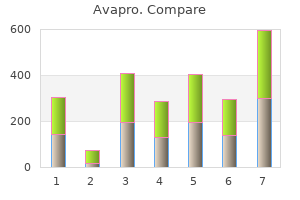
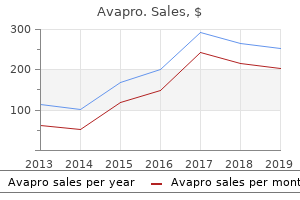
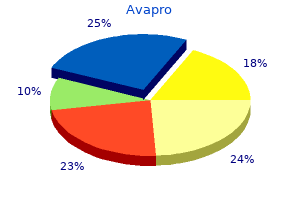
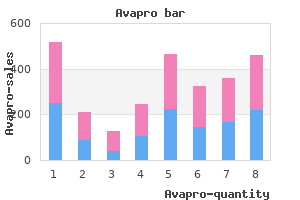
Avapro
"Purchase 150mg avapro otc, diabetes test limits".
By: F. Arakos, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine and Research Institute
This may progress to necrosis of the lining endothelium as well as the collagen blood sugar level control buy avapro 300mg overnight delivery, elastin and reticulin fibers with secondary inflammation diabetes symptoms 5 year old generic 150 mg avapro with mastercard. Uremic mineralization is likely a combination of dystrophic and metastatic mineralization blood glucose negative feedback 150mg avapro free shipping. Renal and hepatic disease are the two primary sources of hypoalbuminemia metabolic disease zoysia purchase avapro 150 mg without a prescription, and only renal disease will preserve globulins as in this case. Plasma antithrombin activity as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator in dogs: a retrospective study of 149 dogs. Autism is a severe neurodevelopmental disorder with a complex genetic predisposition. Linkage findings from several genome scans suggest the presence of an autism susceptibility locus on chromosome 2q24-q33, making this region the focus of candidate gene and association studies. Possible dysfunction of mitochondrial beta-oxidation by long chain acylCoA dehydrogenase. These metabolic changes are also seen as secondary abnormalities in dysfunction of fatty acid beta-oxidation, and have also been reported in autism. Similarities between metabolic disturbances in autism, and those of disorders of fatty acid beta-oxidation are discussed. A random retrospective chart review was conducted to document serum carnitine levels on 100 children with autism. Concurrently drawn serum pyruvate, lactate, ammonia, and alanine levels were also available in many of these children. It is hypothesized that a mitochondrial defect may be the origin of the carnitine deficiency in these autistic children. Two autistic children with a chromosome 15q11-q13 inverted duplication are presented. Both had uneventful perinatal courses, normal electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging scans, moderate motor delay, lethargy, severe hypotonia, and modest lactic acidosis. Mitochondrial structural abnormalities were present in three of four patients examined. Furthermore, recent studies have pointed to a subset of autism associated with the biochemical endophenotype of mitochondrial energy deficiency, identified as a subtle impairment in fat and carbohydrate oxidation. During his second year of life, he lost previously acquired language skills and developed marked hyperactivity with toe-walking, abnormal reciprocal social interaction, stereotyped mannerisms, restricted interests, self-injurious behavior, and seizures. His older sister developed signs of Leigh syndrome with progressive ataxia, myoclonus, seizures, and cognitive regression. Recently, there have been articles describing the association of autism with mitochondrial abnormalities. Most patients will present with multisystem abnormalities associated with autistic behavior. Finding biochemical or structural mitochondrial abnormalities in an autistic child does not necessarily imply a primary mitochondrial disorder but can also be secondary to technical inaccuracies or another genetic disorder. Clinicians should be careful in diagnosing a mitochondrial disorder in an autistic child because it has important implications for accurate genetic counseling, prognosis, and therapy. Autism is a developmental disorder characterized by disturbance in language, perception and socialization. A likely etiological possibility may involve mitochondrial dysfunction with concomitant defects in neuronal oxidative phosphorylation within the central nervous system. Mitochondria are vulnerable to a wide array of endogenous and exogenous factors which appear to be linked by excessive nitric oxide production. Strategies to augment mitochondrial function, either by decreasing production of endogenous toxic metabolites, reducing nitric oxide production, or stimulating mitochondrial enzyme activity may be beneficial in the treatment of autism. A school survey was conducted in elementary schools, targeting 332,808 school-aged children in the mainland and 10,910 in the Azores islands. In parallel, a systematic multi-source search of children known to have autism was carried out in a restricted region.
