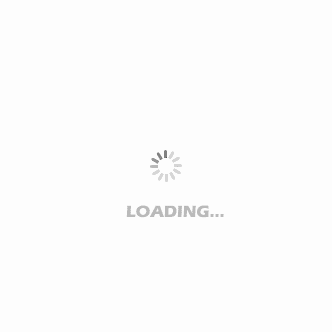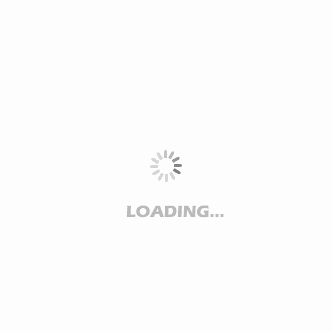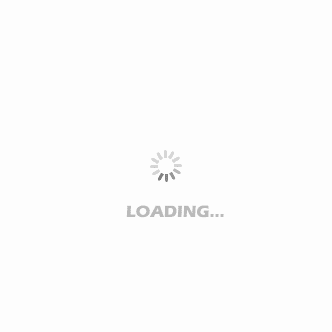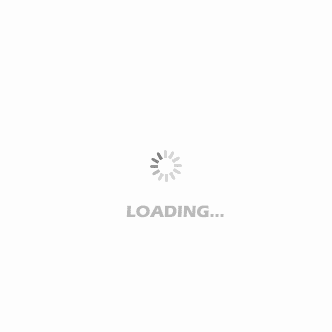
Terazosin
"Best 2 mg terazosin, arteria y vena femoral".
By: C. Amul, M.A., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Osteopathic Medical College of Wisconsin
Excessive hypertension has been associated with phenylephrine blood pressure 4080 buy terazosin 5 mg online, ephedrine blood pressure medication recall 2015 trusted 2mg terazosin, dopamine hypertension jnc 8 pdf terazosin 2 mg low cost, and isoprenaline blood pressure medication and gout discount 5mg terazosin with amex. Small-fiber sensory and autonomic nerve abnormalities correlate with overall prognosis and outcome. The lack of orthostatic hypotension in patients with the cholinergic form of the disorder makes laboratory testing especially valuable in establishing the diagnosis. Nerve conduction studies typically show normal findings or minor sensory abnormalities. Acute Autonomic Neuropathy (Acute Pandysautonomia) Differential Diagnosis A paraneoplastic form, which develops over a similar time course, is indistinguishable on clinical or laboratory grounds prior to tumor discovery. An attenuated form of this disorder may underlie some cases of orthostatic intolerance, discussed later. Botulism (cholinergic), diphtheria, and acute intermittent porphyria are other diagnostic considerations. General Considerations Acute or subacute autonomic neuropathy (acute pandysautonomia) primarily but not exclusively affects peripheral autonomic fibers. Diagnosis is frequently delayed due to lack of recognition, which reduces the potential for timely, beneficial treatment. There is strong clinical and experimental evidence that the ganglionic acetylcholine receptor antibodies are pathogenic in patients with positive antibody titers. Of note, the antibody titer is relevant; high titers support clinical significance and treatment response. Because of the probable immune mechanisms, steroids, plasmapheresis, and intravenous immunoglobulin have all been used, with anecdotal reports of benefit. Symptoms and Signs Roughly half of cases are preceded by a viral prodrome, including herpes simplex, mononucleosis, rubella, and nondescript febrile illnesses. The neuropathy is monophasic, with acute or subacute onset and progression over several weeks. Acute signs such as ileus may develop into lesser degrees of dysmotility, including bloating, early satiety, nausea, vomiting, and alternating diarrhea and constipation. Predominantly adrenergic and cholinergic variants are sometimes seen, but pandysautonomia is most common. One third of patients make a good functional recovery; one third have a partial recovery with persistent symptoms, including orthostatic hypotension; and the remainder of patients do not improve. Improvement in autonomic function sometimes follows treatment for the underlying cancer. Enteric Neuronopathy Enteric neuronopathy causes intestinal pseudo-obstruction and marked derangement of function on gastric and intestinal motility studies. Neurons of the enteric nervous system are the presumed target of immunologic attack. Symptoms include abrupt onset of progressive constipation, crampy abdominal pain, and vomiting, which can be severe enough to mimic an acute bowel obstruction. Symptoms and signs of more widespread autonomic involvement are often present and are similar but less severe than those in other paraneoplastic autonomic neuropathies. Symptoms occasionally remit spontaneously or after chemotherapy or radiation treatments. Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome is an acquired disorder of presynaptic neuromuscular junction transmission. Roughly half of affected patients have an associated neoplasm, about 80% of which are small cell lung cancer.
