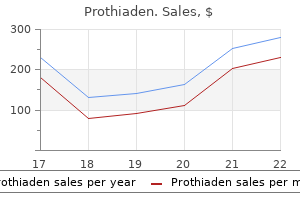
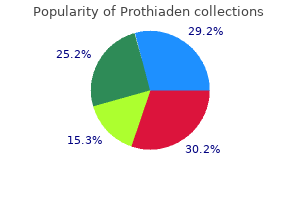
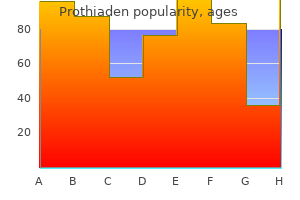
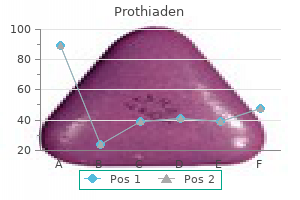
Prothiaden
Prothiaden dosages: 75 mg
Prothiaden packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills

Prothiaden 75 mg generic
Aberrations in midtarsal joint alignment that produce symptoms in weightbearing can also be undetectable with radiography as a end result of foot radiographs are sometimes obtained in nonweightbearing symptoms yeast infection prothiaden 75 mg discount on-line. Nonetheless medicine for vertigo 75mg prothiaden discount with visa, plain radiographs ought to be obtained to rule out fractures or other significant bony abnormalities and to assist set up a differential diagnosis. Approximately 90% of tarsal coalitions occur both on the calcaneonavicular joint or the talocalcaneal joint, with the distribution of these two varieties being equal. Solitary fractures of the cuboid are uncommon as are cuboid dislocations, with only thirteen reported instances in the literature. Cuboid syndrome can be simply ignored when it develops in conjunction with a lateral ankle sprain. Therefore, screening for cuboid syndrome ought to be thought-about for all patients with lateral ankle sprains. The manipulative methods described as follows are comparatively simple to perform and will present dramatic symptom reduction or decision. Two manipulative methods have been described- the "cuboid whip" and the "cuboid squeeze. Marshall and Hamilton (1992) described a variation of the cuboid whip that they named the cuboid squeeze. Instead of "whipping" the foot/ankle, the clinician slowly stretches the ankle into maximal plantarflexion and the foot and toes into maximal flexion. The cuboid squeeze requires maximal ankle plantarflexion, which may be inappropriate for patients with a coincident ankle sprain. Immediately after manipulation, medical tests must be repeated to determine remedy efficacy. Patients who experience partial or incomplete symptom decision might benefit from additional manipulations. Patients who expertise no aid in any respect after manipulation ought to be re-examined and other diagnoses must be considered. Following the manipulation, low Dye or arch taping, orthotics, and/or cuboid padding could additionally be used to stop recurrence. Felt padding (~� inch) to buttress the plantar cuboid and/or orthotics that reduce extreme pronation could additionally be helpful in decreasing signs and preventing recurrence. This author has discovered Ankle Sprain Rehabilitation 359 orthotics to be much more effective than cuboid padding for reducing symptoms and preventing recurrence. Stretching the gastrocnemius, soleus, hamstring, and/ or fibularis longus and strengthening the intrinsic and extrinsic foot muscular tissues have been reported to be useful in stopping recurrence of cuboid syndrome. Oral or injectable anti-inflammatory and/ or anesthetic agents can also be useful. Based on anecdotal evidence, cuboid syndrome usually responds favorably to cuboid manipulation. Continued on following page 362 Foot and Ankle Injuries After Modified Brostr�m Ankle Ligament Reconstruction (Continued) Unilateral balancing for timed intervals. Dancers should carry out peroneal workout routines in full plantarflexion, the place of function in these athletes. Dancers ought to carry out plantarflexion/eversion workout routines with a weighted belt (2�20 pounds). Weeks 8�12 Patient can return to dancing or sport if peroneal strength is regular and symmetric with uninvolved limb. Illustration Stretch 2 In standing place, with concerned foot furthest away from the wall, lean forward whereas preserving your heel on the floor and the again knee straight. Perform this exercise at home three instances every day for two repetitions, holding each for 30 seconds. Use your different hand to grasp the back a part of your foot and push toward the floor. Self-stretching and mobilization of plantar fascia and flexor hallucis longus Cross the affected leg over the nonaffected leg. While inserting your fingers over the bottom of your toes, pull the toes back towards your shin till a stretch is felt in your plantar fascia. With your other hand, mobilize the plantar fascia and flexor hallucis longus from your heel toward your toes. Manual physical remedy and exercise versus electrophysical brokers and exercise within the administration of plantar heel ache: A multicenter randomized medical trial. For this cause, cortisone injections should not often, if ever, be utilized in high-impact athletes. Gentle calf, Achilles, and hamstring stretching is finished three to four times a day. Protocol for Nonoperative Management of an Achilles Rupture 365 rehAbIlItAtIon protocol 5-8 General Guidelines for Achilles Tendonitis, Paratenonitis, and Tendinosis in High-Impact Athletes Brotzman � Establish right prognosis. First strive 1/4-inch heel insert for a 1/2-inch leg-length discrepancy; if not improved, go to 1/2-inch insert. Boot removed 5 minutes per hour when awake to perform exercise of lively dorsiflexion to neutral with passive plantarflexion. Nonweightbearing briefly then initiate weight bearing with walking boot and small felt heel carry (Hapad). Patients instructed on how to slowly bring the boot fastened angle from 20 degrees of plantarflexion to 0 levels of plantarflexion over 2 to three weeks. All sufferers taught lively ankle gentle dorsiflexion vary of movement exercises and to carry out twice every day as tolerated. Progression of dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, and vary of movement workouts with resistance tubing. Malliaropoulos N, Ntessalen M, Papcostas E, et al: Reinjury after acute lateral ankle sprains in elite observe and area athletes, Am J Sports Med 37:1755�1761, 2009. Balance coaching for neuromuscular management and performance enhancement: a scientific review. Hopper D, Samsson K, Hulenik T, et al: the influence of Mulligan ankle taping during stability performance in subjects with unilateral persistent ankle instability, Phys Ther Sport 10:125�130, 2009. Krips R, Brandsson C, Swensson C, et al: Anatomical reconstruction and Evans tenodesis of the lateral ligaments of the ankle. Clinical and radiological findings after follow-up for 15 to 30 years, J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:232�236, 2002. Sugimoto K, Takakura Y, Okahashi K, et al: Chondral accidents of the ankle with recurrent lateral instability: an arthroscopic study, J Bone Joint Surg Am ninety one:99�106, 2009. Kiter E, Bozkurt M: the crossed-leg test for examination of ankle syndesmosis accidents, Foot Ankle Int 26:187�188, 2005. Zalavras C, Thordarson D: Ankle syndesmotic harm, J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15:330�339, 2007.
