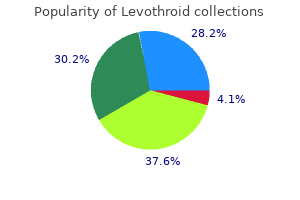
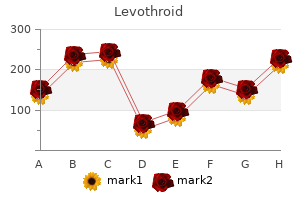
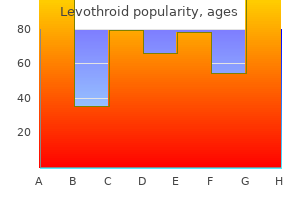
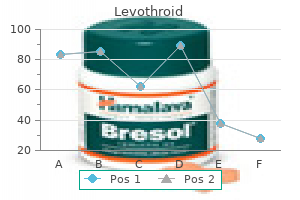
Levothroid
"Generic 50 mcg levothroid with amex, thyroid symptoms after pregnancy".
By: K. Kasim, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine
This pulls the visceral pleura outwards too thyroid cancer nih order levothroid 200mcg without prescription, since the two pleura are held together by the thin film of pleural fluid thyroid cancer trusted 200 mcg levothroid. Because the visceral pleura is firmly adherent to the lung thyroid symptoms horses order levothroid 100mcg free shipping, the lung tissue is thyroid cancer percentage discount levothroid 200mcg on-line, therefore, pulled up and out with the ribs, and downwards with the diaphragm. This expands the lungs, and the pressure within the alveoli and in the air passages falls, drawing air into the lungs in an attempt to equalise the atmospheric and alveolar air pressures. The negative pressure created in the thoracic cavity aids venous return to the heart and is known as the respiratory pump. Expiration Relaxation of the external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm results in downward and inward movement of the ribcage. As this occurs, pressure inside the lungs rises and expels air from the respiratory tract. The lungs still contain some air, and are prevented from complete collapse by the intact pleura. At rest, expiration lasts about 3 seconds, and after expiration there is a pause before the next cycle begins. Physiological variables affecting breathing Elasticity Elasticity is the term used to describe the ability of the lung to return to its normal shape after each breath. Loss of elasticity of the connective tissue in the lungs necessitates forced expiration and increased effort on inspiration. When compliance is low the effort needed to inflate the lungs is greater than normal. The lungs and the air passages are never empty and, as the exchange of gases takes place only across the walls of the alveolar ducts and alveoli, the remaining capacity of the respiratory passages is called the anatomical dead space (about 150 ml). Tidal air mixes with this air, causing relatively small changes in the composition of alveolar air. As blood flows continuously through the pulmonary capillaries, this means that exchange of gases is not interrupted between breaths, preventing moment-to-moment changes in the concentration of blood gases. The functional residual volume also prevents collapse of the alveoli on expiration. Total lung capacity represents the sum of the vital capacity and the residual volume. It cannot be directly measured in clinical tests because even after forced expiration, the residual volume of air still remains in the lungs. Alveolar ventilation this is the volume of air that moves into and out of the alveoli per minute. It is equal to the tidal volume minus the anatomical dead space, multiplied by the respiratory rate: Lung function tests are carried out to determine respiratory function and are based on the parameters outlined above. Results of these tests can help in diagnosis and monitoring of respiratory disorders. Exchange of gases Although breathing involves the alternating processes of inspiration and expiration, gas exchange at the respiratory membrane and in the tissues is a continuous and ongoing process. With increasing height above sea level, atmospheric pressure is progressively reduced and at 5500 m, about two-thirds the height of Mount Everest (8850 m), it is about half that at sea level. Under water, pressure increases by approximately 1 atmosphere per 10 m below sea level. Air is a mixture of gases: nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and small quantities of inert gases. Each gas in the mixture exerts a part of the total pressure proportional to its concentration, i. It is saturated with water vapour, and contains more carbon dioxide and less oxygen. Gaseous exchange between the alveoli and the bloodstream (external respiration) is a continuous process, as the alveoli are never empty, so it is independent of the respiratory cycle. Diffusion of gases Exchange of gases occurs when a difference in partial pressure exists across a semipermeable membrane. Gases move by diffusion from the higher concentration to the lower until equilibrium is established (p. Atmospheric nitrogen is not used by the body so its partial pressure remains unchanged and is the same in inspired and expired air, alveolar air and in the blood. External respiration this is exchange of gases by diffusion between the alveoli and the blood in the alveolar capillaries, across the respiratory membrane. Each alveolar wall is one cell thick and is surrounded by a network of tiny capillaries (the walls of which are also only one cell thick).
