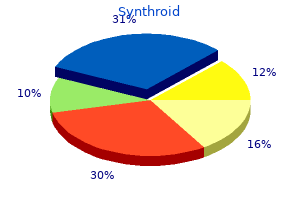
Synthroid
Synthroid dosages: 200 mcg, 125 mcg, 100 mcg, 75 mcg, 50 mcg, 25 mcg
Synthroid packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 100 pills, 200 pills, 300 pills

100 mcg synthroid generic with visa
More vital from a toxicologic viewpoint are the degenerative results of chemical substances on the adrenal cortex that result in primary adrenal cortical hypofunction treatment yeast infection synthroid 25 mcg purchase mastercard. Disturbances in adrenal�cortical operate have been greatest characterised within the canine symptoms neck pain order 75 mcg synthroid overnight delivery. Because of this, and the reality that canine hyper- and hypoadrenocorticism are similar to the corresponding medical syndromes in people, the remaining dialogue on this section will be principally confined to the canine. Exogenous glucocorticoid hormone remedy (daily at excessive doses) typically mimics naturally occurring instances of hypercortisolism. Clinical observations embrace polyuria, polydipsia, an enlarged pendulous abdomen, muscular losing, alopecia, thinning of the skin with cutaneous pigmentation and mineralization, and hepatomegaly. Significant laboratory findings embrace an increase in alkaline phosphatase (steroid-induced isoenzyme), an eosinopenia with marked lymphopenia, and leukocytosis due to the elevated formation of neutrophils. These electrocardiographic alterations seem to be as a result of the outstanding improve in serum potassium in dogs with hypoadrenocorticism and subnormal secretion of aldosterone. Plasma and urinary 17-hydroxycorticosteroids usually are at low levels within the resting state. Effects During Embryogenesis It is properly documented that artificial and naturally occurring corticosteroids are potent teratogens in laboratory animals. Adrenal aplasia has occurred in a subset of white Danish rabbits when thalidomide was given to their dams. Morphologic Alterations Macroscopic lesions of chemically affected adrenal glands are characterised by both enlargement or reduction in dimension that often is bilateral. Initially, cortical hypertrophy or swelling due to impaired steroidogenesis or hyperplasia as a end result of long-term stimulation typically is seen when the adrenal is increased in dimension. Similar gross findings may be the results of medullary hyperplasia or pheochromocytoma. In distinction, small adrenal glands typically are indicative of degenerative modifications, leading to atrophy. Midsagittal longitudinal sections of the glands will reveal a disproportionately wider cortex relative to the medulla, or vice versa, resulting in an irregular cortical:medullary ratio. Nonneoplastic Lesions Histologically, nonneoplastic lesions of the adrenal cortex induced by chemical brokers are characterized by changes starting from acute progressive degenerative to reparative in nature. These could additionally be exacerbations of normal spontaneous findings or immediately compound-induced lesions. It may additionally be elevated after feeding diets excessive in saturated fat and with Vitamin E deficiency. Early degenerative lesions characterised by enlarged-cortical cells crammed with cytoplasmic vacuoles (often lipid) may end in a diffuse hypertrophy of the cortex. This vacuolar sort of degeneration is a mirrored image of impaired steroidogenesis, leading to extra storage of unmetabolized steroid precursors. More destructive lesions may be observed in the form of hemorrhage and/or necrosis, often in association with an inflammatory response. Usually, the adrenal cortex might be shrunken or atrophic with fibrosis and areas of multinodular hyperplasia. Occasionally, the impact of a chemical is proscribed to a specific zone of the adrenal cortex and could also be species particular. In distinction, all three cortical zones are affected in the adrenal glands of canine handled with this compound. Xenobiotic chemical compounds that trigger degeneration of the adrenal cortex are summarized in Table 20. Note vacuolated mitochondria (m) and some lipid droplets undergoing lipolysis (arrow). The elevated accumulation of lipid and severe mitochondrial vacuolization correspond to gentle microscopic findings of marked cytoplasmic vacuolar and granular degeneration. More extreme ultrastructural damage might end result with some parenchymal cells of the cortex having an electron-dense cytoplasm, chromatolysis, and disruption of the plasma membranes (necrosis). Frequently, macrophages containing cholesterol clefts, quite a few lipid droplets, and membranous particles may be observed among the many necrotic cells. Proliferative Lesions Spontaneous hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex is frequent in the rat, rabbit, golden hamster, mouse, dog, cat, horse, and baboon. Cortical adenomas and, to a lesser extent, cortical carcinomas have been reported in reasonably high incidence in sure strains of rat. A excessive incidence of cortical adenomas and fewer carcinomas have additionally been reported within the laboratory hamster. Subcapsular cortical cell proliferation and adenoma are widespread in laboratory mice; nevertheless, neoplasms arising deep within the adrenal cortex are rare however could also be induced by gonadectomy. Naturally occurring adrenal cortical tumors are discovered occasionally in home animals, besides in grownup canine and castrated male goats. Less regularly reported are chemically induced proliferative lesions of the adrenal cortex. Each focus or larger nodule is an oval-to-spherical lesion of variable dimension consisting of enlarged regular or vacuolated cells. Most of the reported tumors are most likely to be benign (adenoma), though an occasional one may be malignant (carcinoma). Tumorigenic brokers of the adrenal cortex have a various chemical nature and use (Table 20. Several of the compounds have a steroid nucleus and are synthetic or natural estrogens or androgens. Linoleic acid a Carcinoma Rat Predilection websites are the zona reticularis and fasiculata. Adrenal cortical carcinomas are composed of enormous polyhedral or pleomorphic cells with an eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm. Tumor cells have outstanding nucleoli and variable numbers of mitotic figures, and type different histologic patterns, including sheets, lobules, and cords. The invasive nature of the malignant cells can additionally be apparent by penetration through the capsule, obliteration of the conventional architecture of the affected gland, and metastasis to distant sites. Toxicity in these different websites due to this fact might ultimately influence the adrenal cortex. Additionally, the adrenal cortex has each anatomic and molecular characteristics that convey vulnerability to toxic insult, and the next factors predispose the adrenal cortex to poisonous insult in vivo. Functional dependence on the hypothalamus and pituitary and peripheral hormone-carrier molecules. High vascularity and disproportionately giant blood volume acquired per unit mass of adrenal tissue guaranteeing excessive exposures to toxicants. The high content of unsaturated fatty acids in adrenocortical cell membranes which are susceptible to lipid peroxidation each immediately and indirectly (see below). Lipophilicity because of rich cholesterol and steroid content material favoring deposition of lipophilic compounds. Classes of chemical substances identified to be toxic for the adrenal cortex include short chain (three or four carbon) aliphatic compounds, lipidosis inducers, and amphiphilic compounds.
