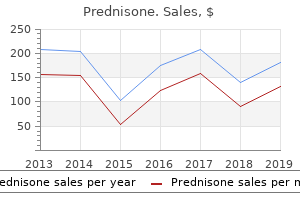
Prednisone
"5 mg prednisone with visa, allergy medicine best".
By: N. Grompel, M.B.A., M.D.
Professor, East Tennessee State University James H. Quillen College of Medicine
Hormones are specific as to which cells they affect and the cellular changes they elicit allergy symptoms vomiting diarrhea order 40 mg prednisone otc. The arrival of a hormone at a target site triggers a sequential series of biochemical events that lead to a specific response (action) kirkland allergy medicine 600 purchase 40mg prednisone amex. The hormone binds to specific allergy center buy prednisone 10 mg low price, high-affinity protein receptors located on the cell surface allergy cream generic prednisone 20mg without a prescription, in the cytoplasm (intracellular), or in the nucleus. Receptors for catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine), polypeptides, and glycoproteins are located on or in cellular membranes. They are generally insoluble in lipids and cannot passively cross the cell membrane. Objective C To define negative feedback and positive feedback and to explain their importance in regulating the secretion of hormones. Su rvey ally, an increased amount of end product inhibits the production, mechanism, or action of a starting substance to prohibit further synthesis of the end product. Example: A B C D Negative feedback involves a cascade, or chain, of biochemical or physiological events. As levels of substance D increase, substance A receives "negative feedback" to prevent the process from continuing to produce more D. By contrast, in the case of positive feedback, D would stimulate A to further produce increased amounts of B, and so on to D. Homeostasis is maintained by the continual adjustments of endocrine function in response to changes in our environment. Negative feedback occurs when the product or result of activity in the endocrine system inhibits the factors that produced the product or result so as to maintain a normal range of values. Positive feedback increases the deviation from normal values and thus is not homeostatic. The secretion of oxytocin during labor accompanying childbirth is a positive feedback mechanism. Oxytocin is then carried by the blood to the uterus, causing the uterine muscles to contract even more vigorously and frequently. These contractions force the baby farther into the vagina, and childbirth is accomplished. Once the baby is born, the pressure stimulus for oxytocin release ends, and the positive feedback mechanism is stopped. Temporal oscillations ranging from a few minutes to 24 hours (circadian) to a year occur in endocrine function (fig. The nature of circadian rhythms has been studied in humans isolated in a soundproof chamber with no time cues. Under such conditions, individuals exhibit certain 24-hour rhythms in hormonal secretion. Differentiation between pathologic and normal blood plasma levels of certain hormones is improved by carefully selecting the time the sample is taken (time of day, month, or year). Unlike other body systems in which the organs are physically hooked together in some fashion, rvey endocrine glands are widely scattered throughout the body with no anatomical continuity (fig. The pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and pineal gland are found within the skull; the thyroid and parathyroid glands are in the neck; the pancreas and adrenal glands are in the abdominal region; the ovaries of the female are in the pelvis; and the testes of the male are in the scrotum. These include the thymus, stomach, duodenum, placenta of the fetus, and even the heart. The pancreas is a mixed gland because it serves the digestive system by secreting pancreatic juice (see problem 19. The gonads (testes and ovaries) are also mixed glands because they serve the reproductive system by producing gametes (see problem 23. Objective E To describe the structure of the pituitary gland and to identify the secretory cells of the anterior pituitary. The pituitary gland is attached to the small, pea-shaped pituitary gland (cerebral hypophysis) is located on the inferior side of the the brain by the pituitary stalk (fig. The infundibulum is the portion of the pituitary stalk that connects the hypothalamus to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
