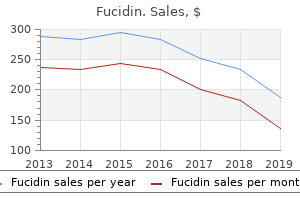
Fucidin
"Purchase fucidin 10gm on line, antibiotic clindamycin".
By: X. Harek, M.A.S., M.D.
Associate Professor, Syracuse University
Midbrain: this most rostral area of the brainstem is characterized by the large pair of cerebral peduncles on its anterior surface and two pairs of nuclei infection nclex questions fucidin 10 gm low price, the superior and inferior colliculi antibiotic resistance meat purchase 10 gm fucidin free shipping, on its posterior surface (see Figure 2 antibiotics for bordetella dogs buy cheap fucidin 10gm on line. The descending corticospinal tract that mediates voluntary motor activity travels through the cerebral peduncles antibiotic resistance human microbiome discount 10 gm fucidin mastercard. The superior colliculi in the rostral midbrain are involved in visual reflexes, whereas the inferior colliculi, in the caudal midbrain, are a major integrating center in the auditory pathway. The cerebral aqueduct connecting the third and fourth ventricles is found in the dorsal area of the midbrain. Important internal structures of the midbrain include the red nucleus and the substantia nigra. Corona radiata Association fibers connect areas Corpus within one callosum hemisphere. Overview of the Central Nervous System Optic tract Mamillary body Interpeduncular fossa Basis pedunculi of cerebral peduncle Inferior colliculus Superior cerebellar peduncle Basal portion of pons Inferior cerebellar peduncle Middle cerebellar peduncle Olive Pyramid Superior colliculus Obex Decussation of pyramids Fasciculus cuneatus Fasciculus gracilis Figure 2. The basal pons consists of bundles of descending, longitudinal corticospinal fibers, and transverse pontocerebellar fibers that carry information from the pontine nuclei to the opposite cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncles, which arise off the lateral surface of the basal pons. The posterior surface of the pons consists of the fourth ventricle and rostrally the superior cerebellar peduncles, containing primarily cerebellar efferents, which form most of the roof of the fourth ventricle (see Figure 2. The medulla: the medulla is the most caudal part of the brainstem and merges at its most caudal end with the spinal cord (see Figure 2. The rostral or "open" portion of the medulla is characterized by the pyramids (descending corticospinal fibers) on its anterior surface, and the caudal part of the fourth ventricle on its posterior surface. The inferior cerebellar peduncles, carrying information from the spinal cord and brainstem, can also be seen on its posterolateral surface. Oval swellings on the lateral surface of the rostral medulla, the olives, overlie the prominent olivary nuclear complex involved in modulating motor activity. The caudal or "closed" portion of the medulla is characterized by pyramids on its anterior surface and prominent sensory tracts, the fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus, on its posterior surface. The pyramids cross, forming the decussation of the pyramids, in the caudal medulla. Cerebellum the cerebellum is an outgrowth of the pons and overlies the fourth ventricle. Given its embryological origin, the cerebellum can be considered part of the pons. The cerebellum has two hemispheres and a central area called the vermis, and its surface is covered by the highly folded cerebellar cortex (Figure 2. The cerebellum is attached to the brainstem by the cerebellar peduncles that carry information to and from the cerebellum. The cerebellum has important roles in processing of sensory information and coordination of voluntary motor activity. More recent evidence indicates a role for the cerebellum in cognitive function as well. It receives sensory input from the limbs, trunk, and many internal organs and plays an important role in the initial processing of this information. It also contains the somatic motor tracts that supply the skeletal muscles as well as visceral efferents to our viscera, smooth muscles, and glands. Spinal cord organization the spinal cord has a clear segmental organization, corresponding to the nerve roots attached to it. A continuous series of posterior rootlets, containing sensory axons, enter the posterior aspect of the spinal cord, and a continuous series of anterior rootlets, containing motor axons, emerge from the anterior aspect of the spinal cord. A bulge in the posterior root, just proximal to the point where the spinal nerve forms, is the spinal ganglion, containing the cell bodies of the sensory nerve fibers. Two areas within the spinal cord, the cervical enlargement and the lumbosacral enlargement, contain increased numbers of motor neurons to supply the arms and legs, respectively (Figure 2. At its caudal pole, the spinal cord tapers off into the conus medullaris and ends in the filum terminale, which anchors the spinal cord. Spinal cord length the segments of the spinal cord are not at the same level as the intervertebral foramina through which the spinal nerves exit. Until about the third month of fetal life, the spinal cord and the vertebral column grow at about the same rate, and the spinal nerves exit through an intervertebral foramen that is lateral to them and at the same level.
