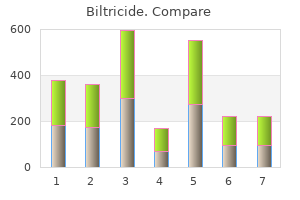
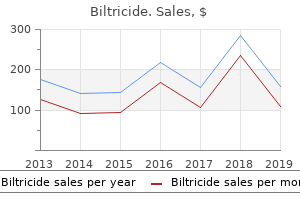
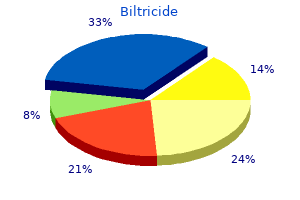
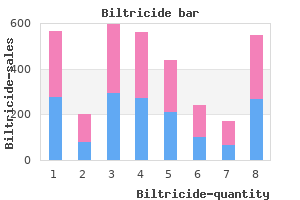
Biltricide
"Purchase biltricide 600 mg with amex, treatment venous stasis".
By: N. Harek, M.S., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Campbell University School of Osteopathic Medicine
These statewide guidelines are intended for patients who have had limited exposure to opioids in the past medications via g tube buy cheap biltricide 600mg line. They are not intended for those who currently receive opioids nor for those with a history of substance use (or opioid use) disorder treatment bronchitis order biltricide 600 mg with mastercard. Similarly treatment molluscum contagiosum quality 600 mg biltricide, while some principles may be appropriate symptoms white tongue buy biltricide 600mg amex, pain in patients at the extremes of the age spectrum. In addition, these guidelines do not address pain treatment for cancer or for palliative or end-of-life situations. Mild to moderate pain can often be treated without opioids by recommending over-the-counter medications, and physical treatments such as ice and immobilization. If non-opioid interventions are ineffective and opioids are appropriate, prescribe the lowest effective dose of short-acting opioids for less than 3 days; in cases of more severe acute pain, limit initial prescription to less than 7 days. Rationale for Oregon guidelines Several lines of evidence have recently emerged that make addressing acute opioid prescribing an urgent matter. Another analysis among postoperative patients found that the majority did not use the quantities of opioids prescribed. Finally, to avoid confusion, Oregon providers, healthcare systems and payers would benefit from a single document that clarifies expectations around opioid prescribing for acute pain. However, their use has inherent risks and prescribers are encouraged to remain up-to-date in current understanding of the pathophysiology of pain and its treatment. The chronic non-cancer pain guideline does not address prescribing for acute conditions in detail. In the absence of a national standard of care for acute opioid prescribing, a variety of specialty-specific guidelines have emerged from the dental, emergency medicine and surgical communities. All emphasize that, for acute pain, clinicians should first use non-opioid medication and then, if needed, judiciously prescribe opioids in small quantities with duration typically limited to less than a week. More detailed guidelines for specific conditions and procedures by practice setting. These companion guidelines will include recommendations for maximum opioid prescription amounts by severity and anticipated duration of acute pain. Children, the elderly and those with existing medical conditions require additional considerations. While these acute pain guidelines cannot address every age group and medical condition, most of the principles are relevant for all patients. For example, these guidelines should be used when prescribing opioids to adolescents after dental procedures. When determining the most appropriate treatment for acute pain consider the type of pain. Depending on the acute condition, evidence-based non-opioid therapies may be the most effective. Always choose specific medications after reviewing precautions and contraindications and make schedule and dose adjustment as needed for each patient. In general, opioids should not be considered first line therapy for mild to moderate pain in patients with limited past exposure to opioids. If other options are not appropriate or effective for acute pain, and the clinician deems that opioids will be effective, follow these recommendations before any new opioid prescription. Avoid prescribing opioids without a direct patient to prescribing clinician assessment. Determine whether the pain is likely to be responsive to opioid or non-opioid therapies. Note that these may cause drug interactions or produce toxic effects if taken with combination drugs, such as Tylenol 3. Include specific documentation of the indication for prescribing opioids in these patients. Review records from other providers and be aware that, for a patient who could be tapering off opioids, a new opioid prescription could jeopardize this progress.
