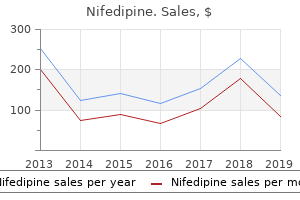
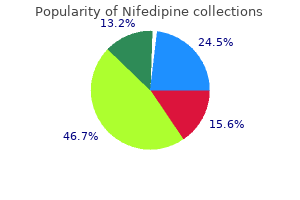
Nifedipine
"Cheap nifedipine 20mg free shipping, blood pressure which arm".
By: L. Lester, MD
Professor, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
Fighting it out An antagonistic effect occurs when the combined response of two drugs is less than the response produced by either drug a lone blood pressure chart pregnancy low proven 20 mg nifedipine. An absorbing problem Two drugs given together can cha nge the absorption of one or both of the drugs: Drugs tha t cha nge the acidity of the stomach can a ffect the ability of another drug to dissolve in the stoma ch prehypertension diet order 20mg nifedipine otc. Sometimes blood pressure chart for 60 year old generic 30 mg nifedipine with mastercard, an a bsorption -related drug intera ction can be avoided by administering the drugs at least 2 hours apart arrhythmia heart murmur buy nifedipine 30 mg visa. When two drugs are given together, they ca n compete for protein -binding sites, leading to an increase in the effects of one drug a s that drug is displa ced f rom the protein and becomes a free, unbound drug. Menu planning Interactions between drugs and food ca n alter the therapeutic effects of the drug. Some drugs stimula the enzyme production, increa sing metabolic rates and the dem and f or vitamins that are enzyme cofactors (which must unite with the enzyme in order for the enzyme to function). Grapefruit ca n inhibit the metabolism of certa in medications, resulting in toxic blood levels; examples include fexofenadine, albendazole, a nd a torvastatin. Because of a ll the interactions food ca n have with drug metabolism, being aware of drug intera ctions is essential. A n a dverse drug reaction (a lso ca lled a side effect or adverse effect), on the other ha nd, is a harmful, undesirable response. Adverse drug reactions can range from mild ones that disappear when the drug is discontinued to debilitating diseases tha t become chronic. A dverse reactions ca n appear shortly after starting a new m edication but m ay become less severe with time. Most a dverse drug reactions result from the known pharmacologic ef fects of a drug and are typically dose -related. Dose -related reactions include: secondary effects hypersusceptibility overdose iatrogenic effects. For exa mple, morphine used f or pain control can lead to two undesirable secondary effects: constipation a nd respira tory depression. Diphenhydramine used a s an antihistamine produces seda tion as a secondary effect and is sometimes used a s a sleep aid. Enhanced action A patient ca n be hypersusceptible to the pharmacologic actions of a drug. Such a patient experiences an excessive thera peutic response or secondary ef fects even when given the usual thera peutic dose. Hypersusceptibility typically results from altered pharmacokinetics (a bsorption, metabolism, and excretion), which leads to higher -than -expected blood concentration levels. A toxic drug reaction can occur when an excessive dose is taken, either intentionally or by a ccident. The result is a n exa ggerated response to the drug that ca n lead to transient changes or more serious reactions, such a s respiratory depression, cardiovascular collapse, and even death. To avoid toxic reactions, chronically ill or elderly patients often receive lower drug doses. Iatrogenic issues Some adverse drug rea ctions, known a s iatrogenic effects, can mimic pathologic disorders. Other examples of iatrogenic effects include induced a sthma with propranolol, induced nephritis with m ethicillin, and induced deafness with gentamicin. These a dverse rea ctions a rise f rom a unique tissue response rather tha n from a n exaggerated pharmacologic action. Extreme pa tient sensitivity can occur a s a drug allergy or an idiosyncratic response. An allergic rea ction not only directly injures cells and tissues but also produces broader systemic damage by initiating cellular release of vasoactive a nd inflammatory substances. The a llergic reaction can vary in intensity from a n immedia te, life -threatening anaphylactic rea ction with circulatory colla pse and swelling of the larynx a nd bronchioles to a m ild rea ction with a ra sh and itching. Quick quiz 1 While teaching a patient about drug therapy for dia betes, you review the absorption, distribution, m etabolism, a nd excretion of insulin a nd ora l antidiabetic agents. Cholinergic drugs Cholinergic drugs promote the a ction of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. These drugs are also called parasympathomimetic drugs because they produce ef fects that imitate parasympathetic nerve stimula tion.
