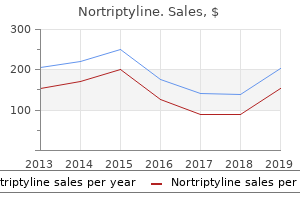
Nortriptyline
"Buy 25 mg nortriptyline with mastercard, anxiety symptoms in 2 year old".
By: W. Randall, M.A., M.D.
Program Director, UAMS College of Medicine
Since then anxiety headaches 25mg nortriptyline with visa, the news media anxiety free cheap nortriptyline 25mg without a prescription, and therefore the general public anxiety symptoms quitting smoking discount 25 mg nortriptyline with amex, have begun to use the term "deepfakes" to refer to this genre of videos that use some form of "deep" or machine learning to hybridize or generate human bodies and faces anxiety symptoms and menopause nortriptyline 25mg visa. Many of the journalists who cover deepfakes have declared them the harbingers of a coming "information apocalypse. In many cases, panic around a new medium has generated an opening for experts to gain juridical, economic, or discursive power. With thousands of images of many of us online, in the cloud, and on our devices, anyone with a public social media profile is fair game to be faked. And we are already seeing that the unbounded use of tools 4 Jean Baudrillard et al. Sheila Faria Glaser, 14th Printing edition (Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1994); John Fiske and Kevin Glynn, "Trials of the Postmodern," Cultural Studies 9, no. Jimerson, Archives Power: Memory, Accountability, and Social Justice (Society of American Archivists, 2009); Saloni Mathur, "Social Thought & Commentary: Museums Globalization," Anthropological Quarterly 78, no. This increase in distribution provides a real challenge to traditional counters to manipulation and makes efforts like moderation or fact-checking harder to accomplish. Further, in some applications, like WhatsApp, encrypted messages are circulated along private connections, achieving a type of hidden virality in which these fake videos can spread to a wide network of viewers while avoiding content moderation or mainstream media coverage. Bijker, "The Social Construction of Facts and Artefacts: Or How the Sociology of Science and the Sociology of Technology Might Benefit Each Other," Social Studies of Science 14, no. But such strategies do not address the thornier, and more important, issues of social, cultural, and historical context. There is a risk that these technical and legal closures will be directed by those who already hold economic and political power in ways that, following the political history of evidence, further consolidate truth for the status quo. Deepfakes-which rely on experimental machine learning- are at one end of this spectrum. The deepfake process is both the most computationally reliant and also the least publicly accessible means of manipulating media. Still other techniques rely on far simpler methods, like mislabeling footage or using lookalike stand-ins. The deepfake process was initially developed by those working in the graphics processing industry. The primary benefit is that it decodes pixels to render smooth 3D animations and video. Machine learning is a set of complicated algorithms used to train machines to perform a task with data, such as sorting a list of names in alphabetical order. The first few times, the lists would be mostly correct, but with a few ordering errors. As it sorts through different hypothetical lists of names, the machine does it faster with fewer errors. Deep learning, on the other hand, is a subset of machine learning that layers these algorithms, called a neural network, to correct one another. It still uses complicated algorithms to train machines to sort through lists of names, but instead of a human correcting errors, the neural network does it. With these techniques, media producers are able to create entirely virtual performances by recognizable figures, as in the cases of synthesizing various performances of Obama in prototypes produced by the University of Washington, Stanford, and at the State University of New York at Albany. It is these spectacular, high-profile experiments 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 12 Economist Special Report, "From Not Working to Neural Networking," the Economist, June 25, 2016. Consumer-grade animation software like Adobe After Effects enables anyone with average computing power and a little time to create similar audiovisual fakes through machine learning. Individual programmers have also created open source projects for deepfake creation-projects like FakeApp, FaceSwap, and DeepFace Lab. Most of these are hosted in public repositories like GitHub and can produce output ranging from facemapped performance videos to artificial lip-synchs. This technique requires creators to manually outline target areas in every frame of a video and is therefore both difficult and time consuming. Many other video producers manipulate media with simple methods of slowing, speeding, or cutting. Countless free mobile apps now offer limited versions of the above techniques: speeding and slowing, but also forms of facial tracking and manipulation.
