Prandin
Prandin dosages: 2 mg, 1 mg, 0.5 mg
Prandin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Buy prandin 0.5 mg mastercard
However juvenile diabetes diet buy generic prandin 2 mg line, the advent of strategies such as reverse vaccinology has paved the means in which for the discovery and growth of subunit vaccines based mostly on recombinant pathogen-derived antigens diabetes video safe prandin 1 mg. However, most subunit formulations have confirmed to be weakly immunogenic and virtually all require the inclusion of an immunostimulatory compound or novel delivery system to elicit an effect. Furthermore, the route by which vaccines are administered has additionally been revisited and much work is now specializing in the development of vaccines that are capable of being administered mucosally. Mucosal supply of vaccines probably presents a selection of significant advantages over standard parenteral vaccination and research into novel approaches to facilitate effective mucosal vaccination is an increasing area. Mucosal vaccines are desirable for a selection of causes including those of sensible, economical, sociological, environmental, and immunological significance as outlined in Box 1. Effective topical immunization has the potential to induce protecting local immunity and parenteral immunization is often suboptimal with regard to the promotion of protective native immunity towards mucosal pathogens. Thus, the power to induce class-switching of B cells to an IgA-secreting cell inhabitants, whereas concurrently eliciting systemic responses, is a key issue supporting the development of mucosal vaccines. However, for all these advantages, putting efficient mucosal immunization methods into place is far more difficult in apply as a number of limitations, each bodily and chemical, must be overcome. Due to the massive portions of nonpathogenic antigens to which mucosal surfaces are continually exposed, surveillance methods are in place at these tissues which are able to distinguish noninfectious, innocuous antigens from people who might be pathogenic and require a strong immune response. Under steady-state situations, these techniques program a state of immune quiescence or hyporesponsiveness, which prevents the induction of unwarranted, effector immune responses to dietary or environmental antigens or commensal microbes. The most putting example of this is seen in oral tolerance the place proteins, which enter by way of the oral route, fail to elicit an effector immune response and may set off a potent regulatory response. The wheat protein gluten is the causative agent of celiac disease-a disease brought on by a breakdown in oral tolerance leading to an uncontrolled effector immune response able to causing vital native tissue injury (see Chapter 80 for a comprehensive overview of celiac disease). Thus, a key problem facing mucosal vaccine design is the requirement to improve the immunogenicity of mucosally administered antigens so as to overcome tolerogenic mechanisms without inflicting vaccine-associated pathogenesis as a result of unacceptably excessive reactogenicity. Orally delivered, reside attenuated vaccines against polio (Aylward, 2006) and rotavirus (Greenberg and Estes, 2009) are extremely efficient, demonstrating the potential of this route of immunization in humans (Pasetti et al. While the obvious reply can be to continue to develop mucosal vaccines based mostly on attenuated reside pathogens, safety concerns have been raised. These concerns pertain particularly to newborns, the aged, and individuals with a specific immunodeficiency where a reversion to virulence may occur following vaccination with a weakened or attenuated microbe. Consequently, the major focus of much current analysis is on the identification and formulation of extremely characterized recombinant subunit vaccines, which typically pose much less of a danger than conventional vaccines. To date, such antigens have incessantly confirmed to be very weakly immunogenic, and thus fail to elicit an immune response of acceptable magnitude to confer protective immunity to the recipient (Medzhitov, 2009). Therefore, despite latest advances within the identification of subunit antigens, significantly because of reverse vaccinology (Rappuoli, 2001), the key to subunit vaccine improvement will depend on the success of strategies to enhance their immunogenicity and talent to confer protecting immunity. Such strategies will embody the identification of novel adjuvants and delivery methods, able to modulating the immune system whereas not exhibiting cellular toxicity and sustaining antigen Antigen Delivery Systems I Chapter sixty three 1213 integrity following administration (Tritto et al. However, to date, no vector has emerged as a transparent leading expertise for mucosal vaccination. Instead, attenuated versions of the pathogens continue to be used and are the premise for many of the currently licensed mucosal vaccines (see Table 1). Potential limitations of those systems embrace the induction of antivector immunity that can scale back the effectiveness of booster doses and potential preexisting antivector immunity. Ideally, nonliving supply systems would facilitate the delivery of subunit antigens, which are prone to degradation on mucosal surfaces. However, regardless of many efforts through the years, the emergence of such a system, which could presumably be used universally for a extensive range of antigens, remains elusive. We will also critically appraise what has been tried prior to now and failed, highlighting why such failures occurred and perhaps suggesting what classes could be learned from these failures. The presence of tight junctions between adjoining enterocytes prevents pathogens from having entry to the underlying submucosae, but also necessitates the event of methods or formulations capable of overcoming this physical barrier so as to elicit a protective immune response. M cells are specialized for uptake of antigen across the epithelium into the underlying subepithelial layers as they lack the thick mucin-protein glycocalyx and brush-border membrane of microvilli covering the surrounding enterocytes (Neutra, 1998; Azizi et al. A further barrier existing at mucosal surfaces is the thick layer of viscous mucin glycoproteins generally known as mucus from which these surfaces get their name. This mucous layer prevents the adherence to and colonization of the epithelia by microorganisms, and mucus-coated microbes could be expelled rapidly due to ciliary beating in the respiratory tract or peristalsis in the gut (Chorny and Cerutti, 2011) (the roles of mucin glycoproteins are handled in Chapter 14). However, regardless of its main defensive perform, such mucociliary clearance can cause issues with regard to nasal immunization whereby the vaccine formulation could also be cleared from the nasal passages earlier than it has been successfully absorbed throughout the epithelia. Thus, ciliary beating reduces vaccine residence time inside the nasal passages, necessitating the development of compounds or strategies capable of rising the effectivity with which the vaccine formulation is absorbed throughout the epithelium (Illum, 2006). The process of peristalsis poses an analogous problem in the small gut, where it limits the residence time of orally administered vaccines. Moreover, the scale of pores in the mucous layer has implications for rational vaccine design, specifically for nonliving delivery methods. Larger proteins/particles are more readily trapped by the mucus and are consequently cleared more readily than smaller peptide antigens. One strategy to address this and improve vaccine residence time is through the use of mucoadhesives such because the cationic polysaccharide chitosan. Alkaline deacetylation of chitin yields chitosan, a negatively charged polymer that has been extensively studied as a candidate mucosal adjuvant for each intranasal. The primary mechanism by which chitosan enhances vaccine residence time is through electrostatic interactions to negatively charged cell floor moieties and mucus. For instance, the mucin glycoproteins of mucus have an abundance of sialic acid residues, which, at physiological pH, have a net adverse charge. Thus, electrostatic binding between the positively charged polymer and these negatively charged residues enhances mucoadhesion and residence time of antigens formulated with or coated with chitosan (Jabbal-Gill et al. In addition to these bodily obstacles, numerous chemical mediators pose further challenges to mucosal delivery of vaccines. Furthermore, substances corresponding to lysozyme and phospholipase A in saliva, while primarily microbicidal, typically degrade protein or peptidoglycan antigens given in answer. This acidic surroundings degrades orally administered antigens and could additionally be adequate to destabilize some particulate supply techniques. This barrier also highlights inadequacies with the preclinical mouse model for testing novel oral vaccines. Another concern with the preclinical mannequin is the probably distinction between murine and human gastric residence instances. The time spent at the gastric mucosa might be decisive by means of whether or not candidate oral vaccine formulations are considered to be protected and efficient. However, such formulations could additionally be cleared from the abdomen quicker in mice than in people and this could impact upon vaccine efficacy. Likewise speciesspecific variations in intestinal residence time also can have an effect on the degree of antigen uptake. As a result, formulations that present efficacy in preclinical small animal fashions is most likely not as effective when introduced to larger animals or even into humans for medical testing.