Patients with personality disorders may have problems maintaining an effective doctor-patient alliance because of poor compliance fetal arrhythmia 33 weeks nifedipine 30mg, distrust pulse pressure 39 cheap 20mg nifedipine overnight delivery, irritability blood pressure quick reduction buy 30mg nifedipine with mastercard, and excessive demands leading to less favorable response to treatment for depression pulse pressure 39 buy nifedipine 30mg mastercard, anxiety disorder, or substance abuse. As a group, they may alienate health care providers with late night phone-calls, angry outbursts, repeated admissions, signing out against medical advice, returning to an abusive spouse after being helped with separation, etc. Like all patients, the patient with a personality disorder is a person with human and legal rights. In the medical context, the same fundamental legal rights that are binding on the physician will apply to a patient who has a personality disorder. Once such a relationship arises, the physician is required to attend to the patient attentively, with continuity, and to exercise reasonable care, skill, and judgment (until the relationship is ended through an appropriate process). Duty of care for a patient with a personality disorder arises out of the doctor/patient relationship. Once such a relationship has been established, the physician is required to attend to the patient attentively, with continuity, and to exercise reasonable care, skill, and judgment until the relationship is ended through an appropriate process. The standard of such care expected is identical to that of any physician under similar circumstances, with the same training, experience, specialization, and standing. Perform in a collegial way within the team structure involving other physicians and mental health workers. Patients with personality disorders may choose to discontinue medication, therapy, or both. Objectives 2 Through efficient, focused, data gathering: Determine whether the patient has one of the edema states such as congestive heart failure, has evidence of an infectious disease, or neoplastic disease. Examine for jugular venous distension, gallop, right ventricular heave, leg swelling, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, or ascites. Provide the theoretical basis for the belief that pleural effusions can be divided into transudative and exudative by comparing measurements of certain parameters in pleural fluid compared to serum. Sympathomimetics/Street drugs (cocaine, amphetamines, methylenedioxymethamphetamine/ecstasy, ephedrine, theophylline) ii. List and interpret critical clinical and laboratory findings which were key in the processes of exclusion, 2 differentiation, and diagnosis: Select and interpret drug screen based on clinical information. Select laboratory and diagnostic imaging investigation for toxic effects in addition to diagnosis. Discuss advantages and disadvantages of various strategies for prevention of poison absorption (also termed decontamination) in a patient who is less than one hour after intake of poison. Discuss strategies for enhancing the elimination from the body of various poisons. With advances in care, the aspirations of patients for good health have expanded and this has placed new demands on physicians to address issues that are not strictly biomedical in nature. These concepts are also important if the physician is to understand health and illness behaviour. Key Objectives 2 Define and discuss the concepts of health, wellness, illness, disease and sickness. Enabling Objectives 2 As defined by Health Canada and the World Health Organization: discuss alternative definitions of health; describe the determinants of health. These include: G Income and Social Status G Social Support Networks G Education and Literacy G Employment and Working Conditions G Social Environment G Physical Environments G Personal Health Practices and Coping Skills G Healthy Child Development G Biology and Genetic Endowment G Health Services G Gender G Culture 2 Discuss the concept of life course, natural history of disease, particularly with respect to possible public health and clinical interventions. Physicians are also active participants in disease surveillance programs, encouraging them to address health needs in the population and not merely health demands. Enabling Objectives 2 Know how to access and collect health information to describe the health of a population: Describe the types of data and common components (both qualitative and quantitative) used in creating a community health needs assessment. Be aware of important sources of clinical / population-level health data and recognise the advantages and disadvantages of each of them. Critically evaluate possible sources of data to describe the health of a population including the importance of accurate coding and recording of health information. Describe the uncertainty associated with capturing data on the number of events and populations at risk.