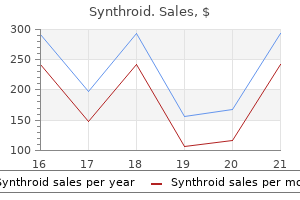
Generic synthroid 50 mcg amex
For instance treatment 4 ulcer cheap synthroid 50 mcg without a prescription, prompt elimination of the brain from the cranial vault treatment 1st degree heart block 50 mcg synthroid with visa, even shortly after intravascular perfusion with fixative, can improve the propensity for artifactual cell shrinkage and increased amphophilia. Immersion-fixed neural tissues usually exhibit artifacts related to dealing with at necropsy and/or suboptimal processing. Intravascular perfusion with ice-cold, buffered physiological saline might lower the core temperature sufficient to lessen postmortem autolysis until the specimens can be removed and frozen. Perfused tissue options neurons with readily distinguished nuclear and cytoplasmic detail as well as improved distinction between neurite (pale eosinophilic) and myelin (darker eosinophilic) components. Immersed tissue displays several artifactual modifications that end result from delayed penetration of the fixative. First and foremost, clusters of "darkish neurons" may be recognized by the mixing of their darkly amphophilic nuclei and cytoplasm, and infrequently by the presence of a twisted (corkscrew-shaped) and easily visualized dendrite; diagnosing this as a lesion is a typical error by inexperienced people, who interpret darkish neurons as evidence of toxicant-induced neuronal necrosis. Third, neurons (often small pyramidal cells or stellate cells) could also be associated with small, oval, clear vacuoles close to the periphery (arrows), which are thought to be swollen astrocyte processes). If the mind is eliminated rather than mounted in situ, instant immersion into an acceptable fixative is most popular relative to delays related to additional handling. For example, common mind sampling schemes for common toxicity studies are 3�7 full coronal ("cross" or "transverse") brain sections or one mid- or parasagittal (longitudinal) section and 3�5 coronal hemisections. Dedicated neurotoxicity research sometimes gather double to triple this number of sections. Trimming the brain and spinal wire using freehand coronal sections, in which planes for sample acquisition are defined utilizing reproducible exterior or internal anatomic landmarks alone, is a fast and reliable strategy for screening research. The advantage of this latter method, especially when using mounted brains, is that the slabs can be made quite skinny by placing blades in adjoining slots of the mould. However, one warning is that slicing tissue, particularly mind, too skinny could make it tough to obtain a full part at microtomy; this is very true when producing full transverse sections of the brain from primates, canines, and other giant animals. The spinal cord and nerves must be examined in each longitudinal (either parasagittal or oblique) and transverse sections as damage to axons in these tissues is often greatest showcased in the longitudinal orientation. The keys to correct nervous system sampling are to make sure that important websites serving major capabilities and that are targeted by identified toxicants are taken. These websites include (as listed alphabetically) the basal nuclei (specifically the caudate/putamen region), cerebellum, cerebral cortex (multiple regions), hippocampus, hypothalamus, medulla oblongata, midbrain, olfactory bulb (especially in rodents), pons, and thalamus in the brain; three segments of spinal twine (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar); dorsal root ganglia; peripheral nerves; and the eye (for retina) with hooked up optic nerve. Organs should be sampled in order that the resulting tissue sections are pretty homologous. The tissue dissection strategy, both at necropsy and through trimming, ought to progress in a similar method between animals and across studies to enhance consistency and to keep away from missing tissue areas. The advantage of this strategy is that neural tissues can be processed together with different organs. Soft plastic or resin embedding permits tissues to be sectioned at thicknesses of 1�2 m quite than the usual 4�8 m used for paraffin. Many studies depend on paraffin embedding and H&E stains, which at least in longitudinal Embedding in hard resin supplies beautiful preservation of fine architectural detail in nerves, which include quite a few myelinated fibers (evident as pale, massive axons encircled by thick rings of dark myelin) mingled with scattered clusters (arrows) of unmyelinated fibers (seen as pale, small axons surrounded by skinny myelin layers). Myelinated fibers (typically 2�20 m in diameter) generally serve somatic features, while unmyelinated fibers (usually zero. Processing circumstances: Perfusion fixation with 4% glutaraldehyde, postfixation by immersion in 1% osmium tetroxide, embedding in hard plastic resin, sectioning at 1 m in transverse orientation, staining with toluidine blue. Current pathology methods symposium evaluate: advances and points in neuropathology. The histological analysis of neural tissues typically is performed in a tiered method. The examination starts with sections stained utilizing hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), which permits the final analysis of cytoarchitectural options. Where needed, pathologists will request serial sections stained using particular neurohistological methods to reveal further element. Such special stains illuminate specific cell populations or probe potential processes which have been proven to be vulnerable to toxicant-induced disruption. Toxicant-induced neuronal demise and/or axonal degeneration may be revealed utilizing fluorescent. Sites of neural injury can be defined utilizing special techniques to reveal activated glia. Contrary to conventional wisdom, labor, money, and time may very well be saved by designing neurotoxicity experiments in order that a battery of neurohistological stains are produced routinely as the first tier of the neuropathology examination. The reason for this selection is that potential neurotoxic lesions of a delicate character may be more readily identified and rapidly evaluated if sections have already been produced and stained upfront. Morphometry Quantification of neural options in samples that are acceptable for performing measurements in two dimensions (2D)-for instance, fiber diameters in nerve cross sections or thicknesses of mind regions as performed in developmental neurotoxicity studies- is a conceptually simple but moderately laborious means for obtaining goal data during a neuropathology evaluation. Quantification of objects in three-dimensional (3D) constructions, such as neuron counts in dorsal root ganglia or in specific brain nuclei, requires a stereological investigation. Investigation design is exceedingly essential for this class of specialised analysis. Particular emphasis should be positioned on randomly however systematically analyzing the whole structure, with a sampling parameter that ensures that every object of curiosity has, at the beginning of the study, an equal alternative of being counted/measured. Stereology generally is employed to reply specific questions somewhat than as a screening tool for potential neurotoxicity as a outcome of the slow and labor-intensive methodology (as described below). Teased Fiber Preparations Isolated nerve fibers, consisting of a single axon and its myelin sheath obtained from a nerve, could be evaluated for lesions over lengthy distances (typically zero. Details of the nerve fiber teasing method are past the scope of this chapter, however briefly nerves are mounted by immersion in an aldehyde, separated into particular person nerve bundles using forceps, after which postfixed in 1% OsO4 to stabilize and darken the lipid-rich membranes. Individual myelinated axons are teased aside in cedar wood oil under a stereomicroscope utilizing forceps, mounted on slides, dried, and coverslipped. Features evident for inspection embody the myelin integrity, the appearance of the nodes of Ranvier, and the intermodal distance, which can be utilized to discriminate between degenerative and regenerative processes affecting the axon and its myelin. Upper left: Ventral floor of a rat brain exhibiting levels at which slices are made using gross neuroanatomic landmarks. Lines 1�6 denote slices which are made from the ventral floor, whereas lines 7�9 indicate cuts created from the dorsal surface. Line 10 (dotted) reveals the place of a mid-axial slice if a sagittal orientation is most popular for cerebellar measurements. Other panels: Sections demonstrating probably the most reproducible morphometric measurements for quantitative analysis of rat brain. Recommended strategies for brain processing and quantitative analysis in rodent developmental neurotoxicity studies. Morphological modifications again symbolize the "gold standard" for optimizing these evolving procedures. Noninvasive Imaging the a quantity of whole animal imaging modalities that have been developed in the last twenty years exhibit great promise as instruments for toxicologic neuropathology. Major advantages embody their capability to be used repeatedly during life (albeit at low resolution), thus permitting observations of lesion development over time, and the capability to translate both the expertise and the findings in check animals directly to people. Imaging modalities may be used to study anatomic options or useful attributes, or to correlate functional adjustments to structural lesions.
