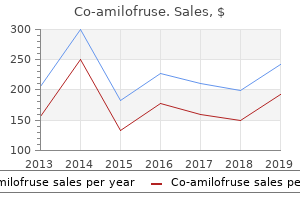
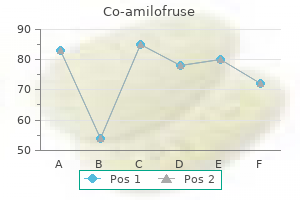
Co-amilofruse
"Purchase co-amilofruse 40/5 mg without prescription, treatment yeast infection male".
By: J. Riordian, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine
The radioactive material collects in the bones and is detected by a scanner (instrument that takes pictures of the inside of the body) medicine hat college generic 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse mastercard. The pictures are taken from different angles and create 3-D views of tissues and organs medicine 6 times a day buy 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse. It uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to create detailed pictures of organs and tissues treatment diabetes type 2 generic 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse overnight delivery. Sometimes a special dye is injected into a vein or swallowed to help organs or tissues show up more clearly 88 treatment essence co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg line. Sometimes a special dye is injected into a vein to make any cancer cells show up brighter in the pictures. Because cancer cells often take up more glucose than normal cells, the pictures can be used to find cancer cells in the body. A spinal tap (also called a lumbar puncture) is a procedure in which a thin needle called a spinal needle is put into the lower part of the spinal column to collect cerebrospinal fluid for examination or to give drugs. During the procedure, your child will lie still on a table, which moves back and forth through a scanner that makes pictures. Spinal cord During this test, your child will either lie curled up on Cerebrospinal fluid their side or be seated and Spinal needle leaning over with their head on a pillow. A sample (such as a stool, blood, urine, or other bodily fluid or tissue, depending on the marker to be measured) will be taken and sent to a lab for testing. This test may be used together with other tests to help diagnose cancer, plan treatment, find out how well treatment is working, or tell if cancer has come back. The sound waves bounce off structures in the body, making echoes that a computer uses to form pictures of the tissues and organs on a computer screen (sonogram). During treatment for cancer it may be used to help make a diagnosis and to guide biopsies. Your child will lie on a table while a technician slowly moves a wand, with warm clear gel on it, on the skin over the part of the body being examined. Your child will need to stay very still and may need to hold his breath when the images are taken. Sedatives and anesthesia Each child has unique needs based on their age and the type of procedure. Children may be given medicine (called a sedative) to help them relax, stay very still, or sleep during a procedure. Types of anesthesia include: Local anesthesia causes a loss of feeling in one small area of the body. Regional anesthesia causes a loss of feeling in one part of the body, such as an arm or leg. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure referrals are processed timely we do require that items listed in the Referral Documentation section be submitted with the initial referral. The Endocrine System Chapter 16 Lesson 3 Structure of the Endocrine System the principal structures of the endocrine system are the endocrine glands- ductless, tubeless structures that secrete hormones. And hormones- chemical substances produced by ductless glands that regulate the activities of all the different body cells. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands and carried to their destinations via the bloodstream. Endocrine glands are scattered throughout the body and work independently from one another. Major glands of the endocrine system include: the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, and gonads. The Pituitary Gland Considered the "master gland" because it regulates and controls the activities of all other endocrine glands. Located at the midpoint of the skull it has three sections, the anterior lobe, intermediate lobe, and posterior lobe. Anterior lobe (front)- regulates metabolic activities of cells and stimulate other endocrine glands. Oxytocin stimulates the smooth muscles in the uterus of a pregnant female, causing contractions during childbirth. Principal hormone produced is thyroxine, which regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients. Too little thyroxine (hypothyroidism) causes tiredness, weight gain, constipation, and sensitivity to cold.