0.5 mg prandin buy visa
Eczema is most frequently diffuse blood sugar how low is too low prandin 0.5 mg purchase amex, involving the whole skin diabetes symptoms double vision prandin 1 mg low price, and should show follicular dermatitis. Further signs such as thyroiditis, hematological abnormalities (Coombs-positive anemia, neutropenia (Russo et al. Thyroiditis most often occurs in the type of hypothyroidism requiring substitutive therapy. Usually all sufferers require stabilization with steroids and immunomodulatorbased medicine (Ferguson et al. Autoimmune enteropathy varieties 1 and a pair of most often require bowel rest and total parenteral diet with albumin substitution in the first (diagnostic) part. X-linked syndrome of polyendocrinoptahy, immune dysfunction and diarrhea maps to Xp 11. The mouse scurfy (sf) mutation is tightly linked to Gata1 and Tfe3 on the proximal X chromosome. Disruption of a new fokhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the deadly lymphoproliferative dysfunction of the scurfy mouse. Autoimmune enteropathy and nephropathy with circulating anti-epithelial cell antibodies. Classification of intractable diarrhea in infancy utilizing scientific and immunohistological standards. Manifestations and linkage evaluation in X-linked autoimmunity-immunodeficiency syndrome. Syndrome of intractable diarrhoea with persistent villous atrophy in early childhood: a clinicopathological survey of forty seven. A seventy five kDa autoantigen acknowledged by sera from sufferers with X-linked autoimmune enteropathy related to nephropathy. A long-term survivor with the immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome. The scurfy mouse mutant has previously unrecognized hemetological abnormalities and resembles Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Enteropathy and renal involvement in an toddler with proof of widespread autoimmune disturbance. A Japanese household of X-linked autoimmune enteropathy with haemolytic anaemia and polyendocrinopathy. X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equal of mouse scurfy. In the case of serum or circulating proteins, synthesis happens in cells that are in shut proximity to a central compartment comprising the intravascular or circulating protein pool; thus, such proteins enter the central compartment nearly instantaneously. Once in this compartment, the protein may either circulate throughout the compartment or transfer into considered one of a collection of extravascular compartments. The metabolic parameter that gives the best measurement of serum protein catabolism for most serum proteins is the fractional catabolic fee. Synthesis of serum proteins is followed by their fast introduction into the intravascular compartment. Proteins may circulate on this compartment, leave briefly by entering the extravascular compartment, or depart the intravascular area completely as a end result of endogenous catabolism or loss of intact protein into the bowel (stool). The rate at which a protein leaves the intravascular space is expressed as a fractional catabolic price (the fraction of the intravascular compartment pool catabolized per unit of time). The fractional catabolic price, multiplied by the worth for the total quantity of protein in the intravascular compartment, is the whole or absolute catabolic rate. The fractional catabolic rate of a given serum protein may be determined by measuring the die-away of a labeled protein within the serum, in addition to by the looks of labeled protein or free label (generated from the endogenous catabolism of the protein) in the urine, i. The evaluation of metabolic knowledge thus obtained to calculate the fractional catabolic fee (as nicely as different metabolic parameters) is a posh mathematical process that was initially carried out by computational evaluation of the metabolic information mentioned beforehand. The radioactive label normally utilized in metabolic research is radioiodine, since this label properly fulfills the requirements for a metabolic label as outlined above. The benefit of this substance was that the 51Cr label is well measurable within the stool and, in addition, has an vitality peak distinct from that of 125I (iodine), in order that the latter could be utilized in simultaneous research of overall albumin metabolism (in the form of 125I-albumin). On this basis, 51CrCl3, a substance that attaches to many serum proteins following its injection into blood and that thus, in effect, labels circulating proteins in the same manner as does 51Cr initially bound to albumin, got here to supplant 51Cralbumin (Van Tongeren and Reichert, 1966; Waldmann et al. As famous earlier, the energy peaks of 125I and 51Cr are sufficiently different, in order that the quantity of every may be measured independently in the identical samples. The substance that has made this potential is 1-antitrypsin, a 54-Da glycoprotein that may be a normally occurring 1-globulin synthesized within the liver (Florent et al. This turns into clinically apparent when the prevalence of hypoproteinemia and the concomitant lack of oncotic strain result in peripheral edema. Thus if a given fractional quantity misplaced is added to a low endogenous fractional catabolic price, the share change in overall catabolism is way larger than if the identical fractional amount lost is added to a excessive endogenous fractional catabolic rate; these differences are, in flip, mirrored in the share change within the serum protein degree. In the measurement of total labeled protein loss, one merely measures label output; for 1-antitrypsin the upper restrict of normal is less than 140 g/100 g dry stool. By contrast, within the clearance methods, one measures each the label output and the serum label in the course of the output period; for 1-antitrypsin, the normal clearance is 13�14 ml/day. A broad number of radionucleotides have been used for this function, including technetium (Tc)99 m-human serum albumin and other Tc-99m-labeled substances, as well as 111In transferrin (Saverymuttu et al. The use of 51Cr-labeled albumin supplies correct data on protein loss into the gastrointestinal tract (see text). Also proven are stool excretion information (expressed as a fractional loss rate); 51Cr excretion is nearly nonexistent in the normal management but is appreciable within the affected person. Diseases associated with widespread activation of mast cells, similar to allergic states, eosinophilic gastroenteropathies, and systemic mastocytosis, are the most common on this class. Various associated extragastrointestinal manifestations have also been reported, corresponding to eosinophilic cystitis, splenitis, and hepatitis (Greg et al. The analysis may be made on the basis of one or more abnormalities of gastrointestinal perform and the incidence of eosinophilic infiltration of some area of the gastrointestinal tract. Peripheral eosinophilia may also be found, however its presence as a diagnostic indicator remains unsure (Talley et al. Mucosal involvement of the colon gives rise to comparable signs, in addition to bloody diarrhea, which may be mistaken for inflammatory bowel illness. By distinction, with eosinophilic infiltration concentrated in deeper mucosal layers, obstructive symptoms could happen and with serosal involvement eosinophilic ascites might develop, in each cases in the absence of malabsorption (Klein et al. In different studies relating to these genetic findings, varied cytokine abnormalities have been identified. In about 50% of circumstances of eosinophilic gastroenteropathy, IgE ranges are elevated and an allergic etiology could be inferred; in lots of different instances, nevertheless, IgE ranges are normal, and allergen-specific antibodies remain unreliable as evidence of allergic hypersensitivity (reviewed in Kelly et al. When allergy does seem to be present, the patients are nearly all the time allergic to a couple of meals part, and elimination diets are only partially effective, notably in older sufferers, possibly as a end result of preliminary sensitization with one allergen leads quickly to sensitization to a host of other antigens due to allergy-induced modifications in mucosal permeability.