Control of appendages such as fins medications for bipolar disorder purchase biltricide 600mg line, wings symptoms 5 days after conception order biltricide 600 mg overnight delivery, and legs lends speed and scope to exploration medications hair loss best 600mg biltricide, so that vastly more small patterns are encountered which then require selection and assembly counterfeit medications 60 minutes buy biltricide 600mg mastercard. More large patterns require more comparisons, requiring a larger library; more comparisons also require more decisions, and these require more evaluation. Naturally, more neurons are needed, and since neuronal components are irreducibly small (chapter 7), a brain must enlarge. One need not watch a sloth for very long to realize the limits to life in slow motion. The larger, faster brain must still remain portable and also metabolically affordable. These demands for speed, portability, and affordability all interact; therefore, individually and together they raise questions of brain design. We turn now to the fundamental constraint on any brain design that leads to the first three design principles. Then, in the context of these few principles, we discuss some actual designs (mammal and insect). Design constraints the fundamental constraint on brain design emerges from a law of physics. This law, embodied in a family of equations developed by Claude Shannon, applies equally to a telephone line and a neural cable, equally to a silicon circuit and a neural circuit. This law constrains neural design at all scales and cannot be avoided any more than a B-29 bomber can avoid the law of gravity. But, though the brain is fundamentally an organ that manipulates information, few neuroscientists are familiar with this law or aware of its value for understanding brain organization. Information is the reduction of uncertainty about some situation X associated with observing any variable Y that is causally correlated with X. Uncertainty defines the standard measure: one bit is the information needed to decide between two equally likely alternatives. Information depends on causality because, to reduce uncertainty, a message must be reliably relatable to its source, the event that caused it. Any factor that reduces the reliability of this connection, such as noise, increases uncertainty and destroys information. And when the brain matches the sensory pattern coded by a patch of ganglion cells to a stored pattern, it reduces a key uncertainty: "Friend or foe To this end, a motor neuron spike decreases the uncertainty that its target muscle fibers will contract and help the animal move in the appropriate direction. In short, to achieve its core purpose, the brain uses physical devices (neurons and circuits) that represent and manipulate information. So now we must ask: how much information can a neuron represent, and what constrains its capacity The number of different outputs a spiking neuron can generate in a given time is the number of distinctly different spike trains that it can produce in that time. This depends on two factors, mean firing rate (R spikes per second) and the precision of spike timing (t seconds). The upper bound on firing rate is set by spike duration plus the period following a spike when a neuron is refractory (cannot spike). Certain neurons reach this limit during brief bursts, but most neurons operate far below this limit. What is the relation between spike rate, timing precision, and the number of different spike trains a neuron can produce When a neuron transmits for 1 s, it produces R spikes with a timing precision of t (Rieke et al. The number of different spike trains, M, is the number of ways the neuron can place its R spikes in T = 1/t intervals (figure 3. Deriving M is a standard exercise in calculating combinations that is often set to students in quaint terms, such as placing peas in pots.
Additional information can be obtained in medical dictionaries medicine while pregnant generic biltricide 600 mg otc, reference texts kerafill keratin treatment purchase 600 mg biltricide mastercard, on the Internet or from professionals such as doctors medications not to mix cheap 600mg biltricide with mastercard, pharmacists medications or drugs generic 600mg biltricide with visa, therapists or mental health professionals. This is a classification manual of mental disorders that includes descriptions of diagnostic categories. The Diagnostic & Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is the most widely accepted system of classifying abnormal behaviors used in the United States today. Examples include grooming, bathing, dressing, using the telephone, preparing meals, cleaning house, taking medicines, doing laundry, handling finances, getting to the bus stop and shopping at the grocery. For example, a client may be said to have a flat affect, meaning that there is an absence or a near absence of facial expression when there is an experience or emotion that would usually cause an emotional response. For example, a person may be unable to identify familiar sounds, such as the ringing of a doorbell (auditory agnosia), or familiar objects, such as a toothbrush or keys (visual agnosia). For example, a person may be unable to shave, to dress, or to do other previously learned and purposeful tasks. Examples of behavioral therapy techniques include operant conditioning, token economy, systematic desensitization, aversion therapy and flooding. This abnormality can cause hydrocephalus, severe headaches and a variety of other neurological symptoms. This condition is due to shortening of muscles, tendons and/or ligaments around joints. This response is useful in emergencies; however, a sustained response can result in pathophysiological changes such as high blood pressure, ulcers, cardiac problems and more. Manipulation is maladaptive when: 1) it is the primary method used for getting needs met; 2) the needs, goals and feelings of others are disregarded; and 3) others are treated as objects in order to fulfill the needs of the manipulator. Behavior may seem passive but is motivated by unconscious anger, often triggering anger and frustration in others. Disturbance of perception is an inability to register and interpret sensory stimuli based on past experiences. The term is used in reference to certain diseases thought to be caused by psychological factors. The degree of stiffness is velocity dependent; the more quickly a muscle is stretched, the stiffer it becomes. These helmets can be made of rigid or soft flexible foam and usually are found in therapeutic equipment catalogs, custom made or available for other sports. Because they are not standardized or tested for sport impact or equestrian activities, they are to be used only with extreme caution.