Acrophobia zoloft and diabetes type 1 avapro 150 mg with visa, a fear of heights blood sugar lowering foods order avapro 300mg with visa, is taken from the root acro- diabetes type 2 rates by country 300 mg avapro with mastercard, meaning terminal diabetes diet menu lose weight discount 300 mg avapro with amex, highest, or topmost. The causes of schizophrenia are unknown, but there is evidence of hereditary factors and imbalance in brain chemistry. Autism Autism is a complex disorder of unknown cause that usually appears before age 3. It is marked by selfabsorption and lack of response to social contact and affection. He or she responds inappropriately to stimuli and may show self-destructive behavior. There may also be stereotyped (repetitive) behavior, preoccupations, and resistance to change. This category of drugs includes antianxiety drugs or anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and antipsychotics, also called neuroleptics. In practice, the term is applied more broadly to a range of language disorders, both spoken and written. May affect ability to understand speech (receptive aphasia) or the ability to produce speech (expressive aphasia). Insufficient or nonrestorative sleep despite ample opportunity to sleep Tumor of the meninges Inflammation of the meninges Dementia caused by chronic cerebral ischemia (lack of blood supply to the tissues) as a result of multiple small strokes. There is progressive loss of cognitive function, memory, and judgment as well as altered motor and sensory function. Flaccid paralysis involves loss of muscle tone and reflexes and degeneration of muscles. A disorder originating in the basal ganglia and characterized by slow movements, tremor, rigidity, and masklike face. Most of the fibers in these tracts cross in the medulla to the opposite side of the spinal cord and affect the opposite side of the body. A sudden and temporary state of confusion marked by excitement, physical restlessness, and incoherence Defect in speech articulation caused by lack of control over the required muscles Disturbance in the path or placement of a limb during active movement. The patient shows progressive dementia and chorea, and death occurs within 10 to 15 years. Possible causes include genetic factors, stress, trauma, and hormonal fluctuations. Headache might be signaled by visual disturbances, nausea, photophobia, and tingling sensations. There also may be obsessive and compulsive behavior, hyperactivity, and distractibility. A sudden, brief, and temporary cerebral dysfunction usually caused by interruption of blood flow to the brain Degeneration of a nerve distal to an injury Cervical injury caused by rapid acceleration and deceleration resulting in damage to muscles, ligaments, disks, and nerves Additional terms related to neurologic symptoms can be found in Chapters 18 (on the senses) and 20 (on the muscular system). This response is normal in infants but indicates a lesion of specific motor tracts in adults. Brain Central nervous system Cranial nerves Peripheral nervous system Spinal cord Spinal nerves 1 3 2 4 6 5 1. Axon Axon branch Cell body Dendrites Muscle Myelin Neuromuscular junction Nucleus 1 2 3 5 4 6 1. Brain Brainstem Cervical nerves Coccygeal nerve Lumbar nerves Sacral nerves Spinal cord Thoracic nerves 1 2 4 3 5 6 1. He had presented with an acute onset of headaches, vomiting on waking in the morning, and progressive ataxia. The cerebellar tumor was found to be noninfiltrating and was enclosed within a cyst, which was totally removed. He was scheduled for 6 weeks of outpatient rehabilitation, and his prognosis was good. Her secondary diagnosis was stated as neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a rare and life-threatening disorder associated with the use of antipsychotic medications. She was treated with Bromocriptine, a dopamine antagonist, and Dantrolene, a muscle relaxant and antispasmodic. A diagnostic procedure in which fluid is withdrawn from the spinal subarachnoid space is a(n): a.
