hemisphere. Below and in entrance, the place the stalk of the olfactory tract is connected, it constitutes part of the piriform space. In this region the neural progenitors of the creating cortex proliferate and migrate, and the wall of the hemisphere thickens and produces A E 21 weeks B 30 weeks F 24 weeks C 34 weeks 26 weeks G D 28 weeks 40 weeks. Note the changing prominence and relative positions of the frontal, occipital and significantly temporal poles of the hemisphere. At the earliest stage (A), the lateral cerebral fossa is already obvious; its flooring covers the developing corpus striatum within the depths of the hemisphere and progressively matures into the cortex of the insula. The fossa is bounded by overgrowing cortical regions-the frontal, temporal and parietal opercula-which progressively converge to bury the insula; their approximation types the lateral cerebral sulcus. By the sixth month, the central, pre- and postcentral, superior temporal, intraparietal and parieto-occipital sulci are all clearly seen. In the next stages shown, all of the remaining principal and subsidiary sulci quickly seem, and by forty weeks (G), all the options that characterize the adult hemisphere in terms of floor topography are current in miniature. It seems first on the medial wall of the hemisphere within the space above and in entrance of the lamina terminalis (paraterminal area) and progressively extends backward, curving into the region of the temporal pole, where it adjoins the piriform area. The marginal zone in the neighbourhood of the hippocampus is invaded by neuroblasts to form the dentate gyrus. Both prolong from the paraterminal area backward, above the choroid fissure, and comply with its curve downward and forward towards the temporal pole, where they continue into the piriform space. A shallow groove (the hippocampal sulcus) crosses the medial surface of the hemisphere throughout the hippocampal formation. The efferent fibres from the cells of the hippocampus acquire alongside its medial edge and run ahead immediately above the choroid fissure. Anteriorly they flip ventrally and enter the lateral part of the lamina terminalis to gain the hypothalamus, the place they finish in and around the mammillary body and neighbouring nuclei. These fibres follow the route supplied by the apposition of the lateral side of the thalamus with the medial aspect of the corpus striatum, and as they accomplish that, they divide the latter nearly completely into a lateral half, the lentiform nucleus, and a medial part, the caudate nucleus; these two nuclei stay confluent solely of their anteroinferior areas. The corticospinal tracts begin to develop within the ninth week of fetal life and have reached their caudal limits by the twenty-ninth week. The fibres destined for the cervical and upper thoracic areas and concerned in innervation of the higher limbs are upfront of these involved with the decrease limbs, which in flip are in advance of those involved with the face. The appearance of reflexes in these three parts of the body follows a comparable sequence. The majority of subcortical nuclear lots receive terminals from descending fibres of cortical origin. These are joined by thalamocortical, hypothalamocortical and different afferent ascending bundles. The internal capsular fibres pass lateral to the pinnacle and physique of the caudate nucleus, anterior cornu and central part of the lateral ventricle, rostroventral extensions and physique of the fornix and dorsal thalamus and dorsal choroidal fissure; they pass medial to the lentiform nucleus. Formation of gyri and sulci - Apart from the shallow hippocampal sulcus and the lateral cerebral fossa, the surfaces of the hemisphere stay clean and uninterrupted till early within the fourth month. The parieto-occipital sulcus seems at about that time on the medial facet of the hemisphere. Its look appears to be related to an increase within the number of splenial fibres within the corpus callosum. Over the same interval, the posterior a half of the calcarine sulcus seems as a shallow groove extending forward from a area close to the occipital pole. It is a real infolding of the cortex within the lengthy axis of the striate area and produces an elevation, the calcar avis, on the medial wall of the posterior horn of the ventricle. During the fifth month the cingulate sulcus seems on the medial aspect of the hemisphere, and sulci seem on the inferior and superolateral aspects B Posterior commissure Habenular commissure Splenium of corpus callosum Corpus callosum Hippocampal commissure Anterior commissure Optic chiasma 16 weeks. The telencephalon gives rise to commissural tracts that integrate the actions of the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The central, precentral and postcentral sulci appear, every in higher and lower elements; these two parts often coalesce shortly afterward, although they might stay discontinuous. The superior and inferior frontal, intraparietal, occipital, superior and inferior temporal, occipitotemporal, collateral and rhinal sulci all make their appearance during the identical period. Development of commissures - the development of the commissures causes a profound alteration within the medial wall of the hemisphere. At the time of their appearance, the 2 hemispheres are related to one another by the median part of the telencephalon. The roof plate of this area remains epithelial, whereas its ground turns into invaded by the decussating fibres of the optic nerves and creating hypothalamic nuclei. These two routes are thus not obtainable for the passage of commissural fibres from hemisphere to hemisphere across the median aircraft; these fibres therefore pass by way of the anterior wall of the interventricular foramen, the lamina terminalis. The first commissures to develop are these related to the palaeocortex and archicortex. Fibres of the olfactory tracts cross in the ventral or decrease part of the lamina terminalis and, together with fibres from the piriform and prepiriform areas and the amygdaloid our bodies, kind the anterior a part of the anterior commissure. In addition, the two hippocampi turn into interconnected by transverse fibres that cross from fornix to fornix in the higher a part of the lamina terminalis as the commissure of the fornix. The commissures of the neocortex develop later and comply with the pathways already established by the commissures of the limbic system. Fibres from the tentorial surface of the hemisphere be a part of the anterior commissure and represent its larger posterior part. All the opposite commissural fibres of the neocortex affiliate themselves closely with the commissure of the fornix and lie on its dorsal surface. These fibres increase enormously in number, and the bundle rapidly outgrows its neighbours to kind the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum originates as a thick mass connecting the 2 cerebral hemispheres round and above the anterior commissure. The rostrum of the corpus callosum develops later and separates part of the rostral end of the limbic space from the remainder of the cerebral hemisphere. Further backward progress of the trunk of the corpus callosum then leads to the entrapped part of the limbic space becoming stretched out to kind the bilateral septum pellucidum. As the corpus callosum grows backward, it extends above the choroidal fissure, carrying the commissure of the fornix on its undersurface. In this way a model new ground is fashioned for the longitudinal fissure, and extra buildings come to lie above the epithelial roof of the third ventricle. In its backward development, the corpus callosum invades the area hitherto occupied by the higher part of the archaeocortical hippocampal formation, and the corresponding components of the dentate gyrus and hippocampus are reduced to vestiges, the indusium griseum and the longitudinal striae.