Cheap prothiaden 75 mg mastercard
MedIaL tensIon InjurIes Medial rigidity injuries mostly include medial epicondylar apophysitis 68w medications discount prothiaden 75mg overnight delivery. With repetitive stress to the medial elbow in the throwing adolescent 4 medications at target buy cheap prothiaden 75 mg line, the flexor pronator mass and the ulnar collateral ligament apply tensile forces that trigger medial epicondyle apophysitis (Pappas 1982, Rudzki and Paletta 2004). This apophysitis is thought to occur quite than rupture of the ulnar collateral ligament (Joyce et al. Chronic attritional tears of the ulnar collateral ligament are fairly rare in adolescent athletes (Ireland and Andrews 1988). Despite this rarity, it seems that ulnar collateral injuries are growing in highschool athletes. Injuries to the ulnar collateral ligament in adolescent athletes generally occur as acute events, rather than through attrition as in older, extra skeletally mature athletes. LateraL coMpressIon InjurIes Several circumstances brought on by compression of the lateral aspect of the elbow can happen in youthful pitchers. Younger throwing athletes should take a 2- to 3-month rest from all throwing annually, doing shoulder and elbow exercises throughout this period. A young pitcher ought to be wary of pitching backto-back days or overthrowing at essential parts of the season, especially in tournaments, playoffs, or showcases by which such overuse is tempting. Throwing curveballs or breaking pitches before the age of 14 must be discouraged. Several associations have supplied suggestions regarding adolescent athletes and prevention of each elbow and shoulder issues. They found that more than half of 476 pitchers between the ages of 9 and 14 years of age had shoulder or elbow pain during a single season. Throwing a curveball was related to a 52% increased danger of creating shoulder ache, and throwing a slider was related to an 86% elevated danger of elbow pain. They also discovered a significant relationship between the number of pitches thrown throughout a recreation and during a season and the rate of elbow ache and shoulder pain. Additionally, pitchers 16 years of age or younger should adhere to the following rest necessities: � If throwing sixty one or extra pitches in a day, three calendar days of relaxation must be observed. The synovium may be pinched in the olecranon when the elbow is in full extension, resulting in posterior impingement syndrome, or the posterior apophysis could be careworn by triceps traction, causing olecranon apophysitis (Crowther 2009). Unfortunately, these are mostly the "higher players," which is why they may develop these issues to begin with. Coaches and fogeys of younger baseball gamers should be educated on the risks of overuse. This may be nice for position gamers, but for pitchers, this may have a dramatic unfavorable effect on throwing well being. These showcases are typically close to the tip of the season, when the pitcher might be already fatigued and in determined want of relaxation and recovery. If the season ended abruptly, this younger participant may be out of throwing shape and should attempt to compensate by throwing more durable on a deconditioned arm. Overthrowing in an attempt to impress higher-level coaches is most certainly a method to produce shoulder and elbow accidents. Recommendations are for pitchers to not take part in showcases due to the chance of damage. The importance of showcases must be de-emphasized, and pitchers must be given adequate rest and recovery time to appropriately put together. Pitchers 17 to 18 years of age should adhere to the next relaxation necessities: � If throwing seventy six or more pitches in a day, three calendar days of relaxation must be noticed. This is particularly true in southern states that typically have relatively heat weather all 12 months. Year-round throwing dramatically will increase the danger of injury to the elbow and shoulder. Injuries happen most frequently in baseball gamers, particularly pitchers; however, injuries in different throwing athletes similar to quarterbacks and javelin throwers have been documented. In addition, the angular velocity of the elbow from flexion to extension has been documented to reach 3000 degrees/second. Conservative remedy of those accidents has been poorly documented 58 Elbow Injuries and without passable outcomes. Improved surgical methods and greater understanding of rehabilitation principles have made surgical procedure a more successful choice for return to throwing. The history is commonly continual medial elbow pain with throwing, especially in the course of the late cocking and early acceleration phases. Physical examination includes a valgus stress take a look at that reproduces the signs of elevated valgus laxity. Finally, a optimistic arthroscopic take a look at, which is defined as greater than 1 mm of opening between the coronoid and the medial humerus, is often used. The anterior bundle runs from the elegant tubercle of the ulna and inserts on the inferior floor of the medial epicondyle. This method also minimizes the variety of tunnels and reduces the scale of the drill holes. Repetitive overloading may end up in irritation and microtears of the ligament, which can finally lead to failure. Continuing to throw with instability can result in degenerative changes in the elbow. Repetitive valgus stresses also can end in injury to the ulnar nerve, which may be exacerbated by ligamentous insufficiency. These stresses may result in medial traction on the ulnar nerve, resulting in continual subluxation or dislocation of the nerve outside the ulnar groove. In addition, throwers often have a hypertrophied flexor�pronator mass, which may result in compression of the nerve throughout muscle contraction. By transferring the nerve anteriorly, the nerve is successfully lengthened, thus reducing tension on it in flexion. The ulnar nerve is faraway from the cubital tunnel and transferred anteriorly to the medial epicondyle. It is then secured with a fascial sling to avoid ulnar subluxation again over the medial epicondyle. Time frames for returning to certain activities are based on permitting the graft to each strengthen adequately and regain sufficient flexibility. Range of movement is increased progressively in the brace over the initial 6-week postoperative period. Elbow extension is restored utilizing a low-load, long-duration stretch, which has been demonstrated to be an effective methodology for restoring vary of movement. Strengthening is initiated at 6 weeks and, following kinetic chain principles, the main focus of the rehabilitation program is on the scapula and glenohumeral joint.
