Prevacid
Prevacid dosages: 30 mg, 15 mg
Prevacid packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Prevacid 30 mg cheap amex
The most severely affected elements of the world are central Asia and western areas of Africa gastritis vomiting blood buy generic prevacid 15 mg online. In North America congestive gastritis definition generic 30 mg prevacid, anthrax is endemic in northern Alberta and the Northwest Territories. In the United States, sporadic outbreaks of anthrax occur in northwest Mississippi/southeast Arkansas and western Texas. The illness is also endemic throughout Mexico, Central America, and many South American international locations. Data from research of central Asia help seasonal outbreaks, with the largest variety of cases occurring in late summer season (77, 78). Concentrations of spores following disease outbreaks are thought to end result from rains that pool spores in low-lying areas, versus bacterial proliferation. Decomposition of contaminated animals at anthrax carcass websites results in increased numbers of vegetative cells, however ultimately the numbers lower as cells sporulate or die (79). Domestic livestock, including sheep and cattle, and wild herbivores, corresponding to bison, elephants, hippopotami, and kudu, are particularly prone to infection (83). Today, most naturally acquired human instances of anthrax are cutaneous infections ensuing from contact with dead contaminated animals or their merchandise. Eleven inhalation and eleven cutaneous circumstances of anthrax in people have been traced to 4 envelopes containing B. This tragic occasion demonstrated the obvious ease with which the organism could be dispersed and solidified the position of B. Following spore germination, vegetative cells produce the antiphagocytic capsule and the anthrax toxin proteins, virulence elements which are crucial for initiation of systemic illness (85, 86). In humans, bacteremia begins after an asymptomatic incubation interval of 1 to 6 days. Following the onset of bacteremia, sufferers can experience flu-like signs for 1 to 5 days prior to an acute illness stage that lasts 1 to 2 days. In addition to toxin and capsule, other secreted and nonsecreted elements have been reported to affect hostpathogen interactions and have an effect on host pathology (98, 99). Among these are extracellular proteases that interfere with the immune response by cleaving antimicrobial peptides (100). Crossing of the mind barrier is taken into account to be key to the intensive mind pathology that has been reported for human disease (104). The emetic syndrome is the results of an intoxication attributable to the single depsipeptide toxin cereulide, which is preformed in meals. The genes encoding the cereulide synthetase toxin genes are primarily found in a definite subgroup of B. Intoxication associated to cereulide has been linked to extreme medical manifestation, similar to acute liver failures and acute encephalopathy (110). Due to the high organic exercise of the cereulide toxin, occasionally liver transplantation is critical as a life saving measure (111, 112). In addition to intrinsic strain-associated variations in pathogenic potential, virulence is affected by environmental elements (58, a hundred and fifteen, 116). The diarrheal syndrome has been linked to completely different enterotoxins thought to be produced after outgrowth of spores, taken up with contaminated meals, and fifty five. The Bacillus cereus Group 879 this regulon, which incorporates genes encoding varied degradative enzymes, is activated by the quorum sensing regulator NprR and allows B. Altogether, these pathogenic and saprophytic capabilities are highly efficient adaptive traits that allow the species to grow and survive in varied natural situations and niches. Generally, vegetative cells appear in chains, with the square ends of the cells fitting carefully together. Variations in chain size occur as a standard facet of development in different media and environments (34, 130). Fine features of spores may be altered in numerous growth and sporulation conditions. Depletion of the glycosyltransferases ends in irregularly formed, nonviable cells (132). The S-layers are paracrystalline arrays of protein that serve as protective limitations and as scaffolds for housekeeping enzymes and virulence factors (136). Mutants deleted for putative acetyltransferases are unable to deposit the S-layer-associated murein hydrolase BslO at cell division septa and have altered chain lengths (137). The capsule degradation merchandise are thought to inhibit the innate immune response by way of targeting of cytokine pathways (142). Further investigations are needed to decide the precise features of these capsules. Germinant receptors in the internal membrane initiate the signal transduction pathway that results in outgrowth of the spore and the vegetative cell state (143). A shell of peptidoglycan containing two sublayers, the cortex and the germ cell wall, surrounds the inner membrane. At outgrowth of the spore, the germ cell wall becomes the nascent cell wall of the vegetative cell. Surrounding the cortex is the spore coat, which accommodates approximately 70 proteins arranged in layers to form a considerably versatile structure (143). The exosporium, an extra layer surrounding the spore coat of some Bacillus species that has been most well studied in B. Among the roughly 20 proteins of the basal layer is ExsY, which can self-assemble into structures resembling the intact basal layer and thus seems to be a key participant in exosporium formation (146). It additionally supplies resistance to specific chemical substances in vitro and to nitric oxide within the context of the macrophage (147�149). However, the exosporium protein BclA binds macrophage receptors to mediate interactions with epithelial cells and extracellular matrix proteins (153, 154), suggesting a job for the exosporium in pathogenesis (145). It must be noted however, that the spore surface-Cry protein association could merely result from concomitant synthesis somewhat than from a particular interaction. Sporulation the sporulation signal cascade has been well studied in Bacillus subtilis, and the pathways and regulators of sporulation within the B. In the wild, spores (which are the infectious type of the bacterium) only form when the blood of an infected carcass is uncovered to the environment (78). The lack of sporulation in the mammalian host appears to outcome from a particular configuration of the phosphorylation cascade in this species (170�172). The Rap phosphatases negatively control sporulation by stimulating a element of the phosphorelay concerned within the phosphorylation of Spo0A, the grasp regulator of sporulation initiation (175). Rap activity is managed by the Phr signaling peptides through a quorum sensing system. These plasmid-borne Rap-Phr techniques may present advantages for adaptation of those pathogenic bacteria to their respective ecological niches. Germination Dynamics and Signals the overall means of germination, in which spores transition to metabolically lively vegetative cells, is very conserved within the Bacillus genus, but the particular indicators and related receptors range among species. Many germinant receptors have been described within the inner membrane of Bacillus species. Once Bacillus spores germinate, spore cortex lytic enzymes degrade the cortex peptidoglycan, allowing core rehydration and cell outgrowth (160).
