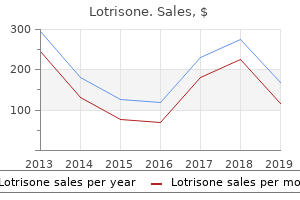
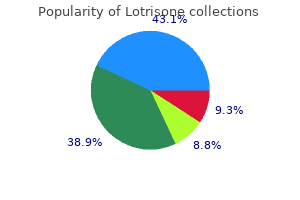
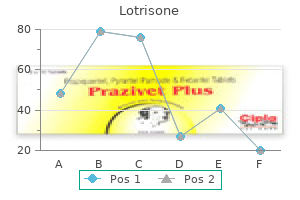
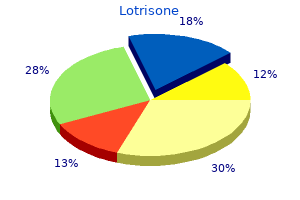
Lotrisone
"Generic lotrisone 10mg line, antifungal amazon".
By: V. Anktos, M.S., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of South Carolina School of Medicine
Some of the glutamate nitrogen is released as ammonium ions by the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase (see below) fungus gnat/rootknot gall exterminator buy cheap lotrisone 10mg line. Aminotransferases are intracellular enzymes that have both cytosolic and mitochondria1 isoforms fungus habitat buy lotrisone 10 mg line. When there is liver damage antifungal for diaper rash generic 10mg lotrisone mastercard, as occurs with cirrhosis or viral hepatitis fungus yellow foamy lotrisone 10mg with mastercard, these aminotransferase are released from the hepatocytes. Although all 20 common amino acids, except threonine, lysine, and proline, can be transaminated, many of the amino acids can also be catabolized by pathways that do not involve transamination. One such example is the dehydratase-catalyzed reactions that remove water from both serine and threonine and generate intermediates that contain unstable imino groups. Catabolism of proline involves oxidation and opening of the ring to generate glutamate semialdehyde, which is then converted to glutamate (see Chapter 20). The effect of the next two steps in the urea cycle is to add an amino group to citrulline to generate arginine. The urea cycle is completed by the hydrolysis of arginine, which generates urea plus ornithine: arginine + H20 + urea + ornithine Urea is secreted from hepatocytes and transported to the kidney for excretion in the urine. Ornithine generated by arginase is transported back into mitochondria to continue the cyclic process of urea synthesis. Some of the ornithine utilized in the urea cycle is derived through the action of arginase on dietary arginine. Ornithine transaminase then acts on glutamate semialdehyde to generate ornithine: glutamate semialdehyde + glutamate + ornithine + a-ketoglutarate Synthesis of Arginine from Ornithine Is Not Limited to the Liver. As described above, the enzymes of the urea cycle convert ornithine into arginine. For example, the intestinal mucosa can convert ornithine to citrulline, and the kidney can convert the resultant citrulline to arginine. However, since the kidney and intestine lack arginase, they cannot synthesize urea. Like fructose 2,6-bisphosphate which regulates glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, N-acetylglutamate is not an intermediate in the metabolic pathway that it regulates, but instead. Thus, N-acetylglutamate synthesis occurs only when the supply of both glutamate and ornithine is adequate. Induction of urea cycle enzymes thus occurs under conditions of starvation and stress. The enzymes of the urea cycle are also induced by high-protein diets, which provide excess amino acids to the liver. Hyperammonemia in adults is usually the consequence of impaired liver function, secondary to liver disease. Transient hyperammonemia is often seen in premature neonates with immature liver function and/or inadequate hepatic blood flow. Impaired urea synthesis may also be the result of a genetic defect in one of the enzymes of the urea cycle. Regardless of its etiology, hyperammonemia is usually accompanied by increased plasma levels of glutamine, the amino acid that the brain uses as a vehicle to export excess ammonium ions. Treatment for hyperammonemia involves hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis to remove the excess ammonia. In acute cases, oral sodium benzoate and sodium phenylbutyrate are sometimes administered to provide alternate pathways for nitrogen excretion as hippurate and phenylacetylglutamine, respectively. Protein intake should also be severely restricted in patients with hyperammonemia. At the same time, it is important to provide adequate intake of carbohydrates to minimize further catabolism of endogenous protein. Prompt treatment is critical because prolonged hyperammonemia can result in irreversible brain damage, coma, and even death. The differential diagnosis of inborn errors of the urea cycle is usually made from quantitative analysis of plasma amino acids, which identifies increased levels of urea-cycle intermediates upstream of the specific enzyme blockage.