Neck flexion may precipitate sensation of electric shock running down spine (Lhermitte phenomenon) diabetes wound healing buy avapro 150mg low cost. Periventricular plaques A (areas of oligodendrocyte loss and reactive gliosis) with preservation of axons diabetes insipidus caused by lithium 300 mg avapro for sale. Autoimmune condition that destroys Schwann cells inflammation and demyelination of peripheral nerves and motor fibers diabetes symptoms elderly order 300mg avapro with amex. May see autonomic dysregulation (eg diabetes medicines banned in india purchase 300mg avapro otc, cardiac irregularities, hypertension, hypotension) or sensory abnormalities. Associated with infections (eg, Campylobacter jejuni, viral) autoimmune attack of peripheral myelin due to molecular mimicry, inoculations, and stress, but no definitive link to pathogens. Presents with rapidly progressive multifocal neurologic symptoms, altered mental status. Group of progressive hereditary nerve disorders related to the defective production of proteins involved in the structure and function of peripheral nerves or the myelin sheath. Typically autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and associated with foot deformities (eg, pes cavus, hammer toe), lower extremity weakness (eg, foot drop) and sensory deficits. Autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease due to deficiency of galactocerebrosidase. Findings: peripheral neuropathy, developmental delay, optic atrophy, globoid cells. Autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease, most commonly due to arylsulfatase A deficiency. Krabbe disease Metachromatic leukodystrophy Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy A Adrenoleukodystrophy X-linked genetic disorder typically affecting males. Disrupts metabolism of very-long-chain fatty acids excessive buildup in nervous system, adrenal gland, testes. Findings: bilateral acoustic schwannomas, juvenile cataracts, meningiomas, and ependymomas. Extra-axial (external to brain parenchyma) and may have a dural attachment ("tail" E). Sequelae include hyperor hypopituitarism, which may be caused by pituitary apoplexy. Classically at the cerebellopontine angle K, but can be along any peripheral nerve. Hyperplasia of only one type of endocrine cells found in pituitary (ie, lactotroph, gonadotroph, somatotroph, corticotroph). Caudal displacement of brain stem rupture of paramedian basilar artery branches Duret hemorrhages. Results from degeneration (demyelination) of dorsal columns and roots progressive sensory ataxia (impaired proprioception poor coordination). Unilateral symptoms including radicular pain, absent knee and ankle reflex, loss of bladder and anal sphincter control. Due to compression of spinal roots from L2 and below, often caused by intravertebral disk herniation or tumors. Contralateral pain, temperature, and crude (non-discriminative) touch below level of lesion (due to spinothalamic tract damage) If lesion occurs above T1, patient may present with ipsilateral Horner syndrome due to damage of oculosympathetic pathway. Staggering gait, frequent falling, nystagmus, dysarthria, pes cavus, hammer toes, diabetes mellitus, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cause of death). Tongue deviates toward side of lesion ("lick your wounds") due to weakened tongue muscles on affected side. May also be caused by Lyme disease, herpes simplex, herpes zoster (Ramsay Hunt syndrome), sarcoidosis, tumors (eg, parotid gland), diabetes mellitus. Vibration transduced via specialized hair cells auditory nerve signaling brain stem. Each frequency leads to vibration at specific location on basilar membrane (tonotopy): Low frequency heard at apex near helicotrema (wide and flexible). Sudden extremely loud noises can produce hearing loss due to tympanic membrane rupture. Aging-related sensorineural hearing loss (often of higher frequencies) due to destruction of hair cells at the cochlear base (preserved low-frequency hearing at apex). Brain stem or cerebellar lesion (eg, stroke affecting vestibular nuclei or posterior fossa tumor). Findings: directional or purely vertical nystagmus, skew deviation, diplopia, dysmetria.
