Sinequan
Sinequan dosages: 75 mg, 25 mg, 10 mg
Sinequan packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

Sinequan 10 mg otc
An evaluation of the lowest efficient depth of prophylactic anticoagulation for sufferers with nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation anxiety jury duty sinequan 75 mg lowest price. Increased danger of intracranial hemorrhage when aspirin is combined with warfarin: a metaanalysis and speculation anxiety symptoms women buy generic sinequan 75 mg. A clinical trial comparing three antithromboticdrug regimens after coronaryartery stenting. Use of clopidogrel with or without aspirin in patients taking oral anticoagulant therapy and present process percutaneous coronary intervention: an openlabel, randomised, controlled trial. Edoxaban versus References 853 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of recent oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta evaluation of randomised trials. Comparison of warfarin versus aspirin for the prevention of recurrent stroke or demise: subgroup analyses from the Warfarin Aspirin Recurrent Stroke Study. Aspirin consumption through the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital anomalies: a metaanalysis. Lowmolecularweight heparin versus a coumarin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Metaanalysis of wine and beer 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 consumption in relation to vascular risk. Review of moderate alcohol consumption and lowered threat of coronary heart disease: is the effect due to beer, wine, or spirits Association of alcohol consumption with selected cardiovascular disease outcomes: a systematic evaluate and metaanalysis. Cardiovascular danger components and confounders among nondrinking and reasonable drinking U. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic assault: a suggestion for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/ American Stroke Association. Salt consumption, stroke, and cardiovascular disease: meta analysis of potential studies. Effect of elevated potassium intake on cardiovascular risk components and disease: systematic review and metaanalyses. Dietary lipids and blood ldl cholesterol: quantitative metaanalysis of metabolic ward studies. Systematic evaluate of dietary intervention trials to lower blood whole cholesterol in freeliving subjects Commentary: Dietary change, ldl cholesterol reduction, and the general public health � what does metaanalysis add Body weight: implications for the prevention of coronary coronary heart illness, stroke, and diabetes mellitus in a cohort research of middle aged males. Systematic evaluate of the longterm effects and financial penalties of treatments for obesity and implications for health enchancment. The scientific effectiveness and cost effectiveness of surgical procedure for people with morbid weight problems: a scientific evaluation and economic evaluation. The function of food regimen, fruit and vegetables and antioxidants within the aetiology of stroke. Fruit and vegetables and ischaemic heart illness: systematic evaluation or deceptive metaanalysis References 855 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 Mediterranean food plan, life-style components, and 10year mortality in aged european women and men. Risks and advantages of omega three fat for mortality, heart problems, and most cancers: systematic evaluation. Exercisebased rehabilitation for patients with coronary coronary heart disease: systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized managed trials. Homocysteine and heart problems: proof on causality from a metaanalysis. Lowering blood homocysteine with folic acid based mostly supplements: metaanalysis of randomised trials. Efficacy of folic acid supplementation in stroke prevention: new insight from a metaanalysis. The antioxidant nutritional vitamins and cardiovascular disease: a critical evaluation of epidemiologic and scientific trial knowledge. Use of antioxidant vitamins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: metaanalysis of randomised trials. Abnormal glucose regulation in sufferers with acute stroke throughout China: prevalence and baseline affected person characteristics. Epidemiology of ischemic 856 17 Preventing recurrent stroke 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 stroke in sufferers with diabetes: the greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study. Incidence and determinants of mortality and cardiovascular occasions in diabetes mellitus: a metaanalysis. Fasting plasma glucose and danger of incident ischemic stroke or transient ischemic assaults: a prospective cohort examine. A comparability of fee control and rhythm management in patients with atrial fibrillation. Association of obstructive sleep apnea with threat of serious cardiovascular events: a scientific evaluation and metaanalysis. The evolution of surgical procedure for the remedy and prevention of stroke: the Willis Lecture. Reconstruction of inside carotid artery in a patient with intermittent attacks of hemiplegia. Dramatic adjustments in the efficiency of endarterectomy for ailments of the extracranial arteries of the head. Joint examine of extracranial arterial 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 occlusion. Beneficial impact of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic sufferers with highgrade carotid stenosis. Carotid endarterectomy and prevention of cerebral ischemia in symptomatic carotid stenosis. Trends within the inhospital stroke price following carotid endarterectomy in California and Maryland. An epidemiological wants assessment of carotid endarterectomy in an English well being area. Underinvestigation and undertreatment of carotid disease in elderly sufferers with transient ischaemic attack and stroke: comparative population based mostly study. Eversion endarterectomy of the interior carotid artery: Technique and results in 449 procedures. A randomized study on eversion versus commonplace carotid endarterectomy: study design and preliminary outcomes: the Everest Trial. Initial experience with eversion carotid endarterectomy: absence of a learning curve for the first a hundred patients.
Sinequan 25 mg generic fast delivery
The evidence Although there are some clinically useful subgroup observations within the pooled evaluation of the trials anxiety symptoms shortness of breath sinequan 10 mg cheap visa, univariate subgroup analysis is commonly of only limited use in scientific follow anxiety symptoms even on medication sinequan 10 mg discount amex. For example, what would be the probably profit from surgery in a 78yearold (increased benefit) feminine (reduced benefit) with 70% stenosis who presented within two weeks (increased benefit) of an ocular ischemic occasion (reduced benefit) and who was found to have an ulcerated carotid plaque (increased benefit) One approach to weigh the oftenconflicting results of the necessary traits of an individual patient on the probably benefit from treatment is to base decisions on the predicted absolute risks of a poor end result with every remedy choice, using prognostic fashions. Thus, when the operative danger and the small extra residual threat of stroke following successful endarterectomy were taken into consideration, profit from endarterectomy at 5 years varied considerably throughout the quintiles, with no profit in patients within the lower three quintiles of predicted medical risk (absolute risk reduction 0�2%), moderate benefit within the fourth quintile (absolute danger reduction 12%), and substantial profit in the highest quintile (absolute danger reduction 32%). As another, a simplified threat score based mostly on the 824 17 Preventing recurrent stroke Table 17. The score for the 5year risk of stroke is the product of the individual scores for each of the risk elements current. Presenting event is coded as essentially the most severe ipsilateral symptomatic occasion in the final six months (severity is as ordered above, i. As is shown in the example, the entire danger score is the product of the scores for every risk issue. However, this poses extra issues for generalizability of the overall trial results than for the riskmodeling approach. For example, it would take only a comparatively modest enchancment within the effectiveness of medical therapy to erode the general good factor about endarterectomy in sufferers with 50�69% stenosis. This should be used as a nomogram for the conversion of the rating into a prediction of the percentage threat [1]. Thus, the probability that ancillary treatments have improved, and are likely to continue to enhance, is an argument in favor of a threat primarily based approach to focusing on remedy. Other prognostic instruments, corresponding to measurements of cerebral reactivity and emboli load on transcranial Doppler (Section 6. The quantity above every error bar refers to the variety of patients in each stenosis group. Therefore, even in this optimal trial surroundings, absolutely the reduction in risk of stroke with endarterectomy was only about 1% per yr before the widespread use of statin drugs, which probably would have improved the outcomes of the medical group. Selection of patients was primarily based on the "uncertainty precept," with very few exclusion criteria. Despite the differences in their strategies, absolutely the reductions in 5year threat of stroke with surgical procedure were 17. Until the second of stroke, any stenosis in the other 80% of the patients had been "asymptomatic. When asymptomatic carotid stenosis does come to attention, 4 questions come up: What is the chance of operating on it The primary difference between the trials was within the 30day operative risks of demise of 0. Applying the same arithmetical method used for symptomatic stenosis (Section 17. Furthermore, given the high cost of surgery even for symptomatic carotid stenosis, we want to pay attention to the healtheconomic