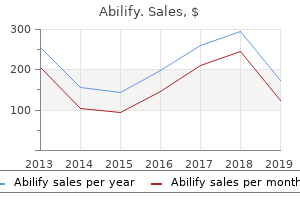
Abilify
"Discount abilify 10 mg with visa, anxiety tips".
By: N. Rhobar, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of South Florida College of Medicine
Proper patient selection jobless depression symptoms cheap 20 mg abilify overnight delivery, dosage depression symptoms memory problems cheap abilify 5mg without a prescription, and i nstr uctions are important to avoid hypoglycemic episodes depression symptoms behaviour purchase abilify 10 mg on line. At such t imes depression screening purchase 20 mg abilify with visa, it may be necessary to discontinue glyburide and administer insulin. Th is has been reported more frequently with the use of agents with prolonged half -l ives. Proper patient selection, dosage, and i nstr uctions are important to avoid hypoglycemic episodes. At such t imes, it may be necessary to discontinue glyburide and administer insulin. Th is has been reported more frequently with the use of agents with prolonged half -l ives. If the fasting blood glucose value is greater than 200 mg/dL, the starting dose is 250 mg/day as a single dose. If the patient is malnourished, underweight, elderly, or not eating properly, the initial therapy should be 100 mg once a day. There are no specific dosage adjust ments provided in product labeling for patient s with renal impairment; however, conservative initial and maintenance doses are recommended because t olazamide is metabolized to active metabolit es, wh ich are eliminated in the urine. Following a single oral dose of t rit iated tolazam ide, 85% of the dose was excreted in the urine and 7% in the feces over a fiveday period. Most of the urinary excretion of the drug occurred w ithin the first 24 hours post admi nistration. Renal insufficiency may cause elevated blood levels of tolazamide, which increase the risk of serious hypoglycemic reactions. Elderly patients are prone to develop renal insufficiency, which may put them at risk of hypoglycem ia. At such t imes, it may be necessary to discontinue glipizide and administer insuli n. Transfer of patients from other oral antihyperglycem ic regimens to tolbutamide tablets should be done conservatively. There is no dosage adjustment provided in product labeli ng for patients w it h renal impairment; however, conse rvat ive initial and mai nt enance doses are recommended. Proper patient selection, dosage, and i nst r uctions are important to avoid hypoglycemic episodes. Th is has been reported more frequently with the use of agents with prolonged half -l ives. If there is inadequate glycemic control, the dose can be increased in 15 mg increments up to a maximum of 45 mg once daily. If abnormal, use caution when treating with Acros, investigate the probable ause, treat (if possible) and follow appropriately. Renal elimination of pioglitazone is negligible, and the drug is excreted primaril y as metabolites and their conj ugates. It is presumed that most of the oral dose is excreted into the bile either unchanged or as metabolites and eliminated in the feces. Therefore, no dose adj ustment in patients with rena l impairment is requ ired with pioglitazone monotherapy. In postmarketing experience, reports of new onset or worsen ing edema have been received. Because thiazolid inediones, including pioglitazone, can cause fl uid retention, wh ich can exacerbate or lead to congestive heart failure, pioglitazone shou ld be used with caution in patients at risk for congestive heart fa ilure. Caution shou ld also be advised with the use of pioglitazone in patients with underlying renal impairment who may already be at risk of volume overload. After init iation of Actos, and after dose increases, monitor patients carefully for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart fa ilure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of ca re and discontinuation or dose reduction of Acros must be considered.