A trained Surgical Technologist Sunrise Page 102 monkey can pass an instrument anxiety reduction techniques order 25 mg nortriptyline amex, but knowing the 1 anxiety young children cheap 25mg nortriptyline mastercard,000s of instruments and their applications along with anticipating what the surgeon needs takes extensive skills and knowledge anxiety symptoms early pregnancy buy nortriptyline 25 mg line. In regard to the harm question anxiety symptoms for hiv purchase nortriptyline 25 mg amex, she said she can provide an anecdotal example from her experience. She gave an example of an on-the-job trained surgical technologist who all the doctors loved. She had a great personality and showed great potential and aptitude for learning the instruments. A surgical technologist with education is taught to check everything before the procedure, to look through the instrument pan to ensure everything is in its place, and to check the sizes. This surgical technologist learned on the job that things should be in the right place. She handed the wrong size instrument for a total hip procedure which took the "cup" part of the hip up to five sizes larger than what the surgeon intended to put in, adding one hour to the surgery. The doctor trusted the surgical technologist to know the steps and said, "hand me the fifty," and she handed him the fifty-five without checking to ensure it was in the proper place. Students have to learn pharmacology and the interactions that happen with certain medications. One of the local anesthetic drugs they use is marcaine and they were putting in a post-operative pain pump a the incisional site that helps keep pain to a minimum. She wanted to reiterate they demand each person involved in a procedure have the appropriate school, training and certification within their profession to act appropriately. Staley asked since she works at the community college, could she estimate how many who finish the program obtain the certification exam. McRae responded she has been there seven years and the last three years she has required the certification exam to graduate from the program. She said with all the people they have trained, is it the fact that the surgeon recognizes she has the theory and background to pick it right up and do it. Frazee asked whether the other surgical technologists at that facility are certified. She said she appreciates their willingness to look in-house but the theory behind that is far different than working in surgery. McRae responded that their program is a 24-month program where students graduate with an associate in applied science degree. There is about six months of theory and in-lab practice and the last six months is clinical where they are out in the clinic doing surgery in many different specialties. They need 120 surgeries in all the specialties to graduate with an entry-level proficiency. They have to pass certain lab skills testing in order to progress into the clinical rounds. McRae stated they have clinical affiliations with hospitals and she must show them her students have passed lab skills testing before they can progress to the clinical rounds at their facilities. He said they do a large number of outpatient surgeries, many in small ambulatory surgical facilities. He said he agrees with what Carl Nelson and Emily Studebaker have already mentioned. Certified staff are people much more interested in regular surgeries and are typically employed by hospitals or large centers where they can be used on a regular basis. It takes months under supervision of nurses and doctors and he is dedicated to having excellent results. He said aseptic technique needs to be adhered to because infection in the eye is blinding in many cases. Their outcomes are dependent upon the technique Surgical Technologist Sunrise Page 104 and ability of his staff. Medicare defines a major surgical procedure, he believes, as one with a 90-day post-operative period. Almost everything he does in a surgery center that involves a scalpel, such as cataract or glaucoma surgery or retina lasers would all be considered by Medicare as major procedures, despite the intent that these might not need to be included in the proposal. Fernando wrapped up the hearing and gave next steps: · There is an additional 10-day written comment period starting today through August 24 at 5:00 for anything you feel has not been addressed.
25mg nortriptyline with visa. Episode 1: Social Anxiety Disorder.
