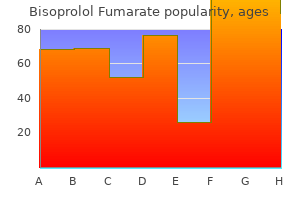
Bisoprolol Fumarate
"Discount bisoprolol 10mg free shipping, arrhythmia test".
By: G. Thorus, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science
Possible mechanisms include increased -cell proliferation and differentiation blood pressure formula cheap bisoprolol 10mg with visa, slowing of -cell apoptosis and increased -cell neogenesis from ductal progenitor cells blood pressure questions trusted bisoprolol 5 mg. A dose of 25 mmol was injected subcutaneously into the gluteal region 5 minutes before a standard meal blood pressure for 12 year old buy bisoprolol 10 mg. The plasma insulin and C-peptide responses were significantly greater blood pressure chart game purchase 10mg bisoprolol mastercard, and the plasma glucose response significantly flatter (all P < 0. The glucose-dependent nature of the insulin-releasing and glucagonsuppressing effects is reflected in the limited risk of hypoglycemia, while the satiety effect has assisted weight loss and favored use in obese patients. Indeed, insulin has important genomic effects that determine the expression levels of many cellular components that are directly and indirectly involved in metabolic homeostasis. Defects of insulin receptor structure are uncommon, and reductions in insulin receptor number are not usually rate limiting. Thus, the therapeutic challenge of insulin resistance appears to require interventions at diverse intracellular targets [52]. In theory, agents that address defects of insulin receptor signaling or early post-receptor lesions might be expected to produce a broader spectrum of benefits, but if the rate-limiting defects occur at more distal locations their therapeutic efficacy will be compromised. Potential target sites to obviate cellular defects of insulin action are shown in Figure 60. Insulin receptor activation Evidence that an orally active, non-peptide molecule can mimic the gluco-regulatory actions of insulin was obtained with L-783,281 (demethylasterriquinone; Figure 60. Studies with mutated subunits of the insulin receptor showed that L-783,281 interacted selectively with the -subunit (without requiring insulin to bind to the -subunit), and its activity could not be attributed to inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases. C peptide Insulin C-peptide, which is secreted from pancreatic -cells along with insulin, appears to bind to G-protein coupled receptors in several insulin-sensitive tissues. Insulin receptor potentiation Insulin receptor signaling after initial activation by insulin binding at the -subunit can be enhanced and/or prolonged by several different mechanisms (Figure 60. These mice also show an increased metabolic rate and resistance to diet-induced obesity. Other insulin receptor potentiators Various substances that increase the number of insulin receptors and/or appear to improve insulin receptor function have been mooted as possible therapeutic leads but have not given rise to new therapeutic entities. The insulin signaling intermediate Akt appears to participate in a negative feedback effect on the signaling pathway. Insulin receptor and early post-receptor potentiation the divergent pathways of post-receptor insulin signaling contain many potential rate-limiting steps for insulin action. Most of these pathways are not specific to insulin and impact activities as disparate as cell differentiation and apoptosis. They also include a controlling influence exerted through the feedback of more distal signaling components on more proximal steps [50,51]. Adipokines Adipose tissue is a source of many autocrine, paracrine and endocrine factors that affect insulin action (Figure 60. Adipocyte hormones Leptin Leptin is an adipocyte hormone that exerts centrally mediated satiety and thermogenic effects, as well as direct effects on cellular nutrient metabolism. Administration of large doses of leptin can produce weight loss and improve insulin action, but the development of leptin resistance and leptin antibodies has compromised long-term efficacy [88]. Adiponectin concentrations become reduced as adipose mass increases, and therapeutic approaches to raise adiponectin levels, develop analogs and non-peptide receptor agonists are under investigation. Part of the insulin-sensitizing effect of thiazolidinediones may reflect increased adiponectin production. Subsequently, however, no correlation was observed between plasma visfatin concentrations and insulin sensitivity in human subjects [91]. Vaspin Vaspin (visceral adipose tissue-derived serpin) is an adipocyte serine protease inhibitor which improved insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis in obese insulin-resistant rodents, and might therefore offer a therapeutic lead [93]. Omentin Omentin, a peptide from visceral adipose tissue, increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by adipocytes [94], and might indicate a potential therapeutic approach. Other potentiators of insulin action Bromocriptine the dopamine D2 receptor agonist bromocriptine (Figure 60. Bromocriptine as monotherapy or an adjunct to other antidiabetic agents for up to 1 year has reduced HbA1c by 0.