and public health points related to surgical procedure for asymptomatic stenosis [551, 552]. It follows that intentionally screening apparently healthy people for carotid stenosis is also unwise. What is required is a prognostic mannequin to pick out these only a few sufferers whose asymptomatic stenosis is particularly prone to cause stroke, and then operate solely on them. There are a quantity of potential explanations for this: First, ultrasound may be less accurate than catheter angiography in measuring the degree of stenosis. Third, the speed of stenosis progression might decide the risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic stenosis, which is doubtlessly important contemplating the longer time-frame over which strokes happen in contrast with symptomatic stenosis. The overall balance of hazard and profit, which is of most significance to sufferers and clinicians, was not reported. In patients with symptomatic 70�99% stenosis, the surgical complication threat is higher in the presence of contralateral occlusion, although the proof still favors endarterectomy in these sufferers [508]. A riskmodeling approach much like that utilized in symptomatic carotid stenosis is required, perhaps combining patient scientific features with the results of doubtless prognostic investigations, similar to transcranial Dopplerdetected emboli, impaired cerebral reactivity, the morphology of the stenotic plaque on imaging, the rate of plaque development, and the presence of silent embolic infarcts on neuroimaging. There is rising evidence that embolic alerts detected on transcranial Doppler ultrasound scanning present prognostically useful info [43, 558�560]. Interestingly, in a potential examine of 468 sufferers with 60�99% carotid stenosis, marked decreased in microemboli detection and cardiovascular occasions after the institution of intensive medical remedy has been reported [561], providing additional evidence of transcranial Doppler as a potential device to monitor efficacy of medical remedy and identification of highrisk patients. In the same study, a mixture of microemboli detection and plaque morphology identified a highrisk group with an annual stroke threat of 8%, and a lowrisk group with a danger of <1% per annum. However, large potential research are required to decide whether or not any of those imaging characteristics predict the risk of stroke well enough to assist choose asymptomatic stenosis patients for endarterectomy. Neuroimaging findings according to infarcts ipsilateral to the asymptomatic carotid stenosis that had been presumably clinically "silent" may be predictive of patients at higher danger of stroke. The annual fee of ipsilateral stroke was considerably higher in these with evidence of silent embolic infarcts at enrollment (1. The presence or absence of ipsilateral silent infarcts might help in identifying highrisk sufferers but extra data are wanted to affirm the utility of this approach. This trial will randomize patients to both uniform intensive medical management or endarterectomy. The carotid revascularization group will be randomized to both carotid stenting with embolic protection or endarterectomy. The research will comply with sufferers for roughly 4 years to assess stroke and dying (clinicaltrials. However, the argument goes that if carotid endarterectomy of a just lately symptomatic extreme carotid stenosis kind of abolishes the danger of ipsilateral ischemic 17. Indeed, carotid angioplasty/stenting has now turn out to be extensively used, significantly when carotid pathology makes endarterectomy tough. Of course, carotid angioplasty/stenting is typically less invasive than carotid endarterectomy, and customarily extra convenient and quicker. It is unlikely to trigger nerve accidents, wound infection, venous thromboembolism, or myocardial infarction, and hospital stay may be shorter. However, there are potential disadvantages of ischemic stroke from periprocedural embolization, dissection of the vessel, restenosis of the stent, and groin hematoma issues. The procedural 30day risk of stroke or dying was nonsignificantly greater within the angioplasty/ stenting group with 37 (6. At the 2year followup, the rate of recurrent ipsilateral ischemic strokes reported was similar for both treatment teams however recurrent carotid stenosis of 70% was considerably larger after carotid angioplasty/stenting [571]. The trial stopped early after a high 30day procedural threat was found after carotid angioplasty/stenting. The cumulative chance of periprocedural stroke or dying and nonprocedural ipsilateral stroke after four years of followup was greater with carotid angioplasty/ stenting than with carotid endarterectomy (11. Importantly, a hazard perform evaluation confirmed the 4year differences in the cumulative chances of outcomes between stenting and endarterectomy were largely accounted for by the upper periprocedural danger of stenting compared with endarterectomy. After the periprocedural period, the risk of ipsilateral stroke was low and related in both remedy groups [573].
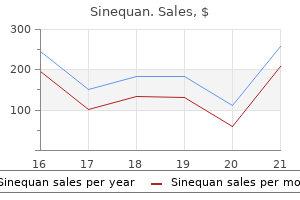
Sinequan 10 mg cheap fast delivery
Raised osmolality has been related to worse survival at three months [192] and elevated plasma urea with a larger frequency of venous thromboembolism [135] (Section 11 anxiety symptoms videos sinequan 10 mg buy mastercard. Very occasionally anxiety symptoms of flu buy discount sinequan 10 mg line, hypernatremia signifies a diabetic hyperosmolar state (Section 11. Tachycardia, poor peripheral perfusion, and low jugular venous strain could also be helpful in extreme instances. Investigations including the measurement of urinary particular gravity or osmolality and plasma sodium, urea (and creatinine to permit the urea/creatinine ratio to be determined), and osmolality are most likely extra dependable than the bedside evaluation [194]. Where a patient may be very unwell with hypotension or renal failure, cannulation of a central vein to measure the right atrial pressure directly and to monitor fluid substitute might often be priceless. Intravenous fluids are generally required where the patient is dehydrated while subcutaneous fluids are often enough to preserve hydration [195] (Table 11. There is a consensus that dextrose infusions should be avoided in the first day or two after acute stroke (Section eleven. If sufferers are willing and able to take fluids orally they need to be given enough access to fluids. Where the affected person is hypernatremic, sufficient isotonic fluid replacement will normally normalize the serum sodium. Thirst Reduced skin turgor Dry mucous membranes Sunken eyes Cool peripheries Collapsed peripheral veins Postural hypotension Low jugular venous pulse or central venous strain Low urine output Rising urinary particular gravity Raised hemoglobin focus Raised hematocrit Raised serum sodium (evidence of water depletion) Raised serum urea (out of proportion to the serum creatinine) 11. It could also be due to extra salt loss due to, for instance, diuretics, or it might be dilutional (reflecting inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone) in response to the mind harm, treatment, or medical complications [196]. Dilution is the conventional rationalization for hyponatremia after ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage, however after subarachnoid hemorrhage, hyponatremia has been attributed more typically to excessive renal salt loss (Section 15. It is unclear how typically this socalled "cerebral salt losing" happens in other kinds of stroke. Medication Likely indication Section We measure urea and electrolytes in all stroke sufferers as part of the baseline evaluation, and we monitor them often the place the baseline assessment signifies an abnormality, in sufferers with extreme stroke, and people with swallowing issues. A low serum sodium should prompt a seek for the cause including review of the medicine (Table 11. Treatment Diuretics High blood pressure/cardiac failure Seizures Depression/ emotionalism High blood pressure/cardiac failure eleven. It is usually beneficial that hyponatremia is corrected slowly, over days somewhat than hours, to reduce the risk of central pontine myelinolysis [198]. About onequarter of those with hyperglycemia are known to have diabetes mellitus already and one other quarter have a raised HbA1C, which suggests that their blood glucose has been high for some time earlier than the stroke, referred to as "latent diabetes" [200]. Whether the hyperglycemia in nondiabetic patients is because of launch of catecholamines and corticosteroids as a half of the stress response is controversial [201]. Hyperglycemia after a stroke, no less than in nondiabetic patients, is associated with elevated case fatality and poor functional outcome [199, 202]. This might be defined by more extreme strokes producing a greater stress response and, thus, hyperglycemia in order that hyperglycemia is just a marker of extreme stroke. However, some research have demonstrated that hyperglycemia is related to a poor end result having adjusted for stroke severity and different baseline prognostic components [199]. Hypoglycemia also happens after stroke due to efforts to normalize blood sugar in these with hyperglycemia (Section 11. Since hypoglycemia could, if extreme or undetected, cause worsening of the neurological deficit, the blood sugar must be monitored notably carefully in diabetic sufferers on hypoglycemic treatment. Inevitably, the reported frequency of malnutrition after stroke has diversified relying on patient selection, the definitions of malnutrition, and the method and timing of assessments. In a proportion of stroke patients, nutritional standing could worsen during hospital admission [210, 211]. Like any acute illness, stroke may trigger a adverse energy balance and greater nutritional calls for however, on the similar time, stroke sufferers may be less capable of adapt to