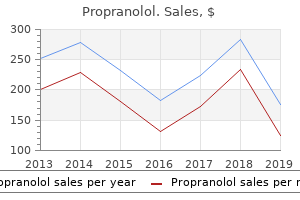
Propranolol
"Cheap 40 mg propranolol fast delivery, cardiovascular disease treatment plans".
By: T. Knut, M.S., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences College of Osteopathic Medicine
Assessment and monitoring of glycemic control in children and adolescents with diabetes coronary artery treatment buy 20mg propranolol fast delivery. Care of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a statement of the American Diabetes Association blood vessels rash buy propranolol 80mg mastercard. Drug therapy of high-risk lipid abnormalities in children and adolescents: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis cardiovascular disease other names generic 80mg propranolol otc, Hypertension cardiovascular kingsport tn cheap 40mg propranolol with visa, and Obesity in Youth Committee, Council of Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, with the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Type 1 diabetes-associated autoimmunity: natural history, genetic associations, and screening. Introduction Adolescence is a life stage characterized by transition and change regardless of health status. Diabetes in adolescence is a life-changing condition requiring diligent and consistent management by a multidisciplinary team of clinicians in addition to comprehensive care and support provided by the family unit. Many young people with diabetes establish a long-term positive bond with their pediatric health care team. Consequently, the transition to an adult diabetes service provider is a significant event. The seamless transfer of adolescents with diabetes from pediatric to adult services can also be a challenge for health services and clinicians. Young people may mourn the loss of the relationships they had with the pediatric health team and can become distressed about learning to trust new staff [1]. There is evidence to suggest that during the time of transfer, adolescents are at risk of dropping away from health care professional contact and follow-up which may be detrimental to their physical and psychologic well-being [2]. As a result, it has been estimated that 1060% of adolescents do not make the transition successfully from pediatric to adult health services [3,4]. The purpose of this chapter is to enhance understanding of the key issues presenting for adolescents and clinicians, and to consider effective models of care that will facilitate seamless transition from pediatric to adult diabetes care. Transition Transition is the reorientation that people experience to a change event [5]. Events that change our lives occur constantly, but they often go unnoticed, unless we are disrupted by them. Transition is the way people respond to the changes that are occurring in their lives. Transition is the movement people make through a disruptive life event so that they can continue to live with a coherent and continuing sense of self [7]. Health care professionals are frequently in the position of supporting people who are in transition because of the changes associated with the impact of illness. During the last three decades, the concept of transition has evolved in the social sciences and health disciplines, with nurses contributing to more recent understandings of the transition process as it relates to life and health [815]. Transitional definitions alter according to the disciplinary focus, but there is broad agreement that transition involves the way people respond to change. Transition occurs over time and entails change and adaptation, for example developmental, personal, relational, situational, societal or environmental change, but not all change Textbook of Diabetes, 4th edition. Transition is not an event, but rather the inner reorientation and self-redefinition that people go through in order to incorporate changes into their lives [5]. The transition focused on here when discussing adolescent transfer to adult services is when one "chapter" of life is over and the person is unable to go back to the way life was before the change event occurred. The change event under particular focus is the shift to a new and unfamiliar service environment. To enable a "new chapter" to begin these adolescents will need to respond to the changes in their lives, sorting out what can be retained of their former way of living and what has to be released, in order to move forward [15]. This is often the experience of the adolescent moving from child to adult health services. Understanding transition theory will enable health care professionals to assist young people to make this transition during a life stage that is characterized by constant change. This is a key point in enabling successful transition for adolescents moving to adult diabetes care. Adolescence as a time of transition Adolescence is a transitional stage of human development that occurs between childhood and adulthood. This transition is characterized by significant and complex biologic, social and psychologic changes that occur during the teenage years. During this time the adolescent is developing a sense of self and identity, establishing autonomy and understanding sexuality. Adolescence is a stage of life where controlautonomydependence are pertinent issues in the lives of young people [16].