In the interaction of microwave radiation and human beings anxiety lexapro purchase nortriptyline 25 mg without a prescription, the skin is traditionally considered as just an absorbing sponge stratum filled with water anxiety 4 year old purchase nortriptyline 25 mg overnight delivery. This approach is justified when the impinging wavelength is greater than the dimensions of the skin layer anxiety symptoms relief order 25 mg nortriptyline mastercard. The full ramifications of what these findings represent in the human condition are still very unclear anxiety symptoms gastrointestinal order 25 mg nortriptyline visa, but it is obvious that the absorption of electromagnetic energy is governed by the topology for the skin and its organelles, especially the sweat duct. The affinity of atmospheric absorption in this band means that 217 many small short range and relatively powerful transmitters will be required for decent coverage. The results of our study emphasize that rather than gallop toward these solutions with abandon, the human health implications must be considered first, as wavelengths approach the dimensions of skin-based features. However, their deleterious effects on the body, particularly on the nervous system, are well known. Antioxidant defense systems exist in order to keep free radical formation under control and to prevent their harmful effects on the biological system. Free radical formation can take place in various ways, including ultraviolet light, drugs, lipid oxidation, immunological reactions, radiation, stress, smoking, alcohol and biochemical redox reactions. Oxidative stress occurs if the antioxidant defense system is unable to prevent the harmful effects of free radicals. The purpose of this review was to highlight the impact of oxidative stress on antioxidant systems. Any health safety standard must protect not just those who are healthy but include those in poor health, the young and the pregnant women. Should we wait another 20 years for severe biological effects to show up and then regret that we did not do something earlier? If the committees still think that the results are inconclusive, then they may want to define a set of objective specific testing protocols so scientists and researchers can work on it to produce clear and definitive results. Longitudinal associations between risk appraisal of base stations for mobile phones, radio or television and non-specific symptoms. Abstract Introduction: Studies found that higher risk appraisal of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields is associated with reporting more non-specific symptoms such as headache and back pain. There is limited data available on the longitudinal nature of such associations and what aspects of risk appraisal and characteristics of subjects 219 are relevant. Objective: To examine cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between risk appraisal measures and nonspecific symptoms, and assess the role of subject characteristics (sex, age, education, trait negative affect) in a general population cohort. We studied a sample of participants (n=1720) who filled in two follow-up questionnaires in 2013 and 2014, including questions about perceived exposure, perceived risk, and health concerns as indicators of risk appraisal of base stations, and non-specific symptoms. Results: Perceived exposure, perceived risk, and health concerns, respectively, were associated with higher symptom scores in cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Only health concerns (not perceived exposure and perceived risk) temporally preceded high symptom scores and vice versa. Female sex, younger age, higher education, and higher trait negative affect were associated with higher risk appraisal of mobile phone base stations. Discussion: the findings in this study strengthen the evidence base for cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between higher risk appraisal and non-specific symptoms in the general population. However, the directionality of potential causal relations in non-sensitive general population samples should be examined further in future studies, providing information to the benefit of risk communication strategies. Abstract the use of mobile phones is increasing, and the main health concern is the possible deleterious effects of radiation on brain functioning. The results also revealed that post-training, but not pre-training, as well as pre-test intracerebroventricular. Evaluating temperature changes of brain tissue due to induced heating of cell phone waves. Apr 2018 Background: Worries have recently been increased in the absorption of radiofrequency waves and their destructing effects on human health by increasing use of cell phones (mobile phones). This study performed to determine the thermal changes due to mobile phone radio frequency waves in gray and white brain tissue. Results: In confronting of the tissue with the cell phone, the temperature was increased by 0. Brain temperature showed higher rates than the base temperature after 15 min of confrontation with cell phone waves in all the three thicknesses. Conclusions: Cell phone radiated radio frequency waves were effective on increasing brain tissue temperature, and this temperature increase has cumulative effect on the tissue, being higher, for some time after the confrontation than the time with no confrontation.
