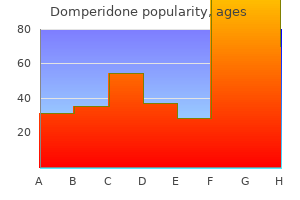
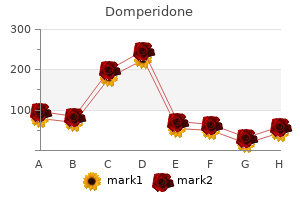
Domperidone
"Discount 10 mg domperidone mastercard, medicine 1975".
By: P. Einar, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Program Director, Montana College of Osteopathic Medicine
School professionals often play an instrumental role in referring a child or adolescent whose correct diagnosis may have otherwise been missed by medical professionals or family members medicine rap song 10mg domperidone with amex. We hope this information helps you make referrals for some of your students whose pattern of symptoms may be very complicated treatment zit order domperidone 10 mg with amex. After all symptoms 37 weeks pregnant discount domperidone 10 mg overnight delivery, the sooner they get the proper diagnosis and support they need treatment impetigo buy domperidone 10mg otc, the more quickly and fully they will achieve their potential. Whenever a psychiatric or psychological disorder is suspected, it is important that a qualified diagnostician conduct a comprehensive assessment and render treatment recommendations. School professionals who have the opportunity to observe the student in a wide variety of circumstances may provide the information essential to making the correct diagnosis. Consider the following diagnostic challenges: A child who is anxious about speaking in public may not only have a common phobia. The same behaviors occur in both children, but there may be very different causes or triggers. The function of the behavior may influence both the diagnosis that is rendered and the treatment that is recommended. It may be particularly difficult to make the distinction between compulsive and self-stimulatory behaviors with children who lack strong communication skills. The appropriateness of specific medical treatments is clearly tied to the correct diagnosis. When the teacher asks about this behavior, he states, "I was just talking to my friends. It " is clear to the front-line interventionists that this child was not speaking to any friends in the classroom! Asking children who are on the spectrum about "hearing voices" or "seeing strange things" is likely to elicit some unusual and misleading responses as well. However, she is referring to people downstairs, down the hall, or outside - not in her head. They may or may not realize that what they are acting out is make-believe or pretend play. If asked, he may insist that he is Spiderman and may have a tantrum when you challenge this statement. He is not truly psychotic, but he may benefit from some guidance in reality testing - mostly for his own safety and the safety of others. While these conditions may be co-morbid, you should consult a qualified professional with sufficient experience with both disorders if a psychotic disorder is suspected. It may not be readily apparent, however, what that environmental stressor might be. They are often inadvertently taught to respond to limit-setting in a negative manner. When positive behavioral supports are provided, they are often able to restructure their responses in a positive and motivated way. In contrast, the child on the autism spectrum may act out because the noise in the next room is highly distressing even though it does not bother any of the other students in the classroom. He may rock back and forth, cover his ears in response to the "noise, " and hit the girl next to him who tries to console him. He is unlikely to calm down until the sensory stressor is removed, or until he has become accustomed to the sound (this is not likely to happen quickly). Determining what caused the behavior in the first place often leads to an accurate diagnosis. Consider the following diagnostic challenges: Children with bipolar disorder can be explosive, impulsive, and highly aggressive. Their symptoms are often cyclical and follow a pattern over time that can be tracked and monitored. However, most people do not regularly monitor these behaviors in a way that makes the pattern readily apparent.
Syndromes
- Depression
- Loss of appetite
- Nezelof syndrome
- Do you wear tight pants or tight pantyhose?
- Chest pain
- Is there any history of a head injury or drug use?
- Loss of sense of vibration and position
- Vision is 20/20 by age 4
In incarcerated subjects ok05 0005 medications and flying cheap domperidone 10 mg line, studies found that one-third of the subjects that committed homicide had used marijuana twenty-four hours before the homicide symptoms 9 weeks pregnant purchase domperidone 10 mg line. Further medicine hat mall cheap domperidone 10mg with visa, three-quarters of those subjects were experiencing at least one mental or physical effect from marijuana intoxication when the homicide occurred medicine pacifier safe domperidone 10mg. Similarly, individuals in remote Aboriginal Australian Communities who reported current cannabis use were nearly four times more likely than nonusers to present at least once for violent trauma. Homicide offenses have been repeatedly documented to be connected to drug use, and marijuana is often one of those drugs [26]. Consistent use of marijuana during adolescence was the most predictive indicator of intimate partner violence [28]. Also, marijuana use during adolescence was associated with perpetration or both perpetration and victimization by an intimate partner in early adulthood [29]. There is also a positive association between peer victimization and cannabis use in adolescents. Cannabis use is likely to be associated with perpetrator victims, those who initiate violence while using marijuana and experience retaliation to their aggressive acts. This trend suggests that cannabis use might be strongly related to outward aggression by the user [30]. In particular, mental effects of cannabis have the potential to decrease the ability to accurately identify, evaluate, or avoid potentially dangerous persons or situations [25]. The risk of individuals having a psychotic disorder showed a roughly three times increase in users of skunk-like cannabis (highpotency) compared with those who never used cannabis. Use of skunklike cannabis everyday conferred the highest risk of psychotic disorders compared with no use of cannabis [6]. Direct administration of cannabis resulted in predictable increased occurrence of paranoia in comparison to those who received placebo. Epidemiological studies showed that cannabis is the most frequently used drug among those diagnosed with bipolar disorder [5]. Studies have also shown that as the frequency of cannabis use increases, so does the risk for psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia [38]. The investigators of Schizophrenia Commission concluded that cannabis use is the most preventable risk factor for psychosis [39-44]. High proportions of persons with schizophrenia report regular cannabis use and meet criteria for cannabis use disorder [45]. Findings suggest that activity in the basal lateral medulla is involved in marijuana-induced paranoia (state of