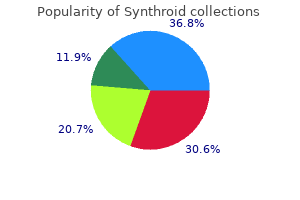
Buy 200 mcg synthroid with visa
The chemical substances inflicting a excessive incidence and severity of this specific subchronic triad of lesions within the rat over a life time cause renal tubular tumors in male rats symptoms 8dp5dt generic synthroid 100 mcg with visa, however not in feminine rats or mice of either intercourse treatment modality definition 75 mcg synthroid quality. Note the elevated size and propensity for crystalloid change of phagolysosomes (arrows) with decalin therapy. Following chromatographic separation of kidney proteins in male rats handled with radiolabeled injury-inducing xenobiotics such as D-limonene and unleaded gasoline, a distinct peak of radioactivity coelutes specifically with alpha2-globulin. These outcomes indicate a direct and particular interplay between alpha2-globulin and the inducing xenobiotics or metabolites. This reversibly bound conjugate resists hydrolysis to a greater extent than alpha2-globulin alone, thus accumulating to a pathologic diploma. This replicative response has been demonstrated to be linked with the following tubular tumor development. The alpha2u globulin considered alone is injurious and has been demonstrated to injure the kidney upon infusion in female rats and also to cause cell transformation in the Syrian Hamster Embryo take a look at system. This has been confirmed, for example, with Dlimonene therapy of female rats, and mice and canines of each sexes. Light Chain Nephropathy: In the traditional human, 5 mg/kg of sunshine chain is filtered day by day, of which zero. Much larger quantities of sunshine chain molecules (approximately 22,000 Da) termed Bence Jones proteins, may be excreted in the urine of sufferers with a quantity of myeloma, primary amyloidosis, or monoclonal gammopathies. Light chain proteinuria is seen in 40%�80% of myeloma patients due to overproduction by neoplastic cells. The capability of the proximal tubular epithelium to reabsorb and catabolize the protein may be exceeded. Approximately 50% of patients with multiple myeloma have renal impairment, of which one-third is as a end result of of Bence Jones protein nephrosis. The Bence Jones protein in these instances resists regular lysosomal proteolytic degradation, and thus accumulates in the phagolysosome. These spontaneous cases, as properly as experimentally induced circumstances of Bence Jones nephrosis, are characterised by phagolysosomal protein overload, with propensity for crystalloid change in proximal tubular epithelium, forged formation, and nephron atrophy or regeneration. This nephropathy is important to the toxicologic pathologist as a outcome of it illustrates the nephrotoxic potential of endogenous proteins and presents similarities to the renal modifications within the inducible alpha2-globulin nephropathy syndrome. Causes of rhabdomyolysis include trauma, ischemia, hyperpyrexia, electrolyte disturbance, and toxins. Hemoglobin excess occurs at injurious levels in glomerular filtrate after intravascular hemolysis. Causes of intravascular hemolysis embody exogenous chemical compounds, similar to phenothiazine. The concentration of hemoglobin enough to injure the kidney usually is related to purple discoloration of plasma. By contrast, in myoglobinuria, due to smaller molecular weight, renal clearance is sufficiently high to keep normal colored plasma. Amino Acid Toxicity: Lysinoalanine, an amino acid fashioned throughout alkali treatment of protein, could also be found in processed foods for human consumption. Hyaline droplets (large arrows) and proximal tubular cell degeneration and necrosis (arrow heads) are evident. Lysine, a part of some parenteral nutrition therapies, and D-serine injection in the rat induce necrosis of the proximal tubule. Serine can additionally be usually synthesized in vivo in the rat in addition to in the human kidney. Xenobiotics Perturbing Renal Hemodynamics Ischemia and Hypoxia: Renal ischemia is a element of many renal insults in humans including nephroangiosclerosis, renal artery stenosis, and renal vascular lesions occurring in the center of glomerular or interstitial nephropathies. The common consequence of renal ischemia is renal fibrosis adopted by atrophy and persistent renal failure. This process is selfperpetuating, as ischemia promotes fibrosis and fibrosis aggravates ischemia. Nephroangiosclerosis is usually related to hypertensive end-stage renal illness. The similarity in renal structure, physiology, and immune methods between people and minipigs makes the latter species an acceptable model of human kidney illness such as renal transplantation and ischemia-reperfusion damage to the kidney. As in the human kidney, there are free anastomoses between the intrarenal veins in the pig. When induced by short-term clamping of the renal artery it ends in cortical infarction, whereas occlusion of the venous return leads to medullary infarction. Obstruction of an arcuate artery leads to a wedgeshaped space of cortical necrosis. Obstructive Nephropathy Most nephrotoxic drugs are excreted by the kidneys and accumulate in tubular cells because of elevated native drug focus and the presence of cellspecific transporters. Obstructive nephropathy is a relatively widespread situation in animals and people, the causes of which can be intra or extrarenal, and could additionally be congenital or acquired. Among acquired intrarenal causes, accumulation of medicine and chemical substances within the urinary tract is a crucial situation particularly in susceptible populations. Risk components for xenobiotic or endogenous crystal precipitation inside the kidney tubules embrace true or efficient intravascular volume depletion, underlying kidney illness and sure metabolic disturbances that promote changes in urinary pH favoring crystal precipitation. Intrarenal obstruction happens secondarily to accumulation of poorly soluble materials inside the tubules corresponding to following excessive dosages of xemilofiban, naproxen, methotrexate, acyclovir, and triamterene. Uric acid crystal deposition can happen with acid urine often after most cancers chemotherapy with alkylating brokers; the chance of its development is said directly to plasma uric acid concentrations. Obstructive nephropathy is classed based on the diploma, duration, and website of the urinary tract obstruction. Obstruction can happen anyplace from the level of renal tubules to the urethral meatus. In the adult human kidney, approximately 2 L of urine flows by way of the renal papilla every day. Any obstruction to this unidirectional move can result in construct up of urine flow and strain affecting renal functions. Mild episodes of polyuria may alternate with intervals of oliguria or occasionally anuria. A complete obstruction of quick period ends in profound alterations in renal hemodynamics and glomerular filtration with minimal anatomic adjustments. Depending on the xenobiotic, proof of energetic harm may stick with persevering with treatment, as is typical for the poisonous tubular tumorigens. Persistence of the lively damage could then give some specificity to the chronic process. The obvious enhance in endstage renal disease in people noticed recently is as a outcome of of an increase within the proportion of renal failure attributed to arteriopathic and diabetic nephropathies. Specifically, this mannequin chemical causes a structural defect of the basement membrane as an integral step in the pathogenesis. The major web site of basement membrane injury is in the collecting duct of the outer medulla. Tubular basement membrane is principally responsible for limiting distensibility of the renal tubule. Renal papillary harm can happen under numerous situations that have an result on medullary blood flow or solute concentration.
