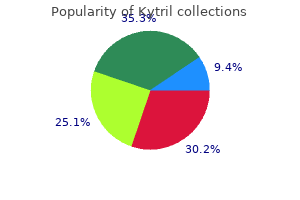
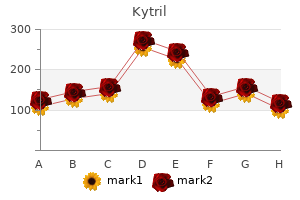
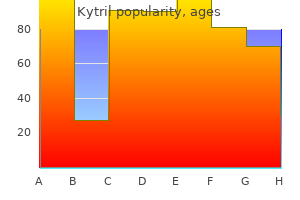
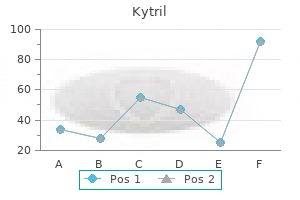
Kytril
"Kytril 1mg low cost, treatment laryngitis".
By: R. Connor, M.A.S., M.D.
Clinical Director, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine and Research Institute
The reverse laser transition produces absorption from the ground state at the laser wavelength treatment lice discount 1mg kytril with mastercard, an effect known as reabsorption loss medications dialyzed out generic 1mg kytril visa. The reverse pump transition limits the extent to which the ground state can be depleted treatment kawasaki disease order kytril 1mg overnight delivery, thereby limiting the population density that can be stored in the upper laser state medicine xl3 buy kytril 1 mg lowest price. It is convenient to work with the normalized upper-state population density, defined by = N2/N. The bold cells are the relevant levels for the 1533 nm pump transition and the 1645 nm laser transition. The ratio of partition functions Z2/Z1 is independent of wavelength; therefore f increases exponentially with decreasing wavelength. The wavelength dependence of reabsorption loss can have a significant impact on quasi-three-level laser performance. In addition to the explicit exponential dependence, the variation of the partition function ratio with temperature is relatively insignificant, as shown in Figure 5. Similar to the wavelength dependence, the temperature dependence of reabsorption loss can have a significant impact on quasi-three-level laser performance. This places an upper limit on the normalized upper-state population, given by max = f/(1 + f). The shift of the crossing point from the nominal value of 1528 nm is a result of the temperature dependence of Z2/Z1. The maximum population density than can be stored in the upper state is substantially higher for the 1470 nm pump transition than for the 1533 nm pump transition. The temperature dependence for the 1533-nm pump wavelength is nearly zero because this wavelength is close to 1/E0. We can define effective cross sections by multiplying by the Boltzmann population factors. The effective absorption cross section for the laser transition is given by a = f1 = /N (5. Similarly, the effective emission cross section for the laser transition is given by e = f2. The emission cross section spectrum is derived from the absorption spectrum by combining Equation 5. Reciprocity of emission and absorption spectra is discussed in references 20 to 25. The emission cross section spectrum derived from the absorption spectrum of Figure 5. The exponential dependence of the Boltzmann ratio f on wavelength results from reabsorption loss and is shown in Figure 5. This dependence accounts for the shift in the relative amplitudes of the 1617-nm and 1645-nm peaks between Figure 5. The absorption coefficient of the 1617-nm line is twice that of the 1645-nm line, whereas the emission cross section of the 1617-nm line is only 25% greater than that of the 1645-nm line. Prior to the past several years, pump intensities sufficient for direct upper-state pumping were not readily available. A technique that has been widely employed to reduce the pump intensity requirement is illustrated in Figure 5. In addition to the lasant ion, a second ion, known as the sensitizer, is introduced into the laser crystal. In this scheme the pump light is absorbed by the sensitizer, which transfers its excitation to the activator. The sensitizer concentration can be relatively high, enabling efficient absorption of the pump, while the activator concentration is relatively low, minimizing reabsorption loss. The 3H4 + 3H6 3F4 + 3F4 crossrelaxation process converts the pump excitation into two ions in the first excited state of Tm3+.