Order nifedipine 20 mg without a prescription. Helvetic Nerds - Blood Pressure (JJD Remix).

The existing literature concerning ovarian stimulation for fertility preservation in women with oestrogen sensitive cancer is limited by its observational nature blood pressure chart for children discount nifedipine 30 mg with amex, small patient numbers and relatively short duration of followup arrhythmia in cats discount nifedipine 30 mg on-line. There are indications that thin endometrium is related to lower ongoing/clinical pregnancy chances as an independent factor diastolic blood pressure 0 nifedipine 20mg with amex. Routine monitoring of endometrial thickness during ovarian stimulation is probably not recommended blood pressure medication kinds discount nifedipine 30 mg overnight delivery. The guideline group suggests performing a single measurement of the endometrium during ultrasound assessment on the day of triggering or oocyte pick-up to counsel patients on potential lower pregnancy chance. The association of follicle size as a triggering criterion with outcome has not been sufficiently studied. Physicians may choose the follicle size upon which final oocyte maturation is triggered on a case to case basis. The decision on timing of triggering in relation to follicle size is multi-factorial, taking into account the size of the growing follicle cohort, the hormonal data on the day of pursued trigger, duration of stimulation, patient burden, financial costs, experience of previous cycles and organizational factors for the centre. Most often, final oocyte maturation is triggered at sizes of several of the leading follicles between 16-22 mm. The association of the oestradiol-to-follicle ratio with clinical outcomes has been studied in several observational studies, but management [22] recommendations cannot be derived from these observational data. The physician should counsel the individual poor responder regarding pregnancy prospects and decide individually whether to continue this and/or further cycles. The available evidence is currently very limited to allow for solid conclusions to be drawn. Any of the previously mentioned administration routes (nonoral) for natural progesterone as luteal phase support can be used. The dosing of natural progesterone has evolved empirically, usually dosages used include: 50 mg once daily for intramuscular progesterone 25 mg once daily for subcutaneous progesterone 90 mg once daily for vaginal progesterone gel 200 mg three times daily for micronized vaginal progesterone in-oil capsules 100 mg two or three times daily for micronized vaginal progesterone in starch suppositories 400 mg two times daily for vaginal pessary. Starting of progesterone for luteal phase support should be in the window between the evening of the day of oocyte retrieval and day 3 post oocyte retrieval. Progesterone for luteal phase support should be administered at least until the day of the pregnancy test. Luteal support should be provided in the window between the evening of the day of oocyte retrieval and D3 post oocyte retrieval. With the current evidence available, no major differences in efficacy have been found comparing the different administration routes of progesterone. Additionally, SoF table 44 a,b [24] patients prefer the oral administration route of dydrogesterone over the vaginal route of progesterone. In the study, there was no comparison with freeze-all, which represents still the best option regarding safety. Prior to start of ovarian stimulation, a risk assessment for high response is advised. The two most relevant studies were both on retrospective data, with inherent methodological and risk of bias problems. The latter urges for follow up of haemo-concentration status even in cases with the freeze-all strategy applied. Implications following the prediction of an extreme ovarian response is relevant for both the clinicians and patients. Clinicians may suggest personalizing the treatment based on that prediction, such strategies will be discussed elsewhere in this guideline. For the patients, ovarian response prediction provides information about the chances of success, the safety risks and complications. Also, several narrative reviews and meta-analyses have been conducted on the subject. Several narrative reviews have been written next to different metaanalyses on the subject. Most of these studies have a limited number of patients, and the definition of a poor and high response has not been uniform. Also, several narrative reviews and metaanalyses have been conducted on the subject. In 2006 a systematic review and meta-analysis (9 studies, 788 cycles) has been performed including inhibin B (Broekmans, et al. Although variations between studies regarding definition of poor response, study quality and study characteristics existed, statistical analysis showed these not related to the predictive performance of inhibin B.