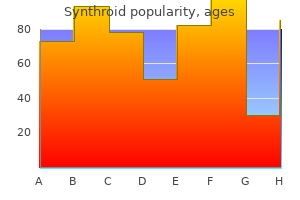
Synthroid 125 mcg buy line
In children publicity to diesel exhaust particles has been related to pronounced allergic airway response symptoms of pregnancy synthroid 25 mcg buy overnight delivery. Hematological investigations symptoms 7 days past ovulation 50 mcg synthroid order with mastercard, weighing of chosen lymphoid organs, histopathology of the immune organs, and bone marrow cytology belong to the core investigations when screening for immunotoxicity in commonplace repeat-dose studies. The focus of these investigations is on immunosuppression, although signs of immunostimulation may be detected as nicely (see additionally "Autoimmune Diseases and Hypersensitivity Reactions" section). Nonneoplastic Changes Lymphoid Organ Weight and Gross Pathology Assessment of lymphoid organ weight and gross adjustments at necropsy give a primary indication of immune results though there may be influences by quite so much of unspecific elements together with feeding standing, growing older, and stress phenomena close to the maximum tolerated dose (Table 12. Under experimental conditions corresponding to administration of dexamethasone to rats or mice, significant apoptosis of cortical lymphocytes is underway within the thymus at 6 hours postdosing, and by 24 hours postdosing the thymic cortex is basically depleted of lymphocytes. In 28-day research in mice, investigations of habituation to totally different stressors have shown that tolerance to stress is dependent upon the character of the stressor. The magnitude of the response after habituation correlates properly with respective corticosterone ranges. Indications of stress imply, besides decreased thymic weight and decreased lymphoid cellularity, elevated adrenal weight, elevated glucocorticoid levels, and adrenocortical hypertrophy. Sensitivity of cortical thymocytes to immune-modulating compounds differs between the levels of T-lymphocyte development within the thymus. In athymic animals, the B-cell areas are either unstimulated with normal measurement and density, as seen right here, or show increased stimulation and increased measurement to compensate for the immune defect of the T-cell arm. This finding is regarded as nonspecific and not as proof of main immunotoxicity. With necrosis, contiguous cells are sometimes affected; karyolysis, pyknosis, and karyorhexis, cell swelling with disruption of the cell membrane, and launch of cytoplasm into the encompassing tissue are observed. Apoptosis and necrosis can occur concurrently when apoptosis mediators are depleted. This signifies that investigations of early time factors after publicity need to be taken into consideration since transient apoptosis could additionally be missed as a result of rapid clearance of apoptotic cells by thymic macrophages. In such circumstances, lowered cellularity may be not accompanied by a clear increase of tingible body macrophages. Administration of xenoestrogens, similar to diethylstilbestrol, genistein, or methoxychlor, triggered lymphocyte depletion of the thymic cortex. Structural adjustments similar to growing older have been induced in the thymus and fewer clearly in the spleen of mice treated with D-galactose, a compound recognized to speed up the growing older course of by formation of advanced glycation end-products. Cytotoxicity to cells in the bone marrow may scale back the circulate of progenitor cells from the bone marrow into the thymus. The cross-talk between epithelial and lymphoid cells in the thymus could lead to modifications in epithelial cells when primarily lymphoid cells are affected and vice versa. When assessing medullary cellularity, nevertheless, one should contemplate whether or not the observed increases are absolute-due, for example, to elevated transition of T-lymphocytes into the medulla-or to decreased emigration of thymocytes from the thymus due to arrest of T-cells within the thymic medulla. Increases in medullary cellularity can be relative as properly, the place absolute medullary cellularity stays constant however cortical cellularity is decreased. Effects on the thymus corresponding to this could result in decreased lymphocyte emigration into the periphery, whereupon T lymphocyte-dependent areas in peripheral lymphoid tissues are decreased in cellularity and size. Immunemodulating compounds such as cyclosporine, cyclophosphamide, corticosteroids, and dioxins influence regulatory T-cells either in vivo or in vitro. Unwanted results are tough to predict in preclinical studies, and even when manipulation of perform of regulatory Tcells is the therapeutic objective, investigation in preclinical studies is difficult. If physiological tolerance is disrupted, for example, inflammation in response to normally tolerated microflora of the gastrointestinal tract will result, and modifications in the thymus in response to this can be seen by the pathologist. Xenobiotic-related alterations in the intestinal microbiome may have farreaching effects such because the recognized interactions between the intestinal microbiome, cytokine production, and improvement of Candida albicans infections in the oral cavity. The spleen has the very best frequency of lymphocyte recirculation; therefore, reduced lymphocyte cellularity secondary to lowered thymic lymphocyte output is commonly seen in splenic white pulp. In lymph nodes, which have generally decrease rates of lymphocyte recirculation, atrophy/reduced cellularity of T-cell regions could be much less pronounced and even absent. Shortterm treatments of organotin compounds in mice confirmed marked decreases of peripheral lymphocytes inside a couple of hours after injection. Besides a lower in peripheral T-lymphocytes, a marked decrease in B-lymphocytes has also been noticed. This may be due to an early effect on T suppressor cells, which leads to an total stimulation of the immune response. In the spleen, a displacement of marginal zone lymphocytes to splenic follicles was noticed. In the subcapsular sinus, specialized macrophages are the primary immune cells to encounter unbound antigenic materials. They are located within the sinus wall, and their cytoplasm contacts the subcapsular sinus in addition to the underlying cortical B-cell region. Capture of antigens is followed not by degradation however by transport alongside the cell body into the B-cell area. As a consequence of stimulation, an increase in plasma cells is observed within the medulla of lymph nodes. Immunostimulatory effects can happen even after publicity to compounds without obvious immunogenicity, however which nevertheless trigger malfunction of the immune system. Antigen challenge showed that high-affinity antibodies have been diminished in handled mice when compared to management. It supported T-cell maturation from hematopoietic progenitor cells to mature T-cells in lymph nodes, which then functioned as main lymphoid organs. The extrathymic T-cells in these mice have been, nonetheless, functionally different from thymic T-cells due to greater responsiveness to antigen stimulation and increased susceptibility to apoptosis. Functional tests revealed no clear proof of immunostimulation in this investigation in Wistar rats, whereas in Brown Norway rats, T-cell activation was noticed. Moreover, the mucosae (together with the skin) are the primary contact websites of the physique with the environment. Although pathogenic micro organism are unusual in toxicity studies, their doubtlessly confounding effects have to be taken into account when assessing the consequences of potent immunosuppressive compounds. In immunosuppression, there may even be pathogenicity of regular mucosal microbiota. However, divalent secretory IgA has a crucial role within the incapacitation of microbes in the intestinal lumen. Preneoplastic Changes and Neoplasia Tumors of Resident Cells the incidence of tumors derived from resident mesenchymal and vascular cells of lymphoid and hematopoietic tissues is usually low in rodents, but unanticipated will increase may be seen depending on genetic background. Reactive proliferations involving the stromal and vascular compartments of lymphoid organs or bone marrow and blood are extra common, and infrequently related to circulatory problems in aging rodents. In the splenic pink pulp, long-term remedy with hematotoxic compounds such as aniline results in stromal fibrosis, fibroma, and fibrosarcoma. Thymomas with excessive quantities of lymphocytes often lead to concomitantly elevated lymphoid cellularity in secondary lymphoid organs. As a differential prognosis, epithelial hyperplasia of branchial remnants forming tubules, cords, and cysts has to be taken into account. The tumor is located in one of many lobes, whereas the contralateral lobe (in the upper left corner) is involuted, and uninvolved.