Purchase persantine 100mg line
Lower lumbar and higher sacral roots are the biggest symptoms questions persantine 100mg purchase with amex, and their rootlets are most numerous treatment zollinger ellison syndrome order 100 mg persantine amex. Kubik and M�ntener (1969) affirm that lumbar, sacral and coccygeal roots descend with growing obliquity to their exits. The spinal twine ends close to the lower border of the primary lumbar vertebra, and the lengths of successive roots quickly increase; the ensuing assortment of roots is the cauda equina. The largest roots, and therefore the biggest spinal nerves, are continuous with the spinal cervical and lumbar swellings and innervate the higher and lower limbs. Dorsal root ganglion Sympathetic ganglion Grey ramus communicans Sympathetic trunk Spinal Ganglia (Dorsal Root Ganglia) Spinal ganglia are large groups of neurones on the dorsal spinal roots. A ganglion is bifid medially the place the two fascicles of the dorsal root emerge to enter the wire. Ganglia are normally situated within the intervertebral foramina, instantly lateral to the perforation of the dura mater by the roots. However, the first and second cervical ganglia lie on the vertebral arches of the atlas and axis, the sacral lies inside the vertebral canal, and the coccygeal ganglion often lies throughout the dura mater. Small aberrant ganglia typically occur on the upper cervical dorsal roots between the spinal ganglia and the wire. These soon divide into dorsal and ventral rami, each of which obtain fibres from both roots. At all ranges above the sacral, this division happens inside the intervertebral foramen. Division of the sacral spinal nerves occurs inside the sacral vertebral canal, and the dorsal and ventral rami exit individually through posterior and anterior sacral foramina at every level. Spinal nerves trifurcate at some cervical and thoracic levels, and the third branch is identified as a ramus intermedius. At or distal to its origin, each ventral ramus gives off recurrent meningeal (sinuvertebral) branches and receives a grey ramus communicans from the corresponding sympathetic ganglion. The thoracic and first and second lumbar ventral rami every contributes a white ramus communicans to the corresponding sympathetic ganglia. The second, third and fourth sacral nerves additionally supply visceral branches, unconnected with sympathetic ganglia, that carry a parasympathetic outflow on to the pelvic plexuses. The seventh and eighth cervical and the first thoracic nerves are similar in measurement to the sixth cervical nerve. The first sacral is the biggest spinal nerve; thereafter, the sacral nerves decrease in measurement. The recurrent meningeal or sinuvertebral nerves quantity two to 4 filaments on all sides and occur in any respect vertebral ranges. Each receives one or more rami from a nearby grey ramus communicans or immediately from a thoracic sympathetic ganglion; most then pursue a recurrent (often perivascular) course into the vertebral canal by way of the intervertebral foramen ventral to the dorsal root ganglion. Here these mixed sensory and sympathetic nerves divide into transverse, ascending and descending branches that are distributed to the dura mater, partitions of blood vessels, periosteum, ligaments and intervertebral discs within the anterolateral area of the vertebral canal. Fine meningeal branches often move dorsal to reach the spinal ganglia to innervate the dorsal dura, periosteum and ligaments; others cross ventrally to the posterior longitudinal ligament. Ascending branches of the higher three cervical meningeal nerves are large and are distributed to the dura mater within the posterior cranial fossa. Meningeal nerves are clinically essential in relation to referred ache, which is characteristic of many spinal problems and occipital headache. The upper part of the diagram shows the somatic components of the spinal nerve roots; the decrease part exhibits the visceral elements: somatic efferent and preganglionic sympathetic fibres (red), somatic and visceral afferent fibres (blue) and postganglionic sympathetic fibres (black). These prolongations, the spinal nerve sheaths (root sheaths), steadily lengthen as the spinal roots turn into more and more oblique. Each individual dorsal and ventral root runs within the subarachnoid space with its own covering of pia mater. Each root pierces the dura separately, taking a sleeve of arachnoid with it, before joining within the dural prolongation simply distal to the spinal ganglion. The dural sheaths of the spinal nerves fuse with the epineurium, within or barely beyond the intervertebral foramina. Shortening or obstruction of this sleeve seen on myelography indicates compression of the spinal nerve. At the cervical degree, where the nerves are brief and the vertebral movement is biggest, the dural sheaths are tethered to the periosteum of the adjoining transverse processes. At the outer finish of the foramen, the nerve could lie above or below transforaminal ligaments. At lumbar ranges, though L5 is the most important nerve, its foramen is smaller than those of L1�4, which renders this nerve particularly vulnerable to compression. Somatic efferent fibres that innervate skeletal muscle tissue are axons of, and neurones in the spinal anterior gray column. Visceral parts - Visceral elements are additionally afferent and efferent and belong to the autonomic nervous system. Preganglionic visceral efferent sympathetic fibres are axons of neurones within the spinal lateral gray column in the thoracic and higher two or three lumbar segments; they be part of the sympathetic trunk alongside corresponding white rami communicantes and synapse with postganglionic neurones distributed to non-striated muscle or glands. The preganglionic visceral efferent parasympathetic fibres are axons of neurones in the spinal lateral grey column of the second to fourth sacral segments; they go away the ventral rami of corresponding sacral nerves and synapse in pelvic ganglia. The postganglionic axons are distributed primarily to muscle or glands in the partitions of the pelvic viscera. Their peripheral processes pass through white rami communicantes and, with out synapsing, by way of a number of sympathetic ganglia to end in viscera. Central processes of ganglionic unipolar neurones enter the spinal wire by posterior roots and synapse on somatic or sympathetic efferent neurones, often via interneurones, finishing reflex paths. Alternatively, they might synapse with different neurones within the spinal or brain stem grey matter, which gives origin to a variety of ascending tracts. The nerves are shown lying on the superficial muscle tissue; on the left side, the restrict of the pores and skin area equipped by these nerves is indicated by the dotted line. The nerves are numbered on the proper aspect; the spines of the seventh cervical, sixth and twelfth thoracic and first and fifth lumbar vertebrae are labelled in bold on the left side. Variations of Spinal Roots and Nerves the programs of spinal roots and nerves in relation to the thecal sac and vertebral and radicular canals could additionally be aberrant. An particular person intervertebral foramen might include a duplicated sheath, nerve and roots, which are then absent at an adjacent level. These anomalies have been described and classified for the lumbosacral backbone by Neidre and Macnab (1983). Thoracic ventral rami run independently and retain a largely segmental distribution. Cervical, Rami of the Spinal Nerves lumbar and sacral ventral rami join near their origins to type plexuses. Dorsal (posterior primary) rami of spinal nerves are normally smaller than the ventral rami and are directed posteriorly. Retaining a segmental distribution, they all (except for the primary cervical, fourth and fifth sacral and coccygeal) divide into medial and lateral branches that supply the muscle tissue and skin of the posterior regions of the neck and trunk. Cervical dorsal spinal rami - Each cervical spinal dorsal ramus, except the primary, divides into medial and lateral branches that innervate muscle tissue.