Diseases
- Lopes Marques de Faria syndrome
- Thrombocytopenic purpura, autoimmune
- Pierre Robin syndrome skeletal dysplasia polydactyly
- Prosencephaly cerebellar dysgenesis
- DOPA-responsive dystonia
- Pseudoprogeria syndrome
- Serum sickness
As a rule symptoms 3 dpo cheap co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg visa, anterior chiasmatic lesions that also involve the optic nerve cause a central scotoma in the eye on the side of the lesion and a superior temporal visual field defect (junction scotoma) in the contralateral eye symptoms jaundice generic co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg overnight delivery. Lateral chiasmatic lesions produce nasal hemianopsia of the ipsilateral eye; those that impinge on the chiasm from both sides produce binasal defects treatment 02 academy buy 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse mastercard. Depending on their location symptoms 6 days after embryo transfer co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg free shipping, retrochiasmatic lesions produce different types of homonymous unilateral scotoma: the defect may be congruent or incongruent, quadrantanopsia or hemianopsia. As a rule, temporal lesions cause contralateral superior quadrantanopsia, while parietal lesions cause contralateral inferior quadrantanopsia. Complete hemianopsia may be caused by a relatively small lesion of the optic tract or lateral geniculate body, or by a more extensive lesion more distally along the visual pathway. The patient suffers from "tunnel vision" but the central visual field remains intact (sparing of macular fibers). Cortical blindness refers to subnormal visual acuity due to bilateral retrogeniculate lesions. Visual Field Defects Visual field Directions tested Blind spot Test object Macular region Patient ca. Cranial Nerves 83 Oculomotor Function the visual axes of the eyes are directed straight ahead on primary gaze. The lateral and medial rectus muscles are responsible for horizontal eye movements. Vertical eye movements are subserved by the superior and inferior rectus as well as superior and inferior oblique muscles. The rectus muscles elevate and depress the eye when it is abducted, the oblique muscles when it is adducted. Impulses arising in the semicircular canals in response to rapid movement of the head induce reflex movement of the eyes in such a way as to stabilize the visual image (p. For example stimulation of the horizontal semicircular canal activates the ipsilateral medial rectus and contralateral lateral rectus muscles, while inhibiting the ipsilateral lateral rectus and contralateral medial rectus muscles. Fixation is active adjustment of the gaze (with or without the aid of eye movement) to keep a visualized object in focus. Saccades are rapid, jerky conjugate movements of the eyes that serve to adjust or set the point of fixation of an object on the fovea. Saccades may be spontaneous, reflexive (in response to acoustic, visual, or tactile stimuli), or voluntary; the rapid phase of nystagmus is a saccade. The speed, direction, and amplitude of a saccadic movement are determined before it is carried out and cannot be influenced voluntarily during its execution. Voluntary ocular pursuit can occur only when triggered by a moving visual stimulus. Conversely, fixation of the gaze on a resting object while the head is moving leads to gliding eye movements. Fixation-independent ocular pursuit also occurs during somnolence and the early stages of sleep ("floating" eye movements). Vergence movements (convergence and divergence) are mirror-image movements of the two eyes toward or away from the midline, evoked by movement of an object toward or away from the head in the sagittal plane. They serve to center the visual image on both foveae and are accompanied by an adjustment of the curvature of the lens (accommodation) to keep the object in focus. Saccades are produced by two parallel systems: Voluntary eye movements are subserved by the frontal system, which consists of the frontal eye fields (areas 4, 6, 8, 9), the supplementary eye field (area 6), the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (area 46), and a portion of the parietal cortex (area 7). Reflex eye movements are initiated in the visual cortex (area 17) and temporal lobe (areas 19, 37, 39) and modulated in the superior colliculus (collicular system). Vergence and accommodation are mediated by the pretectal area in the vicinity of the oculomotor nucleus.
Buy co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg with visa. The most common symptom of multiple sclerosis (MS) - Fatigue.