Lesions often have a fine scale and can be mildly pruritic but are usually asymptomatic hypertension harmony of darkness generic 5mg bisoprolol visa. Given the risk of hepatotoxicity blood pressure ratio buy 5mg bisoprolol overnight delivery, oral azole antifungals are reserved for resistant or widespread disease (oral terbinafine not effective) heart attack women buy cheap bisoprolol 10mg on line. Clinical presentation: Pruritic prehypertension blood pressure diet purchase bisoprolol 5mg amex, erythematous, annular patch, or plaque with central clearing and a scaly raised border. Pathogenesis: Contagious bacterial infection of the skin, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, with a minority of cases caused by group A -hemolytic Streptococcus. Clinical presentation: (1) Nonbullous impetigo: Papules that evolve into erythematous pustules or vesicles that break and form thick, honey-colored crusts and plaques. Pathogenesis: Mostly caused by Trichophyton tonsurans (but Trichophyton violeum and Trichophyton sudanese are clinically similar), sometimes Microsporum canis. African-American children more commonly affected, perhaps owing to the structure of their hair, but any age and ethnicity can be affected. These areas develop alopecia, and black dots are visible on scalp where hair has broken off. Gray patch ("seborrheic dermatitis") tinea capitis: Erythematous, scaling, well-demarcated patch that grows centrifugally. Hair breaks off a few millimeters above the scalp and takes on a gray/frosted appearance. All family members, particularly other children, should be examined carefully for subtle infection and treated. Clinical presentation: Chronic inflammatory (probably autoimmune) disease that starts with small bald patches and normal-appearing underlying skin. Bald patches may enlarge to involve large areas of the scalp or other hair-bearing areas. A minority progress to total loss of all scalp (alopecia totalis) and/or body hair (alopecia universalis). Treatment7: First-line therapy is topical and occasionally intralesional steroids. Minoxidil, anthralin, contact sensitization, and ultraviolet light therapy are second line. No evidence-based data that any therapy is better than placebo, so treatments with significant risk of toxicity should be avoided, particularly in children. Older children, adolescents, and young adults with longstanding localized areas of hair loss have the best prognosis. Pathogenesis: Most common cause of diffuse hair loss, usually after stressful state (major illnesses or surgery, pregnancy, severe weight loss). Mature hair follicles switch prematurely to the telogen (resting) state, with shedding within 3 months. Clinical presentation: Noninflammatory linear areas of hair loss at margins of hairline, part line, or scattered regions, depending on hairstyling procedures used. If traction remains for long periods, condition may progress to permanent scarring hair loss. Onset is usually after age 10 and should be distinguished from hair pulling in younger children that resolves without treatment in most cases. Clinical presentation: Characterized by hair of differing lengths; area of hair loss can be unusual in shape. Adolescents may benefit from psychiatric evaluation; condition can be associated with anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Closed comedo (whitehead): Accumulation of sebum and keratinous material, resulting in white/skin-colored papules without surrounding erythema. Open comedo (blackhead): Dilated follicles packed with keratinocytes, oils, and melanin. Typically appear later in the course of acne and vary from 1- to 2-mm micropapules to nodules >5 mm. Nodulocystic presentations are more likely to lead to permanent scarring and/or hyperpigmentation.
Clinical features include spontaneous bleeding from mucous membranes blood pressure 4060 trusted 10 mg bisoprolol, prolonged bleeding from wounds blood pressure medication starting with d discount 10mg bisoprolol fast delivery, and menorrhagia in young females hypertension interventions bisoprolol 10mg low price. Abnormal platelet response to ristocetin (adhesion defect) is an important diagnostic test hypertension knee bisoprolol 5mg without a prescription. Massive tissue destruction Sepsis Release of tissue factor Widespread microvascular thrombosis Endothelial injury Platelet aggregation Activation of plasmin Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Vascular occlusion Ischemic tissue damage Consumption of clotting factors and platelets Fibrinolysis Proteolysis of clotting factors Fibrin split products Bleeding Inhibition of thrombin, platelet aggregation, and fibrin polymerization Figure 5-3. Outcomes of thrombosis include vascular occlusion and infarctions; embolism; thrombolysis; and organization and recanalization. Symptoms include shortness of breath, hemoptysis, pleuritic chest pain, and pleural effusion. On gross examination infarctions typically have a wedge shape, with the apex of the wedge tending to point to the occlusion. Microscopic pathology of infarction can show either coagulative necrosis (most organs) or liquefactive necrosis (brain). The cellular injury is initially reversible; if the hypoxia persists, the cellular injury becomes irreversible, leading to the death of cells and the patient. Compensation is characterized by increased sympathetic tone, release of catecholamines, and activation of the renin-angiotensin system. The risk increases with maternal age to an incidence of 1 in 25 live births in women age 45. The pathogenesis involves meiotic nondisjunction (95%), Robertsonian translocation (4%), or mosaicism due to mitotic nondisjunction during embryogenesis (1%). Clinical findings can include intellectual disability; mongoloid facial features (flat face, low-bridged nose, and epicanthal folds); Brushfield spots (speckled appearance of the iris); muscular hypotonia; broad short neck; palmar (simian) crease; and congenital heart defects. Endocardial cushion defect, if present, leads to the formation of an atrioventricular canal (a common connection between all 4 chambers of the heart). Prenatal tests include maternal serum tests, ultrasonography, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling. Note Robertsonian Translocation Defined as a translocation involving 2 acrocentric chromosomes with the break points occurring close to the centromeres. This results in an extremely large chromosome and a tiny one, which is typically lost. Note Mosaicism is defined as the presence of 2 populations of cells within an individual. Clinical findings can include intellectual disability; low-set ears and micrognathia; congenital heart defects; overlapping flexed fingers; and rocker-bottom feet. Prominent occiput Short neck Low-set ears Intellectual disability Micrognathia (small jaw) Overlapping fingers Congenital heart defects Renal malformations Limited hip abduction Rocker-bottom feet Figure 6-2. The risk increases with Clinical findings can include intellectual disability; cleft lip and/or palate; cardiac defects; renal abnormalities; microcephaly; holoprosencephaly; and polydactyly. Clini- cal findings include a characteristic high-pitched catlike cry; intellectual disability; congenital heart disease; and microcephaly. Microdeletions are too small to be detected by karyotyping and require molecular techniques for detection. Clinical findings include testicular atrophy, infertility due to azoospermia, eunuchoid body habitus, high-pitched voice; female distribution of hair; and gynecomastia. The second X chromosome is necessary for oogenesis and normal development of the ovary. Clinically, patients fail to develop secondary sex characteristics and have short stature with widely spaced nipples. Other features include gonadal dysgenesis with atrophic streak ovaries; primary amenorrhea; and infertility.
Bisoprolol 10 mg. Proper Diet Plan for High Blood Pressure Patients.