As a result medications with pseudoephedrine generic 1 mg kytril visa, the pulmonary circulation is a low-pressure medicines360 buy 2mg kytril with mastercard, low-resistance flow loop medications zanx discount 1 mg kytril overnight delivery, with inlet pressure approximately equal to 15 mmHg and outlet (return) pressure of approximately 5 mmHg symptoms 3 days after conception kytril 2mg mastercard. In contrast, the flow resistance of the systemic circulation is much higher than that of the pulmonary circulation, and the pressure drop in the systemic loop is large. This necessitates a large inlet pressure on the systemic side in order to maintain an adequate systemic flow rate. Fortunately, the systemic vessels are much more robust than the pulmonary capillaries and can, therefore, tolerate higher pressures. In short, the systemic circulation is best described as a high-pressure, high-resistance flow loop. The use of two pumps in series is, therefore, an excellent design that satisfies the constraints of low pulmonary pressure and higher systemic pressures. Of course, the presence of two pumps rather than a single pump introduces a number of complications. Most importantly, the output of the two halves of the heart must be very closely matched over a wide range of conditions (resting to vigorous exercise). If not, blood would accumulate or be depleted from the pulmonary circulation, with serious consequences. Output matching is in part accomplished by the two half-hearts sharing a common "wiring system" used to control heart rate. Additionally, each half of the heart is able to adjust its output, within certain limits, so that it delivers whatever amount of blood it receives. More specifically, on each side of the heart there is: r a main pumping chamber (the ventricle) r a holding chamber for each ventricle (the atrium) r two check valves, one each for the ventricle and the atrium. The valves are made up of thin tissue leaflets that seal together to prevent backflow when closed. The valve between the left ventricle and the aorta is the aortic valve, and that between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery is the pulmonary valve. The aortic and pulmonary valves do not have chordae tendineae to prevent eversion. Instead, the aortic and pulmonary valves have three leaflets that, when in the closed position, lean up against one another (called coaptation), thereby sealing the valve and preventing the leaflets from being everted. The technical definitions are given below, but as a rule of thumb, systole corresponds approximately to the period of ventricular contraction, while diastole corresponds approximately to the period of ventricular dilation, or relaxation. Below is the sequence of events for a single beat of the left heart (numbers refer to the lower portion of. The pulmonary and aortic valves are closed, so no blood can get out of the ventricles. In response to an electrical stimulus, both atria begin to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. This produces a sound that can be detected with a stethoscope, known as the first heart sound. The ventricles are now sealed shut, and the ventricular muscle tenses, increasing the ventricular pressure. Since blood is incompressible, ventricular volume is unchanged (hence, isovolumetric contraction). However, by convention, the heart is always drawn as seen by the surgeon in the chest. The sequence for the right heart is very similar, with valve names modified as appropriate. The situation during ventricular filling is shown at left, while the situation during ventricular ejection (systole) is shown at right. The aortic and the pulmonary valves move passively in response to the ambient pressure field and rely on their geometry to prevent leakage/backflow (regurgitation).
For developing efficient medicine hollywood undead purchase kytril 2 mg otc, reliable and high power lasers symptoms for diabetes kytril 2 mg with mastercard, the thermal properties play a key part medicine that makes you throw up safe kytril 2 mg. If the crystal tends to store too much heat during pumping process symptoms knee sprain purchase 2 mg kytril amex, some problems of efficiency, stability, or even fracture of the crystal may occur. We have shown in this chapter how the estimation of these parameters in the case of insulating crystals might be carried out. To obtain host materials with a large thermal conductivity value, the following requirements must be fulfilled: low molar mass M; high melting point (high strength atomic bonds); compact crystal structures and covalent character of the chemical bonds. Furthermore, we have also emphasized in this chapter other very important features such as dopant effects on the thermal conductivity and structural effects on the thermo-optical properties. These effects can dramatically affect the gain media performance for the generation of high power laser beams. Finally, in this chapter, the state of the art of femtosecond oscillators based on the Yb-doped materials is presented. The development of new crystal hosts is still very important in order to extend to new application domains by finding crystals with better laser properties. Fan, Quasi-three level lasers, in Solid State Lasers News Developments and Applications, Eds. Vivien, Crystal field calculations of Yb3+-doped double borate crystals for laser applications, J. Vivien, Determination of laser parameters of ytterbium-doped oxide crystalline materials, J. Clarkson, Thermal effects and their mitigation in end-pumped solid-state lasers, J. Clarkson, A review of diode-pumped lasers, in Advances in Lasers and Applications: Proc. Viana, Optical and thermo-mechanical properties of solid state laser materials, Ann. Loutts, Ytterbium-doped apatite-structure crystals: a new class of laser materials, J. Antic-Fidancev, What kind of information is possible to be obtained from 2S+1L terms of 4fN configurations, in Physics of Laser Crystals, Eds. Blasse, the variation of the electron-phonon coupling strength through the trivalent lanthanide ion series, J. Vivien, Spectroscopic and crystal field analysis of new Yb-doped laser materials, J. Edmonds, Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics, Princeton University Press, Princeton, New York, 1960. Auzel, On the maximum splitting of the 2F7/2 ground state in Yb3+ doped solid state laser materials, J. Auzel, A relationship for crystal field strength along the lanthanide series; application to the prediction of the 2F7/2 Yb3+ maximum splitting, Opt. Ferrand, Optical and laser properties of Yb:Y2SiO5 single crystals and discussion of the figure of merit relevant to compare ytterbium-doped laser materials, Opt. Cassanho, Fluorescence quantum efficiency measurements in the presence of Auger upconversion using the thermal lens method, Opt. Hufner, in Optical Spectra of Transparent Rare Earth Compounds, Academic Press, New York, 1978, p 107. Ferrand, Spectroscopic studies of Yb3+-doped rare earth orthosilicate crystals, J. Ferrand, First diode pumped solid state laser continuously tunable between 1000 and 1010 nm, Appl. Larat, Apatitestructure crystal, Yb:SrY4(SiO4)3O, for the development of diode-pumped femtosecond lasers, Opt. Stokowski, Spectroscopic, optical and thermomechanical properties of neodymium and chromium doped gadolinium scandium gallium garnet, J. Kaminskii, Modern developments in the physics of crystalline laser materials, Phys. Fournier, Simple model for the prediction of thermal conductivity in pure and doped insulating crystals, Appl. Oliver, Thermal conductivity of garnets and phonon scattering by rare-earth ions, Phys. Peters, High melting sesquioxides: crystal growth, spectroscopy, and laser experiments, Opt.
