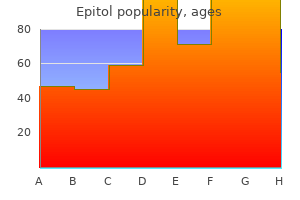
Epitol
"Safe 100mg epitol, symptoms bowel obstruction".
By: Y. Thordir, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Arkansas College of Osteopathic Medicine
Eyes Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in people of working age (see Chapter 36) treatment yeast infection home purchase epitol 100mg mastercard. It is almost invariably asymptomatic until there is a catastrophic sight-threatening hemorrhage medicine 8162 buy epitol 100mg without a prescription. For this reason it is important to screen regularly for retinopathy to allow treatment before hemorrhage and visual loss occur denivit intensive treatment proven epitol 100mg. Traditionally medicine quizlet epitol 100 mg, this has been performed by examination of the visual acuity and fundoscopy within the diabetes clinic at least on an annual basis. Alternatively, in many countries, dilated ophthalmologic examinations are regularly performed by a specialist. The gold standard for screening now is digital retinal photography, which may be undertaken in several different settings. When this is performed outside the traditional diabetes clinic, communication between the screener and diabetes team is essential if other aspects of diabetes care are to take account of the 329 Part 5 Managing the Patient with Diabetes increasing in line with the increased prevalence of diabetes worldwide. The primary prevention of nephropathy relies on excellent glycemic control as well as tight blood pressure control. Once nephropathy is present, blood pressure management is the mainstay as there is little evidence that glycemic control at this stage slows the rate of progression. It is important that the person with diabetes understands the need for screening and then treatment if nephropathy develops. Timely referral to the nephrology team is needed to ensure that the management of renal disease is managed promptly in patients with abnormal renal function. It is important that the person with diabetes is educated about the risk of these and discusses strategies to prevent them. If a person with diabetes has been admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome, the opportunity should be taken to explore the reasons why this episode occurred and to identify what might be changed to prevent this from happening in future. The most common causes of hyperglycemic emergencies in those with pre-existing diabetes are infections and insulin omission and errors. It is particularly important that people with diabetes understand the "sick day" rules: insulin should never be discontinued and indeed doses may need to be increased, even when appetite is diminished. Hypoglycemia can have a major adverse effect on quality of life and is the most important limiting factor in the achievement of good glycemic control. It is important that the person with diabetes is educated about the symptoms of hypoglycemia and the actions to be taken to prevent and treat this. Friends and family members should be invited to learn about hypoglycemia and its management in order to intervene where necessary, for example providing glucagon treatment if the person with diabetes is unconscious. If hypoglycemia becomes disabling or recurrent it is important to explore underlying causes. Lifestyle issues Diabetes has a number of social, as well as medical, consequences and one aspect of diabetes care is to discuss how diabetes is affecting issues such as driving, education and employment (see Chapter 24). The health care professional may need to act as an advocate for the person where discrimination is occurring. Some aspects of lifestyle also affect diabetes care, such as diet, exercise, smoking and alcohol. These issues should be discussed carefully and sensitively in order to help the person with diabetes understand how their lifestyle affects their diabetes and general health. Support should be given to help and encourage a person with diabetes to make changes to their lifestyle. Psychologic issues the diagnosis of diabetes can provoke a number of psychologic reactions, such as anger and sadness in the individual which may be akin to a bereavement reaction (see Chapter 49). While all members of the diabetes team should be able to recognize and address basic psychologic issues, the psychologist is an important team member to address more complex needs, such as eating disorders. Despite the importance of psychologic issues, this need is frequently unmet because of a lack of trained health care professionals. In many instances, the diabetes is coincidental to the admission and the person with diabetes remains capable of managing their own diabetes, often with greater skill than the health care professionals around them. Good diabetes control remains an important goal as this improves the rate of recovery and may lead to an earlier discharge.