Amygdala With connections to both the hypothalamus and bacteria taxonomy trusted fucidin 10gm, indirectly bacteria 4 result in fecalysis purchase fucidin 10 gm without a prescription, the prefrontal cortex antibiotic resistance nhs generic fucidin 10gm with visa, the amygdala is positioned to play a role in both driverelated behaviors and the processing of emotions that are related to these behaviors (Figure 20 antibiotics for sinus infection types cheap fucidin 10gm overnight delivery. Emotional learning and memory: the amygdala plays a key role in emotional learning and memory (an implicit memory function). The emotional significance of inputs from various cortical areas is assessed primarily by the basolateral nucleus (see Figure 20. Efferents from there to the hypothalamus then activate the appropriate visceral and motor responses. Thus, the amygdala is involved in linking perception with visceral and behavioral responses and with memory. In relation to this, it is well known that events or facts associated with strong emotions are more likely to be remembered than emotionally neutral facts or events. Traumatic events can also be remembered easily: People who grew up in the 1960s remember the assassination of John F. The events of September 11, 2001 will always be linked to memories of "where we were when we heard the news. The amygdala works together with, and appears to enhance the function of, the memory system of the hippocampus and associated cortical areas (medial temporal lobe memory system) during memory formation. If the amygdala is damaged, the normal facilitation of attention for and memory of emotional stimuli is greatly reduced or absent entirely. Fear and fear conditioning: the amygdala and its circuitry are key components of the system involved in the recognition and interpretation of emotional behaviors or signals from others. It is also critical for the ability to feel strong emotions (such as fear) personally. A frightening mask (Medusa), for example, can evoke the emotional reaction of fear (see Figure 20. The close link between the amygdala and the medial temporal lobe memory system is important in mediating the acquisition, storage, and expression of fear memory. Following surgery, she could recognize the faces of people who were familiar to her before the operation and performed well on a face-matching task involving faces with neutral expressions. In particular, recognition of fear was differentially severely affected, and recognition of anger and, to a lesser extent, disgust, was also impaired. Similarly, she showed impaired perception of vocal affect, with intonation patterns related to fear and anger particularly affected. Fear conditioning is a form of emotional learning in which a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus) becomes associated with an aversive event (the unconditioned stimulus) such that, similar to conditioned reflexes (described above), presentation of the conditioned stimulus alone can elicit defensive or fear-related behavior and the appropriate visceral and endocrine responses (see Figure 20. Importantly, in humans with damage to the amygdala, processing of social signals of fear and anger is severely impaired, regardless of the input modality. Visceral responses to fear appear to be mediated by the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) through its connections with the midbrain periaqueductal gray, the reticular formation, and the hypothalamus. Vasopressin excites neurons in the medial part of the CeA, which stimulates fear responses. Thus, a balance between vasopressin and oxytocin receptor expression may gate visceral responses to fear, particularly under stressful conditions. Reward and the amygdala: the amygdala has been shown to be just as important for processing positive reward or affect as it is for negative affect. For example, studies were performed in which pictures of faces were associated with positive, negative, or neutral information about a person, or in which abstract images were paired with a high, medium, or low probability of a food reward. The amygdala was shown to mediate an association between sensory inputs and their affective value and to be key in mediating both positive and negative emotions. An interesting finding from these studies is that object-value or object-affect associations that formed during the experiment were not always consciously appreciated by the subjects. Reward Circuitry behave under their influence in making decisions or choices during the test. Together, the research described above highlights the importance of the amygdala in influencing our day-to-day functioning in the environment, even when we are not consciously aware of influences from the environment that have altered our thinking, preferences, or emotions. Imaging of the amygdala has been important in demonstrating that the neural circuitry of emotion and the neural circuitry of cognition interact extensively and that emotion cannot be easily separated from cognitive processing. The amygdala has extensive connections to brain areas thought to underlie cognitive function, such as sensory areas of cortex, the prefrontal cortex, and the hippocampus. Through these connections, the amygdala influences emotional learning and memory and can play an important role in attention, perception, and the processing of the emotional content of social interactions. The presence of a reward circuitry in the brain has been hypothesized since intracranial self-stimulation experiments by James Olds and Peter Milner in the 1950s.