Prevacid 30 mg buy otc
Cutting edge: a new method to modeling early lung immunity in murine tuberculosis gastritis nursing diagnosis prevacid 15 mg purchase overnight delivery. Interleukin 12p40 is required for dendritic cell migration and T cell priming after Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection gastritis symptoms treatment diet prevacid 30 mg purchase line. Regulation of antigen presentation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a role for Tolllike receptors. Dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is influenced by host factors and precedes the initiation of T-cell immunity. Manicassamy B, Manicassamy S, Belicha-Villanueva A, Pisanelli G, Pulendran B, Garc�a-Sastre A. Granuloma correlates of safety against tuberculosis and mechanisms of immune modulation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Novel human immunodeficiencies reveal the essential position of type-I cytokines in immunity to intracellular bacteria. Interferon-gamma-receptor deficiency in an infant with deadly bacille Calmette-Gu�rin infection. A mutation in the interferon-gamma-receptor gene and susceptibility to mycobacterial an infection. Mutation in the signaltransducing chain of the interferon-gamma receptor and susceptibility to mycobacterial an infection. Inherited interleukin 12 deficiency in a child with bacille Calmette-Gu�rin and Salmonella enteritidis disseminated infection. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of inherited autosomal recessive susceptibility to disseminated Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette-Gu�rin an infection. Severe mycobacterial and Salmonella infections in interleukin-12 receptor-deficient sufferers. Interleukin-12 receptor beta1 deficiency in a patient with stomach tuberculosis. Clinical tuberculosis in 2 of 3 siblings with interleukin-12 receptor beta1 deficiency. Mice genetically inactivated in interleukin-17A receptor are faulty in long-term control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis an infection. Interleukin-17 limits hypoxiainducible issue 1a and development of hypoxic granulomas during tuberculosis. Dichotomy of cytokine profiles in sufferers and high-risk wholesome topics exposed to tuberculosis. Depressed T-cell interferon-gamma responses in pulmonary tuberculosis: evaluation of underlying mechanisms and modulation with therapy. Cytokine profiles for peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis and healthy household contacts in response to the 30-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. An essential function for interferon gamma in resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis an infection. Gerosa F, Nisii C, Righetti S, Micciolo R, Marchesini M, Cazzadori A, Trinchieri G. Regulation of neutrophils by interferon-g limits lung inflammation throughout tuberculosis an infection. Interferon-gammaresponsive nonhematopoietic cells regulate the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Regulatory T cells are expanded in blood and illness websites in patients with tuberculosis. Chen X, Zhou B, Li M, Deng Q, Wu X, Le X, Wu C, Larmonier N, Zhang W, Zhang H, Wang H, Katsanis E. Regulatory T cells depress immune responses to protective antigens in energetic tuberculosis. Mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan- and prostaglandin E2-dependent enlargement of regulatory T cells in human Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Pathogen-specific regulatory T cells delay the arrival of effector T cells in the lung during early tuberculosis. Pathogen-specific Treg cells broaden early during mycobacterium tuberculosis infection however are later eradicated in response to interleukin-12. Host defense and recruitment of Foxp3+ T regulatory cells to the lungs in persistent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection requires tolllike receptor 2. Expression levels of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen-encoding genes versus production ranges of antigen-specific T cells throughout stationary level lung an infection in mice. Effect of development state on transcription levels of genes encoding main secreted antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within the mouse lung. Antigen availability shapes T cell differentiation and performance throughout tuberculosis. Intravital imaging reveals limited antigen presentation and T cell effector function in mycobacterial granulomas. A multistage tuberculosis vaccine that confers environment friendly protection earlier than and after publicity. Inhibiting the programmed dying 1 pathway rescues Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific interferon g-producing T cells from apoptosis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Functional capacity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T cell responses in humans is associated with mycobacterial load. The Tim3galectin 9 pathway induces antibacterial exercise in human macrophages contaminated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector capabilities. Memory T cell-mediated resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in innately vulnerable and resistant mice. Specificity of a protective reminiscence immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Characteristics and specificity of acquired immunologic memory to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. B cells and antibodies in the defense towards Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Human tuberculous granulomas induce peripheral lymphoid follicle-like buildings to orchestrate native host defence in the lung. Characterization of the tuberculous granuloma in murine and human lungs: cellular composition and relative tissue oxygen tension. B cells reasonable inflammatory development and improve bacterial containment upon pulmonary problem with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Fc gamma receptors regulate immune activation and susceptibility throughout Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. B cells producing kind I interferon modulate macrophage polarization in tuberculosis. Selective expansion of human gamma delta T cells by monocytes contaminated with reside Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells.
Order prevacid 30 mg overnight delivery
This signifies that intracellular heme acquisition is managed on the membrane level without the necessity for devoted import techniques gastritis muscle pain prevacid 30 mg cheap visa, a minimal of at high heme concentrations (82) chronic gastritis symptoms stress prevacid 15 mg with visa. While pathogens might have access to blood heme throughout infection, the existence of heme-responsive genes in lactococci and other commensal bacteria raises questions concerning the nature of heme sources of their pure ecosystems (48). Cell nucleotide swimming pools are additionally influenced by the presence of exogenous nucleobases or nucleosides in the medium. Pathways of uptake and utilization of those compounds (the so-called salvage pathways, which vary among organisms) are key contributors to bacterial responses to adjustments within the medium and to increased intracellular degradation of nucleic acids as illustrated under. Mutation of the pyrR gene leads to constitutively elevated levels of the pyrimidine biosynthetic enzymes (101). Interestingly, several pyr operons in Mycobacterium smegmatis have been found to be regulated by PyrR by translational repression (105). Interestingly, riboswitch management of the PurRregulated xpt operon is modulated by purine pools (104). In operons activated by PurR, the space between the Pur box and the -10 region was fifty seven to fifty eight bp. The two kinds of PurR proteins are associated, and the Bacillus sort seems to have advanced early from the activator kind of PurR (109). The PurR regulon consists of purine biosynthetic genes but in addition genes concerned in purine uptake and conversion into purine monophosphates. Genes involved in C1 carbon metabolism, guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) metabolism, phosphonate transport, and pyrophosphatase activity were also recognized. Thymine could additionally be incorporated by way of pyrimidine phosphorylase to thymidine and additional phosphorylated by thymidine kinase (tdk) to the corresponding monophosphate (110). Thus, all frequent nucleobases except cytosine could be transported and included into nucleotides. Pyrimidine nucleosides can also be immediately converted to nucleotides because the corresponding nucleoside kinases (udk and tdk) are useful in lactococci. Regulation by Nucleotide Pools Low nucleotide pool sizes may function internal stress indicators that provoke expression of stress response genes in L. An important hyperlink between nucleotide swimming pools and cell wall synthesis was uncovered: as a half of the uridine synthesis pathway, PyrB converts L-aspartate (L-Asp) to N-carbamoyl-L-Asp. PyrB competes with cell wall enzymes for L-Asp; thus, L-Asp consumption during speedy development favors cell wall flexibility, whereas its accumulation in the stationary section might result in a extra inflexible cell envelope (118). These examples suggest that nucleotide swimming pools join nucleotide metabolism to the cell envelope structure. The Spx family is intrinsic to cell responses to oxidative stress and cell wall harm conditions. In distinction to CdaA, small molecules may interact with GdpP to modulate its exercise. Finally, basic cell metabolism can decide how well the bacterium copes with oxidative circumstances. Selections Leading to Improved Adaptation to Environmental Stress Situations Oxygen is a ubiquitous stress. If not eliminated, reactive oxygen derivatives provoke cell injury that can be deadly. An various means of making a more decreasing surroundings is by including glutathione, a redox peptide (141), or dithiothreitol, a reducing agent (75), to the medium. Lactococci lack catalase, which eliminates hydrogen peroxide in lots of aerobic micro organism. Respiration metabolism in lactococci is a "natural" and environment friendly means of eliminating oxygen compared to fermentation, resulting in good survival in the stationary section (46, 72). Significantly, acidification could additionally be more extreme if cells are immobilized, as a outcome of acid diffusion could also be slower. This scenario may provide a natural selection for strains to escape from a constrained setting, and it was proven experimentally to generate multistress-resistant mutants (116). Interestingly, acid-resistant mutants evoked modifications linking nucleotide pools (ppGpp) and cell wall alterations (116, 118). Studies utilizing a semiliquid medium have been used to impose a pure choice for mutants that may extra readily escape a constraining surroundings (144). Salt and acid induce expression of GadB and GadC, which are putatively concerned in glutamate transport by an antiporter; glutamate transport presumably involves efflux of H+, thereby maintaining intracellular pH (130, 131). Toxic products such as bile, quaternary compounds, and antibiotics may be actively pumped out of the cell by specialized transport features. Among the quite a few transport techniques that shuttle metabolites out and in of the cell, some mediate drug expulsion and, consequentially, can confer drug tolerance (132). LmrA (590 amino acids) is just like the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein, thus raising questions concerning the origins of the pump. Judging from sequence analyses, an LmrA dimer could be the practical equal of the P-glycoprotein (LmrA is 32% identical to half of the P-glycoprotein, particularly inside recognized useful domains). Remarkably, LmrA is practical in eukaryotic cells and is in a position to exchange P-glycoprotein defects, thus making L. The CmbT transporter (Llmg 1104), described initially as a cysteine and methionine biosynthesis transporter, was subsequently identified as a multidrug efflux pump that effluxes a variety of antibiotics and toxic medicine (133). When supplemented with hemin, aerobically grown lactococci can bear respiration metabolism. As a end result, cells saved at 4�C show markedly better survival in comparison with cells grown aerobically in the absence of heme or in static circumstances. Use of semiliquid medium for selections would possibly prove efficient in examining factors which might be at work when micro organism are immobilized of their host and has additionally proven helpful in different kinds of alternatives during which surface properties are altered (137). Transposon insertional mutagenesis was additionally used to choose for stress-resistant strains of lactococci. Low intracellular levels of those metabolite swimming pools in the mutants might constitute a hunger signal to induce a stress response. These mutant strains show higher long-term survival than their nonmutated mother and father. An H2O2-resistant mutant was isolated at high temperature (37�C), and though its resistance was 1,000-fold larger than the parental strain, it displayed no different stress resistance phenotypes (148). H2O2resistant mutants might have a survival benefit in coculture with strains producing mM amounts of H2O2. In the former case, use of H2O2-resistant lactococci may result in growth of latest fermented merchandise; in the latter, extra environment friendly growth of lactococci could enhance the hygiene of meals merchandise. Greater oxidative stress tolerance of pst was linked to its results on copper and zinc homeostasis (151). Their larger resistance to stress could overcome survival variability as seen in conventional strains. The specifically acid-resistant strains may provide resistance to extreme acid pH situations or could additionally be better at sustaining a neutral inner pH. Stress-resistant strains might survive longer in fermentation and may be extra proof against harsh storage conditions (such as freezing and lyophilization).