Safe 1 mg prandin
Mucosal and systemic T helper cell function after intragastric colonisation of adult mice with Candida albicans blood sugar of 500 0.5 mg prandin cheap with visa. Do inflammatory bowel disease and periodontal disease have related immunopathogenesis Mechanisms of binding of cutaneous lymphocyte associated antigen optimistic and E7-positive lymphocytes by way of oral and pores and skin keratinocytes diabetes test hong kong prandin 0.5 mg buy amex. Immune response to Candida albicans in monkeys with experimental candidiasis in the palate. Dietary intervention for oral allergy syndrome as a therapy in orofacial granulomatosis: a new approach Review article: cinnamon- and benzoatefree food plan as a primary treatment for orofacial granulomatosis. Antibodies and opsonic activity to plaque bacteria in human gingival crevicular fluid in relation to dental caries. Oral, vaginal and nasal responses after intragastric immunisation with biodegradable microparticles. Human amnion incorporates a novel laminin variant, laminin 7, which like laminin 6, covalently associates with laminin 5 to promote stable epithelial-stromal attachment. Laminin-6 and laminin-5 are recognized by autoantibodies in a subset of cicatricial pemphigoid. Antigenicity of an artificial peptide from glucosyltransferases of Streptococcus mutans in people. The cycle of human herpes simplex virus infection: virus transport and immune control. Gamma interferon production seems to predict time of recurrence of herpes labialis. Cell adhesion molecules in irritation and immunity: relevance to periodontal illnesses. Cholera toxin B subunit as transmucosal carrierdelivery and immunomodulating system for induction of anti-infectious and anti-pathological immunity. Pollen-food syndromes related to weed pollinosis: an update from the molecular point of view. Pathophysiology, etiological elements and clinical administration of oral lichen planus, half I: information and controversies. Human herpes simplex virus infections: epidemiology, pathogenesis, symptomatology, analysis, and management. The malignant transformation of oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: a scientific evaluate. Characterisation of preparations enriched for Streptococcus mutans fimbriae: salivary immunoglobulin A antibodies in caries-free and caries-active topics. Induction of anergy or energetic suppression following oral tolerance is decided by antigen dosage. Protection towards candidiasis by an immunoglobulin G3 (IgG3) monoclonal antibody specific for the same mannotriose as an IgM protecting antibody. The severity of cutaneous and oral pemphigus is related to desmoglein 1 and 3 antibody ranges. Recognition of a novel peptide epitope of the mycobacterial and human warmth shock protein 65�60 antigen by T cells of patients with recurrent oral ulcers. Studies of bactericidal activity to Escherichia coli of porcine serum and colostral immunoglobulins and the role of lysozyme with secretory IgA. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene polymorphisms and periodontitis susceptibility: a meta-analysis based mostly on 11 case-control studies. Novel composite efficacy measure to reveal the rationale and efficacy of combination antiviral-anti-inflammatory therapy for recurrent herpes simplex labialis. Comparison of human immunodeficiency virus sort 1-specific inhibitory actions in saliva and other human mucosal fluids. T-cell, adhesion, and B-cell epitopes of the cell floor Streptococcus mutans antigen 1/11. Scaling and root planing remedy for periodontitis to cut back preterm delivery and low birth weight: a systematic evaluate and meta-analysis of randomized managed trials. Natural prevalence of antibody titers to glucosyltransferase of Streptococcus mutans in serum in excessive and low caries lively children. Kinetics of particular salivary IgA responses in man after oral problem by ribosomal immunostimulant. Human periodontal ligament cells facilitate leukocyte recruitment and are influenced of their immunomodulatory function by Th17 cytokine launch. Cellular and humoral immune responses in vaccination towards dental caries in monkeys. Immunisation with a purified protein from Streptococcus mutans towards dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Passive immunisation with serum and immunoglobulin towards dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Activation of oral keratinocytes by mercuric chloride: relevance to dental amalgam-induced oral lichenoid reactions. Time from seroconversion to oral candidiasis or hairy leukoplakia among gay and bisexual males entrolled in three prospective cohorts. Current controversies in oral lichen planus: report of a world consensus meeting. Natural historical past of periodontal illness in man: speedy, average and no loss of attachment in Sri Lankan laborers 14 to forty six years of age. Gene polymorphism and protein of human pro- and anti inflammatory cytokines in Chinese wholesome subjects and persistent periodontitis sufferers. Induction of tolerance in humans: effectiveness of oral and nasal immunization routes. Neutralizing antibodies inhibit axonal unfold of herpes simplex virus kind 1 to epidermal cells in vitro. Anticell-associated glucosyltransferase immunoglobulin Y suppression of salivary mutans streptococci in wholesome younger adults. Clinical evaluation of oral dryness: growth of a scoring system associated to salivary circulate and mucosal wetness. Clinical proof for allergy in orofacial granulomatosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Innate immune responses of epithelial cells following an infection with bacterial pathogens. Oral passive IgY-based immunotherapeutics: a novel resolution for prevention and remedy of alimentary tract illnesses.