Usual Course this is variable depending on the treatability of the congestive failure hypertension questions purchase nifedipine 20 mg line. Essential Factors Dull aching right upper quadrant and epigastric pain with a large tender liver and elevated liver enzymes in association with other findings of heart failure hypertension va compensation nifedipine 30mg sale. Main Features Prevalence: common blood pressure chart jnc cheap nifedipine 20mg otc, especially in middle age pulse pressure stroke volume trusted nifedipine 30mg, except in ethnic minorities with high prevalence when younger age groups are also often affected. Pain Quality: pain associated with passage of stone into the cystic duct is a severe colic, short lived with associated sweating. Associated Symptoms Anorexia, nausea and vomiting, jaundice, dark urine, pale stool. Neutrophil leucocytosis; hyperbilirubinemia; elevation in serum transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. Usual Course Resolves within two or three days unless stone impacts in common bile duct, causing obstructive jaundice. Complications Obstructive jaundice, mucocele of the gallbladder, empyema of gallbladder with or without rupture. Pathology Gallstones may be cholesterol from lithogenic bile, pigment secondary to chronic hemolysis, or mixed. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria Acute right upper quadrant pain, dyspepsia to fatty foods. Main Features Sex Ratio: males and females are about equally affected, although in some areas it is more common in females. Age of Onset: can occur at any age, but most common in the middle-aged and the elderly. At first may be periodic and infrequent, every two to three months lasting for a few days. Associated Symptoms Anorexia and mild weight loss, often nausea, but vomiting is rare and associated with a prepyloric ulcer. Patient shows site of pain by pointing to diffuse area of upper abdomen with hand. The diagnosis is made on endoscopy or barium meal (upper gastrointestinal series). Usual Course Periodic pain becomes more frequent and perhaps severe and for longer duration until pain-free periods may disappear. Pain commonly responds to regular antacid and anticholinergic therapy and particularly to H2 receptor antagonists, but there is a high incidence of relapse. Complications Gastric ulcers may bleed, usually chronically, presenting with iron-deficiency anemia but occasionally acutely presenting with hematemesis and melena; chronic ulceration leads to scarring so that prepyloric ulcers may cause obstruction with vomiting. Peptic ulcers may perforate, though usually insidiously, resulting in erosion into adjacent structures such as the pancreas. This causes localized but rarely generalized pancreatitis, or acute perforation with resulting acute peritonitis. Social and Physical Disability Recurrent or chronic pain will restrict normal activities and reduce productivity at work. Main Features Prevalence: this pain is a common occurrence soon after the gallbladder has been removed, often with a short initial pain-free period. Pain Quality: the pain is similar to "gallbladder" pain, may be colicky in nature, daily, but not at night, may be dull or very intense lasting all day, and may continue for months or years. Signs and Laboratory Findings Tenderness in right upper quadrant in region of the scar. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria Right upper quadrant pain in a patient following cholecystectomy with no obvious cause. X I Page 153 Pathology Chronic ulceration with transmural inflammation results in localized fibrosis and cicatrization. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria Chronic gastric ulcer is a syndrome of periodic diffuse postprandial upper abdominal pain relieved by antacids. Social and Physical Disability Restriction of normal activities and reduction of productivity at work. Pathology Chronic ulceration with transmural inflammation resulting in localized fibrosis and cicatrization. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria Chronic duodenal ulcer is a syndrome of periodic, highly localized, upper epigastric pain relieved by antacids. Site Pain is classically localized to a spot high in the epigastrium, either central or under the right costal margin, and commonly radiates through to the back.