On the shoulders of compelling evidence treatment 5 alpha reductase deficiency cheap epitol 100 mg without a prescription, greater investment and political will are required to overcome low accessibility and awareness symptoms 6 days before period buy 100mg epitol with visa, as well as to translate the evidence into practical real-life implementation of proven and effective prevention strategies [123] medicine journey epitol 100mg free shipping. The Silent Epidemic: An economic study of diabetes in developed and developing countries 4 medications at walmart buy discount epitol 100 mg. The burden of diabetes and its complications: trends and implications for intervention. Global and regional mortality from ischaemic heart disease and stroke attributable to higher-than-optimum blood glucose concentration: comparative risk assessment. Impact of traditional and novel risk factors on the relationship between socioeconomic status and incident cardiovascular events. Socioeconomic status and ischaemic heart disease mortality in 10 western European populations during the 1990s. Racial and ethnic differences in cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review. Impact of poverty on the prevalence of diabetes and its complications in urban southern India. High prevalence of diabetes, obesity and dyslipidaemia in urban slum population in northern India. Serial epidemiological surveys in an urban Indian population demonstrate increasing coronary risk factors among the lower socioeconomic strata. Determinants and treatment of hypertension in South Africans: the first Demographic and Health Survey. Changes in cardiovascular risk factors in different socioeconomic groups: seven year trends in a Chinese urban population. Diabetic ketoacidosis: comparisons of patient characteristics, clinical presentations and outcomes today and 20 years ago. Diabetic ketoacidosis in Denmark: incidence and mortality estimated from public health registries. Survey on acute and chronic complications in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes at Muhimbili National Hospital in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Access to care for patients with insulin-requiring diabetes in developing countries: case studies of Mozambique and Zambia. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance: mechanistic links and therapeutic targets. The importance of treating cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Epidemiological evidence for the association of hyperglycaemia and atherosclerotic vascular disease in 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 81 Part 1 Diabetes in its Historical and Social Context non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Garattini L, Tediosi F, Chiaffarino F, Roggeri D, Parazzini F, Coscelli C; Gruppo di Studio R. Expenditure on health care incurred by diabetic subjects in a developing country: a study from southern India. Health insurance status, cost-related medication underuse, and outcomes among diabetes patients in three systems of care. The prevalence and cost of diabetes in metropolitan France: what trends between 1998 and 2000 Reductions in individual work productivity associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer disease and decline in cognitive function. Is diabetes associated with cognitive impairment and cognitive decline among older women Health economic benefits and quality of life during improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Addressing the needs of patients with multiple chronic illnesses: the case of diabetes and depression.
We hope you enjoy reading the book and find it useful whether this is helping people with diabetes or teaching physicians and other health professionals how best to manage this disease and its complications treatment quinsy discount epitol 100 mg on-line. Scientific knowledge increases exponentially and our understanding slowly improves although there are still massive gaps in many fundamental aspects of the diabetes story medications like adderall purchase epitol 100mg overnight delivery, such as the mechanisms underlying the development of type 2 diabetes medications list order epitol 100 mg online. Trying to keep up with all the advances is an ever increasing burden medicine zocor epitol 100 mg otc, but with a large array of means to achieve this. Many people use the web, both specific websites and more general search engines, but there are still a large number of people who prefer the printed word and the collection together of an accessible compendium where you can expect to obtain answers to your questions. This volume provides exactly that; namely a series of up-to-date, well referenced, learned articles covering the manifold manifestations of diabetes together with the basic underlying science. It is truly comprehensive and I would challenge any reader to find missing aspects of the pathophysiology, treatment and care of people with diabetes. The book begins with a fascinating historical essay which should be read by anybody who picks up the book. It reminds us that much valuable information is forgotten and many lessons can be learned by going back to pre-internet days! The possibility of using HbA1c for the diagnosis of diabetes is discussed reflecting a potentially seismic shift in our diagnostic armamentarium that has relied on the measurement of glucose since that became avail- able routinely a century ago. The world pandemic of diabetes is described with few populations spared and then each type of diabetes is described together with what is known of their pathophysiology. The management and treatment of diabetes from education through lifestyle modification and the use of oral agents and insulin is dealt with exhaustively with useful chapters on the oft ignored psychological and social aspects of the disorder. Complications are dealt with comprehensively and again the book is of particular value in going beyond the classical complications and dealing with a range of less well defined problems found in people with diabetes. The book finishes with crystal ball gazing: a look at future drugs for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as well as the potential for stem cell therapy, islet cell transplantation and gene therapy, all of which are thought provoking and informative. Overall I feel that this volume fulfils a major need for anyone with an interest in diabetes; it should be available in every setting where people with diabetes receive their care and will serve as an excellent vade mecum. The name "diabetes" comes from the Greek word for a syphon; the sweet taste of diabetic urine was recognized at the beginning of the first millennium, but the adjective "mellitus" (honeyed) was only added by Rollo in the late 18th century. In the 1840s, Bernard showed that glucose was normally present in blood, and showed that it was stored in the liver (as glycogen) for secretion into the bloodstream during fasting. In 1893, Laguesse suggested that the pancreatic "islets" described by Langerhans in 1869 produced an internal secretion that regulated glucose metabolism. These classifications were the forerunners of the etiological classification into type 1 (insulin-dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes. The "insulin clamp" method devised by Andres and DeFronzo was the first accurate technique for measuring insulin action. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young was described as a distinct variant of type 2 diabetes by Tattersall in 1974. Proinsulin was discovered by Steiner in 1967, and the sequence of the human insulin gene by Bell in 1980. The presence of insulin receptors was deduced in 1971 by Freychet, and the receptor protein was isolated in 1972 by Cuatrecasas. Albuminuria was noted as a common abnormality in patients with diabetes in the 19th century and a unique type of kidney disease was described in 1936 by Kimmelstiel and Wilson. The concept of a specific diabetic angiopathy was developed by Lundbaek in the early 1950s. Ancient times Diseases with the cardinal features of diabetes mellitus were recognized in antiquity (Table 1. The patients never stop making water and the flow is incessant, like the opening of aqueducts. Life is short, unpleasant and painful, thirst unquenchable, drinking excessive, and disproportionate to the large quantity of urine, for yet more urine is passed. If for a while they abstain from drinking, their mouths become parched and their bodies dry; the viscera seem scorched up, the patients are affected by nausea, restlessness and a burning thirst, and within a short time, they expire. The Hindu physicians, Charak and Sushrut, who wrote between 400 and 500 bc, were probably the first to recognize the sweetness of diabetic urine (Figure 1. Indeed, the diagnosis was made by tasting the urine or noting that ants congregated round it. Charak and Sushrut noted that the disease was most prevalent in those who were indolent, overweight and gluttonous, and who indulged in sweet and fatty foods.