15 mg prevacid effective
Distinct mutations in PlcR explain why some strains of the Bacillus cereus group are nonhemolytic diet for gastritis and diverticulitis prevacid 15 mg discount free shipping. Structural foundation for the activation mechanism of the PlcR virulence regulator by the quorumsensing sign peptide PapR gastritis what not to eat prevacid 30 mg with amex. Bouillaut L, Perchat S, Arold S, Zorrilla S, Slamti L, Henry C, Gohar M, Declerck N, Lereclus D. Molecular foundation for group-specific activation of the virulence regulator PlcR by PapR heptapeptides. Specificity and polymorphism of the PlcR-PapR quorum-sensing system within the Bacillus cereus group. Peptide-binding dependent conformational modifications regulate the transcriptional exercise of the quorum-sensor NprR. G�lis-Jeanvoine S, Canette A, Gohar M, Caradec T, Lemy C, Gominet M, Jacques P, Lereclus D, Slamti L. Genetic and practical analyses of krs, a locus encoding kurstakin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. A novel sensitive bioassay for detection of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin and associated depsipeptide ionophores. Spores from mesophilic Bacillus cereus strains germinate better and develop faster in simulated gastrointestinal situations than spores from psychrotrophic strains. Ceuppens S, Van de Wiele T, Rajkovic A, FerrerCabaceran T, Heyndrickx M, Boon N, Uyttendaele M. Impact of intestinal microbiota and gastrointestinal circumstances on the in vitro survival and progress of Bacillus cereus. CodY, a pleiotropic regulator, influences multicellular behaviour and efficient production of virulence elements in Bacillus cereus. Global results of virulence gene regulators in a Bacillus anthracis pressure with both virulence plasmids. Cereulide synthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus is controlled by the transition state regulator AbrB, but not by the virulence regulator PlcR. The world regulator CodY regulates toxin gene expression in Bacillus anthracis and is required for full virulence. Ces locus embedded proteins management the non-ribosomal synthesis of the cereulide toxin in emetic Bacillus cereus on a quantity of levels. Activation of the Bacillus subtilis world regulator CodY by direct interplay with branched-chain amino acids. Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY recognized by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis. Positive regulation of Bacillus subtilis ackA by CodY and CcpA: establishing a possible hierarchy in carbon circulate. Transition-state regulators: sentinels of Bacillus subtilis post-exponential gene expression. Perchat S, Talagas A, Poncet S, Lazar N, Li de la SierraGallay I, Gohar M, Lereclus D, Nessler S. How quorum sensing connects sporulation to necrotrophism in Bacillus thuringiensis. Cloning and characterization of a gene whose product is a trans-activator of anthrax toxin synthesis. Characterization of a plasmid area concerned in Bacillus anthracis toxin production and pathogenesis. A plasmid-encoded regulator couples the synthesis of poisons and floor constructions in Bacillus anthracis. Molecular characterization and protein analysis of the cap region, which is essential for encapsulation in Bacillus anthracis. AtxA prompts the transcription of genes harbored by each Bacillus anthracis virulence plasmids. CapE, a 47-aminoacid peptide, is critical for Bacillus anthracis polyglutamate capsule synthesis. The atxA gene product prompts transcription of the anthrax toxin genes and is important for virulence. A twin position for the Bacillus anthracis grasp virulence regulator AtxA: control of sporulation and anthrax toxin manufacturing. Identification and characterization of a trans-activator involved within the regulation of encapsulation by Bacillus anthracis. Capsule synthesis by Bacillus anthracis is required for dissemination in murine inhalation anthrax. Glucosedependent activation of Bacillus anthracis toxin gene expression and virulence requires the carbon catabolite protein CcpA. Two small c-type cytochromes affect virulence gene expression in Bacillus anthracis. The stringent response of Bacillus anthracis contributes to sporulation however not to virulence. Opposing effects of histidine phosphorylation regulate the AtxA virulence transcription consider Bacillus anthracis. Crystal structure of Bacillus anthracis virulence regulator AtxA and results of phosphorylated histidines on multimerization and exercise. Mobilization of "nonmobilizable" plasmids by the aggregation-mediated conjugation system of Bacillus thuringiensis. Construction of novel Bacillus thuringiensis strains with completely different insecticidal activities by transduction and transformation. Mating system for transfer of plasmids amongst Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis. Transformation and expression of a cloned deltaendotoxin gene in Bacillus thuringiensis. The three Bacillus anthracis toxin genes are coordinately regulated by bicarbonate and temperature. Identification of the principle promoter directing cereulide biosynthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus and its software for real-time monitoring of ces gene expression in foods. The transformation frequency of plasmids into Bacillus anthracis is affected by adenine methylation. Genome engineering in Bacillus anthracis utilizing tyrosine site-specific recombinases. Biosynthetic analysis of the petrobactin siderophore pathway from Bacillus anthracis. Identification of self-transmissible plasmids in 4 Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies. Plasmid switch between strains of Bacillus thuringiensis infecting Galleria mellonella and Spodoptera littoralis. Plasmid transfer between the Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki and tenebrionis in laboratory culture and soil and in lepidopteran and coleopteran larvae.
