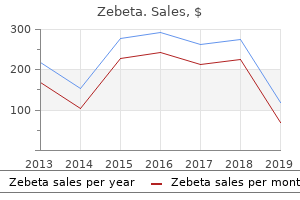
Zebeta
"Buy discount zebeta 10 mg, high blood pressure medication and sperm quality".
By: H. Sulfock, M.B.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, University of Illinois College of Medicine
Passive immunization involves delivery of preformed antibodies to individuals who have no active immunity against a particular disease but who have either been exposed to or are at high risk for exposure to the infectious agent arteria maxillaris buy zebeta 5mg overnight delivery. Visitors to high-risk areas may receive hepatitis A immune globulin before travel blood pressure visual chart trusted zebeta 2.5 mg. Rationale for vaccine: Diphtheria blood pressure response to exercise zebeta 10 mg without a prescription, tetanus arrhythmia dance company order 5mg zebeta visa, and pertussis all may cause serious disease, especially in young infants. Rationale for vaccine: Poliovirus is an enterovirus with propensity for the central nervous system, causing transient or permanent paresis of the extremities and meningoencephalitis. Polio has been eradicated from the Western hemisphere and South Pacific but remains in isolated pockets throughout the world. Advantages include induction of both host immunity and secondary immunity because it is excreted in the stool of the recipient and may infect, and thus immunize, close contacts. Measles is a severe illness with complications that include pneumonia associated with significant mortality. Mumps is most commonly associated with parotitis but may also cause meningoencephalitis and orchitis. Rubella causes a mild viral syndrome in children but may cause severe birth defects in offspring of susceptible women infected during pregnancy. Rationale for vaccine: Varicella is the virus responsible for chicken pox and zoster. Varicella often causes uncomplicated illness but may cause severe disease in very young and in older patients. Rationale for vaccine: Hepatitis A is the most common viral cause of hepatitis worldwide, although it is asymptomatic in up to 70% of infected children younger than 6 years of age. More severe disease is seen in older children and adults, although it is rarely associated with fulminant hepatitis. Timing of vaccination and recommendations: Hep A vaccine is recommended at 2 years of age or older, with a booster 6 months later for the following groups: 1. Individuals in other groups with high hepatitis A rates, including those with chronic liver disease, homosexual and bisexual men, users of illicit drugs, patients with clotting factor disorders receiving blood products, and patients at high risk for occupational exposure. Rationale for vaccine: Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae) is the most common cause of acute otitis media and invasive bacterial infections in children younger than 3 years of age. Pneumovax is composed of polysaccharide capsular antigens from 23 pneumococcal serotypes. Major advantage is that the vaccine contains antigens from pneumococcal strains causing almost all cases of bacteremia and meningitis during childhood. Major disadvantage is that the vaccine has little immunogenicity in children younger than 2 years. Vaccine is used primarily for older children and adults at high risk for pneumococcal disease. Major advantages include immunogenicity and efficacy in preventing meningitis, pneumonia, bacteremia, and otitis media from the most common pneumococcal strains in children younger than 2 years of age. Major disadvantage is that it does not confer as broad coverage against pneumococcal strains as Pneumovax. Vaccine is recommended for all children younger than 2 years of age and for selected children older than 2 years of age who are at high risk for pneumococcal disease. Most vaccine side effects are mild to moderate in severity and occur within the first 24 hours after administration. Serious side effects that may result in permanent disability or be life-threatening are rare. Note that mild illnesses, including febrile illnesses, are not contraindications to immunization. Persistent, inconsolable crying lasting 3 hours occurring within 48 hours after prior vaccination c.