Persantine 100mg purchase free shipping
Following traumatic damage or significant postoperative bleeding symptoms youre pregnant buy discount persantine 100mg, the critical platelet depend for transfusion is often based mostly on consensus remedy somewhat than true objective knowledge medications knowledge buy cheap persantine 100 mg on-line. Although a rely of fifty,000 or extra is beneficial, the brink for administration of platelets, particularly in instances of dilutional coagulopathy, stays unclear as do the perfect ratio of platelets to other blood components. Because of the critical role of fibrinolysis with severe bleeding and trauma, the antifibrinolytic agent tranexamic acid is increasingly used as a therapeutic technique. Inhibiting fibrinolysis during acute bleeding has many beneficial effects including preserving initial clot formation at a bleeding site that will otherwise be broken down. Postpartum hemorrhage is an important explanation for lifethreatening hemorrhage and continues to be a major cause of maternal mortality. As in all life-threatening bleeding, a therapy algorithm that options a large transfusion protocol is necessary. Managing life-threatening and uncontrolled bleeding is a medical problem that can occur following traumatic damage, throughout major surgical procedures, and following supply. A multimodal and multispecialty method has developed for the optimal resuscitative strategy to hemorrhagic shock (Table 31-1). Coagulopathy related to large transfusion is a posh, multifactorial scientific downside. The function of hypothermia, dilutional coagulopathy, platelet dysfunction, and fibrinolysis also wants to be considered. Transfusion algorithms provide enough factor and hemostatic alternative, although the ideal ratio of assorted blood components and issue concentrates are nonetheless being decided. The liver is split into four lobes consisting of fifty,000 to one hundred,000 individual hepatic lobules. Hepatic lobules are lined by macrophages, which phagocytize 99% or extra of bacteria within the portal venous blood (crucial as a end result of the portal venous blood drains the gastrointestinal tract and usually incorporates colon bacteria). The liver receives a twin afferent blood provide from the hepatic artery and portal veins. Total hepatic blood move is roughly 1,450 mL per minute or approximately 29% of the cardiac output (portal vein provides 75% of the total circulate but solely 50% to 55% of the hepatic oxygen supply, and the hepatic artery offers only 25% of total hepatic blood circulate but provides 45% to 50% of the hepatic oxygen requirements). Hepatic artery blood circulate maintains vitamin of connective tissues and partitions of bile ducts (loss of hepatic artery blood move can be fatal due to ensuing necrosis of significant liver structures). Portal vein blood move, mixed with the resistance to portal vein blood move throughout the liver, determines portal venous pressure (normally 7 to 10 mm Hg). Blood from peripherally positioned branches of the hepatic artery and vein perfuses the sinusoids. Sympathetic nervous system innervation is from T3 to T11 and is mediated by way of -adrenergic receptors (principally answerable for resistance and compliance of hepatic venules). Fibrotic constriction attribute of hepatic cirrhosis (most usually due to chronic alcohol abuse and hepatitis C) can increase resistance to portal vein blood flow as evidenced by portal venous pressures of 20 to 30 mm Hg (portal hypertension). The ensuing increased resistance to portal vein blood flow might result in improvement of shunts (varices) to permit blood circulate to bypass the hepatocytes. A decrease in portal vein blood move is accompanied by a rise in hepatic artery blood move by as a lot as one hundred pc. Surgical stimulation may lower hepatic blood move, unbiased of the anesthetic drug administered. The best decreases in hepatic blood circulate happen during intraabdominal operations, presumably due to mechanical interference of blood move produced by retraction within the operative space, in addition to the release of vasoconstricting substances similar to catecholamines. The liver normally incorporates roughly 500 mL of blood or roughly 10% of the total blood volume (may accommodate as much as 1 L of extra blood with elevated venous pressure). The liver is the one most important source of additional blood throughout strenuous exercise or acute hemorrhage. Hepatocytes frequently type bile (500 mL daily) after which secrete it into bile canaliculi, which empty into progressively larger ducts finally reaching the frequent bile duct. The most potent stimulus for emptying the gallbladder is the presence of fats in the duodenum, which evokes the release of the hormone cholecystokinin by the duodenal mucosa (this hormone causes selective contraction of the gallbladder clean muscle). Bile salts mix with lipids within the duodenum to type water-soluble complexes (micelles) that facilitate gastrointestinal absorption of fats (triglycerides) and fat-soluble nutritional vitamins (vitamin K is critical for activation of a number of clotting factors). After roughly 120 days, the cell membranes of erythrocytes rupture and the launched hemoglobin is converted to bilirubin in reticuloendothelial cells. Jaundice is the yellowish tint of physique tissues that accompanies accumulation of bilirubin in extracellular fluid. Skin shade usually begins to change when the plasma focus of bilirubin increases to roughly three times normal. The commonest types of jaundice are hemolytic jaundice, because of elevated destruction of erythrocytes, and obstructive jaundice, due to obstruction of bile ducts. Once cholesterol has reached the liver, it could be excreted within the bile in association with bile acids (may precipitate as gallstones). Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins is decided by regular hepatic perform. Degradation of sure hormones (catecholamines and corticosteroids), as nicely as medication, is a crucial function of the liver. The liver is responsible for -oxidation of fatty acids and formation of acetoacetic acid. The most necessary liver functions in protein metabolism are oxidative deamination of amino Chapter 32 � Gastrointestinal Physiology 557 acids, formation of urea for removing of ammonia, formation of plasma proteins and coagulation components, and interconversions (transfer of 1 amino group to another amino acid) among completely different amino acids. Albumin fashioned in the liver is critically important for maintaining plasma oncotic stress in addition to providing an essential transport position (half-time for albumin is about 21 days such that plasma albumin concentrations are unlikely to be significantly altered in acute hepatic failure). The primary perform of the gastrointestinal tract is to present the body with a continual provide of water, electrolytes, and nutrients. The smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract is a syncytium such that electrical signals originating in one easy muscle fiber are simply propagated from fiber to fiber. Most of the blood circulate to the gastrointestinal tract is to the mucosa to supply power wanted for producing intestinal secretions and absorbing digested materials. Stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system increases native blood flow, whereas stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system causes vasoconstriction (permits shunting of blood from the gastrointestinal tract for brief durations during train or when increased blood move is required by skeletal muscle tissue or the heart). As a result, the strain in the portal vein averages 7 to 10 mm Hg, which is considerably higher than the simply about zero stress in the inferior vena cava. Cirrhosis of the liver, most incessantly attributable to alcoholism, is characterised by elevated resistance to portal vein blood flow due to alternative of hepatic cells with fibrous tissue that contracts across the blood vessels. Approximately 2 L of water are ingested each day and approximately 7 L of varied secretions enter the gastrointestinal tract. The most necessary of those collaterals are from the splenic veins to the esophageal veins. The esophageal mucosa overlying these varicosities might become eroded, leading to life-threatening hemorrhage.