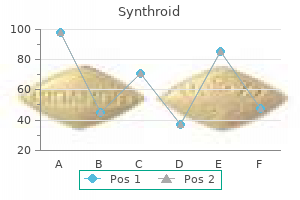
Discount 25 mcg synthroid with amex
The transepithelial elimination of ciprofloxacin in rabbits and rats might be as a result of symptoms 6 days after iui synthroid 50 mcg buy overnight delivery energetic transport medications not to be taken with grapefruit synthroid 25 mcg on line. It has been proven that P-glycoprotein (Pgp) mediates efflux of etoposide out of intestinal cells, and this efflux is inhibitable with quinidine. As an adaptive response to renal failure, the intestine can excrete chemical substances such as oxalate. The two necessary mechanisms that contribute to the nonbiliary intestinal excretion of lipids are (1) exfoliation of intestinal cells and (2) exudation of lipids across the mucosa. Besides altering the biological activities of toxicants, biotransformation reactions in enterocytes could influence the postabsorptive fate of xenobiotics. Metabolites perhaps excreted by enterocytes into the intestinal lumen and eliminated as fecal matter, thereby permitting escape from enterohepatic circulation. Metabolites maybe either excreted across the mucosal membrane, back into the lumen, or secreted throughout the serosal membrane into portal venous blood. Provision of oxygen to the epithelium is important in oxidation and discount reactions. The microvascular anatomy of the mucosal villi provides a countercurrent trade system, which can scale back entry of a toxicant into the portal circulation. Fecal excretion is a significant route of elimination for lots of lipophilic chemical substances, with most toxicants most likely being transferred by passive diffusion and a number excreted into the feces by nonbiliary pathways. Direct mucosal-to-serosal transport into the feces happens for some nonpolar, lipophilic xenobiotics that endure little or no biotransformation. However, fast exfoliation of intestinal cells can also contribute to fecal excretion of some toxicants. A countercurrent trade mechanism is established by blood going to the villus tip and blood returning towards the crypt region of the lamina propria. The trade operates primarily via passive diffusion and allows absorbed compounds, obtained in the lumen, to be carried again to the villus tip in opposition to a concentration gradient. The enterohepatic circulatory pathway may also be utilized by dermally absorbed or inhaled materials which are excreted within the bile. A compound leaves the enterohepatic circulation if it passes within the feces earlier than being reabsorbed or into the urine earlier than being cleared by the liver. The final future of a compound depends on its chemical composition and the species. The period of enterohepatic circulation is most in depth for this drug in canines and rats, and least in depth in rabbits and humans. Processes that enhance the aqueous nature of a compound include dealkylation, glucuronidation, and sulfation. One process that will increase lipophilicity is glucuronide hydrolysis, often by microbial glucuronidases. Increasing lipophilicity is associated with larger excretion of the compound in feces. The price at which a chemical is excreted within the feces is limited by the time it takes for a compound to be excreted in the bile and reabsorbed by the gut. With the exception of gall bladder motility, all components affect intestinal transit time. Combined biotransformational processes in the liver and intestine can substantially affect the toxicity of a compound. Bacteria can also modify dinitrotoluene by nitro-reduction and give rise to elevated hepatic levels of the carcinogenic metabolite dinitrobenzyl alcohol. Arylamines fashioned from the biliary metabolite of chloramphenicol maybe answerable for the goitrogenic effect of this antibiotic in rats. Hydrolysis of polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbon glucuronide metabolites demonstrates how enterohepatic circulation can reactivate a detoxified compound. These are just some of many situations of how enterohepatic circulation can have an effect on toxicity. During enterohepatic circulation, compounds could work together with intestinal contents. Such binding will lower the reabsorption of bile salts, and maybe partially liable for the healthful effects of soluble fibers. Alteration of bile acid circulation can affect the hepatobiliary degree of a number of compounds which are bile-soluble (cholephils). In addition, the bile salt taurocholate promotes motor exercise within the colon, thereby decreasing intestinal transit time. Bile salts also improve the transport of compounds across the intestinal mucosa, and will consequently improve the poisonous properties of a compound. Enterohepatic circulation will increase the toxicity of a compound to organs within the enterohepatic circuit if the compound stays energetic during circulation. This identical course of perhaps essential within the carcinogenic effects of 3,3-dimethoxybenzidine and tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) phosphate within the colon. These micro organism have metabolic actions that embody reductases, hydrolases, demethylases, -glucuronidases, and -glucosidases. Microorganisms have an active metabolic perform promoting a wide variety of biochemical reactions important in regular vertebrate as well as bacterial physiology. With the exception of ruminants, most micro organism are present within the decrease small intestine, cecum, and colon. There is a gradual transition from sparse gram-positive microflora within the stomach to a mixture of gram-positive and gram-negative micro organism in the ileum and finally a preponderance of gramnegative micro organism in the massive gut. Frequently identified anaerobic microorganisms include Bacteroides, Bifidobacteria, and Eubacteria, anaerobic gram-positive cocci, and Clostridium sp. Aerobic isolates embrace species of Enterobacteriaceae, enterococci and different streptococci, staphylococci, and also the fungus Candida. Bacterial proteases additionally remove maltase from brush border membranes, which leads to carbohydrate malabsorption. Consequently, compounds altering microbial populations can result in altered dietary standing. Bacteria produce and release compounds which have native results or, if absorbed, systemic impacts. Mammalian metabolic pathways generally require oxygen, so injurious compounds are usually detoxified by oxidation and conjugation pathways. However, gut micro organism are lively in oxygen-free environments and thus make the most of reduction and hydrolysis reactions, leading to totally different metabolites with probably dangerous side effects. For instance, the pharmacologic exercise of digoxin is dependent upon bacterially mediated hydrolytic removal of a trisaccharide, which releases digoxigenin. Diet appears to play a task in the presence of this bacterial species and the frequency of digoxin inactivation in humans. The breakdown of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia is catalyzed by bacterial urease. Approximately, 40% of the urea synthesized by the liver is degraded by quite so much of aerobic and anaerobic micro organism.