To develop a more realistic estimate of the cost of lost productivity cardiovascular physician assistant propranolol 40mg otc, we considered the percent of people participating in the workforce as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics arteries heart buy propranolol 40 mg with amex. For individuals outside of the workforce cardiovascular questions and answers with rationale cheap 20 mg propranolol otc, the value of lost productivity was estimated to be half of the corresponding lost productivity of those within the workforce coronary heart calcium scoring purchase propranolol 40mg online. The lost productivity of children and those over 65 was also valued at half of the corresponding lost productivity of those within the workforce and recorded as a "restricted activity day" as opposed to a "lost workday. A caregiver was considered to have lost productive time in seeking care for a child or dependent adult. As with the estimates for individuals with the condition, we stratified the value of caregiver lost productive time according to participation in the workforce. Lost Future Earnings Due to Premature Death While few of the skin conditions reviewed in this study are fatal, the value of lost future earnings due to premature death must be considered in calculating the overall burden of skin conditions. Due to the low number of reported deaths for many conditions, only those conditions with an unweighted cell count >10 deaths were used in calculating lost future earnings. Using this criterion, the conditions eligible for evaluation were nonmelanoma skin cancer, bullous diseases, cutaneous lymphoma, psoriasis, herpes simplex and zoster, lupus erythematosus, skin ulcers and wound healing, and melanoma. As such, conservative estimates based on the quality of life considerations for conditions with similar manifestations were used to approximate the effects of these conditions of quality of life. To estimate the burden of skin conditions on quality of life from an economic perspective, a willingness-to-pay approach was adapted, to approximate the average amount that a person with a diagnosed skin condition would be willing to pay for a particular health outcome; in this case, the outcome was defined as relief from symptoms. These costs are considered separately from indirect costs because they do not represent actual expenditures, rather, these intangible costs approximate the intrinsic effect that these conditions have on overall health and quality of life (Gold 1996). From willingness-to-pay studies on atopic eczema, acne, and psoriasis found in the literature, a power curve with the equation y=0. For chronic conditions such as acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and vitiligo, consideration was given to the amount of time per year during which the condition was active or in a state of flare-up. Assessing Data Source Utility After completing all analyses from the individual datasets, the reliability and validity of the data was assessed. The unweighted cell count for each variable, the overall geographic and age distribution of the dataset, and the methods used in sampling the population were all considered in selecting the definitive source for a given data point. Quality of life, health-state utilities and willingness to pay in patients with psoriasis and atopic eczema. Included in this group of conditions are actinic keratosis, melanoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer, cutaneous lymphoma and benign neoplasms such as keloid and hypertrophic scars. The estimated probability of a lesion progressing to squamous cell carcinoma ranges from 0. Other symptoms include pink, brown or red discoloration of the skin with a lesion diameter of less than one centimeter. For this reason, behavioral modifications such as limiting sun exposure and increasing the application of sunscreen are considered to be the most effective prevention strategies. Hospital outpatient departments and emergency rooms were less frequently accessed as sites of care, with 36,000 and 14,900 visits respectively, and a total cost of $29. The remaining $80 million is attributable to caregiver lost workdays, which, due to the higher prevalence of this condition in individuals >65 years of age, is more substantial than for conditions affecting younger individuals. To approximate quality of life, a willingness to pay approach was adopted, whereby the quality of life effects of a particular condition are monetarily quantified to indicate how much individuals with the condition are willing to pay for symptom relief. In other words, the greater the willingness to pay, the more substantial the effects of the condition on quality of life. In 2004, 7,900 of the approximately 55,000 individuals newly diagnosed with melanoma will die of their disease. In addition to its high mortality rate, melanoma is now the second leading cause of lost productive work years due to cancer. In addition to environmental factors, genetic factors contribute to risk for developing melanoma. Diagnosis requires biopsy of the suspected lesion, which typically consists of removal of the entire lesion and a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue (generally 1mm-3mm).