Order 30 mg prevacid amex
Antibodies for the therapy of bacterial infections: present experience and future prospects gastritis diet natural treatment buy 30 mg prevacid with amex. Solonamide B inhibits quorum sensing and reduces Staphylococcus aureus mediated killing of human neutrophils chronic gastritis recovery time 15 mg prevacid proven. Norlichexanthone reduces virulence gene expression and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Structure-activity evaluation of synthetic autoinducing thiolactone peptides from Staphylo- 765 271. Tedizolid: a novel oxazolidinone with potent activity against multidrug-resistant Grampositive pathogens. Lincosamides: chemical construction, biosynthesis, mechanism of action, resistance, and functions. A crucial evaluation of the properties of fusidic acid and analytical strategies for its determination. All of the vaccine candidates functioned nicely in animal fashions, mostly murine fashions, but also in rabbits and primates. The reliance on murine models could be related to the intensive knowledge out there about murine immunity. Based on the big number of failures, a reasonable conclusion is that murine immunity and human preventive immunity towards S. The divergence of human and murine immunity has been detailed within the recent literature (1�6). All of these antigens produced strong humoral immunity that supplied safety in animal models. Information from immune defects, scientific trials, and studies of human sepsis are offering important details about the immune response to S. Vitamin D Deficiency and Dendritic Cell Failure Patients with vitamin D deficiency have elevated numbers of S. This may relate partially to decreased bactericidal exercise of their dendritic cells (17). Therefore, having enough vitamin D levels could assist dendritic cells to express maximal bactericidal activity against S. Prophylactic antibiotics and early aggressive antibiotic therapy are required to deal with infants with these defects. Those youngsters that survive till their teenage years have a decision of frequent invasive infections. While we frequently think of viral infections as being related to lowered cell-mediated immunity, the hyperlink to S. The innate activation of macrophages and dendritic cells, in addition to the surface factors that activate complement, seem enough to control S. A mechanism for this is primarily based on the occurrence of anergy by way of upregulation of inhibitory receptors such as lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (39, forty four, 47). In septic sufferers, the profile of cytokines produced throughout infection is a mirrored image of the cells that are activated (Table 2). Thus, mortality is associated with dysregulation of the immune system in apparently regular individuals. The explanation for the increased mortality was systemic inflammatory response whereby management of the immune response was lost. These unanticipated outcomes show that extra mortality was related to a dysregulated immune response even earlier than the vaccine was given. The knowledge outlined in Table 2, suggesting that immune dysregulation correlates with more extreme illness and mortality, are thought of right here. Of course, extreme trauma itself causes changes within the immune response, so the immune dysregulation noted on this research is much less clear cut than in the S. The elevated mortality suggests that the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory responses is incorrect. This raises the query of why so many humans have a nonprotective response to S. We are acquainted with Mycobacterium leprae and Trypanosoma cruzi as causing immunosuppression of the host, and therefore one speculation is that the stability between the host and S. These interactions might underlie failures of humans to respond with protective immunity towards S. Examples of vaccine biomarkers are anti-hepatitis B viral surface antigen and antimeningococcal capsular antibodies whose presence correlates with protection from an infection. Finally, the relative stability between T cell subsets may be critical to the finish result. Nlrp-3-driven interleukin 17 manufacturing by gdT cells controls an infection outcomes during Staphylococcus aureus surgical web site infection. Minegishi Y, Saito M, Nagasawa M, Takada H, Hara T, Tsuchiya S, Agematsu K, Yamada M, Kawamura N, Ariga T, Tsuge I, Karasuyama H. Molecular explanation for the contradiction between systemic Th17 defect and localized bacterial infection in hyper-IgE syndrome. Association between vitamin D deficiency and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Vitamin D3 and phenylbutyrate promote growth of a human dendritic cell subset displaying enhanced antimicrobial properties. Manipulation of autophagy in phagocytes facilitates Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Contrasting the immune responses to bacteremia to cutaneous infections could make clear the context for T cell activation. Given the multiple potential interpretations of adjustments in cytokines, an in depth evaluation of the kinds of T cells produced, their state of activation, the time course of activation, and the relative stability between the different T cell subsets previous to and during S. In addition, potential data on the kinds of antibodies being produced (opsonic versus toxin-neutralizing), particularly throughout S. This dysregulation is likely at the coronary heart of mortality and extreme disease in people. Thus, while altering intrinsic T cell responses may be therapeutically tough, monoclonal antibodies towards superantigens may have utility in addressing dysfunctional immune responses to S. The models above are hypotheses for inspecting, and potentially dramatically enhancing, the immune response to and safety of S. Recent developments for Staphylococcus aureus vaccines: medical and basic science challenges. A Spaetzle-like function for nerve growth issue b in vertebrate immunity to Staphylococcus aureus. Th1-Th17 cells mediate protective adaptive immunity towards Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans infection in mice.
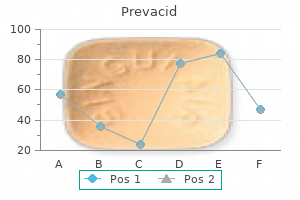
Prevacid 15 mg buy cheap line
In people the 50% deadly dose for diphtheria toxin was discovered to be roughly a hundred ng/kg gastritis diet tips prevacid 30 mg discount amex. After the production of diphtheria toxin and its distribution into vials for formalin detoxification within the preparation of toxoid gastritis esophagitis diet 15 mg prevacid order otc, one vial of toxin was both inadvertently not treated or reverted to full toxicity after formalin treatment and was despatched into the group as a part of the program to immunize kids. Of 606 kids that were "immunized" from this vial, sixty eight kids, principally between the ages of 1 and 2, died of diphtheria intoxication (4, 5). Since the focus of toxin within the vial, the dose that was administered, and the physique weight of the youngsters had been all identified, the human 50% lethal dose for diphtheria toxin might be calculated. While diphtheria toxoid as a vaccine was obtainable as early because the Nineteen Twenties, investigations into the development of a simplified medium for toxin production led Alwin M. In 1935, Pappenheimer, then a Bradford Fellow at the Harvard Medical School, started his laboratory at the Massachusetts Antitoxin and Vaccine Laboratory to work on diphtheria toxin manufacturing. At that time Pyrex glassware was newly obtainable, and he used Pyrex flasks in his first attempts to produce toxin. While he followed established protocols for medium preparation and incubation temperature and time for maximal yields, Pappenheimer was in a position to produce only half as much toxin as that reported by his predecessors who used the older soft glassware flasks in the laboratory. The query was apparent: Why did the glassware make a distinction in toxin production He then added varying amounts of powdered glass to the Pyrex flasks he was utilizing and determined its effect on toxin production. Remarkably, Pappenheimer discovered that the addition of as little as 300 g powdered soft glass resulted in a stimulation of both C. Equally importantly, he found that the addition of 5 or 10 mg of powdered glass resulted in the almost full inhibition of toxin manufacturing without a change within the progress of the diphtheria doi:10. As shown in his classic 1936 paper (6), the stimulation and subsequent inhibition of toxin manufacturing following the addition of both powdered glass or iron salts to the media had been superimposable. The capability to produce a maximal yield of diphtheria toxin within the gentle glass resulted from the leaching of small ranges of iron from the glass into the tradition medium. We now know that maximal yields of diphtheria toxin are produced only when iron turns into the growth-rate-limiting substrate. So, as early as 1936, it was realized that with respect to iron, an essential nutrient for the growth of the bacillus, the physiologic state of toxigenic C. Both genetic and molecular genetic proof suggest that the linear b-genome circularizes by ligation of its cohesive ends (cos) and integrates into the host chromosome as a prophage in a manner that corresponds to that for the integration of l-phage into the Escherichia coli genome (9�11). In its lysogenic state, most b-phage genes seem to be repressed, and the lysogen is immune to superinfection by homoimmune corynebacteriophages. While triple lysogens are unstable and revert to secure double lysogens, beneath iron-limiting conditions, the ultimate yield of diphtheria toxin that could be produced is directly related to the number of built-in prophage genomes (12). This work led to the