Vitamin A can be formed in the body from certain carotenes thyroid cancer recovery rate order levothroid 100 mcg free shipping, the main dietary sources of which are green vegetables thyroid gland secretes buy levothroid 50 mcg fast delivery, fruit and carrots thyroid symptoms wiki order levothroid 50mcg online. Although some is synthesised in the body the daily dietary requirement is 600 to 700 g thyroid cancer growth rate order 200mcg levothroid with visa. The main roles of vitamin A in the body are: generation of the light-sensitive pigment rhodopsin (visual purple) in the retina of the eye cell growth and differentiation; this is especially important in fast-growing cells, such as the epithelial cells covering both internal and external body surfaces promotion of immunity and defence against infection promotion of growth. The first sign of vitamin A deficiency is night blindness due to formation of abnormal retinal pigment. Other consequences include xerophthalmia, which is drying and thickening of the conjunctiva and, ultimately, ulceration and destruction of the conjunctiva. Atrophy and keratinisation of other epithelial tissues leads to increased incidence of infections of the ear, and the respiratory, genitourinary and alimentary tracts. Vitamin D Vitamin D is found mainly in animal fats such as eggs, butter, cheese, fish liver oils. Humans can synthesise vitamin D by the action of the ultraviolet rays in sunlight on a form of cholesterol (7dehydrocholesterol) in the skin (see p. Vitamin D regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism by increasing their absorption from the gut and stimulating their retention by the kidneys. The daily requirement is 10 g and stores in fat and muscle are such that deficiency may not be apparent for several years. Vitamin E is an antioxidant, which means that it protects body constituents such as membrane lipids from being destroyed in oxidative reactions. Recommended daily intake is 10 mg for men and 8 mg for women, but this should be increased in high-fat diets. Deficiency is rare, because this vitamin is present in many foods, and is usually seen only in premature babies and in conditions associated with impaired fat absorption. White blood cells can likewise be affected, and vitamin E supplements boost immune function. Neurological abnormalities such as ataxia and visual disturbances may occur if the deficiency is severe. Vitamin K the sources of vitamin K are liver, some vegetable oils and leafy green vegetables. It is synthesised in the large intestine by microbes and significant amounts are absorbed. The normal daily requirement is 1 g/kg body weight and only a small amount is stored in the liver. It may occur in adults when there is obstruction to the flow of bile, severe liver damage and in malabsorption. Newborn infants may be given vitamin K because their intestines are sterile and require several weeks to become colonised with vitamin K-producing bacteria. Water-soluble vitamins Vitamin B complex this is a group of water-soluble vitamins that promote activity of enzymes involved in the chemical breakdown (catabolism) of nutrients to release energy. Vitamin B1 (thiamin) this vitamin is present in nuts, yeast, egg yolk, liver, legumes, meat and the germ of cereals. Thiamin is essential for the complete aerobic release of energy from carbohydrate. When it is absent there is accumulation of lactic and pyruvic acids, which may lead to accumulation of tissue fluid (oedema) and heart failure. Thiamin is also important for nervous system function because of the dependency of these tissues on glucose for fuel. Deficiency causes beriberi, which occurs mainly in countries where polished rice is the chief constituent of the diet. In beriberi there is: severe muscle wasting delayed growth in children polyneuritis, causing degeneration of motor, sensory and some autonomic nerves susceptibility to infections. If untreated, death occurs owing to cardiac failure or severe microbial infection. The main cause of thiamin deficiency in developed countries is alcoholism, where the diet is usually poor. Neurological symptoms, which are usually irreversible, include memory loss, ataxia and visual disturbances.
The superior mesenteric vein returns venous blood from the small intestine and the proximal parts of the large intestine thyroid cancer kaiser generic levothroid 200mcg free shipping, i thyroid nodules how often to check trusted levothroid 50mcg. The gastric veins drain blood from the stomach and the distal end of the oesophagus thyroid symptoms causes levothroid 100mcg line, then join the portal vein thyroid gland examination video generic levothroid 200mcg visa. The cystic vein, which drains venous blood from the gall bladder, joins the portal vein. Hepatic veins these are very short veins that leave the posterior surface of the liver and, almost immediately, enter the inferior vena cava. Circulation to the pelvis and lower limb Arterial supply Common iliac arteries the right and left common iliac arteries are formed when the abdominal aorta divides at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. In front of the sacroiliac joint each divides into the internal and the external iliac arteries. The internal iliac artery runs medially to supply the organs within the pelvic cavity. In the female, one of the largest branches is the uterine artery, which provides the main arterial blood supply to the reproductive organs. The external iliac artery runs obliquely downwards and passes behind the inguinal ligament into the thigh where it becomes the femoral artery. It supplies blood to the structures of the thigh and some superficial pelvic and inguinal structures. At the lower border of the popliteal fossa it divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. It lies on the tibia, runs in front of the ankle joint and continues over the dorsum (top) of the foot as the dorsalis pedis artery. The dorsalis pedis artery is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery and passes over the dorsum of the foot, where the pulse can be felt, supplying arterial blood to the structures in this area. It ends by passing between the first and second metatarsal bones into the sole of the foot where it contributes to the formation of the plantar arch. Near its origin it gives off a large branch called the peroneal artery, which supplies the lateral aspect of the leg. In the lower part it becomes superficial and passes medial to the ankle joint to reach the sole of the foot, where it continues as the plantar artery. This artery, its branches and the dorsalis pedis artery form the plantar arch from which the digital branches arise to supply the toes. Blood entering the superficial veins passes to the deep veins through communicating veins. Movement of blood towards the heart is partly dependent on contraction of skeletal muscles. Deep veins the deep veins accompany the arteries and their branches and have the same names. They are the: femoral vein, which ascends in the thigh to the level of the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the external iliac vein external iliac vein, the continuation of the femoral vein where it enters the pelvis lying close to the femoral artery. It passes along the brim of the pelvis, and at the level of the sacroiliac joint it is joined by the internal iliac vein to form the common iliac vein internal iliac vein, which receives tributaries from several veins draining the organs of the pelvic cavity two common iliac veins, which begin at the level of the sacroiliac joints. They ascend obliquely and end a little to the right of the body of the 5th lumbar vertebra by uniting to form the inferior vena cava. The small saphenous vein begins behind the ankle joint where many small veins which drain the dorsum of the foot join together. It begins at the medial half of the dorsum of the foot and runs upwards, crossing the medial aspect of the tibia and up the inner side of the thigh. Many communicating veins join the superficial veins, and the superficial and deep veins of the lower limb. Fetal circulation Learning outcomes After studying this section, you should be able to: outline the functions of the placenta describe the fetal circulation compare blood flow through the heart, lungs and liver before and shortly after birth. To this end, both maternal and fetal circulations develop specific adaptations unique to pregnancy.