Discount persantine 25mg with visa
The septum varies in anteroposterior extent from four to 6 mm symptoms 8 days after iui discount persantine 100mg fast delivery, and it diminishes caudally as the canal turns into extra dorsally placed and the wire contracts symptoms 6dpiui cheap persantine 25mg on line. Dorsal roots (strictly rootlets) of spinal nerves enter the wire alongside this sulcus. The white substance between the posterior median and posterolateral sulcus on each side is the posterior funiculus. In cervical and upper thoracic segments, a longitudinal posterointermediate sulcus marks a septum dividing every posterior funiculus into two massive tracts: the fasciculus gracilis (medial) and the fasciculus cuneatus (lateral). Between the posterolateral sulcus and anterior median fissure is the anterolateral funiculus. This is subdivided into anterior and lateral funiculi by ventral spinal roots that cross through its substance to concern from the floor of the twine. The anterior funiculus is medial to , and includes, the emerging ventral roots; the lateral funiculus lies between the roots and the posterolateral sulcus. The filum terminale, a filament of connective tissue approximately 20 cm long, descends from the apex of the conus medullaris. Its upper 15 cm, the filum terminale internum, is sustained within extensions of the dural and arachnoid meninges and reaches the caudal border of the second sacral vertebra. Its ultimate 5 cm, the filum terminale externum, fuses with the investing dura mater after which descends to the dorsum of the first coccygeal vertebral phase. A few strands of nerve fibres, which in all probability symbolize roots of rudimentary second and third coccygeal spinal nerves, adhere to its upper part. A capacious a half of the subarachnoid space surrounds the filum terminale internum and is the standard access website for lumbar puncture. They cross the subarachnoid house and traverse the dura mater individually, uniting in or near their intervertebral foramina to kind the (mixed) spinal nerves. The part has opened up the subarachnoid house as far as the first sacral vertebra. Note the difference in ranges between the inferior limits of the spinal cord and meninges. Lumbar enlargement than the vertebral column, the extra caudal spinal roots descend for various distances round and beyond the cord to attain their corresponding foramina. In so doing they kind, largely distal to the apex of the cord, a divergent sheaf of spinal nerve roots, the cauda equina, which is gathered across the filum terminale within the spinal theca. Ventral spinal roots comprise efferent somatic and, at some ranges, efferent sympathetic nerve fibres that emerge from their spinal sources. The rootlets constituting every ventral root emerge from the anterolateral sulcus over an elongated vertical elliptical space. Dorsal spinal roots bear ovoid swellings, the spinal ganglia, one on each root proximal to its junction with the corresponding ventral root in an intervertebral foramen. Each root followers out into six to eight rootlets before getting into the cord in a vertical row within the posterolateral sulcus. Dorsal roots are normally mentioned to comprise solely afferent axons (both somatic and visceral) from unipolar neurones in spinal root ganglia, but they might also comprise a small quantity (3%) of efferent fibres and autonomic vasodilator fibres. Each ganglionic neurone has a single short stem that divides into a medial department, which enters the spinal cord through a dorsal root, and a lateral department, which passes peripherally to a sensory end-organ. The spinal dura mater forms a tube whose higher finish is hooked up to the sting of the foramen magnum and to the posterior surfaces of the second and third cervical vertebral bodies, in addition to to the posterior longitudinal ligament by fibrous bands, especially toward the caudal end of the vertebral canal. It invests the skinny spinal filum terminale, descends to the again of the coccyx, and blends with the periosteum. The meningeal coverings of the spinal roots and nerves are described later in this chapter. The epidural house lies between the spinal dura mater and the tissues that line the vertebral canal. Within the vertebral column, it has been instructed that the outer endosteal Epidural Space 118 Chapter 8 / Spinal Cord and Nerve Roots. Note the fusiform cervical and lumbar enlargements of the twine and the altering obliquity of the spinal nerve roots as the cord is descended. The cauda equina is undisturbed on the best however has been unfold out on the left to present its particular person components. L1 Posterior funiculus Posterior median septum Lateral funiculus Central canal Posterior column Thoracic nucleus Lateral column Anterior column S1 Anterior funiculus Anterior median fissure. Note the dorsal nerve rootlets in a single linear row, and the ventral rootlets in three or extra rows. It accommodates loosely packed connective tissue, fats, a venous plexus, small arterial branches, lymphatics and fine fibrous bands that join the theca with the liner tissue of the vertebral canal. These bands, the meningovertebral ligaments, are greatest developed anteriorly and laterally. There is also a midline attachment from the posterior spinal dura to the ligamentum nuchae on the atlanto-occipital and atlanto-axial levels (Dean and Mitchell 2002). The venous plexus consists of longitudinally organized chains of vessels linked by circumdural venous `rings. In the lumbar region, the dura mater is apposed to the walls of the vertebral canal anteriorly and hooked up by connective tissue in a way that permits displacement of the dural sac throughout movement and venous engorgement. Adipose tissue is present posteriorly in recesses between the ligamentum flavum and the dura. The connective tissue extends for a brief distance through the intervertebral foramina alongside the sheaths of the spinal nerves. Like the principle thecal sac, the root sheaths are partially tethered to the walls of the foramina by nice meningovertebral Trochlear nerve Tentorial notch Median sulcus of fourth ventricle Trigeminal nerve Transverse dural venous sinus Facial and vestibulocochlear nerves Glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves Accessory nerve, spinal root Vertebral artery First cervical (suboccipital) nerve Atlas, posterior arch Hypoglossal nerve Posterior spinal artery Digastric, posterior belly Atlas, transverse process Spinal accent nerve Second cervical spinal ganglion Vagus nerve Internal jugular vein Sternocleidomastoid Superior cervical sympathetic ganglion Dura mater Third cervical dorsal ramus Denticulate ligament Spinal accent nerve Vagus nerve (displaced medially) Common carotid artery Vertebral artery. On the left, the foramina transversaria of the atlas and of the third, fourth and fifth cervical vertebrae have been opened to expose the vertebral artery. On the best, the posterior arch of the atlas and the laminae of the succeeding cervical vertebrae have been eliminated. Injection of fluid into the subdural space could injury the cord either by direct toxic results or by compression of the vasculature. At websites the place vessels and nerves enter or go away the subarachnoid space, the arachnoid mater is mirrored on to the floor of these structures and varieties a thin coating of leptomeningeal cells over the floor of each vessels and nerves. Thus, a subarachnoid angle is fashioned as nerves cross by way of the dura into the intervertebral foramina. At this level, the layers of leptomeninges fuse and turn into steady with the perineurium. The ligamentum denticulatum is a flat, fibrous sheet that lies on all sides of the spinal twine between the ventral and dorsal spinal roots. Its medial border is steady with the subpial connective tissue of the twine, and its lateral border forms a sequence of triangular processes, the apices of which are fixed at intervals to the dura mater. Its web site of attachment to the dura mater is above the rim of the foramen magnum, simply behind the hypoglossal nerve; the spinal accent nerve ascends on its posterior facet. The last of the dentate ligaments lies between the exiting twelfth thoracic and first lumbar spinal nerves and is a narrow, indirect band that descends laterally from the conus medullaris. Changes in the form and position of the dentate ligaments throughout spinal movements have been demonstrated by cineradiography. Beyond the conus medullaris, the pia mater continues as a coating of the filum terminale.
