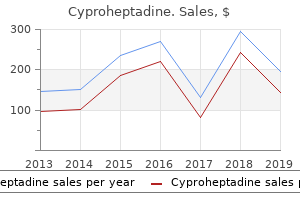
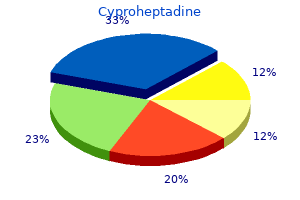
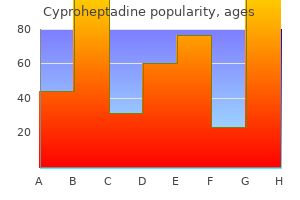
Cyproheptadine
"Cheap 4 mg cyproheptadine overnight delivery, allergy symptoms not responding to medication".
By: M. Tragak, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine
Infections are frequently contracted in families milk allergy symptoms 10 month old purchase cyproheptadine 4mg with amex, schools allergy medicine purchase 4 mg cyproheptadine with mastercard, homes for children allergy relief juice cheap 4 mg cyproheptadine mastercard, work camps allergy high cyproheptadine 4 mg with visa, and military camps. No specific prophylactic measures are available to protect against any of the mycoplasma infections. Nosocomial Infections & Nosocomial infections occur in hospitalized patients as complications of 4 their primary disease. The most frequent types of infection are urinary tract infections (42 %), pneumonia (21 %), surgical wound infections (16 %), and sepsis (8 %). The pathogen types most frequently involved are opportunistic, Gram-negative rods, staphylococci and enterococci, followed by fungi. Control of nosocomial infections requires a number of operational measures (disinfection, asepsis, rationalized antibiotic therapies, isolation), organizational measures (hygiene committee, recognition of infections, procedural guidelines, train& ing programs), and structural measures. Definition the term nosocomial infection designates infections contracted by hospitalized patients 48 hours or more from the beginning of hospitalization. These are secondary infections that occur as complications of the primary diseases to be treated in the hospital. Pathogens, Infections, Frequency the significance of the different human pathogens in nosocomial infections varies widely: & Subcellular entities. Isolated cases of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease due to unsterilized instruments have been described in the literature. An example of a viral nosocomial infection is infectious hepatitis transmitted by blood or blood products. Most of the causative organisms are facultatively pathogenic (opportunistic) bacteria, which are frequently resistant to many different antibiotics. These bacteria have found niches in which they persist as so-called hospital flora. The resistance patters seen in these bacteria reflect the often wide variations between anti-infective regimens as practiced in different hospitals. It can be said in general that they affect immunocompromised patients and that neutropenic patients are particular susceptible. The prevalence and pathogen data shown here approximate what other studies have found. Within a particular hospital, the infection rate is always highest in the intensive care units. The source of infection for exogenous infections is most likely to lie with the medical staff. In most cases, the pathogens are transmitted from patient to patient during medical and nursing activities. Less frequently, the staff is either also infected or colonized by the hospital flora. Another important cause of nosocomial infections is technical medical measures that facilitate passage of the pathogens into the body. The infection control program varies depending on the situation in each particular hospital and can be summarized in three general groups: Operational measures. This category includes all measures pertaining to treatment and care of patients and cleaning measures. Further precautionary operational measures include isolation of patients that would be sources of infection and the economical and specific administration of antibiotic therapies. The organization of hospital infection control must be adapted to the structure of each particular hospital. In order to carry out these tasks efficiently, the committee should have access to a working group of specialists. In larger hospitals, a hospital epidemiologist, and staff as required, are retained for these functions. These measures refer above all to new structures, which must be built in accordance with hygienic criteria.
