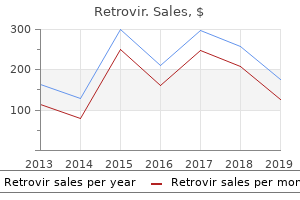
Retrovir
"Retrovir 300 mg line, symptoms anemia".
By: M. Marik, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
Lactate (Lac) medications overactive bladder purchase retrovir 300 mg free shipping, not visible in normal brain symptoms restless leg syndrome purchase 100mg retrovir amex, is a product of anaerobic glycolysis and is thus increased in hypoxic/ischemic encephalopathy medications prescribed for ptsd cheap 100mg retrovir overnight delivery, diabetic acidosis medicine 4212 purchase retrovir 100mg without a prescription, stroke, and recovery from cardiac arrest. A lipid peak is not present in normal brain but is identified in areas of brain necrosis, particularly in rapidly growing tumors. Neurosonography Intracranial Doppler sonography identifies flow of blood in arteries, particularly the middle cerebral artery. The absence of flow in the brain has been used to confirm brain death, particularly in patients who have received sedative drugs that may alter some of the clinical findings (see Chapter 8). If the coma is due to a reversible stenosis or occlusion of a single vessel, it almost always will be in the vertebrobasilar, not the carotid, circulation. Once an imaging study has been performed, it is necessary to proceed with lumbar puncture as soon as possible for patients with no clear diagnosis. Similarly, occasional patients with bacterial meningitis or viral encephalitis may present with a depressed level of consciousness (sometimes after a missed seizure), and may not yet have sufficient meningismus to make the diagnosis of meningitis clear from examination. This may be particularly difficult to determine in patients who have underlying rigidity of the cervical spine (evidenced by resistance to lateral as well as flexion movements Examination of the Comatose Patient 81 of the neck). Nevertheless, it is imperative to identify infection as early as possible to allow the administration of antibiotics or antiviral agents. Patient 22 A 73-year-old woman who was on 10 mg/day of prednisone for her ulcerative colitis had a 2-day history of presumed gastroenteritis, with fever, nausea, and vomiting. By the afternoon she had difficulty swallowing, her voice was hoarse, and her left limbs were clumsy. She was brought to the hospital by ambulance, and examination in the emergency department disclosed a lethargic patient who could be easily wakened. Pupils were equal and constricted from 3 to 2 mm with light, but the left eye was lower than the right, she complained of skewed diplopia, and there was difficulty maintaining gaze to the left. The tongue deviated to the right and there was distal weakness in her arms, and the left limbs were clumsy on fine motor tasks and showed dysmetria. Lumbar puncture disclosed 47 white blood cells/mm3 and elevated protein, and she recovered after being treated for Listeria monocytogenes. This case demonstrates the importance of examining the spinal fluid, even when a presumptive diagnosis of vascular disease is entertained. This is particularly true in patients with fever, elevated white blood cell count, or stiff neck, where infectious disease is a consideration. However, every patient with an undetermined cause of coma requires lumbar puncture as part of the routine evaluation. In these cases it is common to give antibiotics immediately and then do imaging and lumbar puncture up to a few hours later. Hence, deferring lumbar puncture in such cases until after the scanning procedure may do the patient harm. For this reason, when the evidence for meningitis is compelling, it may be necessary to do the lumbar puncture without benefit of prior imaging. As discussed in Chapters 4 and 5, the danger of this procedure is greatly overestimated. If the examination is nonfocal, and there is no evidence of papilledema on funduscopy, it is extremely rare to precipitate brain herniation by lumbar puncture. The benefit of establishing the exact microbial diagnosis far outweighs the risk of herniation. A critical but often overlooked component of the lumbar puncture is to measure and record the opening pressure. Elevated pressure may be a key sign that leads to diagnosis of venous sinus thrombosis, cerebral edema, or other serious conditions that can cause coma. If the tap is bloody, many clinicians send fluid from both tubes 1 and 4 for cell count. Nor does lack of a falling cell count indicate that the blood was there before the tap (the tip of the needle may be partially within or adjacent to a bleeding vein). Examination of the red blood cells under the microscope immediately after the tap may be helpful. Fresh red cells have the typical doughnut-shaped morphology, whereas crenelated cells indicate that they have been in the extravascular space for some time. A positive test indicates breakdown of red blood cells, which typically takes at least 6 hours to occur after a subarachnoid hemorrhage, and demonstrates that the blood was there before the tap. As the patient becomes more drowsy, higher voltage theta rhythms (4 to 7 Hz) become dominant; delta activity (1 to 3 Hz) predominates in patients who are deeply asleep or comatose.