Bipolar versus monopolar transurethral resection of prostate: randomized controlled study cardiovascular accident cheap propranolol 40 mg amex. Quantitative structure-activity relationship study of novel alpha1a-selective adrenoceptor antagonists blood vessels close to skin discount propranolol 80mg with mastercard. Effect of lumbar-epidural administration of tramadol on lower urinary tract function heart disease research propranolol 20mg without prescription. Plasma membrane association of cathepsin B in human prostate cancer: biochemical and immunogold electron microscopic analysis coronary heart gif generic 80mg propranolol mastercard. Cathepsin B expression is similar in African-American and Caucasian prostate cancer patients. Microvessel density as a molecular marker for identifying high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia precursors to prostate cancer. Prediction of pelvic lymph node metastasis by the ratio of cathepsin B to stefin A in patients with prostate carcinoma. Ratio of cathepsin B to stefin A identifies heterogeneity within Gleason histologic scores for human prostate cancer. Level of renal function and serum erythropoietin levels independently predict anaemia post-renal transplantation. Augmented expression of chromogranin A and serotonin in peri-malignant benign prostate epithelium as compared to adenocarcinoma. Lower urinary tract symptoms: shifting our focus from the prostate to the bladder. Decrease of ultrasound estimated bladder weight during tamsulosin treatment in patients with benign prostatic enlargement. Kidney function and thickness of carotid intima-media complex in patients with treated arterial hypertension. A community study of lower urinary tract symptoms in older men in Sydney, Australia. Development of nomogram to predict acute urinary retention or surgical intervention, with or without dutasteride therapy, in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Page 220 106100 114320 117120 127810 153560 121820 105650 130950 134420 114000 126030 156000 106980 139640 165740 100190 September 2010 Appendix 3: Master Bibliography American Urological Association, Inc. In vitro activity of fluoroquinolones, azithromycin and doxycycline against chlamydia trachomatis cultured from men with chronic lower urinary tract symptoms. Drawbacks and prognostic value of formulas estimating renal function in patients with chronic heart failure and systolic dysfunction. Single-institution experience in 110 patients with botulinum toxin A injection into bladder or urethra. Bipolar electrosurgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia: transurethral electrovaporization and resection of the prostate. Relationship between upregulated oestrogen receptors and expression of growth factors in cultured, human, prostatic stromal cells exposed to estradiol or dihydrotestosterone. The biochemical functions of the renal tubules and glomeruli in the course of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy. Messenger ribonucleic acid levels of steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2 in human prostate predict the enzyme activity. Holmium laser ureteroscopic treatment of various pathologic features in pediatrics. Prevalence of nosocomial infections in neonatal intensive care unit patients: Results from the first national point-prevalence survey. Page 221 151570 107400 120460 130100 103980 108140 112720 138350 108650 163770 135820 119470 114790 153740 137140 119750 September 2010 Appendix 3: Master Bibliography American Urological Association, Inc. Combined sabal and urtica extract compared with finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of prostate volume and therapeutic outcome. Rotoresection versus transurethral resection of the prostate: short-term evaluation of a prospective randomized study. Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: latest update on alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonists. Effectiveness of local anaesthesia techniques in patients undergoing transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy: a prospective randomized study.