Puncture Weed (Puncture Vine). Persantine.
- How does Tribulus work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Enhancing athletic performance.
- Dosing considerations for Tribulus.
- What is Tribulus?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96088
Persantine 100 mg discount line
The head of the caudate nucleus seems as three successive parts-medial medications you cant donate blood buy 100 mg persantine otc, lateral and intermediate-which produce elevations in the flooring of the lateral ventricle symptoms 2 days before period purchase persantine 100mg otc. Caudally these merge to kind the tail of the caudate nucleus and the amygdaloid advanced, each of which remain near the temporal pole of the hemisphere. When the occipital pole grows backward and the final enlargement of the hemisphere carries the temporal pole downward and ahead, the tail of the caudate is continued from the ground of the central part (body) of the ventricle into the roof of its temporal extension, the future inferior horn. The lateral stria, clothed by the lateral olfactory gyrus, and, when current, the intermediate stria terminate in the rostral elements of the piriform area. However, the posteroinferior (temporal) archaeocortical regions of each the dentate gyrus and the hippocampus persist and enlarge. First, the neuroblasts turn out to be apposed to the radial glial cells and set up an axis of polarity away from the ventricular floor. They then proceed to differentiate in accordance with their final place, and later-born neuroblasts migrate previous them toward the pial floor. Cortical neurones or cerebellar granule cells appear equally capable of migrating on hippocampal or cerebellar Bergmann glia, indicating conservation of migration mechanisms in several brain areas. Various traces of proof help the proposal that the laminar fate of neurones is decided previous to migration. In the mutant reeler mouse, laminar formation is inverted so that layers kind in an outside-in somewhat than insideout array, but axonal connections and neuronal properties appear normal, suggesting that the cells differentiate based on their time of origin quite than their location. Likewise, the prevention of neuronal migration by irradiation results in the manufacturing of cells that remain apposed to the ventricular surface but develop an applicable phenotype and efferent projections. Transplantation of labelled cells suggests that dedication to a specific cortical lamina occurs shortly after S phase. Neurones of preexisting laminae that have begun axonogenesis could present feedback on the forming cortical layers, providing a type of developmental clock for histogenesis. These embrace main areas such as the motor cortex, unimodal affiliation areas involved with the integration of knowledge from one of many primary areas and multimodal affiliation areas that integrate information from a couple of modality. There are also areas concerned with capabilities which are even much less well understood, such as the frontal lobes, concerned with goal-orientation responsibility and long-term planning. Moreover, some neurones could migrate tangentially on the radial glial cells, because of glial cell branching within the cortical plate. Two models have been proposed to explain the event of this advanced cortical group. The radial glial cells translate this map from the ventricular zone to the cortical plate, the place the sample is refined by innervating axons. Any or all of these may be the parts of short-range signalling centres alongside the sides of the cortex. Manipulations of the creating cortex by deafferentation or manipulation of inputs give some indication of the state of dedication of cortical areas. The columnar cells elongate, and their non-nucleated peripheral processes now constitute a marginal zone, while their nucleated, paraluminal and mitosing regions represent the ventricular zone. Some of their progeny depart the ventricular zone and migrate to occupy an intermediate zone. Ultimately, teams of progenitor cells type: at first, generations of definitive neurones, and later, glial cells that migrate to and mature of their final positions. Subsequently, proliferation wanes in the ventricular zone but persists for appreciable durations within the instantly subjacent subventricular zone. From the pial floor inward, the following zones may be defined: marginal, cortical plate, subplate, intermediate, subventricular and ventricular. The marginal zone provides rise to the outermost layer of the cerebral cortex, and the neuroblasts of the cortical plate and subplate type the neurones of the remaining cortical laminae (the complexity varies in different areas and with additional additions of neurones from the deeper zones). The intermediate zone gradually transforms into the white matter of the hemisphere. Meanwhile, different deep progenitor cells produce generations of glioblasts that also migrate into the more superficial layers. As proliferation wanes and at last ceases within the ventricular and subventricular zones, their remaining cells differentiate into common or specialised ependymal cells, tanycytes or subependymal glial cells. The first teams of cells to migrate are destined for the deep cortical laminae, and later groups cross through them to more superficial areas. The cumulative effect of this radial and tangential growth is obvious in a marked enhance in cortical thickness and surface area. In the pallial walls of the mammalian cerebral hemisphere, the phylogenetically oldest areas, which are the primary to differentiate throughout ontogeny, are those that border the interventricular foramen and its extension the choroidal fissure, the lamina terminalis and the piriform lobe. Note radial glial cells (black) extending from the interior to external limiting membrane; these provide contact guidance paths for neuroblasts. When the lateral geniculate nucleus and the visible cortex had been ablated and area was created in the medial geniculate by ablating the inferior colliculus, cells in the somatosensory or auditory cortex had been visually driven, and receptive area and response properties resembled those seen in the visual cortex. These results recommend that the modality of a sensory thalamic nucleus or cortical area can be specified by inputs throughout development. The improvement of cortical projections has been investigated in terms of both laminar and area-specific connectivity. Recently, consideration has centered on the idea that connections may be influenced by the existence of a transient population of subplate neurones that later dies. The cortex develops within a preplate, consisting of corticopetal nerve fibres and the earliest generated neurones. This zone is then cut up into two zones-the subplate beneath the cortical plate, and the marginal zone at the pial surface-by the arrival of cortical neurones. Subplate neurones lengthen axons by way of the interior capsule to the thalamus and superior colliculus before other cortical neurones have been born. Layer 5 neurones in various cortical areas lengthen axons to totally different repertoires of targets. For occasion, layer 5 neurones of the visible cortex project to the tectum, pons and mesencephalic nuclei, whereas these within the motor cortex project to mesencephalic and pontine targets, the inferior olive and dorsal column nuclei and the spinal wire. An attention-grabbing characteristic of these cortical projections is that they come up by collateral formation quite than by projection of the first axon or by progress cone bifurcation. In the case of the corticopontine projection, collaterals are elicited by a diffusible, chemotrophic agent. Retrograde labelling of neurones at varied times in improvement has proven that quite than being generated de novo, these patterns appear to come up by the pruning of collaterals from a more widespread projection. Visual cortical neurones possess a projection to the spinal cord early in improvement, which is later eradicated. This late emergence of the specificity of projections could be pushed by intrinsic programming of the neurones to be pruned or by a response to positiondependent factors. When pieces of visible cortex had been transplanted into motor areas and the resulting layer 5 projections were labeled later in growth, projections to the spinal twine endured rather than being eradicated, as in regular development. Thus, place performs an necessary function in the modelling of cortical projections, implying that the same courses of neurones exist in several tangential regions of the cortex. Regressive events such as axon and synapse elimination and neuronal dying thus play an essential part in modelling the cortex. For example, in 58 Chapter 3 / Development of the Nervous System rodents, roughly 30% of cortical neurones die, and the number of cells in layer 4 is ruled by thalamic enter. Human cortical malformations are thought to come up as neuronal migration disorders.