Discount prandin 2 mg without a prescription
Progress toward introduction of Haemophilus influenzae sort b vaccine in low-income countries�worldwide diabetes test name prandin 2 mg buy without a prescription, 2004�2007 blood glucose range for diabetics buy discount prandin 0.5 mg on-line. Clinical definitions of pertussis: abstract of a Global Pertussis Initiative roundtable assembly, February 2011. Immunoglobulin G class and subclass antibodies to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides. Dendritic cells pulsed with intact Streptococcus pneumoniae elicit each protein- and polysaccharidespecific immunoglobulin isotype responses in vivo through distinct mechanisms. Efficacy of nine-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine towards pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal disease in the Gambia: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Epidemiology of invasive childhood pneumococcal infections in Israel: the Israeli Pediatric Bacteremia and Meningitis Group. The epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in Alaska, 1986�90: ethnic differences and opportunities for prevention. Immunization with outer membrane protein P6 from nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae induces bactericidal antibody and affords protection within the chinchilla model of otitis media. Diphtheria and theories of infectious illness: centennial appreciation of the critical role of diphtheria in the history of drugs. Impact of the molecular form of IgA on its functional activity in defense against Streptococus pneumoniae. Prevention of Haemophilus influenzae sort b colonization by vaccination: correlation with serum anti-capsular IgG concentration. Induction of useful secretory IgA responses in breast milk by pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides. Haemophilus influenzae resides and multiplies intracellularly in human adenoid tissue as demonstrated by in situ hybridization and bacterial viability assay. Clinical trial of an antipneumococcal vaccine in elderly topics living in institutions. Antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b and Streptococcus pneumoniae vaccines in children with human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae sort b conjugate vaccine in sickle cell disease. A controlled trial of two acellular vaccines and one whole-cell vaccine against pertussis. A controlled trial of a two-component acellular, a five-component acellular, and a whole-cell pertussis vaccine. Aspects on the interaction of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae with human respiratory tract mucosa. Importance of timing of maternal combined tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) immunization and protection of young infants. Purification of the pneumococcal N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase to biochemical homogeneity. Intranasal immunization with recombinant outer membrane protein P6 induces particular immune responses against nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. The ricochet of magic bullets: abstract of the institute of drugs report: antagonistic results of Pertussis and Rubella Vaccines. Identification of phase-variable genes that may contribute to nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae nasopharyngeal colonization in humans contributes to our understanding of specific host-pathogen interactions. Killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae by capsular polysaccharide-specific polymeric IgA, complement, and phagocytes. Orally administered microencapsulated Bordetella pertussis fimbriae protect mice from B. The position of Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors in host respiratory colonization and illness. Anti-capsular polysaccharide antibodies cut back nasopharyngeal colonization by Haemophilus influenzae type b in toddler rats. Mechanism of antibody-mediated discount of nasopharyngeal colonization by Haemophilus influenzae kind b studied in an toddler rat model. Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin: evaluation as a protecting antigen and colonization think about a mouse respiratory infection mannequin. Efficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines and their effect on carriage and antimicrobial resistance. Enhanced respiratory clearance of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae following mucosal immunization with P6 in a rat mannequin. Pilot trial of a pentavalent pneumococcal polysaccharide/protein conjugate vaccine in Gambian infants. Pertactin, an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing Bordetella pertussis floor protein that promotes adherence of mammalian cells. Changing epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease amongst older adults in the period of pediatric pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Rapid killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae with a bacteriophage cell wall hydrolase. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines for preventing vaccine-type invasive pneumococcal illness and X-ray defined pneumonia in youngsters lower than two years of age. Prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia by immunization with specific capsular polysaccharides. Interleukin-12 is produced by macrophages in response to stay or killed Bordetella pertussis and enhances the efficacy of an acellular pertussis vaccine by selling induction of Th1 cells. From Bretonneau to therapeutic antibodies, from specificity to specific remedies, Saint-Cyr-SurLoire, France, November 19, 2012. Marginal zone and B1 B cells unite in the early response against T- impartial blood-borne particulate antigens. Efficacy of 23-valent pneumococcal vaccine in preventing pneumonia and bettering survival in nursing home residents: double blind, randomised and placebo managed trial. Intranasal immunization with genetically detoxified diphtheria toxin induces T cell responses in people: enhancement of Th2 responses and toxin-neutralizing antibodies by formulation with chitosan. Heparin-inhibitable lectin activity of the filamentous hemagglutinin adhesin of Bordetella pertussis. Protective levels of diphtheria-neutralizing antibody induced in wholesome volunteers by unilateral primingboosting intranasal immunization related to restricted ipsilateral mucosal secretory immunoglobulin a. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae illness and epiglottitis among Swiss kids from 1980 to 1993: proof for herd immunity amongst older age groups. Decreased Haemophilus colonization in children vaccinated with Haemophilus influenzae kind b conjugate vaccine. Mortality by trigger for eight regions of the world: global Burden of Disease Study. Emergence of antibody to capsular polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae during outbreaks of pneumonia: affiliation with nasopharyngeal colonization. Severe acute lower respiratory infections working, global and regional burden of hospital admissions for severe acute decrease respiratory infections in younger kids in 2010: a systematic evaluation. Burden of disease brought on by Streptococcus pneumoniae in youngsters youthful than 5 years: world estimates.