isolation of the structural gene for the diphtheria tox repressor, dtxR, which encoded a 226-amino acid protein. Schmitt and Holmes (23) subsequently demonstrated the useful activity of DtxR in C. In this method, diphtheria toxin was expressed in good yield, and remarkably, the in vitro synthesis of the toxin was not inhibited by the addition of iron. In distinction, the addition of cell-free extracts of the nontoxigenic, nonlysogenic C7s(�)tox� pressure of C. These outcomes clearly instructed that the inhibitory effect of iron was mediated by way of a bacterial host-determined factor. Since binding of DtxR to the labeled toxO probe was blocked by the addition of extra unlabeled probe, anti-DtxR antibodies, or the chelator 2,2dipyridyl, DtxR binding was specific and dependent on steel ion activation. Moreover, since this household of associated goal sequences was found to bind DtxR with the identical obvious affinity as the 27-bp tox operator, it was clear that the ironactivated repressor was most likely to operate as a worldwide regulatory component in the regulation of iron-sensitive genes in C. Indeed, a variety of genes which have upstream DtxR-binding websites, together with the operon essential for the expression of siderophores for iron acquisition, have been isolated and characterised (23, 28). IdeR (iron-dependent regulator) which has been found in several species of Mycobacterium and is 78% equivalent and 90% homologous has been isolated and characterized (30). In addition, DtxR homologs have been recognized in numerous genera, together with the species Enterococcus faecalis (34), Streptococcus mutans (35), S. The substitution of Cys102 with all 20 amino acids, apart from Asp, by sitedirected mutagenesis results in the entire lack of repressor exercise. Further characterization of the wild kind and individual mutants demonstrated that Cys102 performs an important function in the coordination of Fe2+ within the activation of apo-DtxR (40). In addition, a quantity of mutations have been also isolated in a predicted a-helical area with the sequence of His98-Cys102-His106 that resembled metal ion-binding motifs in different proteins. DtxR accommodates a complete of eight a-helices, six of that are contained within the N-terminal two-thirds of the protein. As one would anticipate, the solution of the X-ray buildings of DtxR and the ternary complicated that varieties with its binding to toxO confirms and extends the sooner remark that its footprint compasses a region of 30 bp instantly upstream of the transcription initiation sign (46). While the overall mechanism of DtxR binding to toxO is similar to that of different prokaryotic repressors, there are some unique interactions that ought to be famous. Each helix-turn-helix within the dimer makes a complete of 9 interactions with backbone phosphate teams. While saturation and equilibrium dialysis experiments advised that DtxR contained a single metal ion-binding website with an obvious dissociation fixed of 2 � 10�6 to 9 � 10�7 M (46), X-ray crystallographic analysis of transition metallic ion-DtxR complexes clearly revealed two metallic ions sure to each monomer (41, 43). The second steel ionbinding site, or ancillary web site, consists of five residues: His79, His98, Glu83, Glu170, and Gln173 (41, forty three, 49). The function played by the ancillary metallic ion-binding website was elucidated through the evaluation of DtxR(E175K), a hyperactive mutant that remained energetic in vivo even in the presence of the chelator 2,2dipyridyl (50). Nuclear magnetic resonance solution constructions mixed with other biophysical studies have advised that apo-DtxR exists in a partially unstructured molten globule, which upon coordination with divalent transition metallic ions undergoes a structural conversion to a discrete ordered tertiary structure that each dimerizes and is able to bind to the tox operator (52). The resulting conformational modifications then allow the binding of the second metallic ion to the ancillary website and subsequent dimerization of DtxR and the formation of an active repressor (53). Under reducing and denaturing situations, nicked diphtheria toxin may be separated into an enzymatically active N-terminal 24-kDa fragment A and its 38-kDa C-terminal fragment B (54, 55). These preloaded purple cell ghosts had been then fused to diphtheria toxinresistant mouse L-cells by Sendai virus. Using a fluorescenceactivated cell sorter, L-cells that fused with a single purple cell ghost were then isolated and grown for 7 days. Careful analysis of the colony-forming capability of the recipient cells in comparison with the management cells clearly demonstrated that the supply of a single molecule of fragment A to the cytosol was enough to kill that cell. As such, it was realized via biochemical and genetic analyses that native diphtheria toxin was a protein with a minimal of three structural-functional domains: (i) catalytic, (ii) transmembrane or translocation, and (iii) receptor-binding domains. The toxin is instantly purified from the spent culture supernatant by ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by ion trade chromatography on a diethylaminoethyl matrix. While the intact toxin is enzymatically inactive, publicity of purified toxin to trypsin or different serine proteases sixty nine. Diphtheria Toxin and the tox Operon 1159 proved to be right with the dedication of the crystal construction of diphtheria toxin (60, 61). This exposed loop carries an ArgArgValArg protease recognition site for both furin or other trypsin-like proteases. The proteolytic cleavage of this site is crucial for the discharge of the catalytic domain into the eukaryotic cell cytosol (62). The translocation area encompasses amino acids Cys186 to K385 and consists of 9 a-helices and their connecting loops.
Diseases
- Plagiocephaly X linked mental retardation
- Acropectorovertebral dysplasia
- Microcoria, congenital
- Fitzsimmons McLachlan Gilbert syndrome
- Muscle-eye-brain syndrome
- Benign mucosal pemphigoid
- Klippel Feil syndrome recessive type
- Biemond syndrome
- Acroosteolysis neurogenic
15 mg prevacid order with visa
Domain mapping of a claudin-4 modulator gastritis diet treatment infection 30 mg prevacid with visa, the C-terminal area of C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin gastritis management discount prevacid 30 mg with mastercard, by site-directed mutagenesis. Structure of the food-poisoning Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin reveals similarity to the aerolysin-like poreforming toxins. Kitadokoro K, Nishimura K, Kamitani S, FukuiMiyazaki A, Toshima H, Abe H, Kamata Y, SugitaKonishi Y, Yamamoto S, Karatani H, Horiguchi Y. Crystal construction of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin displays options of beta-pore-forming toxins. Molecular cloning of the three half of the Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin gene and demonstration that this area encodes receptor-binding exercise. Localization of the receptor-binding area of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin using cloned toxin fragments and synthetic peptides. Trypsin activation of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens sort A: fragmentation and some physicochemical properties. Identification of a Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin region required for big complex formation and cytotoxicity by random mutagenesis. Fine mapping of the N-terminal cytotoxicity region of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin by site-directed mutagenesis. Cysteine-scanning mutagenesis supports the significance of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin 987 fifty three. Identification of a prepore large-complex stage in the mechanism of motion of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin makes use of two structurally associated membrane proteins as functional receptors in vivo. Molecular cloning and practical characterization of the receptor for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Saitoh Y, Suzuki H, Tani K, Nishikawa K, Irie K, Ogura Y, Tamura A, Tsukita S, Fujiyoshi Y. Structural insight into tight junction disassembly by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin binds to the second extracellular loop of claudin-3, a decent junction integral membrane protein. Molecular determinants of the interaction between Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragments and claudin-3. Human claudin-8 and -14 are receptors capable of conveying the cytotoxic results of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier. Identification of a claudin-4 residue necessary for mediating the host cell binding and action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Formation of tight junction: determinants of homophilic interplay between classic claudins. Shinoda T, Shinya N, Ito K, Ohsawa N, Terada T, Hirata K, Kawano Y, Yamamoto M, Kimura-Someya T, Yokoyama S, Shirouzu M. Structural foundation for disruption of claudin assembly in tight junctions by an enterotoxin. Evidence that an approximately 50-kDa mammalian plasma membrane protein with receptor-like properties mediates the amphiphilicity of particularly certain Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Clostridium perfringens type E animal enteritis isolates with highly conserved, silent enterotoxin gene sequences. Novel insight into the epidemiology of Clostridium perfringens kind A meals poisoning. Skewed genomic variability in strains of the toxigenic bacterial pathogen, Clostridium perfringens. Evidence that Tn5565, which includes the enterotoxin gene in Clostridium perfringens, can have a round type which can be a transposition