these [212, 213]. Poor vitamin has been related to reduced muscle energy, reduced resistance to infection, and impaired wound therapeutic (although not specifically in stroke patients). Among patients with stroke, muscle weak point, infections, and pressure ulcers are frequent and account for many deaths and much morbidity [109]. Malnutrition on admission is related to increased A random blood glucose ought to be measured in all patients with stroke. In these with hyperglycemia, a fasting blood glucose and an HbA1C will assist distinguish latent diabetes from hyperglycemia as a result of the stroke itself. Blood sugar levels are likely to fall spontaneously within the first few days after stroke onset [204]. Patients with established diabetes and latent diabetes ought to be assessed to exclude vascular (both micro and macro) and neurological complications. Treatment We at present purpose to keep the blood sugar less than eleven mmol/L (200 mg/dL) within the first few days after an acute stroke. This will keep the patient free from thirst and keep away from extreme diuresis, which can cause dehydration (Section eleven. Whether extra aggressive management of blood sugar, which has at least theoretical benefits for the ischemic penumbra, is smart will depend upon any advantages, and the dangers of hypoglycemia, which can virtually actually depend on the depth of monitoring available [203]. Where sufferers have restricted mobility, especially where they rely on others for help with transfers, obesity could be a essential consider how lengthy they remain in hospital and the way a lot support they require. It can be a problem in the lengthy term in achieving adequate control of vascular threat elements such as hypertension and diabetes. Patients quite often achieve weight after stroke, presumably due to decreased power expenditure and excessive calorie intake. Laboratory parameters corresponding to hemoglobin, serum protein, albumin, and transferrin could not necessarily replicate dietary standing. Awareness of the potential for malnutrition is a key factor in identifying malnourished sufferers. All sufferers admitted to hospital with stroke should have an early evaluation of their nutritional standing. Patients usually eat very slowly after stroke and want supervision to guarantee safe swallowing. Simple measures similar to offering appetizing meals of an acceptable consistency (Section eleven. Staff shortages might imply that sufferers obtain inadequate meals, which can eventually cause malnutrition, or have meals compelled into them hurriedly, which could be very demeaning and adversely impacts morale. Oral nutritional dietary supplements Routine oral nutritional supplementation that gives each proteins and calories in hospitalized stroke sufferers is probably not worthwhile because it has not been shown to have a clinically helpful impression on outcome. There was no important difference in survival or practical outcomes overall, but there were insufficient patients enrolled who were undernourished to decide if this subgroup would possibly benefit [217]. Also, patients regularly find the nasogastric tube uncomfortable, and feeding is often interrupted by the affected person repeatedly eradicating the tube. About onefifth will develop aspiration pneumonia shortly after insertion, about 10% will develop a wound infection, and potentially lifethreatening issues such as peritonitis and main bleeding occur in about 1% [223�228].
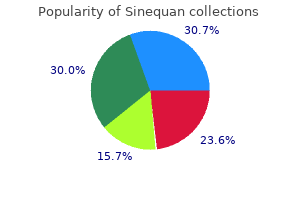
Generic sinequan 25 mg fast delivery
Anticoagulation or inferior vena cava filter placement for patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage developing venous thromboembolism Characteristics and sequelae of intracranial hypertension after intracerebral hemorrhage anxiety 36 weeks pregnant 75 mg sinequan order with mastercard. Occurrence and impression of intracranial stress elevation during treatment of extreme intraventricular hemorrhage anxiety chat rooms purchase 10 mg sinequan otc. Mannitol and end result in intracerebral hemorrhage: propensity rating and multivariable Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage Trial 2 outcomes. Corticosteroids for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and primary intracerebral haemorrhage. Treatment of intracerebral haemorrhage with tranexamic acid � A evaluate of current proof and ongoing trials. Prior antiplatelet therapy and outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic evaluation. Does prior antiplatelet remedy affect hematoma quantity and hematoma growth following intracerebral hemorrhage Guideline for reversal of antithrombotics in intracranial hemorrhage: an announcement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and Society of Critical Care Medicine. The threat of intracerebral hemorrhage throughout oral anticoagulant remedy: a population examine. Anticoagulant reversal, blood strain ranges, and anticoagulant resumption in patients with anticoagulationrelated intracerebral hemorrhage. Outcomes of urgent warfarin reversal with frozen plasma versus prothrombin complicated focus in the emergency department. Characteristics of intracerebral hemorrhage throughout rivaroxaban therapy: comparison with these throughout warfarin. Volume and practical outcome of intracerebral hemorrhage in accordance with oral anticoagulant sort. Intracerebral hematoma occurring throughout warfarin versus nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant therapy. A specific antidote for reversal of anticoagulation by direct and oblique inhibitors of coagulation factor Xa. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage following intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a crucial evaluate of case definitions. Symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage in acute ischemic stroke after thrombolysis with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a review of pure historical past and remedy. Pharmacokinetics and systemic effects of tissuetype plasminogen activator in normal topics. Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E, Feldmann E, Hanley D, Kase C, Krieger D et al. Guidelines for the administration of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: a tenet from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Individual patient data subgroup metaanalysis of surgery for spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Minimally invasive surgery for spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage: a meta evaluation of randomized managed trials. Treatment of cerebral cavernous malformations: a scientific evaluation and meta regression analysis. Clinical course of untreated cerebral cavernous malformations: a metaanalysis of individual affected person data. Stereotactic radiosurgery for symptomatic solitary cerebral cavernous malformations thought-about high threat for resection. Longterm pure historical past of incidentally found cavernous malformations in a singlecenter cohort. Radiological investigation of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: systematic evaluate and trinational survey. Outcome after spontaneous and arteriovenous malformationrelated intracerebral haemorrhage: populationbased research. Outcome after conservative administration or intervention for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. The validity of classification for the medical presentation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Risk components for hemorrhagic presentation in patients with dural arteriovenous fistulae. Prognosis and therapy of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: a scientific evaluation and metaanalysis. Surgical remedy of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: position of venous drainage. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 classification, imaging findings, and treatment. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: medical presentation and management methods. Guidelines for analysis and therapy of moyamoya illness (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis). Effect of direct arterial bypass on the prevention of future stroke in patients with the hemorrhagic variety of moyamoya disease. Effects of extracranial intracranial bypass for sufferers with hemorrhagic moyamoya disease: outcomes of the Japan Adult Moyamoya Trial. Blood pressure reducing for prevention of heart problems and demise: a scientific evaluation and metaanalysis. Randomised trial of a perindoprilbased blood pressure reducing routine among 6,one hundred and five individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic assault. Blood pressure control in hypertension: pros and cons of obtainable remedy methods. No relationship of lipid decreasing agents to hematoma progress: pooled analysis of the intensive blood pressure discount in acute cerebral hemorrhage trials research. Of the 50% who survive the preliminary weeks after the hemorrhage, around half are left with everlasting deficits, often in highlevel (neuropsychological) functioning, leading to impairment of their social function [3]. Patients must be transferred as rapidly as possible to a middle where a multidisciplinary staff is available 24 hours a day, seven days every week, and where sufficient sufferers are managed to give groups sufficient experience to keep and enhance requirements of care [9]. Patients with apnea or cardiac arrest will require intubation and appropriate cardiovascular resuscitation. A full panel of blood work together with arterial blood gas, electrolytes, blood rely, and coagulation parameters must be performed, and any coagualopathy or thrombocytopenia should be corrected. A routine toxicology display screen must be obtained to look at for drugs corresponding to cocaine. Higher scores on each scale correlate with worse outcomes, with grades of four or 5 generally signifying a considerably higher risk of demise or poor end result [16, 17].