If pts are febrile for 7 days despite antibiotic therapy heart attack zippytune order terazosin 2mg without prescription, an evaluation for paravalvular or extracardiac abscesses should be performed arteriogram complications buy terazosin 2mg without prescription. Pts treated with vancomycin or an aminoglycoside should have serum drug levels monitored pulse pressure nhs buy terazosin 2mg on line. If treatment fails or the isolate is resistant to commonly used agents heart attack labs best 1mg terazosin, surgical therapy is advised (see below and Table 85-3). Two other agents in addition to rifampin help prevent the emergence of rifampin resistance in vivo. Susceptibility testing for gentamicin should be performed before rifampin is given; if the strain is resistant, another aminoglycoside or a fluoroquinolone should be substituted. If the pt has a prosthetic valve, those two drugs plus vancomycin should be given. Surgical Treatment Surgery should be considered early in the course of illness in pts with the indications listed in Table 85-3, although most of these indications are not absolute. However, pts who develop acute aortic regurgitation with preclosure of the mitral valve or a sinus of Valsalva abscess rupture into the right heart require emergent surgery. Doses of gentamicin, streptomycin, and vancomycin must be adjusted for reduced renal function. Prophylaxis is recommended for high-risk patients and optional for moderate-risk group (see Table 85-5). Table 85-5 Cardiac Lesions for which Endocarditis Prophylaxis Is Advised High Risk Moderate Risk Prosthetic heart valves Prior bacterial endocarditis Complex cyanotic congenital heart disease; other complex congenital lesions after correction Patent ductus arteriosus Coarctation of the aorta Surgically constructed systemicpulmonary shunts Congenital cardiac malformations (other than high-/low-risk lesions), ventricular septal defect, bicuspid aortic valve Acquired aortic and mitral valve dysfunction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (asymmetric septal hypertrophy) Mitral valve prolapse with valvular regurgitation and/or thickened leaflets Table 85-6 Antibiotic Regimens for Prophylaxis of Endocarditis in Adults at Moderate or High Riska I. Ruptured mycotic aneurysms should be clipped and cerebral edema allowed to resolve prior to cardiac surgery. Prevention the American Heart Association has identified procedures that may cause bacteremia with organisms prone to cause endocarditis (Table 85-4), pts who should receive antibiotic prophylaxis based on their relative risk of developing endocarditis (Table 85-5), and regimens for prophylaxis (Table 85-6). Organisms contained within the bowel or an intraabdominal organ enter the sterile peritoneal cavity, causing peritonitis and- if the infection goes untreated and the pt survives- abscesses. Peritonitis is either primary (without an apparent source) or secondary (bacterial contamination resulting from spillage from an intraabdominal viscus). Clinical Features Pts experience an acute onset of symptoms, with fever, abdominal pain, and signs of peritoneal irritation. Enteric gramnegative bacilli such as Escherichia coli or gram-positive organisms such as streptococci, enterococci, and pneumococci are the most common etiologic agents; a single organism is typically isolated. The organism burden is low, but the culture yield is improved if 10 mL of peritoneal fluid is placed directly into blood culture bottles. However, the risk of serious staphylococcal or antibiotic-resistant infections increases over time. Secondary Peritonitis Secondary peritonitis almost always involves a mixed aerobic and anaerobic flora, especially when the contaminating source is colonic. Clinical Features Initial symptoms may be localized or vague and depend on the primary organ involved. Once infection has spread to the peritoneal cavity, pain increases; pts lie motionless, often with knees drawn up to avoid stretching the nerve fibers of the peritoneal cavity. There is marked voluntary and involuntary guarding of anterior abdominal musculature, tenderness (often with rebound), and fever. The selected antibiotics are aimed at aerobic gram-negative bacilli and anaerobes-. Peritonitis in Pts Undergoing Chronic Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Common etiologic agents include coagulase-negative staphylococci (30% of cases), Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacilli, and fungi such as Candida spp. Several hundred milliliters of removed dialysis fluid should be centrifuged and sent for culture, preferably in blood culture bottles to improve the diagnostic yield. Empirical therapy should be directed against staphylococcal species and gram-negative bacilli. If methicillin resistance is prevalent, vancomycin (2 g) can be administered and should be allowed to remain in the peritoneal cavity for 6 h.