Brody took the ten studies that involved "neurotic" conditions such as agoraphobia and anorexia and did a simple box-score to see if behavior therapy was more effective than placebo conditions medicine vs dentistry generic 600mg biltricide overnight delivery. Brody concluded that there was no evidence for the superiority of behavior therapy medicine cups order biltricide 600 mg amex. Therefore medications neuropathy order 600mg biltricide visa, the outcome studies and the meta-analysis on which they were based did not yield clinically significant information medications bladder infections generic 600mg biltricide with mastercard. The same data prove both that behavior therapy is superior and is not superior to placebo treatment conditions; the result depends on the method of analysis. Relative contribution of specific and nonspecific treatment effects: Meta-analysis of placebo-controlled behavior therapy research. The ethics of methodologically sound psychotherapy-effectiveness research is a good topic for discussion. Ask students to suggest an appropriate control group for a study of treated individuals. If they respond, "people who do not receive treatment," point out the possibility that people who ask for help (and get it) may be different in some outcome-relevant way from people who do not ask for help. Further, how can we be sure that untreated people do not get some other form of help (for example, read a self-help book) that might be much like therapy These questions highlight the problem of random assignment, a key component of true experiments. A second kind of control group, the waiting-list control, includes random assignment but has its own problems. Ask students how they feel about the ethics of arbitrarily placing people in distress on a waiting list. A third option is a pseudotherapy control group-the psychological equivalent of a placebo pill. The American Psychological Association site for ethical principles of psychologists. The common components of psychotherapy mentioned in the text are reasonable and accurate. Frank, in his classic book, Persuasion and Healing, argues that the social aspects of the therapeutic relationship overwhelm any technical or theoretical considerations. According to him, the three active ingredients in the change process are (1) a socially sanctioned healer whose powers and status are respected by the sufferer, (2) a sufferer who seeks relief from symptoms, and (3) a fairly structured set of contacts (with their own rituals) that convinces the sufferer to change his or her attitudes and behavior. Ask students whether the same analysis can be applied to faith-healing evangelists or voodoo doctors. The offending chemicals, this person asserts, come from polyesters and other synthetic fabrics and from modern laundry detergents. The cure is for people to throw away all their garments except for 100 percent natural cottons and wools and to wash only with "pure" soap. Given the mystery of depression and fatigue, the desperation of some, the status afforded television appearances, and the effort involved in the treatment, it is fairly likely that such a "therapy" could catch on (and be successful) with some sufferers. The professionals most often involved have frequent contact with troubled individuals but are not specifically trained to interact with them. For example, school teachers, police officers, and emergency room nurses often come in contact with distressed individuals and need to know how to best interact with them and make referrals to professionals when necessary. Ask students to think of other professions that have this kind of frequent contact with distressed individuals. Some examples are funeral directors, clergymen, general practice physicians, bartenders, hairdressers, and divorce attorneys. The consultee is seen as just as much a professional as the consultant: the consultant never tells the consultee how to do his/her job. The relationship involves only indirect coaching; the consultant has no specific supervisory role. Gerald Caplan (1970) laid out a scheme that indicates the range of mental health consultations that are possible.