Syndromes
- Mesoridazine (Serentil)
- Your surgeon will make 2 to 5 small cuts in your abdomen.
- 19 to 50 years: 18 mg/day
- Examining the back part of the eye, including the retina (ophthalmoscopy)
- Vision problems, including double vision, blind spots, or temporary vision loss in one eye
- Genetic testing of chromosome 4
- Inflammation of blood vessels in the skin (cutaneous vasculitis)
- The doctor uses scissors to cut along the edge of the nail where the skin is growing over. This portion of the nail is removed. This procedure is called a partial nail avulsion.
Persantine 25 mg generic mastercard
Learn to make eye contact with the patient somewhat than the interpreter through the interview symptoms nicotine withdrawal buy cheap persantine 100 mg on-line, otherwise the affected person may feel overlooked of the dialogue medicine for high blood pressure persantine 100 mg purchase amex. Functional history taking: activities and instrumental activities of daily dwelling Elderly patients and sufferers with persistent disabling illnesses need to have their capability to manage normal dwelling assessed. Communication Excellent communication skills are central to greatest medical follow and can be learned. Practise your communication skills with colleagues and video your sessions to study the pitfalls. Patients want the reality, and ethically and legally docs are obliged to present this data. Build a therapeutic environment and relationship (Perceptions of the patient) � Introduce your self. Communicate (Invitation to proceed) � Agree on how much to discuss within the interview; for instance, `We have your results. However, this method should not be used as an excuse for not providing a proper, sympathetic and thorough clarification of the issue and the consequences of ignoring medical advice-to the extent that the patient will enable. The potentialities to be thought of include alcohol or drug withdrawal, an intracranial lesion corresponding to a tumour or subdural haematoma, or a psychiatric illness such as paranoid schizophrenia. Urinary tract infections are a standard reason for recent-onset confusion and delirium in elderly folks. It is important to show restrained interest in these recordings without encouraging excessive enthusiasm. It is important to bear in mind, and maybe to level out, that info obtained in this means might not have been subjected to any type of peer evaluation. People with continual illnesses, however, may know extra about their situation than their clinician. This is a really tough downside and could be approached solely with rigorous application of clinical strategies. The clinician and the affected person must be aware that their meeting is strictly professional and not social. Each station is scored separately and scores are mixed to decide the cross stage. A real patient or an actor may be out there to reply questions and enable the examiner to take a look at your interviewing method and data. In most instances the primary question should most likely be `May I ask you some questions Ask open inquiries to begin with (and resist the urge to interrupt), however end with particular questions to narrow the differential diagnosis. Use the pinnacle nod appropriately, and use silences to encourage the patient to categorical himself or herself. When there are breaks within the narrative, provide a abstract for the affected person, by briefly restating the details or emotions recognized, to maximise accuracy and show lively listening. Clarify the listing of chief or presenting complaints with the patient, somewhat than assuming that you know them. Show empathy and express your help and willingness to cooperate with the patient to assist clear up the problems collectively. Sir William Osler (1849�1919) It is thrilling to seek for objective proof of disease (physical signs). This is arguably a ritual: the laying on of hands after appropriately looking (inspecting) for illness is an age-old method that in our view helps create a therapeutic connection between the patient and the doctor and begins the therapeutic course of. The stethoscope must be sturdy and easily squashed into different-sized pockets. Electronic stethoscopes, which amplify sounds, are particularly useful for students with hearing difficulties. More senior students can normally give advice about the most reliable and cheap models available. Hand-washing Patients should come first and lowering the unfold of an infection is your accountability as a healthcare professional. You should wash your hands before touching a patient (to defend them) and after completing your examination (to shield you) each time 1 It is prone to disappear this century and be replaced by hand-held ultrasonography. Look notably for: � laboured breathing-an obvious increase within the respiratory fee and use of the accessory muscular tissues of respiration recommend critical respiratory, cardiac or metabolic issues; that is typically made extra obvious when the patient mildly exerts himself or herself, similar to by moving round in bed or getting undressed � jaundice (yellow discolouration of the skin and sclerae) � cyanosis (blue discolouration of the skin) � pallor (suggesting anaemia) � diagnostic facies (see Table three. Surgical management of obstructive sleep apnea in acromegaly with mandibular prognathism and macroglossia: a therapy dilemma. Vital signs Vital signs are indicators of the function of essential parts of the physique. They must be assessed in all patients on the time of the initial examination and then as typically as needed. It is usually palpable just medial to the distal radius with the pulps of the forefinger and center finger of the examining hand. However, in obese sufferers with massive arms, this cuff will overestimate the blood stress and subsequently a large cuff have to be used. For an approximate estimation of the systolic blood pressure, the cuff is fully inflated after which deflated slowly (2 mmHg per second) until the radial pulse returns (palpation method). Then, for a more correct estimation of the blood pressure, this manoeuvre is repeated with the stethoscope positioned over the brachial artery (auscultation method). A regular auscultatory gap could sometimes happen (the sounds disappear slightly below systolic pressure however reappear above diastolic). However, if coarctation of the aorta or subclavian artery stenosis is suspected, these readings may be performed. Moderatehypertension(grade2): 160�179 mmHg systolic; and/or 100�109 mmHg diastolic. Blood stress measured at home by the affected person or with a 24-hour monitor will confirm surgery readings that may be artificially excessive (white-coat hypertension, so-called as a result of docs all used to put on white coats). The temperature is taken within the ear and the device beeps in a helpful way when ready. General look Before specifically examining the areas or medical systems of the physique, a general inspection must be made. Important related indicators could additionally be missed except that is accomplished (seeing the wood somewhat than the trees). For instance, a affected person with weight loss may not be recognized as having thyrotoxicosis (see Ch 9) unless the eye indicators. Look particularly for: � � � � obesity wasting (loss of muscle mass) an unusual facial appearance (see Table 3. Look for pallor, which can indicate anaemia, and for a blue tongue (and blue fingers), which may point out central cyanosis, a sign of arterial oxygen desaturation (see p. For instance, the patient with suspected persistent liver disease might have: � liver nails (white nail beds with a rim of pink on the top) � palmar erythema (red palms).