The intake of moderate amounts (515 g/day) is associated with a decreased risk of coronary heart disease cardiovascular system poster buy cheap propranolol 20 mg on-line, while a strong association between excess habitual alcohol intake (>3060 g/day) and undesirable raised blood pressure is found in both men and women cardiovascular journal of africa abbreviation order propranolol 40mg with amex. The amount of alcohol seems to be predictive whereas the type of alcoholcontaining beverages consumed does not appear to be of major importance qrisk cardiovascular disease 10 year risk cheap propranolol 20mg overnight delivery. If people with diabetes choose to drink alcohol blood vessels around nose cheap 80 mg propranolol free shipping, intake should be moderate, with no more than 10 g/day alcohol (1 drink) for females and no more than 20 g/day alcohol (2 drinks) for males [1,2]. These limits are also recommended to the healthy population by nutrition associations. In studies where alcoholic beverages were consumed with carbohydrate-containing food by people with diabetes, no acute effects were seen on blood glucose. The recommendation, particularly to patients treated with insulin or insulin secretagogues, to consume carbohydrate when alcohol is taken is made because of the potential risk of alcohol-induced hypoglycemia [70,71]. The risk increases with the quantity of alcohol consumed and may last well into the following day. Abstention from alcohol is advised in women during pregnancy, people with a history of pancreatitis or alcohol abuse as well as in those with hypertriglyceridemia and advanced neuropathy. Alcohol may also be an important energy source which should be considered in people with overweight. High alcohol consumption is associated with Micronutrients Regular consumption of a variety of vegetables, fresh fruit, legumes, low fat milk products, vegetable oils, nuts, wholegrain breads and oily fish should be encouraged to ensure that recommended vitamin and mineral requirements are met [1]. Salt or sodium intake, respectively, should be limited particularly when elevated blood pressure is a problem [61,62]. Such substitutes may be tried in selected patients but cannot generally be recommended to lower high blood pressure in people with diabetes. People with diabetes may have increased oxidative stress and several studies have investigated the potential benefit of recommending the intake of antioxidant vitamins [63]. The evidence obtained from studies and expert reports concerning alcohol intake are shown in Table 22. Food choices for adequate weight gain, normoglycemia and absence of ketones Weight loss is not recommended For overweight or obese women with gestational diabetes, modest energy and carbohydrate intake Starvation ketosis should be avoided Pregnant women on insulin therapy need individualized carbohydratecontrolled recommendations with consistency of times and amounts of food to avoid hypoglycemia Insulin and meal plan adjustments should be guided by blood glucose self-monitoring Consider changes in insulin sensitivity and the necessity to adjust the insulin dosage during the different trimesters of pregnancy Consider special needs of protein (1. Nutritional therapy should assist in achieving recommended fasting blood glucose values of 6090 mg/dL (3. Energy intake should be adequate to provide appropriate weight gain and nutrient intakes should consider special needs during pregnancy. In women with normal weight additional energy intake may be 70240 kcal/day in the first and second trimester and 300 kcal in the third trimester of pregnancy. Additional calorie intake should be less in obese pregnant women; however, total daily energy should not be under 1600 kcal/day. During pregnancy, hyperglycemia as well as ketonemia and starvation ketosis should be avoided. As in all pregnant women, folic acid supplementation is recommended to prevent neural tube defects. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) have recommended using higher doses of folate supplementation (5. Further individual supplementation with calcium, iron and iodine may be considered to avoid deficiencies (Table 22. It requires the use of currently available scientific evidence on the potential of diet to assist in achieving treatment goals. A knowledgeable diabetes care team including the individual with diabetes should work together to maintain the pleasure of eating and drinking, while only limiting food choices when this is indicated by scientific evidence (Table 22. Furthermore, it has to be taken into account that the therapeutic needs of an individual person will change with time and special life events, and therefore nutritional assessment and continuing dietary advice must be provided. Diet in children with diabetes Dietary recommendations should focus on achieving desirable blood glucose concentrations without severe hypoglycemia. As in all healthy children, energy and nutrient intakes should be adequate to ensure normal growth and development. Healthy nutrition may also contribute to maintaining normal serum lipid values and blood pressure goals. Individualized counseling is necessary to support adequate decision-making for food intake and flexible insulin doses based on blood glucose self-monitoring. Meal plans must be individualized to accommodate food preferences and the eating pattern of the family. As energy requirements change with age, growth rates have to be monitored and the evaluation of a meal plan has to be rechecked at least once a year.
Generic propranolol 80mg on-line. Workout Music Source // Cardio Country Workout Mix 2 (135-145 BPM).