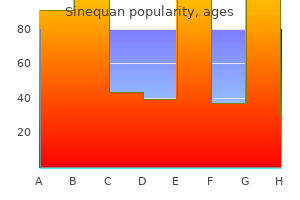
Sinequan 75 mg low cost
The penalties of a stroke should be considered at 5 levels: pathology anxiety 5 senses 25 mg sinequan cheap with visa, impairment anxiety 911 sinequan 75 mg discount line, disability, handicap, and high quality of life. Physical therapies, corresponding to physiotherapy, are directed at this stage (Section 11. Physical therapies are additionally used to attempt to scale back the incapacity related to impairments the disadvantage for a given individual, resulting from an impairment or disability, that limits or prevents the fulfillment of a job (depending on age, sex, social and cultural factors) for that individual. Many elements of remedy including those talked about above will finally impression on handicap, but occupational remedy and social work are these most clearly aimed at influencing this degree Impairment Disability (activity) Handicap (participation) the obvious effects of a stroke are bodily, however in plenty of conditions these may not be as important as the cognitive, psychological, social, and even financial penalties. Thus, treatment that aims to minimize the impact of a stroke on patients and their carers should be directed in any respect of those varied problems. Therefore it follows that remedy should be preceded by a comprehensive evaluation and then tailored to that individual patient. Conventionally, the dialogue of the remedy of stroke is break up into sections on: basic treatment in the acute section; acute medical and surgical remedies; secondary prevention; rehabilitation; and continuing care. Finally, even within every part the delivery of care is a steady course of and not the result of a onceonly choice. Having referred the patient to one or more therapists, a physician then mistakenly believes that "rehabilitation" has been organized. Achieving the absolute best consequence for the affected person requires a broad strategy rather than one which simply focuses on the first lesion, or just on the resulting impairments. Assessment Swallowing Short-loop Intervention Restrict oral consumption Give intravenous uids Risk of aspiration Long-loop Intervention Teach compensatory techniques Identify downside Unable to swallow safely When the issue is considered on this way, it turns into synthetic � and possibly even harmful � to separate stroke management into acute care, secondary prevention, rehabilitation, and continuing care. To compound the problem, these separate parts of care may even be offered by totally different employees in several establishments, which may lead to a breakdown in communication and lack of continuity of care. We ought to abandon the arbitrary division of treatment into acute and rehabilitation phases and undertake an built-in, drawback and goalorientated method. Quite usually an issue corresponding to dysphagia will demand both an immediate intervention. Thus, in follow stroke management includes many such cycles layered on top of one another and cycling at different rates, with every having some affect on the others. This model of administration applies equally nicely to acute basic care, rehabilitation, and persevering with care. A problemorientated approach to the overall administration of stroke: Chapter eleven offers with the issues that will happen after stroke, their assessment, and interventions that will help to stop or clear up these problems. Specific medical and surgical treatments within the acute phase: Chapters 13�15 cope with the pathophysiology of acute stroke and the drug, interventional, and surgical remedies that goal to cut back the severity of mind injury. Preventing recurrent stroke and different serious vascular events: Chapter 16 offers with specific interventions to forestall intracranial hemorrhage while Chapter 17 completes the description of the prognosis of stroke by focusing on the early and later risks of additional stroke and different severe vascular events, earlier than shifting on to describe numerous strategies to scale back these dangers. Organizing stroke services: Finally, Chapter 19 focuses on the organizational points that are important when attempting to deliver all these numerous aspects of remedy to massive numbers of stroke patients as effectively and equitably as possible. Here, the prognosis with respect to survival and total useful outcome is described, since this is related to all elements of therapy. The prognosis for particular individual impairments, disabilities, and handicaps is dealt with in the acceptable sections of Chapter 11, whereas that referring to the risk of late death, recurrent stroke and other vascular occasions is dealt with in Chapter 17. Thus, if a particular affected person could be very unlikely to make an excellent recovery, one might divert resources from that patient to one other with a greater prognosis who could gain more from the interventions out there. It can be wasteful to use resources on patients who will make a great recovery with none intervention at all. Natural history refers to the untreated course of an illness from its onset, whereas prognosis refers to the chance of a selected end result occurring both in an individual or a bunch of sufferers over an outlined period of time after the disease is first identified. Usually the prognosis with therapy is better than the natural historical past, however this will likely not always be the case. No information on the pure history (strictly defined) are available, because in most components of the world, sufferers with stroke are usually given some therapy, and in those places the place minimal or no treatment is given, no research of pure historical past have been reported. Even admission to a hospital, even with none medical or bodily remedy, is an intervention and might be thought to be "treatment" that may affect outcome. Other methodologically sound studies come to broadly comparable conclusions, although to examine them immediately is difficult because of their different strategies, their varying styles of reporting, and because a lot of the variation in prognosis may be accounted for by variations in case mix and by the play of chance because of comparatively small sample sizes. The preferred design of a prognostic study is a potential longitudinal cohort examine. Retrospective research have the disadvantage that particular predictors or outcomes might have been assessed much less properly or not at all. Data from randomized trials may be used for prognostic research if any intervention impact is accounted for and if the recruited patients are typical of the stroke population What was the research setting and where, when, and the way were the patients selected Results from research performed in specific settings could not generalize to different settings because of variations in age, stroke severity, or explanation for stroke. The generalizability of prognostic fashions based on information from randomized trials could also be restricted because of trialspecific inclusion and exclusion standards. With the development of latest and better therapy methods, the generalizability and accuracy of most prognostic research will diminish over time Was consent bias avoided This group will include those who refused consent, those who had been unable to give consent and people in whom there have been inadequate analysis sources to request consent. Predictors should have been measured at the cut-off date after stroke at which you propose to estimate the prognosis of your patients Was complete followup achieved Were all patients who have been entered into the research accounted for, and was their medical status recognized at the last followup Therefore, the effect of incomplete followup on prognosis is troublesome to predict Were goal end result criteria developed and used, and were the criteria reproducible and accurate It is also necessary that the criteria had been utilized persistently What is the medical usefulness of the result measured In most prognostic research in sufferers with acute stroke, the anticipated measure is either dying or poor useful outcome, or both mixed in a single endpoint. When that is outlined as "dependency" or a score on the modified Rankin Scale greater than 2 or 3, this clearly includes outcomes that could be thought-about by some to allow a fair or good quality of life What is the accuracy of the prognostic factor or model To be of use in clinical practice, a prognostic factor or mannequin should have robust discriminative energy. Especially when selections in regards to the continuation of treatment are made, the falsepositive fee of a predicted poor end result should ideally be zero, with a slender 95% confidence interval [12] Was outcome evaluation blind In prognostic studies, the outcome is preferably assessed blinded to information about the predictors. If the observer has a preconceived view that a specific baseline factor is likely to be associated to a specific consequence, data of the presence or absence of that issue on the time of followup might bias that observer. The commonest example of this is age, which partly explains the noticed relationships between different elements. Because of things together with restricted sample size, multiple testing, and publication bias, the predictive efficiency of a new prognostic mannequin is often too optimistic [13].