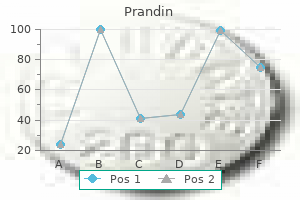
Prandin 2 mg cheap line
Together diabetes liver buy 2 mg prandin otc, trapped antigens and otopathogens activate recruitment of immunocompetent cells and then stimulate local antibody secretion metabolic disease vector discount prandin 1 mg fast delivery, offering evidence that the center ear is an active effector site. These modifications embrace increased numbers of mucous glands, goblet cells, and lymphoid follicles containing germinal facilities. The thickened mucosa also exhibits increased mucus secretion arising from the mucosal hyperplasia throughout the eustachian tube (Matsune et al. Immunoregulatory mucosal immune responses might embody alteration of the secretion and timing of various cytokines, interferons, and chemokines from cells situated within and recruited to the mucosal epithelium. Cross-talk between these molecules may optimize activation of innate immune responses similar to inflammation, but also facilitates attenuation of signaling to decrease the risk of native tissue harm. This synergistic activation of inflammation inducers occurs by way of multiple intracellular signaling pathways (Kweon et al. Only lately, nonetheless, has the relative importance of the person molecules in activation of innate immune responses been described in mice, utilizing dysfunctional or gene knockouts for key molecules of innate immunity. The info portrayed was extracted from published reports of experiments using center ear cell lines and middle ear epithelium and mucosa from animal fashions and human biopsy materials. Inflammatory cytokine expression in these mice typically returns towards regular levels inside per week. In distinction, the resultant middle ear effusion usually lasts significantly Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology Chapter one hundred and one 1931 longer and genes regulating ion and water movement within center ear epithelia are largely downregulated for up to 72 h after an infection, with many remaining downregulated a week after an infection (Macarthur et al. Proliferation of lymphocytes inside the adenoids leads to homing to the center ear; nevertheless, inflammation additionally stimulates elevated native proliferation of lymphocytes throughout the middle ear mucosa itself in a quantity of animal models, including mouse and rat (Takahashi et al. Surprisingly, the variety of proliferating B and T lymphocytes observed in rat center ear mucosa is greater than beforehand noticed in normal lymphatic organs such because the spleen, with dendritic cell, macrophage, and pure killer cell proliferation even higher. Mucosal epithelial cell hyperplasia and edema is stimulated by inflammatory cytokine release and the resultant elevated mucosal thickness reduces the opportunity for pathogen invasion of the epithelial cells through the middle ear mucosa. Mast Cells Mast cell presence and degranulation also contribute to the rapid, nonspecific inflammatory responses by mucosal epithelia to bacterial antigens and lead to phagocytosis of micro organism and launch of proinflammatory cytokines (Mekori, 2004; Dawicki and Marshall, 2007). Reconstitution of the mast cell population in these knockout mice restored the mucosal response, and collectively these findings assist the mast cell role as a mobile sentinel in the normal innate response in the center ear mucosa. Mucus and Fluid Flow Bacterial antigens also quickly stimulate the eustachian tube and middle ear to secrete mucus. The movable mucus layer then permits mucus protection of epithelial cells from pathogens by provision of a mechanism for elimination, via cilia motion, via the eustachian tube to the nasopharynx (Evans and Koo, 2009). Mucin transcription is frequently upregulated in response to common otopathogens similar to S. Mucus manufacturing and its viscosity inside the middle ear are also influenced by water circulate by way of and between the subepithelial, epithelial, and apical or luminal compartments of the mucosal epithelium. Aquaporins are a family of integral membrane proteins that act as specialized channels to facilitate water passage by way of cell membranes in all kinds of organisms together with bacteria, animals, and crops. Aquaporins 1, 4, and 5 are expressed within the rat eustachian tube and center ear epithelium and are localized within the subepithelial fibroblasts, basolateral membranes of the ciliated epithelial cells, and apical surface of the serous glands (Kang et al. Murine expression of aquaporins inside the eustachian tube showed similar localization of aquaporin proteins 1, four, and 5 within the mucosal epithelia, with aquaporin 3 (Takahashi et al. While the proinflammatory cytokine gene expression returned to normal over the following week, ion homeostasis genes remained downregulated, perhaps in response to the fluid within the center ear (Macarthur et al. Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology Chapter 101 1933 Fluid movement over mucosal epithelial surfaces is improved by the motion of surfactant, which reduces surface tension in liquid�air interfaces such because the respiratory tract and tubotympanum. Furthermore, surfactant apoprotein has additionally been detected in human center ear effusions (Yamanaka et al. In distinction, lysozyme was localized to the serous glands and epithelial cells and center ear mucosa in the chinchilla (Hanamure and Lim, 1986). Lysozyme knockout mice (M-/-) are extra prone to pathogen colonization of the middle ear and develop a extra severe center ear inflammatory response after exposure to S. Clearly, antimicrobial proteins similar to lysozyme may act both independently and collectively to stop bacterial colonization and preserve regular function of the center ear. Antimicrobial Proteins and Peptides Overlaying the mucosal epithelial cells, mucus additionally supplies an antimicrobial barrier containing molecules similar to lysozyme, lactoferrin, and -defensins, which act independently and together to inhibit bacterial colonization and stimulate adaptive immune responses (Hellstrom et al. The importance of antimicrobial peptides throughout the middle ear mucosa to scale back middle ear colonization and invasion has been demonstrated in the chinchilla mannequin. Antimicrobial proteins carry out both bactericidal and nonbactericidal actions to maintain normal center ear function. Defensins Defensins are endogenous broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides considered to be antecedents of the immune response. These peptides are lively towards all kinds of bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens and are an evolutionarily conserved characteristic of the innate immune system (Lehrer and Ganz, 1999). Accumulation of lysozyme occurs approximately 6 h earlier than inflammatory cell inflow within the guinea pig mannequin (Kawana, 1995). Streptococcus pneumoniae 6A strains that exhibited either low or high C3 binding have been examined utilizing a murine model and elevated deposition of C3 protein resulted in improved pathogen clearance from the center ear, through facilitated opsonization of invading otopathogens. These responses scale back the opportunity for bacterial adherence to the mucosa and activate adaptive immune responses to upregulate acquired immune responses to then additional reduce pathogen invasion inside the center ear mucosa. Antigen sampling and key immune induction sites could differ between species, and recent focus on improved immune responses to vaccination by way of inhalation have incessantly used murine fashions. Recently, respiratory M cells or isolated individual antigen sampling cells have been recognized in the murine airways. Innate immune responses are quickly induced in response to otopathogens in a nonspecific manner by way of stimulation of a wide selection of cell signaling pathways, together with local production of inflammatory cytokines and sort I interferons (Takeuchi and Akira, 2010). Examination of Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology Chapter a hundred and one 1935 may be identified in the middle ear and eustachian tube epithelium (Matsune et al. Secretory Immunoglobulin A within the Middle Ear Acquired immunological defense within the upper respiratory tract, including the middle ear, in short, depends on the formation of secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA), which may reduce bacterial adherence and enhance bacterial clearance by way of opsonization and phagocytosis. IgA is considered a trademark for local immune responses at mucosal surfaces (Cerutti et al. Antigen-specific IgA-producing cells have been identified in the inflamed middle ear; nevertheless, other immunoglobulin isotypes are also present. It is probably going that the connection between the mucosal and systemic responses might change as the an infection of the center ear progresses, as suggested by Takada et al. Furthermore, the formation of biofilms and/or intracellular colonization of the middle ear epithelia could then scale back the opportunity for the profitable clearance of microbes from the center ear by a subsequent local immune response. Indeed, fast inactivation and clearance of pathogenic bacteria are observed in kids where elevated specific serum antibodies, significantly IgG, are recognized (Freijd et al. In these fashions, the relative paucity of immunocompetent cells inside the center ear mucosa was significantly elevated inside 24 h of otopathogen administration to the middle ear. In response to immune stimulation, lymphocytes have been reported to enter the center ear mucosa from quite so much of lymphatic sources as decided using chromium-51-labeled lymphocytes in guinea pig (Ryan et al. Furthermore, the hypothesis that local proliferation of lymphocytes occurs throughout the center ear mucosa (Takahashi et al.