Safe 75mg prothiaden
Educating healthcare suppliers Ideally medications kosher for passover 75mg prothiaden otc, a staff of healthcare providers should deal with the sexual rehabilitation of most cancers survivors medicine grapefruit interaction prothiaden 75 mg proven, primarily based on the historical past of their illness, and the timeline of development [1]. One research has demonstrated enchancment in sexual functioning of most cancers sufferers following group training about sexual issues [1]. However, counselling must also be obtainable to patients on an individual foundation [11]. Another principle of sexual counselling is to keep an ethically impartial stance, and to refrain from criticising the patient. Patients could develop their own methods to handle their sexual dysfunction merely by having a frank dialogue with a health professional. The model is a framework of interventions to be carried out by health professionals to address sexual problems. It illustrates the skills required to tailor treatment to the vary of sexual problems encountered in a patient, starting from the easy to a posh case scenario. The steps within the administration offered by suitably skilled health professionals, start from basic help to rising levels of experience within the remedy supplied [45]. The focus of this discussion pertains to the population of female most cancers sufferers with sexual dysfunction who represent a novel group. Studies on this group are restricted compared with these on cancer-related sexual dysfunction in males [7,21]. One cause for this is that the sexual functioning of males is evaluated more easily. Additionally, even scientific analysis into sexual function seems to assume that sexual intercourse is central to sexual behaviour. It is well-established for so much of females [46,47] that intimate touching and emotional closeness are more important elements of sexuality than sexual activity. This would even be relevant to the administration of female sexual dysfunction due to the impression of cancer; time is of the essence in providing an improved QoL for so much of patients residing at home preferring to keep away from hospital/ clinic visits. Conclusions There is little disagreement that sexuality comprises an necessary a part of QoL for most cancers sufferers, but the sexual well being of the female patient with cancer is given comparatively less attention during the medical treatment of her illness. Both medical and surgical treatments, together with adjuvant remedy corresponding to radiotherapy and hormonal treatments, have an effect on the sexuality of the patient. Moreover, the age-related needs when treating the feminine with most cancers can vary between totally different age groups. Certain particular requirements of female cancer victims range from when she is a baby to growing into the teenager/young adult, after which the older or postmenopausal adult; these require individualised evaluation, and therapy. Investigating sexual dysfunction, and its association with specific cancer therapies deserves further attention. Sexual operate changes through the 5 years after high-dose remedy and hematopoietic cell transplantation for malignancy, with casematched controls at 5 years. The assessment and management of sexual difficulties after therapy of cervical and endometrial malignancy. Sexuality after breast most cancers treatment: adjustments and coping strategies amongst Japanese survivors. Sexual functioning in patients following radical hysterectomy for stage 1B cancer of the cervix. Quality of life and sexual issues in disease-free survivors of cervical cancer in contrast with common population. Does post-caesarean dyspareunia replicate sexual malfunction, pelvic floor and perineal dysfunction A comparability of their effects on psychosocial adjustment, body image, and sexuality. Acute results of tamoxifen and third-generation aromatase inhibitors on menopausal signs of breast most cancers patients. Tamoxifen effects on subjective and psychosexual well-being, in a randomized breast most cancers examine evaluating high-dose and standard-dose chemotherapy. Effect of endocrine remedy on sexuality in premenopausal breast cancer patients: A prospective randomized examine. Chemotherapy-induced dyspareunia: a case examine of vaginal mucositis and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin injection in superior stage ovarian carcinoma. Fertility preservation methods: laboratory and clinical progress and present issues. It could be on an individual foundation, in small teams, or in giant numbers, with the populace being driven by financial necessity, sociocultural strife, or as a end result of the effects of warfare. Population shift and sociocultural strife can contribute to the technology of physical and psychological disease, with victims making extreme demands on healthcare assets. The breakdown of private and social support networks in cellular populations [1�4], exposed to continuously changing urban agglomerates [5], can initiate and preserve psychosomatic manifestations which have both individual and collective well being implications. These unsettling environmental situations are often associated with urbanisation when members of a rural populace transfer to cities [3,6,7], or from one country to one other. Consequently, such well being situations can be expected to be extra common in emigrants. Under these circumstances, a supportive social restructuring has to be configured, once once more. Oddly enough this is additionally associated with migration from urban to rural areas [4]. In this context, populations moving primarily for financial advantage are referred to as economic migrants, whereas these migrating due to persevering with warfare are often referred to as refugees. Although the challenges associated with any type of migration could additionally be related, refugees are at a greater social drawback regardless of worldwide rules framing resettlement, for they might have skilled higher trauma prior to their unplanned transfer [10�13], which initiates particular biopsychosocial wants. Many migrants could have undergone lengthy journeys, generally perilous, so as to attain their vacation spot, often leaving behind most of their possessions. When planning healthcare for displaced populations nevertheless, clear delineation of the characteristics of the migrant populations being served by the related healthcare facility, could not all the time be attainable. Mass actions regarding migrations between continents, and also from rural to urban settings [3,5�9], have occurred within the residing memory of many, having began in the twentieth century or even earlier, notably in Europe, North America, and Australia [3,5�7]. This brought with it multifarious effects on the bodily and psychosocial well being of settlers [16,17]. Latterly (since 1950), this phenomenon of mass migration and its penalties has been noticed in Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America, with many going through challenges when transferring to an urban township (population of 20 000) or a megacity with a inhabitants of 10 000 000 or more [8,18]. Such a move can, nonetheless, be disconcerting, particularly to migrant households, and in particular to these with young children, who could be exposed to health risks attributable to congestion, environmental hazards, violence, and different crimes [2,17]. The ease of speedier regional and international journey in trendy times, along with more fast financial upheavals arising from political instability, have magnified the associated well being hazards with each ailments of the prosperous or of poverty affecting migrants [18]. The overall influence of migration that results in sociocultural rifts, often with economic uncertainty, could generate psychosomatic illnesses with implications for global healthcare. In general, migration pushed by economic forces not solely leads to alterations in conventional relationships, which maintain well being, but in addition adds an additional burden on these migrants who need to endure economic hardship. They may should wrest with expectations beyond attain, because of unanticipated hazards when adapting to the brand new surroundings, along with the higher prices of dwelling in their adopted metropolis that could be economically draining [2,8,9]. Some migrants may turn out to be part of an urban underclass [18,19], which might in flip impression on sustaining good physical, psychological, and social well being.