If any one of these elements are missing there will be no significant remarkable impact on productivity per hectare of land jojoba antifungal buy 10 mg lotrisone amex. Effects of Green Revolution Green revolution has led to tremendous increase in food grain productivity and improvements in agricultural scientific advancements had been seen fungus on face order 10 mg lotrisone overnight delivery. Let us list and discuss them: (i) Increase in Food Grain Productivity: As a result of new agricultural strategy fungus gnats humans cheap 10mg lotrisone fast delivery, food grains output substantially increased from 81 can fungus gnats kill cannabis purchase lotrisone 10 mg on line. In addition to producing larger quantities of food, the green revolution was also beneficial because it made it possible to grow more crops on roughly the same amount of land with a similar amount of effort. This reduced production costs and also resulted in cheaper prices for food in the market. Self-Insturctional Material 264 Food Production (ii) Scientific Cultivation: A very important effect of green revolution is that traditional agricultural inputs and practices have given way to new and scientific practices. First, the proportion of cereals in the food grains output has increased and the proportion of pulses has declined. Second, the proportion of wheat cereals has increased while that of coarse grains has declined. Many industries related with agriculture, machinery, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides etc. Our farmers have now begun to think that they can change their misfortunes by adopting new technology. Unlike past, they are now giving up traditional agricultural practices for scientific practices. Increase in productivity in these areas has enhanced the status of agriculture from a low level subsistence activity to a money- making activity. The desire for better farming methods and better standard of living is growing up. Limitations of Green Revolution In spite of several achievements, the green revolution has certain limitations. Hence, these farmers are getting the absolute benefits of the green revolution and became comparatively richer than small farmers. On account of the above reasons new agricultural strategy has led to an increase in regional inequalities. Many large farmers have evicted tenants as they now find it more profitable to cultivate land themselves. Wetlands have also attracted outsiders (non-agriculturists from nearby towns to invest capital in buying farms. The attitude of the Government towards the problems of treatment and rehabilitation of victims of accidents on farm machines is that of total ambivalence. Realizing the immense scope for development of fisheries and aquaculture, the Government of India has restructured the Central Plan Scheme under an umbrella of Blue Revolution, provides for a focused development and management of the fisheries sector to increase both fish production and fish productivity from aquaculture and fisheries resources of the inland and marine fisheries sector including deep sea fishing. The blue revolution envisages transformation of the fisheries sector with increased investment, better training and development of infrastructure on the lines of green revolution. Blue revolution aims to double the income of the fishers and fish farmers with inclusive participation of the socioeconomically weaker sections and ensure sustainability with environment and bio-security. The key goal would be to substantially increase the share of Indian fisheries in the export market. There is a remarkable emergence of aquaculture as an important and highly productive agricultural activity. Aquaculture refers to all forms of active culturing of aquatic animals and plants, occurring in marine, brackish, or fresh waters. It commonly involves the management of all stages in the life cycle of the cultivated fish, from the production of eggs and larvae, to growth and eventual harvest of high-quality, market-sized fish. Various species of fish are grown in aquaculture, using a variety of cultivation systems. Many species of molluscs, crustaceans, and other invertebrates are grown in aquaculture, particularly in Asia, but increasingly in other regions as well. Seaweeds are also grown in large quantities for use as food and as feedstock for the production of alginates and other industrial products.