Candida glabrata does not form pseudohyphae or hyphae and is not easily recognized on microscopy treatment bulging disc order retrovir 300mg on-line. Micro-organisms that comprise the vaginal flora symptoms multiple myeloma cheap retrovir 100mg online, such as strict and facultative anaerobes (1160) and G medications qhs buy retrovir 100mg fast delivery. Special Considerations Compromised Host Women with underlying immunodeficiency medicine 44 159 purchase retrovir 100mg on-line, those with poorly controlled diabetes or other immunocompromising conditions. Only topical azole therapies, applied for 7 days, are recommended for use among pregnant women. Epidemiologic studies indicate a single 150-mg dose of fluconazole might be associated with spontaneous abortion (1150) and congenital anomalies; therefore, it should not be used (1151). Although longterm prophylactic therapy with fluconazole 200 mg weekly has been effective in reducing C. Delay in diagnosis and treatment probably contributes to inflammatory sequelae in the upper genital tract. Laparoscopy can be used to obtain a more accurate diagnosis of salpingitis and a more complete bacteriologic diagnosis. However, this diagnostic tool frequently is not readily available, and its use is not easily justifiable when symptoms are mild or vague. Moreover, laparoscopy will not detect endometritis and might not detect subtle inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Although certain cases are asymptomatic, others are not diagnosed because the patient or the health care provider do not recognize the implications of mild or nonspecific symptoms or signs. A diagnostic evaluation that includes some of these more extensive procedures might be warranted in certain cases. For example, the presence of signs of lower genital tract inflammation (predominance of leukocytes in vaginal secretions, cervical discharge, or cervical friability), in addition to one of the three minimum criteria, increases the specificity of the diagnosis. A wet prep of vaginal fluid also can detect the presence of concomitant infections. Multiple parenteral and oral antimicrobial regimens have been effective in achieving clinical and microbiologic cure in randomized clinical trials with short-term follow-up (11711173). However, only a limited number of studies have assessed and compared these regimens with regard to infection elimination in the endometrium and fallopian tubes or determined the incidence of long-term complications. Until treatment regimens that do not cover anaerobic microbes have been demonstrated to prevent long-term sequelae. Treatment should be initiated as soon as the presumptive diagnosis has been made because prevention of long-term sequelae is dependent on early administration of recommended antimicrobials. The decision of whether hospitalization is necessary should be based on provider judgment and whether the woman meets any of the following criteria: · Surgical emergencies. After clinical improvement with parenteral therapy, transition to oral therapy with doxycycline 100 mg 2 times/day and metronidazole 500 mg 2 times/day is recommended to complete 14 days of antimicrobial therapy. Alternative Parenteral Regimens Only limited data are available to support using other parenteral second- or third- generation cephalosporins. Because these cephalosporins are less active than cefotetan or cefoxitin against anaerobic bacteria, the addition of metronidazole should be considered. Ampicillin-sulbactam plus doxycycline has been investigated in at least one clinical trial and has broad-spectrum coverage (1177). Another trial demonstrated short-term clinical cure rates with azithromycin monotherapy or combined with metronidazole (1178). When using the clindamycin and gentamicin alternative parenteral regimen, women with clinical improvement after 2428 hours can be transitioned to clindamycin (450 mg orally 4 times/day) or doxycycline (100 mg orally 2 times/day) to complete the 14-day therapy. However, when tubo-ovarian abscess is present, clindamycin (450 mg orally 4 times/day) or metronidazole (500 mg orally 2 times/day) should be used to complete 14 days of therapy with oral doxycycline to provide more effective anaerobic coverage. Clinical experience should guide decisions regarding transition to oral therapy, which usually can be initiated within 2448 hours of clinical improvement. For women with tubo-ovarian abscesses, >24 hours of inpatient observation is recommended.
Discount 100mg retrovir mastercard. Suboxone withdrawal day 9-10.