Purchase prothiaden 75 mg otc
Another attention-grabbing finding is a change of measurement and consistency throughout the muscle medicine dispenser cheap 75 mg prothiaden amex. When appropriate medications like zoloft order prothiaden 75mg free shipping, progress into functional strengthening utilizing open chain exercises and actions. A easy progression can be utilized whereby within the preliminary therapy part the primary target is on local segmental control, which is then adopted by moving into closed chain segmental control. A pattern of the advised development and a few specific workout routines for every section can be found in Rehabilitation Protocol 8-3. They argue that applications which have a well-defined strengthening component ought to be equal to any specific muscle retraining protocol. However, it should be noted that the proof offered consisted of just two research (Cairns et al. Cairns and others (2006) reported that they supplied a treatment handbook for clinicians that outlined appropriate train development, however they allowed remedy to be individualized at the discretion of the clinician (Cairns et al. Koumantakis and others (2005) had their topics perform frequent warmup train components (exercise bike for 5 minutes, back stretches and pelvic/leg stretches), which may have been detrimental to their stabilizationenhanced group by introducing open chain actions and inappropriate segmental loading too early in this system (Koumantakis et al. For patients with low back pain thought to end result from instability, controlling for the timing and the amount of loading and weightbearing by way of the affected segment may be extra critical to the success of a spinal stabilization program. In essence then, the specific method has extra to do with a specific development rather than merely addressing specific muscles. Retrain the native stabilizing mechanism (segmental control) in nonweightbearing positions. Add coaching to recruit the weightbearing antigravity (one-joint) muscle tissue by emphasizing closed chain workouts and actions. Clinicians must spend time observing how the patient performs deep muscle contractions and devise ways/means to remove any undesirable substitution patterns from world muscular tissues. This could be achieved via the use of methods to scale back activity by choosing closed chain, static weightbearing, antigravity work postures, joint compression, fast and slow "ramp" 532 Spinal Disorders spondylolisThesis Andrew S. This defect of the vertebra could be the results of a broad range of etiologies, from stress fracture to a traumatic bony fracture. Athletic activities that require repetitive hyperextension and rotation predispose athletes to develop pars defects. Most generally spondylolisthesis happens at the L5 vertebral physique level followed by L4, then L3. There are different grades of spondylolisthesis and there are several sorts of spondylolisthesis, as described by Wiltse (1969): Type 1: Congenital spondylolisthesis, characterized by the presence of dysplastic sacral aspect joints permitting anterior translation of one vertebra relative to one other Type 2: Isthmic spondylolisthesis, attributable to the event of a stress fracture of the pars interarticularis Type 3: Degenerative spondylolisthesis, brought on by intersegmental instability from side arthropathy Type 4: Traumatic spondylolisthesis, outcomes from acute trauma to the side or pars interarticularis Type 5: Pathologic spondylolisthesis, results from any bone disorder that will destabilize the side joint. Because spondylolisthesis can lead to compression of the nerve root(s), sufferers can present with radicular pain with or without neurologic deficits. Palpation may identify a step-off over the spinous course of, which can be indicative of spondylolisthesis, notably over the L5-S1 stage. In assessing lumbar range of movement, forward flexion is often diminished secondary to excessive hamstring tightness. Then, the clinician passively hyperextends and rotates the affected person towards the weightbearing aspect. Reproduction of similar pain is a optimistic test and is suggestive of a spondylolysis and attainable spondylolisthesis that wants additional analysis with imaging. Most commonly plain radiographs are the initial imaging modality, with lateral and indirect views exhibiting a break within the pars interarticularis ("neck of the Scottie canine"). Treatment In general, treatment of spondylolisthesis should revolve around getting the patient again to preinjury activity level with damage prevention training additionally offered. The therapy and prevention are continuing to be additional studied, with extra evidence-based therapy methods being investigated. With respect to spondylolysis, scientific outcomes were good to glorious in 78% to 96% of sufferers when treated with antilordotic modified Boston brace for 6 months to 1 year and lordosis-maintaining brace for 6 months, respectively (Standaert and Herring 2000, Standaert et al. In one study, the speed of healing was 78% for unilateral and 8% for bilateral pars interarticularis defects when the athlete was handled with a lordotic brace (Standaert and Herring 2000, Standaert et al. Treatment could additionally be required for four to 12 months, based on unilateral or bilateral involvement and response to bracing. Overall, passive treatments similar to activity restriction and bracing may help create an setting for potential therapeutic of a pars interarticularis fracture. Another key part within the therapy of spondylolisthesis is backbone stabilization workouts. These exercises strengthen the muscle tissue across the lumbar backbone whereas sustaining a impartial spine position. Therapeutic spine stabilization workouts have been shown to be effective in remedy with chronic low again ache with concomitant spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis (Nelson et al. On the lateral view of the lower lumbar backbone (A), the conventional contour of the posterior elements of L4 is outlined by the white dotted lines. On the oblique view (B), that is seen as a fracture through the "neck of the Scottie canine" (arrows). This nonspecific discovering might indicate that left-sided adaptive adjustments caused elevated stress because of the right-sided pars defect or an impending left pars stress fracture. Diagonals are carried out by standing on all fours after which bringing the best hand together with the left knee. Finally, repeat this train for opposite diagonal (Baranto 2009) for 10 repetitions in a three to 5 series. Degree of slippage is outlined by trying on the relationship of the posterior portion of the vertebral our bodies. The stabilization train group had less ache and functional incapacity following a 10-week therapy program than the overall exercise group. Specific workout routines proposed to handle the abdominal muscle tissue in an isolated method involved a curl-up�type maneuver. This exercise provides a challenge to the indirect belly muscular tissues with out imposing excessive compressive or shear loading forces on the lumbar spine. In addition, the horizontal side-support train challenges the quadratus lumborum muscle, which is a crucial spinal stabilizer. These are performed by standing on all fours and then bringing the best hand along with the left knee. Finally, the train is repeated for the alternative diagonal (Baranto 2009), 10 repetitions in a 3 to five sequence. The stomach muscle tissue, notably the transversus abdominis and oblique abdominals, and the multifidus muscle have been proposed to play an essential position in stabilizing the spine by co-contracting in anticipation of an utilized drive. The multifidus muscle, because of its segmental attachments to the lumbar vertebrae, could possibly present segmental control, notably throughout lifting and rotational motions. The patient then lifts the pelvis off the support floor to a place in line with the shoulders, eliminating the side-bending (B).