According to standard descriptions anxiety 9 year old son buy abilify 15mg cheap, the cranial root is formed by a series of rootlets that emerge from the medulla between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle depression checklist buy cheap abilify 5mg. These rootlets are considered to join the spinal root anxiety breathing best 10 mg abilify, travel with it briefly anxiety 4 hereford bull cheap abilify 10mg otc, then separate within the jugular foramen and are distributed with the vagus nerve to supply the musculature of the palate, pharynx and larynx. All the rootlets that form the accessory nerve arise caudal to the olive and no connections can be demonstrated between the accessory nerve and the vagus in the jugular foramen. The accessory nerve thus has no cranial component and consist only of the structure hitherto referred to as the spinal root of the accessory nerve. This spinal root is formed by the union of fibres from an elongated nucleus in the anterior horn of the upper five cervical segments, which leave the cord mid-way between the anterior and posterior roots, join, then pass upwards through the foramen magnum. The accessory nerve and the converging rootlets of the vagus nerve then enter the jugular foramen in a shared sheath of dura. The glossopharyngeal nerve enters the jugular foramen anterior to the vagus through a separate dural sheath. The spinal root passes backwards over (or less often deep to) the internal jugular vein (see. It then crosses the posterior triangle of the neck to enter the deep surface of the trapezius about 5 cm above the clavicle. Isolated lesions of the cranial root of the accessory nerve are infrequent; more commonly it is involved concomitantly with the vagus when it gives rise to paresis of the laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles, resulting in dysphonia and dysphagia. Division of the fibres of the spinal root (or lesions affecting their cells of origin) results in paresis of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. This follows, for example, most block dissections of the lymph nodes of the neck, the nerve being sacrificed in clearing the posterior triangle. It is easy to draw the surface markings of the accessory nerve; one merely constructs a line from the tragus to a point along the anterior border of the trapezius 5 cm above the clavicle. This line will cross the transverse process of the atlas and also the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the posterior border of sternocleidomastoid. From its nucleus, which is part of the somatic efferent column and which lies in the floor of the 4th ventricle, a series of about a dozen rootlets leaves the side of the medulla in the groove between the pyramid and the olive (see. These rootlets unite to leave the skull by way of the anterior condylar, or hypoglossal, canal. Lying at first deep to the internal carotid artery and the jugular vein, the nerve passes downwards between these two vessels to just above the level of the angle of the mandible. On hyoglossus, the nerve is related to the deep aspect of the submandibular gland and then lies inferior to the submandibular duct and the lingual nerve. It then passes on to genioglossus and ends by being distributed to the muscles of the tongue. The hypoglossal nerve receives an important contribution from the anterior primary ramus of the 1st cervical nerve at the level of the atlas. The majority of these C1 fibres pass into the descendens hypoglossi, which is given off as the main trunk of the nerve crosses the internal carotid artery. This descending branch passes downwards on the carotid sheath and is joined by descendens cervicalis derived from C2 and 3, to form a loop, the ansa hypoglossi (see. Other C1 fibres are transmitted by the hypoglossal nerve to thyrohyoid and geniohyoid. Division of the hypoglossal nerve, or lesions involving its nucleus, result in ipsilateral paralysis and wasting of the muscles of the tongue. This is detected clinically by deviation of the protruded tongue to the affected side. Supranuclear paralysis (due to involvement of the corticobulbar pathways) leads to paresis, but not atrophy, of the muscles of the contralateral side. Part 7 the Anatomy of Pain this page intentionally left blank Introduction Our understanding of the human nervous system is incomplete. Much of the knowledge of the anatomy and neurophysiology of pain comes from animal studies and clinical observations in humans with damaged nervous systems. The following chapter is not, like most anatomical texts, based on the observations of the anatomist, but more on the work of neurophysiologists and clinicians. As the importance of pain management increases in anaesthetic practice, so does the relevance of a sound knowledge of the basis of pain transmission and perception.
If a first skin biopsy does not provide an answer anxiety 10 weeks pregnant cheap abilify 20mg without a prescription, it is often necessary and appropriate to resample the area depression medication list buy 5 mg abilify otc. The barrier function of damaged skin is impaired depression definition meteorology order 5mg abilify mastercard, but protection can be provided with dressings as well as by minimizing scratching and avoiding abrasive clothing depression causes cheap abilify 15mg on line, soaps, and chemicals. Removal of debris, such as excessive scale, hyperkeratoses, crusts, and infection, is also crucial. Topical and systemic medications, dressings, and other treatments can alter skin temperature and blood flow and thus favorably affect the metabolism of the skin. Water, with or without various additives, can provide many benefits to the skin, including soothing comfort, antipruritic effects and increased rate of epidermal healing with hydration and debridement of crusts, dead skin, and bacteria. The tub should be one-half full and the soak should last no longer than 20 to 30 minutes to avoid maceration. Medicated baths can evenly distribute soothing antipruritic and anti-inflammatory agents to widespread lesions. Warm baths cause vasodilation and may increase itching; cool baths constrict vessels and usually soothe pruritus. The best time to apply lubricants is immediately after the bath so that they may hold water in the hydrated stratum corneum. Water and medication can be applied to the skin with dressings (finely woven cotton, linen, or gauze) soaked in solution. For maximal benefit from evaporation, dressings should be no more than a few layers thick and should be reapplied every few minutes for 15 to 30 minutes several times a day. Wet compresses, especially with frequent changes, provide gentle debridement of crusts, scales, and cutaneous debris. If the compresses are permitted to dry (wet to dry compresses) and become adherent, the debriding effect is increased but there may be further damage to the skin. Wet