Muscle stretch reflexes are normal blood pressure 7850 cheap terazosin 5mg with visa, unless there is a coexisting myelopathy or neuropathy hypertension headaches buy terazosin 1mg without prescription. Electromyography is sensitive and specific in the diagnosis of myopathy white coat hypertension xanax purchase 2 mg terazosin fast delivery, showing abnormal motor unit action potentials that appear short in amplitude and brief in duration blood pressure chart malaysia generic terazosin 1mg overnight delivery, and abnormal recruitment characterized by an early and full interference pattern. Neurologic examination reveals a combination of upper motor neuron signs, including hyperreflexia, spasticity, and a Babinski sign, as well as lower motor neuron signs such as atrophy and fasciculations. Diagnosis can be confirmed with electromyography, which reveals acute denervation in multiple dermatomes. Clinical presentation varies with the underlying trigger but usually includes focal neurologic deficits and, in the most severe cases, reduced levels of consciousness. In addition, antiretroviral therapy should be continued to avoid the development of antiretroviral therapy resistance. New insights into immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome of the central nervous system. In patients with less severe deterioration, prednisone 60 mg/day can be started followed by a gradual taper. Prion diseases result from accumulation in the brain of an abnormal conformation of the cellular protein called prion protein (PrP). It is expressed in various cell types throughout the body, but is principally expressed in the brain. Normal cellular PrP (called PrPc) is found in neurons and may be involved in copper transportation and synaptic signaling. In the disease state, PrP undergoes an abnormal post-translational change to produce a pathogenic conformation called PrPsc (scrapie inducing) or PrPres (resistant to protease), which differs from PrPc not in its amino acid sequence but rather in its physical properties: the pathologic form includes a greater proportion of -pleated sheet conformation, rendering the protein relatively insoluble, protease-resistant, and liable to the formation of protein deposits. What initiates a conformational shift from PrPc to PrPres is not understood; however, once present, PrPres self-propagates by recruiting and converting the nonpathologic PrPc to the PrPres form. There are no clear modifiable or environmental risk factors, and there is no gender predilection. Diagnostic Studies A probable diagnosis is based on clinical history and examination and is supported by imaging and laboratory studies. Electroencephalography-Findings are typically abnormal at some point in the course of disease. Signal abnormality may be particularly prominent in the cortical ribbon, the basal ganglia (caudate, globus pallidus, and putamen), and less commonly in the thalamus. Neuropathologic examination typically reveals spongiform change, which is a diffuse vacuolation of the neuropil, as well as prominent astrocytic gliosis and neuronal loss. In some cases, there may not be a family history, even though there is a genetic mutation. The earliest symptoms may be vague and constitutional (insomnia, anorexia, or fatigue) or psychiatric (depression, anxiety, emotional lability). Cognitive impairment (memory, concentration, aphasias, perceptual disorders), focal neurologic deficits (hemianopia, focal weakness, ataxia), and psychiatric abnormalities (hallucination and delusions) ensue shortly thereafter. Myoclonus, especially provoked by startle, is present in more than 80% of patients by the middle to late stages of the disease. The neurologic status deteriorates to akinetic-mutism and then to death, typically within months of clinical onset. Psychiatric symptoms (depression, anxiety, psychosis) are prominent early in the illness and are the presenting symptoms in 85% of patients. Painful paresthesias are common early in the disease, presumably resulting from thalamic involvement. Within months, more extensive neurologic findings may develop, including cognitive impairment, cerebellar ataxia, and abnormal movements (chorea, myoclonus, and dystonia). They culminate in death on average 14 months after symptoms start, although some patients have had protracted clinical courses of years. In the past two decades, about 230 cases worldwide have been reported; however, there have been only 2 in the past 6 years.
Discount 2 mg terazosin visa. Obtaining Pediatric Vital Signs - www.simtics.com.