It is assisted in this action by the gastrocnemius muscle allergy shots burning buy 5 mg prednisone fast delivery, which acts to prevent the flexion of the hock allergy shots permanent generic 40mg prednisone fast delivery. The play between the peroneus tertius muscle and the superficial digital flexor muscle ensures that the stifle and hock joints reciprocate their actions; for example allergy eye drops for dogs purchase prednisone 5mg with amex, when the stifle flexes allergy forecast killeen proven 40 mg prednisone, the hock flexes as well. At "stay," the stifle joint is fixed by the contraction of the quadriceps muscle and a locking mechanism involving the patella, which comes to hook on top of the enlarged upper end of the inner trochlear ridge of the femur. A simple contraction of the quadriceps muscle and of the tensor fasciae latae muscle unlocks the patella, lifting it up and laterally off the ridge, thus freeing the stifle so the horse can move. This way, when massaging or assessing a horse in the stay position, you will know what muscles are involved. A solid knowledge of the muscles involved in the different movements of the horse will help you to better locate the muscular tension and possible muscle knots in your horse. The information contained in this chapter will also contribute to you better analysis of all the equine gaits. This better understanding of equine kinesiology will give you confidence when assessing the muscular fitness of your horse. With your knowledge of the bones, muscles, and kinesiology of the horse, we can now talk about the reasons why stretch moves should be part of your massage routine. Regular stretching will benefit your horse and will give you feedback on his condition. Here are some of the benefits of stretching exercises: Relaxation Reduction of overall muscle tension and stiffness Increased circulation of both blood and lymph fluids Increased oxygenation and nutrition in the tissues Increased elasticity of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments Increased flexibility and range of motion of the joints Improved coordination Reduction of muscle strain and ligament sprain Improvement of the stride length Improved reflex time response Note: If your horse has had any recent physical problems that affect the joints and muscles (a fall, direct trauma, kick), or surgery, consult your veterinarian or equine massage therapist before you start a stretching program. A strong prestretched muscle resists stress better than a strong un-stretched muscle. Stretching prevents ligament sprain and loosens the joint capsules; it makes the body feel more relaxed. It releases muscle contracture due to old scar tissue, helps relieve muscle pain from chronic tension, and reduces post-exercise soreness. Better elasticity of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments allows for freer, easier, more controlled, and quicker movements-all resulting in better coordination overall. Muscle stretching increases circulation, bringing more oxygen and nutrients to the body parts; it prevents inflammation and adhesion (scar tissue) formation, trigger point formation, and stress point buildup. You should apply them regularly with your various massage routines and include them in your massage treatments when applicable. Cerebral When we say "cerebral" we refer to the nervous system, which is controlled by the brain and spinal cord. One aspect of stretching can be called cerebral since the activity develops body awareness. And as you stretch various body parts, you help your horse focus on them and become mentally "in touch" with them. The stretching of muscles sends relaxation impulses via sensory nerves to the central nervous system and it will also decrease tension throughout the body. The animal will relax both physically and mentally, an important factor when dealing with animals that have been in accidents or are frightened or in pain. Furthermore, stretching will give you feedback on the condition of the muscle groups and ligament structures, particularly regarding their elasticity and tone. Muscles, tendons, and ligaments (eventually joint capsules) risk damage if stretched when cold. Stretching a horse after a warm-up period will limit the risk of injury from overstretching. Again, if your animal has had any recent physical problems or surgery, particularly of the joints and muscles, or if he has been inactive or sedentary for some time, consult your veterinarian or massage therapist before starting a stretching program. After warm-up and before heavier physical activity, stretching will trigger benefits such as loosening of the muscle fibers, vasodilation to bring more blood, and greater flexibility of the joints. If you need only to stretch a specific area during a localized massage treatment, that area can be warmed up with a hot towel (see chapter 4) or simply by massage (effleurages, wringings, compressions, or shakings). Stretching can be performed as a cool-down immediately after the main exercise or training program. This is actually the best time to stretch because the whole locomotor structure is warm. Stretching will increase circulation, promote relaxation, and cut down on any muscle contracture developed during an intense workout. How to Stretch To attain best results, you need to respect the structures you are working on.