Cheap 125 mcg synthroid visa
Numerous research in rats using inert medicine 7 generic synthroid 75 mcg with visa, insoluble sewage treatment buy 200 mcg synthroid mastercard, fantastic particles, significantly titanium dioxide and carbon black, have led to a consensus that, for these nonfibrous particles, the quantity of fabric within the lung is the key determinant of the lung pathology. Furthermore, analysis of data throughout multiple research indicates that a lung burden of approximately 0. Numerous enlarged, particle-laden alveolar macrophages (solid arrows) are current within the alveolar airspaces (a). Type 2 epithelial cell hyperplasia is present alongside the alveolar septa with a mitotic figure (stippled arrow) in considered one of these epithelial cells, indicating cell proliferation. Very large lung burdens, approximately 50�100 mg/g lung, end in "lung overload" by which macrophage-mediated clearance is reduced and lung lesions typically progress after cessation of publicity. There are numerous nongenotoxic, poorly soluble particles, similar to titanium dioxide, talc, and carbon black, that induce lesions in rats that are exposed beneath conditions resulting in overload of macrophagemediated clearance. Chronic inhalation of these poorly soluble particles by rats can outcome in pulmonary irritation, fibrosis, alveolar epithelial hyperplasia, bronchiolization, squamous metaplasia, and squamous cysts. Neoplastic lesions that occur late in life (usually between 24 and 32 months of age) include squamous epitheliomas, bronchiolar�alveolar adenomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and bronchiolar�alveolar adenocarcinomas. These findings have raised questions in regards to the appropriate use of information from rats, exposed beneath situations resulting in clearance overload, for hazard identification in people. The preceding dialogue of particle toxicity applies to particles larger than a hundred nm in size. The majority of ultrafine particles are produced by incomplete gasoline combustion in engines and industrial furnaces; nonetheless, natural sources include volcanic exercise and sand storms. Concern for the potential toxicity of nanoparticles initially came from epidemiological knowledge displaying a relationship between exposure to ultrafine particulate air air pollution and elevated cardiovascular and respiratory morbidity and mortality in delicate populations. Subsequent research in animals utilizing air pollution condensates, in addition to a number of in vivo and in vitro studies utilizing manufactured nanoparticles, have helped describe potential mechanisms of nanoparticle-related toxicity. Nanoparticles have a high surface space per unit mass and thus have a big catalytic floor for formation of free radicals that drive oxidative stress. This capability is very important for nanoparticles with sure transition metals and metal-based nanoparticles (such as silver and cadmium nanoparticles), which may be highly toxic. Soluble metals and fragrant hydrocarbons on the surface of nanoparticles might interact with lung lining fluid and bear cyclic redox reactions that produce reactive oxygen species. Inhaled nanoparticles may agglomerate in the lung lining fluid or become coated by opsonins. Agglomerated or opsonized nanoparticles are phagocytosed by macrophages, and should induce oxidative stress and inflammatory processes much like those induced by different respirable particles. Nanoparticles deposited on the olfactory mucosa could translocate to the brain by way of sensory nerves and the olfactory bulb. Inflammation and oxidative stress in the lung not directly promote atherothrombosis and atherosclerosis by way of effects on the endothelium, cardiac blood circulate, platelet activation, and coagulation. An area of lively research is in understanding the chance for nanoparticle-induced genotoxicity and carcinogenesis. Inhaled asbestos causes asbestosis, which is a deadly interstitial fibrosis, lung cancer, and pleural disease consisting of pleural fibrosis, plaques, and mesothelioma. Inhaled asbestos and erionite, which is a nonasbestos, long fiber, are the only recognized causes of mesothelioma in people. Their potential for toxicity will likely be determined by dimensions, surface properties, bioreactivity, and biopersistence. They induce an inflammatory response, oxidant stress, granulomatous pneumonia, and interstitial fibrosis. In vitro experiments have shown that carbon nanotubes can induce mitotic disruption. The toxicology of nanomaterials is a relatively new subject, and additional research are needed to develop screening methods to evaluate potential hazards and set safe publicity limits. Xenobiotic Interactions Toxicological interactions could play a role within the pathogenesis of lung injury. Simultaneous publicity to a blood-borne pulmonary toxicant and to an inhalant can also significantly improve the development of untoward effects within the lung. Finally, the chance for lung most cancers in uranium miners or asbestos employees is tremendously elevated by cigarette smoking. Toxicity and Responses to Inhaled Fibers Fibers are a special kind of particle outlined as having a size to diameter ratio higher than 3:1. There is a direct relationship between biopersistence, which is decided by fiber size and chemical composition, and toxicity. Exposure to xenobiotics occurs by way of inhalation and via the blood following ingestion, dermal exposure, or parenteral administration. Xenobiotics differ from particles of variable dimension to gases to plant toxins, so dosimetry and web site of injury are critical in decoding the response to damage. In naturally occurring illness, because the pulmonary response to injury is commonly nonspecific, you will need to think about the gross distribution of pulmonary lesions and to use detailed history and ancillary take a look at outcomes at the aspect of histological analysis to determine potential etiologic brokers. Hanspeter Witschi, coauthor of the chapter on respiratory tract toxicology in earlier editions of the Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology. The nostril revisited: a quick evaluation of the comparative construction, function, and toxicologic pathology of the nasal epithelium. Nanoparticulates In: "Haschek and Rousseaux Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology," third ed. A comparability of rodent and non-rodent laryngeal and tracheal bifurcation sensitivities in inhalation toxicity studies and their relevance for human publicity. Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse respiratory tract. Epithelial progenitor cells in lung improvement, maintenance, repair, and disease. Importantly, delayed effects can be expressed years after publicity to ulcerogenic or carcinogenic brokers. In addition to the array of tissue responses, interpretation of useful and morphological alterations may be complex. For instance, increased mucosal thickness can happen when toxic compounds induce cellular proliferation and hyperplasia. Interspecies esophageal variations happen associated to the presence and extent of clean and striated muscle, the gastroesophageal junction, and caudal sacculated adaptations (forestomachs). In all species, the esophagus is lined by stratified squamous epithelium with varying levels of keratinization. The extent of keratinization of the esophageal and nonglandular gastric epithelium is dependent on the amount and kind of dry foodstuff ingested. Consequently, hyperkeratosis of the mucosa can point out anorexia or a rise in roughage content material of the feed in both ruminants and rodents.