Acquired desire disorders among older individuals are probably three times as common antibiotic resistance occurs quickly because buy fucidin 10 gm visa. Perhaps more than half of women at age 55 years have recognized a deterioration in their sexual function bacteria living or nonliving 10 gm fucidin with amex. Perhaps 25% of women in their twenties have difficulty having orgasm and 33% of men less than age 40 claim to ejaculate too rapidly antibiotic 3 pills purchase fucidin 10 gm with amex. They interviewed men and women between age 18 and 59 years and found that sexual dysfunction is common antimicrobial 7287 msds 10gm fucidin otc, particularly among young women and older men. This is noteworthy for psychiatrists because our studies of sexual dysfunction caused by medications or acquired psychiatric disorders tend to assume that patients are generally functionally intact prior to becoming ill or taking medications. The clinician must be wary when one coupled person is presented as having a sexual dysfunction and the partner is presented as "normal". Sexual dysfunction in a couple is a two-person problem in terms of immediate effects and often in terms of cause as well (Table 57. How a partner regards the sexual characteristics of the other is a subtle ingredient of sexual comfort, competence and dysfunction. Individual psychotherapy is often insufficient to help coupled patients improve their sexual life; 4. Sexual desire diagnoses are often made in persons who have adequate drive manifestations. Children and adolescents acquire values, beliefs, expectations and rules for sexual expression. Young people have to fi nd a way to negotiate their way through the fact that their early motives to behave sexually frequently coexist with their motives not to engage in sexual behavior. Confl icted motives often persist throughout life but the reasons for the confl ict evolve. A teenager possessed of considerable drive and motive to make love may inhibit all sexual activities because of moral considerations emanating from religious education or the sense that he or she is just not developmentally ready yet. The doctor should have separately explored his drive manifestations, his sexual motivation to exchange sexual pleasure with his wife in recent years and his wish for sexual rejuvenation. The appearance and disappearance of sexual desire is often enigmatic to a patient, but its ebb and flow result from the ever-changing intensities of its components, biological drive, psychological motive and socially acquired concepts, wish (Table 57. In women, this interplay is generally more difficult to delineate because drive and motive are sometimes inseparable. The Problems of Sexual Desire Sexual desire manifestations are diverse: erotic fantasies, sexual dreams, initiation of sexual behavior, receptivity to partner-initiated sexual behavior, masturbation, genital sensations, heightened responsivity to erotic environmental cues and sincere statements about wanting to behave sexually. For most of the 20th century, these have been referred to as manifestations of libido. Clinicians will find it far more useful to conceptualize that the diverse and changeable desire manifestations are produced by the intersection of three mental forces: drive (biology), motive (psychology) and wish (culture). Drive By only partially understood psychoneuroendocrine mechanisms, the preoptic area of the anterior-medial hypothalamus and the limbic system periodically produce sexual drive. Drive is recognized by genital tingling, heightened responsivity to erotic environmental cues, plans for self or partner sexual behavior, nocturnal orgasm and increased erotic preoccupations. Although people can become aroused and attain orgasm without evident drive, it propels the entire sexual psychophysiological process. While men as a group seem to have significant more drive than women as a group, in both sexes, drive requires the presence of a modest amount of testosterone. Drive is frequently dampened by medications that act within the central nervous system, substances of abuse, psychiatric illness, systemic physical illness, despair and aging. The differences between the two revolve around the emotional intensity with which the patient avoids sexual behavior. When visceral anxiety, fear, or disgust is routinely felt as sexual behavior becomes a possibility, sexual aversion is diagnosed. It is present in at least twice as many women than men; female to male ratio for aversion is far higher. Like all sexual dysfunctions, the desire diagnoses may be lifelong or may have been acquired after a period of ordinary fluctuations of sexual desire. Acquired disorders may be partner specific ("situational") or may occur with all subsequent partners ("generalized"). Disorders of desire are often listed as "of unknown etiology", but clinicians should be skeptical of this idea because: 1.