Latent impairment Impairment of function that is not accompanied by signs and/or symptoms but is of such a nature that there is reasonable and moral certainty treatment kidney infection safe 100 mg retrovir, according to accepted medical principles medicine administration buy retrovir 300 mg cheap, that signs and/or symptoms will appear within a reasonable period of time or upon change of environment symptoms 11dpo purchase retrovir 100mg without prescription. Manifest impairment Impairment of function that is accompanied by signs and/or symptoms symptoms of pregnancy buy 100mg retrovir mastercard. Medical capability General ability, fitness, or efficiency (to perform military duty) based on accepted medical principles. The presence of physical disability does not necessarily require a finding of unfitness for duty. The term "physical disability" includes mental diseases, other than such inherent defects as personality disorders, and primary mental deficiency. Physician A doctor of medicine or doctor of osteopathy legally qualified to prescribe and administer all drugs and to perform all surgical procedures. Regular Army A federal force of full-time Soldiers and Department of the Army civilians who make up the operational and institutional organizations engaged in the day-to-day missions of the Army. For purposes of this regulation, this includes both temporary and permanent disability retirement. Since our publication last year, our program has grown to continue to serve the needs of our patients. The faculty members of our division now come from four distinct backgrounds: neurology, neurosurgery, internal medicine and, now, anesthesiology. The partnership was positive and we will soon be offering similar services at Bryn Mawr Hospital, part of Main Line Health. Like our program at Kennedy, we will work collaboratively with neurologists, neurosurgeons and critical care physicians to provide specialized care to critically ill patients with neurological disease or injury. This September, Jefferson was the proud host of the 6th International Hypothermia and Temperature Management Symposium. Our neurocritical units are staffed by Neurocritical Care specialists who have been highly-trained to meet the specific, often dire needs of critically ill neurological patients. The units are equipped with advanced neuromonitoring tools and newer technologies have been incorporated into our practice over time. Our fellows also engage in a clinical research training curriculum and present their findings at a national level. Jefferson has a strong engagement with the entire regional medical community and is actively expanding access to our expertise via telemedicine. Jefferson neuroscience has taken the vanguard in these efforts and provides advice to emergency room physicians treating patients with acute stroke via a telemedicine system that serves over 30 area hospitals. The Neurocritical Care team at Jefferson has expanded this model to provide support via telepresence to the medical intensivists providing care to critically ill neurologically injured patients in the Kennedy Health System. Now in its third year, this program has enhanced the already high quality care delivered at Kennedy and has been well received by physicians, nursing, patients, and families. Recent literature on the management of severe traumatic brain injury is also reviewed, as well as the emerging role of biomarkers in brain injured patients. The hyperkalemia protocol was initiated which included calcium gluconate, D50/insulin combination, albuterol, and kayexalate. Sodium bicarbonate was withheld for concern of worsening acidosis since ventilation was suboptimal. Negative enzymes and an echocardiogram that showed no regional wall or structural abnormalities, ruled out myocardial infarction. Aggressive diuresis with Lasix and Diuril in favor of hemodialysis was continued since urine output remained robust. Six hours after repeat diuretics were given and propofol discontinued, the hyperkalemia and acidosis improved. Arriving with significant bronchospasm, the patient required around the clock bronchodilators and deep propofol sedation up to institutional maximum dose of 80 mcg/kg/min. Subsequently, on hospital day three, ketamine and muscle paralysis were added to reduce propofol requirements. Propofol 80 mcg/kg/min was still required to maintain oxygen saturations of 89% while permissive hypercapnia continued. The Brugada syndrome is linked to an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death. Propofol has significant neurologic and myocardial sodium channel inhibitory effects presenting the possible overlap in the two syndromes at the gene level.