Syndromes
- Muscle strain
- Headache
- Pain in the throat
- Hypogammaglobulinemia, which usually leads to respiratory and gastrointestinal infections
- Medications to stimulate ovulation
- Medicines for allergic reactions
- Heart rhythm
- Stupor (a lack of alertness)
- Triamcinolone
- Feeling sad or depressed
Note the close (but not touching) relationship between the input screen and photocathode for maintenance of resolution xl184 thyroid cancer purchase levothroid 50 mcg on line. The light photons interact with the photocathode and approximately 150 electrons are emitted by the photoemissive metal thyroid cancer ata guidelines 200mcg levothroid overnight delivery. The photoelectrons then interact with the output screen thyroid nodules getting bigger levothroid 200mcg otc, and 2000 fluorescent light photons are emitted for every electron thyroid symptoms teenager order levothroid 200mcg mastercard. Input Phosphor Output phosphor X-ray photons 5,000 light photons per interaction exposure rates of up to 20 R/min. Use of the "boost" mode is permitted for only short periods of time and an audible signal is activated during its use. For radiation protection purposes, the fluoroscopic tabletop exposure rate must not exceed 10 R/min and all fluoroscopic equipment must provide at least 12 inches (30 cm), and preferably 15 inches (38 cm), between the x-ray source (focal spot) and the x-ray tabletop. A 5-minute timer is used to measure accumulated fluoroscopic examination time and make an audible sound or interrupt exposure after 5 minutes of fluoroscopy. The fluoroscopic tube is usually equipped with electrically driven collimating shutters. Leaded glass provides shielding from radiation passing through the intensifying screen, and the image intensifier is lead lined. A Bucky slot cover and protective curtain also help reduce exposure to the fluoroscopist. Older fluoroscopes are often equipped with a spot film device to record fluoroscopic images. To expose a spot film, a motor is activated that brings a cassette from a lead-lined compartment within the carriage over into the fluoroscopic field between the intensifying screen and grid. The fluoroscopic x-ray tube current then automatically increases to a conventional radiographic level of approximately 300 mA or more for the cassette exposure. A fluoroscope has two major parts: an x-ray tube and a fluorescent screen, attached at opposite ends of a C-shaped arm. The fluoroscopic tube is usually located (at least 12 inches) under the x-ray table and usually operated at 1 to 3 mA (upto a maximum of 5 mA); mA automatically increases for cassette-loaded spot films. Fluoroscopic patient dose depends on exposure rate, tissue thickness or density, and length of exposure. Fluoroscopic patient dose decreases as the image intensifier is moved closer to the patient. Many guidelines regulate the operation of fluoroscopic equipment because of the unavoidably high patient dose inherent in fluoroscopic procedures (because of the short focus-to-patient distance). Image intensifiers brighten the conventional, dark fluoroscopic image 5000 to 20,000 times. Note that the focal point on the 6inch field, or mode, is further away from the output phosphor; therefore, the output image appears magnified. Because less minification takes place in this instance, the image is not as bright. Exposure factors are automatically increased to compensate for the loss in brightness. Cesium iodide is much more efficient than zinc cadmium sulfide because it absorbs, and converts to fluorescent light, a greater number of the x-ray photons striking it. For each absorbed x-ray photon, approximately 5000 light photons are emitted. A number of electrons are subsequently released from the photocathode and focused toward the output side of the image tube. Although this step actually represents a deamplification, it has very little effect on the end result. The electrons emitted from the photocathode are focused toward the output end of the tube by negatively charged electrostatic focusing lenses. They then pass through the neck of the tube where they are accelerated through a potential difference of 25,000 to 35,000 V and strike the small (0.
Generic levothroid 200 mcg free shipping. 🎧 How to become an Alpha Male Empowering Affirmations Recording Simply Hypnotic success.