Order persantine 25mg fast delivery
Neural crest cells produced from this rostral portion of the brain contribute mesenchymal populations to the frontonasal process medicine 665 persantine 100 mg free shipping. Prior to neural tube closure medications xerostomia persantine 25 mg buy cheap on line, the elevating neural folds contain two distinctive neuronal populations. The bigger inhabitants of neural crest cells migrates from the neural epithelium prior to neural tube fusion. A smaller inhabitants of neuroepithelial cells turns into integrated into the floor ectoderm after neural tube closure. These areas of neuroepithelium throughout the surface ectoderm are termed ectodermal placodes. Although the majority of the ectodermal placodes kind nervous tissue, non-neurogenic placodes also happen (Begbie and Graham 2001). After an applicable inductive stimulus, local clusters of placodal cells remove themselves from the encompassing surface ectoderm both by epithelial�mesenchymal transition or by invagination of the whole placodal region to form a vesicle beneath the remaining floor ectoderm. Paired nonneurogenic placodes invaginate to form the lens vesicles under the inductive affect of the optic vesicles. The neural folds meet within the rostral midline adjoining to the buccopharyngeal membrane. The rostral neural fold additionally offers rise to the olfactory placodes (which stay as paired, laterally placed placodes) and to the epithelium of the nasal cavity. Further caudally, comparable neurogenic placodes could be recognized and divided into three categories: ventrolateral or epibranchial, dorsolateral and intermediate. The epibranchial placodes seem in the surface ectoderm immediately dorsal to the area of pharyngeal (branchial) cleft formation. The first epibranchial placode is situated at the degree of the first pharyngeal groove and contributes cells to the distal (geniculate) ganglion of the facial nerve; the second and third epibranchial placodes contribute cells to the distal ganglia of the glossopharyngeal (petrosal) and vagus (nodose) nerves, respectively. Generally these placodes thicken, and cells start to detach from the epithelium soon after the pharyngeal pouches have contacted the overlying ectoderm. Concurrently the neural crest cells attain and move beyond these lateral extensions of the pharynx. Cells budding off placodes present signs of early differentiation into neurones, including the formation of neurites. Epibranchial placodes may have their origins within the neurones that innervate the taste buds in fishes. Dorsolateral placodes may be associated evolutionarily to the sensory receptors of the lateral line system of lower vertebrates. They are represented by the otic placodes, situated lateral to the myelencephalon, and invaginate to kind otic vesicles from which the membranous labyrinth of the ear develops. Neurones of the vestibulocochlear nerve ganglia come up by budding off the ventromedial facet of the otic cup, after which they can be distinguished within the acoustic and vestibular ganglia. Neural crest populations come up from the neural folds as major neurulation proceeds and concurrently progress rostrally and caudally. Caudally, from somite 27, secondary neurulation processes produce the most caudal neural crest. Two distinct populations of neural crest cells are shaped: a neuronal population produced all through the brain and spinal wire that provides rise to sensory and autonomic neurones and glia, and a non-neuronal mesenchymal population that arises only from the brain. Melanocytes develop from a subpopulation of neural crest cells derived from each the pinnacle and the trunk. They kind one of the three pigment cell types (the others being retinal pigment epithelium and pigment cells of the pineal organ, each of which originate from the diencephalon). In the trunk the migration patterns of neural crest cells are channelled by the somites. Thus the segmental distribution of the spinal and sympathetic ganglia is imposed on the neural crest cells by a prepattern that exists throughout the somitic paraxial mesenchyme. Rostral to the otic vesicle, neural crest cells arise from particular areas of the brain. Within the rhombencephalon a number of transverse subdivisions perpendicular to the lengthy axis of the mind can be seen early in development. Eight primary rhombomeres are acknowledged extending from the midbrain�hindbrain boundary rostrally to the spinal cord caudally. Rhombomeres eight and 7 give rise to crest cells that migrate into the fourth and sixth pharyngeal arches; rhombomere 6 crest invades the third pharyngeal arch. More lateral regions of the neural plate overlie the paraxial mesenchyme (not shown). B, During neurulation, the neural plate bends at its midline, which elevates the lateral edges of the plate as the neural folds. Contact between the midline of the neural plate and the notochord is maintained at this stage. Cells within the area of fusion kind the roof plate, which is a specialized group of dorsal midline cells. D, Cells on the ventral midline of the neural tube retain proximity to the notochord and differentiate into the floor plate. After neural tube closure, neuroepithelial cells continue to proliferate and eventually differentiate into defined lessons of neurones at different dorsoventral positions inside the spinal cord. For instance, sensory relay, commissural and different classes of dorsal neurones (D) differentiate near the roof plate (R), and motor neurones (M) differentiate ventrally close to the floor plate (F), which by this time is no longer in touch with the notochord (N). E�H, Summary of the results of experiments in chick embryos by which the notochord or flooring plate is grafted to the dorsal midline of the neural tube or the notochord is eliminated before neural tube closure. E, the traditional condition, exhibiting the ventral location of motor neurones (M) and the dorsal location of sensory relay neurones (D). F, Dorsal grafts of a notochord lead to induction of a ground plate in the dorsal midline and ectopic dorsal motor neurones (M). G, Dorsal grafts of a flooring plate induce a model new ground plate within the dorsal midline and ectopic dorsal motor neurones (M). H, Removal of the notochord leads to the elimination of the floor plate and motor neurones and the expression of dorsal cells sorts (D) within the ventral region of the spinal wire. Intermediate between the epibranchial and dorsolateral placodes are the profundal and trigeminal placodes, which fuse in people to form a single entity. Prospective neuroblasts migrate from foci dispersed throughout the surface ectoderm lateral and ventrolateral to the caudal mesencephalon and metencephalon to contribute to the distal portions of the trigeminal ganglia. Prior to neurulation the cell populations that give rise to these two parts of the pituitary gland are found next to one another throughout the rostral portion of the ground of the neural plate and the contiguous midline neural fold. As neurulation proceeds the future neurohypophysis remains within the flooring of the prosencephalon, and the cells of the lengthy run adenohypophysis are displaced into the floor ectoderm, where they kind the hypophysial placode. The most rostral portion of the neural plate, which is ready to type the hypothalamus, is in touch rostrally with the future adenohypophysis, within the rostral neural ridge, and caudally with the neurohypophysis, within the flooring of the neural plate. After neurulation the cells of the anterior neural ridge stay in the floor ectoderm and type the hypophysial placode, which is in close apposition and adherent to the overlying prosencephalon.