compresses also leach water-binding proteins from the stratum corneum and epidermis and lead to later skin dryness, which is desirable for 2273 treating acute vesicular, bullous, oozing, or weeping conditions as well as for crusty, swollen, and infected skin. Open wet dressings are applied directly to the skin, leaving the dressing exposed to the air to evaporate. Frequent reapplication debrides exudate, crust, and bacterial contamination and also dries out the skin, thus rapidly decreasing oozing and weeping. Closed wet dressings, in which the moist fabric dressings are applied to the skin and covered with an impervious material such as plastic, oil cloth, or Saran wrap, may be useful when maceration and heat retention are required. For example, closed wet dressings may be appropriate when there is excessive keratin of the palms or soles or when an early abscess needs heat to localize the infection. Dry dressings protect the skin from dirt and irritants and can be used to apply medications, prevent scratching and rubbing by the patient or from clothing and sheets, and keep dirt away. In cases of neurodermatitis or stasis dermatitis, dry dressings often are left in place for several days. The medication most commonly added to baths and dressings is aluminium acetate, which coagulates bacterial and serum protein. Wounds may also be cleansed and debrided by absorption beads or granules that absorb debris and exudate from wounds (Debrisan, DuoDerm granules), hydrogen peroxide, whirlpool treatments, and various enzymatic products, including trypsin/chymotrypsin, fibrinolysin, collagenase, and streptokinase. Antimicrobial agents are seldom applied by surface dressings because huge quantities would be required to reach therapeutic concentrations. Occlusive dressings can treat acute wounds and chronic venous, diabetic, and pressure ulcers. In general, these materials provide good protection, help promote healing, and provide pain reduction of skin ulcerations. Most topical medications consist of two major agents, the active ingredient or specific medications, and the vehicle or base in which the active material is dissolved. Powders promote dryness by absorbing evaporative moisture, and they reduce maceration and friction in intertriginous areas. As water evaporates on the skin surface, it collects and leaves a uniform film of powder behind. Creams are emulsions of oil in water (more water than oil); they vanish into the skin because water evaporates and the residual oil is spread thinly and imperceptibly over the skin. Ointments consist of oils with variably smaller amounts of water added in suspension; they have a pleasant lubricating effect on dry or diseased skin, but they give a greasy feeling to the skin and clothing.
The nerve action potential from a mixed nerve is predominantly from large afferent fibers mood disorder mental illness buy abilify 10mg with amex. Components resulting from activation of small myelinated (delta) fibers and C fibers cannot be identified bipolar depression symptoms in women buy 15mg abilify with visa. Special techniques of measuring distribution of conduction in the activated axons have generally not been accepted anxiety at night buy generic abilify 20mg on line. Changes in the motor fibers depression symptoms icd 9 buy cheap abilify 5 mg on line, as occurs in certain diseases, may affect the conduction time along the fibers. Compound Muscle Action Potentials 345 Mechanisms of Conduction in Myelinated Fibers Conduction in myelinated fibers is saltatory. The action potential jumps from one node of Ranvier to the next, with the action potential of one node providing the current that excites the subsequent node. Conduction velocity is determined by the time required for one node to excite the next. Thus, if the distance between two nodes (internodal distance) is 1 mm and the nodal conduction time is 20 s, the conduction velocity is 50 m/second. The time required for one node to excite the next node is determined by several factors: 1. The faster the rate of rise of the action potential at node 1, the more rapidly node 2 will be activated. The smaller the amount of current required to neutralize the charge held by the membrane capacitance of node 2 and to depolarize the nodal membrane to threshold, the more rapidly an action potential will appear at node 2. Large myelinated fibers have a lower membrane capacitance than unmyelinated fibers and hence have a faster conduction velocity. The more current that is lost in neutralizing the charge across the axonal membrane in the internode and by leakage through the myelin, the longer it will take to activate the next node. Large myelinated fibers lose less charge and hence have a faster conduction velocity. The higher the resistance to current flow in the axoplasm from node 1 to node 2, the longer it will take to activate node 2. Large myelinated fibers have lower resistance than unmyelinated fibers and hence have faster conduction velocity. Mechanisms of Slow Conduction in Disease Paranodal demyelination increases the capacitance of the internodal membrane. More current is needed to neutralize the charge across the internodal membrane and less is available to discharge node 2. Segmental demyelination results in a more profound increase in capacitance and decrease of resistance across the internodal membrane. In smaller diameter fibers, conduction may become continuous, as in unmyelinated fibers, instead of saltatory. It has been consistently shown that there are compressive signs and flattening at the site of compression distally in the carpal tunnel and swelling with an increased cross sectional area at the most proximal aspect of the carpal tunnel. It is the demonstration of the enlarged nerve proximal to the compression that is most reproducible in ultrasonography evaluation and hence is what is measured. Simultaneous reduction in internodal membrane capacitance because of reduced membrane area does not compensate for the higher resistance. With the loss of large-diameter fibers because of conduction block or degeneration, conduction measurements reflect conduction in smaller diameter, more slowly conducting fibers instead of the slowing of conduction in larger fibers. This may account for the slow conduction observed in segments proximal to a focal lesion instead of reflecting an extension of the lesion proximal to the site of compression. With decreased myelin thickness, particularly during remyelination, the number of myelin lamellae is small in proportion to fiber diameter. The capacitance and conductance of the internodal membrane are high, the loss of current through the internode is more than normal, and a longer time is required to excite the next node. Other possible factors in the slowing of conduction are altered characteristics of the nodal membrane, which affect the generation of the action potential.
