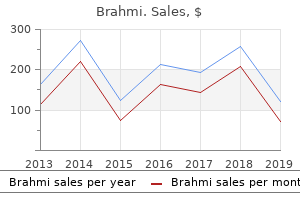
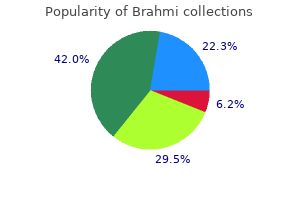
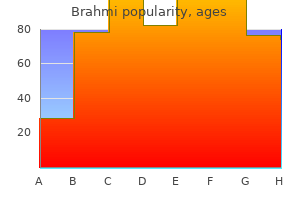
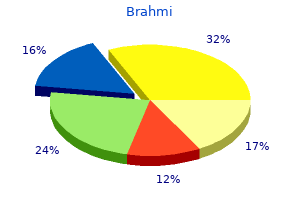
Brahmi
"Cheap brahmi 60caps line, medications qt prolongation".
By: B. Copper, M.A.S., M.D.
Medical Instructor, Nova Southeastern University Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine
Without these nerves treatment 21 hydroxylase deficiency purchase 60caps brahmi with amex, not only would your food be without taste medicine synonym buy brahmi 60 caps visa, but you would also be unable to feel either the food or the structures of your mouth walmart 9 medications buy brahmi 60 caps line, and you would be unable to avoid biting yourself as you chew 5 medications discount brahmi 60caps with amex, an action enabled by the motor branches of cranial nerves. Intrinsic innervation of much of the alimentary canal is provided by the enteric nervous system, which runs from the esophagus to the anus, and contains approximately 100 million motor, sensory, and interneurons (unique to this system compared to all other parts of the peripheral nervous system). The myenteric plexus (plexus of Auerbach) lies in the muscularis layer of the alimentary canal and is responsible for motility, especially the rhythm and force of the contractions of the muscularis. The submucosal plexus (plexus of Meissner) lies in the submucosal layer and is responsible for regulating digestive secretions and reacting to the presence of food (see Figure 23. Extrinsic innervations of the alimentary canal are provided by the autonomic nervous system, which includes both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. They transport the protein and carbohydrate nutrients absorbed by mucosal cells after food is digested in the lumen. Specifically, the more anterior parts of the alimentary canal are supplied with blood by arteries branching off the aortic arch and thoracic aorta. Below this point, the alimentary canal is supplied with blood by arteries branching from the abdominal aorta. The celiac trunk services the liver, stomach, and duodenum, whereas the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries supply blood to the remaining small and large intestines. The veins that collect nutrient-rich blood from the small intestine (where most absorption occurs) empty into the hepatic portal system. This venous network takes the blood into the liver where the nutrients are either processed or stored for later use. Only then does the blood drained from the alimentary canal viscera circulate back to the heart. To appreciate just how demanding the digestive process is on the cardiovascular system, consider that while you are "resting and digesting," about one-fourth of the blood pumped with each heartbeat enters arteries serving the intestines. The Peritoneum the digestive organs within the abdominal cavity are held in place by the peritoneum, a broad serous membranous sac made up of squamous epithelial tissue surrounded by connective tissue. It is composed of two different regions: the parietal peritoneum, which lines the abdominal wall, and the visceral peritoneum, which envelopes the abdominal organs (Figure 23. The peritoneal cavity is the space bounded by the visceral and parietal peritoneal surfaces. A few milliliters of watery fluid act as a lubricant to minimize friction between the serosal surfaces of the peritoneum. Digestive System: Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum is called peritonitis. Chemical peritonitis can develop any time the wall of the alimentary canal is breached, allowing the contents of the lumen entry into the peritoneal cavity. For example, when an ulcer perforates the stomach wall, gastric juices spill into the peritoneal cavity. Hemorrhagic peritonitis occurs after a ruptured tubal pregnancy or traumatic injury to the liver or spleen fills the peritoneal cavity with blood. Even more severe peritonitis is associated with bacterial infections seen with appendicitis, colonic diverticulitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (infection of uterine tubes, usually by sexually transmitted bacteria). Peritonitis is life threatening and often results in emergency surgery to correct the underlying problem and intensive antibiotic therapy. When your great grandparents and even your parents were young, the mortality from peritonitis was high. Aggressive surgery, improvements in anesthesia safety, the advance of critical care expertise, and antibiotics have greatly improved the mortality rate from this condition. The visceral peritoneum includes multiple large folds that envelope various abdominal organs, holding them to the dorsal surface of the body wall. Within these folds are blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves that innervate the organs with which they are in contact, supplying their adjacent organs. Note that during fetal development, certain digestive structures, including the first portion of the small intestine (called the duodenum), the pancreas, and portions of the large intestine (the ascending and descending colon, and the rectum) remain completely or partially posterior to the peritoneum. Note the route of non-fat nutrients from the small intestine to their release as nutrients to the body. The first of these processes, ingestion, refers to the entry of food into the alimentary canal through the mouth. There, the food is chewed and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that begin breaking down the carbohydrates in the food plus some lipid digestion via lingual lipase. Chewing increases the surface area of the food and allows an appropriately sized bolus to be produced.