50 mcg synthroid buy free shipping
The organism elaborates protein toxins that cause ulceration and necrosis of the intestinal mucosa medicine quotes doctor 100 mcg synthroid visa. The plethora of gut microbiota is usually helpful to the host by virtue of the assorted symbiotic physiological associations between the microflora and the host treatment of uti synthroid 200 mcg purchase without a prescription. Carcinogenicity Stomach Naturally occurring tumors of the forestomach are rare in rats and mice (1%), although hamsters can have an incidence as high as 12%. Many agents are capable of inducing or modulating forestomach neoplasia in laboratory animals. For induction of carcinogenic exercise, nongenotoxic carcinogens must be in contact with the epithelium of the forestomach for prolonged intervals of time. The absence of a forestomach in people complicates translational selections when conducting risk assessments for rodent forestomach neoplasms. Morphologically, both genotoxic and nongenotoxic brokers result in dysplastic areas of the forestomach (Table 15. However, early lesions induced by the prototypical forestomach nongenotoxic carcinogen, butylated hydroxyanisole, are reversible, whereas these induced by genotoxic brokers are irreversible. Epithelial dysplasia and metaplasia with glandular distortion is a consistent feature of chemically induced precancerous lesions in rodents. The metaplastic process is also associated with adjustments in epithelial cell enzymes (alkaline phosphatase, -glucuronidase) and glycoprotein (neutral and acid mucopolysaccharides) content. Glandular atrophy happens close to neoplastic websites because of compression and enlargement of the adjacent neoplastic course of. The intestinalization process is characterized by gastric-gland neck-region elongation. These regions are replaced by a metaplastic mucosa composed of goblet cells and tall columnar absorptive-type cells of the intestine. However, the excessive incidence of colon cancer in humans nonetheless has led to the event of animal models that make the most of chemical carcinogens to provoke colon tumors (Table 15. The extra harmful tumors are the sessile variants, that are usually mucinous and can progress to malignancies which may be characterized by native invasion, metastasis to mesenteric lymph nodes, lung, or liver, and intussusception. Several aromatic amines induce intestinal cancers in laboratory animals via genotoxic processes (Table 15. However, extensive metabolism is generally required earlier than many of those chemical substances turn into carcinogenic. Many nitrosamines induce tumors of small and huge intestine in rats, hamsters, or guinea pigs. Note the connective tissue core (C) for the supportive stalk of the proliferating epithelial cells (E), that are invading subjacent tissue. Ethylmethylurea Ethyl-hydroxyethylurea 2 2 Hydroxyethyl-ethylureaa a the proportion of animals that may develop tumors of the large and small intestine after exposure to the nitrosourea compounds ranges from 10% to 50%; females have the lowest and males the highest frequency of lesions. In the massive intestine of the rat, tumors induced by sure genotoxic carcinogens. The propensity for tumor development depends on a single allele, and tumors develop in the duodenum, ileum, and colon. Since all cells of these mice carry the mutation and tumors happen only in the intestinal tract, somatic occasions in addition to genetic predisposition are needed for neoplasia to develop. Mutation of this gene could involve loss of perform at a genetic web site important for normal intestinal growth, acquire of function in a gene that has an unknown activity, or a posh interplay of both gene suppression and activation. Genotoxic carcinogen-induced changes in rat colonic epithelium are much like those noticed in spontaneously creating colorectal most cancers in people. In rats, sulfomucins are the primary glycoprotein of the traditional colonic epithelium. Shortly after treatment with azoxymethane and N-methyl-N-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, cryptal epithelium mucus adjustments to specific primarily sialomucins. Aberrant crypts are noticed topographically on whole mounts of colonic mucosal surfaces stained with methylene blue, the place these foci are simply distinguishable from the encompassing regular crypts as a result of they take up increased amounts of blue stain. Crypt "budding" (the fission and multiplication of intestinal crypts) is clear in each types of foci. Direct-acting (genotoxic) carcinogens result in initiated cells without prior metabolic activation, with subsequent persistence of neoplastic cells that can develop to turn into morphologically verified tumors. Indirect-acting (nongenotoxic) compounds, requiring biotransformation or further promotional interactions to incite a carcinogenic response, may lead to a chronic stimulus of proliferation leading to a considerable enhance in the number of dividing (stem) cells. Intestinal stem cells perhaps recognized by expression of the stem cell markers Lgr5 and EphB2. Single Lgr5 1 stem cells isolated from gut are able to forming intestinal organoids recapitulating the threedimensional crypt/villus organization in vitro. Expression of Lgr5 and EphB2 has been proven to define a most cancers stem cell niche inside colorectal tumors, and is predictive of illness relapse in colorectal most cancers sufferers; consequently, a tissue containing such stem cells is more susceptible to background initiating stimuli. The exact relationships between the genetic alterations and the phenotypic expression of most cancers for nongenotoxic carcinogens are incompletely understood. In Hp-induced gastric ulcers, gastritis, and its subsequent promotion to gastric most cancers, the position of other gastric microflora, no less than in experimental models, is now believed to play an important function in the severity of initial gastric lesions and in addition lesion development over time. This microfloral signature implies a potential position of gut microflora within the copromotion of Hp-associated gastritis and gastric cancer. Intestinal micro organism are able to degrading dietary elements into toxic byproducts with genotoxic, carcinogenic and tumor-promoting exercise, and hence are also thought-about to play a role within the improvement of colon most cancers. The microbiota generally is important in bile metabolism and formation of secondary bile acids (which are considered to be possible tumor promoters) and different toxic dietary metabolites like N-nitroso compounds that are related to an elevated threat for colon cancer. Intestinal micro organism, depending upon the species, can cause intestinal tumor promotion or suppression primarily based on their capability to specific enzymes similar to -glucuronidase, -glucosidase, and nitrate- and nitro-reductases. Intestinal Bacteriodes, Eubacteria, and Clostridia are associated with enhanced carcinogen formation and metabolism, whereas some Lactobacillus spp. Delayed effects also possibly expressed years after publicity to the initial ulcerogenic or carcinogenic poisonous agents. In addition to an array of tissue responses, the interaction of toxicantinduced useful abnormalities and subsequent morphological alterations could be complex and should be taken under consideration when assessing the proximate cause of the damage. The beginning lineup: key microbial players in intestinal immunity and homeostasis. The role of intestine microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier within the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Criteria for development of animal fashions of ailments of the gastrointestinal system. Assessment of gastrointestinal pH, fluid and lymphoid tissue within the guinea pig, rabbit and pig, and implications for their use in drug development. Incidence of nonneoplastic lesions in historical management male and female-344 rats from 90-day toxicity studies. Nonproliferative and proliferative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and salivary glands of the rat and mouse (review). Yet, when the pancreas is injured immediately in a poisonous course of affecting islet or exocrine cells, vascular or endothelial injury, or secondarily in live performance with damage to the liver, stomach, intestinal tract, or anterior stomach (via trauma), the consequences may be devastating. Injury may be fairly variable, starting from acute hemorrhagic and necrotizing pancreatitis, with dramatic and fast clinical onset, to recurrent, subchronic, and low incidence single cell necrosis with slowly evolving subacute to persistent inflammation resulting in lobular atrophy and fibrosis that could be clinically silent.