Buy 75mg prothiaden otc
Kjellman G symptoms vitamin d deficiency buy prothiaden 75mg, Oberg B: A randomized scientific trial evaluating common exercise symptoms 8 days post 5 day transfer cheap prothiaden 75mg line, McKenzie treatment, and a management group in sufferers with neck pain, J Rehabil Med 34:183�190, 2002. McLean L: the impact of postural correction on muscle activation amplitudes recorded from the cervicobrachial region, J Electromyogr Kinesiol 15(6):527�535, 2005. Michaelson P, Michaelson M, Jaric S, et al: Vertical posture and head stability in sufferers with continual neck, J Rehabil Med 35:229�235, 2003. The prevalence of neck pain and related incapacity in Saskatchewan adults, Spine 23:1689�1698, 1998. Jull G: Deep cervical flexor muscle dysfunction in whiplash, J Musculoskel Pain eight:143�154, 2000. Jull G, Trott P, Potter H, et al: A randomized controlled trial of train and manipulative therapy for cervicogenic headache, Spine 27(17):1835�1843, 2002. Jull G, Amiri M, Bullock-Saxton J, et al: Cervical musculoskeletal impairment in frequent intermittent headache. Levoska S, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S: Active or passive physiotherapy for occupational cervicobrachial problems A comparison of two treatment methods with a 1-year follow-up, Arch Phys Med Rehabil seventy four:425�430, 1993. Makela M, Heliovaara M, Sievers K, et al: Prevalence, determinants, and consequences of persistent neck ache in Finland, Am J Epidemiol 134:1356�1367, 1991. Tjell C, Rosenthall U: Smooth pursuit neck torsion take a look at: a specific test for cervical dizziness, Am J Otol 19:76�81, 1998. Treleaven J, Jull G, LowChoy N: the relationship of cervical joint place error to balance and eye motion disturbances in persistent whiplash, Man Ther 11:99�106, 2006. Ylinen J, Ruuska J: Clinical use of neck isometric strength measurement in rehabilitation, Arch Phys Med Rehabil seventy five:465�469, 1994. Binkley J, Finch E, Hall J, et al: Diagnostic classification of patients with low back pain: report on a survey of bodily remedy specialists, Phys Ther 73:138�155, 1993. Randl�v A, �stergaard M, Manniche C, et al: Intensive dynamic training for females with continual neck/shoulder ache. Revel M, Minguel M, Gregory P, et al: Changes in cervicocephalic kinesthesia after a proprioceptive rehabilitation program in sufferers with neck pain: A randomized managed research, Arch Phys Med Rehabil 75:895�899, 1994. Sarig-Bahat H: Evidence for exercise therapy in mechanical neck disorders, Man Ther 8(1):10�20, 2003. Sjolander P, Michaelson P, Jaric S, et al: Sensorimotor disturbances in chronic neck pain-range of movement, peak velocity, smoothness of motion, and repositioning acuity, Man Ther 13:122�131, 2008. Sterling M, Jull G, Vicenzino B, et al: Development of motor system dysfunction following whiplash harm, Pain 103:65�73, 2003. Treleaven J, Jull G, Low Choy N: Smooth pursuit neck torsion test in whiplash associated disorders- relationship to self stories of neck pain and incapacity, dizziness and anxiety, J Rehabil Med 37:219�223, 2005a. Waling K, Sundelin G, Ahlgren C, et al: Perceieved ache earlier than and after three exercise programs-a controlled medical trial of women with work-related trapezius myalgia, Pain 85:201�207, 2000. Ylinen J, H�kkinen A, Nyk�nen M, et al: Neck muscle coaching in the therapy of persistent neck ache: a three-year follow-up research, Eura Medicophys 43:161�169, 2007. Spratt K, Weinstein J, Lehmann T, et al: Efficacy of flexion and extension treatments incorporating braces for low-back ache patients with retrodisplacement, spondylolisthesis, or regular sagittal translation, Spine 18:1839�1849, 1993. Waddell G: Low again ache: a twentieth century well being care enigma, Spine 21:2820�2825, 1996. A evaluate of studies of basic affected person populations, Eur J Spine 12(2):149�165, 2003. Bouisset S: Relationship between postural help and intentional motion: biomechanical strategy, Arch Int Physiol Biochim Biophys ninety nine:77�92, 1991. Cholewicki J, McGill S: Mechanical stability of the in vivo lumbar spine: implications for harm and persistent low again pain, Clin Biomech eleven:1�15, 1996. Gardner-Morse M, Stokes I: the impact of belly muscle coactivation on lumbar spine stability, Spine 23:86�92, 1998. Gracovetsky S, Farfan H, Helleur C: the impact of the stomach mechanism, Spine 10:317�324, 1985. Kavcic N, Grenier S, McGill S: Determining the stabilizing position of particular person torso muscle tissue throughout rehabilitation workouts, Spine 29(2):1254�1265, 2004. Knott M, Voss D: Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation: Patterns and Techniques, New York, 1968, Harper & Row. Macedo L, Maher C, Latimer J, et al: Motor management exericse for persistent, nonspecific low back pain; a scientific evaluation, Phys Ther 89(1):9�25, 2009. McGill S, Brown S: Reassessment of the role of intra-abdominal stress in spinal compression, Ergonomics 30:1565�1588, 1987. McKenzie R, May S: the Lumbar Spine Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy, Volume One and Volume Two, New Zealand, 2004, Spinal Publications New Zealand Ltd, Waikanae. Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, et al: Serial adjustments in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery, Spine 24:1023�1028, 1999. Gille O, Jolivet E, Dousset V, et al: Erector spinae muscle modifications on magnetic resonance imaging following lumbar surgery via a posterior strategy, Spine 32:1236�1241, 2007. Richardson C, Hodges P, Hides J: Therapeutic Exercise For Lumbopelvic Stabilization, ed 2, London, 2004, Churchill Livingstone. Further Readings Bogduk N: Management of persistent low back ache, Med J Aust a hundred and eighty: 79�83, 2004. Buchbinder R, Jolley D, Wyatt M: Volvo award winner in medical studies: results of a media campaign on back pain beliefs and its potential affect on the administration of low back pain in general follow, Spine 26:2535�2542, 2001. Punjabi M, Abumi K, Duranceau J, et al: Spine stability and intersegmental muscle forces: a biomechanical model, Spine 14:194�200, 1989. Kiesel K, Underwood F, Matacolla C, et al: A comparison of choose trunk muscle thickness change between subjects with low again ache classified in the treatment-based classification system and asymptomatic controls, J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 37(10). In Crosbie J, McConnell J, editors: Key Issues in Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy, Oxford, 1993, Butterworth-Heineman. Bogduk N: Clinical Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine and Sacrum, ed three, New York, 1997, Churchill Livingstone. An evaluation of neurodynamic strategies and considerations relating to their software, Man Ther doi: 10. Costa F, Sassi M, Cardia A, et al: Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: analysis of results in a series of 374 sufferers treated with unilateral laminotomy for bilateral microdecompression, J Neurosurg Spine 7:579�586, 2007. Devor M, Seltzer Z: Pathophysiology of broken nerves in relation to chronic pain. Dilley A, Odeyinde S, Greening J, et al: Longitudinal sliding of the median nerve in sufferers with non-specific arm ache, Man Ther doi: 10. A preliminary research of the intraneural circulation and the barrier operate of the perineurium, J Bone Joint Surg Br fifty five:390� 401, 1973. Ogata K, Naito M: Blood circulate of peripheral nerve: results of dissection, stretching and compression, J Hand Surg [Am] 11B:10�14, 1986. Oliveira A, Gevirtz R, Hubbard D: A psycho-educational video used in the emergency department supplies efficient therapy for whiplash injuries, Spine 31:1652�1657, 2006.