Screening of at-risk family members allows for effective primary prevention by instituting statin therapy and dietary modifications at an early stage treatment 3 nail fungus cheap 60caps brahmi visa. Physical findings include short stature; upper limb treatment centers near me brahmi 60 caps otc, lower limb medications knee order 60caps brahmi with visa, and skeletal malformations; and abnormalities of the eyes and genitourinary tract treatment plan template buy cheap brahmi 60caps line. The carrier rate in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is 1/89 and the detection rate for this mutation using this assay is >99%. Useful For: Carrier screening for individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Prenatal diagnosis for at-risk pregnancies Confirmation of suspected clinical diagnosis of Fanconi anemia in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Interpretation: An interpretive report will be provided. Steatorrhea (increased fecal excretion of fat) may reflect a number of pancreatic or intestinal disorders, including chronic pancreatitis with or without stone obstruction, cystic fibrosis, neoplasia, Whipple disease, regional enteritis, tuberculous enteritis, gluten-induced enteropathy (celiac disease), Giardia-associated enteropathy, sprue, or the atrophy of malnutrition. Useful For: Diagnosing fat malabsorption due to pancreatic or intestinal disorders Monitoring effectiveness of enzyme supplementation in certain malabsorption disorders Interpretation: Excretion of >7 grams fat/24 hours, when on a diet of 100 to 150 g of fat, is suggestive of a malabsorption defect. Abnormal results from a random specimen should be confirmed by submission of a timed collection. Test values for timed fecal fat collections will be reported in terms of g/24 hours; the duration of the collection may be 24, 48, 72, or 96 hours. Test values for random fecal fat collections will be reported in terms of percent fat. Commonly used metabolite screens such as urine organic acids, plasma acylcarnitines, and fatty acids are influenced by dietary factors and the clinical status of the patient. This often leads to incomplete diagnostic information or even false-negative results. Enzyme assays are limited to 1 enzyme per assay, and molecular assays for common mutations are limited by the frequent occurrence of compound heterozygous patients with uncommon, private mutations that must be distinguished from unaffected carriers. Furthermore, neither specific enzyme assays nor molecular genetic testing is available for each of the known defects. Interpretation: Abnormal results will include a description of the abnormal profile, in comparison to normal and abnormal co-run controls. In addition, the concentration of those acylcarnitine species that abnormally accumulated in the cell medium are provided and compared to the continuously updated reference range based on analysis of normal controls. Deficient enzymes at any step in this pathway prevent the production of energy during periods of physiologic stress such as fasting or intercurrent illness and can frequently result in life-threatening episodes of metabolic decompensation. Quantitative determination of C8 to C18 fatty acids is an important element of the work-up and differential diagnosis of candidate patients. Fatty acid profiling can detect quantitatively modest, but nevertheless significant, abnormalities even when patients are asymptomatic and under dietary treatment. Fatty Acid Deficiency/Excess: Fats are important sources of energy for tissues and for the function and integrity of cellular membranes. Deficiencies are commonly caused by inadequate dietary intake of lipids due to an unbalanced diet or long-term parenteral nutrition or by intestinal malabsorption. Biochemical abnormalities may be detected before the onset of recognizable clinical manifestations. Excess dietary fatty acids have also been linked to the onset of cardiovascular disease. Elevated levels of linoleic acid can contribute to overproduction of the proinflammatory 2-series local hormones. Peroxisomal Disorders: Peroxisomes are organelles present in all human cells except mature erythrocytes. Peroxisomal disorders consist of 2 major groups, disorders of peroxisomal biogenesis (eg, Zellweger syndrome), in which the organelle is not formed, and defects of single peroxisomal enzymes. Fatty acid oxidation disorders are recognized on the basis of disease-specific patterns that are correlated to the results of other investigations in plasma (carnitine, acylcarnitines) and urine (organic acids, acylglycines). Increased concentrations of serum phytanic acid (along with normal pristanic acid concentrations) are seen in the Refsum disease (phytanase deficiency). Deficiencies are commonly caused by inadequate dietary intake of lipids due to an unbalanced diet or long-term parenteral nutrition, or by intestinal malabsorption, which is common in conditions such as cystic fibrosis and irritable bowel syndrome. Deficiencies can also be caused by an impairment of biomolecular transformations among fatty acids, such as linoleic acid to arachidonic acid. Linoleic and linolenic acids cannot be made by the body and are essential components of the diet (ie, essential fatty acids). It can also be detected by increases in the ratio triene/tetraene ratio (Holman index): (eicosatrienoic [mead] acid [C20:3w9]/arachidonic acid [C20:4w6]). The dietary contents of saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated fatty acids influence the concentration of cholesterol in low-density and high-density lipoproteins, and consequently the development of atherosclerosis.