A patient exposed to liquid nerve agent and not showing any signs or symptoms of intoxication should be watched for a period of at least 18 h treatment programs effective 40mg/5mg co-amilofruse. This is the longest reported time frame for signs and symptoms of liquid nerve agent exposure to develop medications after stroke order co-amilofruse 40/5 mg overnight delivery. Generally medications used for adhd discount co-amilofruse 40mg/5mg with mastercard, the longer it takes for signs and symptoms to develop medicine express co-amilofruse 40/5 mg visa, the milder the physiological changes will be. Three things can occur when liquid nerve agent (or any liquid chemical warfare agent) comes in contact with the skin. It will evaporate into the atmosphere, be removed by the decontamination process, or be absorbed into the skin and then into the systemic circulation. Evaporation and 698 Chemical Warfare Agents: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutics decontamination will not remove any liquid agent that has already been absorbed into the skin, hence the need for early decontamination. The exact same dose of liquid chemical agent can be applied to the skin in one of two ways, as a single larger drop, or as multiple, smaller drops. A significant difference between organophosphate insecticides and organophosphate nerve agents is that the former generally have higher fat solubility, whereas the latter generally have lower fat solubility. This means that with insecticide intoxication fat stores may give up the agent over a long period of time, and blood levels may repeatedly reach concentrations sufficient to cause bouts of acute toxicity including seizures. This is usually not the case with nerve agents as they generally possess lower lipid solubility. As a result, there is less nerve agent to be released from fat stores, and blood concentrations sufficiently high to cause development of status epilepticus usually occur only once with initial intoxication. Exposure to low doses of nerve agent insufficient to cause physiological changes may result in psychological and mental status changes. Such patients may encounter forgetfulness, irritability, impaired judgment, agitation, anxiety, depression, decreased comprehension, nightmares, sleep disturbances, slurred speech, insomnia, expression becoming difficult, and poor concentration. Because the binding site of the affected cholinesterases would already be bound to pyridiostigmine (a carbamate) these cholinesterases could not become combined with, and thereby inhibited by, nerve agent on exposure to it. However, unlike nerve agents, carbamates only temporarily combine with cholinesterases, and later the carbamate will spontaneously dissociate from these cholinesterases. The uninhibited (protected) cholinesterases liberated from carbamates can then resume their normal physiological functions. On the other hand, once a patient has already been exposed to nerve agent, giving the patient pyridostigmine (or any other carbamate) after exposure will only increase the cholinergic crisis. This occurs because none of the cholinesterase would be protected from inhibition by the previously administered nerve agent. The administered carbamate would be read by cholinergic receptors as additional receptor site stimulating material, thereby further hyper-stimulating these receptors. Consequently, giving carbamate after nerve agent exposure should be avoided at all costs. The neuromuscular junctions in skeletal muscle and the sympathetic chain (preganglionic) ganglions exemplify human nicotinic sites. Therefore, oxime therapy is all that is available to combat the signs of nicotinic intoxication including fasciculations (irregular movements of small groups of muscle tissue, which appear as worm-like, irregular muscle movements just below and easily visible through the skin), skeletal muscle weakness, and skeletal muscle flaccidity. More serious complications include unconsciousness, seizures, apnea, and flaccid paralysis (State of New York, unknown year). Although the duration of oxime therapy is controversial, these authors (toxicologists) suggest continuing oxime therapy for at least 24 h after the symptoms resolve (Wiener and Hoffman, 2004). Based on multiple factors (total dose of atropine required; aging half-times of the nerve agent; 2 vs. A major difference between how acids and bases affect the skin is in the type of reaction. When an acid reacts with the skin, it creates a hard coagulum, or scab, that limits deeper penetration of the acid and thus the degree of injury. On the other hand, bases do not create this scab, so the damage can continue to the deeper tissues. Oxidizers react with the skin to create a rapid exothermic reaction and tissue destruction. However, should the chemicals enter the body through respiration or ingestion, they will cause the same corrosive effects with the tissues they come into contact with.
Indian Ginger (Ginger). Co-amilofruse.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Nausea and vomiting following surgery.
- What is Ginger?
- Is Ginger effective?
- Preventing morning sickness, after discussing the possible risks with your healthcare provider.
- Preventing dizziness.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96924