intermediate. The Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin gene is on a transposable factor in type A human meals poisoning strains. Complete sequencing and variety analysis of the enterotoxin-encoding plasmids in Clostridium perfringens sort A non-food-borne human gastrointestinal illness isolates. Osmotic stabilizers differentially inhibit permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. The significance of calcium inflow, calpain and calmodulin for the activation of CaCo-2 cell death pathways by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Calcium-independent and calcium-dependent steps in action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Morphological alterations and changes in cellular cations induced by Clostridium perfringens kind A enterotoxin in tissue tradition cells. The effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on morphology, viability, and macromolecular synthesis in Vero cells. Comparative biochemical and immunocytochemical research reveal differences in the effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on polarized CaCo-2 cells versus Vero cells. CaCo-2 cells handled with Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin kind a number of large complex species, certainly one of which contains the tight junction protein occludin. The enterotoxin gene (cpe) of Clostridium perfringens could be chromosomal or plasmid-borne. Identification and characterization of sporulation-dependent promoters upstream of the enterotoxin gene (cpe) of Clostridium perfringens. Disruption of the gene (spo0A) encoding sporulation transcription issue blocks endospore formation and enterotoxin manufacturing in enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens kind A. Comparative effects of osmotic, sodium nitrite-induced, and pH-induced stress on progress and survival of Clostridium perfringens type A isolates carrying chromosomal or plasmid-borne enterotoxin genes. Further comparability of temperature results on growth and survival of Clostridium perfringens sort A isolates carrying a chromosomal or plasmid-borne enterotoxin gene. Production of small, acidsoluble spore proteins in Clostridium perfringens nonfoodborne gastrointestinal disease isolates. Further characterization of Clostridium perfringens small acid soluble protein-4 (Ssp4) properties and expression. An ultrastructural comparison of spores from varied strains of Clostridium perfringens and correlations with warmth resistance parameters. A survey of human serum samples for antibody against Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin in humans in Korea. The potential therapeutic agent mepacrine protects Caco-2 cells in opposition to Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin action. A conjugated synthetic peptide similar to the C-terminal region of Clostridium perfringens sort A enterotoxin elicits an enterotoxin-neutralizing antibody response in mice. Involvement of bacteria other than Clostridium difficile in antibioticassociated diarrhoea. Clostridium perfringens in spontaneous and antibiotic-associated diarrhoea of man and other animals.
Order prevacid 15 mg with amex
The prfA transcript is expressed from three completely different promoters xanthogranulomatous gastritis prevacid 30 mg purchase on-line, P1 (sA regulated) gastritis diet ������ 15 mg prevacid buy with amex, P2 (sA and sB regulated), and plcA (generating a plcA-prfA bicistronic messenger). The plcA promoter is positively regulated by energetic PrfA, making a constructive suggestions loop of PrfA expression. The stem-loop construction reveals a putative transcriptional terminator positioned three of the plcA gene. In vitro translation of the wild-type prfA showed a thermoregulated expression, with PrfA mostly expressed at greater temperatures. Intriguingly, SreA expression is positively managed by PrfA, making a adverse feedback loop, where excessive levels of active PrfA flip off its personal expression by growing the extent of the repressive element SreA (38). The PrfA cofactor has recently been recognized as glutathione, and PrfA-glutathione cocrystals point out that the cofactor binding website is located on the intraprotein tunnel site, situated between the N- and C-terminal domains of the PrfA monomer (43�46). Working models have instructed that once contained in the cytoplasm, both uptake of cytosolic glutathione and, most significantly, upregulation of the glutathione synthase, gshF, result in elevated glutathione concentrations in L. Interestingly, the authors additional suggested that inhibitory peptides transported 52. Years previous to the identification of glutathione as the PrfA cofactor, Ripio et al. The substitution of a serine for a glycine at position one hundred forty five inside PrfA was the first identification of a PrfA* mutation, so named as a result of it appeared analogous to an A144T mutation identified within Crp that resulted within the constitutive expression of Crp-dependent gene products in the absence of cofactor (Crp* mutants) (49). There have now been numerous extra mutations recognized that confer PrfA activation, albeit at differing ranges of activation. Reported prfA* mutations embrace G145S, Y63C, S71C, E77K, A94T, L140F, Y154C, L148P, G155S, and P219S substitution mutants (52�61). These mutations in some instances map to very totally different regions of PrfA compared to the original G145S PrfA* mutation, and strains containing these completely different prfA* alleles exhibit levels of PrfA-dependent gene expression in broth culture that vary from 4-fold to >200-fold greater than the levels of expression observed in wild-type bacteria (62, 63). The monomers A and B are colored gray, the helix-turn-helix motif is magenta, aD is yellow, and the winged b-hairpin is green. Secreted proteins are sometimes the first bacterial elements to interact with the host, and a comparison of secreted protein profiles derived from the culture supernatants of wild-type, DprfA, and prfA* mutants recognized a minimum of 17 proteins that were differentially secreted following PrfA activation (52). Many of these PrfA-dependent secreted proteins also depended on the presence of the secretion chaperone PrsA2 for full exercise (65). A vital variety of secreted gene products that appear indirectly regulated by PrfA have been demonstrated to contribute to L. Regulation of Listeria monocytogenes Virulence 841 they obtained from the phosphoenolpyruvate system to the incoming sugar. It has been advised that unphosphorylated permeases would possibly bind and sequester PrfA directly, thereby blocking PrfAmediated virulence gene expression (74). Strains containing prfA* are hyperinvasive, mediate more efficient phagosome escape, and provoke bacterial actin-based motility more quickly. Constitutively activated prfA* mutants exhibit impaired flagellum-mediated swimming motility, a defect that might be expected to compromise bacterial fitness in environments the place the bacteria must be succesful of detect and swim towards available nutrient sources and which might additionally impair biofilm formation. The a quantity of mechanisms that thus exist to regulate PrfA exercise appear to have developed to fastidiously balance gene expression patterns so as to maintain bacterial fitness within the soil as properly as in the cytosol. Lmo0514 is required for survival of the micro organism in plasma and through infection of mice (90). A Drli38 mutant pressure exhibited reduced bacterial loads in a quantity of organs compared to the wild-type strain. In distinction to Rli38, the absence of RliB elevated bacterial masses within the liver compared to the wildtype pressure. Another exciting side of the LhrC family is that the expression of individual members is managed by exposure to numerous environmental cues, such as blood and development within the gut and in macrophages via at least one bacterial two-component signaling system (93). This twin regulation permits the expression of the bicistronic inlA-inlB message from two promoters, integrating several external cues and thereby permitting bacterial invasion of a number of host cell sorts. Whether the stressosome is prepared to act as a central hub to integrate exterior alerts to control virulence gene expression in live performance with different regulators. Very little is understood about the mechanisms underlying stressosome sensory notion and signal integration. A small peptide, Prli42, has been demonstrated to bind the stressosome, and its absence reduces sBdependent gene expression while also affecting expression of virulence factors (112). Prli42 harbors a transmembrane area and is related to the membrane, potentially permitting the stressosome to sense stress exerted by way of membrane disturbance. Using the X-ray construction of palmitoleic acid sure to ToxT as a blueprint, extremely efficient ToxT inhibitors were synthesized that were capable of inhibit intestinal colonization in mice (114). Regulation Induced in Response to Environmental Stress During its life as a saprophyte and pathogen, L. Activity of sB is controlled by a fancy relay of protein interactions and phosphorylation events, in the end freeing sB from the anti-sigma issue RsbW. At the highest of this relay hierarchy lies a sensory organelle, the "stressosome," which is a big (1. The stressosome is prepared to detect and integrate environmental cues right into a sign transduction pathway that eventually permits the liberation of sB and initiation of the expression of sB-regulated genes. DegU can be the epistatic regulator of motility by positively activating expression of the antirepressor GmaR, which in flip, inactivates the repressor of motility MogR (129). Having no accompanying kinase, DegU appears to be