75 mg prothiaden quality
Ankle Sprains 319 � Limit the pain symptoms uti buy 75 mg prothiaden visa, swelling symptoms xanax treats purchase 75mg prothiaden with visa, and spasm associated with inflammation. Although the affected person ought to relaxation the injured tissues to limit extra stress and potential damage, you will need to keep in thoughts that absolute rest is seldom a clever choice. The sort of actions that can be safely tolerated range with the severity of the ankle sprain. Typically with grade I ankle sprains, the patient can safely participate in mild to reasonable actions. Because most ankle sprains contain the lateral ligaments and are brought on by plantarflexion and inversion, the affected person should avoid actions that cause extremes of these motions for at least the first several days. Functional rehabilitation has been proven to be related to extra frequent return to sports activities and higher charges of patient satisfaction than immobilization (Kerkhoffs et al. Rest and safety of the injured tissues are necessary to allow the physique to progress by way of its regular healing processes. Toward the end of the acute part, pulsed ultrasound can be utilized to promote tissue healing while limiting undesirable thermal effects obtained with continuous ultrasound. It is essential to remember that the inflammatory course of is a protective mechanism and is critical for the physique to heal; nonetheless, the irritation course of needs to be controlled to reduce affected person suffering and stop continual inflammation. Ice and other types of cryotherapy assist prevent swelling, lower ache, and restrict spasm. Both elevation and compression with elastic wraps or compression stockinet help with minimizing swelling. Therapeutic modalities that mix ice, compression, and elevation, such as an intermittent compression unit, also are beneficial. Grade I joint mobilization techniques to the talus can also be used to decrease pain within the ankle joint. Performing a joint mobilization method to the distal tibiofibular joint typically supplies ache aid when a "positional fault" is current. An anterior positional fault of the distal fibula is often seen in sufferers with a lateral ankle sprain. Although rest could also be wanted for the injured ankle ligaments, muscles, tendons, and joint capsule, regular operate of the noninjured tissues should be maintained with activity. Prolonged use of those assistive and protective devices can result in disuse of healthy tissues around the ankle. One method to embrace cryokinetics is to place the injured ankle in a cold whirlpool bathtub for 15 to 20 minutes or until it becomes "numb. This permits the affected person to perform the appropriate activities in a pain-free state. Patients must be inspired to have interaction in pain-free bodily actions to maintain their total body conditioning. The underwrap should go up to the base of the calf muscle or roughly 5 to 6 inches above the malleoli. D, Apply three stirrup strips (5�7), beginning at the medial facet of the decrease leg running inferiorly alongside the leg then laterally beneath the rearfoot and ending on the lateral facet of the lower leg. Each strip should overlap the previous one by approximately one half of the width of the tape. E, Apply three horseshoe strips (8�10) running from the medial side of the foot to the lateral aspect beginning and ending on the distal anchor (See #4 in Part C). Note: An different method, called a "closed basketweave," alternates one stirrup strip with one horseshoe strip until three of each are applied. If this were to be carried out, strip 5 could be followed by strip eight, then strip 6 can be followed by strip 9, and strip 7 can be adopted by strip 10. The first heel lock (11) begins excessive on the anterior aspect of the lower leg, runs posteriorly behind the calcaneus, circles alongside the medial aspect of the calcaneus, then finishes alongside the anterior� medial aspect of the midfoot. The second heel lock (12) begins high on the anterior side of the lower leg, runs posteriorly behind the calcaneus, circles along the lateral facet of the calcaneus, then finishes along the anterior�lateral facet of the midfoot. Begin the strips at the superior side of the lower leg and work inferiorly, overlapping the previous strip by roughly one half of the width of the tape. These exercises also assist to prevent disuse problems with the noninjured physique areas while minimizing stress on the injured tissues. Patients should also proceed their regular strength coaching workout routines for the trunk and upper extremities. The use of a compression stockinet or elastic wrap while performing these workout routines might help prevent the inflow of edema to the area. Subacute Stage: Goals and Interventions During the subacute section the first targets are as follows: Prevent further harm. Although the initial inflammatory response has ended and the early scar 322 Foot and Ankle Injuries tissue is beginning to develop, it may be very important keep in thoughts that the scar tissue remains to be very weak and improper actions can simply trigger reinjury. In the early days of this section, extremes of plantarflexion and inversion ought to still be minimized to forestall injury to the newly fashioned scar tissue. As the preliminary indicators and symptoms of acute irritation diminish, thermotherapy techniques such as heat whirlpools and sizzling packs ought to be introduced. Therapeutic ultrasound can also be used presently, progressing from pulsed to continuous duty cycles. Continuous ultrasound additionally assists with ache aid, tissue therapeutic, and reduction of subacute edema. The continued use of electrical stimulation can assist with minimizing ache and irritation. The clinician locations the palm of the hand on the lateral malleolus and provides a posterior pressure to the lateral malleolus. Continuing to protect the injured ligaments from reinjury will permit the body to go through its regular healing course of. The continued use of therapeutic modalities such as ultrasound and thermotherapy assist promote tissue therapeutic. Therapeutic therapeutic massage strategies can also be used beginning with "flushingtype" methods corresponding to p�trissage to promote blood move and circulation and progressing to more aggressive strategies such as cross-friction massage to promote tissue alignment. The affected person should be instructed to perform the motions in a gradual and managed manner at all times. The affected person ought to start with dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, and eversion earlier than incorporating inversion, then progress to circling the board whereas touching all sides of the board in each clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Goal J: Re-Establish Neuromuscular Control and Restore Muscular Strength and Endurance. Patients can start isometric workout routines in a neutral ankle place against plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion forces. Isometric workout routines should begin with submaximal contractions and progress to maximal contractions. Cryokinetics are still indicated in the early portion of the subacute phase and can be used till the patient has little to no discomfort with the actions. The patient can perform uniplanar motions in plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion or multiplanar motions by performing "circles," which require the patient to contact all of the edges of the board in both a clockwise and counterclockwise course. Early exercises to encourage loading of the ankle include "weight shifts" in numerous instructions.