Abduction is movement away from the midline of the body or a body part; adduction is movement toward the midline or a body part allergy symptoms muscle aches best 5 mg prednisone. Rotation is the movement of a bone around its own axis allergy medicine zantac buy cheap prednisone 40mg on-line, without lateral displacement allergy medicine cetirizine order prednisone 20mg amex. Key Clinical Terms Arthritis An inflammatory joint disease allergy medicine effect on liver proven 5mg prednisone, usually associated with the synovial membrane and the articular cartilage. Dislocation Displacement of one bone away from its natural articulation with another. Kyphosis (humpback) An abnormal posterior convexity of the lower vertebral column. Causes include aging, prolonged inactivity, malnutrition, and an unbalanced secretion of hormones. Spina bifida Developmental flaw in which the laminae of the vertebrae fail to fuse. Mitosis resulting in elongation of bone occurs at (a) the articular cartilage, (b) the periosteum, (c) the epiphyseal plate, (d) the diploл. Synovial fluid that lubricates a synovial joint is produced by (a) a meniscus, (b) the synovial membrane, (c) a bursa, (d) the articular cartilage, (e) the mucous membrane. A flattened or shallow articulating surface of a bone is called (a) a tubercle, (b) a fossa, (c) a fovea, (d) a facet. A facial bone that is not paired is (a) the maxilla, (b) the lacrimal bone, (c) the vomer, (d) the nasal bone, (e) the palatine bone. Hematopotesis would most likely take place in (a) the hyoid bone, (b) a vertebra, (c) the maxilla, (d) the scapula. The optic foramen is located within (a) the ethmoid bone, (b) the occipital bone, (c) the palatine bone, (d) the sphenoid bone. An example of a gliding joint is (a) the intercarpal joint, (b) the radiocarpal joint, (c) the intervertebral joint, (d) the phalangeal joint. Teeth are supported by (a) the maxillae and mandible, (b) the mandible and palatine bones, (c) the maxillae and palatine bones, (d) the maxillae, mandible, and palatine bones. The mastoid process is a structural prominence of (a) the sphenoid bone, (b) the parietal bone, (c) the occipital bone, (d) the temporal bone, (e) the ethmoid bone. A joint characterized by an epiphyseal plate is called (a) a synovial joint, (b) a suture, (c) a symphysis, (d) a synchondrosis. Which of the following bones is characterized by the presence of a diaphysis and epiphyses, articular cartilages, and a medullary cavity? Remodeling of bone is a function of (a) osteoclasts and osteoblasts, (b) osteoblasts and osteocytes, (c) chondrocytes and osteocytes, (d) chondroblasts and osteoblasts. A fractured coracoid process would involve (a) the clavicle, (b) the scapula, (c) the ulna, (d) the radius, (e) the tibia. The false pelvis is (a) inferior to the true pelvis, (b) found in men only, (c) narrower in men than in women, (d) not really part of the skeletal system. A fracture of the lateral malleolus would involve (a) the fibula, (b) the tibia, (c) the ulna, (d) a rib, (e) the femur. On a skeleton in the anatomical position, which of the following structures faces anteriorly? The sagittal suture is positioned between (a) the sphenoid and temporal bones, (b) the temporal and parietal bones, (c) the occipital and parietal bones, (d) the occipital and frontal bones, (e) the right and left parietal bones. Surgical entry through the roof of the mouth to remove a tumor of the pituitary gland would involve (a) the mastoid process, (b) the pterygoid process, (c) the styloid process, (d) the sella turcica. True or False 1. Yellow bone marrow in certain long bones of an adult produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Bone matrix is composed primarily of calcium and magnesium, which may be withdrawn in small amounts as needed elsewhere in the body.