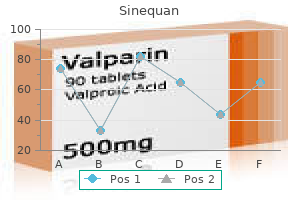
Order 75 mg sinequan
Furthermore anxiety support groups sinequan 75 mg order with amex, this research was printed previous to anxiety symptoms medication sinequan 75 mg cheap overnight delivery our current understanding of pelvic parameters. The affect of pelvic tilt on the deformities in addition to reaching a balanced relationship between the pelvic incidence and the lumbar lordosis postoperatively, that are recognized key determinants of medical end result,2 had been due to this fact not addressed on this collection. Sagittal steadiness refers to whether or not the middle of mass is centered over the pelvis and feet. Chapter 46 � Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy 235 the selection of osteotomy must be primarily based on the morphology and rigidity of the deformity. This contributed to a really low pseudarthrosis rate at the stage of the osteotomy of three. Current research describe methods that involve larger posterior bone resection and leave gaps within the posterior column following osteotomy closure. Two-rod constructs and adjoining interbody fusion could lessen the speed of early rod fracture. Reducing these constructions to each other with osteotomy closure achieves direct bone apposition, restoring the integrity of the posterior column. This examine had a major influence in demonstrating the outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies in addressing extreme sagittal malalignment. With higher understanding of sagittal parameters and the restrictions and strengths of assorted osteotomies, refining of the indications and surgical methods will further outline the function of pedicle subtraction osteotomies within the treatment of fixed spinal deformities. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the remedy of mounted sagittal imbalance: Surgical approach. Classification of sagittal imbalance primarily based on spinal alignment and compensatory mechanisms. An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in one hundred asymptomatic center and older aged volunteers. Successful correction of sagittal imbalance may be calculated on the basis of pelvic incidence and age. Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of fastened sagittal imbalance. Comparison of pedicle subtraction and Smith-Petersen osteotomies in correcting thoracic kyphosis when closed with a central hook-rod assemble. Assessment of symptomatic rod fracture after posterior instrumented fusion for grownup spinal deformity. Reducing rod breakage and pseudarthrosis in pedicle subtraction osteotomy: the significance of rod number and configuration in 264 patients with 2-year follow-up. Construct rigidity after fatigue loading in pedicle subtraction osteotomy with or with out adjacent interbody structural cages. Neurosurgery 48(3):569�574, 2001 Reviewed by James Stenson and Kris Radcliff Research Question/Objective forty seven Circumferential fusion improves charges of fusion and medical outcomes when utilized to deal with lumbosacral spine pathologies. Historically, surgeons had the selection of both a sequential two-step anterior and posterior fusion or posterior lumbar interbody fusion with simultaneous posterolateral fusion to obtain circumferential fusion. However, these approaches are fraught with their respective individual problems. The authors attempted to look at and report their findings of ache relief after surgery, intraoperative problems, an infection rate, and postoperative issues. Five patients previously underwent lumbosacral backbone surgical procedure, considered one of which was an tried lumbar fusion. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Technique, complications, and early outcomes. Intervention Results Low back ache dissipated fully in sixteen sufferers following surgical procedure. Five sufferers had reasonably persistent low again ache requiring oral narcotics for pain administration. Fortunately, the index process resolved radicular signs in all 19 patients who offered with radiculopathy on the time of surgery. Additional postoperative problems included transient postoperative brachial neuralgia secondary to intraoperative positioning, distal neuropathy in the arm because of prolonged blood strain cuff inflation, and L5 motor weakness. The affected person with distal arm neuropathy handed away 3 months following surgical procedure from cardiomyopathy. The acknowledged affected person was still affected by distal neuropathy at the time of demise. The L5 motor weak spot was discovered only when the affected person tried to resume jogging. Second, the already restricted pattern size is additional hindered by a relatively quick follow-up interval. Longer-term follow-up can be perfect because it takes as much as 12 months for fusion charges to be determined. Although not supposed to be an end result study, the article would benefit from goal and validated pain and performance scales such because the preoperative and postoperative Visual Analog Scale and the Oswestry Disability Index. Furthermore, patient selection was not discussed in the textual content, which created an inherent bias for the study pool. The traditional open approach requires a large soft tissue dissection to expose anatomic landmarks for pedicle screw fixation, leading to elevated postoperative ache, longer recovery, and impaired spinal perform. Radiographic restoration of lumbar alignment after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: A retrospective examine of long-term pain reduction and fusion outcomes. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Surgical method and leads to 24 patients. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Clinical and radiographic outcomes and problems in 100 consecutive patients. The difference of surgical website infection according to the strategies of lumbar fusion surgery. Comparison of medical and radiological outcomes of posterolateral fusion, posterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion techniques within the therapy of degenerative lumbar spine. Analytical comparison examine of the medical and radiological end result of spine fixation using posterolateral, posterior lumber interbody and transforaminal lumber interbody spinal fixation methods to deal with lumber spine degenerative disc disease. The cost-effectiveness of interbody fusions versus posterolateral fusions in 137 patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. A randomized controlled trial comparing transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and uninstrumented posterolateral fusion within the degenerative lumbar spine. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative disk disease and spondylolisthesis Grade I: Minimally invasive versus open surgical procedure. Transforaminal lumbar interbody graft placement using an articulating delivery arm facilitates elevated segmental lordosis with superior anterior and midline graft placement.