Think About It If the pH outside the cell decreases medications you can take during pregnancy buy brahmi 60 caps, would you expect the amount of amino acids and glucose transported into the cell to increase or decrease? As sodium ion concentrations build outside of the plasma membrane because of the action of the primary active transport process medications herpes cheap 60caps brahmi mastercard, an electrochemical gradient is created treatment jock itch generic brahmi 60 caps otc. If a channel protein exists and is open symptoms 8 days post 5 day transfer order brahmi 60 caps with mastercard, the sodium ions will be pulled through the membrane. This movement is used to transport other substances that can attach themselves to the transport protein through the membrane (Figure 5. Excess potassium increases action potential generation, leading to uncoordinated organ activity. Potassium dissipates the electrochemical gradient in cardiac muscle cells, preventing them from contracting. Potassium creates a new concentration gradient across the cell membrane, preventing sodium from leaving the cell. However, sometimes large particles, such as macromolecules, parts of cells, or even unicellular microorganisms, can be engulfed by other cells in a process called phagocytosis or "cell eating. For example, when bacteria invade the human body, a type of white blood cell called a neutrophil will remove the invaders by this process. Similarly, in pinocytosis or "cell drinking," the cell takes in droplets of liquid. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, uptake of substances by the cell is targeted to a single type of substance that binds to a specific receptor protein on the external surface of the cell membrane. Some human diseases, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, are caused by the failure of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Exocytosis is the process of exporting this OpenStax book is available for free at cnx. The secretion of neurotransmitters at synapses between neurons is an example of exocytosis. Big Idea 2 Enduring Growth, reproduction and dynamic homeostasis require that cells create and maintain Understanding internal environments that are different from their external environments. In addition to moving small ions and molecules through the membrane, cells also need to remove and take in larger molecules and particles (see Table 5. You might have correctly hypothesized that the uptake and release of large particles by the cell requires energy. A large particle, however, cannot pass through the membrane, even with energy supplied by the cell. There are different variations of endocytosis, but all share a common characteristic: the plasma membrane of the cell invaginates, forming a pocket around the target particle. Phagocytosis Phagocytosis (the condition of "cell eating") is the process by which large particles, such as cells or relatively large particles, are taken in by a cell. When accessible nutrients from the degradation of the vesicular contents have been extracted, the newly formed endosome merges with the plasma membrane and releases its contents into the extracellular fluid. Activity Create a representation/diagram to describe how a neutrophil, a type of human white blood cell, attacks and destroys an invading bacterium. This literally means "cell drinking" and was named at a time when the assumption was that the cell was purposefully taking in extracellular fluid. This process uses a coating protein, called caveolin, on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane, which performs a similar function to clathrin. Receptor-mediated Endocytosis A targeted variation of endocytosis employs receptor proteins in the plasma membrane that have a specific binding affinity for certain substances (Figure 5. When salmonella bacteria are engulfed by a white blood cell during phagocytosis, it secretes a protein that prevents the fusion of the encased bacteria with the lysosome of the cell. Exocytosis the reverse process of moving material into a cell is the process of exocytosis. This fusion opens the membranous envelope on the exterior of the cell, and the waste material is expelled into the extracellular space (Figure 5. The landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. Carbohydrates are attached to some of the proteins and lipids on the outward-facing surface of the membrane, forming complexes that function to identify the cell to other cells. Plasma membranes enclose and define the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux.