The results depression dsm cheap 20 mg abilify mastercard, which were encouraging overall depression symptoms numbness order abilify 20 mg fast delivery, are now excellent owing to repair surgery that is perfect from the anatomical aspect and provides exceptional functional results depression hashtags proven abilify 5mg. The only issue that remains to be resolved is to simplify this technique so that it can be performed in acceptable operating times depression test detailed buy discount abilify 5mg on line. Only a thorough evaluation of all defects that need to be treated will allow surgical repair in a single operative session and minimize the risks of postoperative functional sequelae and recurrences. Standard clinical examination must attempt to define the degree of prolapse involving the uterus, bladder and rectum. Lateral cystocele with the vaginal rugae preserved must be distinguished from central cystoceles with elimination of the vaginal rugae. The former is due to detachment of the vagina from the tendinous arc of the pelvic fascia while the latter is due to a break of the vesicovaginal fascia. The muscular tonus of the levator ani muscles must be assessed in terms of quality and quantity. Preparation of the vaginal tissues to promote healing and bowel preparation to optimize the endoscopic space are particularly useful. Preparation begins with a classical low-fiber diet for the five days prior to surgery. This chronological order is particularly important in order to avoid anal leakage on the operating table during surgery, which exposes the patient to a greater risk of infection. Finally, immediately before surgery, a solution of Betadine is applied prior to sterile draping. Optimizing the surgical technique and reducing operating times require ergonomic management of the operation, and correct arrangement of the patient is fundamental. The patient must be positioned well down the table the better to allow movements of the uterine manipulator. The greater the possibilities for moving the uterine manipulator, the better will be the exposure of the different organs during surgery. The abdominal wall and vagina are disinfected carefully and the operation area is prepared prior to introduction of the Foley catheter and uterine manipulator. It is imperative that the perineal region is sterile and accessible to the surgeon, who should perform a vaginal or rectal examination during the operation and position the uterine manipulator. Muscle relaxation is necessary only where it is not possible to obtain sufficient distension of the abdominal wall with a pneumoperitoneum of 12 mmHg. General anesthesia can be combined with locoregional epidural or spinal anesthesia to improve the postoperative course. This position allows three surgeons to take up position: the operating surgeon is situated on the left of the patient. The first assistant stands opposite to the surgeon on the right side of the patient, and the second assistant is positioned between the patient`s legs. The balloon is inflated with 15cc of saline and the catheter is placed under traction to make it easier to demonstrate the bladder neck. The catheter is connected to a collecting bag which is placed in visible position so that the urine can be monitored (volume, color, presence of air in the bag). This reassessment under anesthesia can provide new information that may modify the operative strategy. The assessment is performed with the aid of vaginal dilators and will allow evaluation of the line of the vagina and better distinction of its upward and downward movements. This will also allow a better assessment of the retrovaginal space and its mobility. In the event of hysterectomy, assessment of the size and mobility of the uterus will allow correct choice of trocar positions. The obesity of the abdominal wall must be assessed because the trocars are easier to position where the wall is thinner. However, more elastic areas should be avoided because of the difficulty if they need to be reinserted. The laxity of the peritoneum will give an idea of the operation space and the positioning of the trocars will therefore depend on this. If the size of the uterus is normal or below normal and the pubis-umbilicus distance is sufficient, this trocar will be used for the laparoscope; if, on the contrary, the uterus is large and the pubis-umbilicus line is short, this trocar will be the central operating port.
Generic abilify 15mg fast delivery. Physical Signs of Depression & Anxiety.