Diseases
- Hiccups
- Trigonocephaly ptosis coloboma
- Adducted thumb club foot syndrome
- Familial amyloid polyneuropathy
- Juvenile dermatomyositis
- Phytophotodermatitis
- Hyperekplexia
- Shellfish poisoning, neurotoxic (NSP)
- Kniest-like dysplasia lethal
Purchase sinequan 10 mg mastercard
For instance anxietyzone symptoms poll order 25 mg sinequan visa, a larger proportion of strokes are attributed to hemorrhage in Asia than in Europe [33] (Section 14 anxiety research generic 75 mg sinequan with amex. Referral bias: In any hospital, the prognosis of sufferers will be affected by referral bias (see Table 10. In general, stroke patients admitted to hospital can be expected to have a worse prognosis. Differences in consequence between hospitals usually have a tendency to replicate the variations in the proportions of patients with extreme stroke than any variations in treatment given (Section 19. Selection bias: Hospital admission rates range significantly from place to place, from nation to nation, and from time to time. Admission rates reported in research need to be interpreted within the information that definitions of hospital admission differ. And how were patients who had their stroke while in hospital, or who were admitted late after the stroke, handled in the evaluation Followup method: Unless patients are adopted up using related definitions of end result and for a similar time interval as those within the published research, their prognosis might be completely different (see Table 10. Also, the explanation why patients are lost to followup may be associated to their consequence. Random errors and small samples: If the estimate of the result is based on the followup of too few patients, it might differ from that in printed research just by chance alone. Differences in administration: Patients may be managed more or less effectively than these in revealed studies, and thus the outcomes may be higher or worse. However, the likely influence of differences in therapy between centers is likely to be swamped by different factors that have a a lot higher affect on end result. The variations in outcome between your service and those of your colleagues in other hospitals are extra likely to replicate differences in the patients you deal with than any variations within the quality of care you provide. It is also tough to determine on the acceptable accuracy of any predictive tool, as a result of this is decided by the consequences, or value, of getting it incorrect. Taking an excessive example: If the clinician was sure that a patient with an apparently severe stroke who was being supported on a ventilator was not going to have a suitable longterm quality of life, then they 464 10 A practical strategy to the management of sufferers Table 10. Predicting early dying Failure to describe adequately the group of patients in whom the work was accomplished Use of unrepresentative cohorts of sufferers. These medical options in combination with radiological features such as huge intracerebral hemorrhage with mass impact may help information management decisions [12, 38]. Predicting long run outcomes might withdraw ventilatory support, notably if the patient had an applicable superior directive. However, on this state of affairs the clinician would have to be very confident of their prediction [12]. Unfortunately, methodological issues have so far restricted the usefulness of these studies [12, 35�37] (Table 10. Many of the components that predict a excessive early threat of dying additionally predict a high threat of longterm dependency if the affected person survives. Methods of prediction A variety of different approaches have been taken in predicting consequence after stroke. The singlefactor strategy the simplest method is to establish a single issue, the presence or absence of which early after the stroke signifies the likelihood that the affected person could have an excellent or unhealthy consequence. The most widely used examples are age, severity of the neurological deficit, decreased level of consciousness, or lesion measurement, which have each been associated to poor survival and useful consequence [12, 38]. Although such models are simple to use, and can guide clinical management, the consumer should pay consideration to their inaccuracy. Higher age, a extreme neurological deficit, a lowered degree of consciousness, and a large lesion dimension within the first few days after stroke are every related, in general, with a poor end result. Nonetheless, such fashions have been used to stratify groups of sufferers by predicted prognosis in large randomized trials [42]. Indeed, massive randomized trials provide a wonderful alternative to check such predictive fashions prospectively [43, 44]. Stroke scales the extent of brain harm In general, the greater the volume of mind broken the extra severe the clinical outcome, aside from critically sited strokes, significantly in the brainstem, where even quite small lesions could be fatal. Many of the medical indicators of poor prognosis relate quite carefully to the scale of the mind lesion. For ischemic stroke, imaging typically provides little to the accuracy of clinical predictors [36]. In general, the larger the stroke lesion, the worse the doubtless outcome, apart from small, critically sited lesions, which may be related to a poor consequence. These provide scores which, depending on the presence, absence, or severity of various neurological impairments, are frequently used to describe the severity of stroke in the acute phase and have additionally been used to predict outcome. Predictions based on measures of operate early after a stroke Scales such because the Barthel Index have been used to predict eventual useful end result and may be notably helpful for these working in rehabilitation services [45, 46]. Predictions for individuals would then rely upon the pattern of recovery noticed in giant cohorts of sufferers. Informal judgment Multifactor fashions these are most frequently primarily based on regression analyses and have been developed by a quantity of groups to predict each survival and functional end result [35�37, 40, 41]. Although these are generally extra accurate than models based mostly on a single variable, these are usually not sufficiently correct to information medical choice making on the level of the individual affected person, and plenty of are restricted by intrinsic methodological shortcomings and by an absence of external validation [12]. If such models are to be utilized in routine medical follow, they should be additional refined, and then examined in giant independ- the most common technique of prediction is the informal judgments we make about patients throughout our daily work. The accuracy appears to be similar to these of mathematical models, at least in predicting a simple dichotomous consequence (dependent or independent), however that is bound to rely upon the experience of the clinician [49]. In patients with acute stroke admitted in tertiary care facilities, early prediction of a poor practical outcome or death by the treating doctor was appropriate in about 90% of the instances [50, 51]. However, the flexibility to predict future high quality of life was substantially less good [51]. In addition, a consequence of the rising trend that clinicians concentrate on sure phases of illness administration. This is more likely to limit their capacity to predict practical consequence and high quality of life appropriately. However, they could be helpful as tools to: guide much less experienced clinicians in what to say to patients and carers; choose who to randomize in trials of acute therapy; help resolve which patient is more probably to require an prolonged period of rehabilitation; assess the standard of care. For example by adjusting consequence data from completely different teams of patients for differences in case combine at baseline, the standard of care given by completely different hospitals or models can start to be compared (Section 19. These deficits are layered on a fancy mixture of preexisting illness, character, and social and environmental elements. We have already seen the range of attainable pathological types (see Chapter 3) and causes (see Chapters 6�9), however every affected person requires a management plan tailor-made to his or her own particular person needs. For a patient whose symptoms resolve fully within a couple of days, the emphasis must be on analysis and secondary prevention.
Purchase sinequan 10 mg with mastercard
Chapter Radiotherapy and Radiosurgery for Metastatic Spine Disease: What Are the Options anxiety symptoms but not anxious sinequan 75 mg generic overnight delivery, Indications anxiety home remedies sinequan 10 mg cheap fast delivery, and Outcomes Articles in the Englishlanguage literature were reviewed, and references from every publication had been searched for extra articles. Radiotherapy and radiosurgery for metastatic spine illness: What are the options, indications, and outcomes Data printed earlier than 1980, in addition to publications describing lower than 10 patients, have been excluded. Articles elaborating primarily surgical remedy and/ r o without radiation remedy knowledge were excluded. Surgical data describing cohorts who had radiotherapy with out surgery had been included if sufficient data relating to radiation and outcomes was supplied. As no standardized treatment exists, there was a large heterogeneity of radiation regimen acquired by the sufferers. Ability for nonambulant sufferers to stroll after radiation showed broad variation (20%�60%), and research with higher level of proof confirmed much less optimistic results (19%�33%). However, no validated instruments were used, and length of follow-up various considerably. Retrospective knowledge recommend that an extended course (>1 week) presents higher motor function score in comparability with a shorter course (<1 week). However, a shorter course should be indicated for patients with a limited life expectancy. Progression occurring at adjoining ranges is uncommon, but progression on the epidural area has been described. Study Limitations the metastatic backbone population is a difficult group to study given its heterogeneity. Patient survival can be restricted in this inhabitants, and length of follow-up within the reported literature varies widely. Different outcome measures had been used and none is particular to the metastatic spine inhabitants. However, most of their results are constant and in accordance with the higher degree of evidence articles. There was no important distinction between radiation schedules (single dose, brief course, and split course). An prevalence between 11% and 39% has been reported and danger components recognized: lytic lesion, malalignment, 20 Gy or higher per fraction. Health-related quality of life evaluation in metastatic disease of the backbone: A systematic evaluate. Introducing a brand new health-related high quality of life outcome device for metastatic illness of the backbone: Content validation utilizing the international classification of functioning, incapacity, and health; on behalf of the Spine Oncology Study Group. Interventions for the treatment of metastatic extradural spinal cord compression in adults (Review). Surgical resection of epidural illness improves local control following postoperative backbone stereotactic body radiotherapy. Local disease control for spinal metastases following "separation surgical procedure" and adjuvant hypofractionated or high-dose single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery: Outcome evaluation in 186 patients. Stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal metastases with or with out separation surgery. Vertebral compression fracture after stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastases. Vertebral compression fractures after stereotactic body radiation remedy: A massive, multi-institutional, multinational analysis. Vertebral compression fracture after spine stereotactic body radiotherapy: A multi-institutional evaluation with a concentrate on radiation dose and the spinal instability neoplastic rating. Rhines Research Question/Objective eight the appliance of surgical oncologic principles to the resection of primary malignant tumors of the backbone requires consideration of en bloc resection-where a tumor is removed in a single, intact piece, fully encased by a continuous layer of regular tissue-to provide one of the best likelihood of disease-free survival. However, since surgical procedures performed with this technique are technically challenging, useful resource intensive, and related to early morbidity, their adoption was met with reluctance within the backbone neighborhood. Procedures performed in nonspecialty centers typically resulted in contaminated margins, which have been felt to cause greater charges of recurrence as nicely as complicate and scale back the effectiveness of more definitive resection. The purposes of this study were to decide the impact of incisional biopsy prior to resection, and to current the cumulative results of research reporting en bloc resection to find a way to weigh the influence of reaching appropriate surgical margins against the perceived high morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization of these procedures. Second, presenting the evidence using standardized oncologic terminology utilized to major spine tumors was done with the objective of accelerating consciousness of the nuances associated with the surgical administration of these rare tumors and to encourage broader use of acceptable terminology in order that future studies would be primarily based on a common language. Study Design A systematic evaluate of the literature was carried out with impartial reviewers and standardized examine selection criteria. Feasibility and security of en bloc resection for major backbone tumors: A systematic evaluation by the Spine Oncology Study Group. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria Studies have been identified on the criteria that each reported more than 10 low-grade malignant tumors of the cellular backbone and described oncologic staging standards, biopsy approach, tissue margins, complications, and disease-free survival. In addition, some sufferers within the reported research acquired radiation therapy either alone or together with either intralesional or en bloc resection. Results Evidence from the reviewed research demonstrates that en bloc resection is associated with considerably improved continuous diseasefree survival in patients the place adequate margins had been achieved at surgery. Achievement of long term (>5 year) disease-free survival is finest achieved with en bloc resection. Both open biopsy and beforehand tried intralesional resection are associated with decreased chance of achieving acceptable margins and decreased disease-free survival, and are due to this fact strongly discouraged. The threat of those problems was seen to be significantly larger in revision surgeries. The situations studied are rare illnesses, so even in combining these research, low numbers of sufferers are reported. While the rules guiding these surgical strategies are standardized, the exact procedures performed are highly individualized and could make these data tough to extrapolate. Relevant Studies Advances in surgical approaches, anesthesia, and reconstructive methods have made en bloc resection of spine tumors potential. Compared to intralesional resection, these methods have improved disease-free survival and offer sufferers their greatest chance for cure. Performing these complicated procedures leads to improved oncologic consequence at the price of elevated however acceptable morbidity, particularly when carried out in specialised centers. Several collaborative case series reporting large numbers of chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the sacrum and cellular backbone handled at main worldwide centers help the conclusions of this study: that these methods, when feasible, provide the most effective oncologic consequence in phrases of freedom from native development. Interestingly, not all such4�10 sequence report enhancements in general survival, which is somewhat paradoxical provided that local recurrence typically impacts survival. Last, the optimal integration of centered radiation strategies with surgical resection of these lesions remains to be elucidated. A small case collection with limited follow-up indicating that significant charges of disease-free survival could be achieved by combining much less invasive surgical procedure with targeted radiation was just lately reported.
Buy sinequan 75 mg amex
Patient satisfaction Many healthcare systems are being influenced by market forces and the concept that patients are consumers anxiety online test sinequan 25 mg cheap overnight delivery. Many well being service managers regard affected person satisfaction as being an important end result anxiety unspecified buy discount sinequan 75 mg online, although some think about satisfaction to be a measure of process; measures of affected person and carer satisfaction with hospital and residential care have been developed [102]. Improvements in satisfaction have been observed in trials of occupa tional therapy [169] and early supported discharge ser vices [76]. As one would expect, these with poorer physical outcomes and despair are prone to report much less satisfaction with care [170]. However, sufferers � notably ladies and aged patients � appear to have low expectations and are sometimes satisfied with what professionals would regard as poor therapy [71, 170]. Nevertheless, in studies including massive numbers, such dichotomized outcomes could additionally be sufficient [172]. Thus, you will want to measure outcomes in a big, consultant sample of patients or carers. This has implications for the sort of measure of outcome used, because it have to be easy and sensible to administer to giant numbers, exactly as in massive randomized trials. It may take several years for a hospital to accumulate sufficient information to present precise estimates of end result, for example, of its case fatality. Although massive observational studies [173] have shown a relationship between group of care and survival, the boldness interval around the esti mates of case fatality are surprisingly broad, especially after adjustment for confounding elements. We suggest that energy calculations must be carried out (as for randomized trials) earlier than instigating any audit to dem onstrate changes within the outcomes following modifica tion of a service. When planning an audit, estimate the doubtless number of circumstances that might need to be included so as to determine a difference reliably. Outcomes some months after the stroke are most likely most relevant to sufferers, but are more difficult and expensive to measure than at an earlier stage. However, as a end result of patients normally improve for a quantity of months after a stroke, the longer they keep in hospital the higher their consequence at discharge. It is way more rele vant to measure the result at a exhausting and fast interval after the stroke, however after discharge it will inevitably be more timeconsuming and expensive. However, some of the simpler measures could be completed by phone or postal questionnaire [158, 161, 168]. EuroQol), which appear ideally suited for use as postal ques tionnaires, embrace visible analog scales, but these appear to be notably unreliable in stroke sufferers [171]. Because many patients die after stroke, consequence meas urements can solely be utilized to the survivors. If these measures are averaged, and teams of sufferers compared, then there could also be a significant issue of interpretation if there are extra survivors in a single group than in the different. Some try and get round this by giving the worst rating to the useless sufferers after which including them in the Although the evidence that establishments with larger throughput have higher outcomes is inconclusive. If outcomes are measured in a relatively small number of patients or carers, dangerous outcomes may replicate bad luck rather than bad care, whereas conversely, good outcomes could replicate good luck somewhat than good care. That is why massive randomized trials are required to reveal modest treatment effects. Good case combine descriptors embrace those factors which might be extremely predictive of consequence. Also, we will solely correct for these prognos tic components that we are in a position to determine and measure reliably. In the report comparing outcomes after stroke in Scottish hospitals, the one prognostic elements that have been routinely collected, and could due to this fact be adjusted for, have been age, sex, and social deprivation [144]. If more highly effective predictive factors are taken under consideration, most of the variation between hospitals with respect to case fatality disappears and could be accounted for by probability alone [144]. In accounting for ran dom variation, one should additionally acknowledge the imprecision of any statistical model used, which is able to depend on the dimensions of the cohort from which the mannequin was derived. The problems of adjusting for case mix are even larger if one considers other related outcomes corresponding to quality of life, the place we all know virtually nothing about the components that predict this. A change of 10 points at one end of the dimensions is therefore not equivalent to a 10point change at the different. Also, if one relies on only a small variety of performance indi cators, it could have a number of opposed effects on well being companies. Effort and assets may be directed at improv ing one service or one side of a service, to the detri ment of different areas (socalled "measure fixation"). Clinicians and managers whose revenue or reputations rely upon the symptoms may alter their apply. One of one of the best examples of such gaming was following the publication of institu tionspecific and surgeonspecific death charges for car diac surgical procedure in New York [175]. The reported proportion of sufferers with comorbidities, similar to renal failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which were used to modify outcomes for case mix, increased several fold over 2 years. We suggest the next method to assessing the standard of stroke providers, although that is prone to change as our understanding improves: 1) Perform a structural audit to make positive that providers embody access to the services shown in Table 19. Also, by setting challenging targets one could use this strategy to drive ahead enhancements in services. Any interpretation would require extra complicated knowledge in regards to the sufferers treated by the service. The case combine and consequence knowledge collectively might type the premise for a minimal knowledge set; our suggestions are outlined in Table 19. These items embrace some demographic information, that are usu ally collected routinely. Prestroke func tion, which will also replicate comorbidity, relates carefully to useful outcome, and, to a lesser extent, increases the risk of dying. Other possible indicators of stroke severity are level of consciousness, urinary incontinence, severity of motor weak spot, or the pro portion of patients with whole anterior circulation syn dromes (Chapter 11). Although that is unlikely to provide any quantitative details about the standard of care, the info may be used to determine issues. For instance, a excessive or rising proportion of sufferers with pressure sores could indicate inadequate numbers of nurses, poorquality nursing care, or delays in discharging dependent patients. Unfortunately, there are considerable problems in defining problems and in providing reliable diag nostic standards to allow monitoring [22, 176, 177]. A sys tem of critical incident recording might concentrate on these and other issues and supply a simple indicator that the service could also be performing poorly. This reflects identified factors that affect the finish result after stroke and also information that might be routinely available to well being service workers. Case mix data Age Sex Marital status, or dwelling alone before the stroke Prestroke function, i. It is important that politicians and well being service managers perceive the difficulties in decoding measures of process and end result, and their limitations. They should not make important selections in regards to the distribution of resources on the idea of simplistic analyses of crude data.