Cost: Certain teaching aids like films trichophyton fungus definition lotrisone 10mg without a prescription, slides fungus zombie last of us generic 10 mg lotrisone visa, overhead projectors are expensive and the fund allotted to the educator must also be considered before deciding the choice of teaching aids antifungal zinc generic lotrisone 10mg with mastercard. Putting the entire Schedule into a Time Frame: Time frame for each content should be determined fungus resistant grass lotrisone 10 mg with visa, so that the total time period for the entire programme can be planned. With the time frame, appropriate venue, type of approach whether individual or group approach etc. Teaching Skills to the Trainers: the three main skills that the nutrition educator must be trained are for: Manual skills- Using hands skillfully for nutritional assessment (anthropometrics and survey methods). Nutrition education is a set of planned educational activities targeted at certain population groups and aimed at acquiring healthy nutrition behaviors. To assist the individual to identify resources for continuing access to sound food and nutrition information. The need for nutrition education has been strongly reinforced by the concept of the Right to Food. To provide information and education on good diet, food safety, food-borne diseases, food labelling and processing, production and preparation; while in the school curriculum integrating agriculture, food safety, environment, nutrition and health education builds citizens` capacity to achieve and maintain their own food security. Nutrition education provided at elementary level lays a strong foundation for promoting lifelong healthy eating and improving long- term, sustainable nutrition security. To educate about the use of locally available and seasonal foods, and Self-Insturctional Material 240 Nutrition Education highlighting that optimal nutrition need not be expensive always. For instance, most mothers are not so poor as not to be able to afford 50-100 gmsof green leafy vegetables to child daily, if they realize that this may make a difference between blindness and normal vision. Nutrition education is an essential means to ensure better health practices and food habits through an increase knowledge and favorable attitudes. To improve the nutritional levels of the community by wise use of the available means that control malnutrition 3. Advantagesof mass methods: Suitable for creating general awareness amongst the people. Radio: Radio is a good communication or information media to the community people especially in a country like India and can reach large numbers of people at any given time, even in remote places. Radio is a mass-communication method that can inform, stimulate curiosity, arouse and build interest, create the desire to learn, see, hear and act, widen horizon and mental outlook, breakdown prejudice, and bring enlightenment, promote favorable attitudes and influence emotions, interpret policies, guide listener`s interest and helps them grasp the significant new ideas and thought. It carries news bulletins, stories, warnings regarding outbreak of diseases, interviews, short talks, plays, documentaries, question and answer sessions, and special programmes for rural people, urban slum people, housewives and children to disseminate knowledge related to health, nutrition, good living etc. The major focus of this type of nutrition education is not knowledge and facts, but rather the development of permanent behavioral changes that improve the nutritional status of the community. Also, educating the masses is not an easy task and the educators must be trained systematically and develop the skills of both teaching and learning process. Nutrition education should be practical and should be easily adoptable to the socioeconomic status, food habits and the available local food resource generally needed for the purpose of demonstration and feeding of the locally available audience. Such, programmes well organized by trained educators will be wise and efficient to bring out a change in the community. In this unit, we shall discuss about planning, executing and evaluation of nutrition education programmes. We have already in unit 10 discussed on planning a training programme for training the trainers. Now, let us discuss the systematic way of planning of nutrition education programme for the community, which also correlates with the previous one. For conducting causal analysis specific to a community, formative research is conducted that describes investigations conducted for programme design and planning. Formulation Phase:Here, the objectives of nutrition education are set, designing messages are carried out, in short the elements conceptualized in the previous phase are given shape and structure. Identification of Target Audience: Target audience are the group of people with whom the trainer communicates for change in behavior. The target audience can be classified into three segments as Primary, Secondary and Tertiary audience.