The Navy and others in the national security community disagreed on the extent to which American national interests might be susceptible to anxiety exhaustion discount nortriptyline 25mg on line, and in need of anxiety symptoms returning buy discount nortriptyline 25 mg, redefinition anxiety 4th breeders nortriptyline 25mg line. Community policy analysts believed that a number of international and domestic factors either permitted or required the United States to conceive its interests in less sweeping and less burdensome terms in coming years anxiety hotline generic 25 mg nortriptyline with amex. In this regard, and against the preferences of a naval establishment still committed to a larger view of American national interest and a more traditional view of American commitments, the Carter administration developed strategy and guidance intended to realize lines of policy indicated, though unexecuted, in the Nixon years. The primary meaning of the Nixon Doctrine, for instance, was that the time had come to scale down American commitments so as to permit a reduction of force structure. The United States had become overextended materially in attempting to make containment an effectual, worldwide policy and strategy principally by material means: commitments, aid, deployments. When Nixon left office, American commitments were larger than American capabilities. The naval establishment, and probably other military leaders, had hoped to spur the growth of force structure to meet commitments rather then the reduction of commitments to accord with capabilities. The Navy and others in the national security community disagreed on the relative promise of diplomatic maneuver versus political-military coercion in attaining national objectives in coming years. In pursuing American national interests, the Carter administration apparently intended to rely more on diplomatic maneuver 278 than on the threat or use of military force. In contrast, Navy leaders, when pressed, were likely to admit the conviction that, over the years, the gunboats have proven just as effective as diplomats, and often a good deal more effective. In recent moments of political tension, some of the smallest and weakest countries in the world denied bunkering to warships of the United States, surely a sign of the times. Correspondingly, as in the cases of Vietnam and Angola, neither the American public nor its elected representatives in the middle and latter 1970s hesitated to end administration involvements in foreign military or clandestine operations. There was no difficulty in finding places where one could fight traditional enemies for important stakes. But it seemed more difficult than ever to find places where one could do so with reasonable confidence that results would be favorable, significant in terms of larger American interests, and likely to obtain the requisite support in Congress and from the public. Thus the interest of the Carter administration in retaining worldwide interventionarycoercive-power projection forces or capabilities reached its lowest point since the Korean War. The Navy and others in the national security community disagreed on the extent to which American political-military problems grow out of differences with allies or differences with enemies. The Carter administration adopted the view that many American problems lay in relations with allies rather than with enemies. With allies, presumably, it was necessary to proceed by bargaining and maneuver rather than coercion-a view not always held by American leaders, to be sure. The Navy, in contrast, continued to emphasize American problems with enemies, and to suppose that problems with allies were of a lesser order in proportion to overall national interest and national security calculations. Parenthetically, one must note that the Navy and others in the national security community disagreed not only on the proportion of problems as between friends and enemies but even on the extent to which real conflicts of interest, whether with friends or with enemies, might be resolvable by increases in coercive capacity. This reflected basic differences on ideas concerning the definition of power, in which the administration appeared to hold somewhat broader ideas than did the Navy about what power is and how to use it. Conversely, a strategic arms agreement that contained technical shortcomings or appeared to involve significant American concessions was unwelcome to Navy and other military leaders. Further, they tended to believe that deterrence, even when it worked, led not to increased maneuver policy but to an increase in the use of limited war-in the little wars so much discussed by strategic theorists of the latter 1950s. In the view of many military leaders, either to maintain reliable deterrence or to cope with the lesser conflicts permitted in a deterrent framework would impose on the United States a requirement for increased military expenditures and a larger force structure, both strategic and conventional. The Navy and others in the national security community disagreed in selecting the enemies against which to size and configure American naval forces. It was obvious to everyone that the most capable possible enemy of the United States was the Soviet Union. But the Carter administration stressed its convictions that maneuver and not coercion would likely predominate in relations with principal powers; that deterrence would be effective; that the Russians did not, and would not, consider war an attractive option; and that Russian and American interests converged rather than conflicted on a number of current and coming issues. All this made the prospect of Soviet-American war seem remote to administration analysts. Thus the consolidated defense guidance for fiscal 1980, issued early in 1978, emphasized that the Navy should concentrate on "localized contingencies outside Europe. They insisted that a Navy able to handle the worst case could cope with anything else.