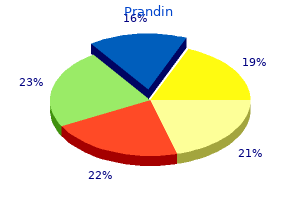
0.5 mg prandin order
The authors concluded that this was most likely as a outcome of diabetes mellitus is characterized by the following except cheap prandin 1 mg with amex an inadequate oral dose gestational diabetes diet kemh buy 0.5 mg prandin visa, which is, generally, significantly higher than that required to stimulate a protecting immune response following i. Furthermore, in addition they demonstrated that their formulation was extraordinarily secure and that it elicited related responses even after storage for 1 yr at 4 �C. Therefore, it seems this novel strategy could additionally be a beautiful basis for mucosal vaccine improvement, owing to its potent adjuvanticity and memorable stability. They belong to the "First Generation" of vaccine adjuvants and have been extensively studied as supply techniques. Such studies present proof that these methods may doubtlessly be efficient towards pathogens of each viral and nonviral origin. While capable of rising antigen uptake and immune responses, a quantity of components affect the adjuvanticity of liposomes. Of those listed in Box 4, the floor charge of a liposome appears to be a key property in figuring out its efficacy as an adjuvant. Cationic liposomes are superior to their adverse or impartial charged counterparts when it comes to the adjuvant impact they exhibit (Nakanishi et al. This interaction resulted in uptake of the liposomes and should clarify the flexibility of liposomes to improve antigen uptake and presentation compared to soluble antigen alone. Another desirable property of liposomes is their potential to stimulate cell-mediated as well as humoral immune responses. Owing to their natural hydrophobicity, liposomes are capable of fusing with target cell membranes, thereby mediating uptake and supply of antigen into the cytosol. The potential of cationic liposomes as efficient mucosal adjuvants has also lately been demonstrated. It therefore appears unlikely that these techniques would have the ability to maintain their structural integrity underneath such conditions, and the chance of antigen degradation is far higher than various, extra robust delivery techniques. This latter function is a result of the formation of a "depot," whereby a drug is launched slowly on the site of injection because the ester linkages holding the copolymers together progressively degrade by a hydrolysis-mediated course of (Shive and Anderson, 1997). The fee at which degradation happens may be manipulated by altering the lactide:glycolide ratio from which the microparticle is prepared. Increasing the quantity of glycolide used to formulate the microparticle has been proven to increase water uptake into the particle, favoring a extra rapid degradation and drug release rate (Miller et al. For occasion, early research within the Nineteen Nineties demonstrated that whereas a 50:50 mix of lactide:glycolide will naturally degrade in approximately 2 months, a particle prepared with an 85:15 lactide:glycolide ratio will stay stable for 5 months or more (Lewis, 1990). Furthermore, the physical dimensions of the microparticle affect their ability to stimulate an immune response. The use of microparticles as vaccine adjuvants has been restricted due to antigen stability issues in the course of the encapsulation process. Exposure of antigens to organic solvents has been reported by a quantity of groups to cause the degradation of antigen, thus rendering the adjuvant system redundant. This different methodology of preparation of antigenassociated microparticles has been reported to retain potent antibody stimulatory capabilities, whereas ensuring the tertiary construction of the antigen is maintained. However, it remains to be seen whether this method will prove to be efficient at inducing a response following oral administration of microparticles with adsorbed antigens. Techniques to ensure antigen stability in the intestine will thus need to be devised in order for these techniques to be used as part of an effective oral vaccine (see below). Microparticles as Mucosal Adjuvants There have been a quantity of research reporting the efficacy of microparticles as mucosal delivery methods, as measured by the protective immune responses elicited towards a extensive range of pathogens, toxins, and purified antigens including Bordetella pertussis (Cahill et al. This discovering means that oral immunization primed a protective immune response at a distal mucosal site. It is necessary to note that in this study, however, a single oral immunization was inadequate, and a systemic prime was required to confer protective immunity on the take a look at subjects. The requirement for a systemic prime was additionally demonstrated in a separate problem study with staphyloccal entertoxin B (Marx et al. It is unlikely, however, that this might show an insurmountable hurdle in the design of microparticlebased oral vaccines, though a major advantage of the utilization of microparticles as antigen delivery techniques is the convenience with which antigens, immune potentiators, or concentrating on molecules could be associated with them. Thus, the incorporation of antigen-adjuvant mixtures into microparticlebased supply systems is believable, additional emphasizing Antigen Delivery Systems I Chapter 63 1225 the idea that these systems are effective platforms round which mucosal vaccines could possibly be based mostly. Furthermore, the potential to prepare microparticulate systems from bio- and mucoadhesive polymers, similar to chitosan, offers a major advantage for antigen retention at mucosal sites over alternative delivery techniques or soluble antigen. Indeed, chitosan-coated microparticles have been studied as a delivery system for a nasal influenza vaccine (Illum et al. This group discovered that each influenza and diphtheria antigens encapsulated inside chitosan-coated microparticles elicited significantly greater titres of antigen-specific serum IgG antibodies following i. Similarly to oral immunization, nasal administration of microencapsulated antigen has also been shown to stimulate the production of protecting mucosal antibodies in the urogenital tract of mice (Ugozzoli et al. Furthermore, the size of the polymer-coated particles (10 m) had been massive enough so that premature uptake in the small gut was prevented. The authors discovered that this strategy was capable of inducing a protective immune response to viral challenge no less than comparable to that following i. While alternatives, such because the nasal or sublingual routes of immunization, have certainly shown promise, the efficacy noticed in small animal fashions should be translated into human trials earlier than such routes can be thought-about as viable choices, able to inducing protective immune responses with out compromising affected person security. While rectal supply might well be an effective means by which to induce genital tract immunity, rectal immunization is unlikely to be well acquired by most people, and cultural obstacles might prevent the implementation of such an immunization technique. Studies demonstrating that nasal and, extra recently, sublingual and huge intestinal immunization can induce both antibody and cellular immunity in the murine genital tract are extraordinarily constructive. The optimal nonliving particulate formulation is prone to be an integrated system combining antigens with adjuvant and delivery methods. Going forward, our view is that the long run for oral vaccines will lie in the growth of built-in, multicomponent techniques facilitating the focused supply of coadministered antigens with adjuvant and supply techniques. These methods ought to facilitate site-specific launch in the gastrointestinal tract so as to promote protecting immunity at websites focused for particular pathogens. Genetically engineered nontoxic vaccine adjuvant that combines B cell targeting with immunomodulation by cholera toxin A1 subunit. Quillaja saponaria extract as mucosal adjuvant with chitosan functionalized gold nanoparticles for mucosal vaccine supply: stability and immunoefficiency studies. Safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of intranasal, reside attenuated influenza vaccine. Immune responses and safety towards Bordetella pertussis infection after intranasal immunization of mice with filamentous haemagglutinin in solution or incorporated in biodegradable microparticles. Prepandemic influenza vaccine H5N1 (split virion, inactivated, adjuvanted) (Prepandrix): a evaluation of its use as an lively immunization in opposition to influenza A subtype H5N1 virus. M-cell targeting of entire killed bacteria induces protecting immunity in opposition to gastrointestinal pathogens. Langerhans cells require indicators from each tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta for migration. Crucial position for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants.