75mg prothiaden buy
It is suggested that exercise and especially loadbearing exercise may assist (a little) with this diffusion course of (sponge effect) symptoms 3 days after embryo transfer generic prothiaden 75 mg fast delivery, which might make the reciprocal movement of the pelvis in the course of the gait cycle a viable exercise to assist facilitate this course of medications used to treat adhd cheap prothiaden 75 mg with visa. There is proof that treadmill walking is helpful for sufferers with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Normal gait requires roughly 35 levels of hip flexion, and a strolling program aimed at helping "neural mobilization" could probably be seen as a straightforward means of bettering the normal motion properties of the sciatic nerve. Second, to date, postoperative discectomy studies have focused on the utilization of train; no research have been done on using manual therapy. It could probably be argued that mild, passive manual techniques provide effects similar to these of passive stretches and workouts, but therapists must be cautioned regarding using robust, end-range handbook methods on the surgical degree within the acute and subacute phases. A well-reasoning therapist could contemplate guide therapy strategies on adjacent regions such as the thoracic spine and/or hip joints as a way of "borrowing" motion from these areas and thus lowering load on the surgical level. Care ought to be taken to consider the positioning of the sufferers in guide remedy procedures for these areas, and the loads occurring across the surgical degree should be thought of. Neural Tissue Mobilization Neural tissue mobilization is another controversial topic, primarily because of a scarcity of proof of its use on this population. It can be essential that therapists understand that neural tissue mobilization is relatively "new" in comparability with time-tested therapies corresponding to train, modalities, and spinal manual remedy. There is growing proof as to the scientific use and efficacy of neural tissue mobilization techniques in different issues. The case for adding neural tissue mobilization also can middle on primary science research. Basic science research signifies that a traditional, wholesome nervous system requires certain bodily properties to perform properly and when these are violated. Three bodily properties have been identified: Space: An straightforward means for clinicians to view the nervous system is to envision the fragile nerves, spinal twine, and meninges all touring inside containers or passageways. For nerves to correctly perform, they should have the flexibility to "slide" and "glide" unhindered through completely different areas of the body. As nerves journey via the body, they encounter many surrounding tissues including muscle, bone, ligaments, and fascia. Numerous research have shown that if the interface is injured or damaged, it could have repercussions for the adjoining neural tissues. When these areas are compromised and nerves maintain undesirable stress or irritation, it could result in the onset of symptoms. Early cadaver studies confirmed that the nervous system is extremely nicely designed to deal with movement. It has also been shown that the spinal canal (the "container") can lengthen approximately 30% from spinal extension to spinal flexion. The concept of neural tissue motion problems has lead to the event of structured neurodynamic checks to assess the movement capabilities of a selected nerve department. After the event and refinement of those checks, clinicians started to use them in numerous forms of therapy, in essence making an attempt to restore and maintain the conventional anatomic and physiologic requirements of the nervous system. Additionally, it has been proven that if a nerve is "lengthened" greater than 6% to 8% of its size, blood flow in the peripheral nerve slows. If the nerve is elongated approximately 15%, blood move may be fully occluded. Adequate blood flow, nutrition, and motion (previous section) are due to this fact interdependent. If blood flow to neural tissue is interrupted, it could result in a hypoxic state, which can in turn result in an ischemicbased pain state. Ischemic pain is a class of nociceptive ache by which lack of motion, sustained posturing, or decreased circulation creates an acidic setting (lower pH), which has been linked to ache. Exercise such as a walking program and cardiovascular train can be seen as a means of helping the affected person restore or keep sufficient blood circulate to the nervous system. From the fundamental science literature, it appears clear that therapy techniques geared toward restoring movement, and thus blood move, have the potential to decrease ischemic-based ache and preserve regular motion and function of the nervous system. An important consideration when including neural tissue mobilization to the therapy plan for a patient who has had discectomy is nerve sensitivity. Several studies have proven that disc herniation is related to demyelinization. The demyelinization might in turn result in "peripheral sensitization" the place responses to mechanical, chemical, and/or thermal stimuli are exaggerated. Timing, Dosage, and Frequency Little proof is out there for figuring out the quick start of a postoperative program. A typical surgical patient visits his or her surgeon in 2 to 3 weeks after the surgery and, if the patient nonetheless experiences incapacity, he or she might then be referred to physical therapy. This practical/clinical situation means that sufferers may not show up for rehabilitation for four weeks postoperatively. This matches with research that show that rehabilitation began four to 6 weeks after surgery is efficient in bettering short-term disabilities (Dolan et al. Based on the analysis and medical expertise, it seems believable that such a program might run two to three times a week for six to eight weeks (Dolan et al. Patients must also be instructed in a home train program, permitting them to turn into self-sufficient and in a place to manage their very own well-being as they progress by way of formal rehabilitation toward discharge. It ought to as quickly as again be emphasized that good early postoperative data is necessary. The acute care therapist is in a perfect position to not solely help ambulate and mobilize a patient postoperatively, but also provide info that can reassure the patient, decrease fear, and set applicable goals. Current data recommend that one in five individuals within the United States has an ongoing (chronic) pain state, implying that roughly 65 to 70 million Americans have persistent ache (Wall and Melzack 2005). Additionally, the definition indicates that pain could be skilled with tissue harm and even potential harm or the menace of injury. The bio-psycho-social method combines biology, psychology, and social interaction/ consciousness in treating a patient. The reality is that many physical therapists (based on their training) nonetheless are inclined to be closely geared toward the biological part. Compared to showing a affected person a nice healthy disc, a therapist shows a affected person a "unhealthy" disc, or knee, or foot. Although broken tissue may lead to pain and type a major component in acute, tissue-based pain states, it has limitations in explaining persistent pain. First, spinal degeneration is common and is a standard finding on any adult spine imaging examine. Second, if spinal degeneration from age 20 to age 80 had been plotted on a graph, it might point out a linear upward progression-with increased age comes increased spinal degeneration. Therapists have to have a good understanding of pathoanatomy including healing rates and phases of therapeutic. Although tissues heal, many patients have persistent pain well past the "regular healing section" for these tissues. Current information point out that pathoanatomy fashions not only have limited impact in explaining pain to sufferers, but also may very well make them worse. Images, posters, and spine models of "unhealthy anatomy" might invoke worry instead of helping ease ache or discomfort.