With regard to degrees of functional cognitive impairment treatment definition discount epitol 100mg without a prescription, it was originally suggested that this is greater in symptomatic cases when compared with asymptomatic controls (Maj et al symptoms vitamin b deficiency proven epitol 100 mg. Memory impairment is clearly an important indicator of decreased likelihood of return to work (van Gorp et al treatment goals and objectives buy epitol 100mg otc. They find that there is little to suggest neuropsychological deterioration in asymptomatic cases up to 36 months follow-up treatment naive definition purchase 100mg epitol with mastercard. The latter may sometimes show an admixture of organic psychiatric symptoms, since mood disorder and psychoses can be early manifestations of brain disease. Patients with primary mental disorder are also disproportionately represented in those who have contracted the virus. As a result comorbid mental ill health is often poorly recognised in those with the virus (Evans et al. Other factors have been noted as contributing to psychiatric morbidity over and above the threats inherent in a longterm life-threatening, condition. The acquisition of infection can increase feelings of stigma or guilt, and provoke intense concern about others to whom the disease may have been transmitted. An additional stress is the uncertainty, extending sometimes over many years, about the course the disease will take, occurring often against a background of illness and losses among close friends and partners. In consequence it is scarcely surprising that a high prevalence of psychiatric disorder is reported in both physically asymptomatic and symptomatic persons. Similarly, interest has been directed at the relationship between behavioural manifestations of psychosocial factors and disease progression including the impact of treatment compliance, illicit substance misuse, sexual risk behaviours and physical exercise (for a review see Gore-Felton & Koopman 2008). The principal manifestations are acute shock, bewilderment and anxiety, typically lasting for several weeks. Major depression may be precipitated, with depersonalisation, insomnia and suicidal ideation. A preoccupation may develop with bodily symptoms thought to be indicative of commencing disease. Other reactions include anger, despair, guilt, increased use of alcohol or drugs, social withdrawal or denial. Denial may lead to a dangerous disregard of medical advice and failure to take precautions against infecting others. The incidence of acute psychological reactions at the time of testing has varied widely in different reports, perhaps reflecting the adequacy of pre- and post-test counselling. Longer-term psychiatric disorder Longer-lasting psychiatric disorders may emerge during the asymptomatic or symptomatic stages of infection, but it is uncertain whether this is more common than in patients with other serious medical conditions (King 1989, 1993). The risk of infecting others, or of being identified as homosexual or a drug abuser, may be at the forefront of concerns. Somatic symptoms of anxiety are sometimes interpreted as evidence of progression to further stages of the disorder, giving rise to an escalating vicious circle. Alcohol or drugs may be abused in attempts to self-medicate the symptoms of anxiety. Depression has a varied reported prevalence, ranging from 2% to 48% of patients in different surveys, depending on those studied (Perkins et al. The risk of depression in seropositive individuals is double that seen in an uninfected control group, independent of sexual orientation (Ciesla & Roberts 2001). Confirmation of the diagnosis brings the realisation of fears that may have long been present, also the need to tell others, including sexual partners. Lifestyles which have previously 416 Chapter 7 depression as the most significant predictors of depressive illness (Atkinson et al. Interestingly, the presence of baseline cognitive impairment, pathology identified on neuroimaging and adverse life events did not predict a depressive episode in this study, although it is acknowledged that this may be a feature of the cohort and needs further confirmation. Depression and withdrawal can significantly interfere with the ability to cope with the procedures required for management of the illness (Ostrow 1990; Cruess et al. Nonetheless, severe depressive symptoms should not be assumed to be understandable and justified, and must always receive full evaluation and treatment. Anhedonia and diurnal mood variation may be useful discriminating symptoms suggestive of depression (Treisman et al. This can occur with or without depressed mood, commonly involving repeated bodily scrutiny for evidence of progression of disease. Obsessive ruminations may centre on death and dying, or endeavours to recollect past sexual partners to whom the infection may have been transmitted.
Discount 100mg epitol. What is Sadhana- Awakening Here and Now.