phosphorylated by intracellular acetyl phosphate (130). VirR controls the expression of several virulence-associated genes upregulated throughout infection (12). Regulation of Virulence by way of Peptide Pheromones In addition to the peptide-responsive Agr system discussed above, an extra peptide pheromone system has been lately proven to contribute to L. Studies of mutants lacking both the PplA lipoprotein and its signal sequenceencoded peptide pheromone versus the lipoprotein alone have demonstrated that the pPplA peptide pheromone is a crucial virulence issue that contributes to each bacterial aggregation in broth culture and survival in mouse fashions of an infection. The PplA lipoprotein has no apparent role in vacuolar escape; however, its function as an extracellular electron transport protein that contributes to bacterial health throughout the gut has recently been described (134). Interestingly, all bacterial virulence defects associated with the lack of the pPplA peptide could presumably be completely compensated for by the introduction of constitutively energetic PrfA*, suggesting a possible connection between the pPplA signaling pathway and PrfA activation (132). In addition to the pPplA peptide-signaling pathway, another potential peptide-based signaling system associated to competence growth has been implicated in enhancing escape of L. A pressure cured of the prophage and containing an intact comK gene grew similarly to wild-type L. The confined area of the vacuole leads to import of the secreted pPplA pheromone, presumably stimulating a signaling cascade that results in the manufacturing of an unknown factor(s) that contributes to vacuole lysis. As part of a separate pathway, an unknown signal, doubtlessly also involving a peptide pheromone, results in the expression of ComK and the expression of a competence-associated pilus which will also help in vacuole membrane disruption. For strains that do comprise prophages, information recommend that prophage integration/excision serves to regulate virulence gene expression and that the ComK system is one means or the other involved in sensing the presence of L.
Prevacid 30 mg discount overnight delivery
Superantigens mediate massive cytokine production and trigger T and B cell proliferation gastritis duodenitis 15 mg prevacid cheap with mastercard. Collectively gastritis vomiting blood generic prevacid 15 mg fast delivery, these exotoxins modulate the host immune system and are important for S. For many years, a-toxin was thought to mediate cytolysis through nonspecific binding to the lipid bilayer of cells. Nanogram to microgram quantities of a-toxin could cause extreme dermonecrosis when administered subcutaneously in rabbits and mice (20, 21). Moreover, intravenous administration of this toxin also results in speedy lethality of the animals (20, 21). Like all conventionally secreted proteins, a-toxin is synthesized with an N-terminal sign peptide. The b-barrel pore is fashioned from a prepore by a conformational change in a toxin substructure known as the amino latch (5). Although less than 40% of scientific isolates from the United States carry a pvl-encoding prophage, over 90% of strains related to severe necrotizing pneumonia and community-acquired infections carry pvl (1, 52). Deletion of pvl ends in less inflammation, reduces tissue injuries and bacterial burden, and promotes host survival (57, 60). This locus includes three genes: the hlgA gene, transcribed by its personal promoter, adopted by an operon containing hlgC and hlgB, transcribed by a special promoter (66). Intravitreal injection of g-hemolysins in rabbits is very toxic, leading to destruction of the attention and tissue injury in surrounding areas (69). The tissue damage could possibly be the result of a mix of toxin-mediated cell lysis and pyroptosis brought on by sublytic focus of the psma1 to psma 4 Phenol soluble modulins Exfoliative toxin A eta Exfoliative toxin B etb slow-eluting subunit, S-subunit, named on the premise of their liquid chromatography behavior (28, 29). The present mannequin for leukocidin pore formation suggests that the S-subunit recognizes and binds to a floor receptor on the goal cell and then recruits the F-subunit for dimerization (30�32). This is adopted by oligomerization with three additional dimers to type an octameric prepore on the target cell membrane (33). LukA has an 33-amino acid sequence on the N-terminus and a 10-amino acid C-terminal tail which may be absent from other S-subunits, contributing to its divergence. The prestem domains of the prepore then prolong to kind a b-barrel pore that punctures the goal cell membrane. Upon receptor binding, the S-subunit dimerizes with the F-subunit, adopted by oligomerization of three extra leukocidin dimers, leading to an octameric prepore. Similar to the a-toxin pore formation model, the prestem domains of the prepore prolong to kind a b-barrel pore, thus disrupting the target cell membrane. The two genes in the locus, lukE and lukD, are cotranscribed during the late exponential section (73). Retroorbital administration of microgram amounts of the toxin leads to acute lethality in mice (68). The amino latch is colored blue, the cap area pink, the rim area pink, and the prestem domain green. The amino latch of HlgB is blue; the cap domain for HlgA is cyan and HlgB is beige; the rim domains are yellow for HlgA and pink for HlgB; and the prestem domains are green. The HlgA protomers are cyan, the HlgB protomers are beige, and the b-barrel pore is green. The toxin is found in abundance within the secreted proteome through the late exponential growth part, which led to its discovery (78, 79). The C-terminal area of LukA is crucial for toxin exercise, as a outcome of its deletion or mutation inside this area. Since it is a recently identified toxin, the regulation of e-toxin expression and the mode of motion of the toxin are unknown. Lytic concentration of e-toxin in keratinocytes promotes the secretion proinflammatory cytokine, interleukin 8 (105). In contrast, sublytic concentration of e-toxin slows the rate of keratinocyte proliferation, suggesting a task for the toxin in impairing regular wound healing (105). A microgram amount of e-toxin can outcome in neutrophil recruitment to the injection web site when administered subcutaneously in rabbits (105). Moreover, the identical dosage of e-toxin could cause rabbits to develop fever after intravenous administration of the toxin (105). Due to their extreme stability and excessive toxicity in humans, some of them are classified as select agents for bioterrorism. However, the International Nomenclature Committee for Staphylococcal Superantigens renamed them in 2004 to reflect their lack of emetic and mitogenic properties (114). They were originally named for his or her capacity to induce emesis, a key attribute of staphylococcal food poisoning (114). Conventional antigens bind to B cell receptors on the complementarity-determining region (blue), a hypervariable region that confers antigen specificities. SpA binds at a continuing area of the receptor to activate B cells for supraclonal enlargement, which ends up in clonal deletion of SpA-activated B cells. B cell Superantigen Staphylococcal protein A (SpA) is the one identified B cell superantigen produced by S. Mature SpA has 4 to five highly conserved immunoglobulin (Ig) binding domains related by quick linkers at the N-terminus (131). These are adopted by a hypervariable area referred to as area X, which comprises subregions Xr and Xc (132). The extremely variable and repetitive octapeptide in Xr is the idea of SpAtyping, a high-throughput methodology of grouping S. However, SpA proteins may be released from the cell wall by the cell wall hydrolase, LytM (133). The Ig binding domains confer upon SpA the power to bind the Fcg portion of Igs to prevent opsonization (134). During intravenous infection, SpA prevents opsonophagocytosis of the micro organism by sequestering Igs and impedes the development of specific anti-S. Cytotoxic Enzymes b-toxin (also generally recognized as b-hemolysin) the b-toxin encoding gene, hlb, is part of the core S. The prophage carries the immune evasion gene cluster encoding for immune evasion elements, such as the staphylococcal complement inhibitor proteins, chemotaxisinhibitory proteins, and staphylokinase (145). This toxin was first recognized in 1935 by Glenny and Stevens based mostly on a number of distinctive observations: hemolysis of erythrocytes within the presence of a-toxin neutralizing serum, lysis of sheep however not rabbit erythrocytes, and enhanced hemolysis brought on by the temperature shifting from 37�C to a decrease temperature (152). This distinctive phenomenon is the outcomes of ceramide hydrolysis products at 37�C being held collectively by cohesive forces within the membrane. Later, b-toxin was shown to improve biofilm formation through catalyzing the formation of nucleoprotein matrix in biofilms; due to this fact, b-toxin is also a biofilm ligase (155). Intranasal administration of b-toxin induces the shedding of syndecan1, a serious heparan sulfate proteoglycan molecule on lung epithelial cells, and causes neutrophil infiltration into the lungs in mice (162). Desmogleins are cadherins which are required for desmosome cell-to-cell adhesion to keep the integrity of the dermis. Cleavage of Dsg1 disrupts the cell-to-cell adhesion of the epidermis, resulting in blistering and desquamation of the superficial pores and skin. The earlier part discussed the mechanisms of toxin-mediated host immune evasion and their roles in S. They can be broadly categorized into two teams: cofactors that activate host zymogens and enzymes for degradation of tissue parts (Table 2).