After initial stabilization of the patient and definitive diagnosis by echocardiography allergy medicine removed from market buy cheap cyproheptadine 4mg on-line, transcatheter balloon valvotomy is the treatment of choice for this lesion allergy testing no antihistamines buy generic cyproheptadine 4mg line, although surgical valvotomy may be used in specific cases allergy symptoms to xanthan gum cyproheptadine 4mg visa. Despite successful relief of the obstruction during catheterization allergy shots tree nuts cheap cyproheptadine 4 mg without prescription, cyanosis is usually not completely relieved but rather resolves gradually over the first weeks of life as the right ventricle becomes more compliant, tricuspid regurgitation lessens, and there is less right-to-left shunting at the atrial level. Successful balloon Cardiovascular Disorders 499 Valvar Pulmonary Stenosis 80% 65 40 58% 58% 65 30 m=5 58% m=8 65 5 120 10 Figure 41. Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum ("hypoplastic right heart syndrome," see. The coronary arteries may be quite abnormal, including areas of stenoses or complete atresia. Many patients have significant coronary abnormalities with sinusoidal or fistulous connections to the hypertensive right ventricle or significant coronary stenoses (not shown). Because there is no outlet of the right ventricle, there is typically suprasystemic pressure in the right ventricle and some tricuspid regurgitation. Surgical management is often preceded by catheterization to define the coronary artery anatomy. Usually, at the time of this procedure, a systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt (most often a Blalock-Taussig shunt) is constructed to also augment pulmonary blood flow. In 70% of cases, the great arteries are normally aligned with the ventricles; however, in the remaining 30%, the great arteries are transposed. An atrial level communication is necessary for blood to exit the right atrium; there is an obligatory right-to-left shunt at this level. In patients with normally related great arteries, pulmonary blood flow is derived from the right ventricle; if the right ventricle (or its connection with the left ventricle through a ventricular septal defect) is severely diminutive, the pulmonary blood flow may be duct dependent; closure of the ductus leads to profound hypoxemia and acidosis. Immediate medical management is primarily aimed at maintenance of adequate pulmonary blood flow. In the usual case of severe pulmonary stenosis Tricuspid Atresia Normally Related Great Arteries 78% 70 45 20 10 95% 78% 78% m=6 55% 60% m=6 78% 70 6 Figure 41. Tricuspid atresia with normally related great arteries and a small patent ductus arteriosus. Typical anatomic and hemodynamic findings include (i) atresia of the tricuspid valve; (ii) hypoplasia of the right ventricle; (iii) restriction to pulmonary blood flow at two levels: a (usually) small ventricular septal defect and a stenotic pulmonary valve; (iv) all systemic venous return must pass through the patent foramen ovale to reach the left ventricle; (v) complete mixing at the left atrial level, with systemic oxygen saturation of 78% (in FiO2 of 0. Surgical creation of a more permanent source of pulmonary blood flow (usually a Blalock-Taussig shunt) is undertaken as soon as possible. Detailed anatomic definition particularly regarding Tetralogy of Fallot 82% 82 55 79% 20 15 58% 98% m=6 66% m=8 80% 80 6 79% 80 6 Figure 41. Typical anatomic and hemodynamic findings include (i) an anteriorly displaced infundibular septum, resulting in subpulmonary stenosis, a large ventricular septal defect, and overriding of the aorta over the muscular septum; (ii) hypoplasia of the pulmonary valve, main, and branch pulmonary arteries; (iii) equal right and left ventricular pressures; (iv) a right-to-left shunt at ventricular level, with a systemic oxygen saturation of 82%. Cardiovascular Disorders 503 coronary artery anatomy, the presence of additional ventricular septal defects, and the sources of pulmonary blood flow (systemic to pulmonary collateral vessels) are necessary before surgical intervention. If echocardiography is not able to fully show these details, then diagnostic catheterization is performed. Surgical repair of the asymptomatic child with tetralogy of Fallot is usually recommended within the first 6 months of life. Complete repair is generally performed at our institution, although a systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt is sometimes employed in unusual cases such as multiple ventricular septal defects or coronary anomalies. Anatomically, there is "downward displacement" of the tricuspid valve into the body of the right Ebstein Anomaly 78% 75 50 48% 75 30 m=5 48% m = 13 74 5 75 13 A B Figure 41. Typical anatomic and hemodynamic findings include (i) inferior displacement of the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, which may also cause subpulmonary obstruction, (ii) diminutive muscular right ventricle, (iii) marked enlargement of the right atrium due to "atrialized" portion of right ventricle as well as tricuspid regurgitation, (iv) right-to-left shunting at the atrial level (note arterial oxygen saturation of 78%), (v) a left-to-right shunt and pulmonary hypertension secondary to a large patent ductus arteriosus supplying the pulmonary blood flow, (vi) low cardiac output (note low mixed venous oxygen saturation in the superior vena cava). B: Chest radiograph in a neonate with severe Ebstein anomaly and no significant pulmonary blood flow from the ductus arteriosus. The pulmonary vascular markings are diminished due to the decreased pulmonary blood flow. Hypoplasia of the lungs is common due to the large heart causing a "space-occupying lesion. The prognosis for neonates presenting with profound cyanosis due to Ebstein anomaly is quite grave.