While the alpha subunits are identical in all inhibins medications made easy order 60caps brahmi otc, the beta subunits exist in 2 major forms medicine checker cheap brahmi 60caps on line, termed A and B medicine 4 the people buy brahmi 60caps low cost, each of which can occur in different isoforms treatment hypothyroidism buy brahmi 60 caps free shipping. Depending on whether an inhibin heterodimer contains a beta-A or a beta-B chain, they are designated as inhibin A or inhibin B, respectively. Together with the related activins, which are homodimers or heterodimers of beta-A and beta-B chains, the inhibins are involved in gonadal-pituitary feedback and in paracrine regulation of germ cell growth and maturation. They are secreted into the coelomic and amniotic fluid, but only inhibin A is found in appreciable quantities in the maternal circulation during the first and second trimesters. Down Syndrome Sequential Maternal Screening, Part 2, Serum results are negative when the calculated risk is below 1/270 (0. Results are positive when the risk is greater than the established cutoff (> or =1/270 in Sequential Maternal Screening, Part 2, Serum). Risks <1% are screen-negative; negative results do not guarantee the absence of trisomy 18. Babies with trisomy 18 tend to be small, which can lead to underestimation of gestational age and an increased risk of missing a true-positive. If the results are positive, the patient is typically offered counseling, ultrasound, diagnostic testing, and, possibly, a referral to genetics counseling or a high-risk clinic. Kato M, Serretti A: Review and meta-analysis of antidepressant pharmacogenetic findings in major depressive disorder. Despite the wide array of drugs available for treatment, some patients do not initially respond to treatment, and others who respond early may eventually relapse or develop serious side effects. Individuals with major depression disorders are more likely to respond to citalopram if they are homozygous for the -1438G promoter allele. The short allele is dominant and results in decreased concentration of the transporter protein and a poorer response to stressful events. Even 1 copy of the short allele (heterozygous) decreases the amount of the transporter protein present, increasing the time to response. They are subdivided into foregut carcinoids, arising from respiratory tract, stomach, pancreas, or duodenum (approximately 15% of cases); midgut carcinoids, occurring within jejunum, ileum, or appendix (approximately 70% of cases); and hindgut carcinoids, which are found in the colon or rectum (approximately 15% of cases). The carcinoid syndrome is usually caused by midgut tumors, as foregut and hindgut neoplasms produce far lesser amounts of serotonin. Because midgut tumors drain into the portal circulation, which passes into the liver, undergoing extensive hepatic (first-pass) serotonin degradation, symptoms do not usually occur until liver or other distant metastases have developed, producing serotonin that bypasses the hepatic degradation. Urine serotonin is, in most circumstances, the least likely marker to be elevated (see Interpretation). By contrast, 1 or more of these markers are elevated in most patients with more advanced and symptomatic tumors, usually to levels several times the upper limit of the reference interval. Chromogranin A is also elevated in 80% to 90% of patients with symptomatic foregut and midgut tumors. Urine serotonin measurements are not commonly employed in carcinoid tumor follow-up. In these individuals, urine serotonin is the tumor marker of choice to monitor disease progression. Of the remaining 10%, almost all is taken up by platelets, where it remains until it is released during clotting, promoting further platelet aggregation. They are subdivided into foregut carcinoids, arising from respiratory tract, stomach, pancreas or duodenum (approximately 15% of cases); midgut carcinoids, occurring within jejunum, ileum, or appendix (approximately 70% of cases); and hindgut carcinoids, which are found in the colon or rectum (approximately 15% of cases). This includes the differential diagnosis of isolated symptoms suggestive of carcinoid syndrome, in particular flushing. Chromogranin A is also elevated in 80% to 90% of patients with foregut and midgut tumors. In most cases, if none of these 3 analytes is elevated, carcinoids can be excluded as a cause of symptoms suggestive of carcinoid syndrome. They are subdivided into foregut carcinoids, arising from respiratory tract, stomach, pancreas, or duodenum (approximately 15% of cases); midgut arcinoids, occurring within jejunum, ileum, or appendix (approximately 70% of cases); and hindgut carcinoids, which are found in the colon or rectum (approximately 15% of cases). Carcinoids display a spectrum of aggressiveness with no clear distinguishing line between benign and malignant.