Prevacid 30 mg visa
Acetate eosinophilic gastritis symptoms prevacid 15 mg discount visa, acetoin gastritis diet ������� prevacid 30 mg buy otc, diacetyl, and a pair of,3-butanediol diffuse or are secreted into the medium. To establish a low redox potential, oxygen should be eliminated and oxidized compounds ought to be decreased. The redox potential of milk is thought to have an result on the microbiota and sensorial quality of fermented dairy merchandise. Nitrogen Metabolism In a milk medium, lactococci derive amino acids from casein via hydrolysis by the extracellular protease PrtP, transport of the generated peptides, and further degradation by a massive number of intracellular and envelope proteases and peptidases (97, 98). Amino acids readily available in milk are used each directly as amino acid constructing blocks and as a general carbon provide for different forms of anabolism in lactococci. Extracellular proteases plus no less than 14 intracellular peptidases are of key significance for amino acid utilization. Lactococci grow poorly or die in milk fermentation situations in mutants that are devoid of various mixtures of these peptidases (99). Dairy lactococci differ from plant lactococci in that they require several amino acids for progress. Surprisingly, strains of each origins seem to have the required genes for biosynthesis. Nevertheless, dairy lactococci require Ile, Leu, Val, and His, and sometimes Arg, Met, Pro, and/or Glu (100). These amino acid necessities in dairy strains appear to result from a quantity of mutations rather than deletions in the structural genes (39). This could suggest that mutations accrued as an economic measure in strains maintained in a dairy environment. In distinction, heme import mechanisms remain elusive, regardless of a partial position for fhu (75). Membrane-associated menaquinones had been shown to favor the accumulation of lowered heme in membranes (82). An oxidative setting, provided by oxygen, prevents and reverses hemin reduction by menaquinone and thus limits heme accumulation in membranes (82). Second, as a outcome of such strains might survive the cruel environments in the intestine higher, they could be engaging for probiotic uses. A proof of idea mouse inflammatory gut model provided evidence that antioxidant superoxide dismutase produced by wild-type L. Note that an analogous strategy of semiliquid medium selection was used to uncover the existence of a cell-surface carbohydrate pellicle in L. Via respiration Respiration growth leads to larger pH and environment friendly oxygen consumption. Interbacterial Cross-Inhibition Via secreted merchandise Lactococci, like different Streptococcaceae, produce poisonous hydrogen peroxide under cardio fermentation conditions, which may inhibit growth of peroxide-sensitive bacteria (72). This property has led to broader potential applications in the probiotic subject. Unexpectedly, menaquinone-deficient strains can overcome this deficiency through contacts with menaquinone producer species. Thus, environmental nonpathogens may contribute to the fitness, and potentially virulence, of neighboring pathogens. Nonrespiring cydA grew less nicely and showed poor survival when maintained in an aerobic medium with heme over a 3-day interval. In distinction, the cydA strain fared a lot better when grown in coculture with the wild-type strain, as determined by cell count determinations. Production of lysins could act to regulate bacterial cell wall properties in trans (158). These findings open prospects for antibiotic options for prevention of infection, although their applicability to food trade and in vivo conditions stays to be confirmed. Prior to this replace, numerous reports described encouraging outcomes of using lactococci for (i) prophylaxis to stop bacterial infection (161), (ii) treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (3), (iii) prophylaxis and/or treatment of virally induced tumors (162), and (iv) allergy prevention (163, 164). Other properties of lactococci, together with the expression of pili that might mediate bacterial adhesion in situ (135, 136), and novel purposes have since been reported (165) which assist their uses in biomolecule delivery. Reported success with bioactive molecules would possibly change this picture sooner or later. Numerous functions using lactococci resulted from the event of genetic tools. The thermosensitive replication protein has been retooled to produce numerous derivatives. The promoter for the nisin biosynthesis gene, nisA, is regulated by nisR and nisK gene products. In the absence of nisin, or of nisR and nisK genes, promoter exercise could be very low. Addition of sublethal quantities of nisin leads to strong induction of promoter activity, as demonstrated in innumerable applications of this method. This system has been proven to be practical in other Firmicutes (see 172 for review). Expression techniques have additionally been developed for wider use amongst Firmicutes and in some cases may be advantageous over the nisin system. Controlled expression methods have arisen from research of pH, salt, metallic, heme, chloride, and sugar-regulated promoters (see 115 for review); some techniques may overcome two probably essential limitations of the nisin system: (i) the requirement for either a selected host pressure or a second plasmid (to present nisR and nisK genes) and (ii) results of nisin on the membrane, which may be notably undesirable in research of membrane proteins. This and other heme-responsive promoters have been developed as delicate heme sensors, with proof of activity in vivo (81; D. Constitutive expression of promoters at fastened ranges can be useful for quantitative physiological research or for finetuning of gene expression in biotechnology. A set of artificial promoters that differ by the sequence and length of spacers between the consensus sequences allows a broad range of constitutive actions (57, 174). A high-expression promoter based on the phosphotransferase system is additional enhanced by cellobiose and was proven to be lively in B. Site-Specific Single-Copy Integration Lactococcal bacteriophages have been initially studied with the goal of controlling starter tradition lysis throughout fermentation. These phage research led to the characterization of numerous bacterial methods to abort phage exercise. Phage research have also been exploited to develop a site-specific integration system. This system should enable secure insertion and expression of international genes and can additionally be used to examine the expression of genes in single copies under totally different progress conditions. Another integration system primarily based on a lactococcal intron led to environment friendly and stable insertion of genes with out the need for choice (178). Protein Export and Display Systems Protein export reporters have been developed to probe the membrane protein construction and determine export signals (182� 184). The major advantages of using the nuclease over previously described export reporters are that it quickly assumes its conformation and thus avoids degradation, and as few as 300 nuclease molecules per cell can be detected in colony assays (183�186).