Adverse effects: Side effects reported for oral or parenteral use of ribavirin have included dose-dependent transient anemia allergy symptoms 8dp5dt buy 4mg cyproheptadine with amex. The aerosol may be safer allergy shots left out of fridge proven cyproheptadine 4 mg, although respiratory function in infants can deteriorate quickly after initiation of aerosol treatment treatment allergy to cats buy cheap cyproheptadine 4mg. Because of teratogenic effects in experimental animals allergy jobs california buy cyproheptadine 4 mg amex, ribavirin is contraindicated in pregnancy (Figure 38. Of this group, hepatitis B and hepatitis C are the most common causes of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (Figure 38. Combination therapy of an interferon plus lamivudine is no more effective than monotherapy with lamivudine. In the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, the preferred treatment is the combination of peginterferon-α-2a or peginterferon-α-2b plus ribavirin, which is more effective than the combination of standard interferons and ribavirin. Although interferon inhibits the growth of many viruses in vitro, its activity in vivo against viruses has been disappointing. The larger molecular size delays absorption from the injection site, lengthening the duration of action of the drug, and also decreases its clearance. Pharmacokinetics: Interferon is not active orally, but it may be administered intralesionally, subcutaneously, or intravenously. Very little active compound is found in the plasma, and its presence is not correlated with clinical responses. Cellular uptake and metabolism by the liver and kidney account for the disappearance of interferon from the plasma. Adverse effects: Adverse effects include flu-like symptoms on injection, such as fever, chills, myalgias, arthralgias, and gastrointestinal disturbances. The principal dose-limiting toxicities are bone marrow suppression including granulocytopenia, neurotoxicity characterized by somnolence and behavioral disturbances, severe fatigue and weight loss, autoimmune P. Drug interactions: Interferon interferes with hepatic drug metabolism, and toxic accumulations of theophylline have been reported. As with many nucleotide analogs, the intracellular half-life of the triphosphate is many hours longer than its plasma half-life, which permits infrequent dosing. Dose reductions are necessary when there is moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min). Adefovir is administered once a day and is excreted in the urine, with 45 percent as the active compound. Both decreased viral load and improved liver function have occurred in patients treated with adefovir. As with other agents, discontinuation of adefovir results in severe exacerbation of hepatitis in about 25 percent of patients. Following intracellular phosphorylation to the triphosphate, it competes with the natural substrate, deoxyguanosine triphosphate, for viral reverse transcriptase. Renal function must be assessed periodically, and drugs that have renal toxicity should be avoided. Patients should be monitored closely for several months after discontinuation of therapy because of the possibility of severe hepatitis. Telbivudine is eliminated by glomerular filtration as the unchanged drug, and no metabolites have been detected. Combination of telbivudine with lamivudine has been no more effective than telbivudine alone. The drugs that are effective against these viruses exert their actions during the acute phase of viral infections and are without effect during the latent phase. It is also given prophylactically to seropositive patients before bone marrow and after heart transplants to protect such individuals during posttransplant immunosuppressive treatments. The monophosphate analog is converted to the di- and triphosphate forms by the host cells.
Without adequate knowledge and training in self-care skills allergy shots vs allergy drops generic 4mg cyproheptadine overnight delivery, consumers cannot make effective decisions about their health allergy shots lower immune system 4mg cyproheptadine with mastercard. As the life span of our population continues to increase allergy drops for eyes quality cyproheptadine 4mg, the number of people with such illnesses will also increase allergy testing madison wi 4mg cyproheptadine for sale. People with chronic illness need health care information to participate actively in and assume responsibility for much of their own care. Health education can help these individuals to adapt to illness, prevent complications, carry out prescribed therapy, and solve problems when confronted with new situations. It can also prevent crisis situations and reduce the potential for rehospitalization resulting from inadequate information about selfcare. The goal of health education is to teach people to live life to its healthiest-that is, to strive toward achieving their maximum health potential. For health care agencies, offering community wellness programs is a public relations tool for increasing patient satisfaction and for developing a positive image of the institution. Significant factors for the nurse to consider when planning patient education include the availability of health care outside the conventional hospital setting, the employment of diverse health care providers to accomplish care management goals, and the increased use of alternative strategies rather than traditional approaches to care. The careful consideration of these factors can provide patients with the comprehensive information that is essential for making informed decisions about health care. The nurse as a teacher is challenged, not only to provide specific patient and family education, but also to focus on the educational needs of communities. Health education is important to nursing care, because it can determine how well individuals and families are able to perform behaviors conducive to optimal self-care. Health education is an independent function of nursing practice and is a primary responsibility of the nursing profession. All nursing care is directed toward promoting, maintaining, and restoring health; preventing illness; and assisting people to adapt to the residual effects of illness. Many of these nursing activities are accomplished through health education or patient teaching. Every contact a nurse has with a health care consumer, whether that person is ill or not, should be considered an opportunity for health teaching. Although the person has a right to decide whether or not to learn, the nurse has the responsibility to present information that will motivate the person to recognize the need to learn. Therefore, the nurse must seize opportunities both inside and outside health care settings to facilitate wellness. Educational environments can include homes, hospitals, community health centers, places of business, service organizations, shelters, and consumer action or support groups. Adherence to the Therapeutic Regimen One of the goals of patient education is to encourage people to adhere to their therapeutic regimen. Adherence to a therapeutic regimen usually requires that the person make one or more lifestyle changes to carry out specific activities that promote and maintain health. The fact that many people do not adhere to their prescribed regimens cannot be ignored or minimized; rates of adherence are generally low, especially when the regimens are complex or of long duration. For the most part, the findings have been inconclusive, and no one predominant causative factor has been found. Elderly people frequently have one or more chronic illnesses that are managed with numerous medications and complicated by periodic acute episodes. Elderly people may also have other problems that affect adherence to therapeutic regimens, such as increased sensitivity to medications and their side effects, difficulty in adjusting to change and stress, financial constraints, forgetfulness, inadequate support systems, lifetime habits of self-treatment with over-the-counter medications, visual and hearing impairments, and mobility limitations. To promote adherence among the elderly, time and effort must be taken to assess all variables that may affect health behavior.
Order 4mg cyproheptadine visa. Allergies to Cats in Humans : Treating Allergies.