Purchase persantine 25 mg on-line
Absent reflexes may be a results of an higher motor neuron lesion symptoms 3 days after embryo transfer 100mg persantine discount with mastercard, however lax stomach muscles or earlier surgery that has reduce the superficial abdominal nerves may cause loss of this reflex medications list form generic 25 mg persantine amex. Lay the affected person flat and slowly flex the hip while maintaining the knee totally extended. With extra severe nerve root irritation the ache will be felt in the different lower limb as well (crossed straight leg elevating internalmedicinebook. Test the higher lumbar roots by laying the patient prone and extending the hip (while the knee is flexed to 90�) (see femoral nerve stretch take a look at, p. Note: � any issue getting up from the chair � hemiplegic gait � wide-based (ataxic) gait (cerebellar disease, peripheral neuropathy). A careful neurological historical past should direct the neurological examination to essentially the most relevant areas. Symptoms might happen before indicators can be detected, however within the absence of signs any signs are less likely to be essential. The methodical method that characterises the expert neurological examination helps define the anatomical site of the abnormality. A careful neurological examination will normally allow you to develop a wise differential diagnosis. Note the distribution of indicators and look significantly for asymmetrical abnormalities. Absent tendon reflexes usually point out an abnormality in the sensory or motor system. Sir William Osler (1849�1919) the examination of the eyes, ears, nose and throat is often directed by the history. These small parts of the body could pro vide very important diagnostic clues in neurological or systemic illness. Standing well back from the patient, inspect for: � ptosis (drooping of one or each higher eyelids) � color of the sclerae: internalmedicinebook. Pull down the lower lid and look for the normal distinction between the pearly white posterior conjunctiva and the red anterior part. Look additionally for fatigability of eye muscles by asking the patient to lookup at a hatpin or finger for about half a minute. Red desaturation (impaired ability to see purple objects) can occur with optic nerve illness. This must be suspected if visible acuity is zero in one eye and no pupillary reaction is apparent. This causes: � partial ptosis (as sympathetic fibres supply the smooth muscle of both eyelids) � a constricted pupil (because of an unbalanced parasympathetic action), which reacts usually to mild. Note that perceptible anisocoria (in equality of the diameters of the pupils) is present in 20% of people. The patient must be requested to stare at a point on the alternative wall or on the ceiling and to ignore the sunshine of the ophthalmoscope. Patients will often attempt to concentrate on the ophthalmoscope light and should be requested to not do that initially. Turn the ophthalmoscope lens to +20 and study the cornea from about 20 cm away from the patient. Structures, including the lens, humour and then the retina at growing distance into the eye, will swim into focus. Inspect the the rest of the retina and particularly search for the retinal modifications of diabetes mellitus or hypertension. Inspect fastidiously for central retinal artery occlusion, the place the entire fundus appears milkywhite due to retinal oedema and the arteries turn out to be significantly decreased in diameter. Central retinal vein thrombosis causes tortuous retinal veins and haemorrhages scattered over the whole retina, significantly occurring alongside the veins. Retinitis pigmentosa causes a scattering of black pigment in a crisscross pattern. Tests of hearing also can provide information about the severity and anatomical website of hearing loss. Pull down the pinna gently; an infection of the exterior canal often causes tenderness of the pinna. Typically a speculum with a 4-mm tip will swimsuit adults and a 2-mm tip will suit youngsters. Auriscopic examination of the ears requires use of an earpiece that fits comfortably in the ear canal to permit inspection of the ear canal and tympanic membrane. Note: � color � transparency � any evidence of dilated blood vessels � bulging or retraction (bulging can suggest underlying fluid or pus in the middle ear) � any perforation of the tympanic membrane. When the bulb is squeezed gently, air stress within the canal is increased and the tympanic membrane ought to move promptly inwards. Look (and smell) for: � peridental irritation � gingivitis � poor dentition � leucoplakia � tongue fissures � oral cancers � fasciculations � fetor hepaticus. Decide whether or not conjunctival redness (injection) is central (iritis) or spares the central region (conjunctivitis). Note whether or not the disc is swollen and is abnormally pink or white (ischaemic optic neuropathy). Note any retinal fundal pallor (arterial occlusion), haemorrhages (venous occlusion) or an apparent embolus (at an arterial bifurcation). Important native and systemic illness may be missed except the eyes are examined as part of a general medical examination. Complete examination of the mouth and throat includes palpating the draining lymph nodes (cervical nodes). Skill and nicety in manipulation, whether or not within the simple act of feeling the heartbeat or in the performance of any minor operation will do extra towards establishing confidence in you, than a string of diplomas, or the popularity of extensive hospital experience. Under- or overactivity produces characteristic symptoms and indicators: � Thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormone production) could cause a preference for cooler weather, weight reduction, elevated appetite (polyphagia), palpitations (sinus tachycardia or atrial fibrillation), increased sweating, nervousness, irritability, diarrhoea, amenorrhoea, muscle weakness and exertional dyspnoea. Find out the place the affected person grew up (there are areas of endemic goitre brought on by iodine deficiency). Inspect for palmar erythema (a purple appearance of the outer components of the palms) and feel the palms for heat and sweatiness (from sympathetic over-activity). Test for proximal myopathy (weakness of the muscle tissue at the shoulders and hips) and faucet the arm reflexes for irregular briskness, especially in the leisure section. Look for pretibial myxoedema (bilateral agency and signs of cardiac failure (see Ch 4). Note peripheral cyanosis, a cool and dry skin and the yellow skin discolouration of hypercarotenaemia (a results of reduced metabolism of carotene). The pores and skin could additionally be usually thickened, and alopecia (loss of hair) could additionally be current, as may vitiligo (an associated autoimmune disease). Inspect the eyes for periorbital oedema and xanthelasma and note loss or thinning of the outer third of the eyebrows. Look for speedy dorsiflexion followed by gradual plantar flexion after the tendon is tapped.