Syndromes
- Chest CT scan
- Rash
- Change the shape of the tip or the nasal bridge
- Concussion, the most common type of traumatic brain injury, in which the brain is shaken
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Platelet count
Journal of Morphology 168:5-15 medications for osteoporosis generic 2mg kytril visa, Copyright C 1981 medicine zolpidem buy discount kytril 2mg line, and is used with permission of Wiley-Liss medicine norco buy cheap kytril 2 mg line, Inc medicine 752 kytril 1mg lowest price. The lungs are contained within the thoracic cage, consisting of the ribs, intercostal muscles, sternum (breastbone), spine, diaphragm, and neck and shoulder muscles. Attached to the exterior surface of the lung and to the interior surface of the thoracic cage is the pleural membrane. The space enclosed by this membrane is the pleural space, which is normally filled with the intrapleural fluid. The diaphragm is the large muscle at the base of the lungs, familiar to anyone who has been "winded. There is a gradually increasing trend until about age six, after which the number of alveoli is essentially constant. Reprinted by permission of the publisher from the Pathway for Oxygen: Structure and Function in the Mammalian Respiratory System by Ewald R. Note that there is no communication between the right and left intrapleural fluids. The solid and dashed lines indicate expiratory and inspiratory positions, respectively. Rather, the necessary forces are transmitted to the lungs through the intrapleural fluid via the mechanisms described below. This system allows a uniform inflation of the lungs while avoiding the high stresses and deformations that would result if a muscle inserted into the soft lung tissue. Inspiration and expiration proceed by two very different mechanisms, as described below. In quiet inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, thereby increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. In addition, the external intercostal muscles and the scalene muscles (at the neck) contract to move the rib cage up and out. This also increases thoracic cavity volume, although the contribution of the intercostal and scalene muscles is minimal during quiet inspiration. Since the intrapleural fluid is essentially incompressible, an increase in thoracic cage volume must be accompanied by an increase in lung volume. The best analogy is that of a balloon inside a fluid-filled container of variable volume 288 the respiratory system. However, the contribution of the intercostal and scalene muscles becomes more pronounced. Quiet expiration is a passive process that relies on the natural tendency of the lung to collapse (see Section 7. The diaphragm, the external intercostal muscles, and the scalene muscles relax, allowing the lung and the thoracic cage to decrease in volume. In addition to the relaxations of quiet expiration, the internal intercostal muscles contract to pivot the ribs downward and in. Also, the abdominal muscles contract, pulling down the rib cage, increasing abdominal pressure, and thereby forcing the diaphragm upwards. These mechanisms together act to reduce thoracic cavity volume, which allows a large quantity of air to be quickly expelled from the lungs. Before examining why this is the case, we briefly look at what this fact implies about the intrapleural pressure. At rest, when the subject is neither inspiring nor expiring, the pressure within the conducting airways is essentially atmospheric. In other words, the pressure in the lung must exceed the surrounding pressure, which in this case is the intrapleural pressure. This is confirmed by measurements, with typical intrapleural pressures of -3 to -4 mmHg (gauge) at rest. During inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressures deviate from this resting value. For example, during rapid inspiration, intrapleural pressure can fall to as low as -100 mmHg, while it can become slightly positive during forced expiration.
Generic kytril 1 mg with amex. My Journey With MS: Life The Signs and the Diagnosis.