Buy 600 mg biltricide with amex. SHINee (샤이니) - View (Color Coded Han|Rom|Eng Lyrics).
Critical Thinking Questions Why are the concepts of reliability and validity so important in psychological and neuropsychological assessment What kinds of questions and tests do neuropsychologists use in a neuropsychological evaluation What sort of recommendations and treatments can neuropsychologists give to brain-impaired people that will be useful in their daily lives How do the major two approaches (process and battery) to interpreting neuropsychological data differ K e y The r m s Neuropsychological evaluation Psychometrics Standardized test Reliability Validity Construct validity Content validity Criterion validity False positive Base rate Achievement tests Behavioral-adaptive scales Intelligence tests Neuropsychological tests Personality tests Vocational inventories Crystallized functions Fluid functions Orientation Sensation Perception Motor apraxia Ideomotor apraxia Malingering Interpretive hypotheses Standard battery approach Process approach Normative data Cutoff score Specificity Sensitivity Normal distribution Deficit measurement Pattern analysis Pathognomonic signs We b C o n n e c t i o n s ericae medicine venlafaxine buy cheap biltricide 600mg online. Within this site you can find concrete examples of simple statistical terms and validity and reliability procedures on interpretation discussed in this chapter medications 122 purchase biltricide 600 mg mastercard. Evolutionarily old symptoms tracker discount 600mg biltricide fast delivery, one-celled creatures such as the amoeba show elementary responses to sensation and have decision-making capabilities symptoms your dog is sick buy 600mg biltricide visa. In their universe of a droplet of water, amoebas can move about, locate food, and engulf it. This unicellular organism uses complex electrochemical processes, but has no nervous system and no brain. Moving up the evolutionary ladder, increased complexity of behavior corresponds with a more specialized nervous system, which is essential for speeded communication. The "jellyfish," for example, has a rudimentary nervous system, which allows coordinated movement, but still has no brain. Of the two main types of cells, neurons alone account for about 100 billion cells, and estimates suggest that glial cells outnumber neurons by 10 to 1. Considering there are approximately 6 billion people on earth, the number of cells in one human brain is more like the number of stars in the sky. If 1 neuron connected only to 100 others, the emerging network would be staggering in its size and complexity. However, evidence suggests that the number of connections actually ranges from 1000 to 100,000, averaging about 10,000 per neuron (Beatty, 1995; Hubel, 1988). Their processing systems require a great deal of energy and consume the most oxygen and glucose of any bodily system. This chapter focuses on the essential building blocks of thought and behavior: neurons and glial cells. Neurons and glia are classes of cells that contain subtypes based on their structure and function. Neurons are considered the most important cells, and the basic electrical-chemical processes of neuronal communication have been well described by scientists. Although glial cells traditionally have been described as having a supporting function for neurons, science now suggests that glial cells may have a larger role to play in thought and learning. The neuron can be studied as a universe unto itself, but neuropsychology is also focused on the effect of behavior related to neuronal disruption. The ability of the neuron to repair itself is intriguing because of the enormous implications for treatment. Neurons and Glial Cells the neuron differs from other cells in that it is specialized for information processing. To some degree all functions that sustain life, as well as those that make us human, are coordinated and depend on the communication of neurons. Neurons are anatomically independent; they come very close to each other but do not touch. The nervous system thus consists of separate units rather than one continuous structure. The neuron has often been studied by scientists with the idea that by studying the fundamental parts, a better understanding of the whole can be achieved. The neuron hypothesis is in accord with this viewpoint suggesting that (1) all neural function is reflected in behavior, and (2) all behavior has an underlying neural correlate (Pincus & Tucker, 1985). In other words, the reductionist viewpoint argues that every human experience can be reduced to a physical phenomenon. Although reductionism is considered outdated and oversimplified because it is not possible to correlate behavior with individual neurons, some neuropsychologists study the relation of behavior to assemblies of neurons and interconnected neural networks. The structure of neurons is similar to that of other body cells in that they have a cell body that contains a nucleus, genes, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and other organelles necessary to conduct protein synthesis and energy production.