To investigate whether there was any indication that adverse events depended on the sex of the participants treatment 4 hiv buy cheap retrovir 300 mg on line, we added gender as a moderator in a metaregression model medicine wheel native american discount retrovir 100mg otc. In both analyses symptoms miscarriage best retrovir 100 mg, there was no indication that encountered adverse events due to probiotics compared to control was more common in female or in male participant groups based on the number of participants (categorical variable analysis: p=0 treatment borderline personality disorder purchase 300mg retrovir fast delivery. Health Status the clinical characteristics of participants included in the identified studies are reported in Evidence Table C1, Participant and Study Details. The included studies report on participants with widely varying health conditions. In addition to indicating the specific clinical condition (where applicable), we also differentiated participants on a continuum ranging from generally healthy to critically ill. A large number of included studies (229 studies) could not be classified as enrolling either critically ill or generally healthy persons but fell into the middle of this continuum. Of all included studies, 83 were in participants that could be classified as generally healthy. In all, 76 studies described high-risk patients, that is, those hospitalized for serious health concerns and critically ill patients. Of note, 13 percent of included studies reported explicitly that immunocompromised participants were excluded from identified studies. First, of all included case studies that reported cases of serious adverse events such as fungemia and bacteremia, only one reported case (see Jensen, 1974) was considered generally healthy before the onset of the observed adverse event. To investigate whether healthy participants using probiotics were more likely to experience adverse events compared to control group participants not using probiotics we undertook a subgroup analysis for all studies enrolling generally healthy participants. To explore the nature of encountered adverse events, we differentiated gastrointestinal complaints, infections and infestations, and other adverse events. For 17 case studies, the preceding health status of the presented patients was categorized as medium on a scale ranging from generally healthy to critically ill, the described patients varied, or the health status before the probiotic associated adverse event was not reported. Twenty-five case studies reporting on 42 cases (Barton, 2001; Cesaro, 2000; De Groote, 2005; Force, 1995; Hennequin, 2000; Henry, 2004; Kniehl, 2003; Ku, 2006; Kunz, 2004; Land, 2005; Ledoux, 2006; Lestin, 2003; Lherm, 2002; Lolis, 2008; Oggioni, 1998; Ohishi, 2010; Perapoch, 2000; Piechno, 2007; Richard, 1988; Rijnders, 2000; Riquelme, 2003; Trautmann, 2008; Viggiano, 1995; Zein, 2008; Zunic, 1991) explicitly described a high-risk patient, an individual who was critically ill before consuming probiotic organisms and experienced any subsequent associated harms. Described cases were patients who were already hospitalized for other conditions, who suffered from multiple health concerns, or who had to be considered high risk due to a serious health condition. Adverse events are more likely and potentially more harmful in critically ill and high-risk patients. This analysis can show whether participants using probiotics were more likely to experience adverse events compared to a control group with similar health status and similar co interventions and risk factors apart from the probiotics intake. Almost all interventions in critically ill patients included Lactobacillus strains. Some studies used Bifidobacterium strains alone or in combination with Lactobacillus. The observed risk difference across treatment and control group participants was 0. Using the alternative measure, the number of incidences per treatment arm, the relative risk for treatment group participants was 0. To explore the nature of adverse events encountered in studies of critically ill or high risk participants, we differentiated gastrointestinal symptoms, infections and infestations, and other adverse events. In our categorization system, the patients and their baseline disease were not seen as critically ill, but the patients were predicted to have a severe disease course; hence, it is possible to classify them as critically ill/high risk. Health status: To investigate whether the reported adverse events differed across the three types of studies, we undertook a metaregression. There was no indication that adverse events differed statistically significantly depending on the health status of the participants, based on the number of participants with adverse events (p=0. In total, 59 percent of included studies that monitored the presence or absence of harms described the intervention as effective; 23 percent described the intervention as not effective, and for the remaining studies, it was not clearly stated or the authors reported mixed results. The efficacy of the included interventions was not the target of the review; hence, we did not extract data that would allow an independent analysis of the efficacy or effectiveness of the intervention. Whether interventions were considered effective by the authors is indicated for each study in the Evidence Table C4, Results. To investigate whether reported adverse events are associated with the efficacy of the intervention, we differentiated studies where the intervention was described as effective and studies where it was described as not effective and added this variable as a moderator to a meta analysis. There was no statistically significant indication that adverse event results differed across studies based on the efficacy of the intervention using the number of participants with adverse events (relative risk ratio 0. Summary and Strength of Evidence Key Question 4 How do the harms of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, and Bacillus vary based on (a) dose (cfu); (b) timing; (c) mode of administration. Volume: Varied across questions Risk of bias: Medium 89 the evidence to answer this Key Question stem from a variety of study designs and quality.