Third maxilliped slender allergy testing via blood discount prednisone 20mg online, leg-like; first maxilliped with caridean lobe of exopod distinctly overreaching endite; mandible with prominent incisor process allergy testing la crosse wi generic 10 mg prednisone otc. Second maxilliped with terminal segment broadly ovate allergy treatment sample buy prednisone 10mg overnight delivery, penultimate segment convexly produced mesiad allergy shots post nasal drip order 5 mg prednisone fast delivery, causing endopod to appear bilobate distally. Second maxilliped not markedly bilobate distally; first maxilliped with palp not unusually broad. Palaemonidae caridean lobe acutely produced palp slender endopod not bilobate distally 1 maxilliped st 2 nd maxilliped. Eyes unusually elongate, reaching nearly to distal end of antennular peduncle; first pair of legs about as robust as second pair. Eyes normal in shape, short, not reaching beyond end of first segment of antennular peduncle, sometimes covered by carapace; first pair of legs more robust then second pair. Eyes often partly or entirely covered by carapace; first pair of legs often unequal and swollen. Science series of the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, 39(iviii): 1124. Eyestalks always with a tubercle at middle of inner margins or near base of cornea (very small in Aristaeomorpha). Carapace without postorbital spines; cervical grooves long, extending almost to dorsal midline of carapace. Endopods of second pair of pleopods bearing an appendix masculina (in males) and an appendix interna, but no lateral projection. Colour: typical coloration of deep-sea crustaceans: body reddish or scarlet, sometimes pale white and with red cross bands on abdomen. D eyestalk upper antennular flagellum short 1 2 chelae Aristaeomorpha foliacea female 3 4 5 Habitat, biology and fisheries: the species in this family usually inhabit deep waters, are benthic and prefer soft bottoms. Some of them are actively fished in the area because of their large size (up to 33 cm) and high commercial value. The sexes are easily distinguished by the presence of a large copulatory organ (petasma) on the first pair of pleopods (abdominal appendages) of males, while the females have the posterior thoracic sternites modified into a large sperm receptacle process (thelycum) which holds the spermatophores or sperm sacs (usually whitish or yellowish in colour) after mating. Dendrobranchiata: Penaeidea: Penaeoidea: Aristeidae Similar families occurring in the area 53 Benthesicymidae: only 1 or 2 (occasionally 3) rostral/postrostral teeth; shell soft, thin; upper antennular flagellum long. Solenoceridae: rostrum always armed with more then 3 teeth; either postorbital or postantennal spine present on carapace; upper antennular flagellum long; endopods of second pair of pleopods (in males) with an appendix masculina, an appendix interna and a lateral projection; telson with a fixed spine on each side of tip. Shrimps of the infraorder Caridea: pleura of second abdominal segment overlapping those of first and third segments; no pincers on third pair of pereiopods. Plesiopenaeus rudimentary exopods a) basal part of thoracal appendages b) habitus. Third abdominal segment with posteromedian tooth; carpus of fifth leg shorter than merus. Third abdominal segment without posteromedian tooth; carpus of fifth leg as long as merus. Aristeus varidens 56 List of species occurring in the area the symbol is given when species accounts are included Shrimps and Prawns Aristaeomorpha foliacea (Risso, 1827). Dendrobranchiata: Penaeidea: Penaeoidea: Aristeidae 57 Aristaeomorpha foliacea (Risso, 1827) Frequent synonyms / misidentifications: Aristaeomorpha rostridentata (Risso, 1827) / None. Rostrum either long and bent upward, its dorsal margin bearing 5 or 6 rather stout teeth along its base, and some small denticles extending almost to tip (females and young males), or much shorter and bearing only the 5 or 6 basal teeth (adult males). Grooves and crests on carapace rather well developed, particularly the dorsal keel (postrostral crest), the antennal crest and the branchiocardiac groove; antennal, hepatic, and branchiostegal spines present. Abdomen slightly keeled along the dorsal midline of third segment, the keel becoming strongly developed on segments 4 to 6; abdominal segments 3 to 6 with posteromedian tooth. Colour: wine red with darker violet reflections on upper side of carapace; eyes black. Habitat, biology, and fisheries: Although the nature of the substrate is apparently not a determining factor of its occurrence, this species is usually caught on muddy and sandy bottoms of the continental slope (beds of Isidella elongata), most frequently at depths between 400 and 600 m but occurring as deep as 1 300 m. A carnivorous species, feeding mainly on euphausiids and other species of crustaceans (mainly shrimp-like decapods).
Order prednisone 5mg mastercard. बेबी को चेहरे पर दाने होने पर क्या करे Baby Acne in hindi।Baby skin rash treatment.