Lactase functions on the brush border to digest lactose (in human and cow milk) into glucose and galactose diabetes symptoms kid generic avapro 150 mg overnight delivery. Primary: age-dependent decline after childhood (absence of lactase-persistent allele) diabetes medications and hair loss buy generic avapro 300mg line, common in people of Asian diabetes mellitus zuckerkrankheit generic 300mg avapro mastercard, African diabetes risk factors avapro 300 mg with amex, or Native American descent. Secondary: loss of brush border due to gastroenteritis (eg, rotavirus), autoimmune disease, etc. Stool demonstrates pH and breath shows hydrogen content with lactose hydrogen breath test. Intestinal biopsy reveals normal mucosa in patients with hereditary lactose intolerance. Excess nitrogen generated by this process is converted to urea and excreted by the kidneys. Benzoate, phenylacetate, or phenylbutyrate react with glycine or glutamine, forming products that are renally excreted. Ammonia accumulation-tremor (asterixis), slurring of speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurring of vision. X-linked recessive (vs other urea cycle enzyme deficiencies, which are autosomal recessive). Excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted to orotic acid (part of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway). Findings: intellectual disability, growth retardation, seizures, fair skin, eczema, musty body odor. Treatment: phenylalanine and tyrosine in diet, tetrahydrobiopterin supplementation. Findings in infant: microcephaly, intellectual disability, growth retardation, congenital heart defects. Maple syrup urine disease Blocked degradation of branched amino acids (Isoleucine, Leucine, Valine) due to branched-chain -ketoacid dehydrogenase (B1). Treatment: restriction of isoleucine, leucine, valine in diet, and thiamine supplementation. Alkaptonuria A Congenital deficiency of homogentisate oxidase in the degradative pathway of tyrosine to fumarate pigment-forming homogentisic acid accumulates in tissue A. Homocystinuria Types (all autosomal recessive): Cystathionine synthase deficiency (treatment: methionine, cysteine, B6, B12, and folate in diet) affinity of cystathionine synthase for pyridoxal phosphate (treatment: B6 and cysteine in diet) Methionine synthase (homocysteine methyltransferase) deficiency (treatment: methionine in diet) Methionine Methionine synthase B12 Serine Homocysteine All forms result in excess homocysteine. Excess cystine in the urine can lead to recurrent precipitation of hexagonal cystine stones A. Glycogen undergoes glycogenolysis glucose-1-phosphate rapidly metabolized during exercise. Glycogen phosphorylase liberates glucose-1-phosphate residues off branched glycogen until 4 glucose units remain on a branch. Then 4-d-glucanotransferase (debranching enzyme) moves 3 molecules of glucose-1-phosphate from the branch to the linkage. Then -1,6-glucosidase (debranching enzyme) cleaves off the last residue, liberating glucose. Cardiomegaly, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, exercise intolerance, and systemic findings lead to early death. Peripheral neuropathy, destruction of oligodendrocytes, developmental delay, optic atrophy, globoid cells. Hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis of femur, bone crises, Gaucher cells C (lipid-laden macrophages resembling crumpled tissue paper). Progressive neurodegeneration, hepatosplenomegaly, foam cells (lipid-laden macrophages) D, "cherry-red" spot on macula A. Hunters see clearly (no corneal clouding) and aggressively aim for the X (X-linked recessive). Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency- ability to break down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA accumulation of fatty acyl carnitines in the blood with hypoketotic hypoglycemia. In prolonged starvation and diabetic ketoacidosis, oxaloacetate is depleted for gluconeogenesis. After these are depleted, vital protein degradation accelerates, leading to organ failure and death. Affected infants present with severe fat malabsorption, steatorrhea, failure to thrive. Later manifestations include retinitis pigmentosa, spinocerebellar degeneration due to vitamin E deficiency, progressive ataxia, acanthocytosis.
Cheap avapro 150 mg mastercard. Type 2 Diabetes. How it works.