Levothyroxine therapy and serum free thyroxine and free triiodothyronine concentrations prehypertension home remedies order 2.5mg zebeta visa. Effects of thyroxine as compared with thyroxine plus triiodothyronine in patients with hypothyroidism blood pressure medication with food generic zebeta 2.5mg online. Weston Area T4/T3 (thyroid hormone replacement) study: psychological effects of combined T4/t3 therapy arteria doo zebeta 10mg with amex. Combined thyroxine/liothyronine treatment does not improve well-being hypertension exercise generic zebeta 5mg amex, quality of life or cognitive functions compared to thyroxine alone: a randomized controlled trial in patients with primary hypothyroidism. Combined levothyroxine plus liothyronine compared to levothyroxine alone in the treatment of primary hypothyroidism: a randomized controlled trial. Thyroxine prescription in the community: serum thyroid stimulating hormone level assays as an indicator of undertreatment or overtreatment. Changes in bone mass during prolonged subclinical hyperthyroidism due to L-thyroxine treatment: a meta-analysis. Effects on bone mass of long term treatment with thyroid hormone: a meta-analysis. Thyroxine treatment in patients with symptoms of hypothyroidism but thyroid function tests within the reference range: randomised double blind placebo controlled crossover trial. Geographical distribution of subclinical autoimmune thyroid disease in Britain: a study using highly sensitive direct assays for autoantibodies to thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase. Prevalence of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies in serum in the elderly: comparison with other tests for anti-thyroid antibodies. Thyrotropin secretion in patients with central hypothyroidism: evidence for reduced biological activity of immunoreactive thyrotropin. Lesson of the week: Deterioration of symptoms after start of thyroid hormone replacement. Evaluation of the adequacy of levothyroxine replacement therapy in patients with central hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 924-929 Shimon I, Cohen O, Lubetsky A, Olchovsky D. Thyrotropin suppression by thyroid hormone replacement is correlated with thyroxine level normalization in central hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2002; 12: 823-827 Newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism: recommended guidelines. Paediatrics 1993; 91: 1203-1209 Policies and standards for newborn blood spot screening. The use and limitations of a chemiluminescent thyrotropin assay as a single thyroid function test in an out-patient endocrine clinic. Suppression of thyrotropin in the low-thyroxine state of severe nonthyroidal illness. Hyperthyroidism without triiodothyronine excess: an effect of severe non-thyroidal illness. Consensus statement for good practice and audit measures in the management of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Propothiouracil before 131I therapy of hyperthyroid diseases; effect on cure rate evaluated by a randomized clinical trial. The European Multicentre Trial Group of the Treatment of Hyperthyroidism with Antithyroid Drugs. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1998; 49: 451-457 Schleusener H, Schwander J, Fischer C et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of subclinical thyroid disease. Prediction of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in elderly people from one low serum thyrotropin result: a 10-year cohort study. Comparison of thyroid function in pregnant and nonpregnant Asian and western Caucasian women.
Following ductal closure in the newborn with a critical coarctation blood pressure of 100/70 trusted 5mg zebeta, the left ventricle must suddenly generate adequate pressure and volume to pump the entire cardiac output past a significant point of obstruction blood pressure yahoo health buy zebeta 10 mg on line. This sudden pressure load may be poorly tolerated by the neonatal myocardium heart attack american buy 10 mg zebeta visa, and the neonate may become rapidly and critically ill because of lower body hypoperfusion arrhythmia kardiak generic zebeta 10 mg on line. In infants with symptomatic coarctation, surgical repair is performed as soon as the infant has been resuscitated and medically stabilized. In infants with symptomatic coarctation and a large, coexisting ventricular septal defect, consideration should be given to repair both defects in the initial procedure through a median sternotomy. Balloon dilation of native coarctation is not routinely done at our institution because of the high incidence of restenosis and aneurysm formation, especially given the safe and effective surgical alternative. There are three anatomic subtypes of interrupted aortic arch based on the location of the interruption: distal to the left subclavian artery (type A), between the left subclavian artery and the left carotid artery (type B), and between the innominate artery and the left carotid artery (type C). More than 99% of these patients have a ventricular septal defect; abnormalities of the aortic valve and narrowed subaortic regions are associated anomalies. All other resuscitative measures will be ineffective if blood flow to the lower body is not restored. Oxygen saturations should be measured in the upper body; pulse oximetry readings in the lower body are reflective of the pulmonary artery oxygen saturation, and are typically lower than that distributed to the central nervous system and coronary arteries. High concentrations of inspired oxygen may result in low pulmonary vascular resistance, a large left-to-right shunt, and a "runoff " during diastole from the lower body into the pulmonary circulation. Inspired oxygen levels should therefore be minimized, aiming for normal (95%) oxygen saturations in the upper body. Surgical reconstruction should be performed as soon as metabolic acidosis (if present) has resolved, end-organ dysfunction has improved, and the patient Cardiovascular Disorders 495 Interrupted Aortic Arch 95% 75 45 70% 88% 95% 75 30 m = 12 55% m = 10 95% 75 10 82% 75 10 88% 60 40 Figure 41. Typical anatomic and hemodynamic findings include (i) atresia of a segment of the aortic arch between the left subclavian artery and the left common carotid (the most common type of interrupted aortic arch-break "type B"); (ii) a posterior malalignment of the conal septum resulting in a large ventricular septal defect and a narrow subaortic area; (iii) a bicuspid aortic valve occurs in 60% of patients; (iv) systemic pressure in the right ventricle and pulmonary artery (due to the large, nonrestrictive ventricular septal defect); (v) increased oxygen saturation in the pulmonary artery due to left-to-right shunting at the ventricular level; (vi) "differential cyanosis" with a lower oxygen saturation in the descending aorta due to a right-to-left shunt at the patent ductus. The repair typically entails a corrective approach through a median sternotomy, with arch reconstruction (usually an end-to-end anastomosis) and closure of the ventricular septal defect. Arch reconstruction and a pulmonary artery band (through a lateral thoracotomy) are generally not recommended, typically reserved for patients with multiple ventricular septal defects. A: Hypoplastic left heart syndrome in a 24-hour-old patient with falling pulmonary vascular resistance and a nonrestrictive ductus arteriosus. Typical anatomic and hemodynamic findings include (i) atresia or hypoplasia of the left ventricle, mitral, and aortic valves; (ii) a diminutive ascending aorta and transverse aortic arch, usually with an associated coarctation; (iii) coronary blood flow is usually retrograde from the ductus arteriosus through the tiny ascending aorta; (iv) systemic arterial oxygen saturation (in FiO2 of 0. B: Acute circulatory collapse following constriction of the ductus arteriosus in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. These neonates are typically in shock with poor perfusion, tachycardia, acidosis, and respiratory distress. Note (i) the low cardiac output (as evidenced by the low mixed venous oxygen saturation in the superior vena cava of 55%); (ii) narrow pulse pressure; (iii) elevated atrial and ventricular end-diastolic pressure-elevated left atrial pressure may cause pulmonary edema (note left atrial saturation of 93%); (iv) significantly increased pulmonary blood flow, as reflected in an arterial oxygen saturation (in FiO2 of 0. As systemic blood flow decreases, stroke volume and Cardiovascular Disorders 497 heart rate increase as a mechanism to preserve systemic cardiac output. The right ventricle becomes progressively volume overloaded with mildly elevated end-diastolic and left atrial pressures. The infant may be tachypneic or in respiratory distress; hepatomegaly may be present. The greater proportion of pulmonary venous return in the mixed ventricular blood results in a mildly decreased systemic arterial oxygen saturation (80%), and visible cyanosis may be mild or absent. Not infrequently, these infants are discharged from the nursery as normal newborns. At this point, the continued fall in pulmonary vascular resistance results in a progressive increase in pulmonary blood flow and relative decrease in systemic cardiac output. There is a decreased systemic perfusion and an increased pulmonary blood flow, which is largely independent of the pulmonary vascular resistance. Renal, hepatic, coronary, and central nervous system perfusion is compromised, possibly resulting in acute tubular necrosis, necrotizing enterocolitis, or cerebral infarction or hemorrhage.
Because the development of retinoblastoma requires two deletions or mutations (one on each allele) heart attack coub zebeta 5 mg for sale, the cause has been termed the "twohit" model blood pressure and pregnancy buy cheap zebeta 10mg online. Glaucoma hypertension arterielle generic 2.5 mg zebeta visa, vitreous hemorrhage blood pressure chart according to age and weight buy zebeta 10mg, retinal detachment, and hyphema are less common presenting signs. Calcification within the tumor, identified on imaging studies of the eye, is a hallmark of retinoblastoma. Ocular ultrasound or computed tomographic scan of the orbit can further evaluate the tumor and assess for tumor extension. Large tumors involving the macula have a poor prognosis and are generally treated by removal of the entire eye. Smaller tumors may be treated with external beam radiation; however, radiation may induce formation of secondary tumors. Very small peripheral tumors may be treated with cryotherapy or laser photocoagulation. The cure rate is 90% if the tumor does not extend beyond the sclera or into the orbit. Pseudostrabismus is a prominence of the epicanthal folds that results in the false appearance of strabismus, even though the eyes are actually appropriately aligned. Acquired strabismus, decreased eye movement, ptosis, decreased vision, and abnormal red reflex are all red flags that suggest a dangerous underlying cause, such as a tumor or neurologic process. Strabismus associated with farsightedness is initially treated with corrective lenses. Surgery is often required to correct any misalignment that does not respond to patching or glasses. A 1-month-old male infant is brought to the office for a routine health maintenance visit. A 3-year-old girl with a normal past medical history presents with a 5-day history of bilateral mucoid conjunctival discharge and conjunctival hyperemia. A 14-year-old boy who wears contact lenses presents with conjunctival hyperemia and severe photophobia of the right eye. Which of the following statements regarding his diagnosis and management is most correct% (A) Immediate ophthalmologic evaluation is necessary. A 5-year-old boy presents with a history of fever, bilateral watery conjunctival discharge, sore throat, and a foreign body sensation in his eyes. Physical examination is notable for bilateral conjunctival hyperemia with watery discharge and bilateral preauricular lymphadenopathy. Which of the following statements regarding the most likely diagnosis is correct% (A) Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated in the management of this illness. Which of the following statements regarding the diagnosis is most correct% (A) this tumor occurs sporadically and is not inherited. A 10-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department after sustaining a baseball injury to the right eye. A 7-day-old male infant with purulent conjunctival discharge and mild lid swelling. A 10-day-old female infant with unilateral serous conjunctival discharge and multinucleated giant cells on Gram stain. Surgery must occur within the first several weeks of life to ensure a good prognosis. If an opacity is not removed promptly in a young infant, the retina and nervous connections are not appropriately stimulated, and amblyopia (poor vision caused by abnormal retinal stimulation) may develop. The majority of cataracts are idiopathic, although known causes include trauma, metabolic abnormalities, genetic syndromes, and nonsyndromic genetic inheritance.
Order zebeta 10 mg mastercard. Blood Pressure: Korotkoff Sounds 1.