The reduction of calcium from the bones can make them weak and subject to fracture treatment quadratus lumborum safe brahmi 60caps. It is centrally located medications similar to gabapentin discount 60caps brahmi overnight delivery, where it forms portions of the rounded brain case and cranial base symptoms gout cheap 60caps brahmi visa. When this occurs in thoracic vertebrae symptoms hiv 60caps brahmi with mastercard, the bodies may collapse producing kyphosis, an enhanced anterior curvature of the thoracic vertebral column. The bones of the limbs, ribs, and vertebrae develop when cartilage models of the bones ossify into bone. It consists of 80 bones that include the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs. It also gives bony protections for the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs; stores fat and minerals; and houses the blood-cell producing tissue. It is subdivided into the rounded top of the skull, called the calvaria, and the base of the skull. These are the paired parietal and temporal bones, plus the unpaired frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. The facial bones support the facial structures, and form the upper and lower jaws, nasal cavity, nasal septum, and orbit. These are the paired maxillary, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior nasal conchae bones, and the unpaired vomer and mandible bones. The lambdoid suture is located on the posterior skull and has an inverted V-shape. It extends from the frontal bone anteriorly to the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone posteriorly. It is divided at the midline by the crista galli and cribriform plates of the ethmoid bone. The middle cranial fossa is located in the central skull, and is deeper than the anterior fossa. The middle fossa extends from the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone anteriorly to the petrous ridge posteriorly. The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the superior part of the septum. In the living skull, the septal cartilage completes the septum by filling in the anterior area between the bony components and extending outward into the nose. There are seven cervical vertebrae (C1C7), 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1T12), and five lumbar vertebrae (L1L5). The sacrum is derived from the fusion of five sacral vertebrae and the coccyx is formed by the fusion of four small coccygeal vertebrae. The vertebral arch is formed by the pedicles, which are attached to the posterior side of the vertebral body, and the lamina, which come together to form the top of the arch. A pair of transverse processes extends laterally from the vertebral arch, at the junction between each pedicle and lamina. A pair of superior articular processes project upward and a pair of inferior articular processes project downward. Together, the notches found in the margins of the pedicles of adjacent vertebrae form an intervertebral foramen. On the posterior sacrum, the median sacral crest is derived from the fused spinous processes, and the lateral sacral crest results from the fused transverse processes. The sacral canal contains the sacral spinal nerves, which exit via the anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) sacral foramina. The anulus fibrosus strongly anchors the adjacent vertebrae to each other, and the high water content of the nucleus pulposus resists compression for weight bearing and can change shape to allow for vertebral column movements. The supraspinous ligament is located on the posterior side, where it interconnects the thoracic and lumbar spinous processes. In the posterior neck, this ligament expands to become the nuchal ligament, which attaches to the cervical spinous processes and the base of the skull. The posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum are located inside the vertebral canal.
Discount brahmi 60caps fast delivery. Top 10 Signs You Have Health Anxiety.