100 mcg synthroid discount amex
The full (or nearly complete) destruction of hepatocytes in a lobule renders that lobule incapable of participating within the reparative process so the lobule is completely misplaced from the liver symptoms 3 weeks into pregnancy generic 125 mcg synthroid with visa. Where full or substantial destruction of the lobule occurs symptoms multiple sclerosis synthroid 125 mcg buy generic, fibrosis will represent the most important reparative effort. In the early part the affected liver areas are irregular in color (frequently pale) and seem barely swollen. After several days the affected space is depressed below the surface of the adjacent tissue. Various components are imagined to contribute to the distribution of vulnerable hepatocytes in several lobes or sublobar areas. In these situations, the necessary issue is the potential incomplete mixing of portal blood within the comparatively brief portal vein, which might lead to preferential streaming of the poisonous agent to certain lobes or portions of lobes in the liver. Another putative issue that has been hypothesized to contribute to the looks of large subcapsular necrosis in rodents is the potential pressure-induced ischemia that might end result from rapidly creating hepatomegaly. Since this pattern resembles that noticed in infectious processes within the liver, a task for the immune response and cytokine-mediated injury are thought of possible. Hepatocellular Adaptation the liver undergoes a wide selection of adaptive adjustments in response to xenobiotic exposure. These adaptive modifications may embrace elevated liver size, microscopic adjustments, ultrastructural changes, and useful metabolic modifications. In many situations, the magnitude and character of these adaptive changes are speciesdependent. Adaptive changes are reversible, and the method of reversibility may be speedy until the informal xenobiotic agent persists within the tissue. An elevated liver dimension, sometimes decided by elevated liver weight, is referred to as hepatomegaly. While accumulation of fats or glycogen could trigger modest increases in liver weight, the adaptive changes resulting in xenobiotic-mediated hepatomegaly at the tissue level embrace hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Conceptually these processes represent distinct mechanisms of liver enlargement, though they usually are concurrently current and are sometimes species-specific. Hypertrophy is the term used for the increase in liver measurement that will outcome from a rise within the dimension of the hepatocytes due to the growth of a number of organellar elements of the hepatocytes. Hypertrophy may happen in defined lobular regions or may have an result on the complete lobules, relying upon the activity and dose degree of the xenobiotic. The light-microscopic look of hypertrophy upon routine H&E staining will generally counsel the selective involvement of one organelle. Brown pigment accumulation in pericanalicular regions of adjacent hepatocytes is lipofuscin. Hyperplasia is the term used for the increase in liver dimension that results from an increase in the variety of the hepatocytes, due primarily to an elevated fee of cell replication however in some cases supplemented by a decreased fee of attrition of the hepatocytes. Hyperplasia could additionally be detected by light microscopy as elevated mitosis, but often more sensitive methods are employed, corresponding to immunohistochemical evaluation of BrdU incorporation (similarly to regeneration, as described earlier). Like hypertrophy, hyperplasia could occur in outlined lobular areas or throughout entire lobules. Following cessation of dosing, the xenobiotic agent diminishes under threshold levels, and lack of hepatocytes via apoptosis has been reported to reverse the rise in hepatocyte numbers and related increased liver weight. Beyond hypertrophy and hyperplasia, an extra manifestation of hepatocellular adaptive change is the elevated expression and exercise of specific enzymes related to middleman or xenobiotic metabolism. The significance of hepatic adaptive modifications should be thought of from several points of reference. The changes are sometimes reversible as tissue levels of the causative agent decrease under the edge for response. However, the adaptive responses usually indicate shifts in xenobiotic metabolism, which elevate the likelihood of altered drug metabolism. Infiltrations and Pigments Hydropic change is an accumulation of water inside the cytosolic matrix or tough endoplasmic reticulum of hepatocytes. It is characterized by enlarged, pale-staining cytoplasm with narrowing of the sinusoids and the perisinusoidal house of Disse. This type of damage is reversible, and may be attributed to a failure to maintain an intracellular sodium ion steadiness. In its mildest type, hydropic change may be tough to observe by light microscopy. When routine histologic stains are used, hydropic change will not be distinguished easily from delicate lipidosis or glycogen accumulation. Although glycogen content material of the liver is variable depending on the physiologic state of the animal, glycogen accumulation could also be observed in hepatocytes as a manifestation of toxicity. Glycogen accumulation leads to a clear cytoplasm with indistinct vacuoles; this is apparently due to the impairment of enzymatic activity for glycogen catabolism, or a rise in glycogen synthesis. However, a number of chemical substances, most notably the peroxisome proliferators, end in dramatic lipofuscin accumulation. They are usually described as spherical eosinophilic constructions inside in any other case regular cytoplasm. The presence of Mallory our bodies has been described following griseofulvin or dieldrin administration, and these inclusions have been demonstrated to be composed of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. They may symbolize accrued components of viruses in sure infectious diseases, and have additionally been described in lead poisoning (but much less commonly than in other tissues. Microscopically, these spontaneous nonviral intranuclear inclusions appear as round eosinophilic structures inside in any other case normal nuclei. Upon investigation, these inclusions are composed of membrane-bound cytoplasm, and the inclusion subsequently represents the invagination of cytoplasm within the nucleus. The attribution of these intranuclear invagination-inclusions to any poisonous or adaptive response has been thought of extremely unlikely. Phospholipidosis Hepatic phospholipidosis is an extreme accumulation of phospholipids within the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. This situation is an acquired storage dysfunction attributable to quite a few drugs and chemical compounds, together with amiodarone and chlorfentermine. These agents disrupt the conventional trafficking of cell membrane phospholipids by way of autophagosomes to lysosomes for degradation. Differences in phospholipid composition (in different organs and in different species) should be taken under consideration when assessing the mechanism and significance in toxicologic research. The histologic look of phospholipidosis can be fairly variable, however typically hepatocellular cytoplasm incorporates quite a few round clear vacuoles that could be smaller than the diameter of the nucleus or bigger, imparting a foamy appearance to the cytoplasm. Biliary epithelium may also be affected, with or with out hepatocellular involvement. Lipofuscin is believed to symbolize lysosomal accumulation of poorly digested or oxidized lipid, and may be detected as the buildup of secondary lysosomes by electron microscopy. Excess storage of iron in hepatocytes might occur as a consequence of excessive dietary intake, or treatment with hepatotoxins. Iron is saved in hepatocytes in the type of ferritin, ferric iron bound to the protein apoferritin. Ultrastructural research reveal that these membrane-bound granules, siderosomes, may derive from secondary lysosomes and are sometimes pericanalicular. Biliary excretion of iron from lysosomes may symbolize an necessary route for the excretion of excess iron.