Buy prandin 1 mg with mastercard
Known host restrictions that restrict the capacity of feminine mice to mimic gonorrhea in people embody the absence of human-specific receptors for adherence and invasion pathways blood glucose goals in pregnancy generic prandin 1 mg online, human transferrin and lactoferrin glycoproteins canine diabetes in older dogs buy generic prandin 2 mg on line, soluble regulators of the complement cascade (factor H, C4b-binding protein), and IgA1, the substrate of gonococcal IgA1 protease (extensively reviewed in Jerse et al. Establishment of Experimental Murine Infection Female mice can be transiently colonized with N. Colonization clears upon transition into the postovulatory, progesterone-dominant phases of the estrous cycle (Braude, 1982; Johnson et al. The histology and physiology of the genital tracts of estradiol-treated mice mimic essentially the most hospitable stages of the estrous cycle for N. Neutrophils from untreated and estradiol-treated mice show no difference in the capability to kill N. In one examine on women with gonorrhea who have been left untreated, 4 to six consecutive cultures have been negative for N. A similar recovery pattern happens throughout experimental an infection of estradiol-treated mice. After vaginal inoculation, excessive numbers of gonococci are recovered early in an infection, after which intervals of significantly decreased recovery or culture-negative "windows" occurs. This culture-negative interval is often adopted by a rise in the variety of gonococci recovered (Jerse, 1999; Simms and Jerse, 2006). Characteristics of Experimental Murine Infection Infection of estradiol-treated mice persists for an average of 10�12 days and as long as 40 days. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is localized within the cervicovaginal lumen and inside genital tract tissue, including the lamina propria (Song et al. This rate may be dose dependent and truly larger when based mostly on the detection of gonococci in endometrial tissue by confocal fluorescent microscopy after vaginal inoculation (Imarai et al. In competitive infections with the wild-type strain, the lptA mutant was attenuated as could be predicted by its increased susceptibility to host defenses. Recently, an lptA mutant was additionally shown to be attenuated throughout aggressive infection with the wild-type father or mother pressure in the human urethral challenge mannequin. This discovering supports the capacity of feminine mice to predict some occasions in people (Hobbs et al. The Th17 Pathway the immunological basis of the extreme inflammatory response noticed throughout acute gonorrhea has been further elucidated by the current demonstration that N. The Th17 pathway is induced in other pyogenic organism infections, which, much like N. Lipocalin-2 and S100 A8/A9 proteins are elevated in vaginal washes from contaminated mice (Yedery and Jerse, unpublished observations). Although untreated gonococcal urethritis in people clears inside a couple of weeks, different mucosal websites help extra persistent infections. Host restrictions may also confound comparisons between mouse and human infections. Longer time period persistence of infection in mice may be challenged by host-restricted receptors that provide an intracellular niche to the gonococcus throughout human an infection, or by the shortcoming of N. Complement Complement is current at comparatively high basal levels in the feminine genital tract and in inflammatory exudates. This mechanism of complement evasion is most likely going instrumental for blood-stream an infection on the basis of the strong correlation between disseminated gonococcal an infection and strains that reveal PorB-mediated serum resistance (Ram et al. There is also no evidence that any of the numerous antioxidative elements produced by N. It is interesting to observe that full piliation ensuing from the motion of a metalloprotease also protects N. Hormonal Factors As discussed, gonococcal genital tract infections in girls are sometimes inapparent, with rates of inapparent cervical infections ranging between 19% and 80% (McCormack et al. Repeat infections are common and might happen with the identical PorB serovar (Brooks et al. However, because the humoral immune response to infection is transient and the titer of particular antibody in serum and genital secretions is undetectable or not exceptional (Hedges et al. The lack of an adaptive response to gonococcal mucosal infection has additionally been investigated using the mouse an infection mannequin. Estradiol-treated mice develop a transient and insignificant humoral response to N. These stories are the primary in vivo demonstrations that protection against gonococcal an infection and induction of a reminiscence response could be obtained by strategically manipulating the host response. Several mechanisms have been described that result in immunosuppression of Th1-/Th2-mediated particular immune responses. Gonorrhea Vaccine Development Progress in the improvement of a gonorrhea vaccine has been gradual. Difficulties in growing a vaccine towards gonorrhea embrace the lack of recognized correlates of protection against gonorrhea and the excessive variety of antigenically or section variable N. Early research in chimpanzees showed promising outcomes with outer membrane vesicle-based vaccines, but solely two vaccines, a killed entire cell vaccine and a purified pilin vaccine, have been tested in scientific trials, neither of which was efficient (reviewed in Zhu et al. The transferrin receptor is a promising target on the idea of its surface publicity, limited antigenic variability, and significance for experimental urethritis of male topics (Cornelissen et al. The antisera are bactericidal and block Gc development on media containing only human transferrin as an iron source (Price et al. PorB is an attractive vaccine target because of its stable expression, abundance within the outer membrane, and roles in pathogenesis. Immunization of mice with recombinant PorB devoid of Rmp (reduction-modifiable protein) was not protecting, though reduced colonization occurred in mice that developed a Th1 response after footpad immunizations with viral replicon particles expressing recombinant PorB (Zhu et al. The PorB monomer has eight surfaceexposed loops, most of which have antigenic heterogeneity due to immune pressure. The sequence heterogeneity of most of the surface-exposed PorB loops could be circumvented by the use of cyclic PorB loop peptides that mimic conformational epitopes. Cyclic PorB loop peptides can elicit antibodies that crossreact with gonococcal strains of various porB variable region types; some elicit antibodies that are crossreactive for strains of the PorB1a and PorB1b serotypes (Garvin et al. Further development of broadly reactive PorB peptide antigens would require the introduction of Th cell epitopes or conjugation to larger antigens. Many antigens have been unsuccessfully examined in the mouse model (Jerse, unpublished observation). The basic lack of success in identifying a protective antigen in this model suggests the need for a larger understanding of the mechanisms by which N. The number of infected people increases with age, and more ladies are contaminated than males (Xu et al. The lowest charges are in West Europe, the place the prevalence is roughly 18% for ladies and 13% for males. When present, the signs consist of localized painful genital lesions and swollen regional lymph nodes. The lesions are mucocutaneous and the result of direct infection and the cytopathic impact of the virus, resulting in cellular lysis and focal necrosis of the genital epithelium. The lesions, when present, can be very painful and a supply of great morbidity for the affected person.