Discount sinequan 25 mg on-line
Interestingly anxiety and alcohol sinequan 75 mg cheap on line, the transradial strategy could also be related to increased risk of cerebral ischemia anxiety in college students generic sinequan 10 mg. Coronary bypass Coronary artery bypass grafting is a commonly carried out surgical process. Valve restore: open versus endovascular Openchamber cardiac surgeries were beforehand thought to carry greater risk of cerebral ischemic problems because of increased risk of thrombi, air, and other particles created inside the intraoperative interval [337]; however, latest studies have shown related rates of stroke complicating open and transcatheter approach aortic valve alternative (5. Twenty percent of issues occur within the first two weeks postop, 80% within the late postoperative part. In the perioperative interval, hemodynamic instability, cardiac arrest, extracorporeal circulation over 2 hours, prior historical past of stroke, and carotid stenosis larger than 50% have been reported to be danger elements for the occurrence of cerebrovascular problems [341]. Risk elements embrace prior stroke history, vascular illness, and cardiopulmonary disease [342]. Many stroke mechanisms are attainable depending on the kind of surgery, underlying disease, and drugs used intra and perioperatively such as anesthetics and antithrombotics (Table 7. Intra or postoperative hypotension causing lowflow infarction, significantly if there are stenotic or occluded arteries supplying the mind (Chapter 6) Hemostatic defect resulting from antithrombotic medication, or disseminated intravascular coagulation, inflicting intracranial hemorrhage Occlusion or dissection of neck arteries caused by faulty dealing with and positioning throughout common anesthesia (Section 7. Thromboembolism from crossclamp and arterial dissection is usually cited as supply of stroke. Stroke threat appears to be highest in sufferers with lung, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers [352]. Delineating the cause of cerebral ischemic damage might alter treatment and affect stroke recurrence. Patients typically have low grade activation of the coagulation system which might be expected to enhance the danger of arterial and venous thrombosis [354, 355]. Consumptive coagulation disorders could additionally be related to the tumor itself or with chemotherapy. After evaluating for various etiologies, strokes attributed to malignancy associated hypercoagulable state can often be handled with anticoagulation, low molecular weight heparin is a most popular agent for stopping recurrent venous thromboembolic events [356], but the perfect routine for stroke prevention has not been confirmed. Intracerebral hemorrhage can also occur in the setting of thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, and disseminated intravascular coagulation, which are often related Current guidelines for the temporary withdrawal of antithrombotics for nonvascular and noncardiac surgical procedure in patients with recognized cerebrovascular disease are incomplete, significantly for antiplatelet agents and for novel anticoagulants [343]. What must be balanced is the danger of hemorrhage through the process with the underlying risk of thromboembolism that provoked the initiation of treatment. Coil occlusion of a cerebral aneurysm is associated with a 5�9% fee of neurologic deficits, up to 28% with thromboembolic vessel occlusion [334]. Procedures carried out for stroke prevention related to atherosclerotic carotid stenosis carry a danger of periprocedural stroke. Transesophageal echocardiogram exhibits a 2 cm wellcircumscribed mass attached by a broad base to the interatrial septum. Lepto/dural sinus invasion Skull and dural metastasis can infiltrate or compress dural sinuses causing stasis and thrombosis. Metastatic venous occlusion is usually treated with radiation, and the benefit of anticoagulation on this setting is unknown. Benign tumors include atrial myxoma and fibroelastoma, and malignant tumors embrace left atrial rhabdosarcoma and aortic sarcoma. Sarcomas are exceptionally rare invasive tumors and may trigger widespread embolic vascular metastases. An acute rise in peripheral blast cells could cause smallvessel occlusion, endothelial damage, hyperviscosity, and direct vessel rupture [354]. Immunemediated injury to heart valves results in sterile vegetations of plateletfibrin, which then embolize into the arterial system [362]. The following drugs are reported to be associated with a rise in stroke: 1) lasparaginase is an enzyme inhibitor of protein synthesis commonly used in induction of acute leukemia. The effects of aromatase inhibitors on lipid levels are variable and correlation with vascular events is unknown [372, 373]. There appears to be a dosedependent stroke threat with elevated stroke risk in older studies where estrogen doses were greater than at current [380]. Several mechanisms (including hypercoagulability, vasculopathy, or facilitation of other stroke causes) are proposed but the exact mechanism is unknown. Progesteroneonly pills appear to be related to no to very low threat of stroke. Individuals might consider the health and social penalties of an unplanned pregnancy (given a maternal mortality rate of around 1 in 1000) to be more important. However, randomized studies have proven a one third increase in the danger of ischemic stroke and no protecting effect for vascular disease [381, 382]. The hypothesized mechanism was increased plasma viscosity notably in sufferers with impaired circulation, however a current metaanalysis discovered no proof for such an affiliation [392]. Acute cocaine use can trigger stroke within hours of use; continual use also will increase stoke threat. Proposed mechanisms include sympathomimetic effect inflicting hypertension and vasoconstriction, effects on myocardial contractility and arrhythmias, prothrombotic state [393], enhanced platelet aggregation [394], or vasculitis or vasculopathy [395] inflicting largevessel atherosclerosis [396, 397], lacunar [398], cardiogenic, or cryptogenic nonlacunar strokes. A clear mechanistic link is missing and the pathophysiology might have a number of parts. Other potential factors embrace elevated platelet aggregation, cardioembolism, and hypertensive surges. This elevated risk is assumed to be associated to inhibition of the manufacturing of prostacyclin in the vascular endothelium. Conflicting outcomes have been reported in investigating increased stroke threat in secondgeneration antipsychotics [390]. Potential mechanisms embody increased metabolic risk, thrombotic effects, cardiovascular results together with orthostasis, and sedation resulting in dehydration. Observational research present a relatively low threat of recurrent dissection with pregnancy 1 12 months after preliminary dissection in ladies with out underlying connective tissue disease [412]. Likely mechanisms of vasculopathy include hypertension and hormoneinduced vasoconstriction, endothelial adjustments, and impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation [414]. Pituitary apoplexy, amniotic fluid and air embolism are rare issues in being pregnant and the peripartum interval. Several entities might contribute to ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage risk. Hormone levels are in flux throughout these durations and combined with the acute stress response can lead to a transient hypercoagulable state. Hormones doubtless also play a role in endothelial activation triggering vascular changes. In pregnant girls, stroke danger appears to be higher in the third trimester of being pregnant through to six weeks postpartum. Several of the mechanisms leading to stroke current with headache and suspicion should be raised within the acceptable context [410]. In association is the increased threat of arterial ischemic strokes and cerebral venous thrombosis. Population research have proven an elevated risk of postpartum stroke in caesarean section deliveries.