Large postmortem clots may have a "chicken fat" appearance overlying a dark "currant jelly" base diabetes medications for renal failure buy avapro 150mg. These thromboemboli diabetic apple pie purchase avapro 150mg visa, most of which originate in the deep veins of the lower extremities diabetes diet rules discount avapro 150mg free shipping, may embolize to the lungs diabetes type 2 with hyperglycemia purchase avapro 300mg with visa. The majority of small pulmonary emboli do no harm, but, if they are large enough, they may occlude the bifurcation of the pulmonary arteries (saddle embolus), causing sudden death. Arterial emboli most commonly originate within the heart on abnormal valves (vegetations) or mural thrombi following myocardial infarctions. If there is a patent foramen ovale, a venous embolus may cross over through the heart to the arterial circulation, producing an arterial (paradoxical) embolus. Types of nonthrombotic emboli include fat emboli, air emboli, and amniotic fluid emboli. Fat emboli, which result from severe trauma and fractures of long bones, can be fatal as they can damage the endothelial cells and pneumocytes within the lungs. Air emboli are seen in decompression sickness, called caisson disease or the bends, while amniotic fluid emboli are related to the rupture of uterine venous sinuses as a complication of childbirth. They can be classified on the basis of their color into either red or white infarcts, or by the presence or absence of bacterial contamination into either septic or bland infarcts. White infarcts, also referred to as pale or anemic infarcts, are usually the 112 Pathology result of arterial occlusion. Red or hemorrhagic infarcts, in contrast, may result from either arterial or venous occlusion. They occur in organs with a dual blood supply, such as the lung, or in organs with extensive collateral circulation, such as the small intestine and brain. These infarcts are hemorrhagic because there is bleeding into the necrotic area from the adjacent arteries and veins that remain patent. Hemorrhagic infarcts also occur in organs in which the venous outflow is obstructed (venous occlusion). In the latter, twisting of the spermatic cord occludes the venous outflow, but the arterial inflow remains patent because these arterial blood vessels have much thicker walls. Testicular torsion is usually the result of physical trauma in an individual with a predisposing abnormality, such as abnormal development of the gubernaculum testis. A deficiency of either of these two enzymes leads to a disorder called orotic aciduria, which is characterized by orotate in the urine, abnormal growth, and megaloblastic anemia. An association is a pattern of nonrandom General Pathology Answers 113 anomalies with an unknown mechanism. A deformation is an alteration of a normally formed body part by mechanical forces. A disruption is a defect that results from interference in a normally developing process. A malformation is a morphologic defect that results from an intrinsically abnormal developmental process. A sequence is a recognized pattern that results from a single preexisting abnormality. Syndrome refers to multiple anomalies having a recognizable pattern and known pathogenesis. Autosomal dominant inheritance characterizes both myotonic dystrophy and the facioscapulohumeral type, while limb-girdle dystrophy is autosomal recessive. In Duchenne muscular dystrophy, males are affected and symptoms begin before the age of 4. Pelvic girdle muscles are affected, with resultant difficulty in walking, and this is followed by shoulder girdle weakness and eventual involvement of respiratory and cardiac muscles with death from respiratory failure before age 20. To calculate the probability that two or more events that are independent of each other will all occur, you must multiply the probabilities for each of these events together. Diagnosis requires General Pathology Answers 115 biopsy demonstration of excess liver glycogen plus either absent or low liver glucose-6-phosphatase activity, or a diabetic glucose tolerance curve, or hyperuricemia. Division of this disease into five categories is generally accepted: type A, the acute neuronopathic form, is the one that has the highest incidence. The lack of sphingomyelinase in type A is the metabolic defect that prevents the hydrolytic cleavage of sphingomyelin, which then accumulates in the brain. Patients who have the type A form usually show hepatosplenomegaly at 6 months of age, progressively lose motor functions and mental capabilities, and die during the third year of life. These patients are prone to development of subluxation of the spine, which can produce quadriplegia.