2 mg prandin purchase free shipping
For wholesome kids diabetes medications linked to pancreatic cancer prandin 2 mg discount line, center ear effusion usually resolves inside 7 days in 40% of cases diabetes type 1 meal plan order prandin 2 mg on-line, and in 75�90% of circumstances decision happens inside four weeks (Mandel et al. Persistent bacterial infection of the adenoids has been the main focus of recent microbial research that demonstrated that S. Furthermore, intracellular localization of bacteria throughout the center ear mucosal cells has now been confirmed and the bacterial species subsequently identified (Coates et al. Multispecies bacterial biofilms containing these species have been visualized on the middle ear mucosa and characterized using confocal microscopy. The presence of multiple bacterial species, within the similar center ear mucosal samples, could provide additional protection to every microbe, protecting them from host innate and bought immune defenses (Armbruster et al. Biofilm formation is thought to significantly improve bacterial protection from antibiotic therapy (Slinger et al. Biofilm formation has also been noticed in each the nasopharynx and center ear within the chinchilla model after initial intranasal inoculation with influenza A followed by S. Biofilm formation happens rapidly and the presence of micro organism, not efficiently cleared by native or systemic immune responses or antibiotic remedy, poses a challenge for vaccine efficacy. The resultant reduced pressurization of the center ear causes extravasation of fluid into the middle ear chamber. Within the middle ear mucosa, the native proliferation fee ranged between 2% and 9% inside immunocyte subsets (Jecker et al. T-cell Regulation and Implication for the Middle Ear the middle ear mucosa is the first target for adenoidderived lymphocytes. These cells were observed in larger numbers in youngsters who were tradition optimistic for S. Alternatively, Treg cells throughout continual middle ear effusion could carry out a significant position within the homeostatic control of inflammation in tissues incessantly exposed to pathogens, not simply by suppression of T cell production in total but by increasing the chance for T cells that recognize self-antigens to escape choice within the thymus and thus contribute actively to continual inflammatory processes. Immune responses to common otopathogens throughout the center ear have to be tightly regulated provided that mucosal surfaces are delicate, often one cell thick. Active regulation of innate immune response is due to this fact vital to decrease immune-generated tissue destruction and harm. Thus, mucosal immunization could considerably cut back induction of immune-mediated harm in the center ear by way of decreased risk of reduction of IgG-induced mucosal inflammation and increased antigenspecific S-IgA secretion. However, given observations within the adenoid, Treg cell immunity could additionally be necessary in the control of inflammatory processes in middle ear an infection. There are a variety of pneumococcal vaccines, developed primarily Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology Chapter a hundred and one 1937 for prevention of invasive pneumococcal disease, presently obtainable (Cripps and Otczyk, 2006; Cripps et al. Studies using animal models and the mucosal immunization route have demonstrated that immunization was able to significantly enhance clearance of every bacterium from the center ear when subsequently challenged with reside bacteria (Cripps and Kyd, 2007). Finally, the function of regulatory T cells in controlling the middle ear immune response to pathogens requires further investigation. Rate of concurrent otitis media in upper respiratory tract infections with specific viruses. Indirect pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis in polymicrobial otitis media happens by way of interspecies quorum signaling. Respiratory viruses augment the adhesion of bacterial pathogens to respiratory epithelium in a viral species- and cell type-dependent manner. Immunological responsiveness of chinchillas to outer membrane and isolated fimbrial proteins of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Immunoglobulin G, complete and subclass, in children with or with out recurrent otitis media. Amoxicillin center ear fluid penetration and pharmacokinetics in youngsters with acute otitis media. Ascension of commensal micro organism from the nasopharynx by way of the eustachian tube to the center ear initiates innate responses inside the center ear mucosa that, through a fancy series of signaling cascades, result in both clearance or failure to clear the pathogen from the middle ear. Although nearly all of childhood middle ear infections resolve uneventfully in most youngsters, very younger kids are at higher risk of pathogen colonization regardless of upregulation of innate and purchased immune responses by the middle ear. Respiratory viruses interfere with bacteriologic response to antibiotic in kids with acute otitis media. Role of leukotriene B4 and interleukin-8 in acute bacterial and viral otitis media. Viral higher respiratory tract an infection and otitis media complication in younger children. Presence of viral nucleic acids in the center ear: acute otitis media pathogen or bystander Cytological and histological changes within the middle ear after inoculation of influenza A virus. The role of chronic an infection in children with otitis media with effusion: evidence for intracellular persistence of bacteria. High pneumococcal serotype specific IgG, IgG1 and IgG2 ranges in serum and the middle ear of children with recurrent acute otitis media receiving air flow tubes. Comparison of mucosal and parenteral immunisation in two animal fashions of pneumococcal an infection: otitis media and acute pneumonia. Serum IgA and IgG practical antibodies and their subclasses to Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular antigen found in two aged-matched cohorts of youngsters with and without otitis media with effusion. Role of complement in protection of the middle ear revealed by restoring the virulence of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae siaB mutants. Plasma anti-pneumococcal antibody activity of the IgG class and subclasses in otitis inclined youngsters. A potential examine demonstrating an association between plasma IgG2 concentrations and susceptibility to otitis media in youngsters. Jun N-terminal protein kinase enhances middle ear mucosal proliferation throughout bacterial otitis media. Phenotypic and useful plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Experimental otitis media after nasal inoculation of Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza A virus in chinchillas. Eustachian tube histopathology throughout experimental influenza A virus an infection in the chinchilla. Normal distribution of lysozyme- and lactoferrin-secreting cells in the chinchilla tubotympanum. Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology Chapter a hundred and one 1939 Harabuchi, Y. Nasopharyngeal colonization with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and recurrent otitis media. Isolation and characterization of human beta-defensin-3, a novel human inducible peptide antibiotic. Myeloid differentiation main response gene 88 is required for the decision of otitis media. Proliferating macrophages, dendritic cells, pure killer cells, T and B lymphocytes within the center ear and Eustachian tube mucosa throughout experimental acute otitis media in the rat. The role of inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of otitis media and sequelae.