becoming afraid of things that would normally trigger fear) [44]. That means marijuana is actually enhancing type of learning about fear, leading the brain to jump to conclusions about the mild experiences, perceiving them as scarier as and more strongly connected to other scary situations than they are. This marijuana induced fear-based learning helps explain why marijuana users tend to see patterns in events that are not real, such as conspiracies [45] (Table 1). In a study analyzing a college population, heavy users of marijuana displayed significantly greater impairment than light users on intentional/executive functions. This led to the conclusion that heavy marijuana use is associated with residual neuropsychological effects even after a day of supervised abstinence from the drug [46,47]. Cases of Marijuana Use and Symptoms Case Michael Brown Trayvon Martin Laquan McDonald Devon Guilford Freddie Gray Lakeisha Holloway Robert Lewis Dear Joseph Jesse Aldridge Gerard Lee Loughner Tsarnaev Brothers Khalil Abu-Rayyam Symptoms Aggressiveness, Personality Change, Paranoia Aggressiveness, Personality Change, Paranoia Aggressiveness, Personality Change Aggressiveness, Personality Change Paranoia Aggressiveness, Personality Change Psychosis Psychosis Aggressiveness, Personality Change, Psychosis Aggressiveness, Personality Change Psychosis Studies show psychosis and paranoia Cannabis intoxication leads to acute psychosis in many individuals and can produce short-term exacerbations of pre-existing psychotic diseases [31-34]. Cannabis use also causes symptoms of depersonalization, fear of dying, irrational panic and paranoid ideas which coincide with acute intoxication and remit quickly [35]. It was reported that 15% of cannabis users identified psychotic-like symptoms, the most common being hearing voices or having unwarranted feelings of intimidation and persecution or paranoid thoughts [36]. Discussion We apply the results of the research regarding the role of marijuana in violence. We use concepts such as personality changes, perpetrator violence, and psychosis to establish our association of marijuana with the unfortunate cases. The purpose is to illustrate negative but preventable tragic outcomes due to marijuana and its role in violence. The overall objective is to identify the role of marijuana and to suggest it is avoidable and causal nature in inducing violence [48-50].
Purchase domperidone 10 mg with visa. FM102/1 Summerfest Atlas Genius.
There are many clues that the family can give you before you even identify the first individual medicine zalim lotion cheap 10 mg domperidone with visa. First the number and composition of the group might help medicine 95a pill purchase domperidone 10 mg visa, then the area the group is found in may add another piece to the puzzle; and even the behaviour of the members treatment zinc deficiency order 10mg domperidone mastercard, whether they run away or are tolerant treatment table buy generic domperidone 10 mg line, might be suggestive of who they are. But of course, ultimately you will have to look at their ears and tusks and body characteristics to identify the individuals. If you can recognise one adult female, the chances of identifying the others are much improved. For this reason it is generally best to file the recognition cards by family rather than by age or ear characteristics. Thus once you find the card for the known individual and then look through the cards for the other family members, you should be able to identify the other adults fairly quickly. Needless to say, you cannot assume that the others are present or that there are no new ones there. This system of indexing ensures that duplicates can be readily produced from the negatives and provides a means of matching each photo with the field notes recorded at the time. It might also be helpful to include information on where and when the animal was first seen. If you will be dealing with a large population and do not expect to resight individuals often, you could include each sighting of the individual on the back of the card. The types and topic of your study will determine how you will design the data base. You will save youeself much tedious work and dissapointment if the record-keeping is efficient and flexible. A computer is probably essential in most cases, but where one is not available good check sheets (see Chapter 10) and other t kinds of record sheets on which tabulations can easily be made are invaluable. A variety of direct measures of stature and weight, as well as a number of techniques for non-invasive assessment, have been attempted. A number of studies have measured shoulder height in wild African elephants, using a variety of photographic techniques (Douglas-Hamilton 1972; Croze 1972; Jachmann 1988; Lee & Moss 1995). These techniques rely on using either a reference height during photographing, or measuring the distance to the elephant for a known lens focal length. The elephant as measured on the photograph can then be compared with the pole measures on the second photograph (Western et al. Another similar technique is to use a lens with a fixed digital caliper to accurately measure lens extension (invented for whales, Jacobsen 1991) to photograph the elephant. The extensions are calibrated against known pole heights and a simple linear formula then can be derived for relating the extension recorded in the field when photographing the elephants to the distance measured on the print. Photographic techniques are quick and relatively accurate, although expensive in terms of film. Another statural measure that gives reliable information about size and age is that of backlength. This can be recorded in the same way as shoulder height, and such measures can also be made from an aeroplane traveling at a specific height (Croze 1972). Again, some calibration against a known measure must be made for each flight and height. The differences between measures of total head to anal flap backlength and scapula to anal flap backlength appear to be relatively unimportant (Lindeque & van Jaarsveld 1993), and both give reliable indices of overall size. It is also possible to estimate stature indirectly, especially in populations living in areas where a good impression of the hind footprint length can be obtained. Hind footprint length is known to relate to shoulder height and age in African elephants and thus can be used to assess age distributions in a population as well as overall size of the animals (Western et al. This measure can be reliably determined, and is easily replicated across observers. The length from the hell of the foot through to the arch (rather than the tip) of the toe is made on footprints which are clearly visible and not in deep soil, mud or sand.
Diseases
- Nakajo syndrome
- Basilar artery migraines
- Cleidocranial dysplasia micrognathia absent thumbs
- Syringocystadenoma papilliferum
- Plasmacytoma anaplastic
- Pancreatic islet cell neoplasm
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3