One of the record number of times reported was someone who said that he had been self manipulating his upper back for 25 years every 5-10 minutes! After his first Prolotherapy treatment he reduced it even further to 2 or 3 times per day treatment for uti macrobid discount 10gm fucidin free shipping. Obviously we urged him to completely stop bacteria h pylori espanol order fucidin 10gm overnight delivery, so that he could allow the Prolotherapy to do its job: strengthen and tighten loose ligaments and joints virus definition biology buy cheap fucidin 10gm. Patients who already have loose or lax ligaments should avoid these entirely because high velocity manipulations can put extra strain on ligament tissue antibiotic resistant e coli buy fucidin 10gm without prescription, further causing it to become damaged or lax. Those with this condition already have loose ligaments to begin with, so if they continue to receive high velocity adjustments on a regular basis they could potentially set themselves up for further pain and complications. If you need to self manipulate or receive chiropractic manipulation repeatedly then you need to consider resolving the issue with Prolotherapy. We feel our comprehensive approach at Caring Medical is highly effective and our study results prove that. This means that all of the injured structures are treated with a strong enough solution to heal the area in a reasonable period of time. We have heard of people getting 30 or 40 sessions of Prolotherapy without good results, or receiving three injections during a Prolotherapy session for the lower back. As this book discusses, most people are cured of their pain with 3-6 Prolotherapy sessions. If by the sixth Prolotherapy session, a patient has not experienced significant improvement, we search for an additional cause of his/her pain. A general rule of thumb when receiving the HackettHemwall-Hauser technique of Prolotherapy, is to receive 30 to 40 injections for an extremity (knee, ankle, or shoulder) and anywhere from 50 to 80 injections for the neck, back, or thoracic spine. As you Prolotherapy, but most likely can see, it is a much more comprehensive treatment trigger point injections. Some doctors who administer cellular forms of Prolotherapy, such as Platelet Rich Plasma or Stem Cell Prolotherapy, will only provide one injection into the joint. We find that the entire support structure of the joint needs to be treated in order to fully treat the painful area. This involves injecting at all of the attachments that support the joint versus just providing one injection into the joint. Another reason for suboptimal results with Prolotherapy is due to inadequate inflammation with the Prolotherapy treatment. In some people, stronger Prolotherapy solutions are needed to achieve an adequate inflammatory reaction after the treatment. Until the injured structures are completely treated with Prolotherapy-with a strong enough solution-Prolotherapy has not failed. If the stiffness after the treatment lasts only a few hours, then the immune reaction to the treatment, most likely, will not be enough to regenerate the connective tissue needed for healing. First, figure out why you have a poor immune response by doing metabolic, nutritional, and hormonal testing, or, second, use a stronger Prolotherapy solution. Physicians who have a lot of experience doing Prolotherapy may have a dozen different solutions they can use, depending on the individual case. If you do not feel rested in the morning or if you rely on an alarm clock to wake you up, you may not be getting enough sleep. Insomnia is a common cause of chronic fatigue, body pain, poor concentration, anxiety, depression, and poor athletic performance. Mednick documents very well in this book how there are two periods of drowsiness one during the day but another one just after lunch. Blood cortisol levels are supposed to be high in the morning and low in the evening. The high levels in the morning help you wake up and the low levels in the evening help you feel tired in preparation for sleep. Excessive thirst or urination can, however, be related to a significant problem called diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus can cause dehydration, joint pain, vertebral disc dehydration, cartilage problems, dizziness, and fatigue.
Fucidin 10 gm low price. Pharmacology – ANTIBIOTICS – DNA RNA FOLIC ACID PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS (MADE EASY).