Most lesions are well-differentiated and comprise neoplastic glandular structures lined by one or more layers of plump blood pressure medication helps acne purchase terazosin 2mg, cuboidal to columnar cells that have moderately enlarged blood pressure z score calculator order terazosin 5 mg without prescription, vesicular nuclei arrhythmia triggers discount 1 mg terazosin with mastercard, and small nucleoli radial pulse blood pressure 90 buy terazosin 1 mg free shipping. Irregular glandular structures are distributed through an abundant collagenous stroma. Poorly-differentiated variants of apocrine adenocarcinoma are infiltrative neoplasms with ill-defined borders. They are composed of large cuboidal to polygonal cells arranged in glandular and solid aggregates in varying proportions. The neoplastic cells generally have amphophilic cytoplasm, large vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and moderate to high mitotic activity. Poorly-differentiated apocrine adenocarcinomas have a moderate to abundant stroma of reactive collagenous tissue. Stromal invasion by cords and clusters of neoplastic epithelial cells is common; tumor cells may be detected within lymphatic vessels in stroma and adjacent dermis. Differential diagnoses for well-differentiated apocrine adenocarcinoma are apocrine adenoma and mammary adenocarcinoma. Mammary lobules and/or ducts can usually be identified adjacent to mammary neoplasms. Distinction between apocrine adenoma and well- differentiated adenocarcinoma may be problematic. The differential diagnoses of poorly differentiated apocrine adenocarcinoma include mammary carcinoma as well as other poorly differentiated carcinomas, which may be primary or metastatic in the skin. Careful search for residual mammary lobules or ducts is required for neoplasms located on the ventrum. Hemorrhage and/or abundant fibroplasia and neovascularization extending peripheral to the mass are suggestive of metastatic disease. Distinction from acantholytic (pseudoglandular) squamous cell carcinoma (see Chapter 22) can be difficult in apocrine adenocarcinomas with squamous metaplasia. Multifocal epidermal contiguity and active acantholysis, characterized by individualized keratinized cells and elongated intercellular bridges within pseudolumens, support a 680 Epithelial neoplasms and other tumors. Irregular acinar structures containing secretory material and necrotic debris are lined by one or more layers of epithelial cells. Papillary structures lined by pleomorphic epithelial cells blend into a large island of plump, spindle-shaped myoepithelial cells. Enlarged, hyperchromatic nuclei are present in both glandular and myoepithelial components. Immunohistochemistry can definitively distinguish between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, but distinction of apocrine from other glandular origin may not be feasible with these techniques (see below). The myoepithelial portion of the tumor usually has a benign histologic appearance with myxoid or chondroid features, as in complex sweat gland adenomas (see p. The mesenchymal component is usually characterized by multiple nodules of small spindle and stellate cells with pale cytoplasm and bland, ovoid to fusiform nuclei. The mesenchymal cells are separated by a lightly- basophilic mucinous stroma or are entrapped in lacunar spaces within a more deeply basophilic chondroid matrix. Occasionally, the myoepithelial component is diffuse and predominates over the epithelial aggregates. In rare instances, when the mesenchymal cells demonstrate nuclear atypia and mitotic activity, a designation of apocrine carcinosarcoma or malignant mixed sweat gland tumor is appropriate. Small numbers of poorlydifferentiated apocrine adenocarcinomas show multifocal myoepithelial proliferation with myxoid, chondroid or osseous features. Differential diagnoses of complex apocrine adenocarcinomas are essentially limited to complex mammary adenocarcinomas and carcinosarcomas. Thus, distinction is based on anatomic location and presence or absence of identifiable residual mammary tissue. Other glands, such as salivary and thyroid, can give rise to neoplasms with mixed epithelial and mesenchymal components, but metastasis to skin has not been reported in dogs or cats. Differentiation between sweat gland and mammary gland origin remains problematic; no markers have been found to be consistently beneficial in making this distinction. Although the neoplasm may show some divergent adnexal differentiation, a phenomenon that occurs in a wide variety of tumors of the folliculosebaceous-apocrine unit, the authors believe that the morphologic and immunohistochemical appearance confirm a predominance of sweat gland features (see below). Clinical features Malignant neoplasms of apocrine sweat glands in general occur uncommonly in dogs and cats. Apocrine carcinomas of ductular origin were not named as specific entities in animals until 1992 (Walder & Gross, 1992), making application of numeric data somewhat difficult.