Generic 75 mg prothiaden
The three subsystems are thought of to be interdependent components with one capable of compensating for deficits in one other treatment neuropathy prothiaden 75mg purchase on line. The physiological motions of flexion-extension occur across the x-axis; rotation occurs across the y-axis; and lateral flexion happens around the z-axis 911 treatment for hair 75mg prothiaden buy with amex. Accessory motions of anterior-posterior translation happen along the z-axis; left and proper translation along the x-axis; and superior-inferior translation alongside the y-axis. Specific Lumbopelvic Stabilization Control 525 Table 8-22 Passive Subsystem: Osseoligamentous Structures of the Spine Neural arch ligaments Ligamentum flavum Interspinous ligament Supraspinous ligament (posteriorly) Intertransverse ligament (laterally) Zygapophyseal joint capsule Anterior longitudinal ligament Posterior longitudinal ligament Intervertebral disc Articular capsular ligaments Ventral ligaments Active Passive (2) capsular ligaments, and (3) ventral or vertebral body ligaments (Table 8-22). The intervertebral disc is included as one of many ventral or vertebral body ligaments as a result of it does function to restrict intervertebral segmental movement, and in reality, it does so best when loaded. The importance of the passive subsystem throughout the interdependent subsystems for spinal stability may be seen in pressure transmission and aiding the action of the energetic muscular system. The continuous connective tissue stocking also plays a key function within the self-bracing mechanism (form and force closure) of the pelvis, a mechanism that capabilities to preserve the integrity of the low back and pelvis during the switch of energy from the spine to the decrease extremities (Vleeming 1989a and 1989b). The passive subsystem entails the bones and ligaments forming the lumbar backbone, the lively subsystem entails the muscular tissues appearing on the spine, and the management subsystem refers to the nervous system that displays for position and sends impulses prematurely of expected challenges and in response to unexpected challenges to spinal stability. The muscle system can solely be as good as the system that drives it (neural system) and the system that connects it (passive system). This reiterates the concept of three interconnected parts to spinal stability. The neural system must (1) coordinate muscle exercise in advance of predictable challenges to stability and (2) coordinate responses to afferent feedback from unpredictable challenges. The system must activate the muscles "at the proper time, by the right quantity, within the correct sequence, and then flip the muscles off appropriately" (Hodges 2004). The active subsystem (muscles) offers the mechanism by which the neural subsystem can modulate/adjust the stability of the backbone. Many biomechanical models have discovered that stability is perfect if stiffness is maximized and no lumbopelvic movement is allowed. Movement is required to help in dissipation of forces and to minimize power expenditure-as an example, energy expenditure in gait is shown to improve if pelvic movement is decreased (Perry and Burnfield 2010). Movement can also been seen as essential for spinal well being when it comes to circulation and fluid exchange through the tissues. Asking which muscle tissue contribute the "most" to stability might be the wrong question on account of lack of management of spinal stabilization. This model recognizes that muscle tissue of the spine need to be programmed upfront of movement and in response to suggestions from motion to regulate to any condition, at any cut-off date, in order that appropriate muscular tissues are activated at applicable ranges. This mannequin also permits for an understanding of the maintenance of stability, the entity of instability, and the scientific paradigm for assessment and treatment of muscle dysfunction in the patient with low back pain (Hodges 2004). These fibrous buildings really type a continuous ligamentous stocking during which the lumbar vertebrae and sacrum are positioned (Willard 1997). For ease of description, the vertebral connective tissue sheath may be divided into three elements: (1) neural arch ligaments, 526 Spinal Disorders in view of the complexity of stability. It means that no single muscle might provide the greatest contribution to all parts of stability. It is extra important to look at the differential control of the separate parts for stability (Hodges 2004). The idea of specific muscular tissues being designed for spinal help was first advised by Leonardo DaVinci (Crisco and Panjabi 1991). DaVinci suggested that some muscular tissues surrounding the spine have been primarily involved with stability, and he theorized that those extra centrally positioned muscle tissue offered stability at the segmental degree, whereas extra laterally placed muscles acted as "man ropes" and were more concerned with bending/moving the backbone. This idea led to researchers categorizing the trunk muscle tissue into local and international muscle systems based mostly on their architectural properties (Table 8-23) (Bergmark 1989). The local muscle system included deep muscular tissues and the deep parts of some muscles that have their attachment onto the lumbar vertebrae. These muscular tissues control the stiffness and intervertebral relationship of the spinal segments and the posture of the lumbar segments. They are considered the torque turbines for spinal movement and are mentioned to act as guy ropes to management spinal orientation. These muscular tissues have been proven to stability the exterior loads utilized to the trunk and switch masses from the thorax to the pelvis (Bergmark 1989). The massive variations in exterior hundreds that can occur with daily exercise are accommodated by the global muscle system in order that the ensuing load on the lumbar backbone and its segments are regularly minimized. Cholewicki and others, in a biomechanical in vivo mannequin, discovered that though the global muscle tissue offered a significant quantity of stiffness to the spinal column, exercise of the local system was vital in producing stability on the intervertebral/segmental degree (Cholewicki et al. Even when forces generated by the worldwide muscular tissues have been substantial, the backbone was unstable without native muscle exercise. Hodges (2004) famous that this local/global muscle system is likely an oversimplification of the complex management of spinal stability; nevertheless, it does present a useful model to consider clinically because proof suggests that the local muscle system is most impaired in low back ache sufferers despite the precise fact that both techniques are seen as necessary to meet the calls for of spinal stability (Hodges 2004). Modeling research (Cholewicki and McGill 1996) counsel that world muscles present the optimum control of buckling forces, but training those muscles is unlikely to resolve deficits in muscle management. The deep system is seen to provide minimal contribution to management of buckling forces, but it does produce an environment friendly mechanism to fine-tune the control of intervertebral motion and segments of the pelvis. Finally, the native muscle control is seen to be required over the spectrum of practical calls for from light duties, corresponding to reaching or moving while seated, to the heavier weightlifting tasks. The requirement for sturdy global muscle motion during gentle tasks is seen as minimal, but the local system is needed for protected perform at the segmental level. Table 8-23 Active Subsystem: the Trunk Muscles Can Be Categorized into Local and Global Muscle Systems Based on Their Architectural Properties native Stabilizing System Intertransversarii Interspinales Multifidus Lumbar part of longissimus thoracis Lumbar part of iliocostalis lumborum Quadratus lumborum, medial fibers Transversus abdominis world Stabilizing System Thoracic a half of longissimus thoracis Thoracic a half of iliocostalis lumborum Quadratus lumborum, lateral fibers External indirect Internal indirect Rectus abdominis feedforward control of lumbopelvic Stability Lumbopelvic stability is managed prematurely of imposed forces. Studies have demonstrated that exercise of the trunk muscular tissues happens upfront of the muscle tissue responsible for movement of the decrease limb (Hodges and Richardson 1997b) and upper limb (Aruin and Latash 1995, Bouisset and Zattara 1987, Hodges and Richardson 1997a) and previous to loading when a mass is added to the trunk in a predictable manner (Cresswell et al. This is according to the architectural properties of these muscles to provide a common increase in intervertebral control. Thus, these simple responses are rigid and represent a primary mechanism for the motor control system to appropriate an error-resisting an imposed stretch. Some integration of reflexes is seen when reflex modifications occur in different related muscle tissue, including contralateral muscular tissues (Beith and Harrison 2004). This means that afferent enter from distant segments (arm) could also be involved in initiation of the trunk muscle response. This also is seen to happen when paraspinal muscle exercise is decreased when a load is removed from the trunk by removal of a load from the upper limbs (Hodges et al. Other fundamental reflex responses have been recognized utilizing electrical and/or mechanical stimulation of afferents in ligaments, annulus, aspect joint capsule, and sacroiliac joint (Solomonow et al. In common, exercise of multifidus was initiated with short latency, on either side and over a quantity of segments in response to the applied stimulus. These responses have an extended latency, are more versatile, and could be modified voluntarily. As an instance, when the support floor on which a person is standing is rapidly moved, a posh interplay of several physique segments, together with the trunk, is initiated to keep equilibrium of the physique (Horak and Nashner 1986, Keshner and Allum 1990).