Clinically fungus gnats thrips cheap lotrisone 10 mg free shipping, Budd-Chiari syndrome is characterized by the sudden onset of severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain lung fungus x ray cheap lotrisone 10 mg online, ascites antifungal herbal supplements purchase lotrisone 10mg with amex, tender hepatomegaly fungus under fingernails discount lotrisone 10mg with visa, and hematemesis. Gastrointestinal System Answers 339 Occlusion of the central veins, called venoocclusive disease, may be rarely seen in Jamaican drinkers of alkaloid-containing bush tea, but is much more commonly found following bone marrow transplantation (up to 25% of allogenic marrow transplants). Asymptomatic infection in individuals is documented by serologic abnormalities only. Liver biopsies in patients with acute hepatitis, either the anicteric phase or the icteric phase, reveal focal necrosis of hepatocytes (forming Councilman bodies) and lobular disarray resulting from ballooning degeneration of the hepatocytes. During the prodrome phase, patients may develop symptoms that include anorexia, nausea and vomiting, headaches, photophobia, and myalgia. An unusual symptom associated with acute viral hepatitis is altered olfaction and taste, especially the loss of taste for coffee and cigarettes. The next phase, the icteric phase, involves jaundice produced by increased bilirubin. Patients may also develop light stools and dark urine (due to disrupted bile flow) and ecchymoses (due to decreased vitamin K). Fulminant hepatitis refers to massive necrosis and is seen in about 1% of patients with either hepatitis B or C, but very rarely with hepatitis A infection. The biggest risk for fulminant hepatitis is coinfection with both hepatitis B and D. Chronic hepatitis is defined as elevated serum liver enzymes for longer than 6 months. It is associated with small outbreaks of hepatitis in the United States, especially among young children at day care centers. Hepatitis C virus is characterized by episodic elevations in serum transaminases, and also by fatty change in liver biopsy specimens. It is found in underdeveloped countries and has an unusually high mortality in pregnant females. The latter is characterized histologically by intranuclear eosinophilic inclusions (Cowdry bodies) and nuclei that have a ground-glass appearance. It appears before symptoms begin, peaks during overt disease, and declines to undetectable levels in 3 to 6 months. In chronic active hepatitis, an intense inflammatory reaction with numerous plasma cells spreads from portal tracts into periportal areas. The reaction destroys the limiting plate and results in formation of periportal hepatocytic islets. Chronic persistent hepatitis is usually a sequela of acute viral hepatitis and has a benign course without progression to chronic active hepatitis or cirrhosis. The portal inflammation does not extend into the periportal areas, and this differentiates chronic persistent hepatitis from chronic active hepatitis. Neither hepatitis A nor hepatitis E virus infection is associated with the development of chronic hepatitis. About 5% of adults infected with hepatitis B develop chronic hepatitis, and about one-half of these patients progress to cirrhosis. In contrast to hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis develops in about 50% of patients with hepatitis C. Clinically, chronic hepatitis C is characterized by episodic elevations in serum transaminases, and also by fatty change in liver biopsy specimens. There might be acute coinfection by hepatitis D and hepatitis B, which results in chronic hepatitis in less than 5% of cases. If, instead, hepatitis D is superinfected upon a chronic carrier of hepatitis B virus, then about 80% of cases progress to chronic hepatitis. Liver biopsies in patients with chronic hepatitis may reveal inflammation that is limited to the portal areas (chronic persistent hepatitis), or the inflammation may extend into the adjacent hepatocytes. This inflammation causes necrosis of the hepatocytes (piecemeal necrosis) and is called chronic active hepatitis. A clinically distinct subtype of chronic hepatitis is called chronic autoimmune ("lupoid") hepatitis. This disease occurs in young females who have no serologic evidence of viral disease. These patients have increased IgG levels and high titers of autoantibodies, such as anti-smooth-muscle antibodies and antinuclear antibodies.
Order 10 mg lotrisone visa. Making Herbal Glycerites.